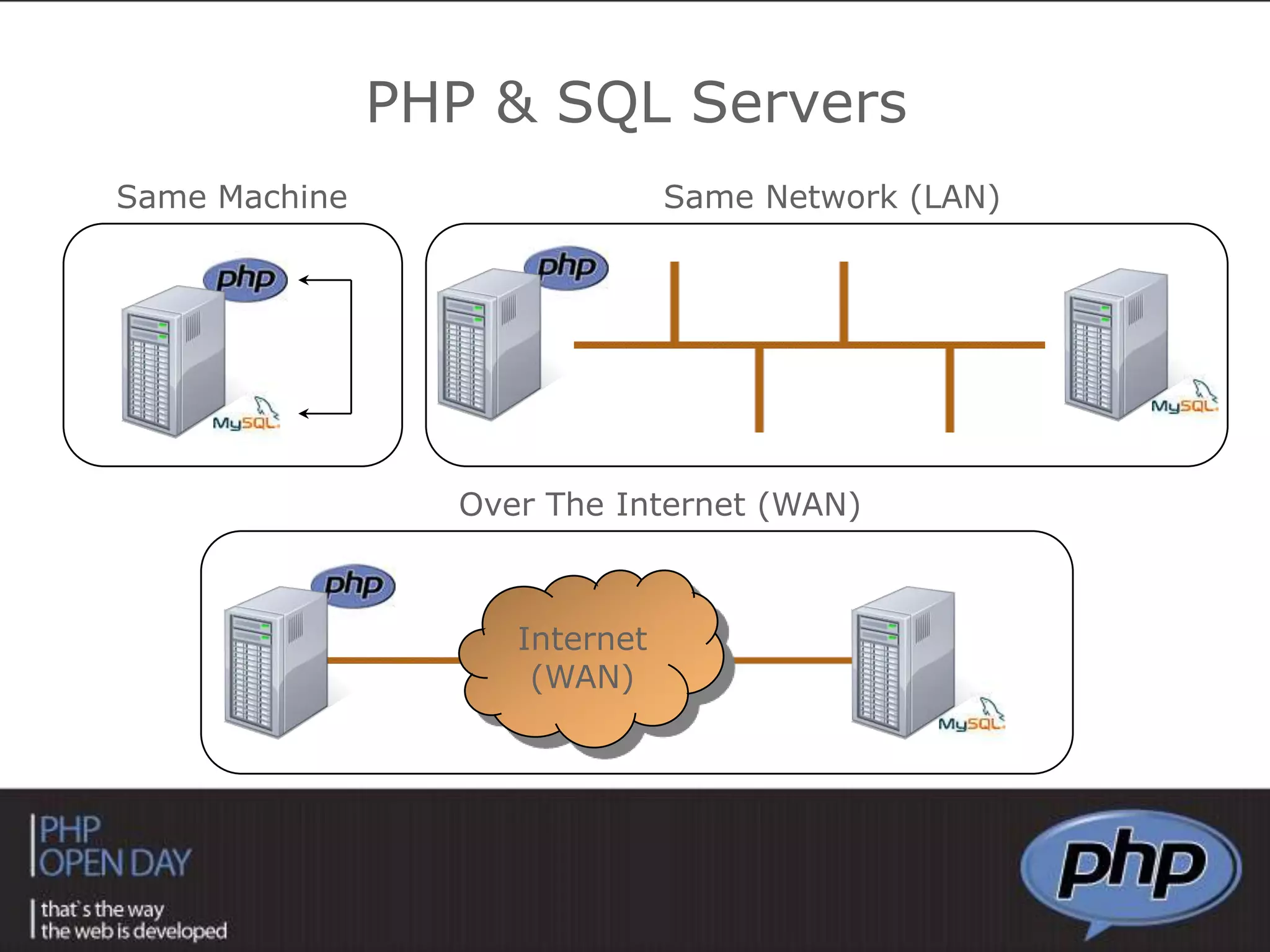
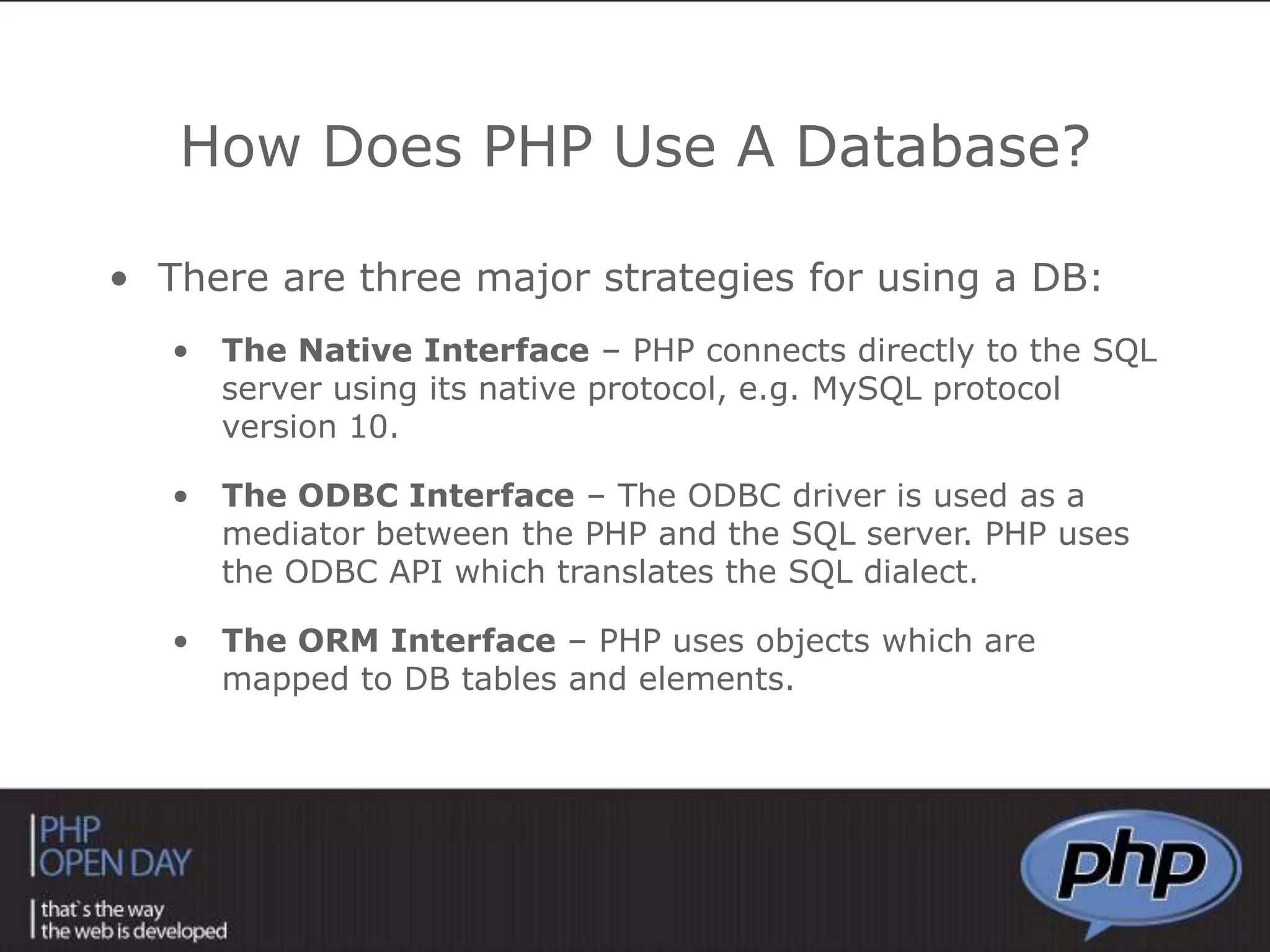
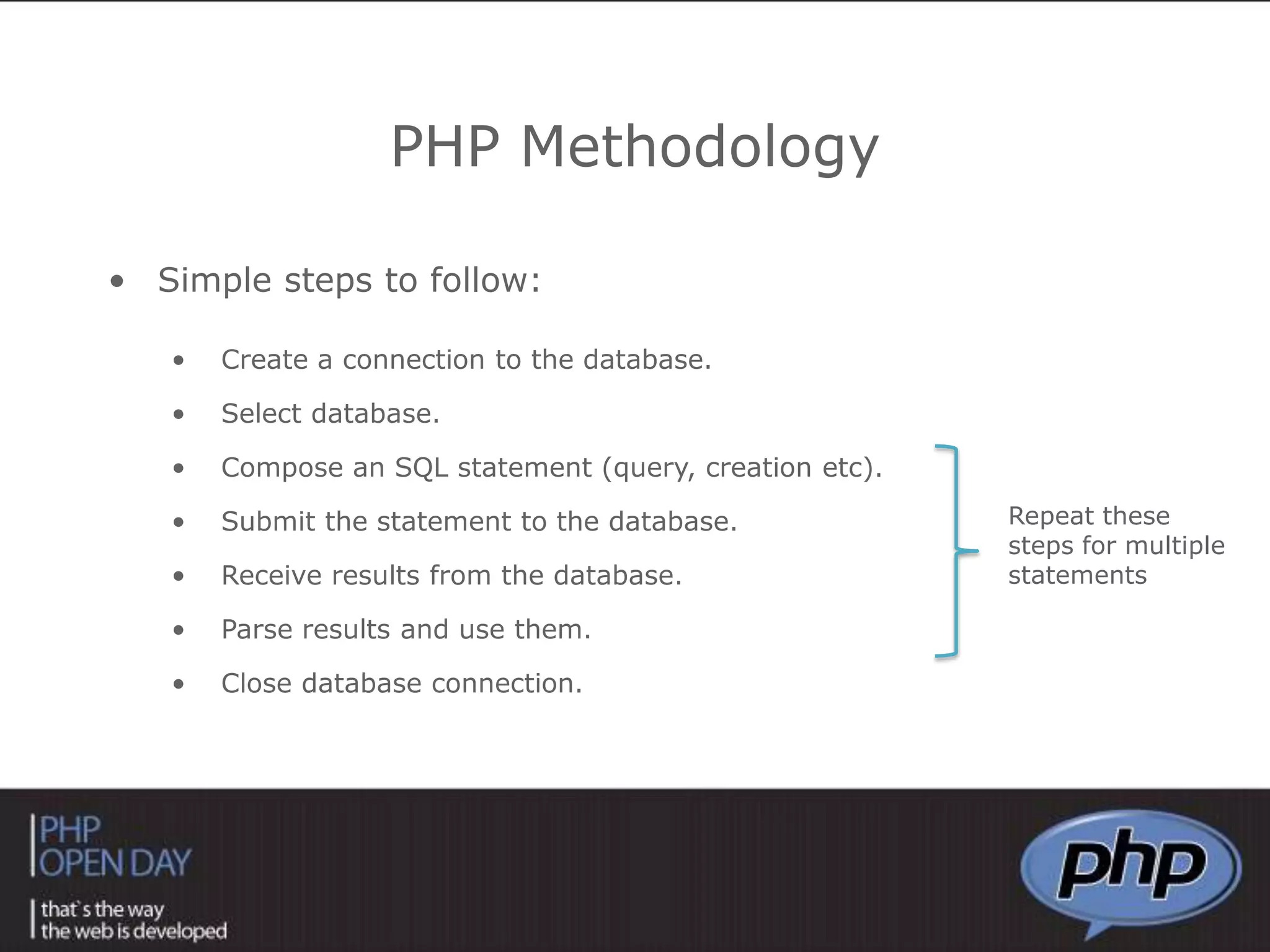
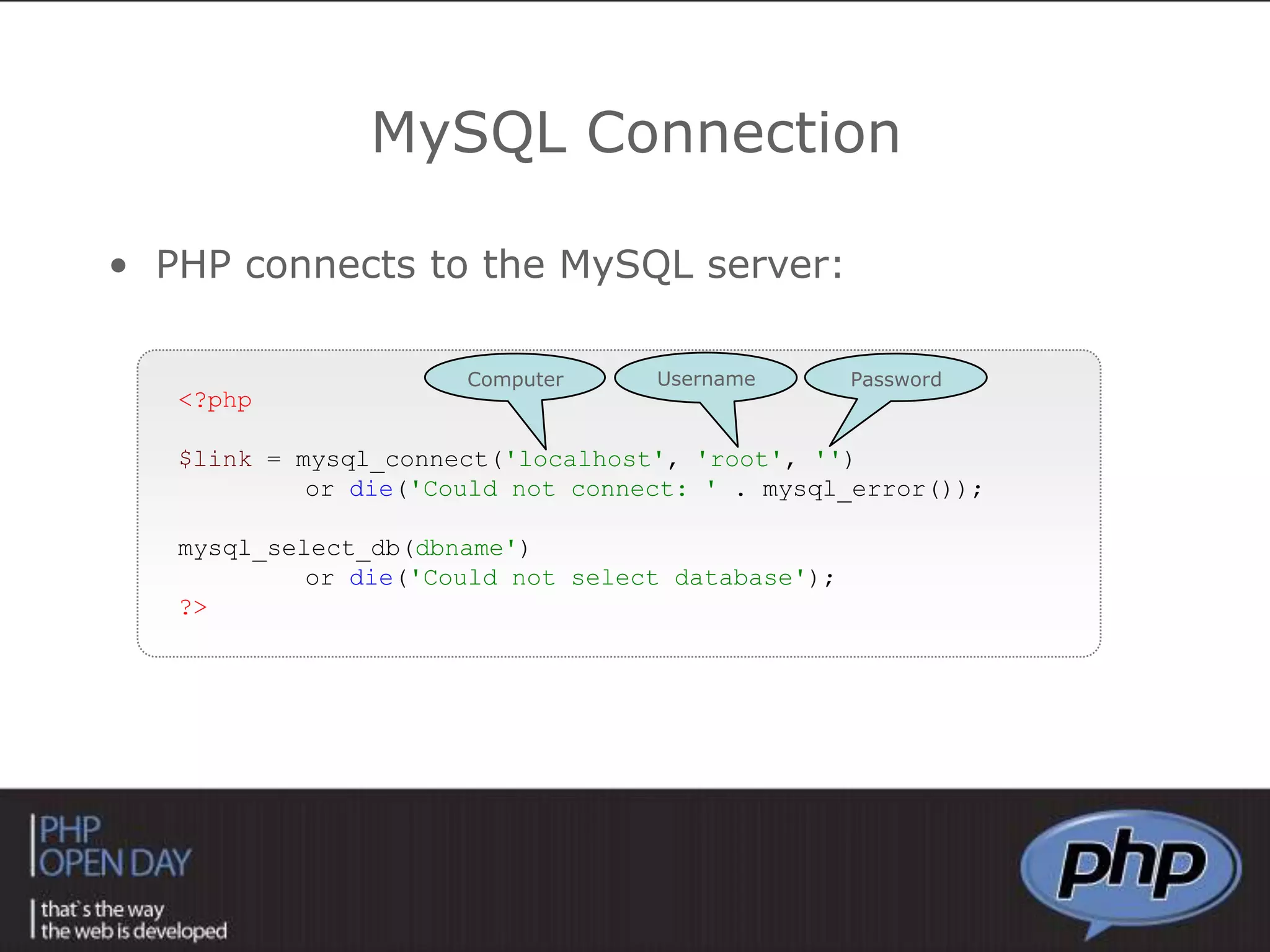
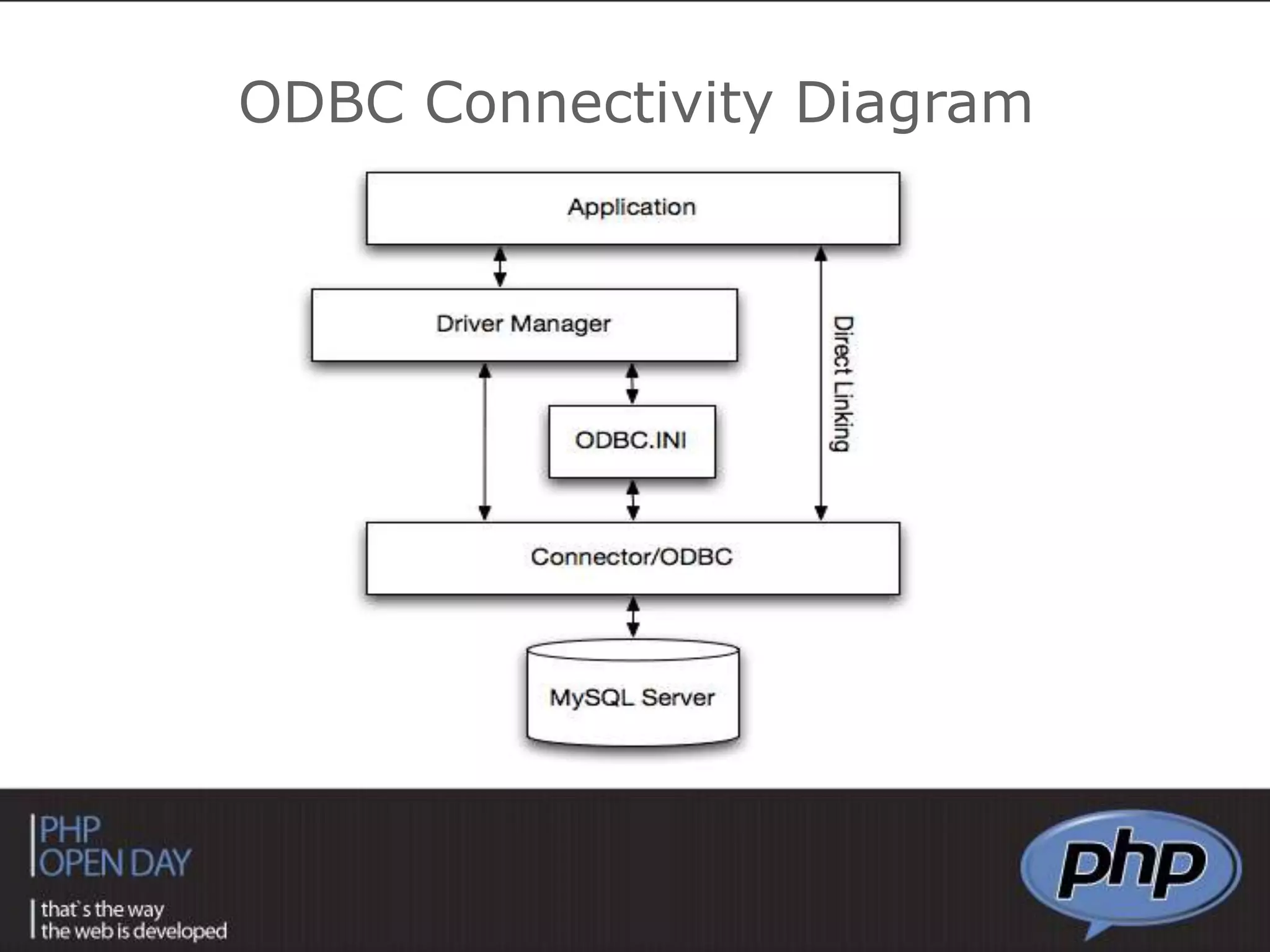
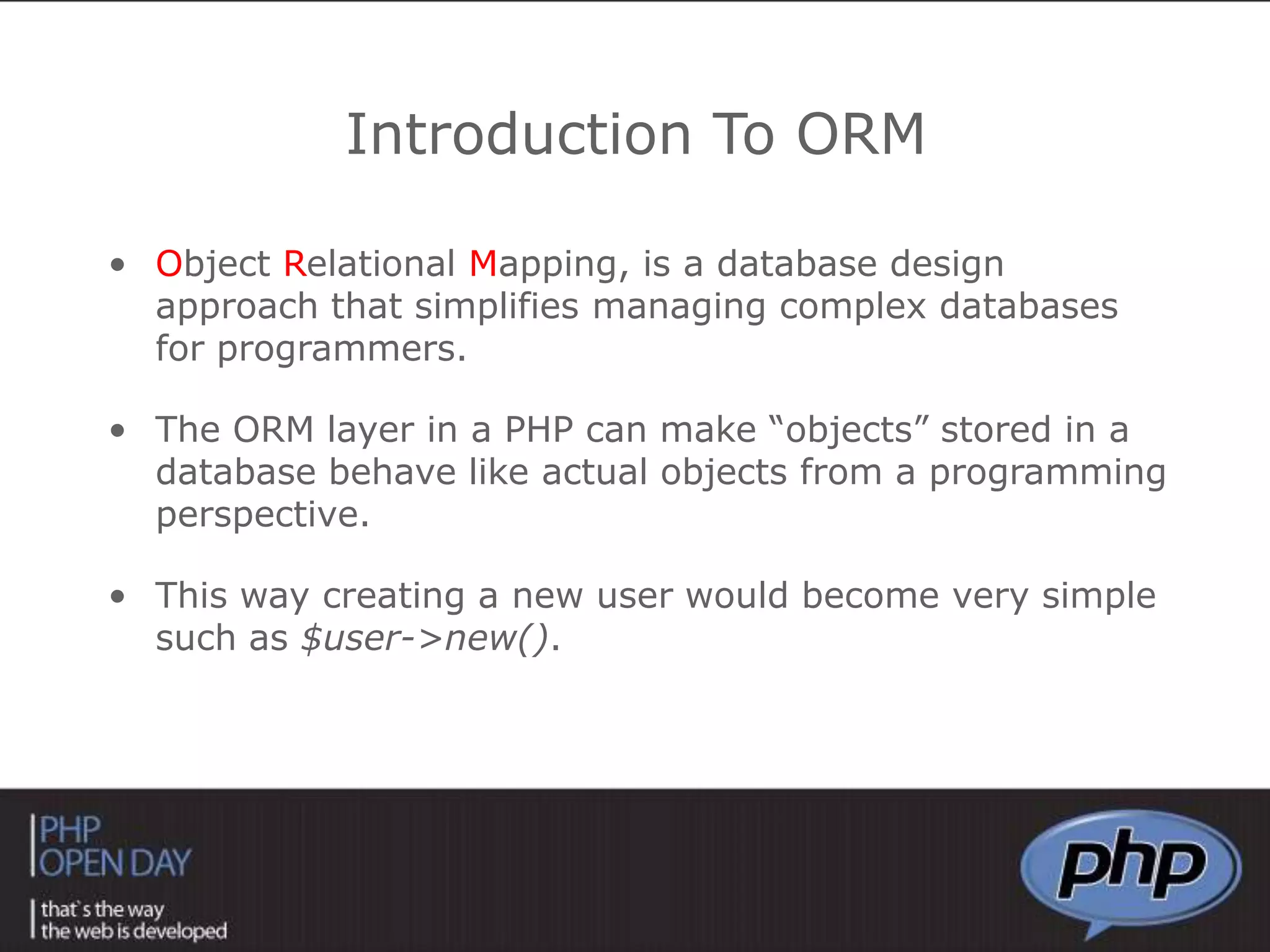
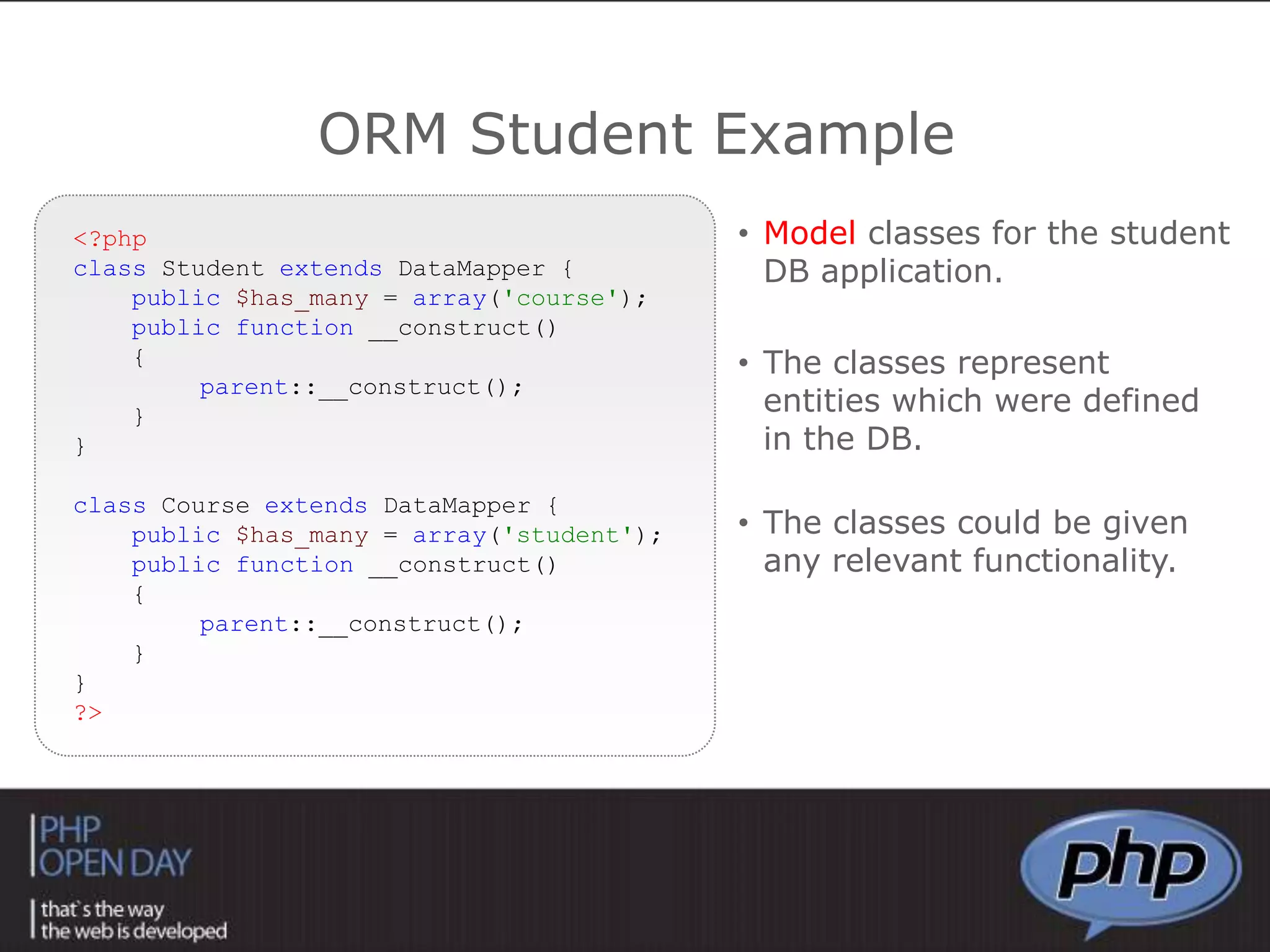
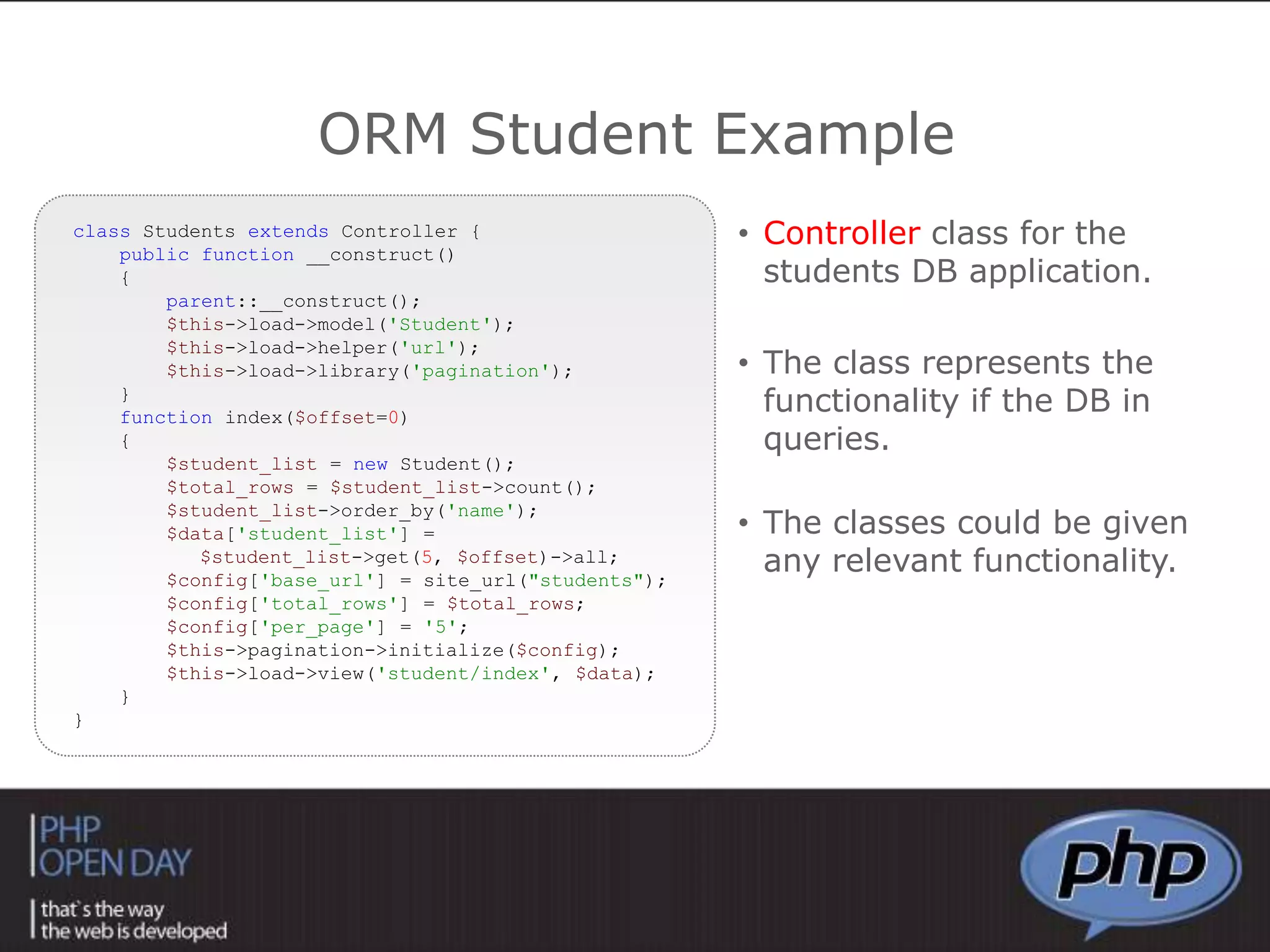
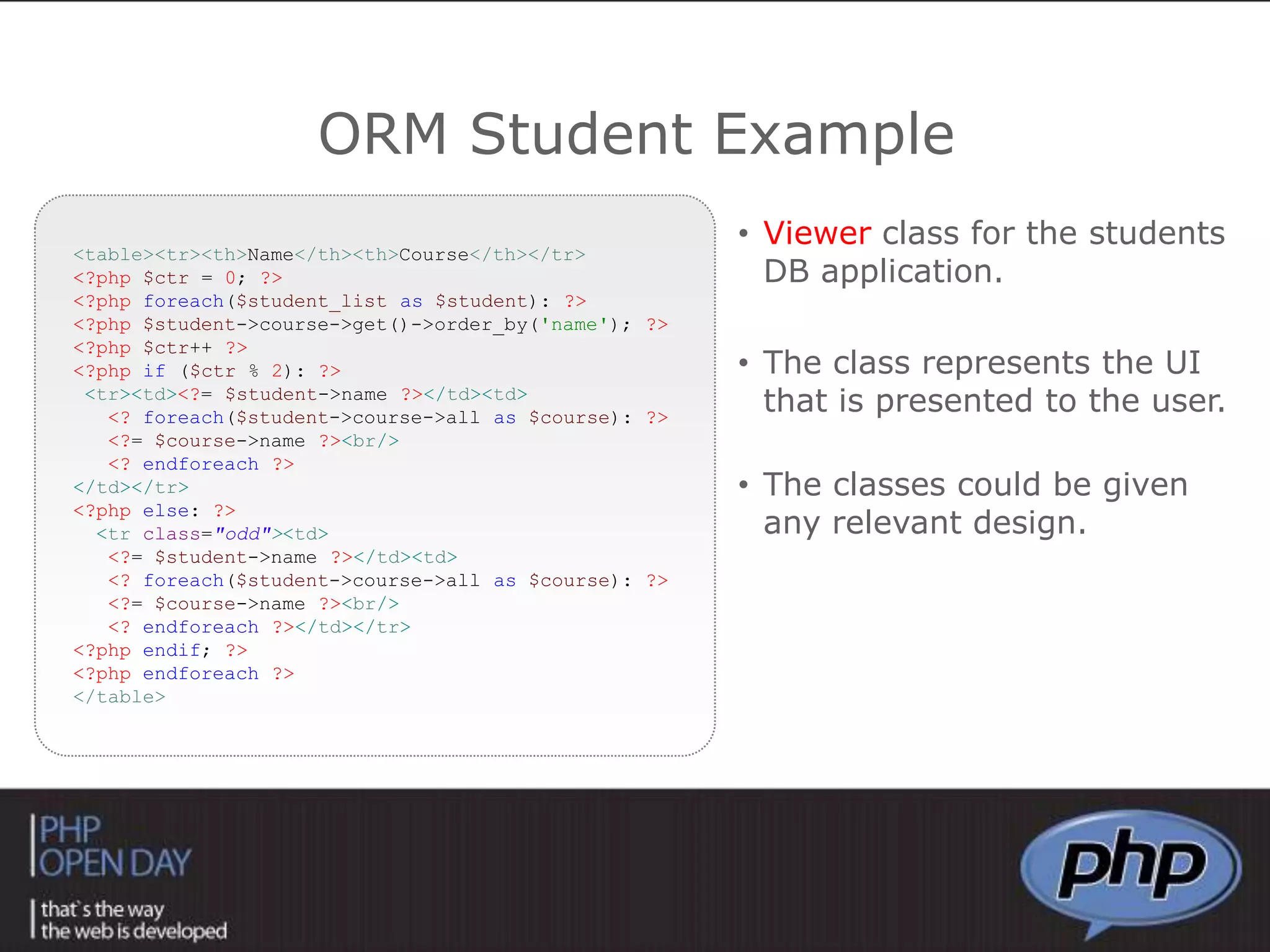
This document discusses different approaches to connecting PHP with databases. It begins with an introduction to using PHP with databases. It then describes three major strategies: the native interface, where PHP connects directly to the database server; the ODBC interface, which uses a driver; and the ORM interface, which maps database elements to objects. It provides examples of code for each approach and discusses how frameworks often implement ORM.







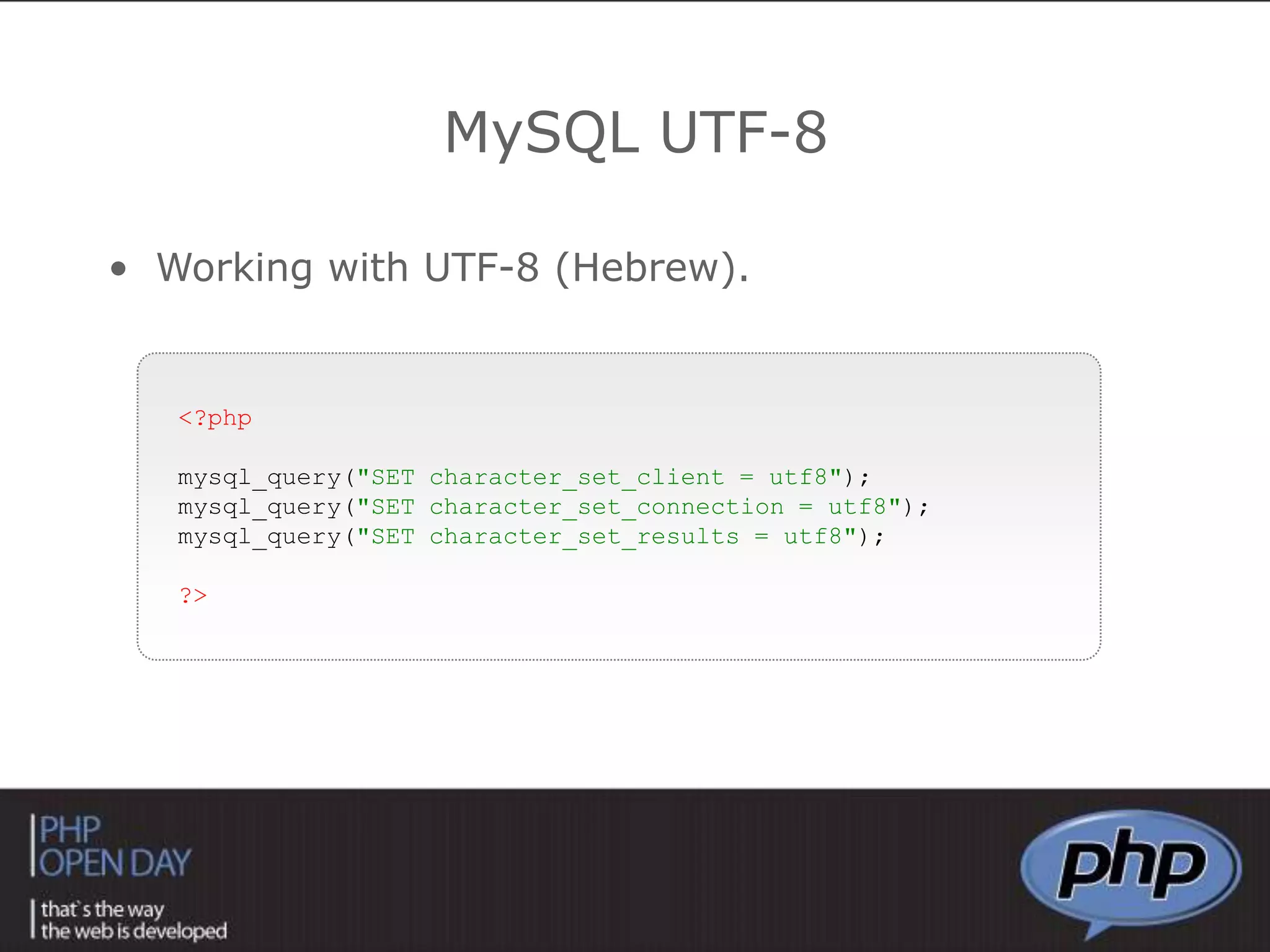




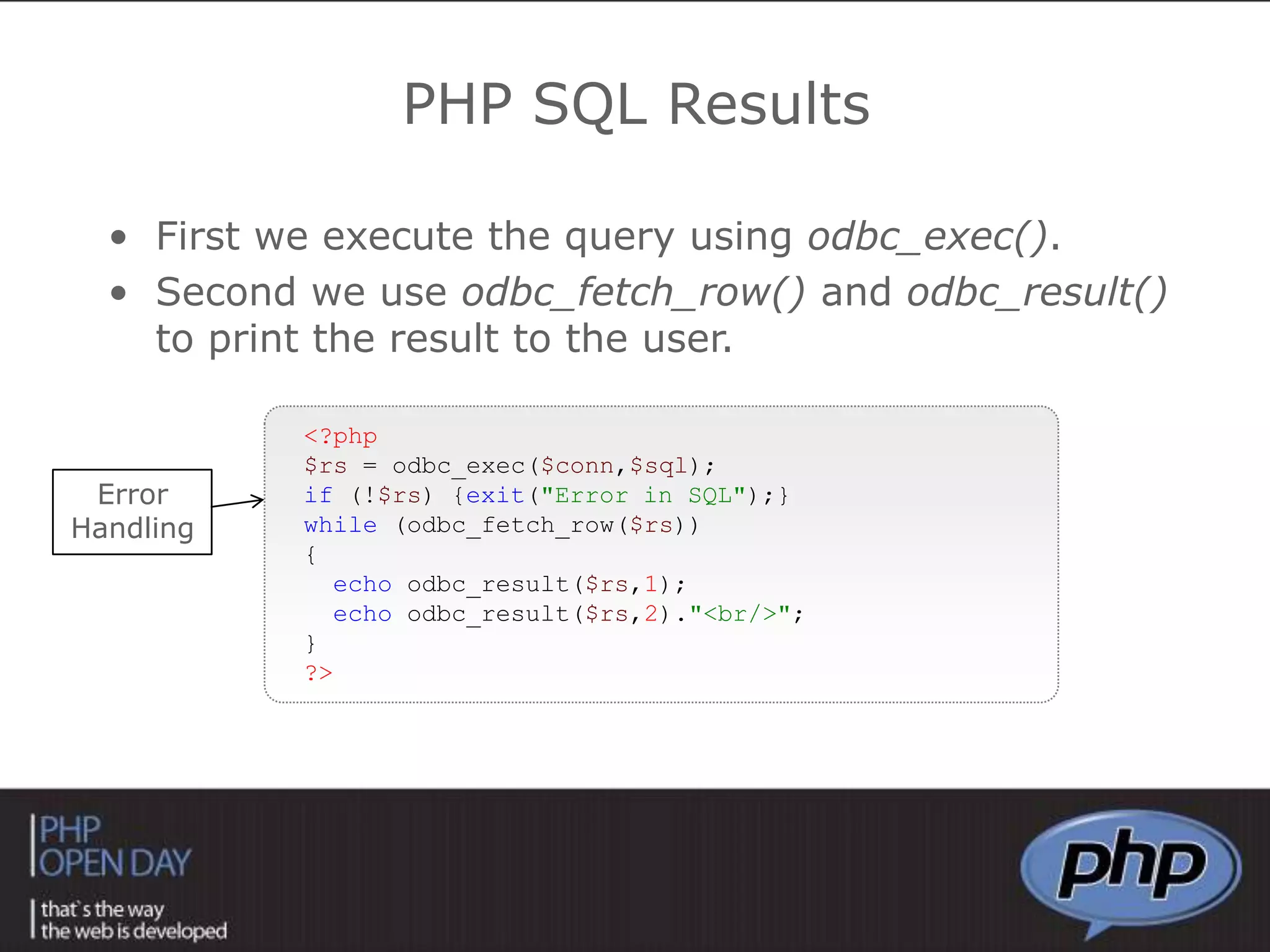

![<?phpmysql_query("SET character_set_client = utf8");mysql_query("SET character_set_connection = utf8");mysql_query("SET character_set_results = utf8"); ?>MySQL UTF-8Working with UTF-8 (Hebrew).<?php$sql= "SELECT * FROM students WHERE ID > 5 order by id";$result = mysql_query($sql) or die ("Unable to SELECT FROM DB: ".$sql);while($line = mysql_fetch_array($result, MYSQL_ASSOC)){ echo $line["id"]."<br/>";}?>MySQL QueryPreparing, sending and receiving the query.MYSQL_ASSOC – Associative Array MYSQL_NUM – Numeric Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workingwithphpanddbs-taltamir-110404034940-phpapp01/75/working-with-PHP-DB-s-33-2048.jpg)