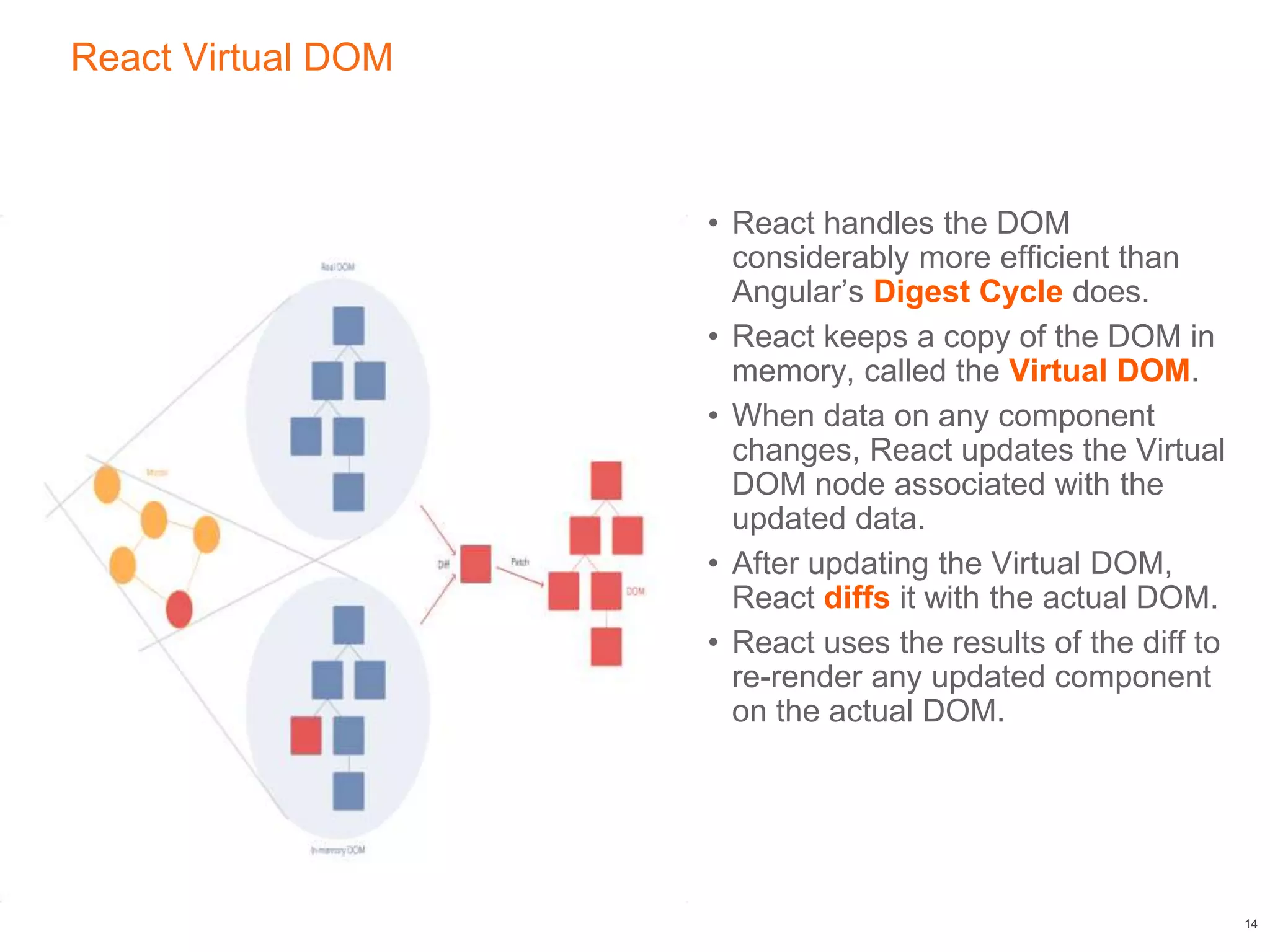
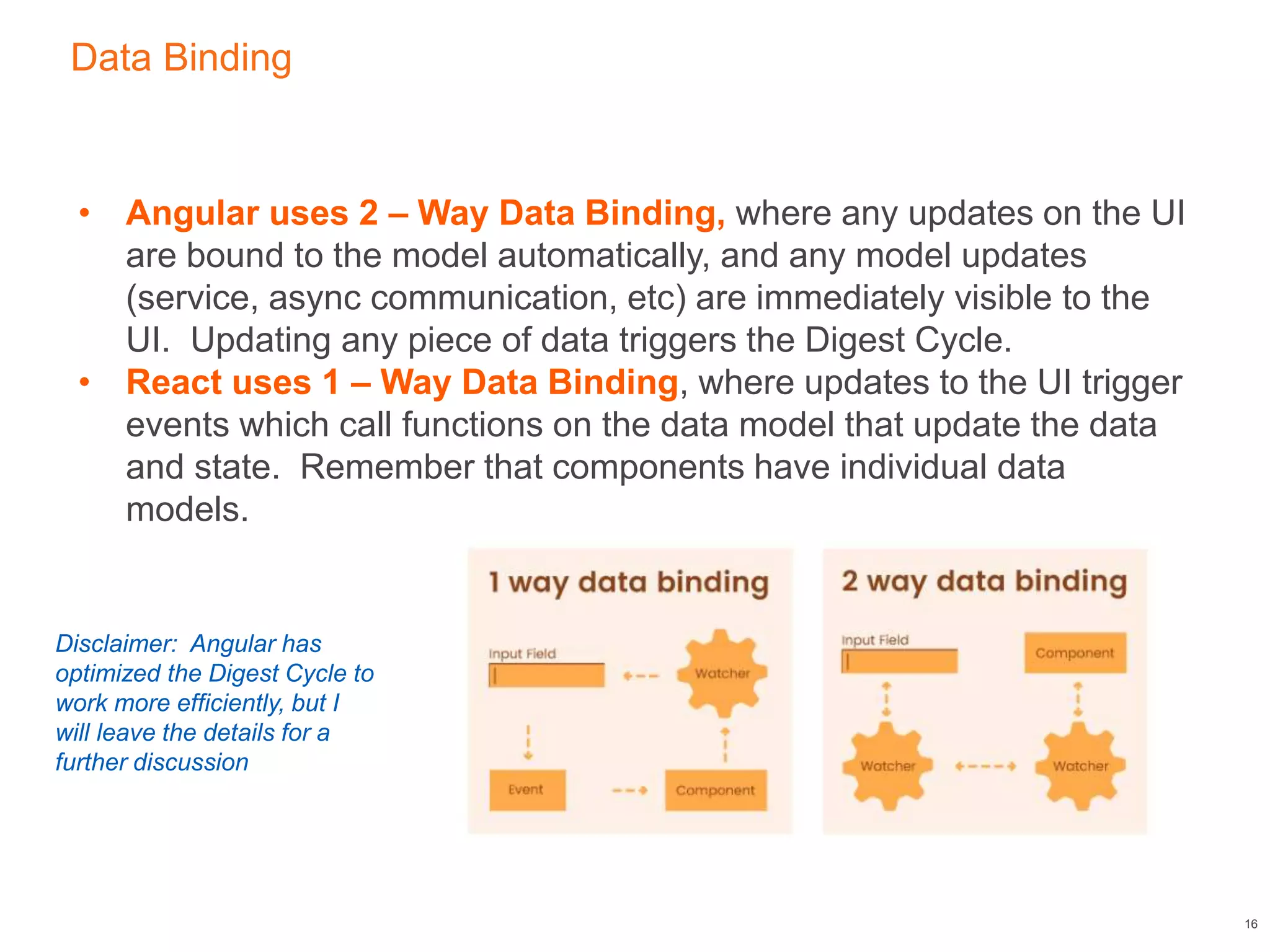
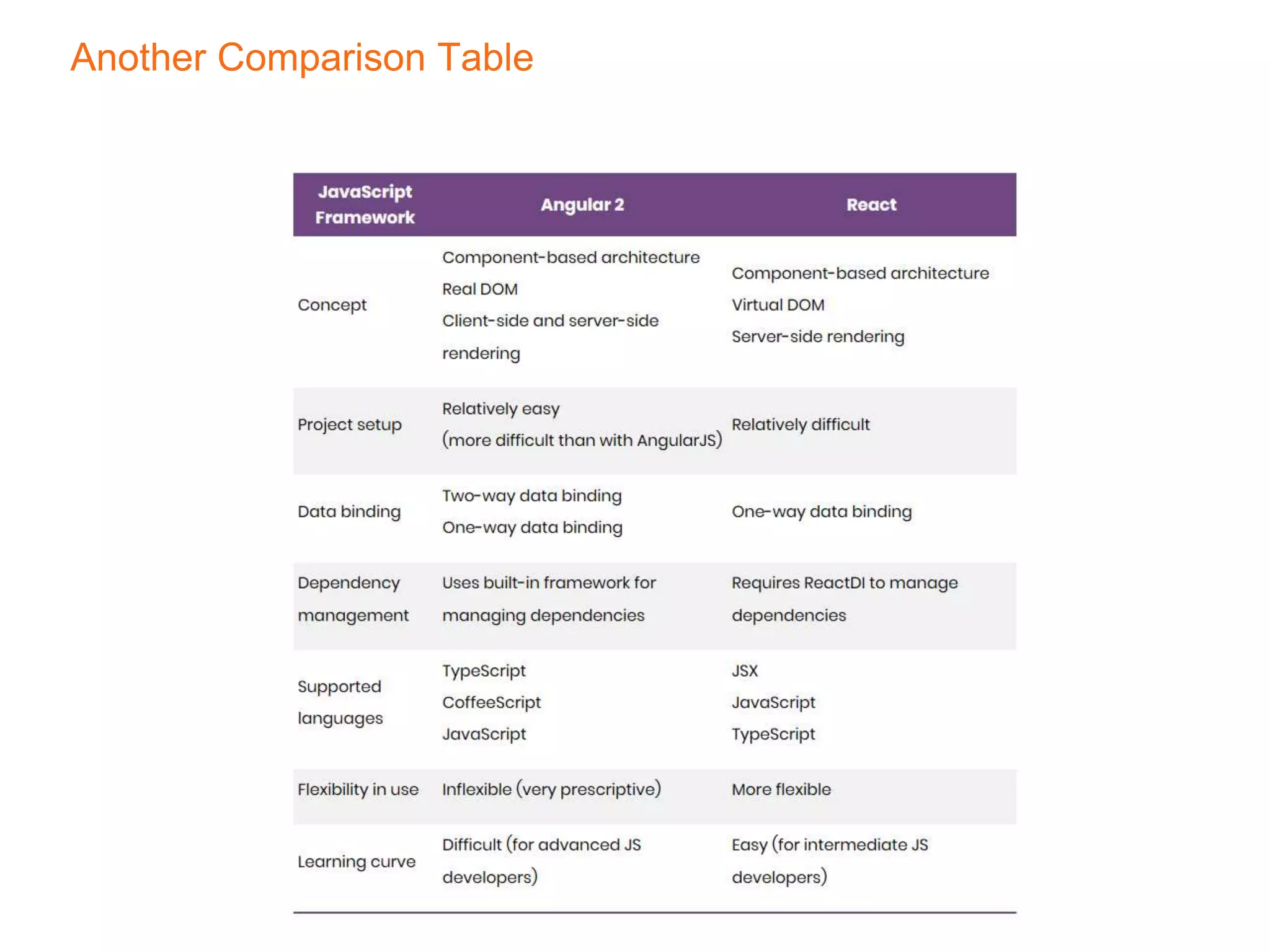
This document compares React, a JavaScript library for building user interfaces, and Angular, a TypeScript-based framework for single-page applications. It discusses their architectural differences, such as React's virtual DOM and one-way data binding against Angular's digest cycle and two-way data binding. The document highlights that while Angular offers more out-of-the-box functionality, React provides a more modular and flexible approach, making it easier to debug and integrate with other libraries.







![Sample Code <form (ngSubmit)="onSubmit(heroForm)" #heroForm="ngForm"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="name">Name <input class="form-control" name="name" required [(ngModel)]="hero.name"> </label> </div> <button type="submit" [disabled]="!heroForm.form.valid">Submit</b utton> </form> <div [hidden]="!heroForm.form.valid"> {{submitMessage}} </div> 10 var Saves = React.createClass({ getInitialState: function(){ ….. }, handleSubmit: function(e) { … }, render: function() { var savedText = ''; var submitText = 'Save'; if (this.state.saved) { savedText = 'You have saved this home.'; submitText = 'Remove'; } return ( <div className="saves"> <form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}> <input type="submit" value={submitText} /> </form> {this.state.numSaves} saves. {savedText} </div> ); } }); JavaScript in HTML! JS Render function contains HTML! Angular Template React JS Class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maycomparingangularandreactpublic-181227213735/75/Comparing-Angular-and-React-JS-for-SPAs-10-2048.jpg)