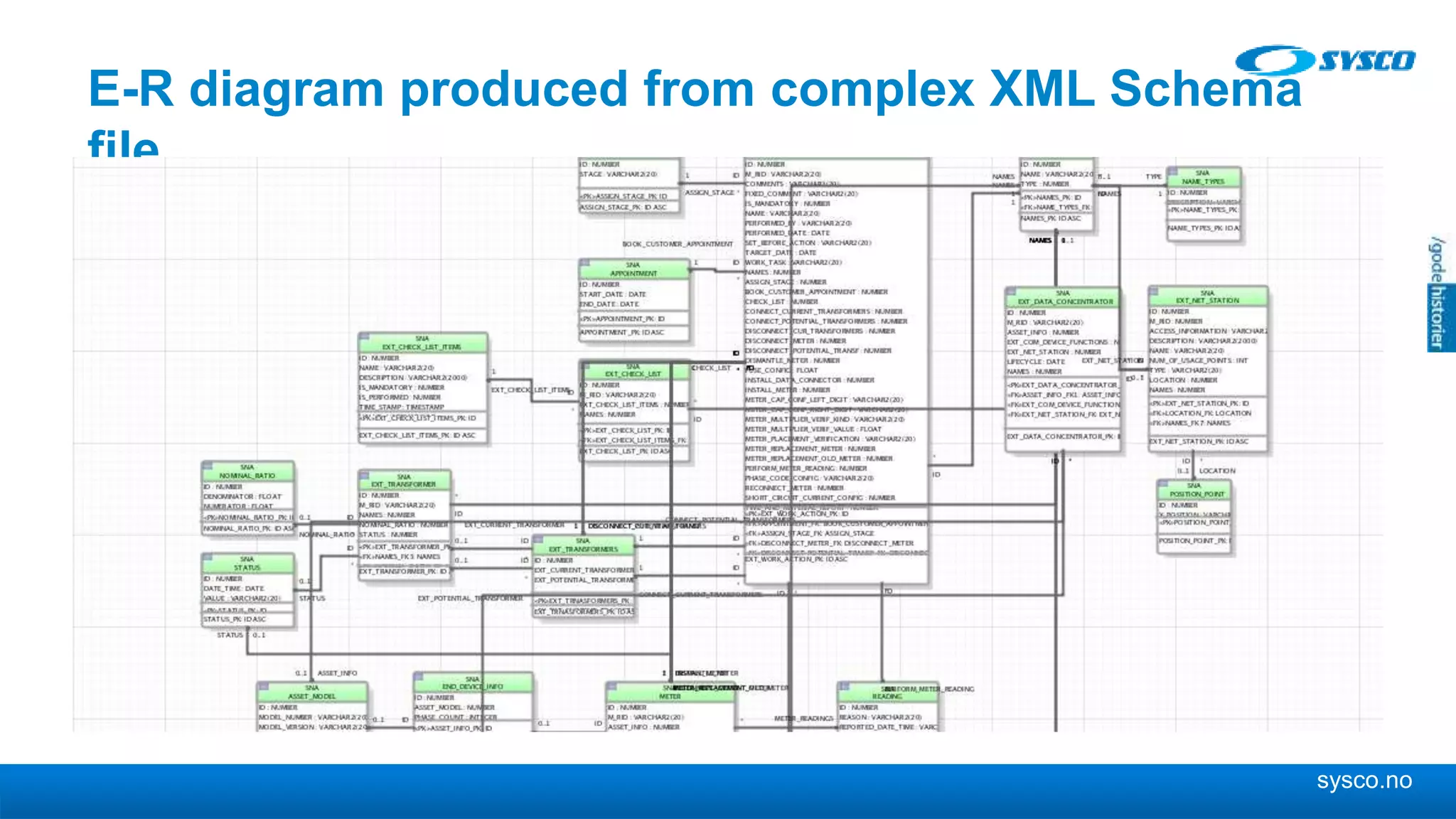
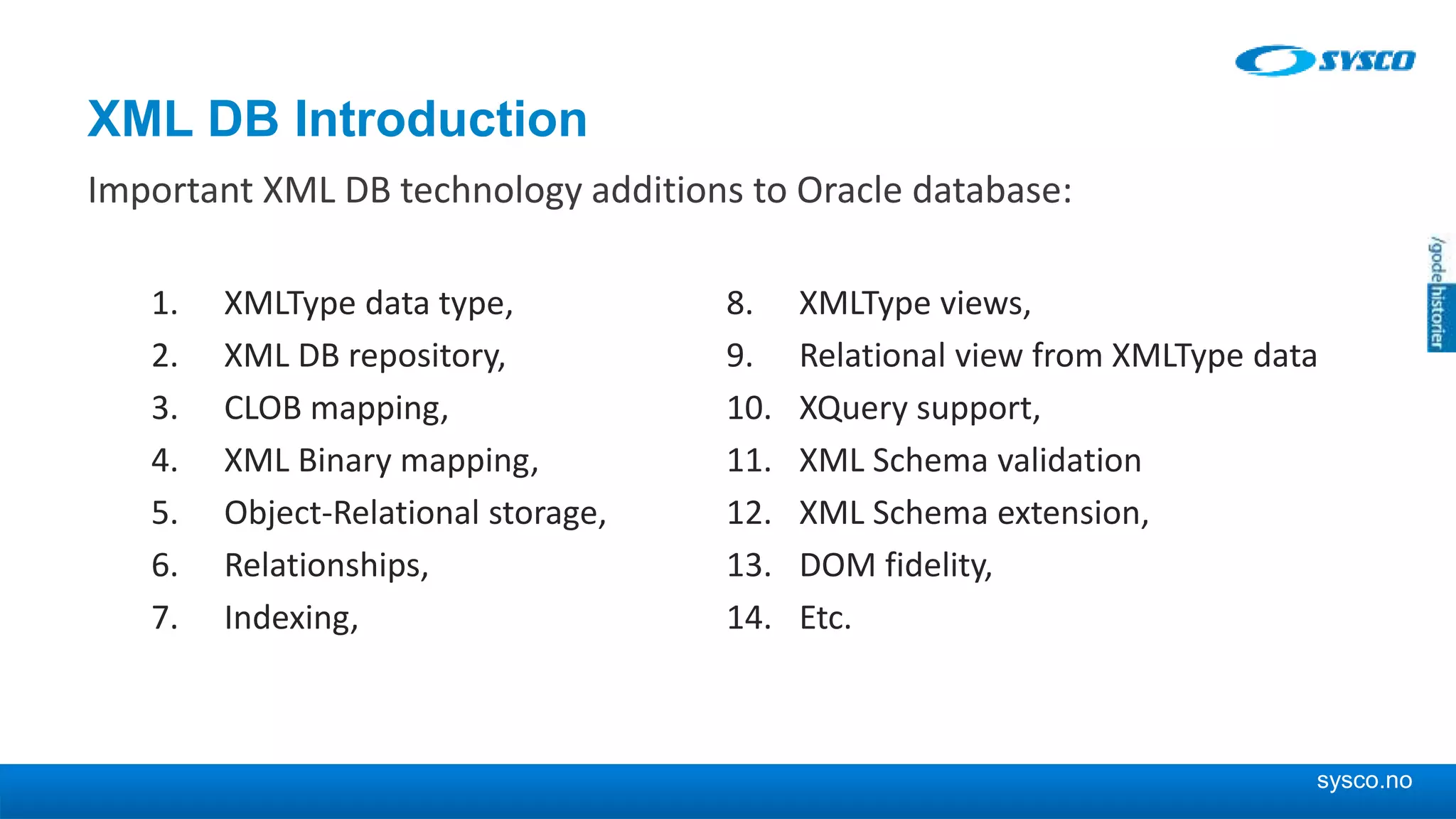
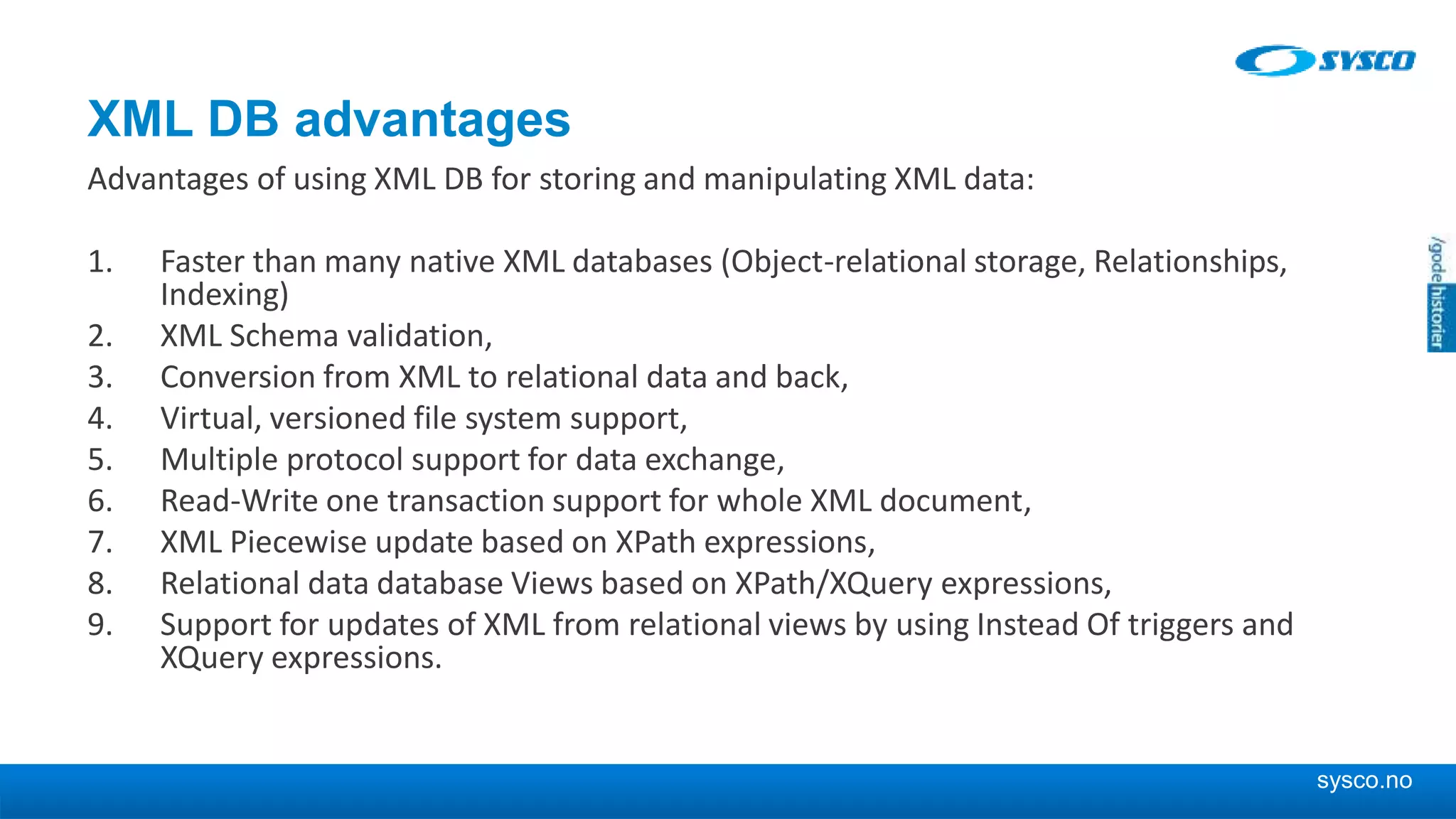
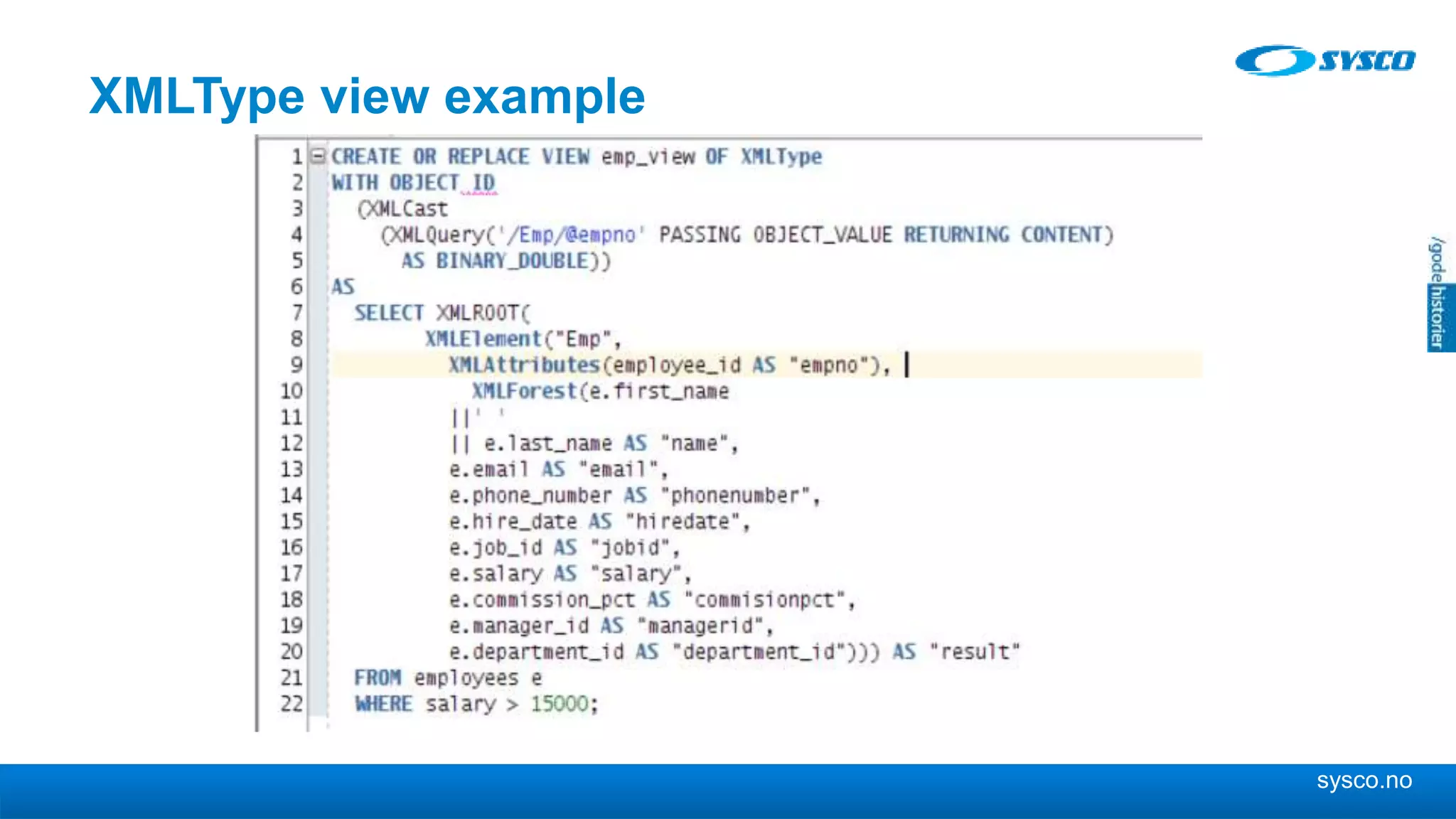
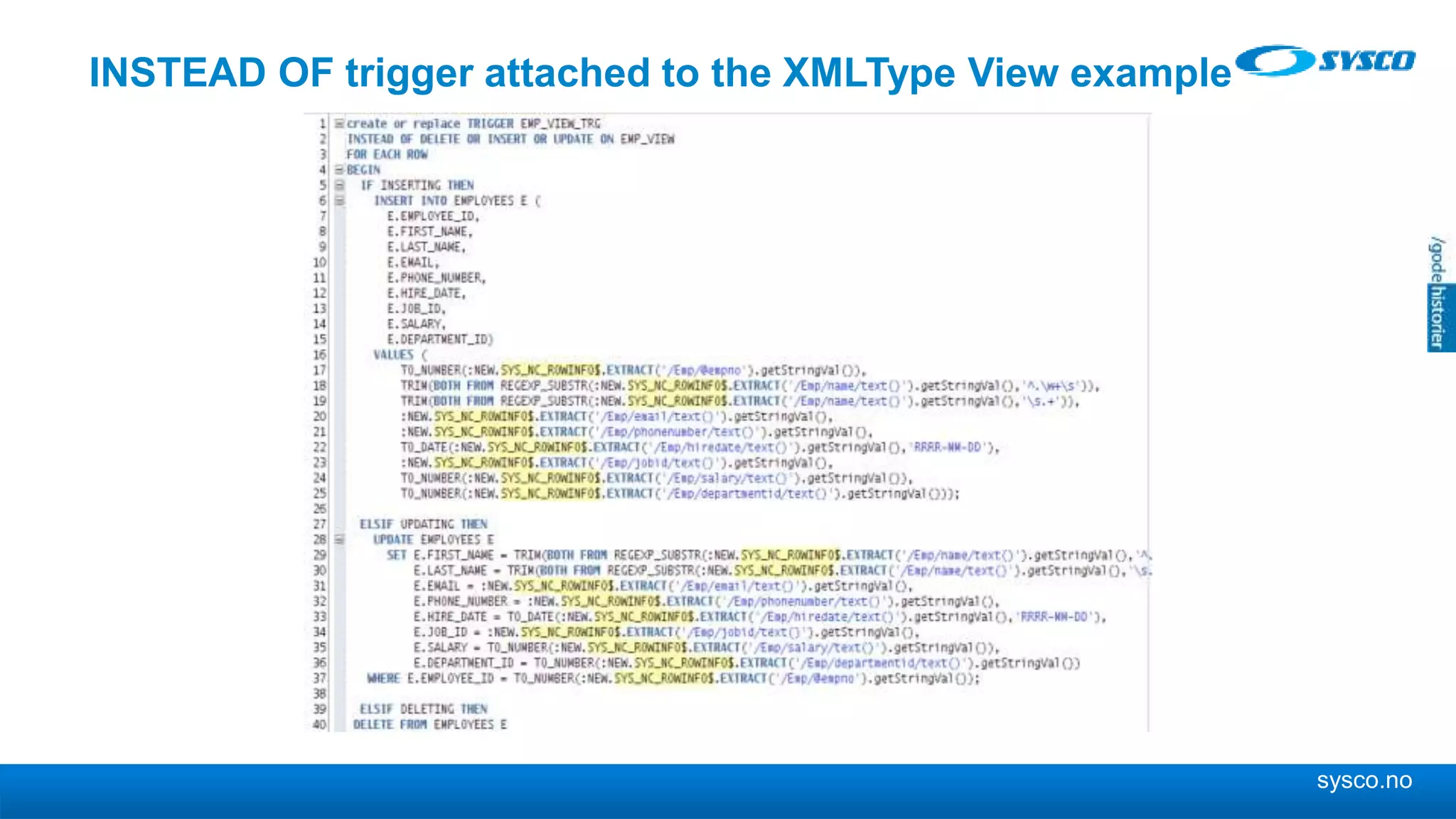
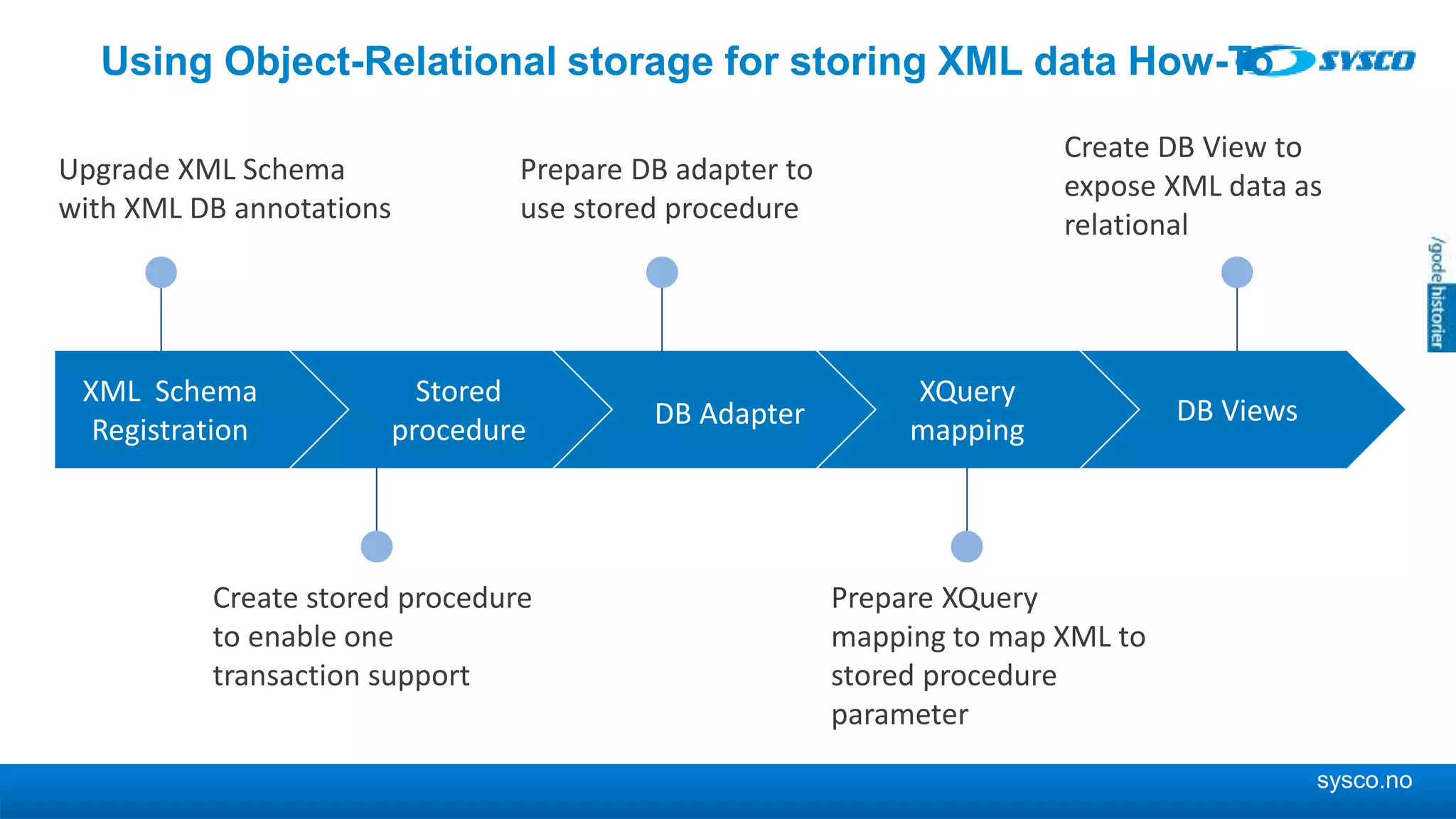
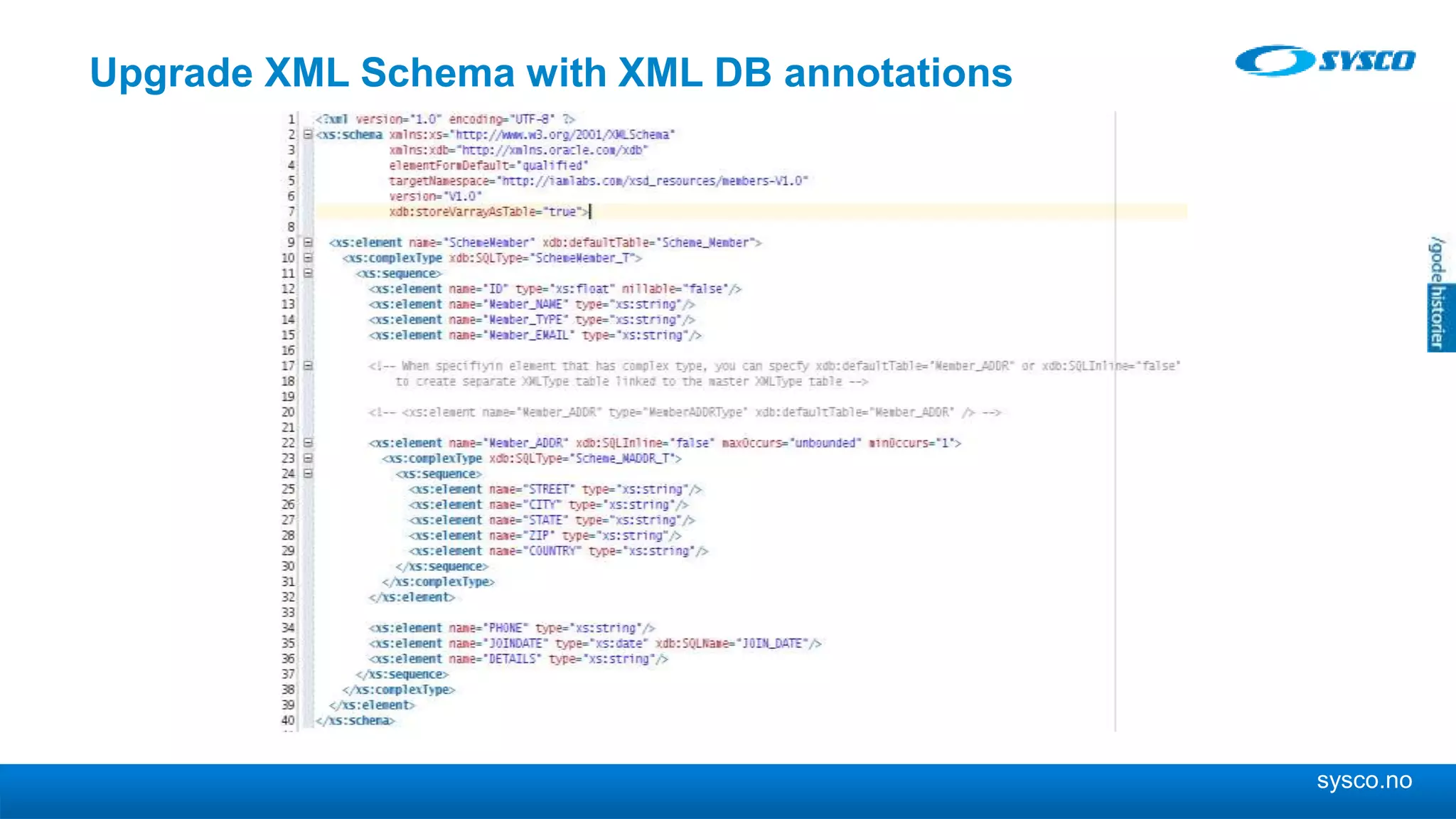
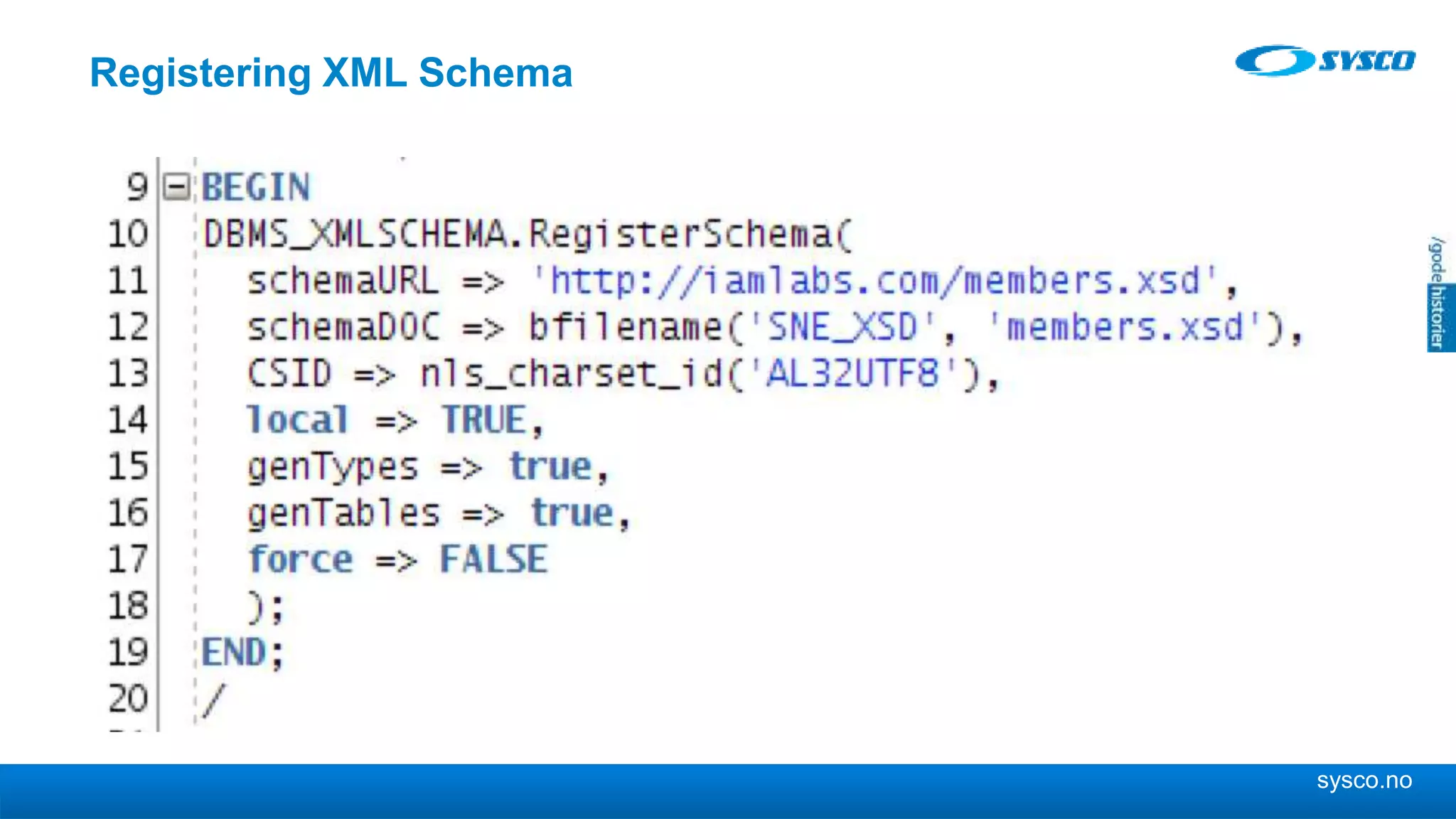
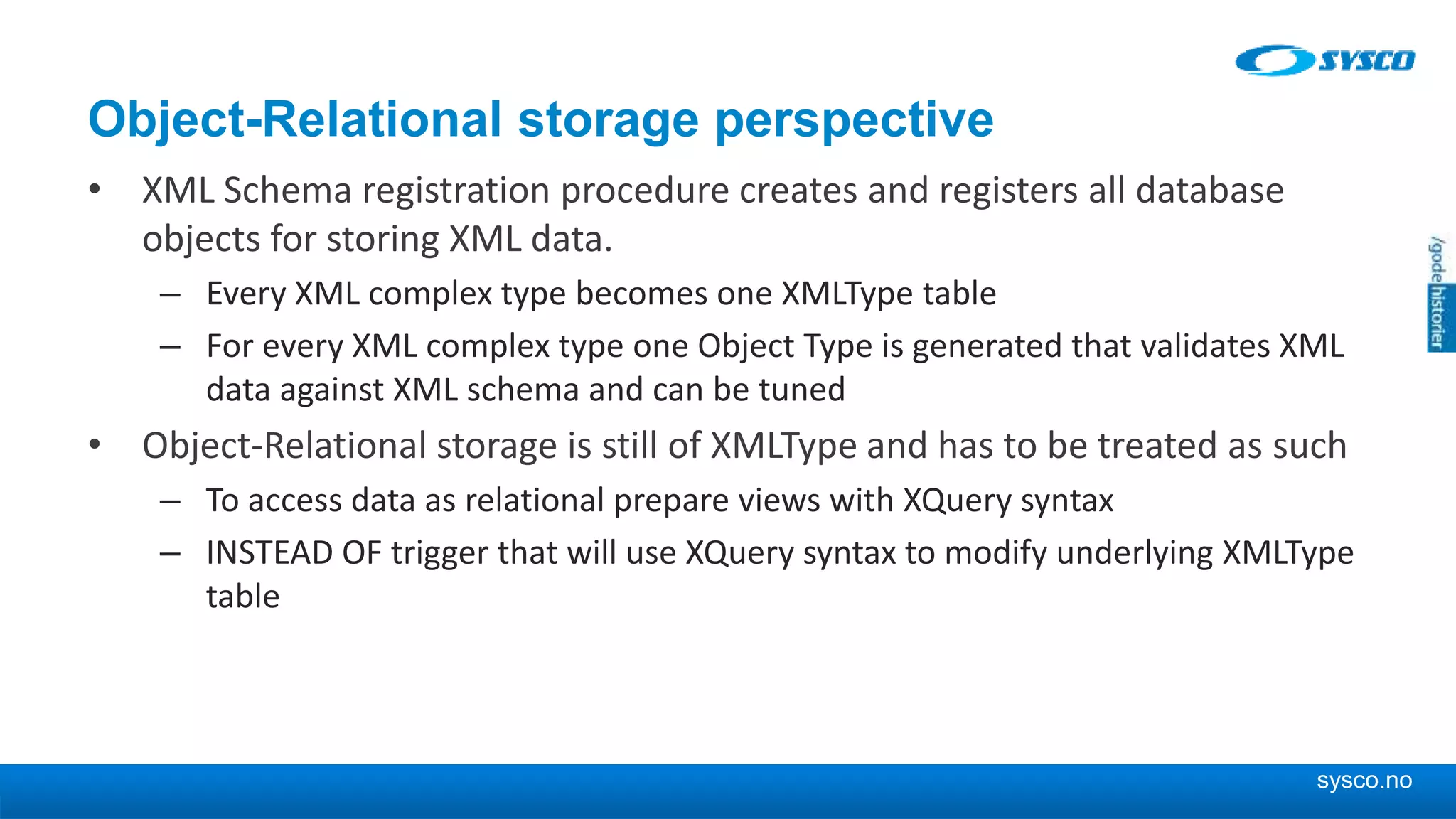
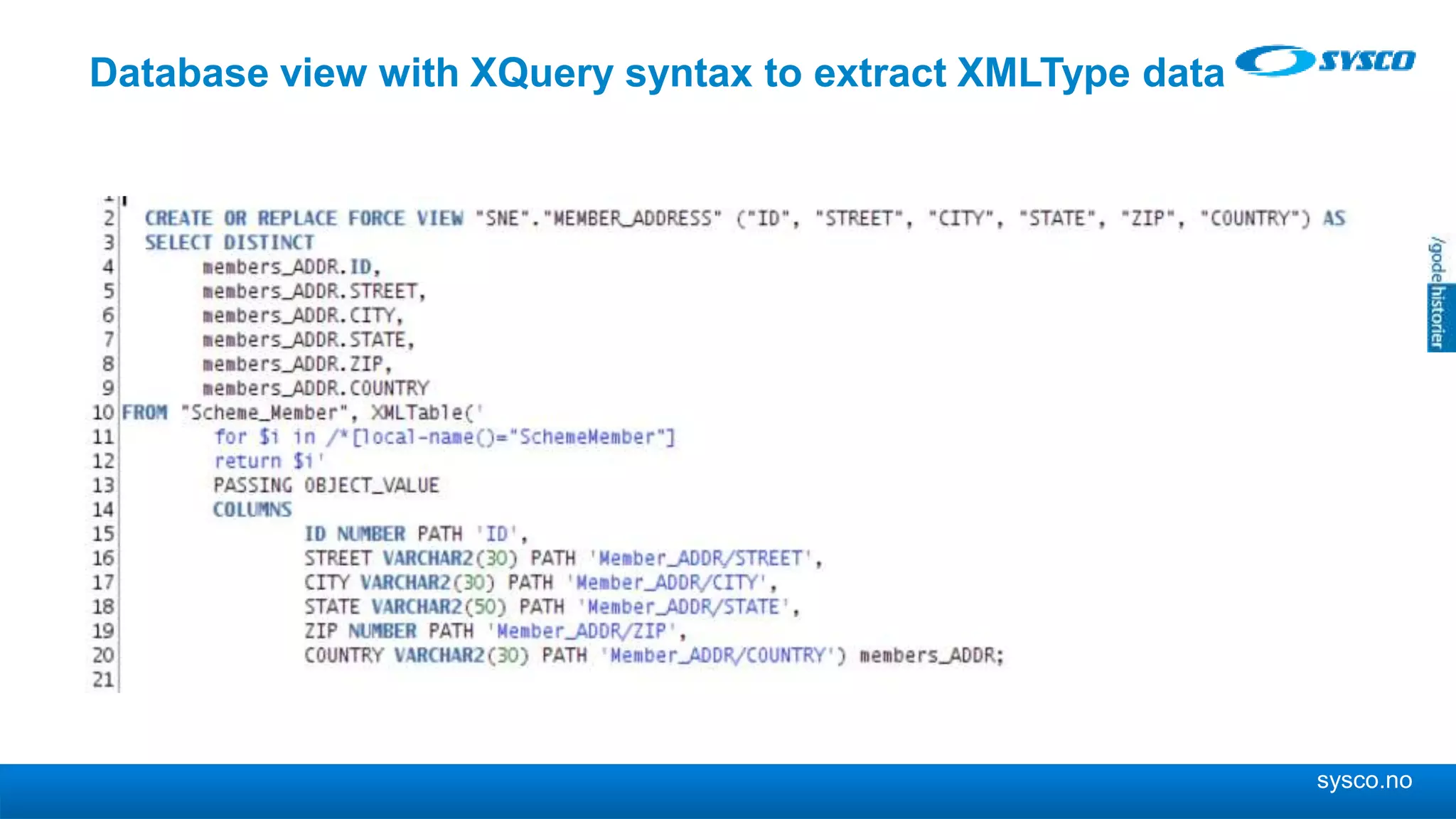
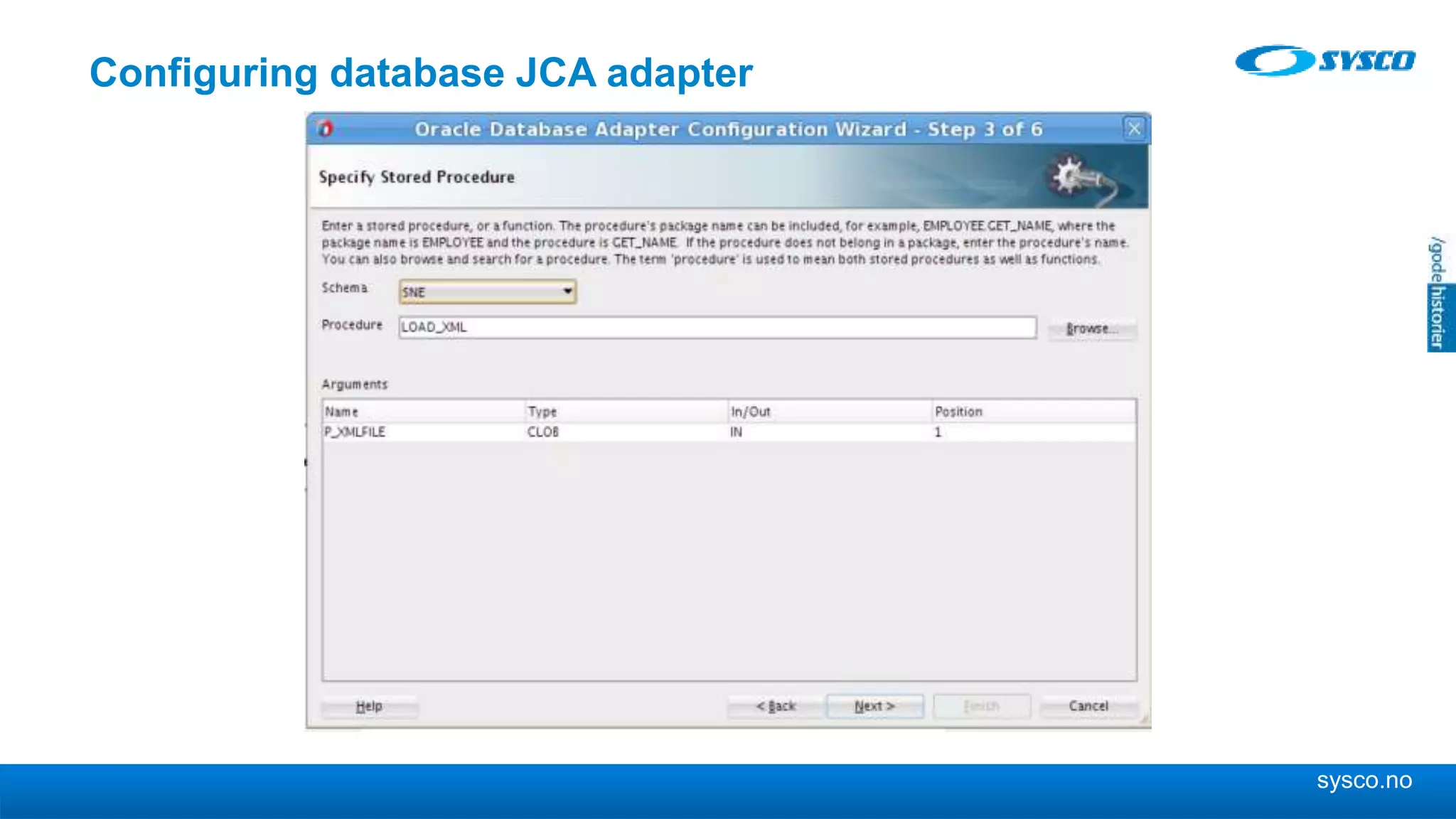
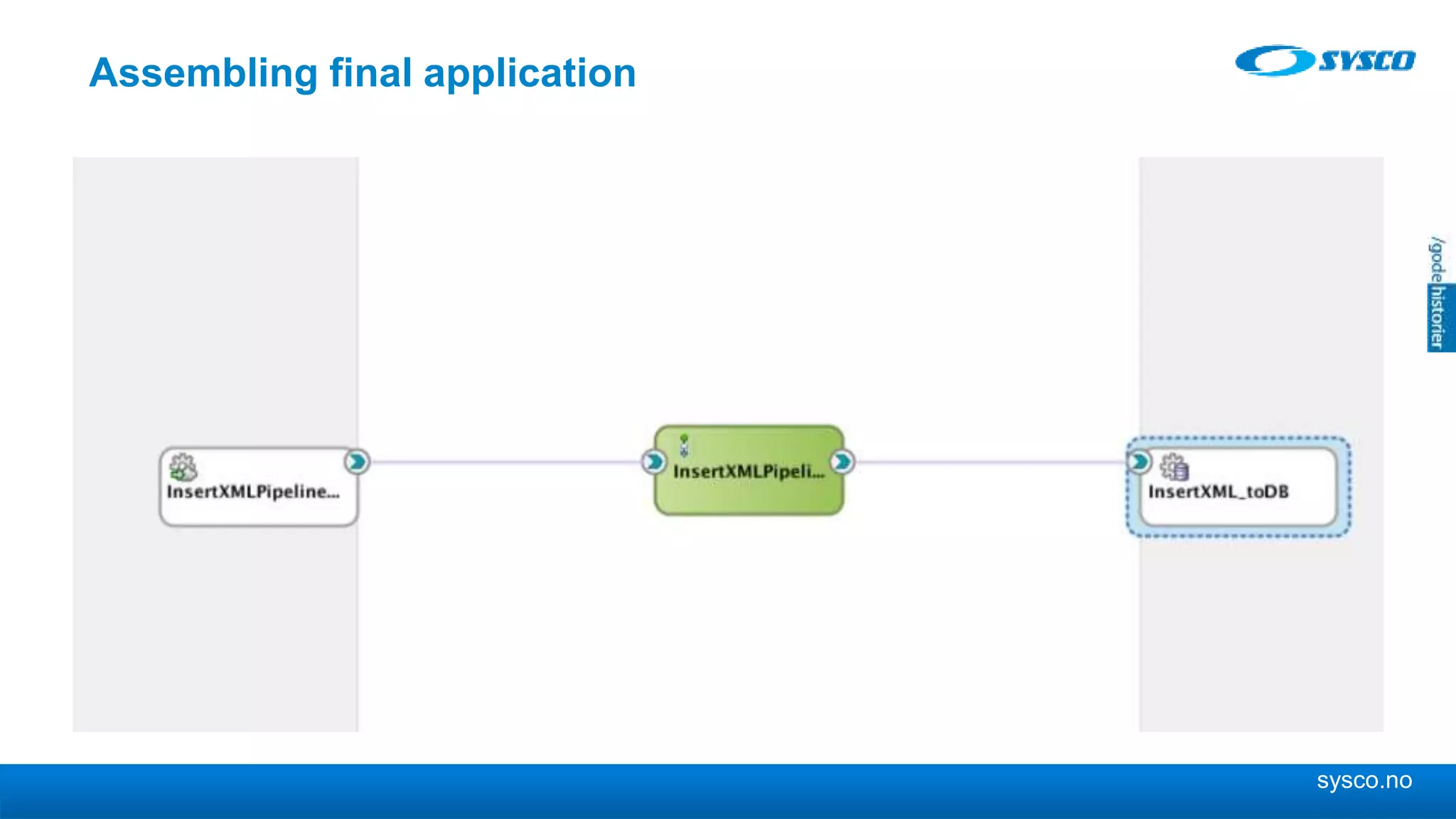
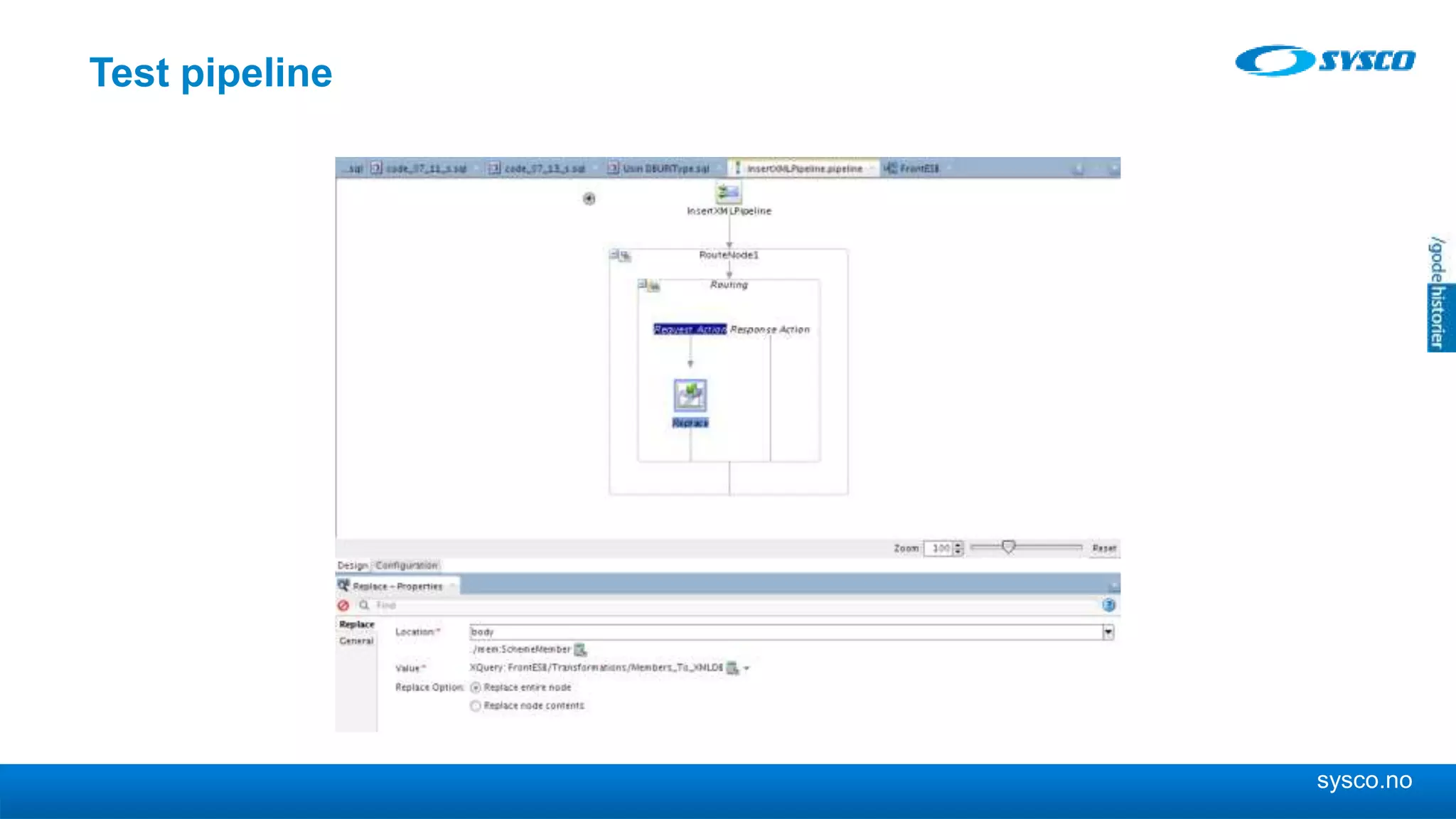
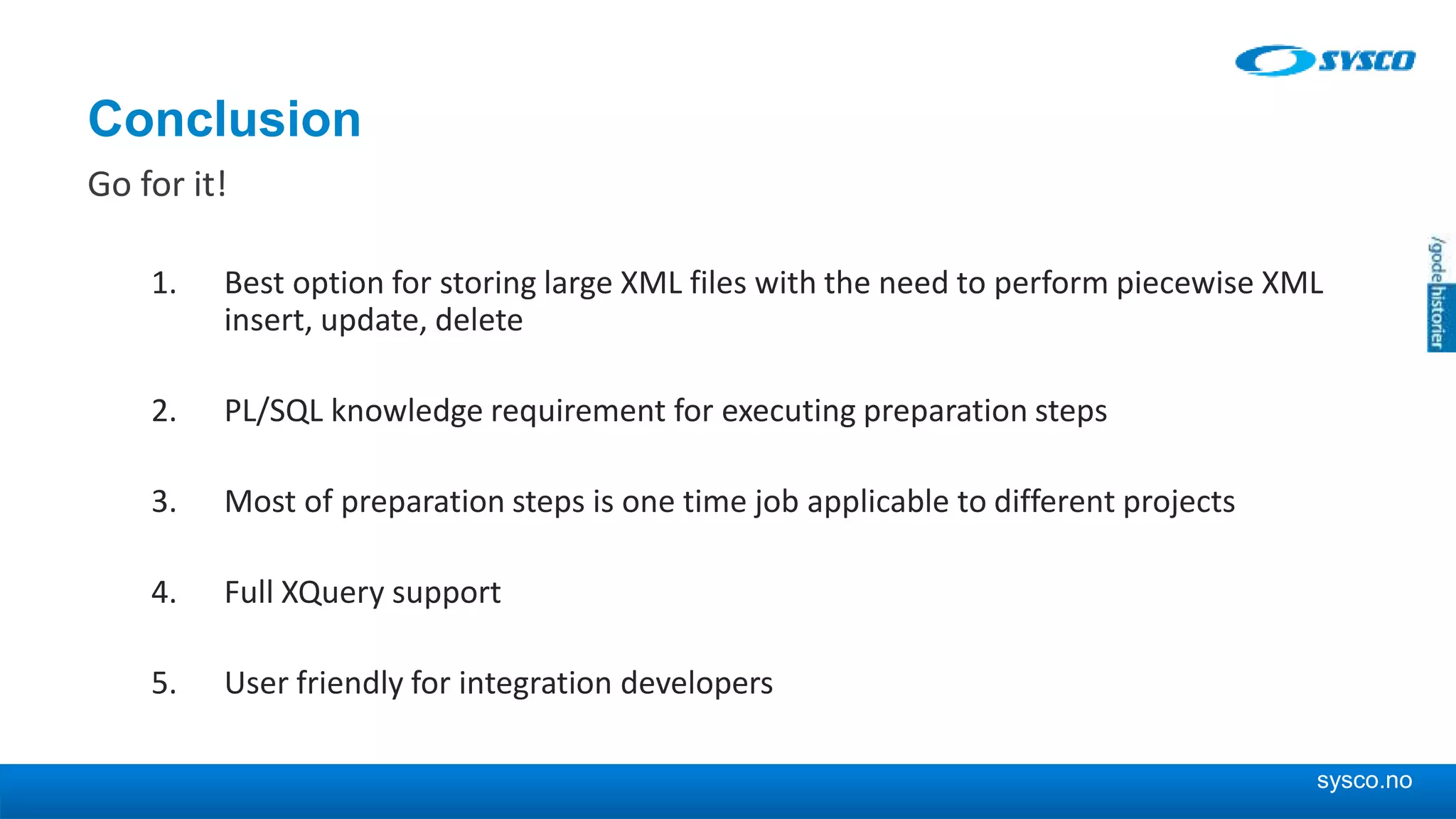
This document discusses storing and manipulating XML data in an Oracle database. It describes several options for storing XML in the database, including using a relational model with one table per XML type, XMLType views, and storing XML directly as CLOB or binary XML. It recommends using Oracle's object-relational storage, which optimizes storage, supports indexing and relationships, and enables piecewise updates through XPath expressions. It provides steps for upgrading an XML schema, registering it in the database, creating stored procedures and views to enable reading and writing XML as a single transaction through SOA/ESB.