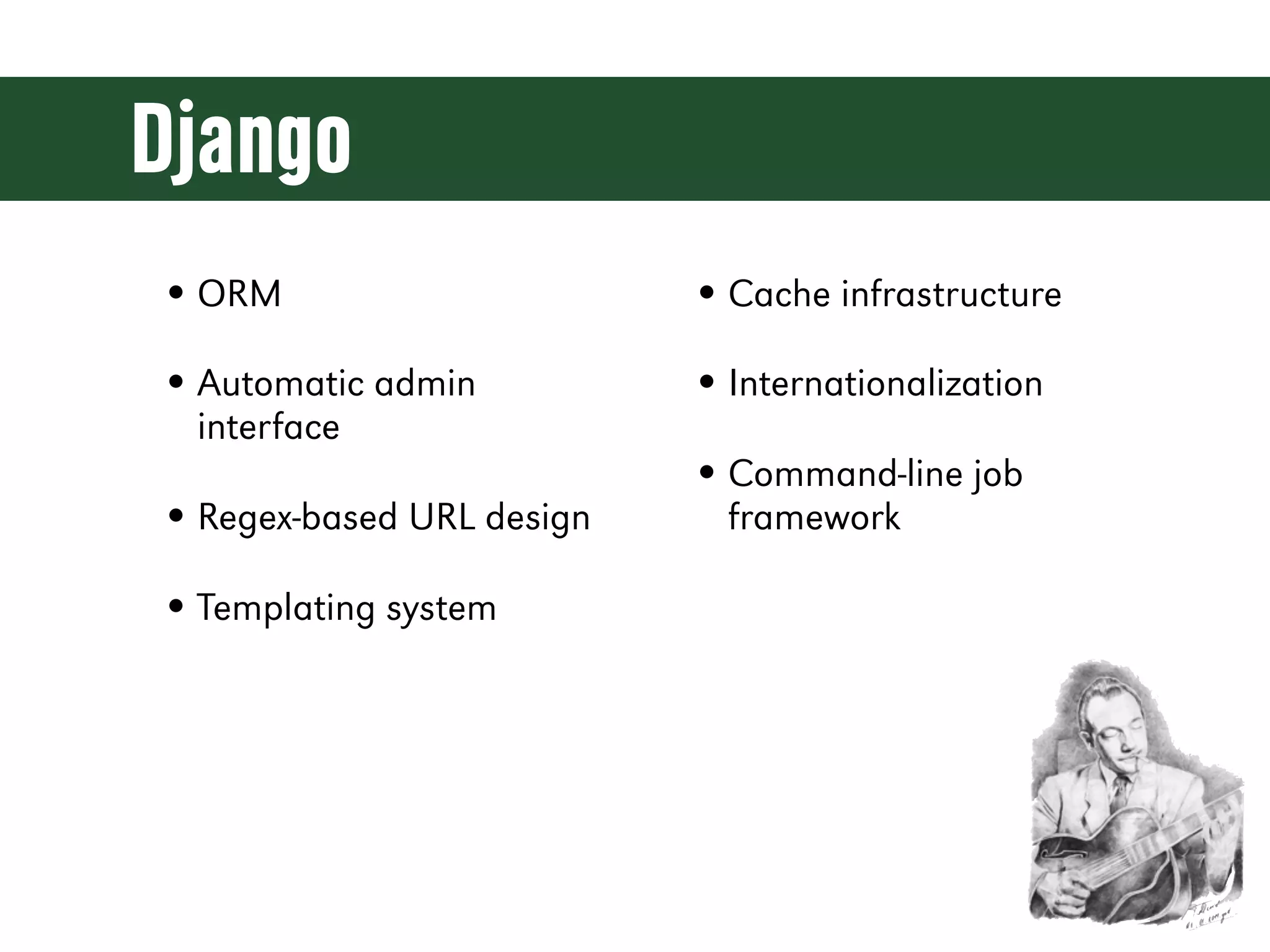
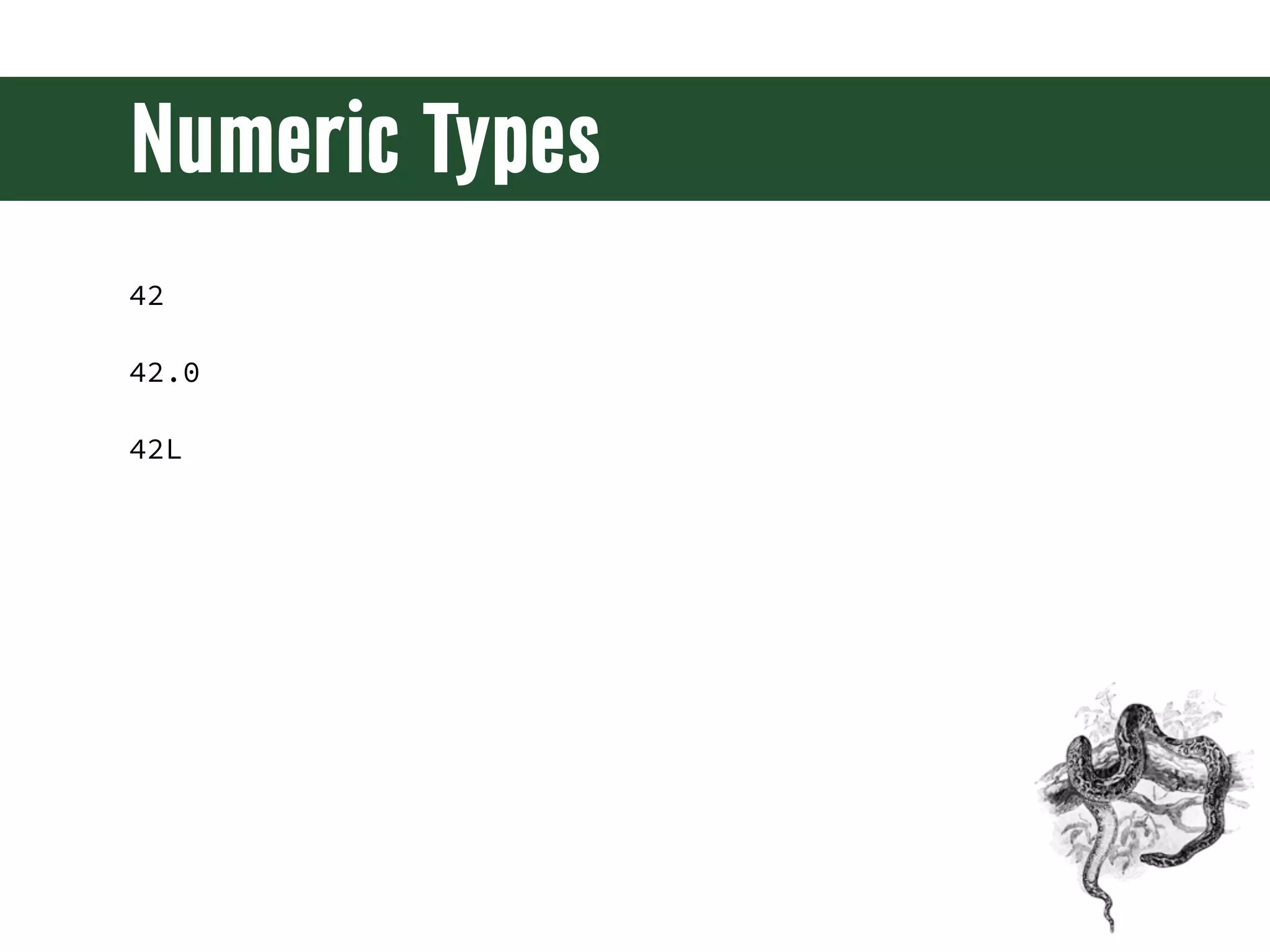
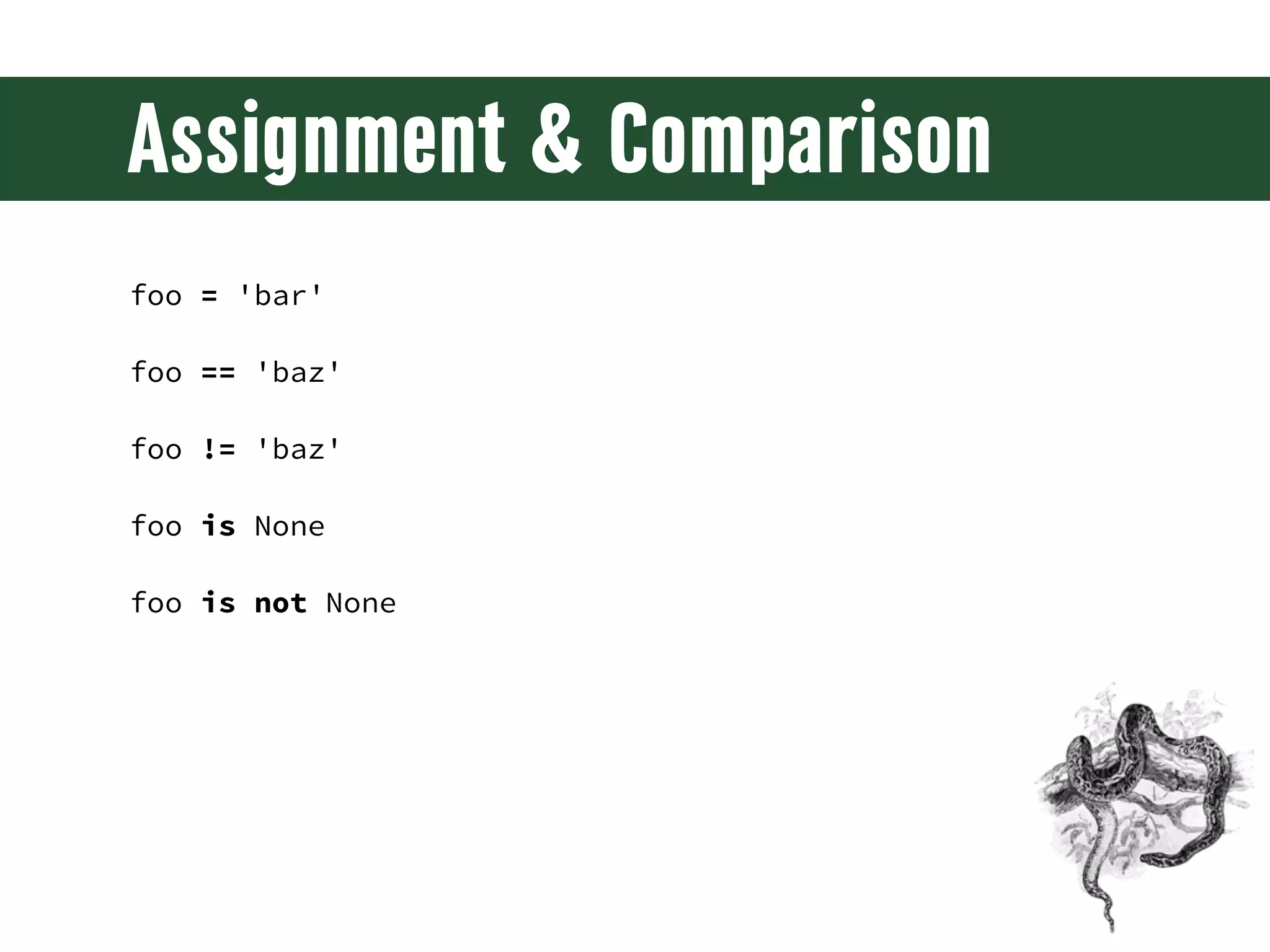
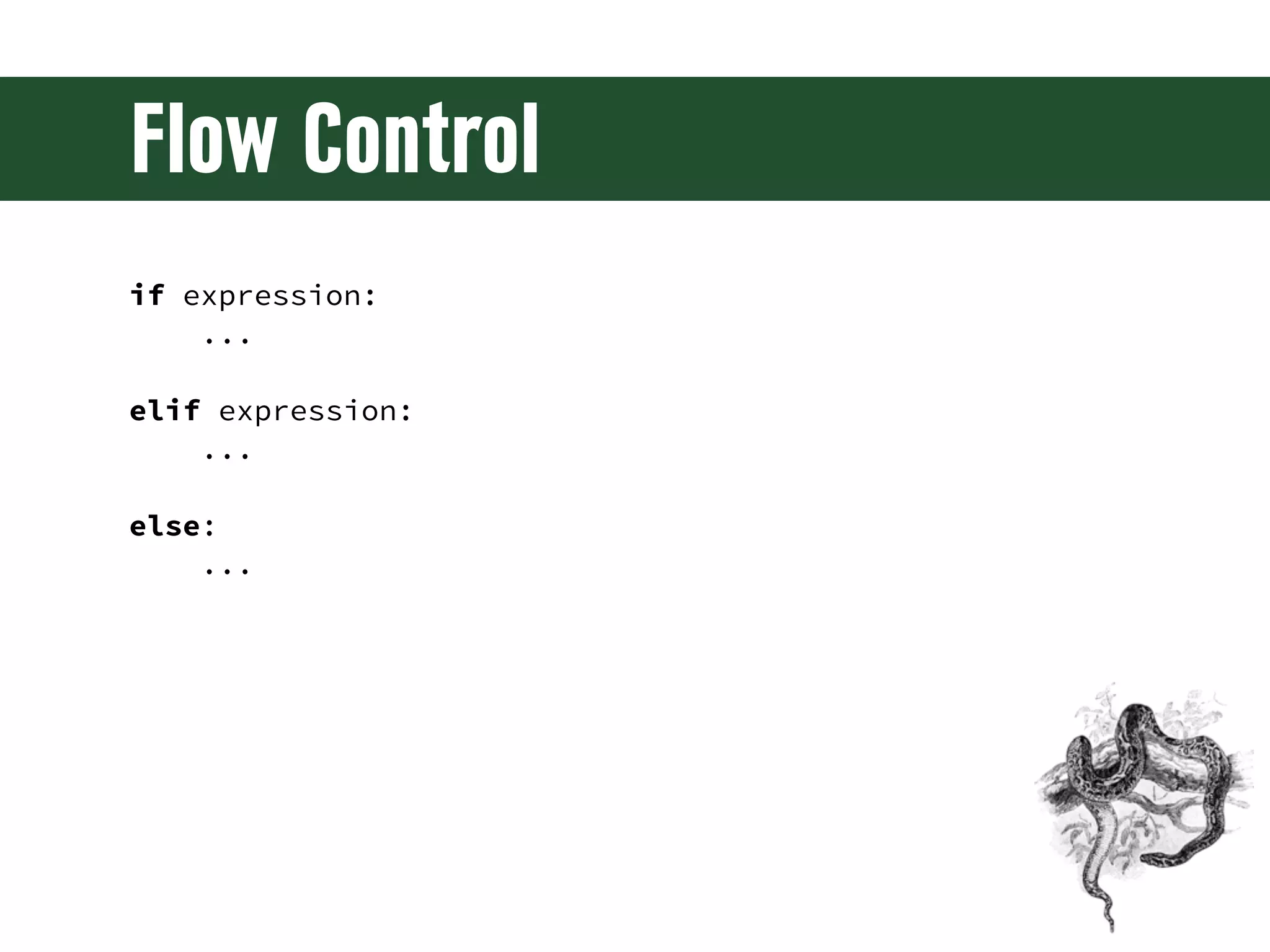
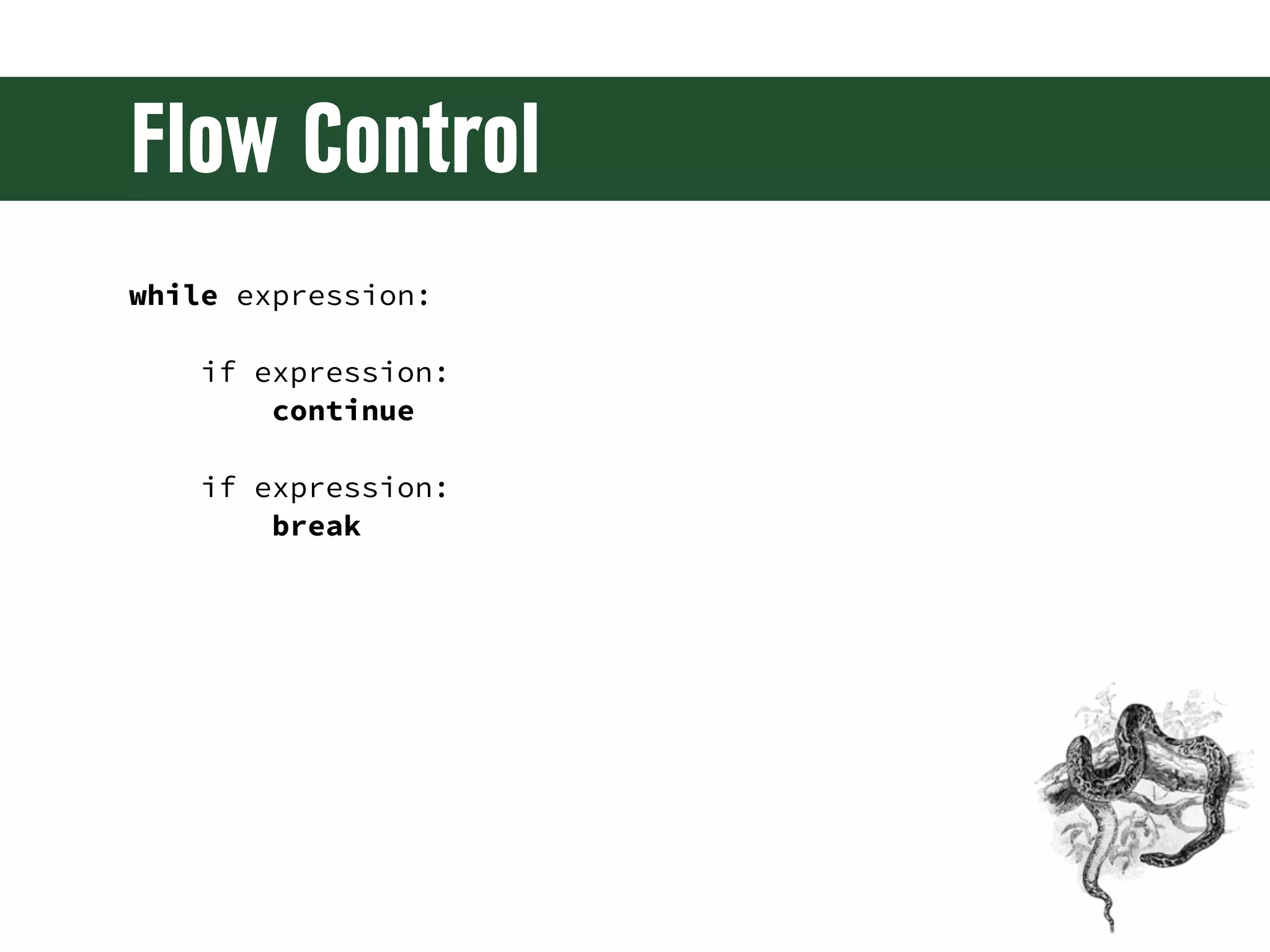
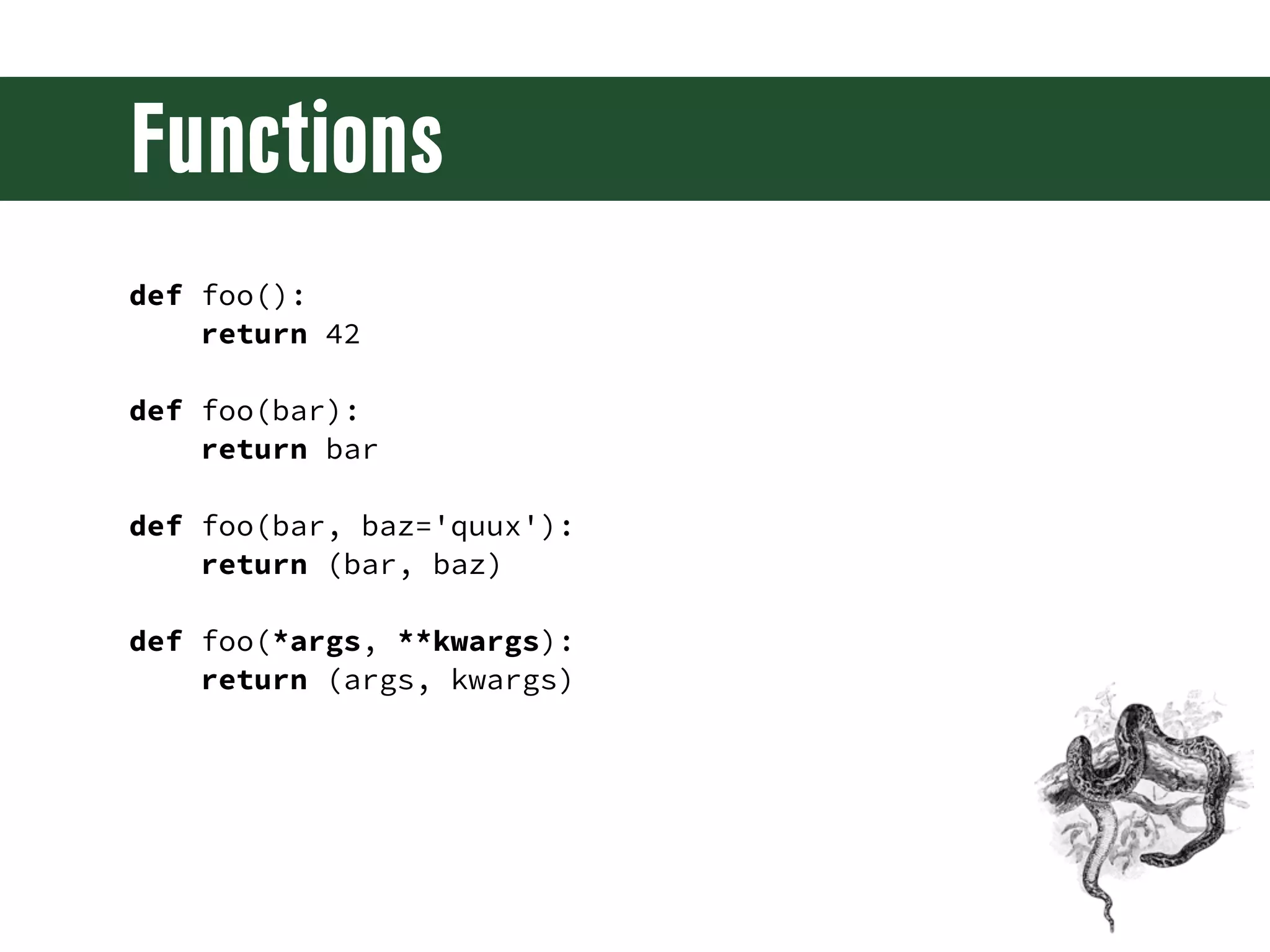
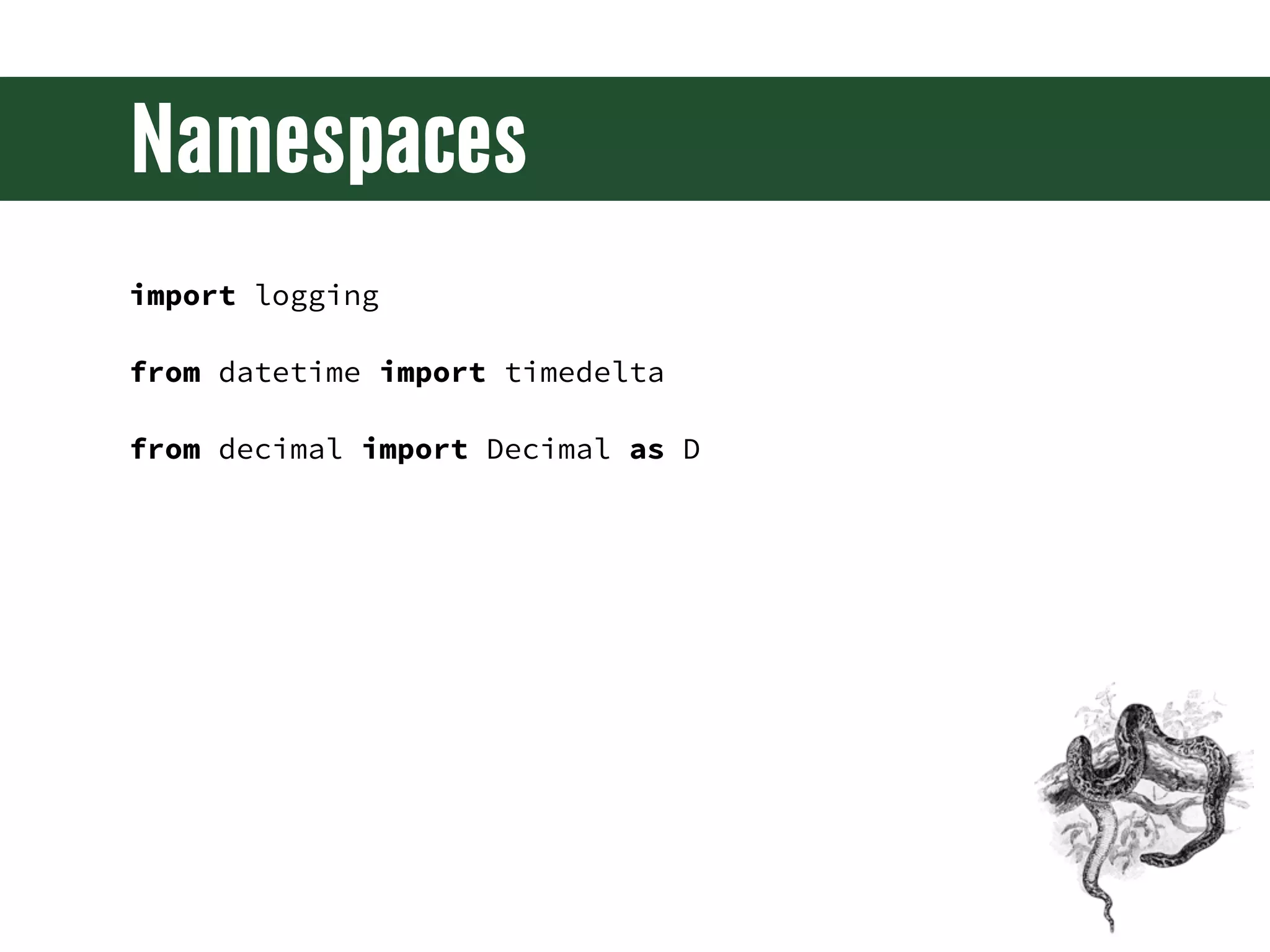
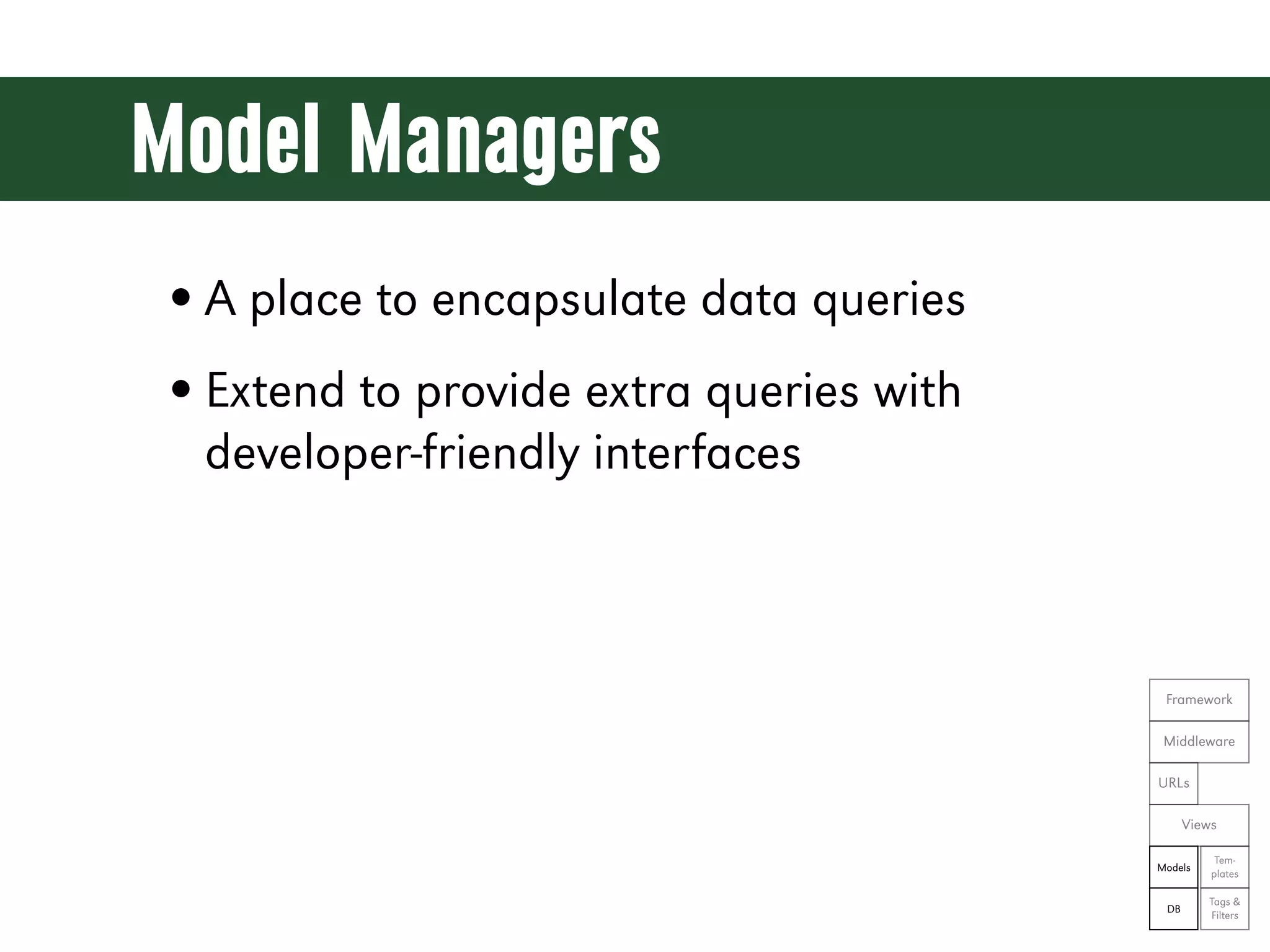
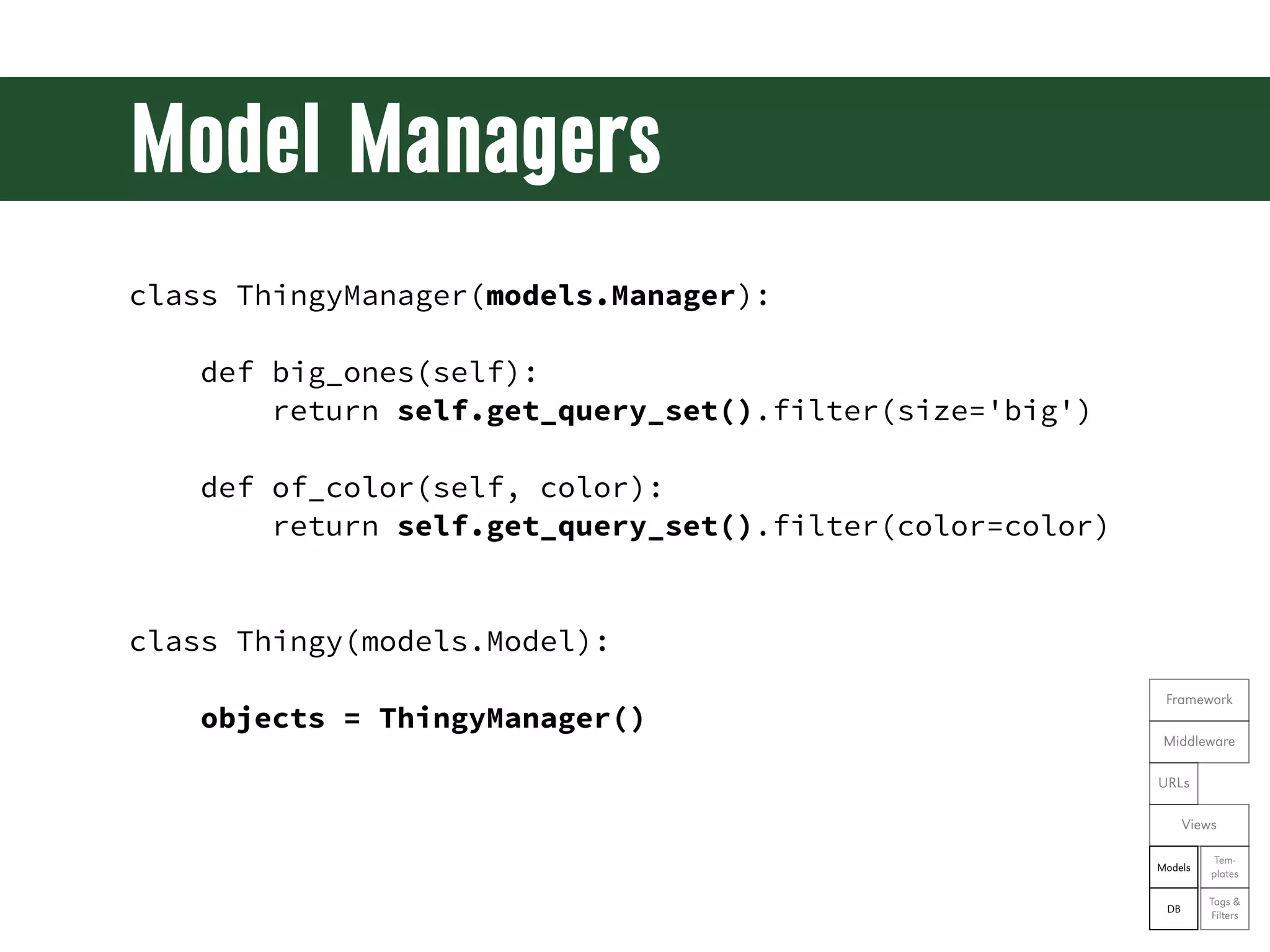
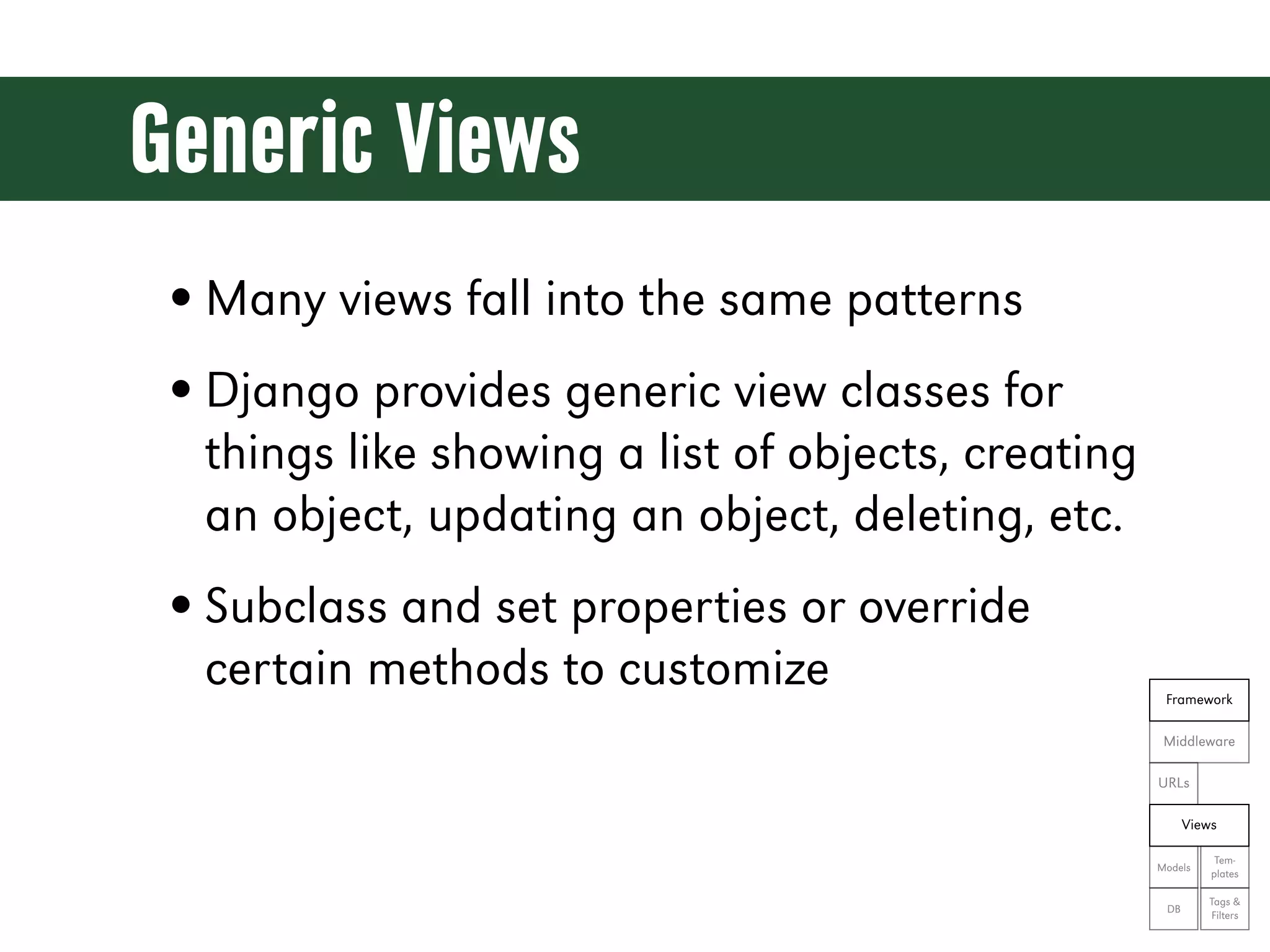
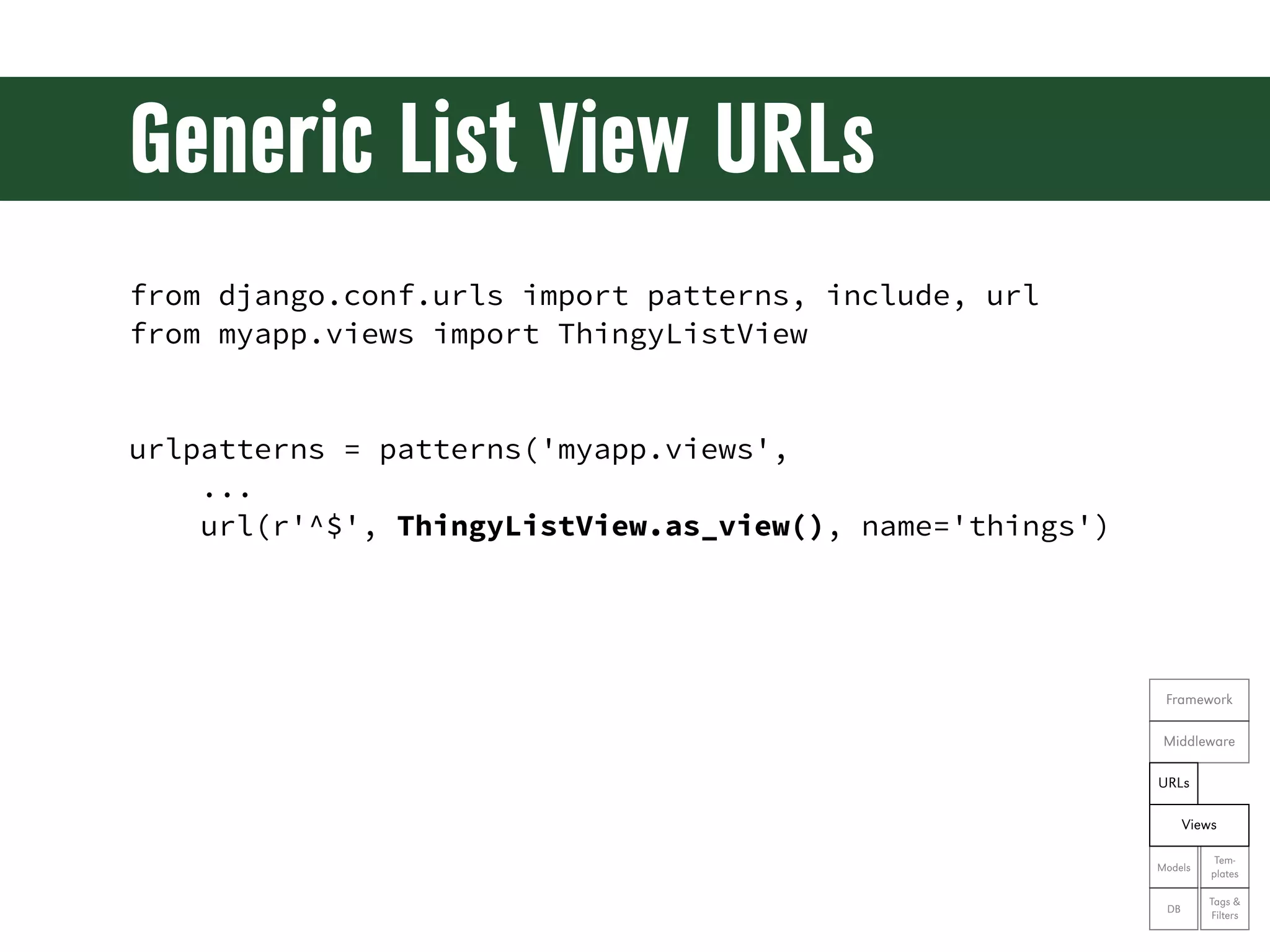
The document is a comprehensive guide on web development using Python and Django, covering topics such as project setup, creating apps, building views and templates, handling forms, and managing user authentication. It emphasizes Django's features like ORM, middleware, and template inheritance while providing code examples and exercises. The guide also discusses best practices for environment setup, package management, and code organization.













![String Operations "foo" + "bar" "foo"[0] "foo"[:1] "foo".upper() "{0}: {1}".format("foo", "bar") "{foo}: {bar}".format(foo=42, bar=1138) len("foo")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-17-2048.jpg)
![Lists, Tuples, and Sets ['a', 'b', 'c'] ('Rush', '2112', 5.0) set(['a', 'b', 'c'])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-19-2048.jpg)
![Sequence Operations [...][0] [...][-1] [...][:1] # same as [...][0:1] [...].append(4) [...].extend([4, 5, 6]) [...].pop() len([...])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-20-2048.jpg)

![Dictionary Operations {...}['key1'] {...}.get('key2', default) {...}.keys() {...}.values() {...}.items() len({...})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-22-2048.jpg)





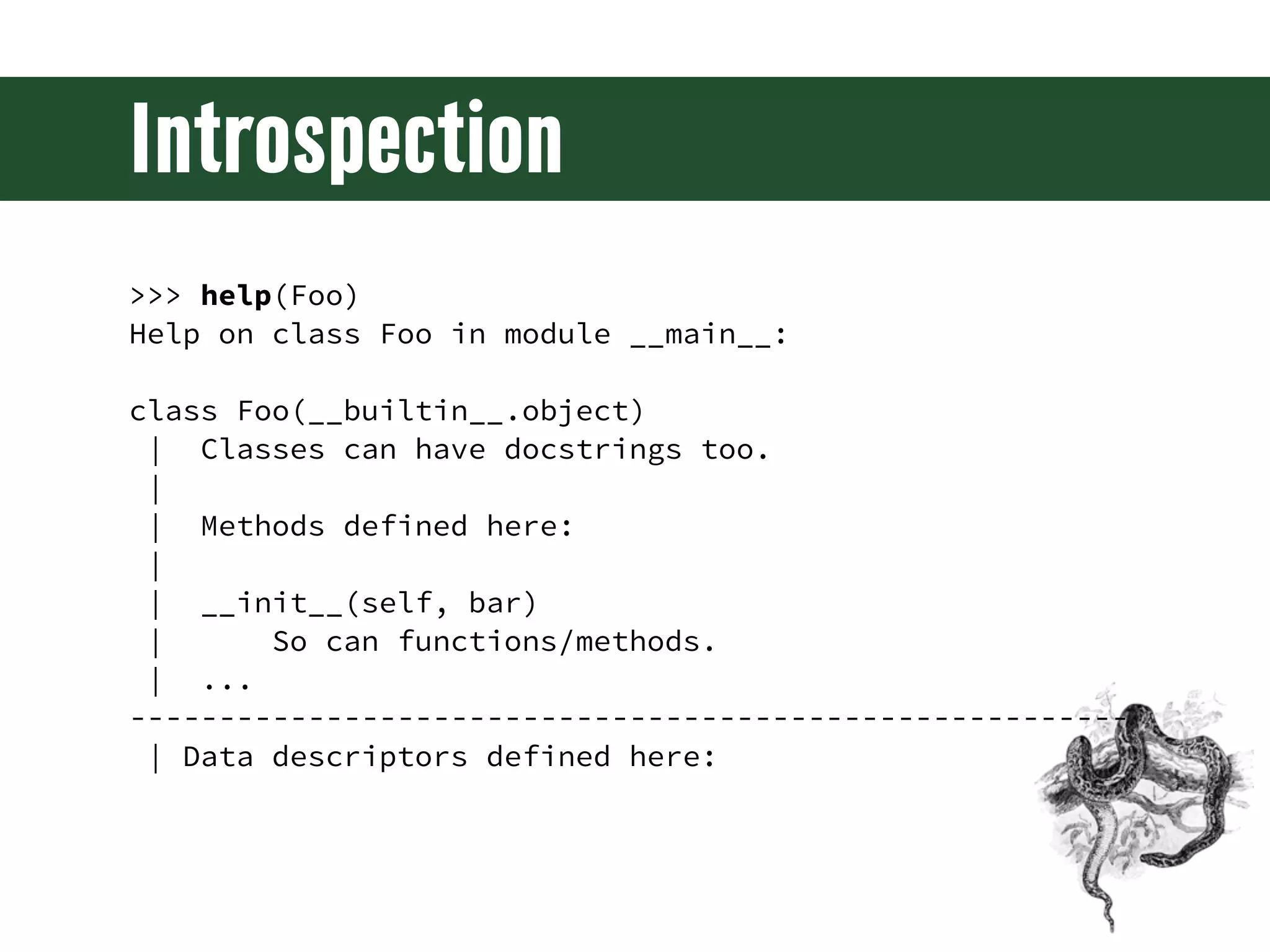
![Introspection >>> dir(Foo) ['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__doc__', '__format__', '__getattribute__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__module__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-33-2048.jpg)














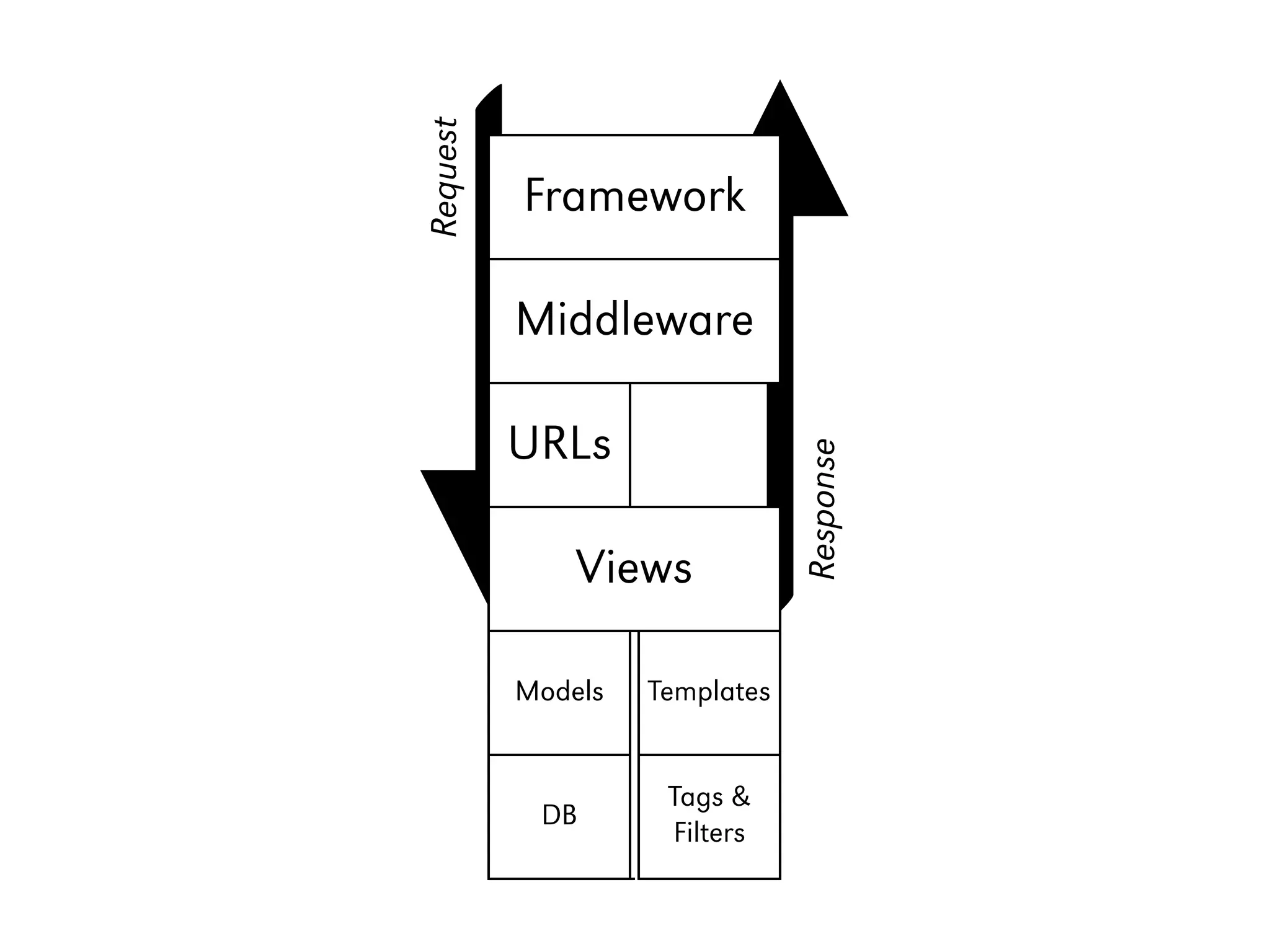






















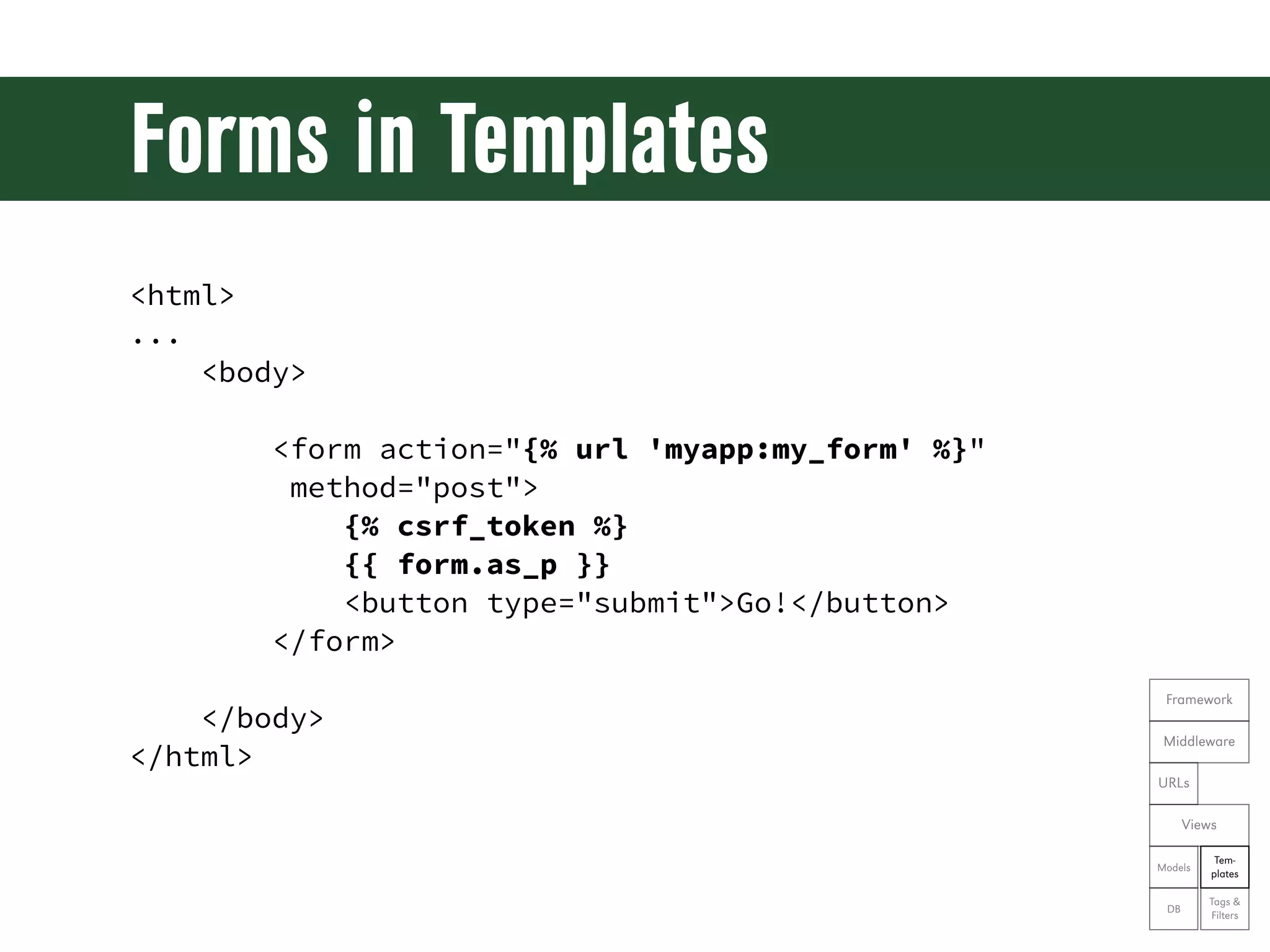
![Using a Form in a View from myapp.forms import MyForm def my_view(request): form = MyForm(request.POST or None) if request.method == "POST" and form.is_valid(): name = form.cleaned_data['name'] email = form.cleaned_data['email'] # do something great with that data return render(request, 'myapp/myform.html', { 'form': form Framework }) Middleware URLs Views Tem- Models plates Tags & DB Filters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-76-2048.jpg)

![Sending Mail • Add an EMAIL_BACKEND in settings.py EMAIL_BACKEND = 'django.core.mail.backends.console.EmailBackend' • Import and use from django.core.mail import send_mail send_mail('subject', 'message', 'sender', ['recipient', ...]) Framework Middleware URLs Views Tem- Models plates Tags & DB Filters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-79-2048.jpg)

















![Login Aer Registration from django.contrib.auth import authenticate, login user = authenticate( username=form.cleaned_data['username'], password=form.cleaned_data['password1']) login(request, user) Framework Middleware URLs Views Tem- Models plates Tags & DB Filters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-98-2048.jpg)


























![Saving a Model Object thingy = Thingy() thingy.size = 'big' thingy.save() gadget = Gadget(thingy=thingy) gadget.save() gizmo = Gizmo(thingies=[thingy]) gizmo.save() Framework Middleware URLs Views Tem- Models plates Tags & DB Filters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-134-2048.jpg)












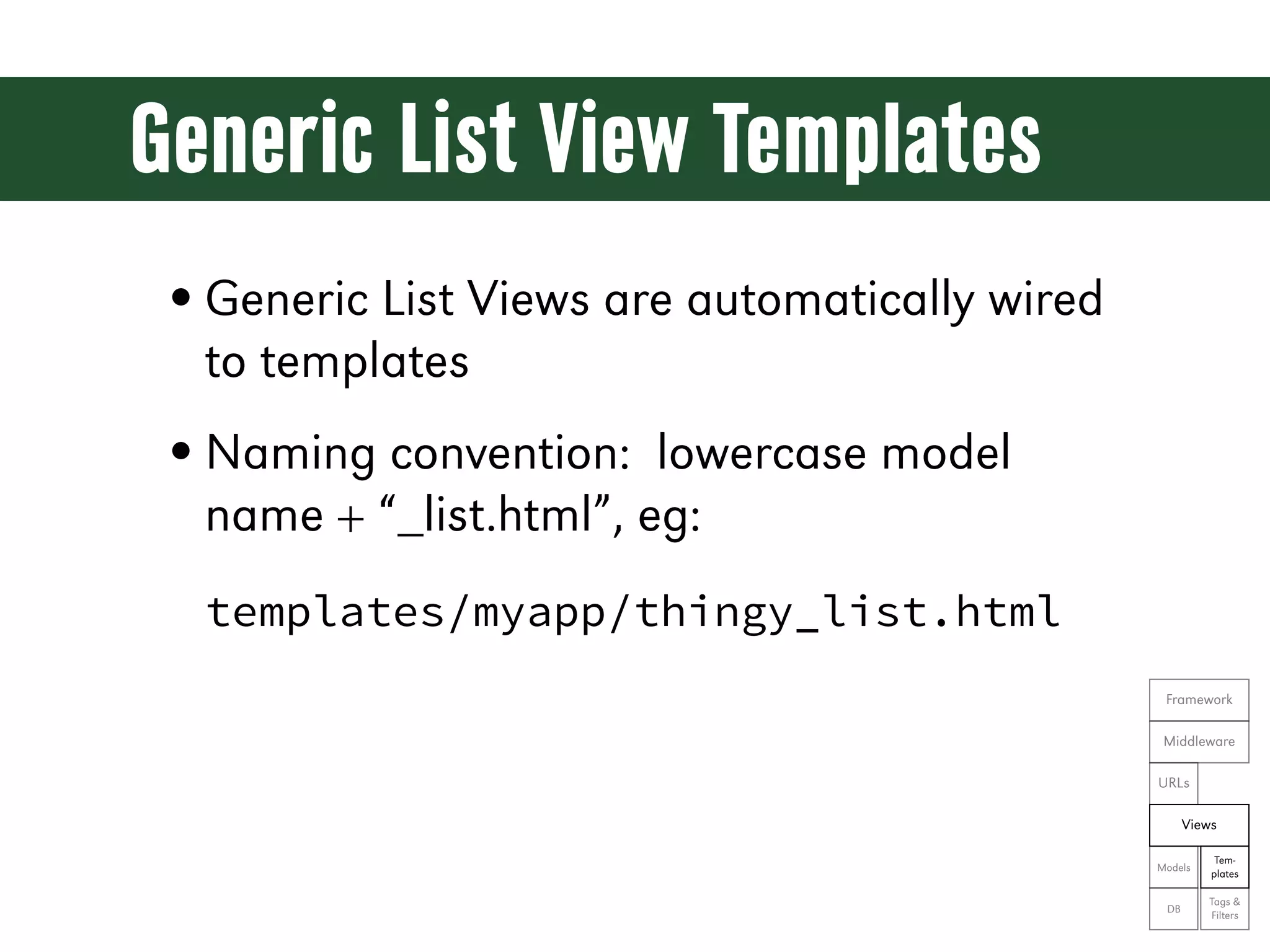



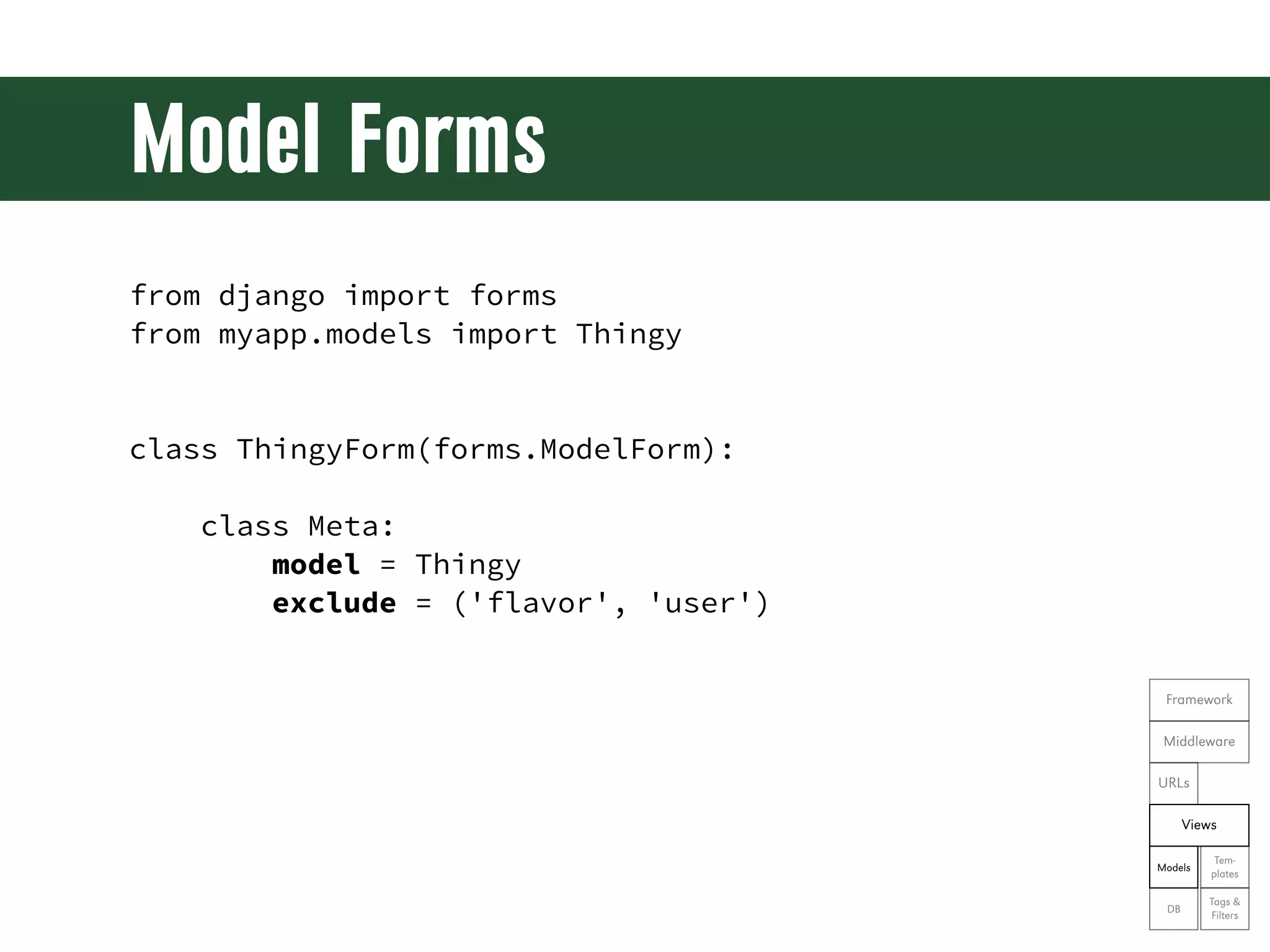

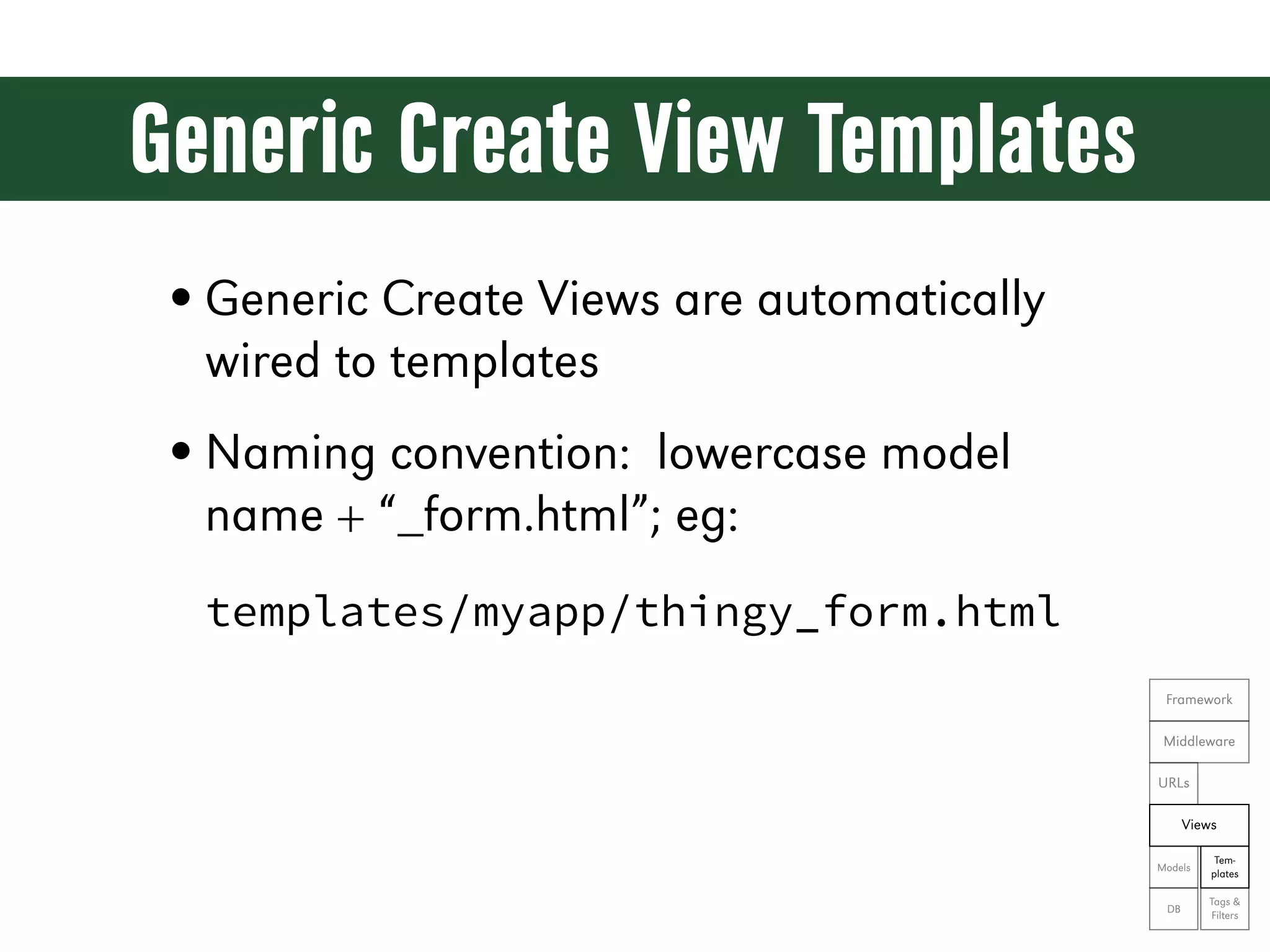


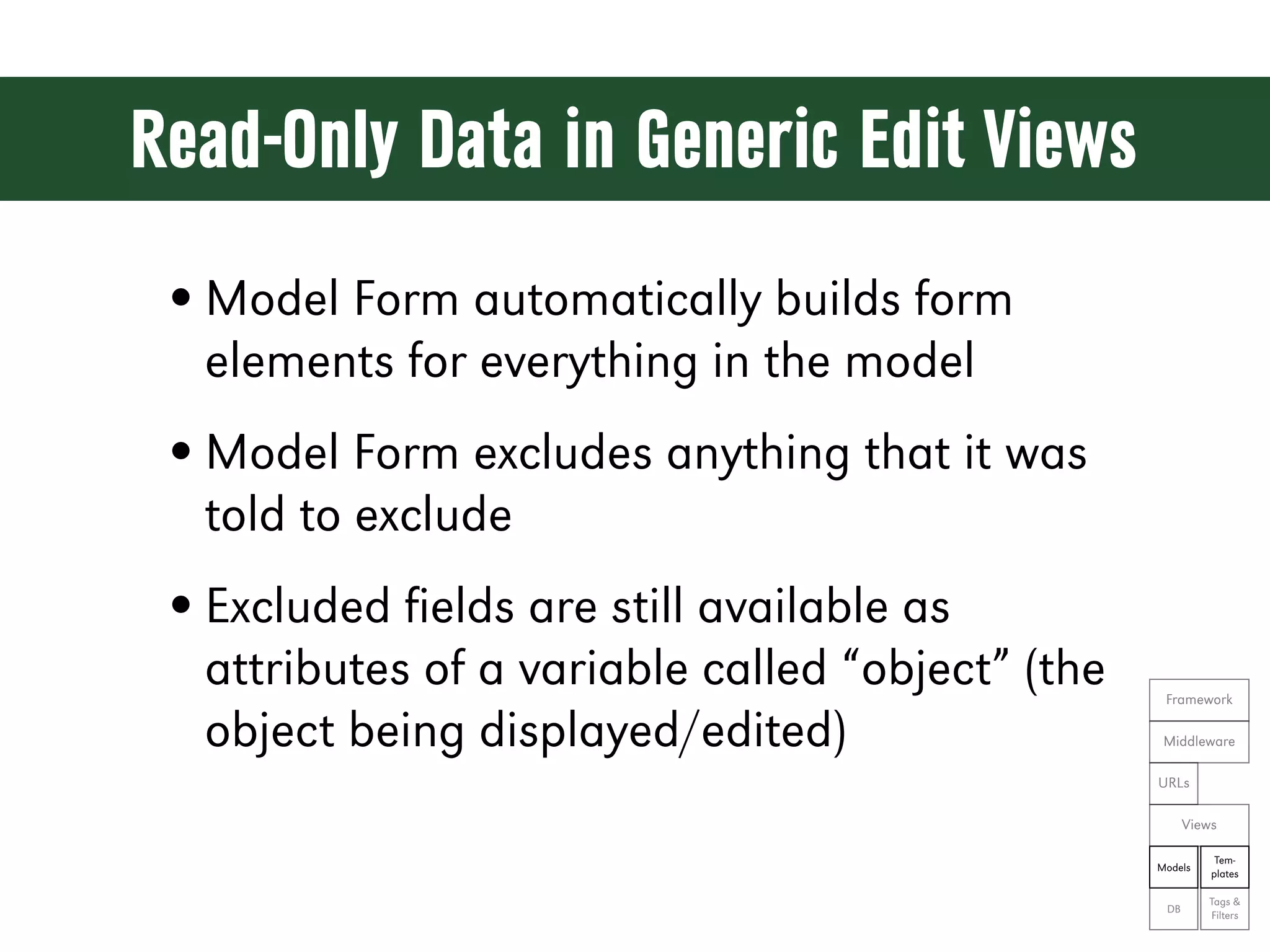
![Generic Edit Views from django.shortcuts import resolve_url from django.view.generic.edit import UpdateView from myapp.forms import ThingyForm class ThingyUpdateView(UpdateView): form_class = ThingyForm queryset = Thingy.objects.all() def get_success_url(self): return resolve_url('myapp:thingy') def get_context_data(self, **kwargs): Framework context = super(ThingyUpdateView, self).get_context_data(**kwargs) context['editing'] = True Middleware return context URLs Views Tem- Models plates Tags & DB Filters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-163-2048.jpg)
![Generic Edit View URLs from django.conf.urls import patterns, include, url from myapp.views import ThingyUpdateView urlpatterns = patterns('myapp.views', ... url(r'(?P<pk>[0-9]+)$', ThingyUpdateView.as_view(), name='update'), ) Framework Middleware URLs Views Tem- Models plates Tags & DB Filters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-164-2048.jpg)












![Exercise 20 • Create a custom filter function “boolean_icon” that will show one image if a value is True and another if it’s False • Use the boolean_icon in the user’s profile to indicate whether a talk has been approved • Use static icons from the admin site: Framework from django.contrib.admin.templatetags.admin_static import static Middleware icon_url = static('admin/img/icon-{0}.gif'.format( URLs {True: 'yes', False: 'no', None: 'unknown'}[value]) Views Tem- Models plates Tags & DB Filters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/djangoprecompiler-130113213208-phpapp02/75/Web-Development-with-Python-and-Django-181-2048.jpg)