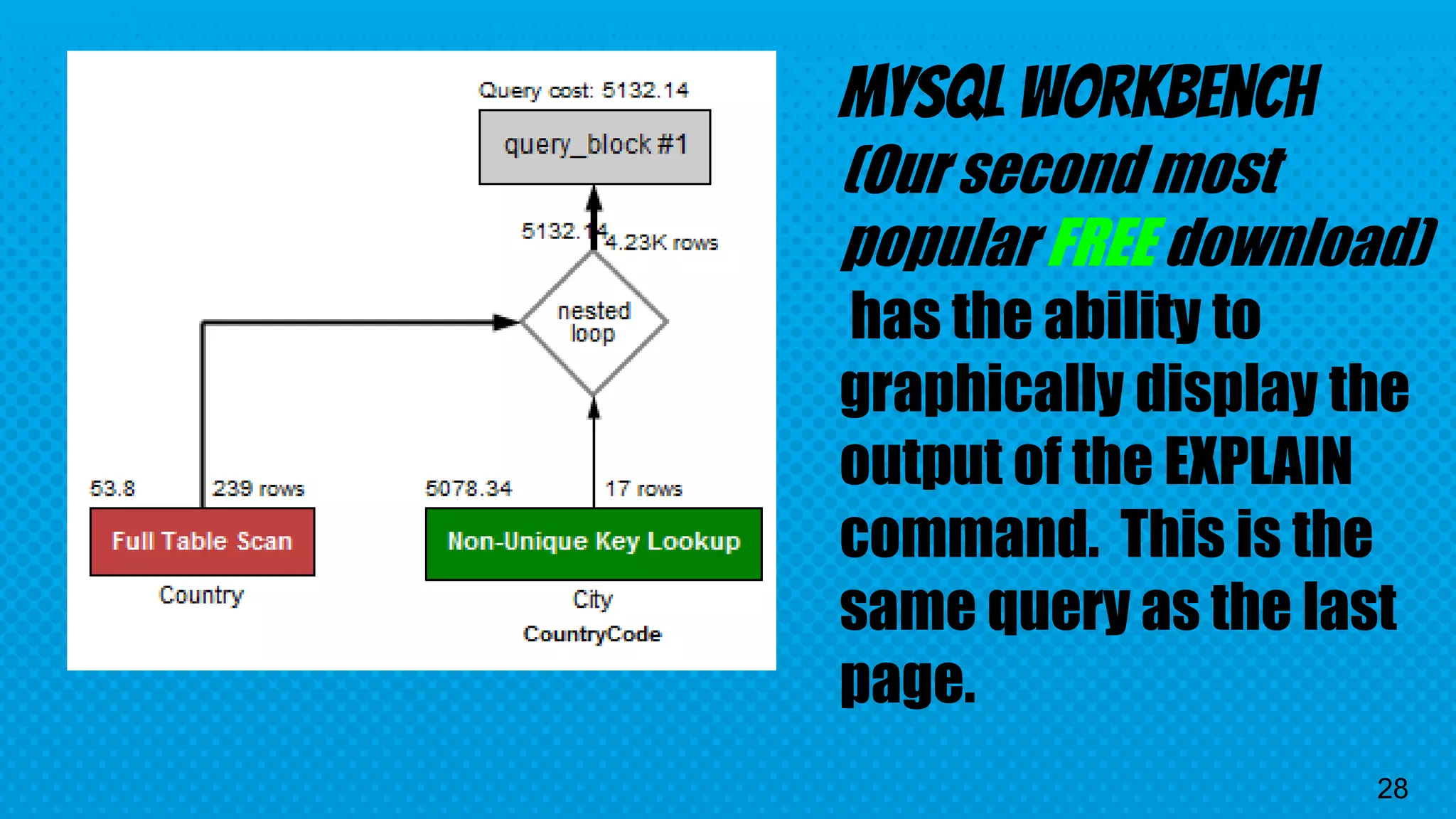
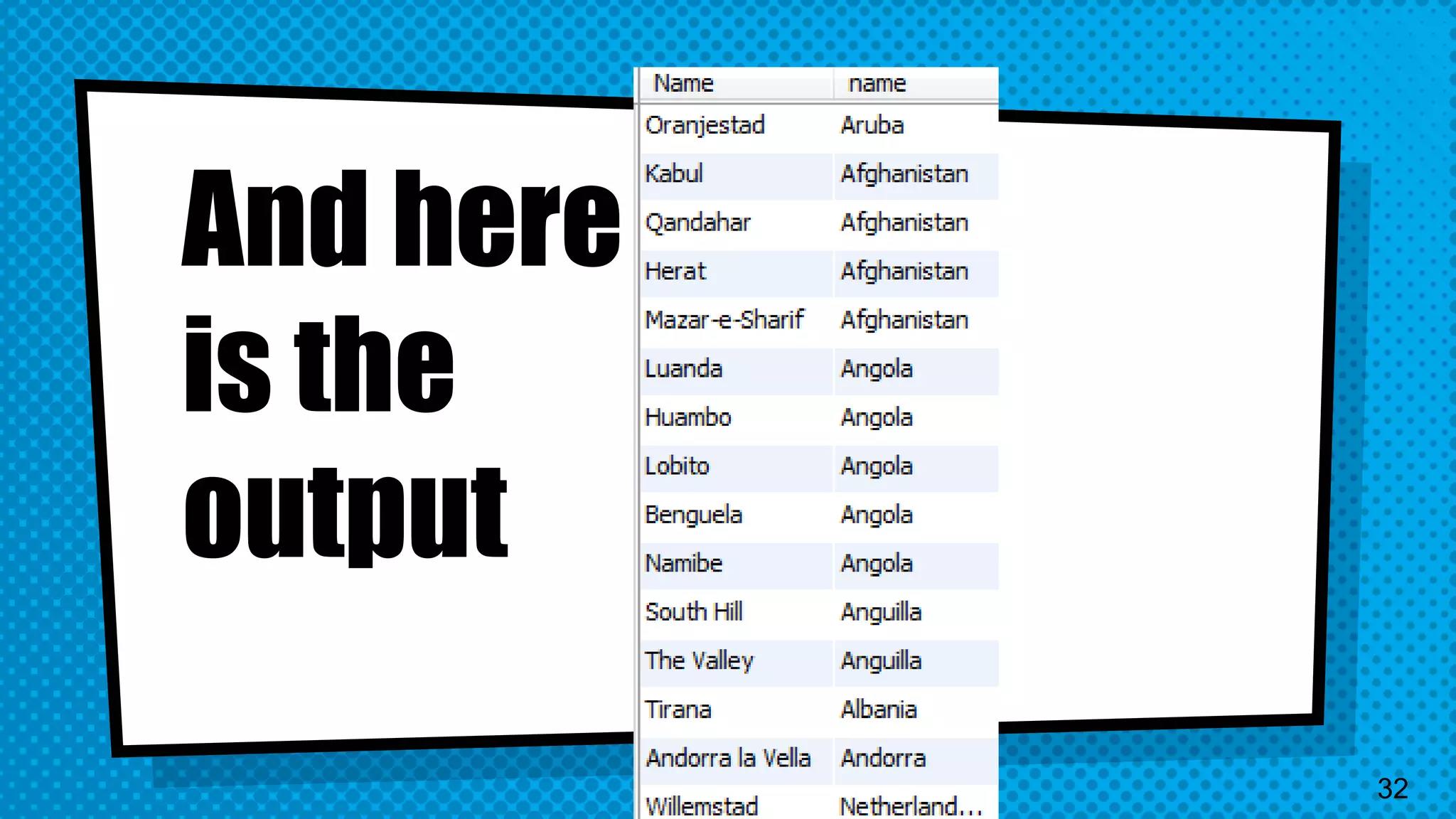
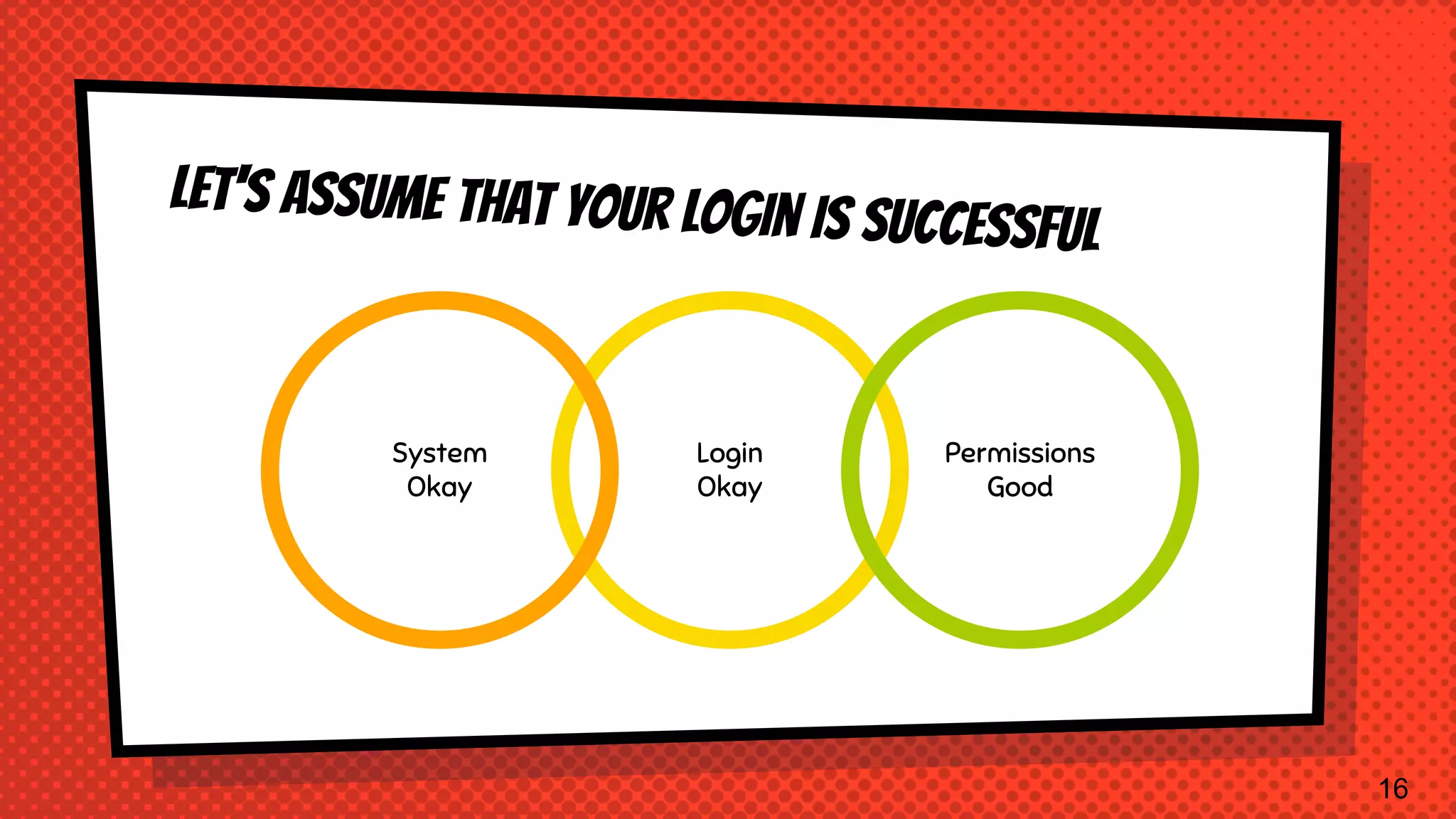
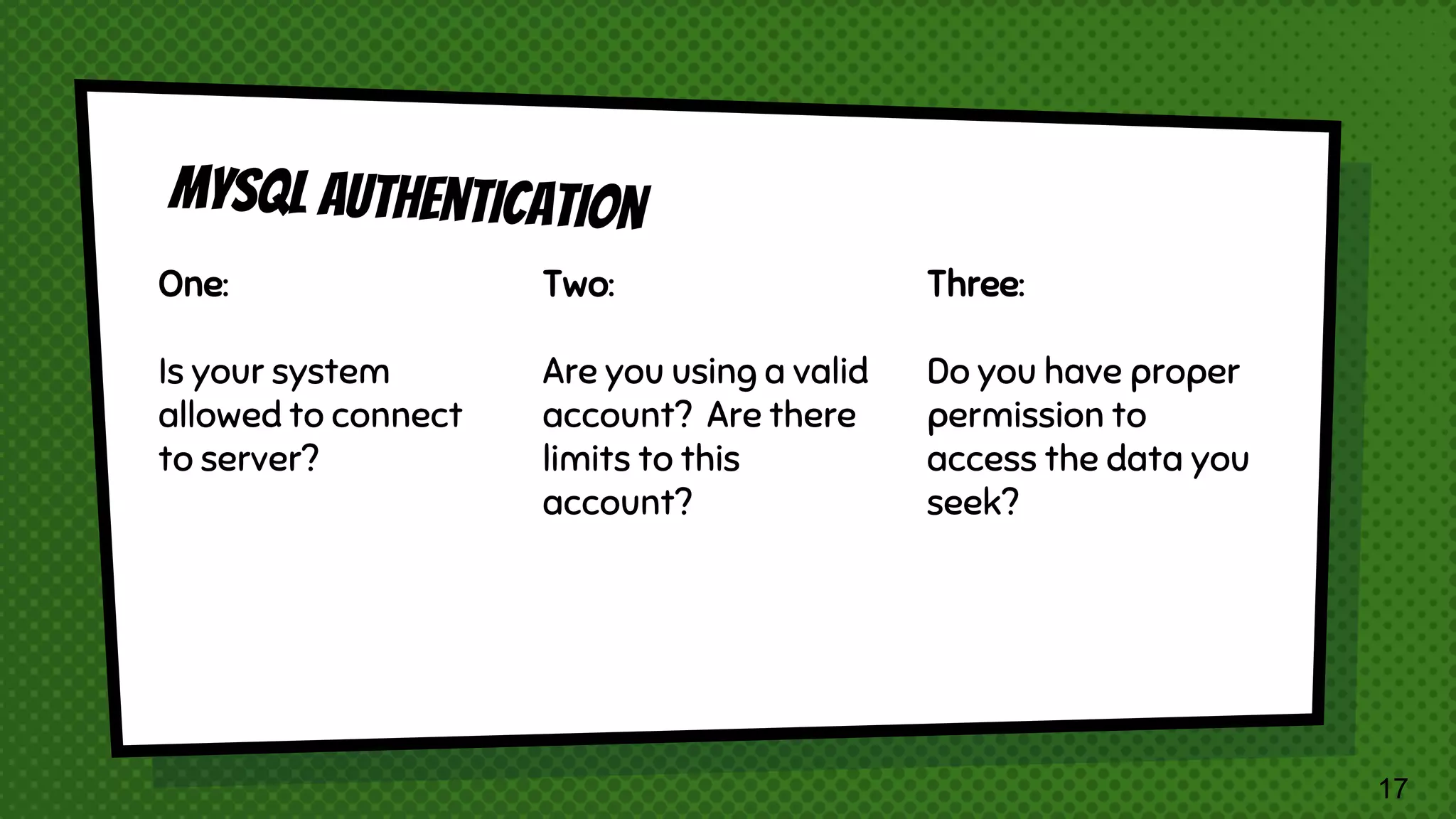
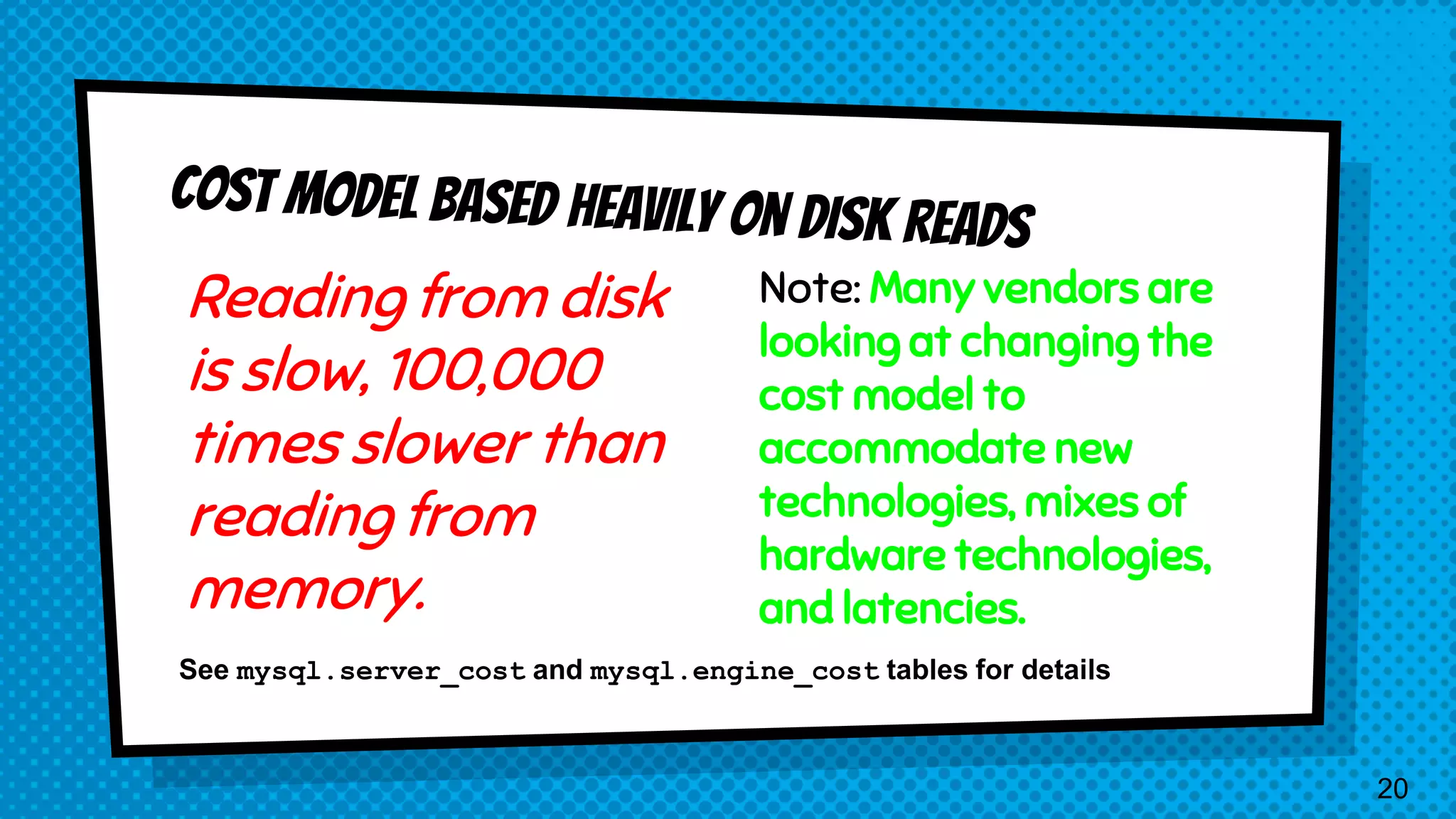
The document explains the inner workings of how SQL queries are processed by MySQL servers, detailing the roles of the query optimizer and cost-based optimization. It emphasizes the importance of proper query formulation, indexing, and data normalization to enhance performance and avoid common pitfalls. Additionally, it highlights features of MySQL 8 and provides insights on troubleshooting and improving query efficiency.















![{ "query_block": { "select_id": 1, "cost_info": { "query_cost": "5132.14" }, "nested_loop": [ { "table": { "table_name": "Country", "access_type": "ALL", "possible_keys": [ "PRIMARY" ], "rows_examined_per_scan": 239, "rows_produced_per_join": 239, "filtered": "100.00", "cost_info": { "read_cost": "6.00", "eval_cost": "47.80", "prefix_cost": "53.80", "data_read_per_join": "61K" }, "used_columns": [ "Code", "Name" ] } }, { "table": { "table_name": "City", "access_type": "ref", "possible_keys": [ "CountryCode" ], "key": "CountryCode", "used_key_parts": [ "CountryCode" ], "key_length": "3", "ref": [ "world.Country.Code" ], "rows_examined_per_scan": 17, "rows_produced_per_join": 4231, "filtered": "100.00", "cost_info": { "read_cost": "4231.95", "eval_cost": "846.39", "prefix_cost": "5132.14", "data_read_per_join": "727K" }, "used_columns": [ "Name", "CountryCode" ] } } ] } } 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatyourdatabasequeryisreallydoing-160928194457/75/What-Your-Database-Query-is-Really-Doing-23-2048.jpg)
!["nested_loop": [ { "table": { "table_name": "Country", "access_type": "ALL", "possible_keys": [ "PRIMARY" ], "rows_examined_per_scan": 239, "rows_produced_per_join": 239, "filtered": "100.00", "cost_info": { "read_cost": "6.00", "eval_cost": "47.80", "prefix_cost": "53.80", "data_read_per_join": "61K" }, "used_columns": [ "Code", "Name" ] Nested loop join for Country Table We DO have an index for the JOIN :-) Statistics 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatyourdatabasequeryisreallydoing-160928194457/75/What-Your-Database-Query-is-Really-Doing-24-2048.jpg)