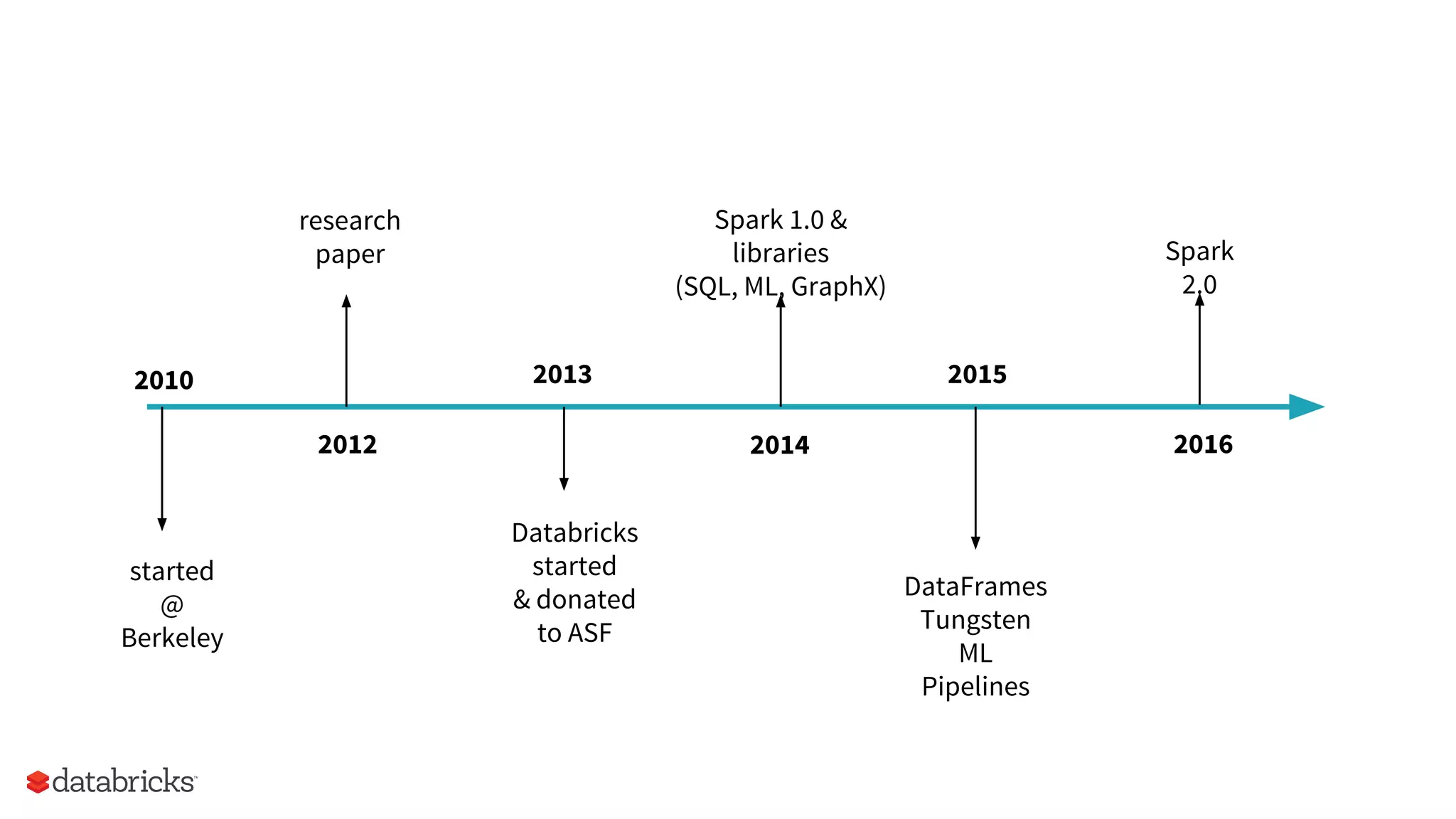
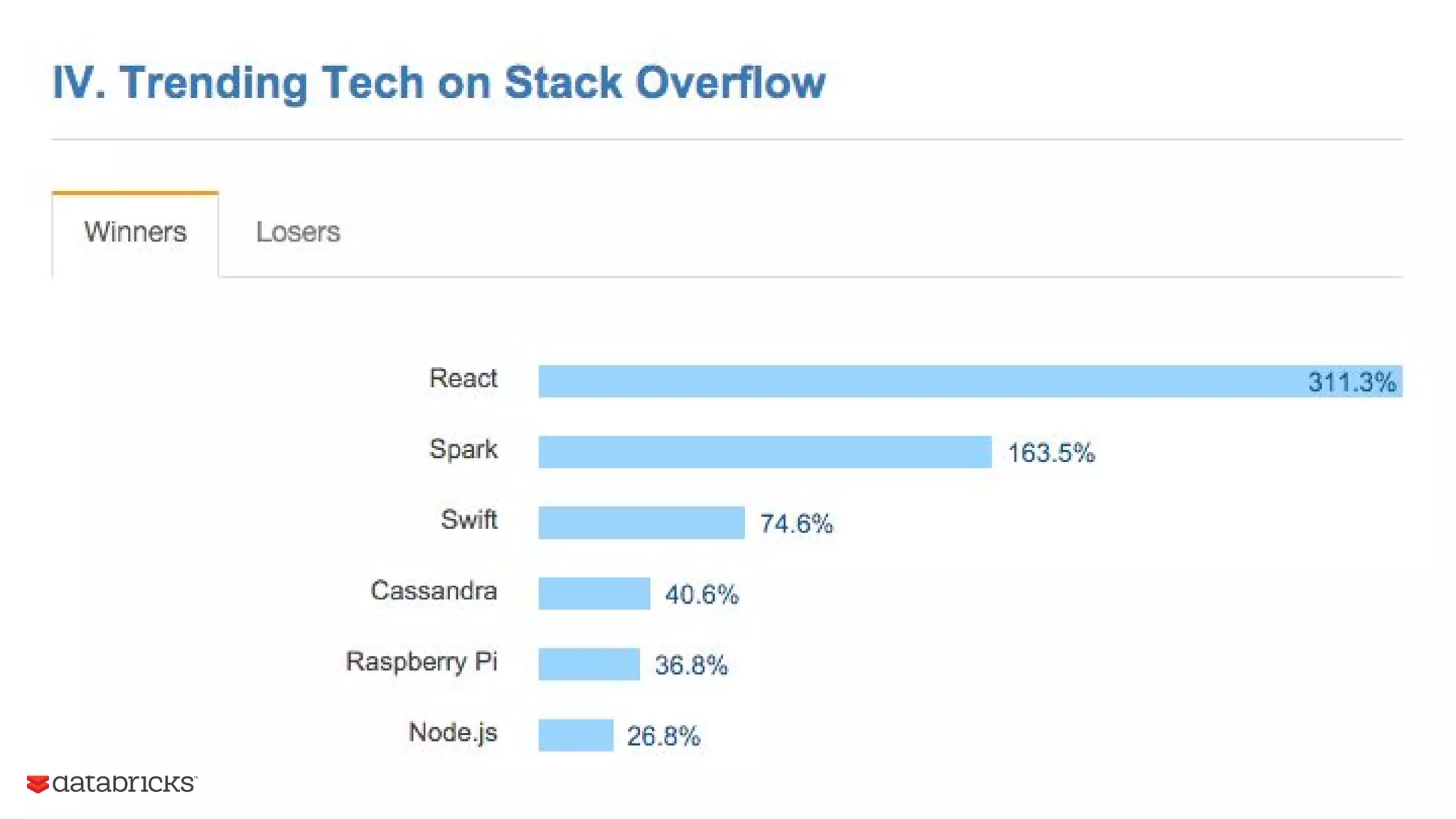
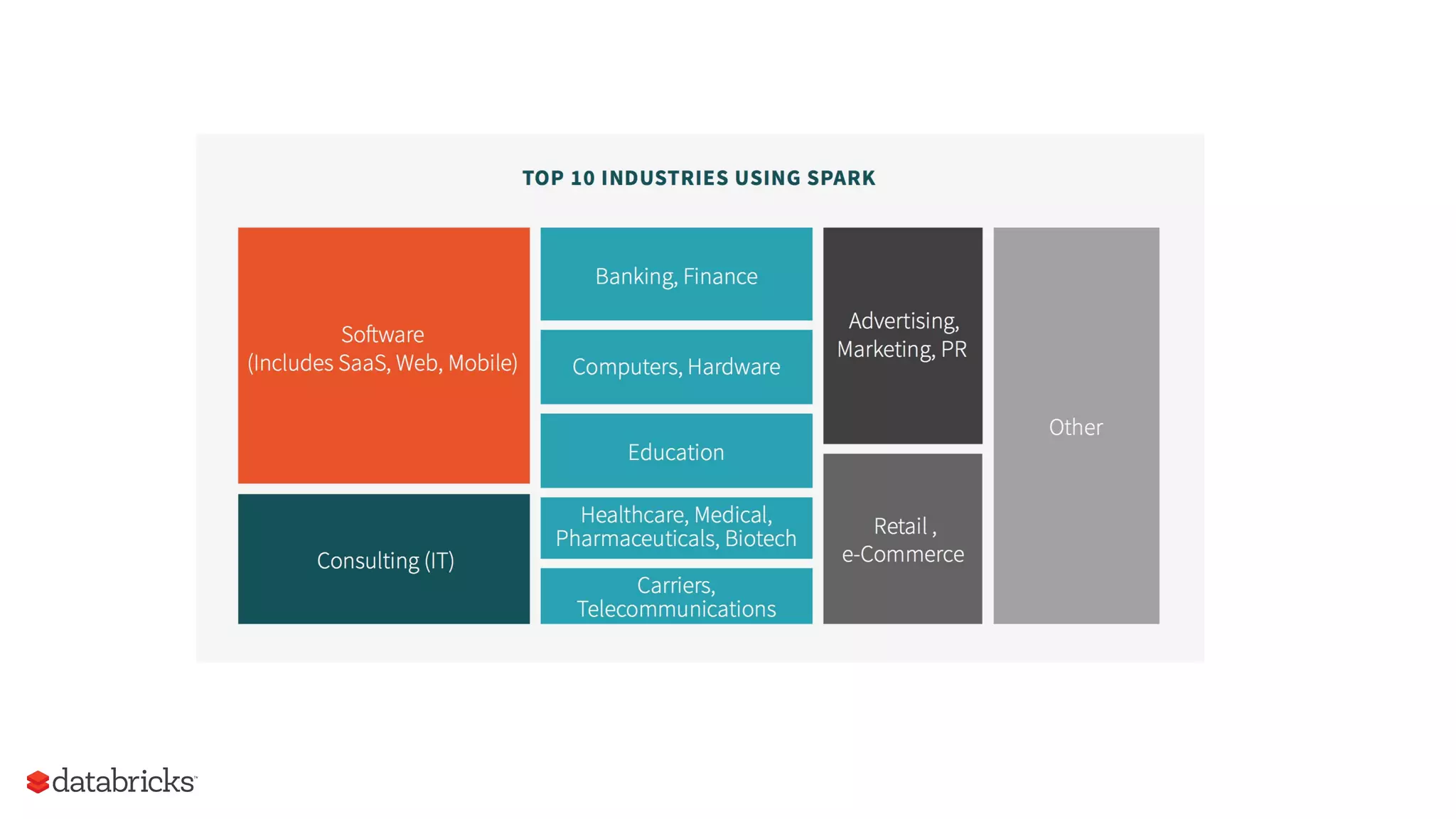
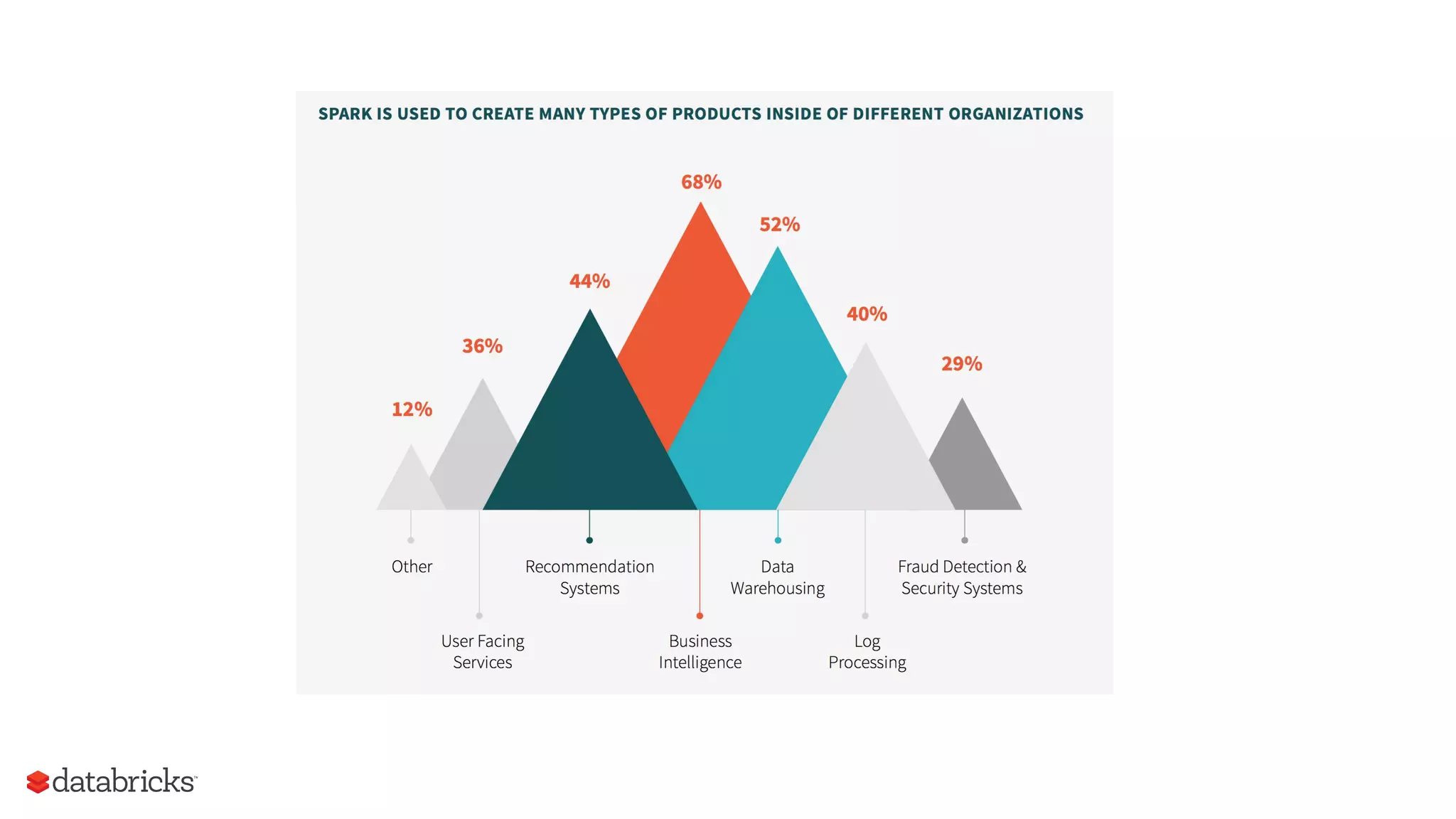
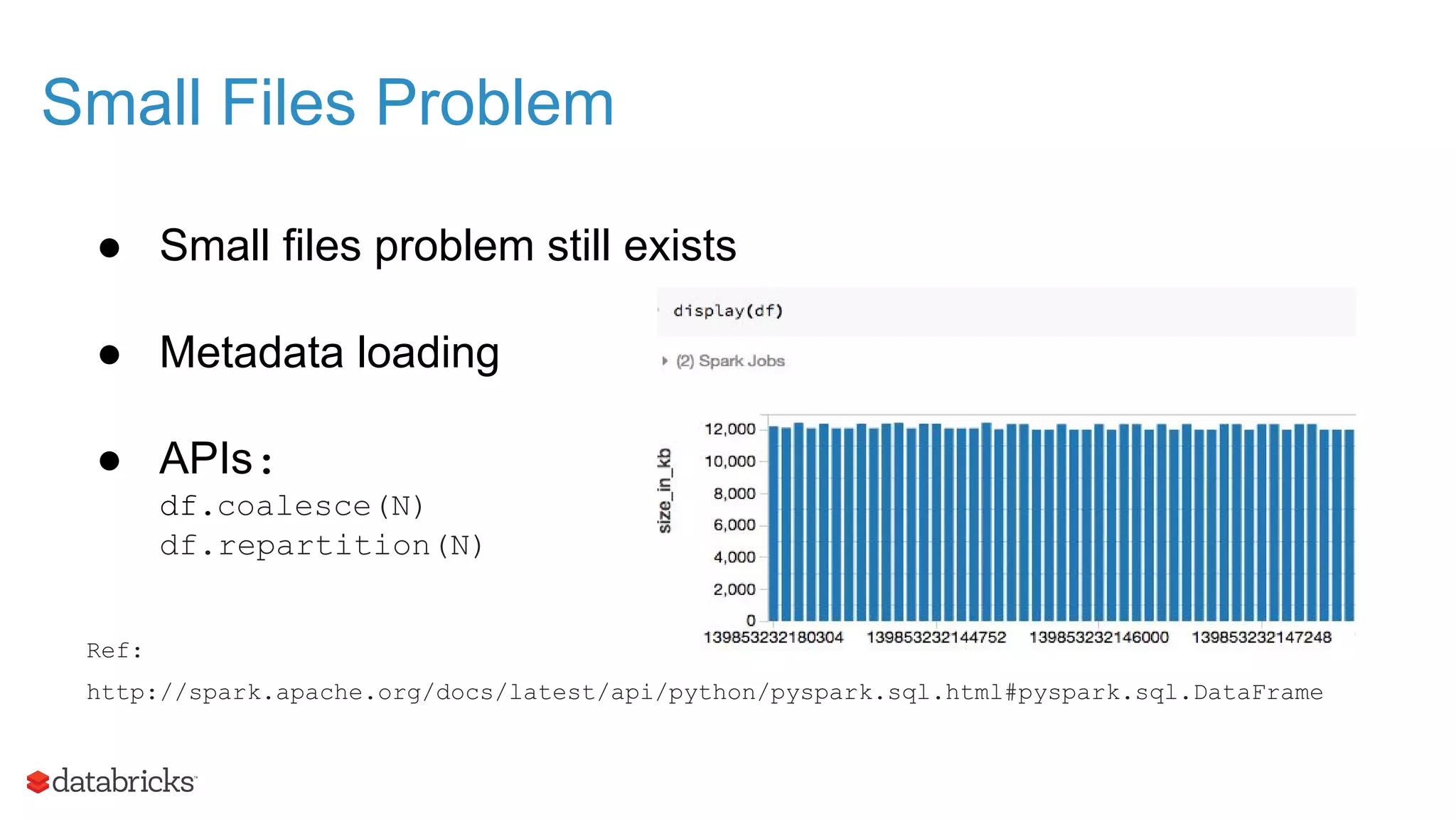
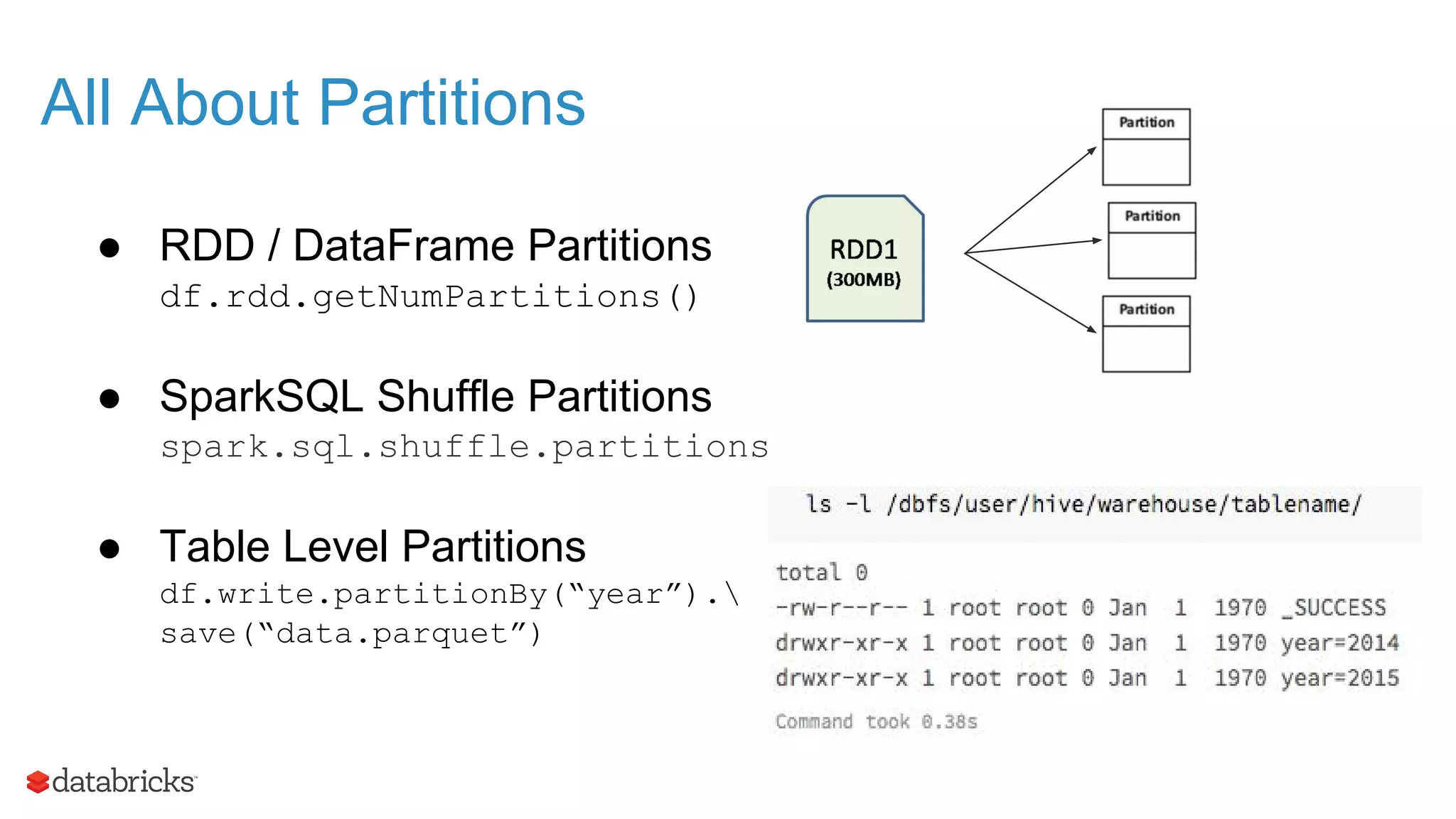
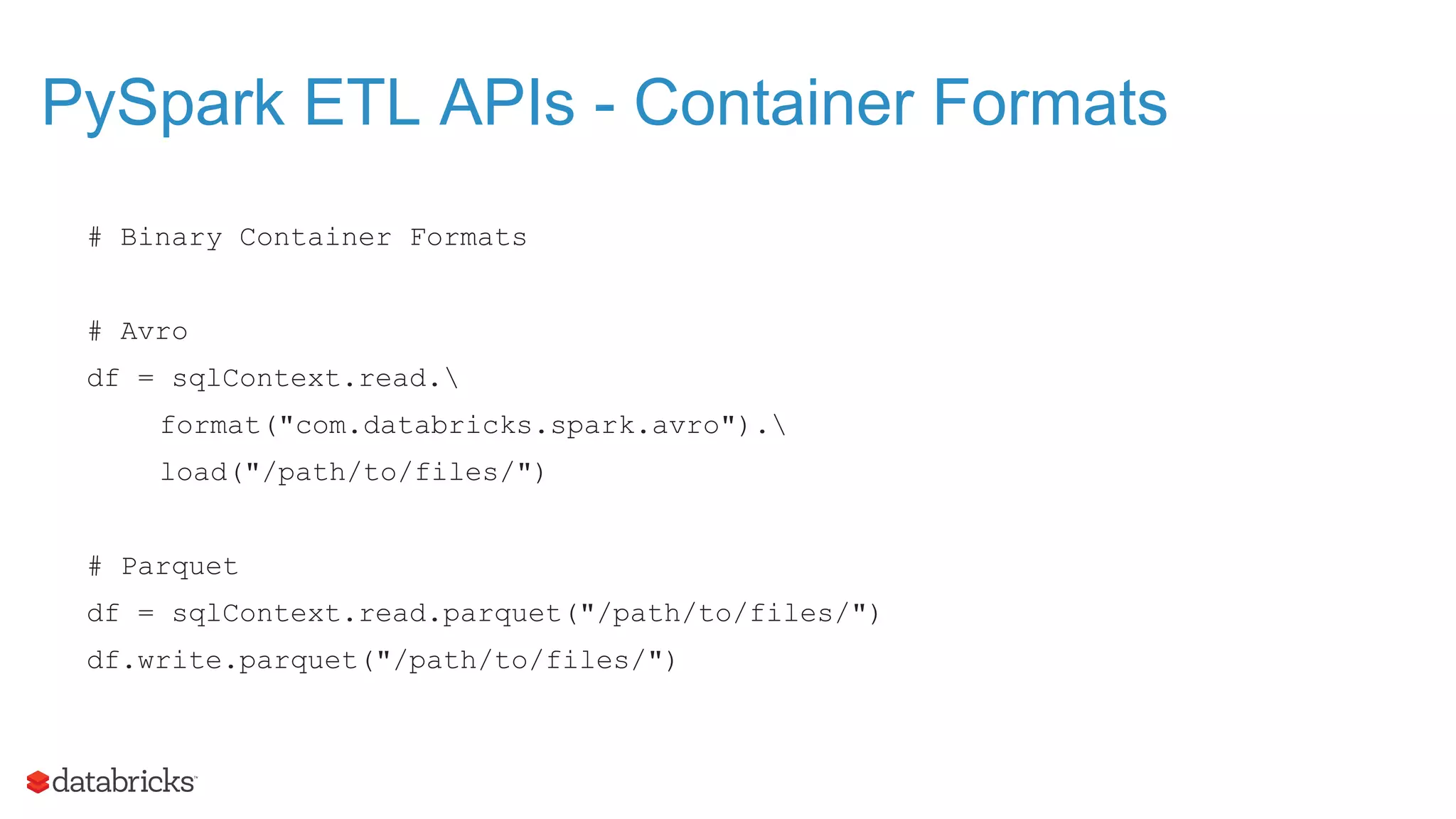
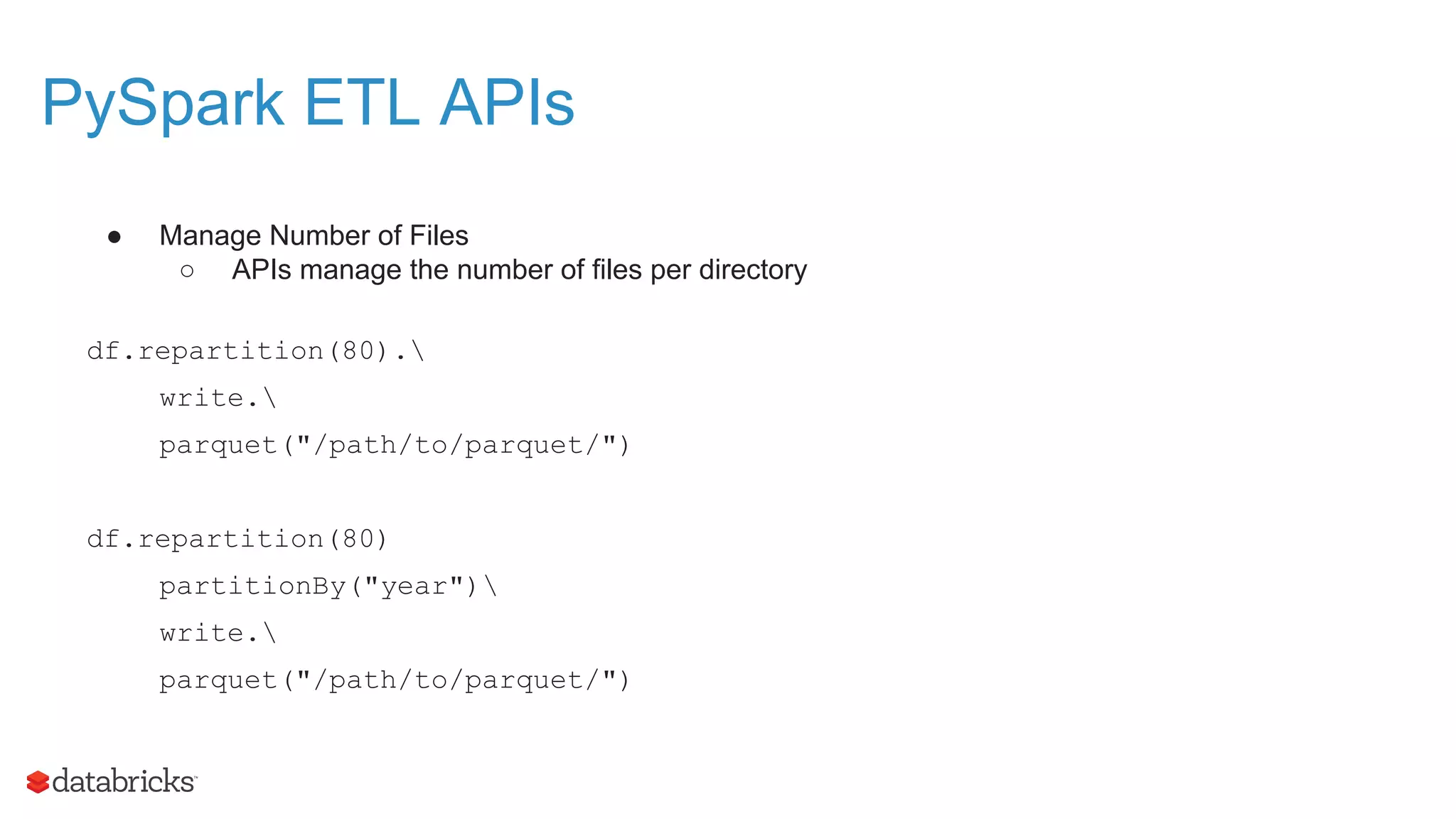
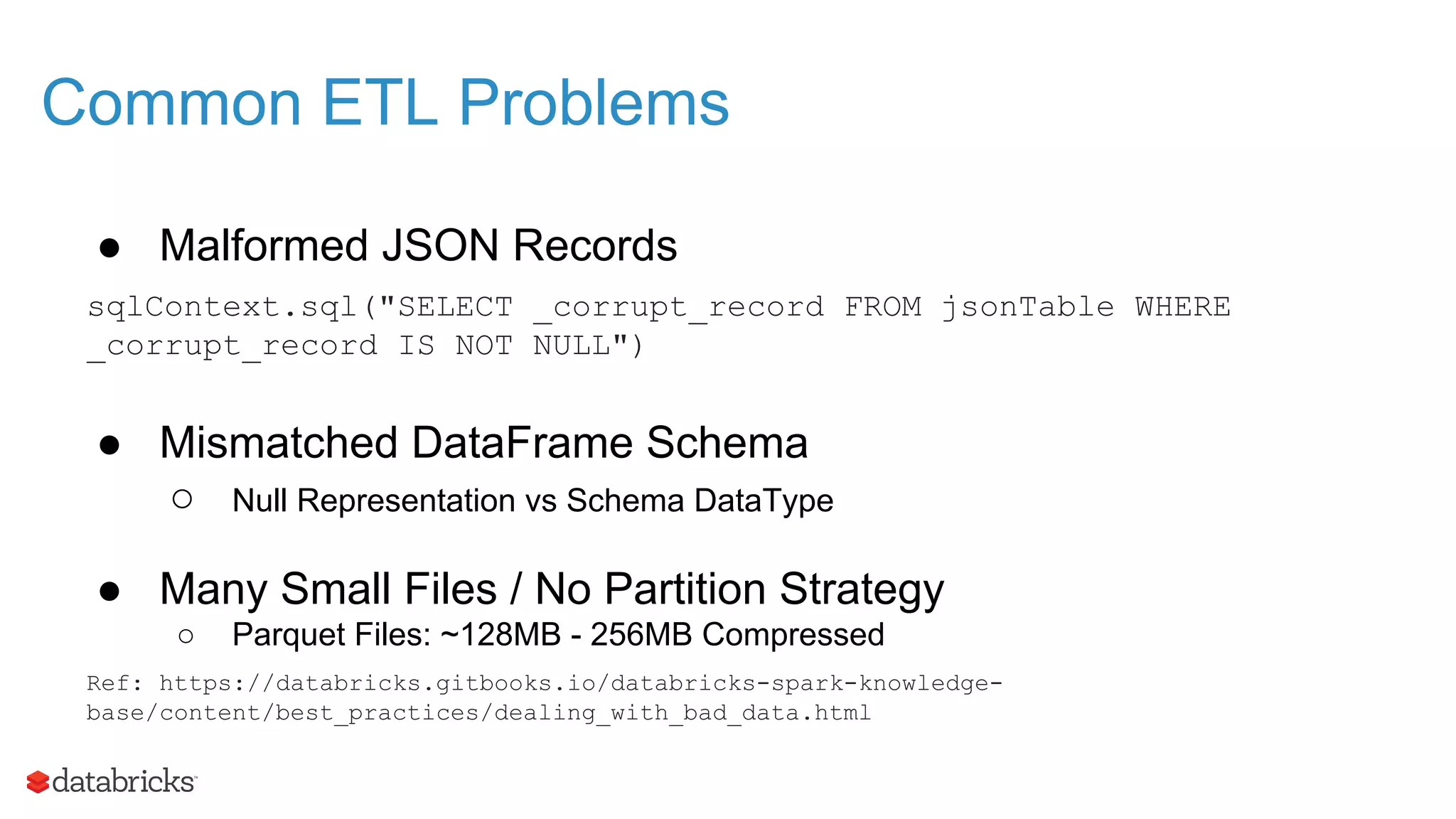
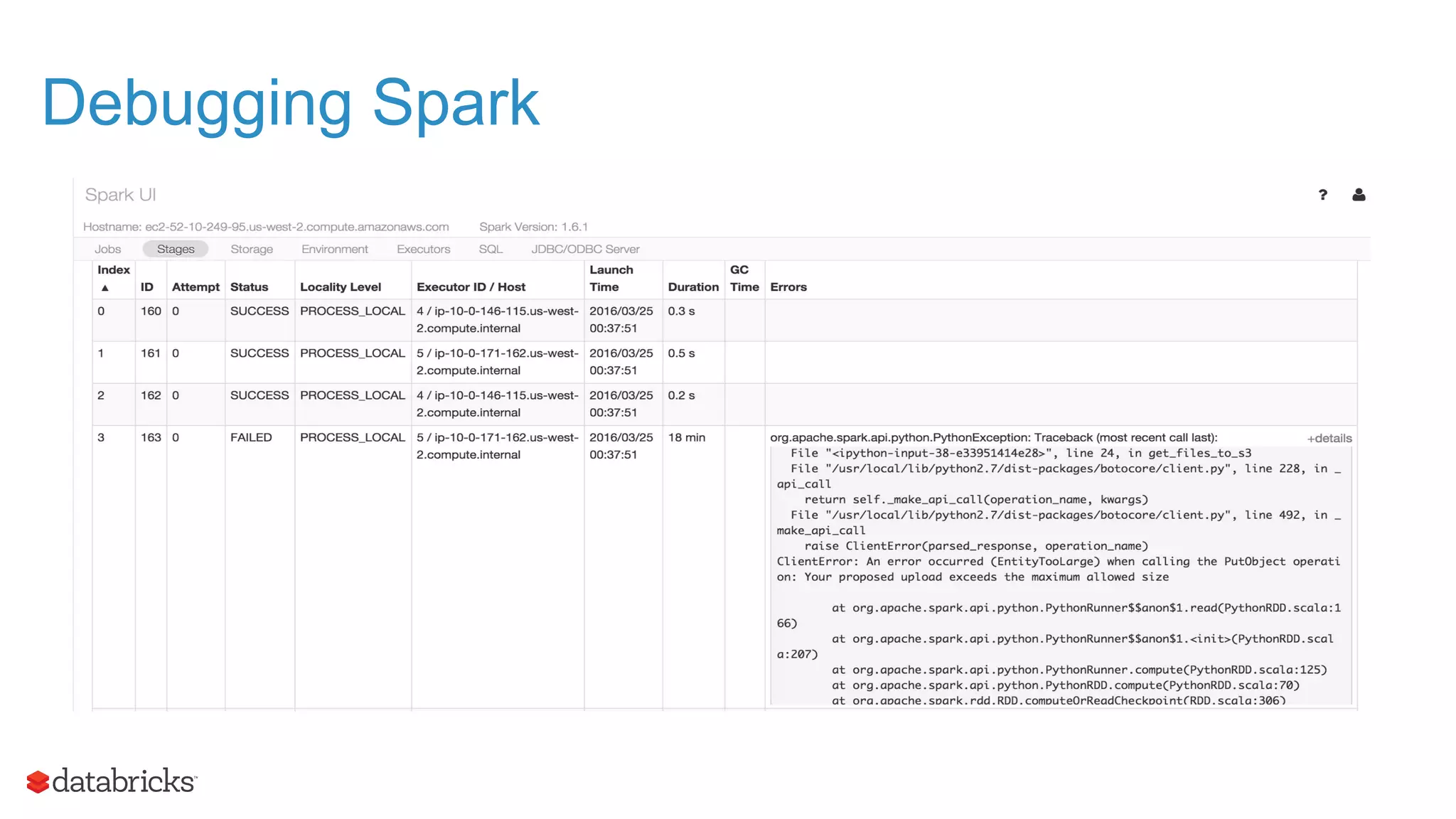
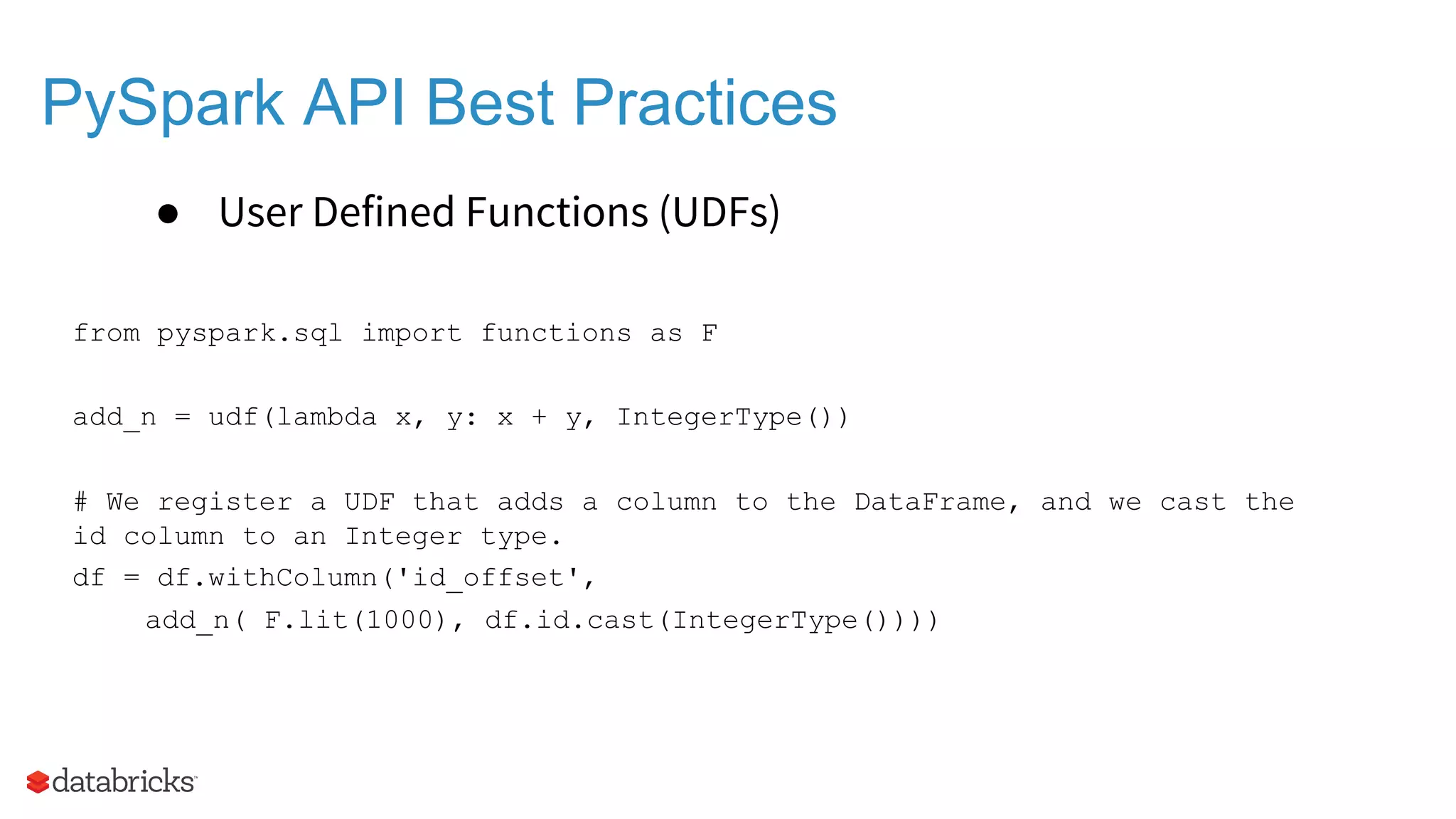
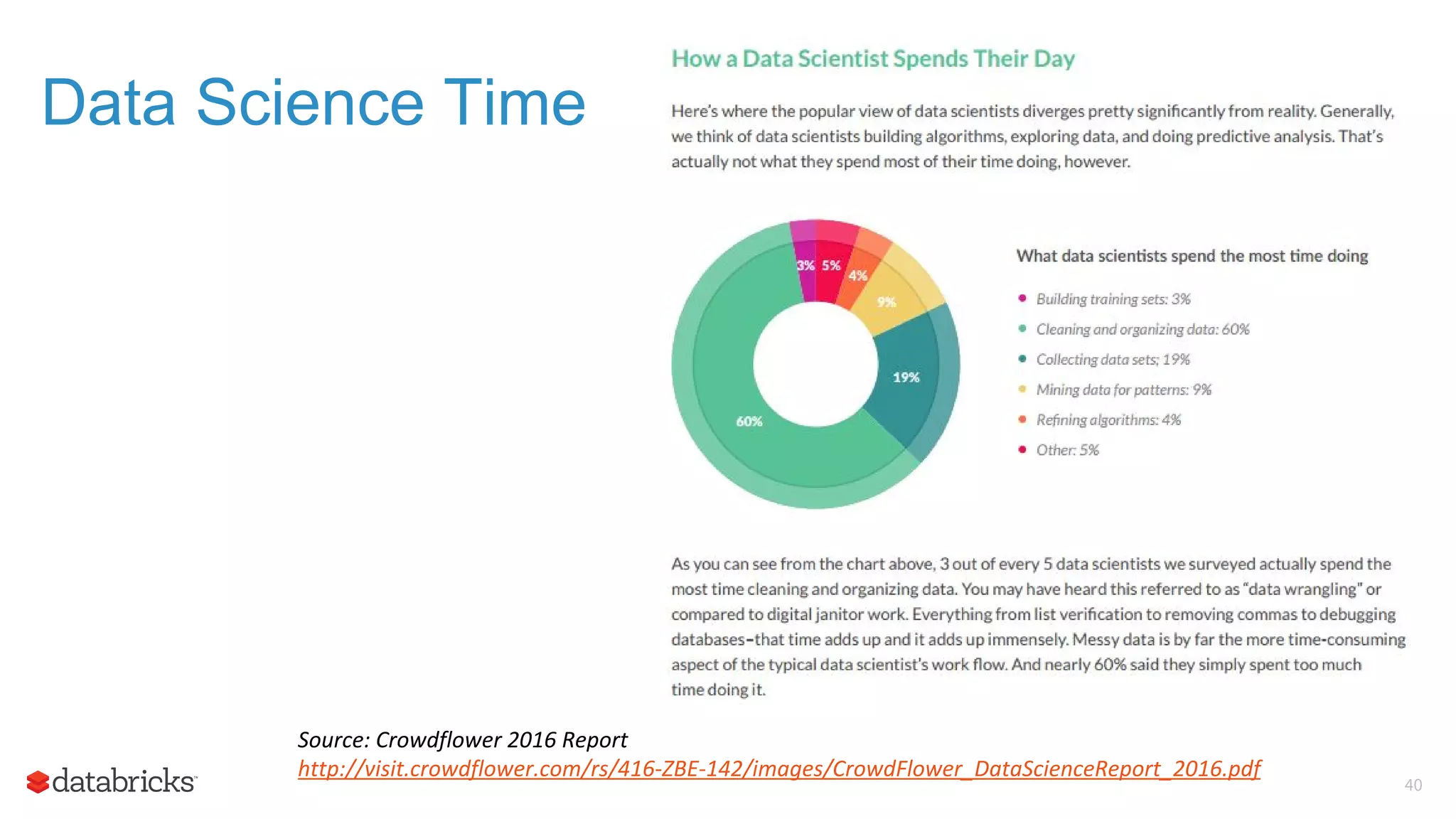
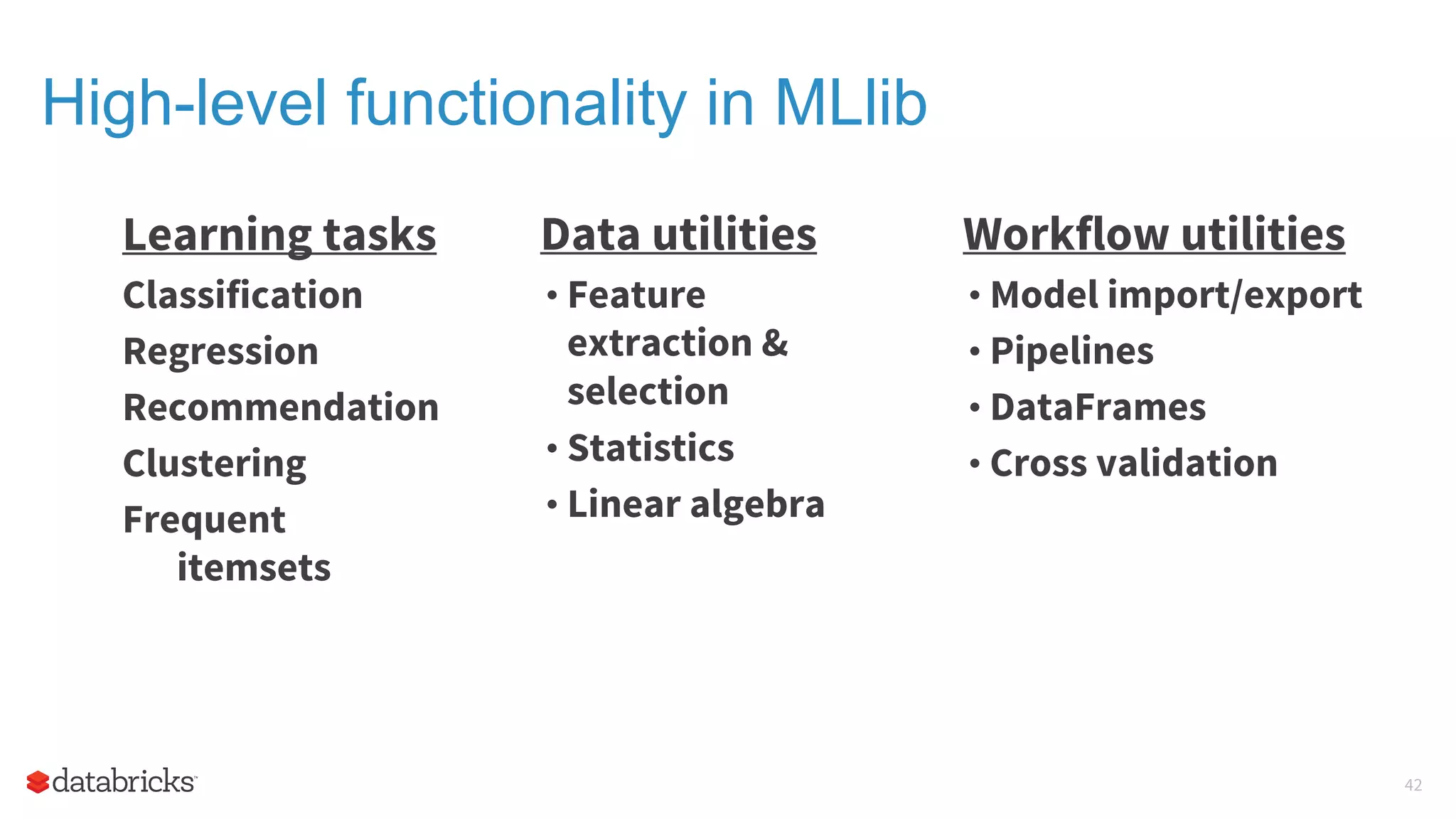
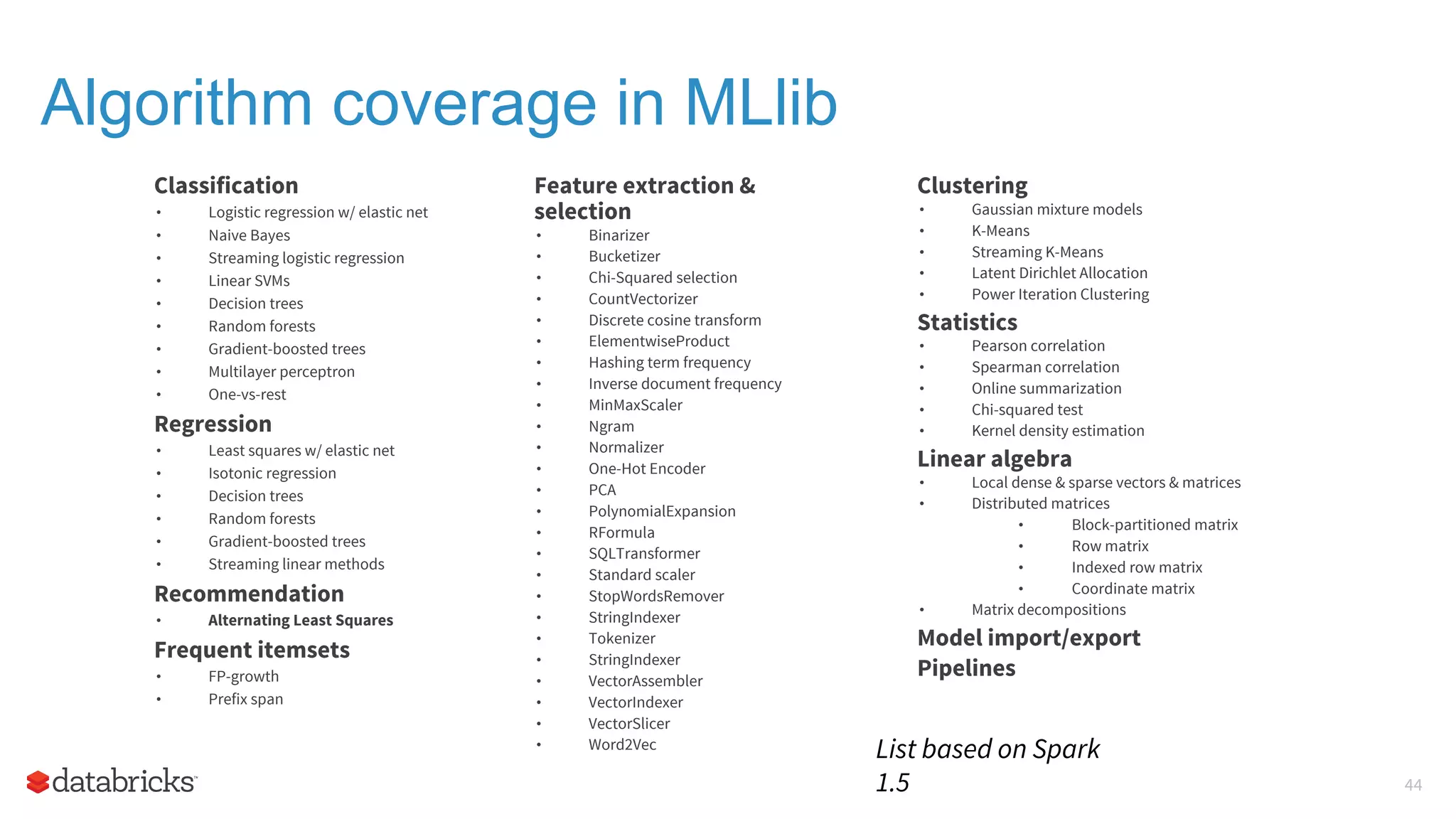
The document outlines the evolution and features of Apache Spark, highlighting its capabilities in advanced analytics and machine learning. It details Spark's architecture, usage statistics, best practices for ETL processes, and challenges like the small files problem. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of using built-in functions and pipelines in Spark ML for efficient model building and data processing.



















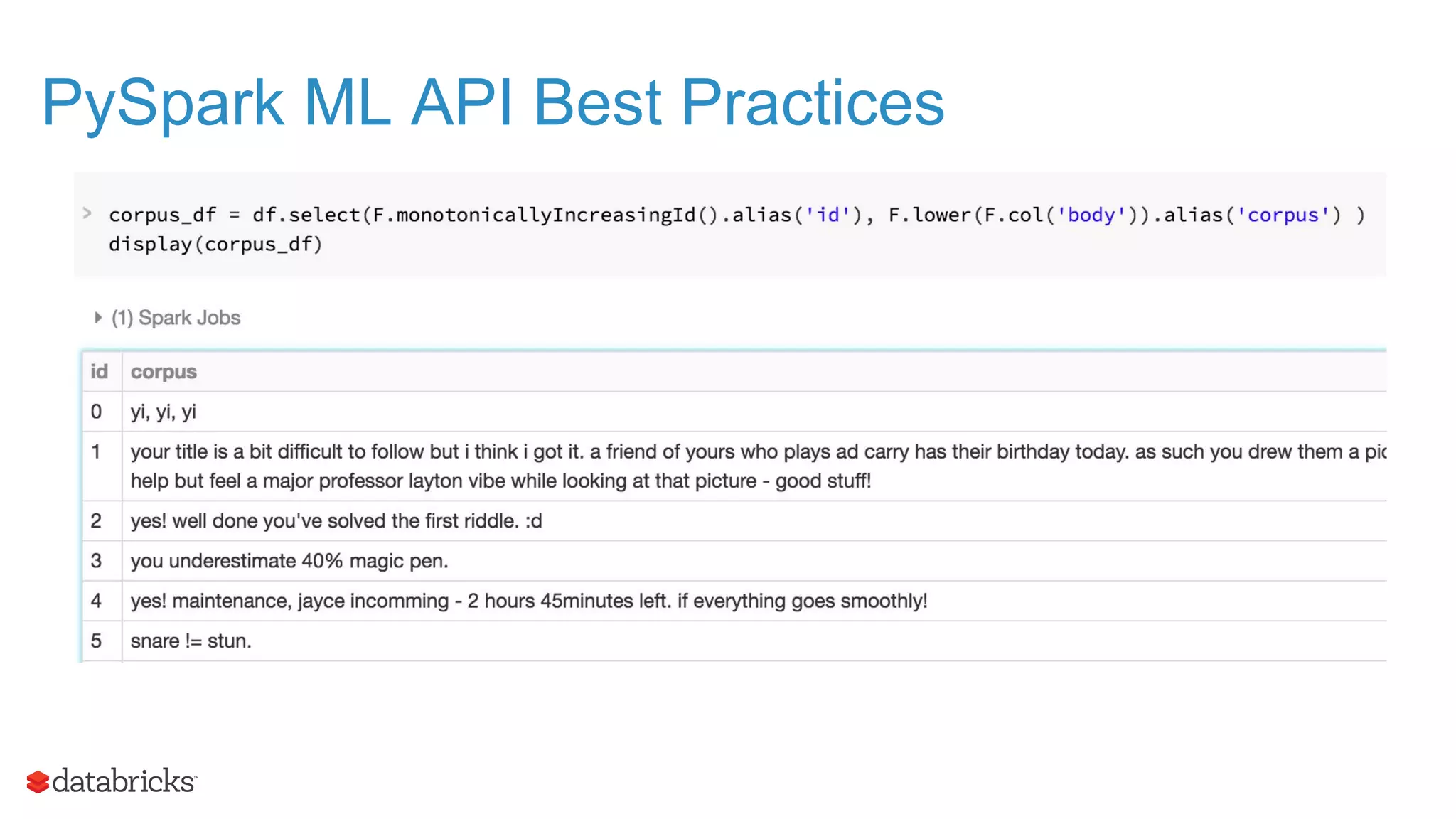
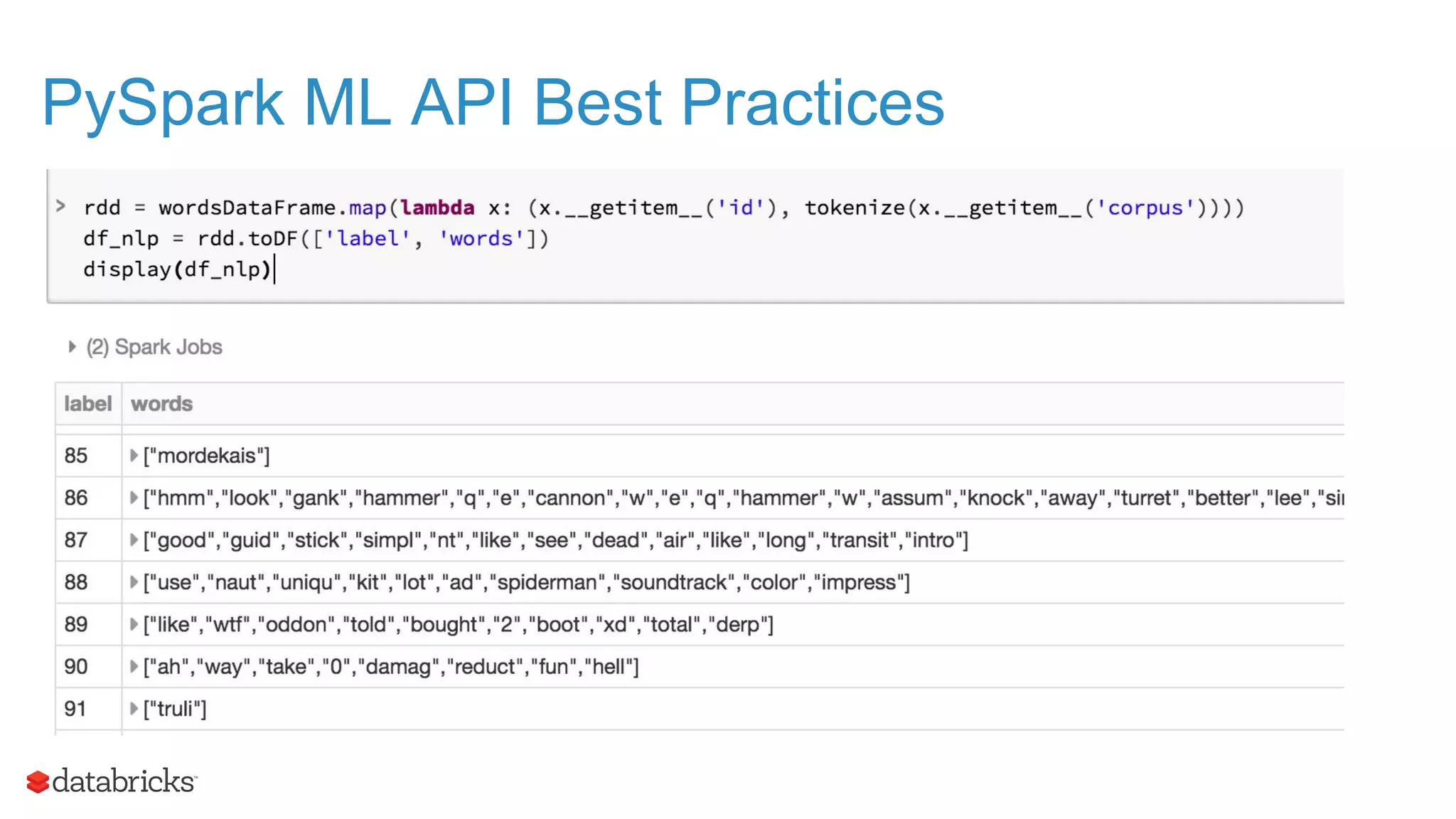
![● DataFrame to RDD Mapping def tokenize(text): tokens = word_tokenize(text) lowercased = [t.lower() for t in tokens] no_punctuation = [] for word in lowercased: punct_removed = ''.join([letter for letter in word if not letter in PUNCTUATION]) no_punctuation.append(punct_removed) no_stopwords = [w for w in no_punctuation if not w in STOPWORDS] stemmed = [STEMMER.stem(w) for w in no_stopwords] return [w for w in stemmed if w] rdd = wordsDataFrame.map(lambda x: (x.__getitem__('id'), tokenize(x.__getitem__('corpus')))) PySpark ML API Best Practices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nittygrittypyspark-160510133236/75/The-Nitty-Gritty-of-Advanced-Analytics-Using-Apache-Spark-in-Python-48-2048.jpg)