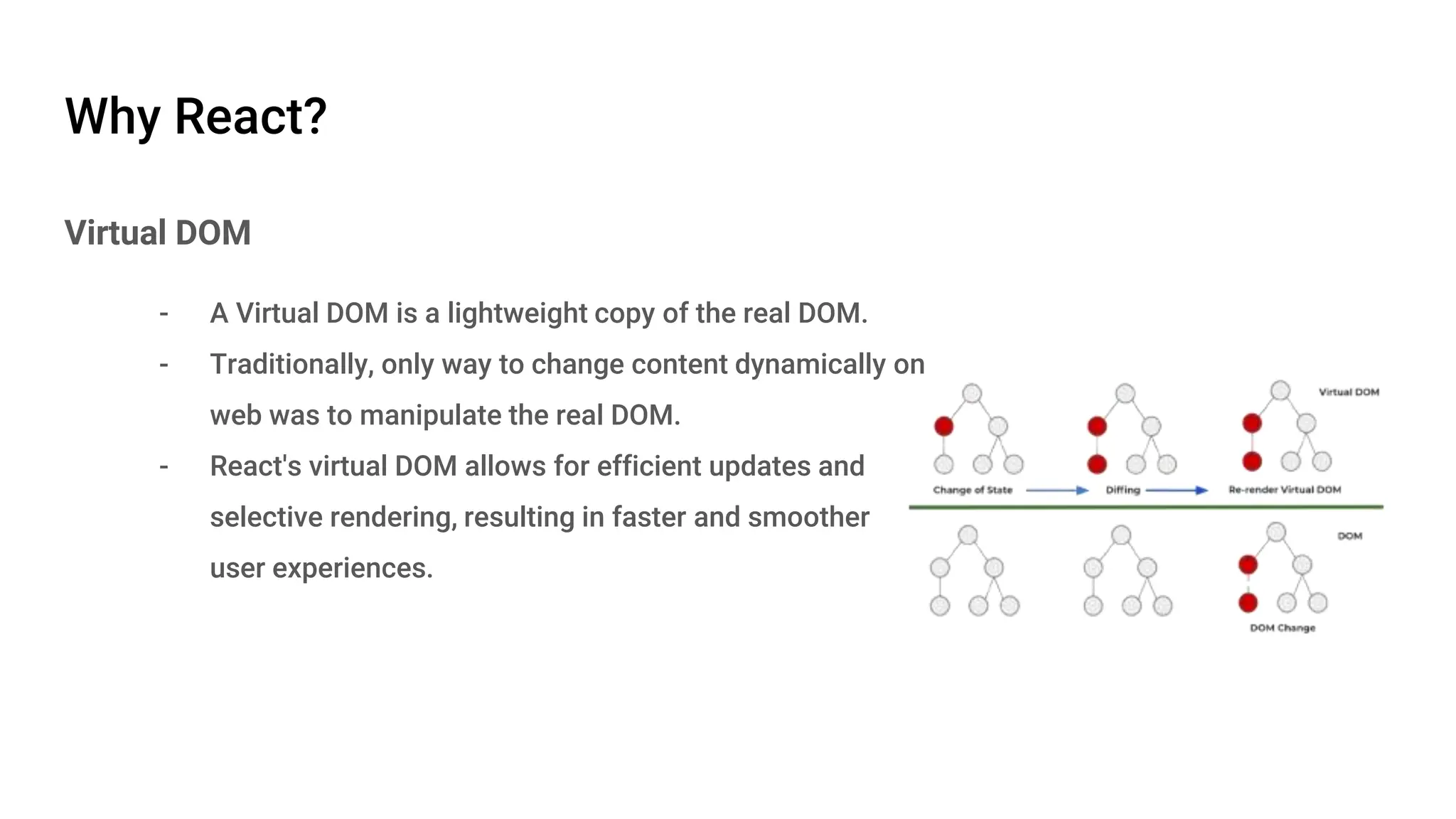
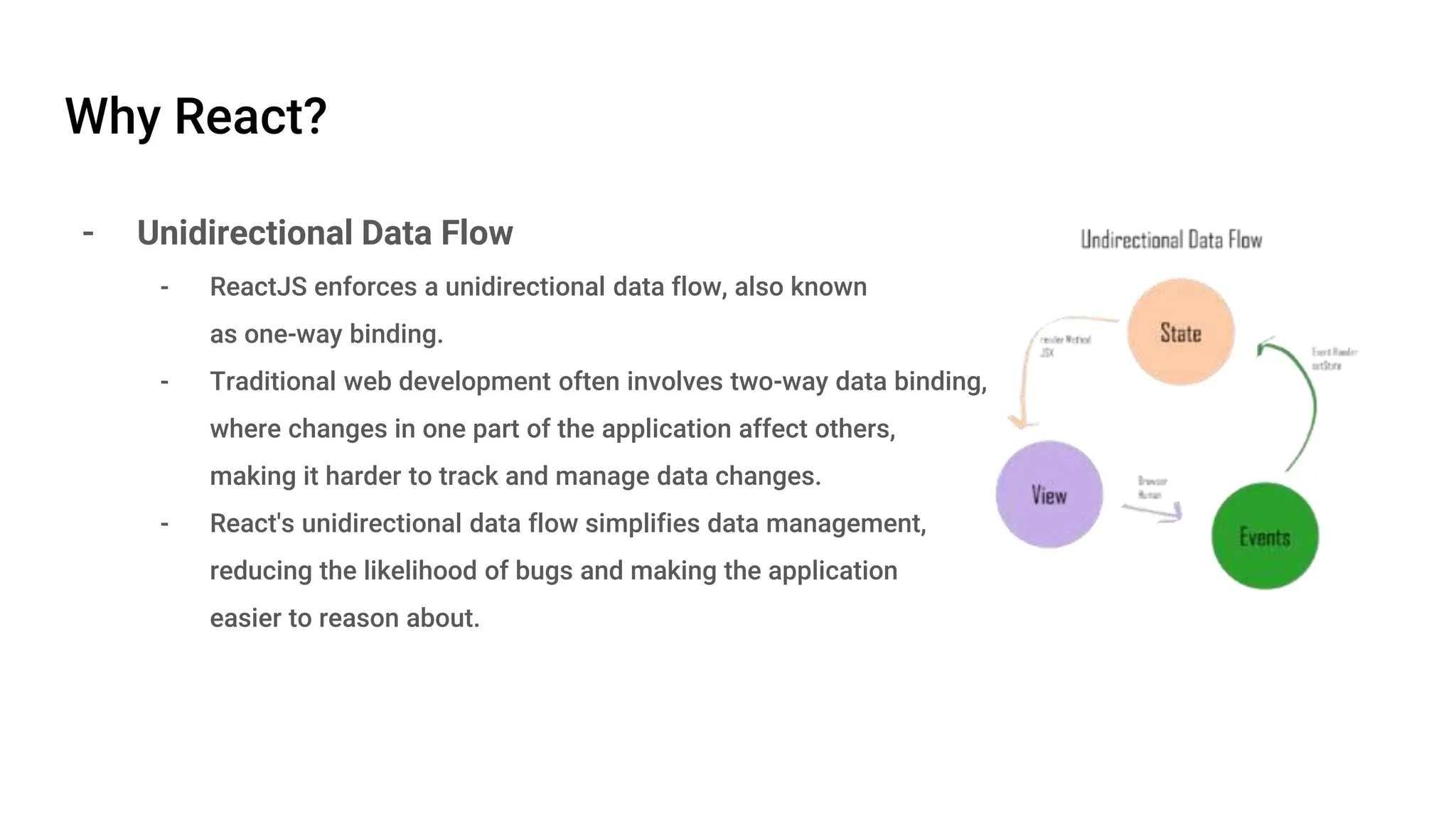
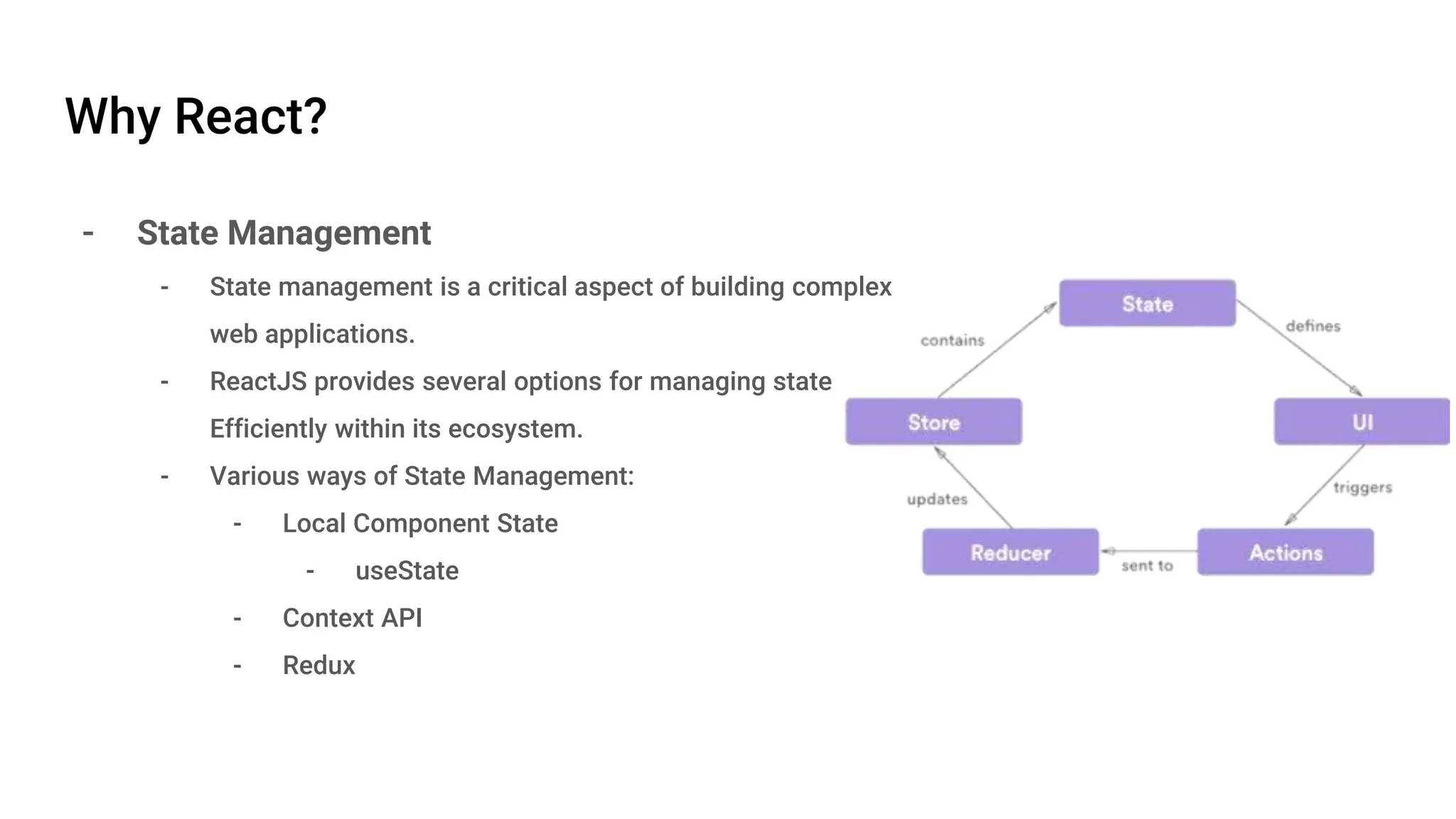
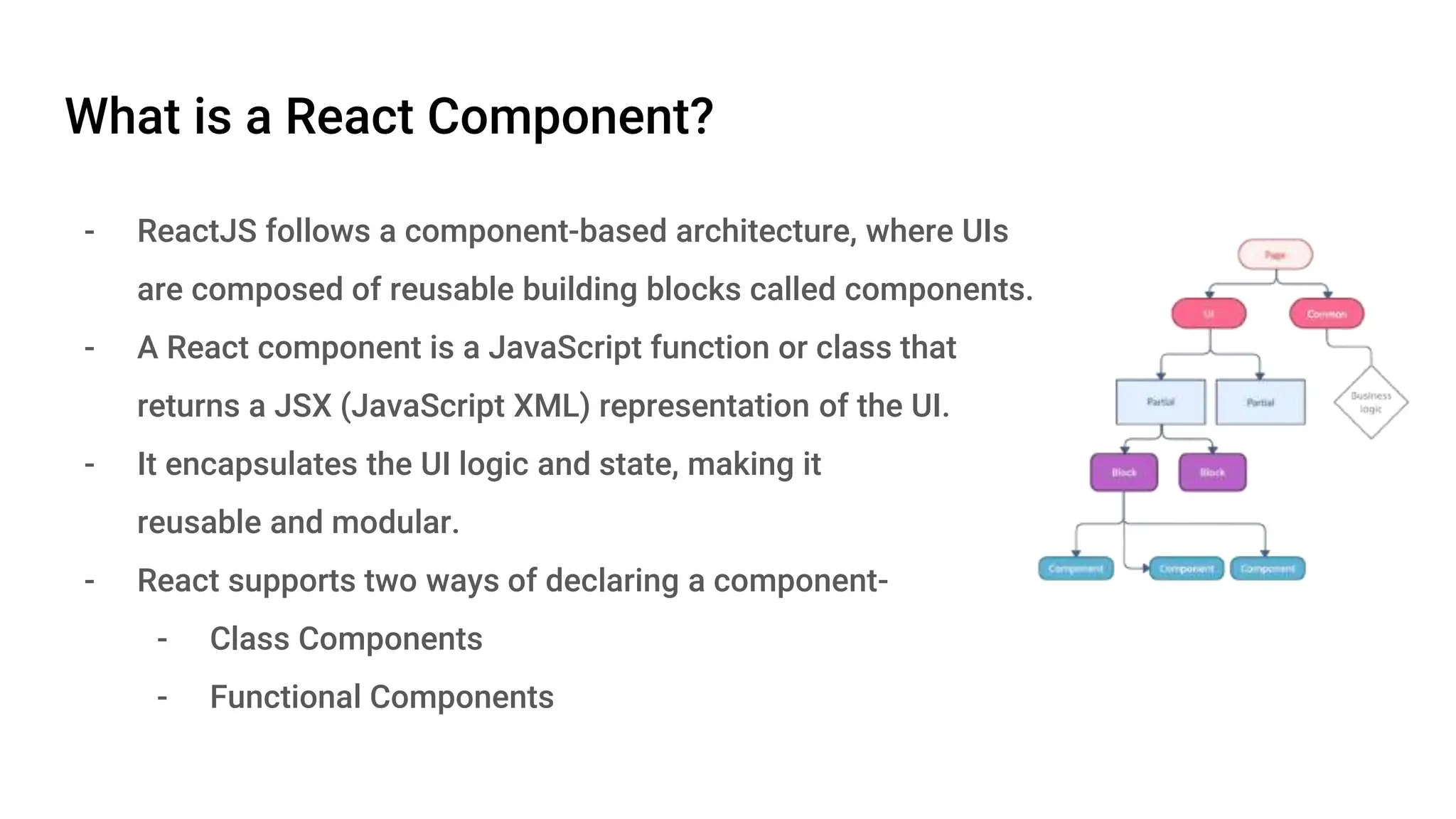
React is an open-source JavaScript library developed by Meta in 2013, focusing on building interactive UI components using a component-based architecture. It features a virtual DOM for efficient updates, unidirectional data flow for simpler data management, and various state management options. React components are modular and reusable, making it a powerful choice for front-end development.