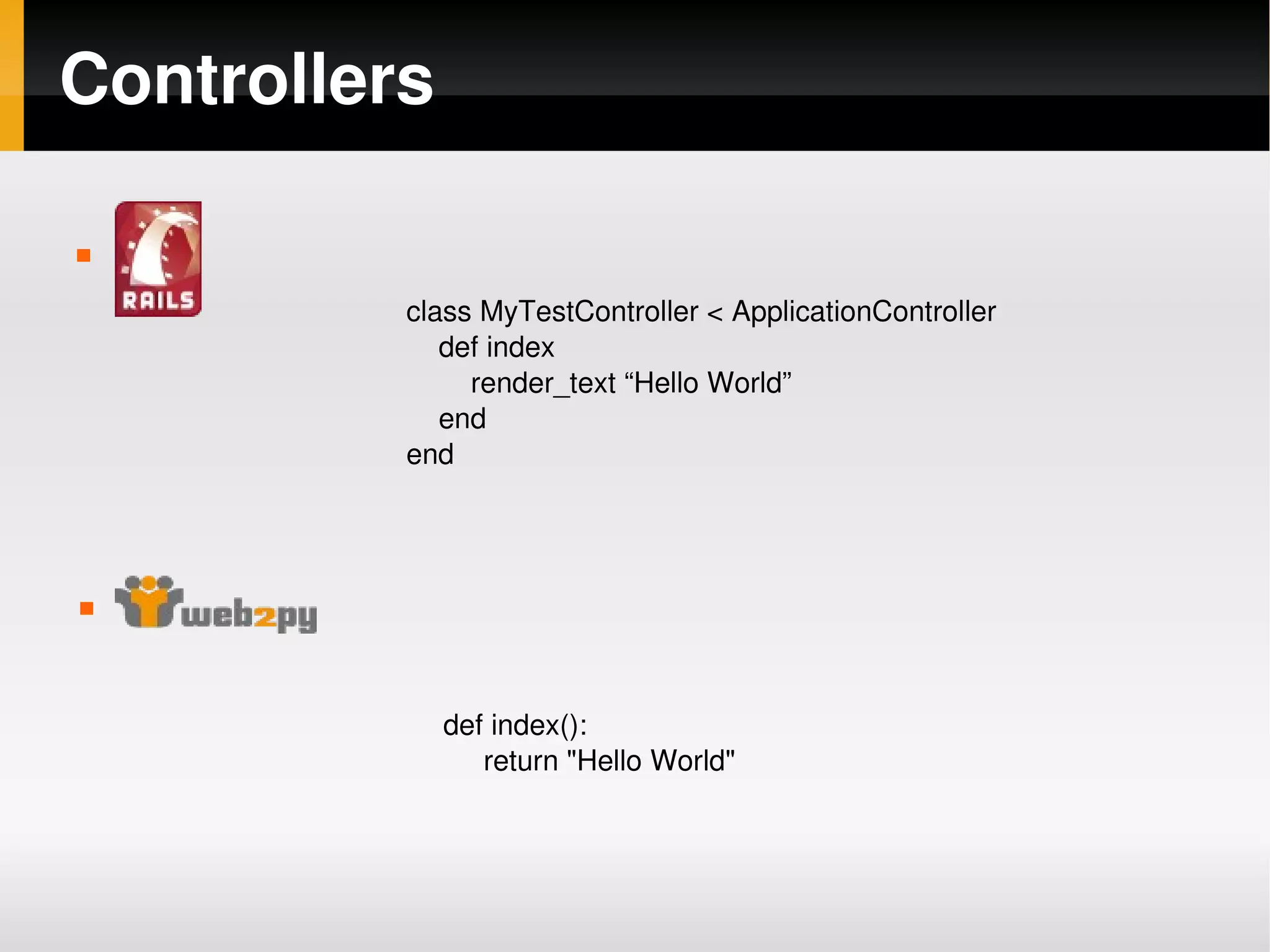
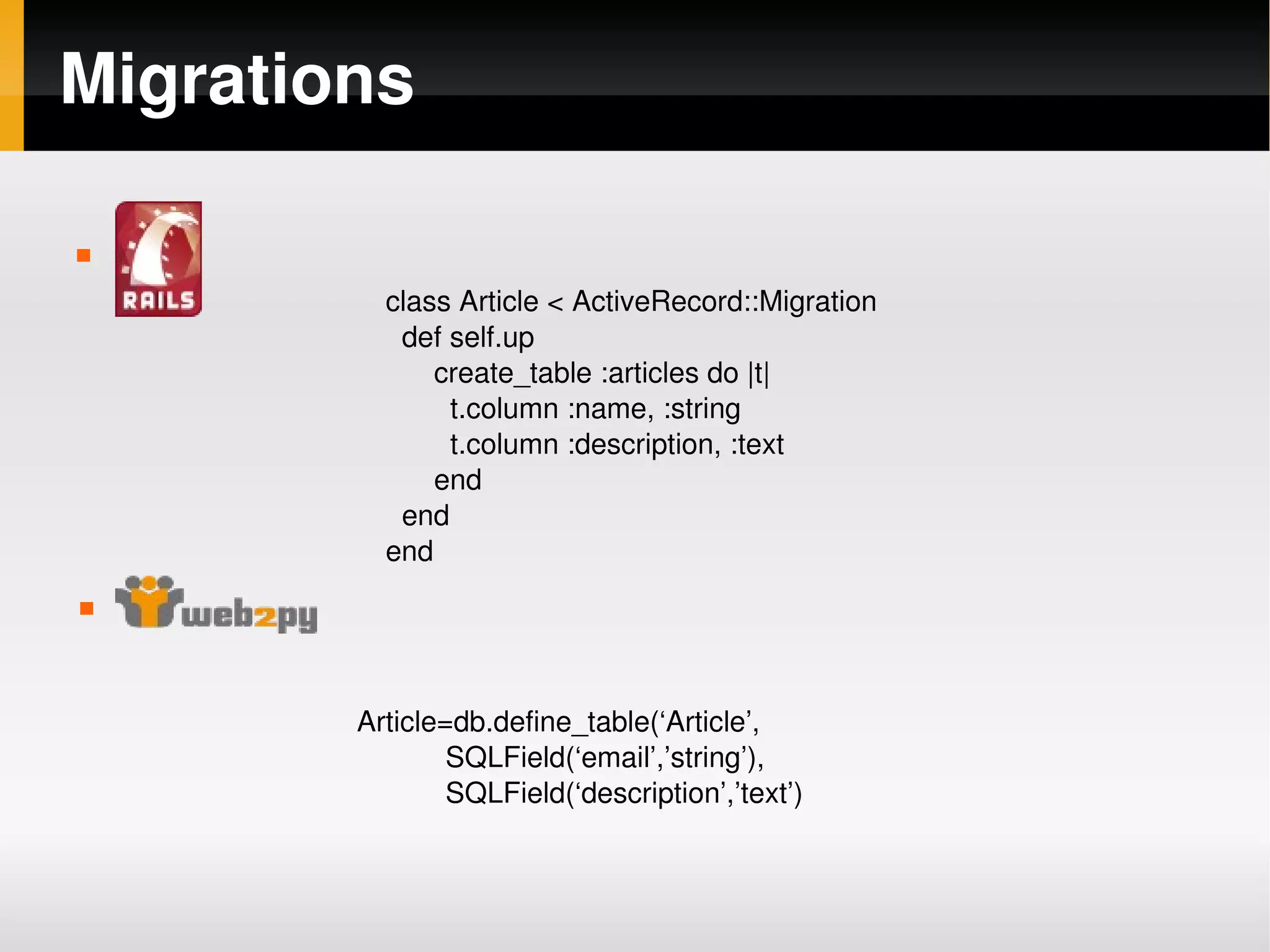
Rails vs Web2Py compares the popular web frameworks Ruby on Rails and Web2Py. Some key differences include: - Controllers are defined as classes in Rails and functions in Web2Py. - Routing is defined in a routes.rb file in Rails and routes.py in Web2Py, which supports reversed routing and regex. - Views use ERB templates in Rails and native Python templates in Web2Py. - Web2Py has built-in support for forms, validation, users/roles, caching, translations and more while these require additional gems/plugins in Rails. - Web2Py is designed to be easier to install

![Params class MyTestController < ApplicationController def index render_text “Hello ”+params[:who] end end def index(): return "Hello %s" % request.vars.who def index(): return "Hello %s" % request.args[0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/athensdigitalweek-091017105304-phpapp02/75/Rails-vs-Web2py-3-2048.jpg)







![Queries Article.find(:first,:conditions => [ "id > :id AND name = :name", {:id => 3, :name => "test" }]) db(Article.id>3 and Article.name==’test’).select()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/athensdigitalweek-091017105304-phpapp02/75/Rails-vs-Web2py-12-2048.jpg)