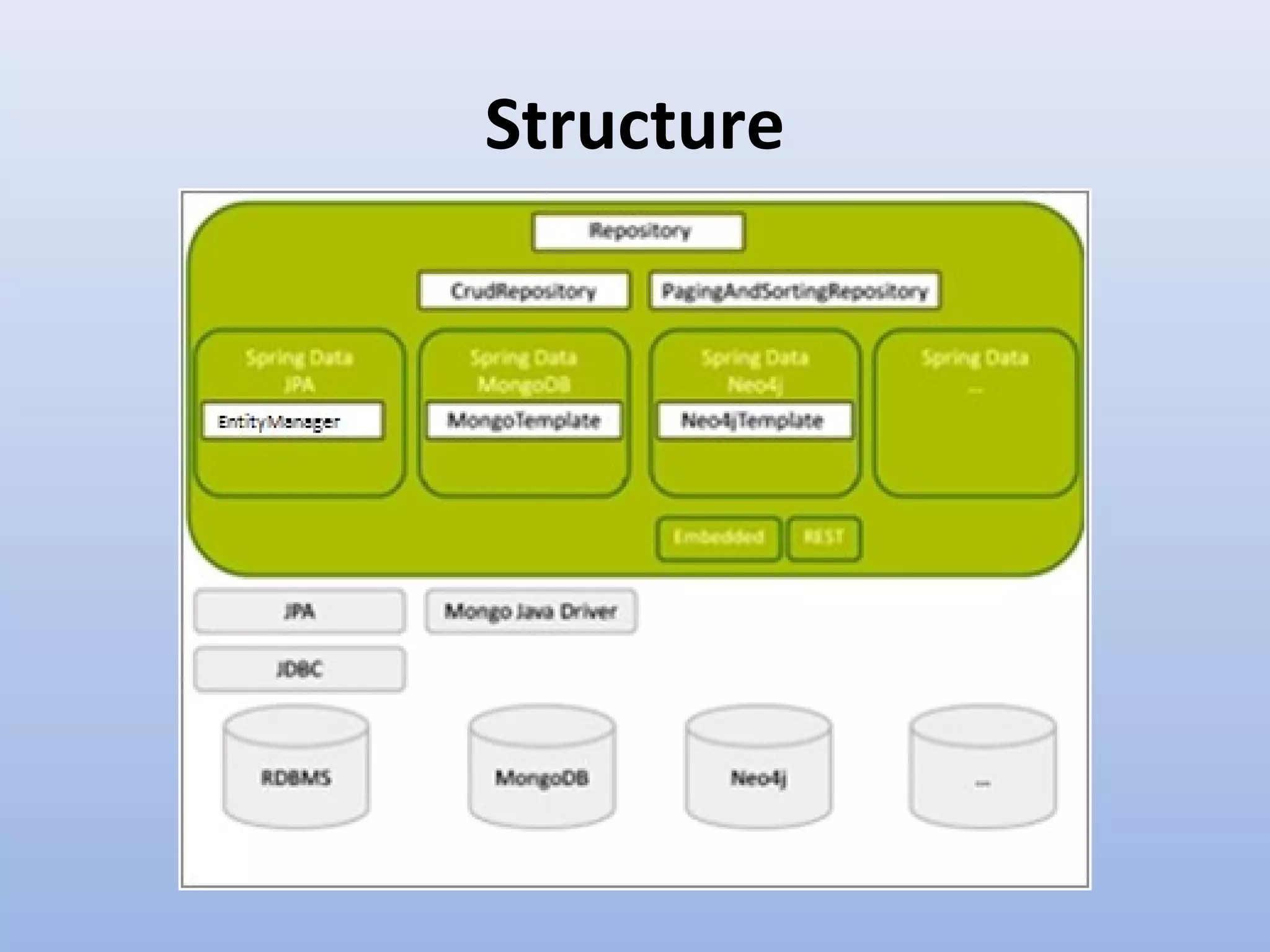
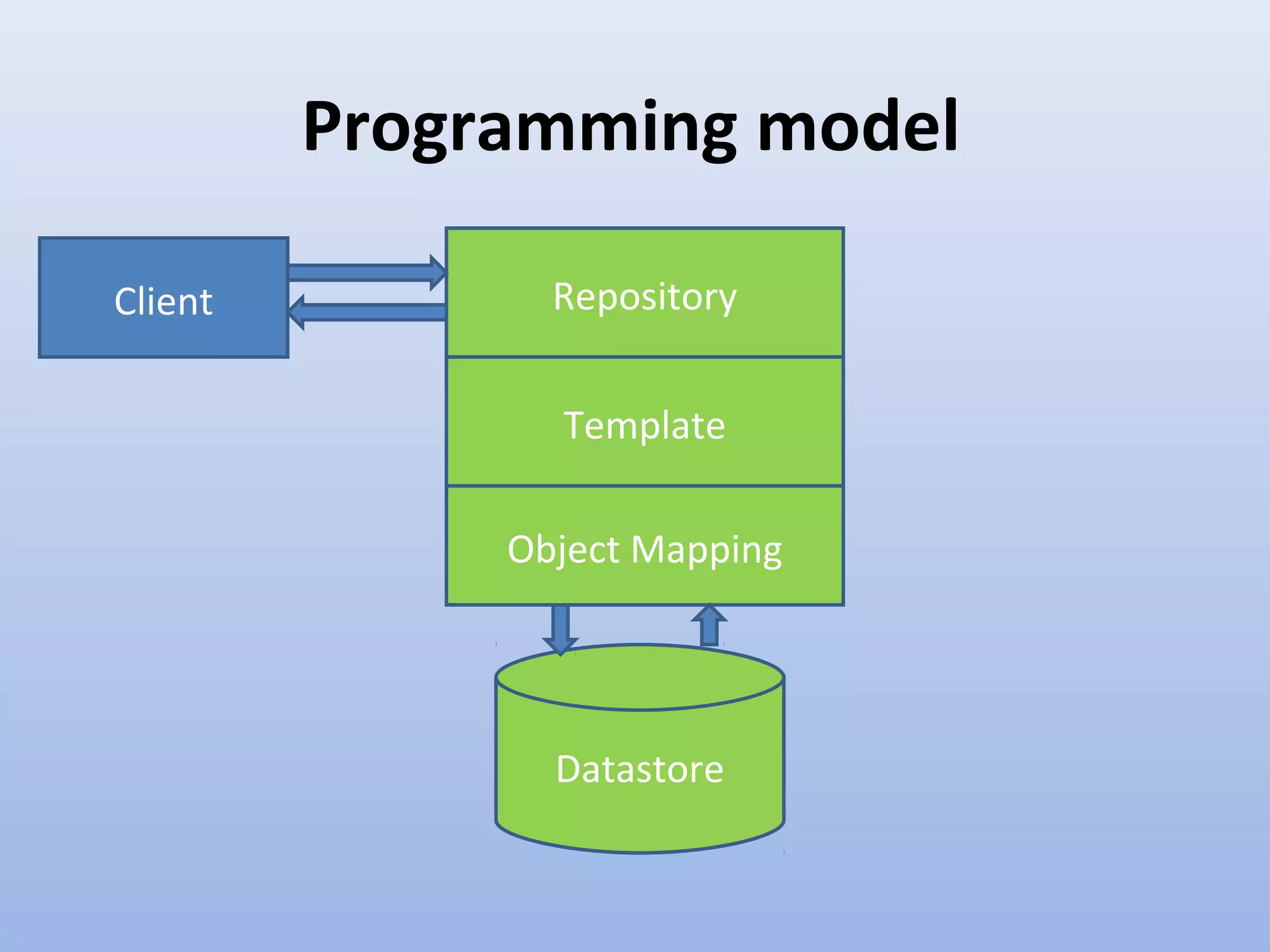
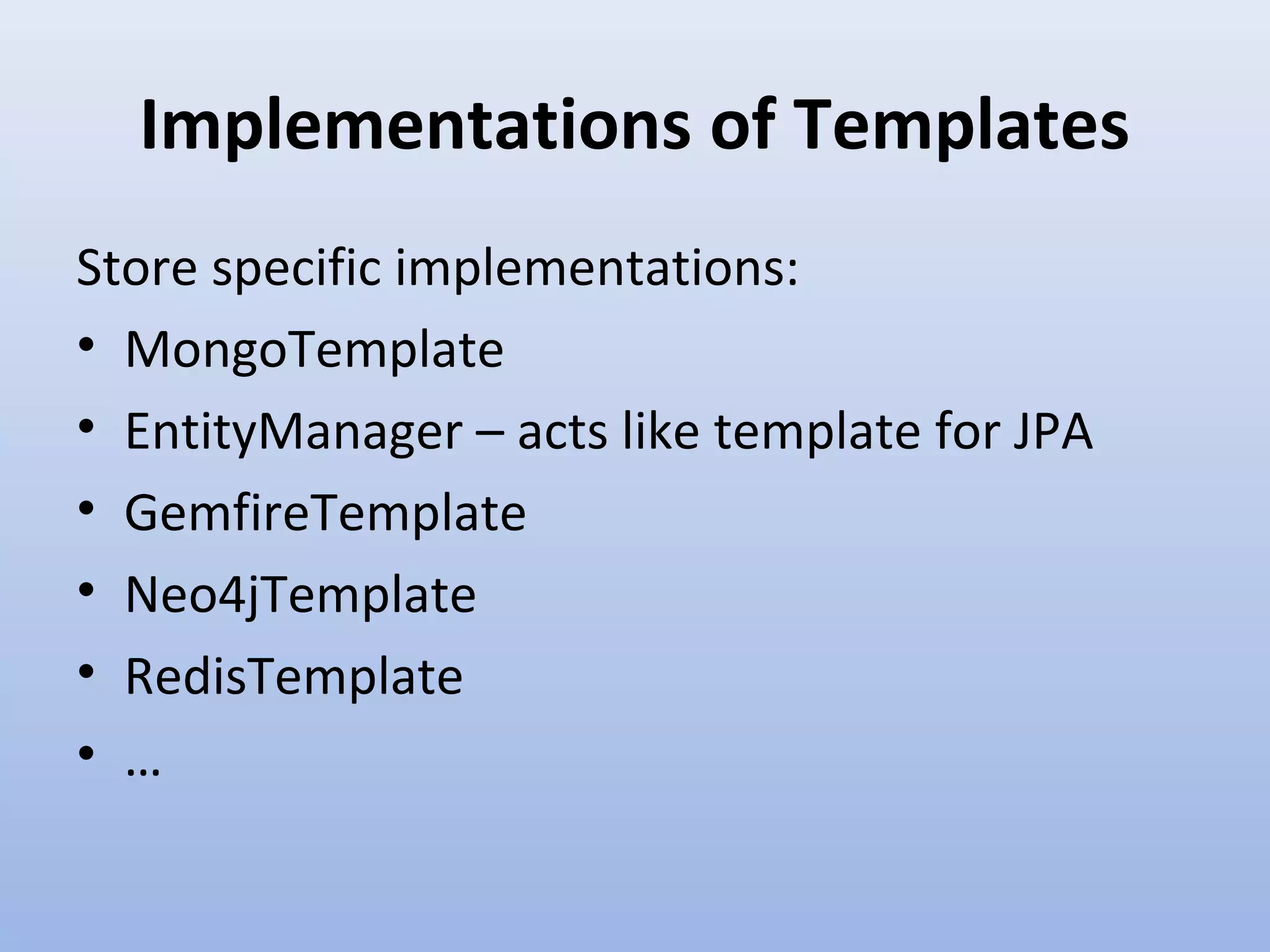
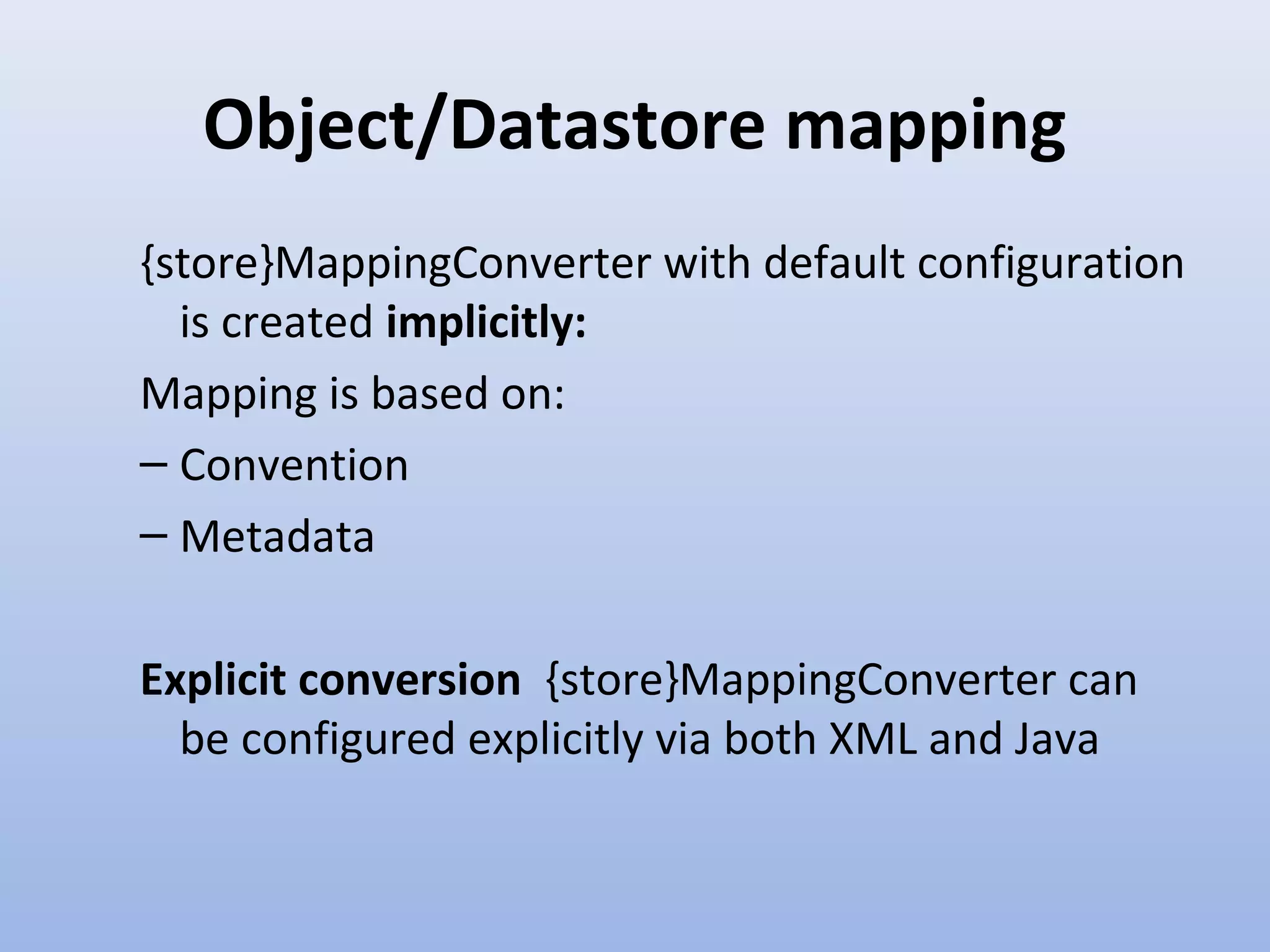
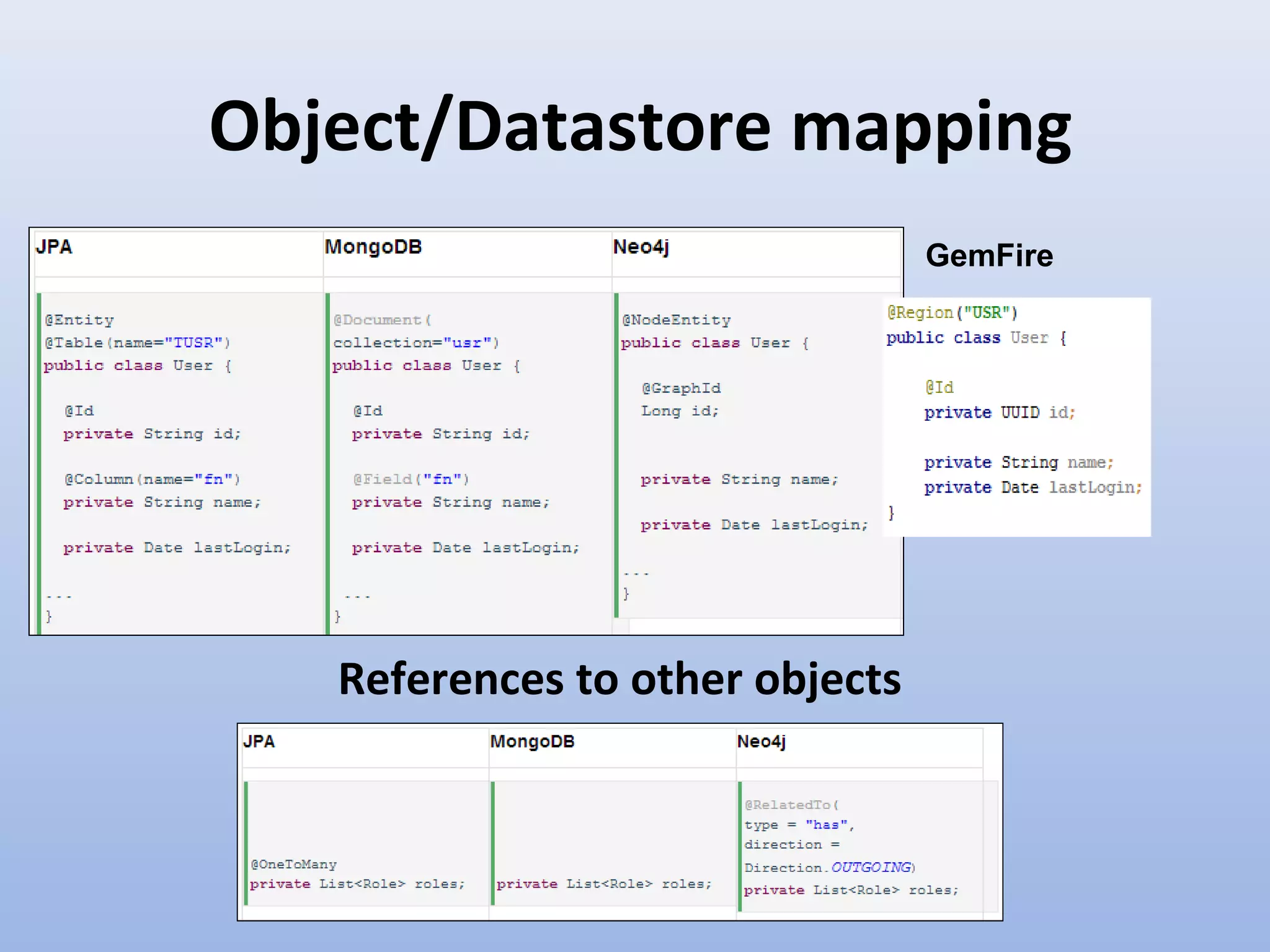
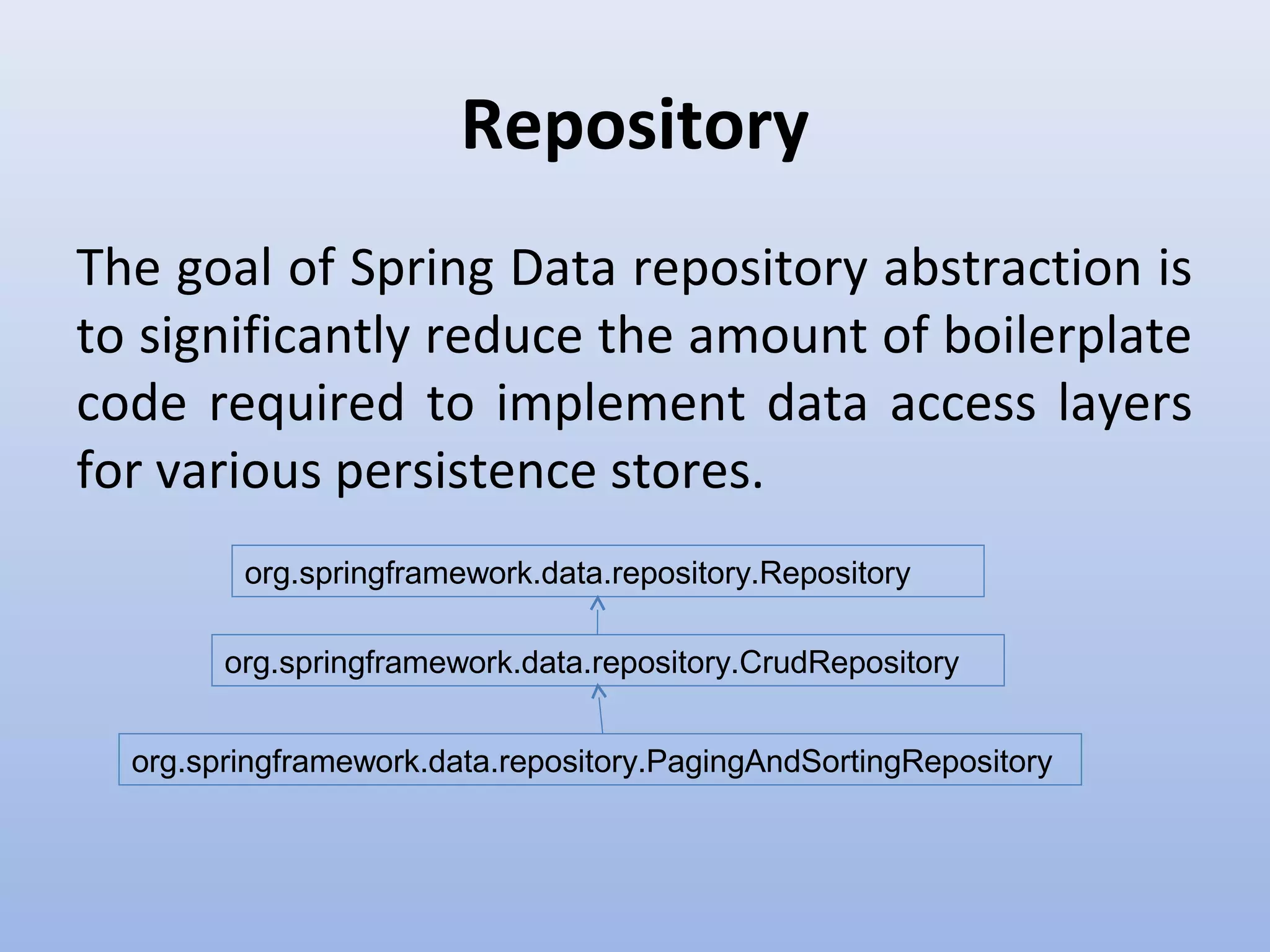
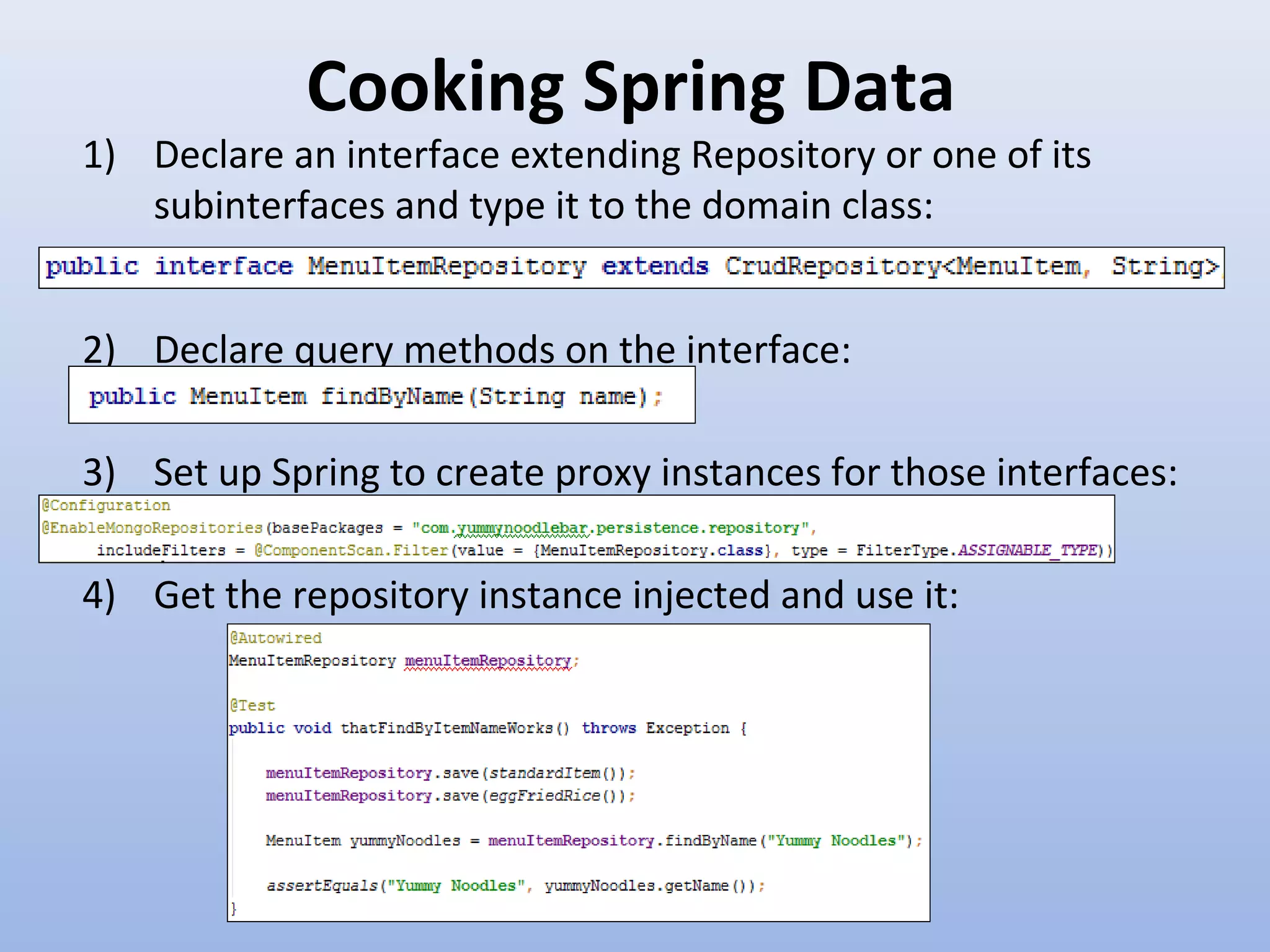
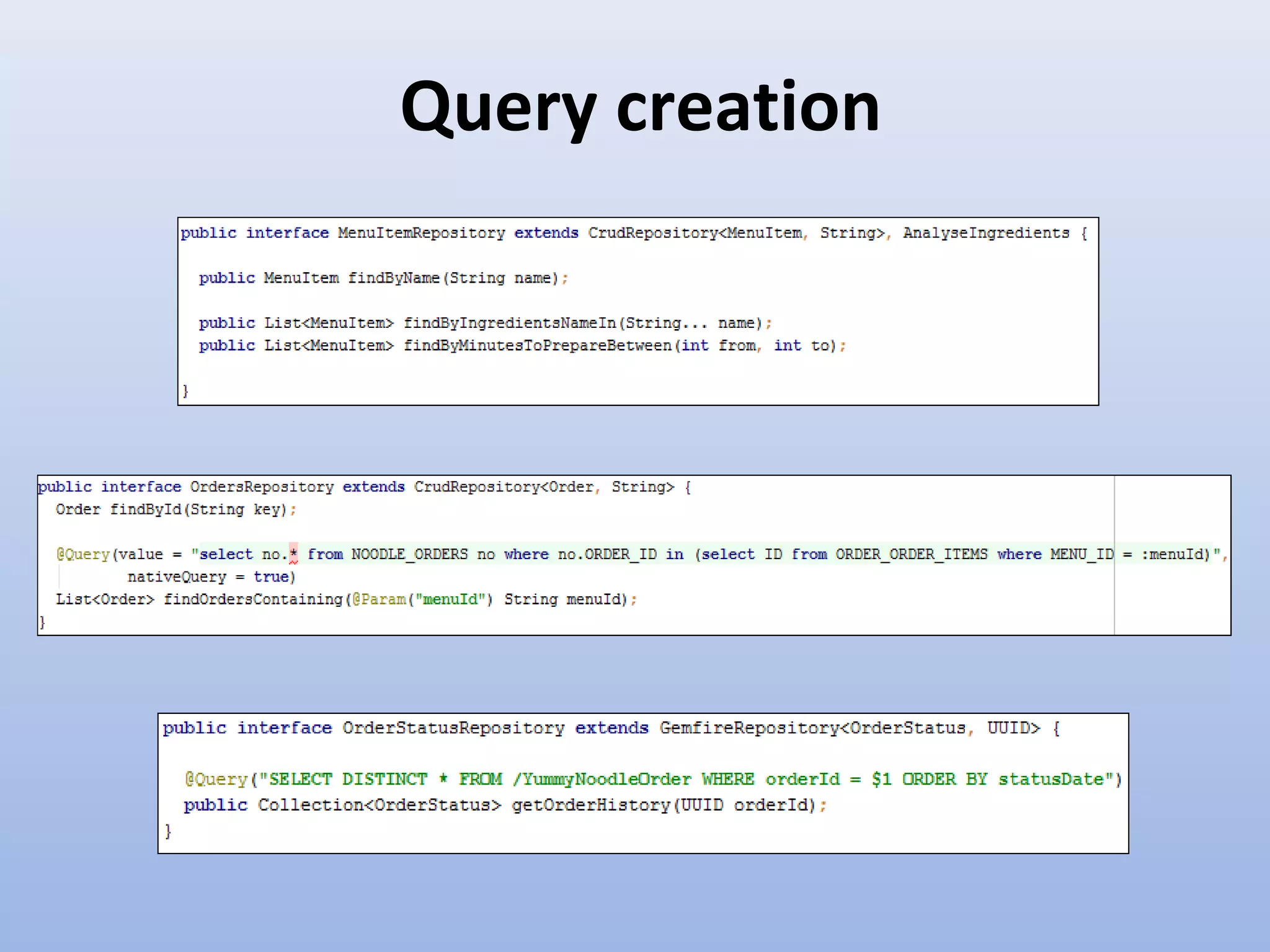
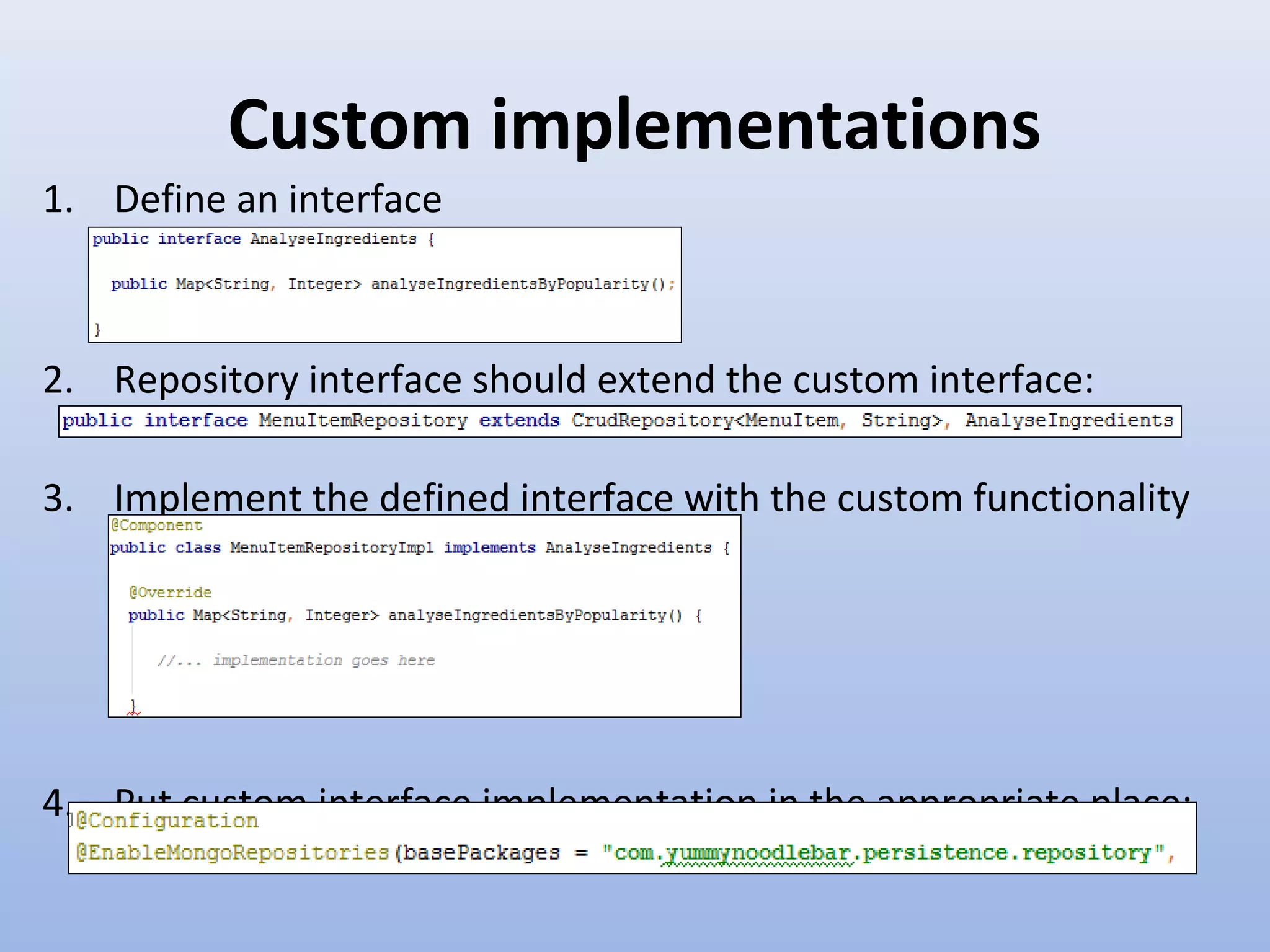
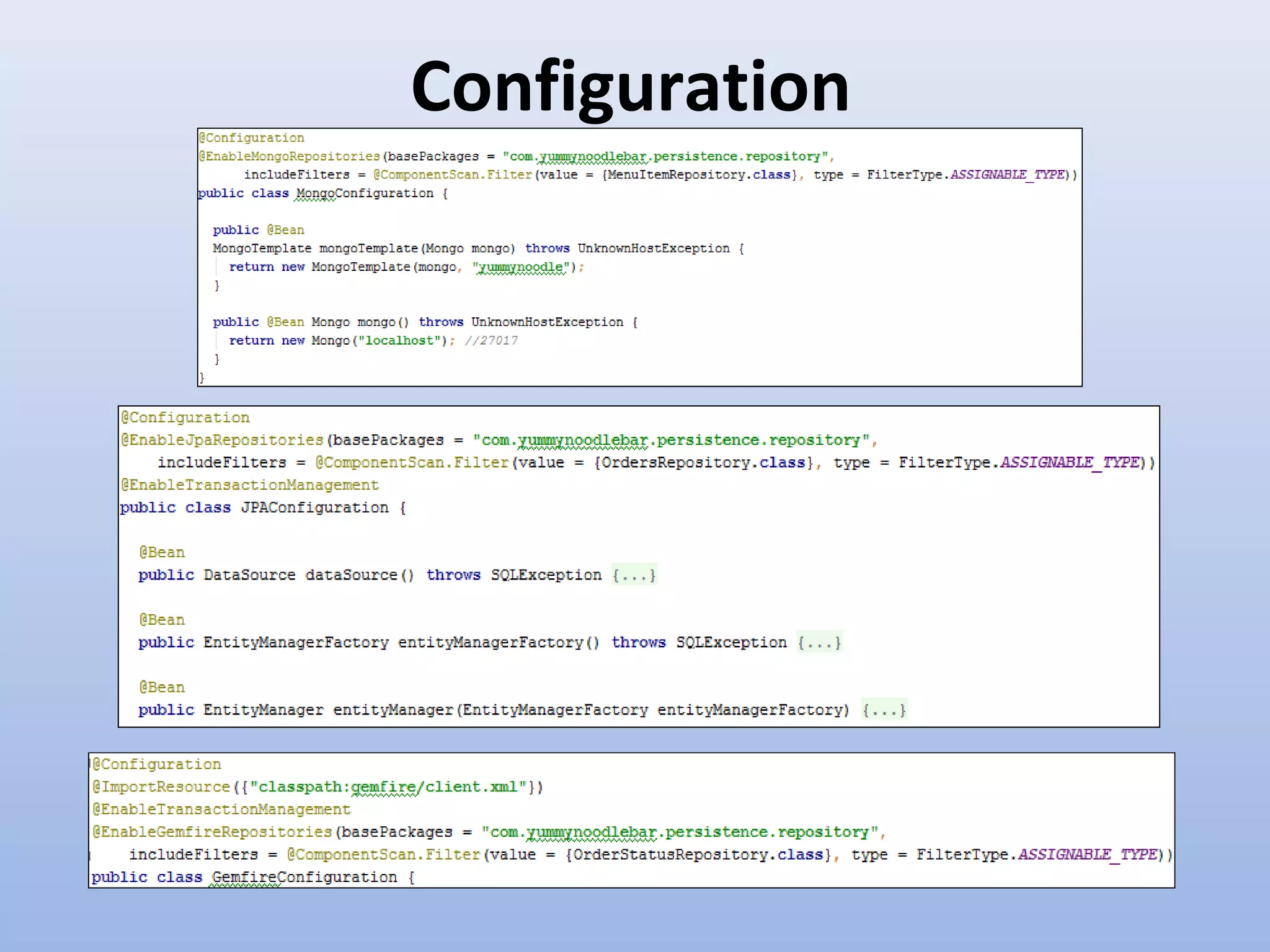
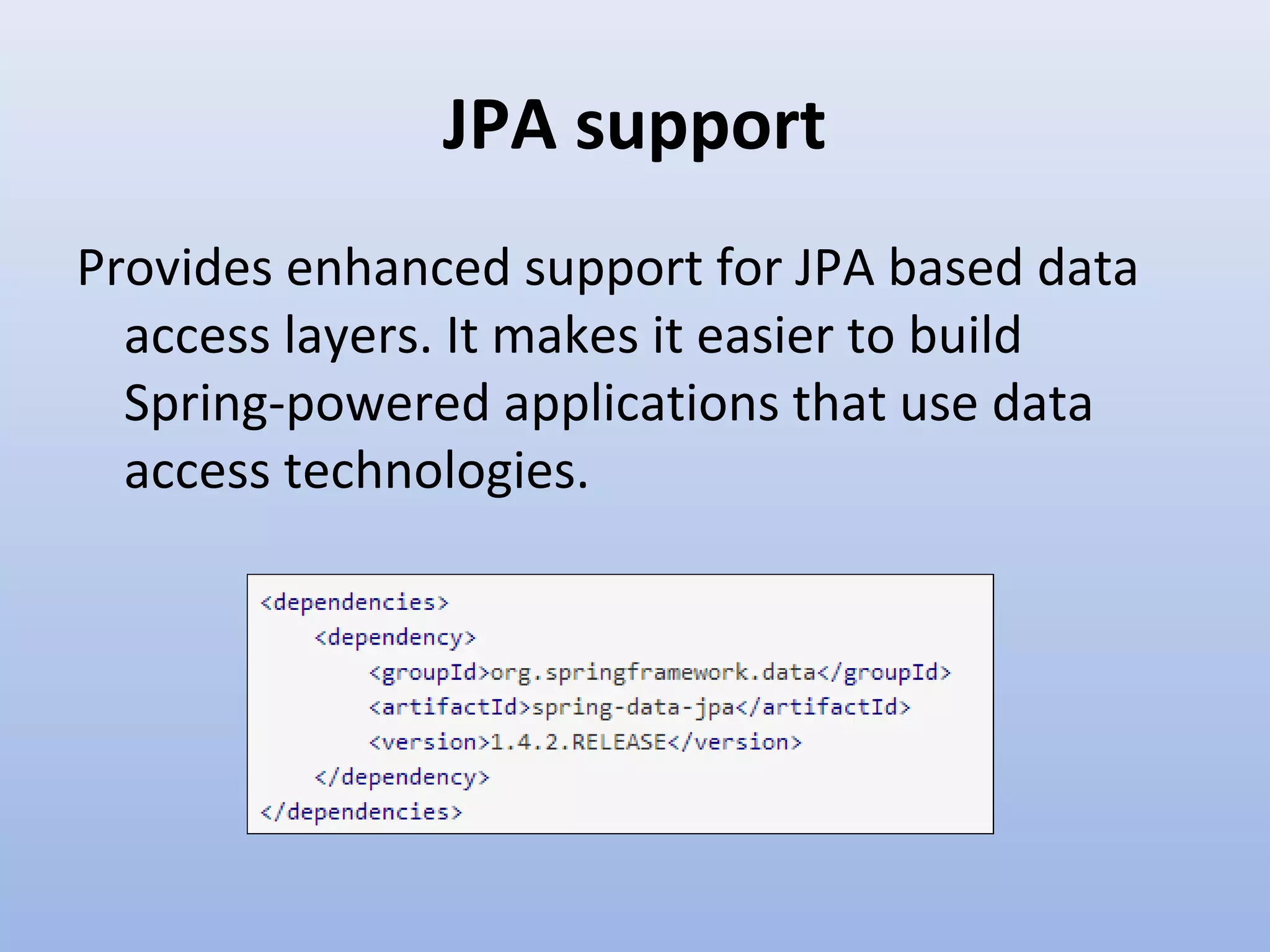
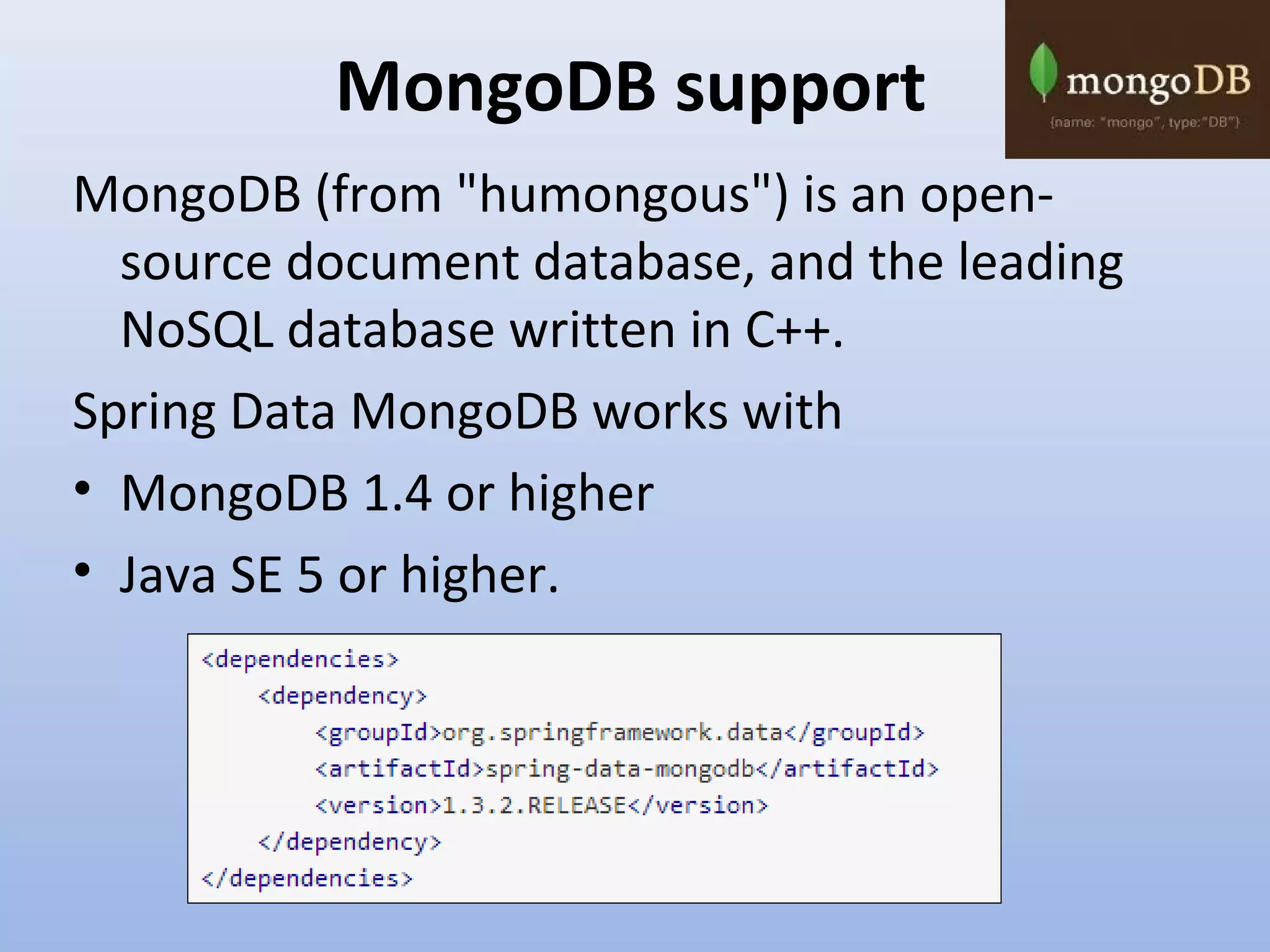
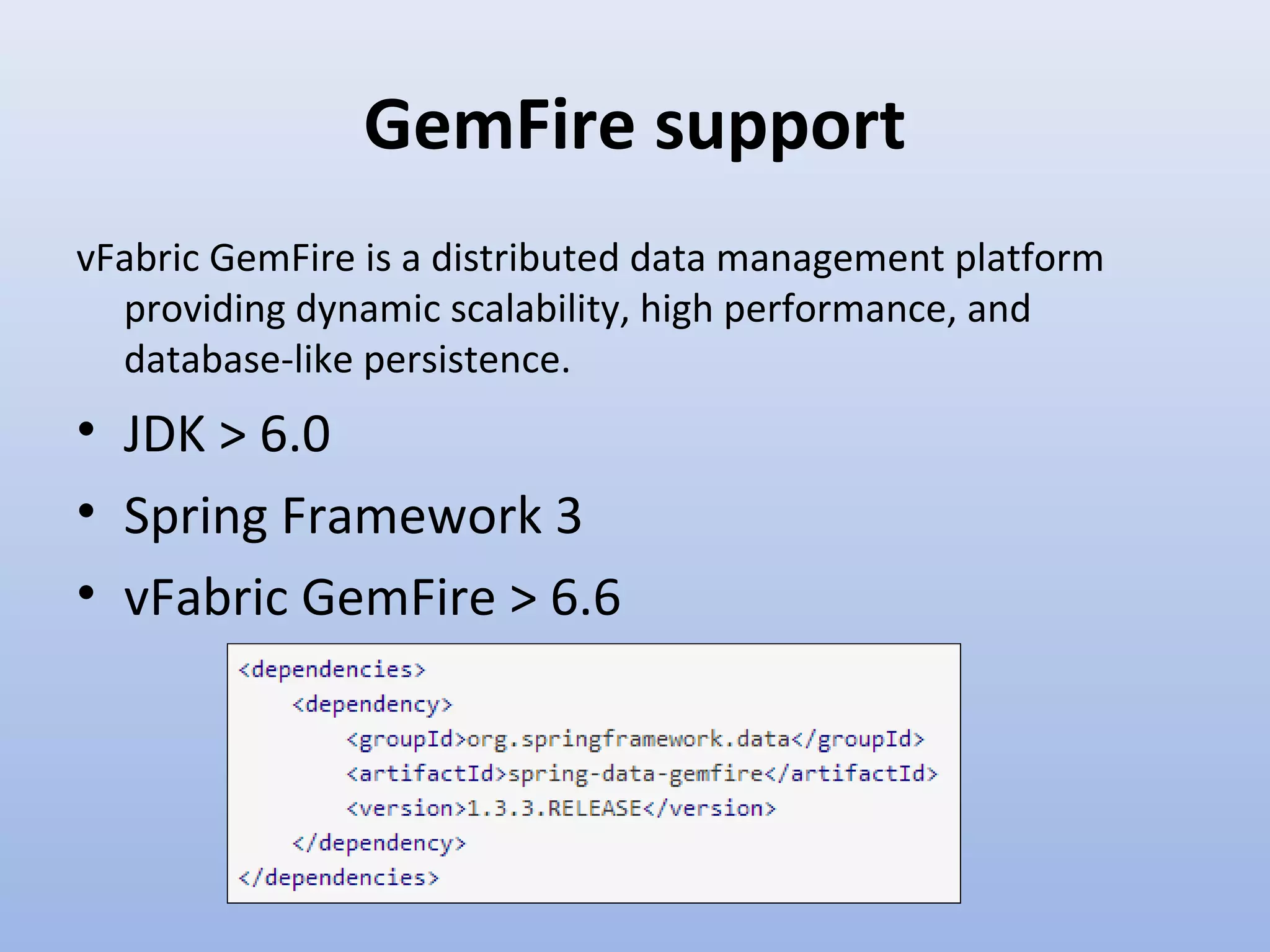
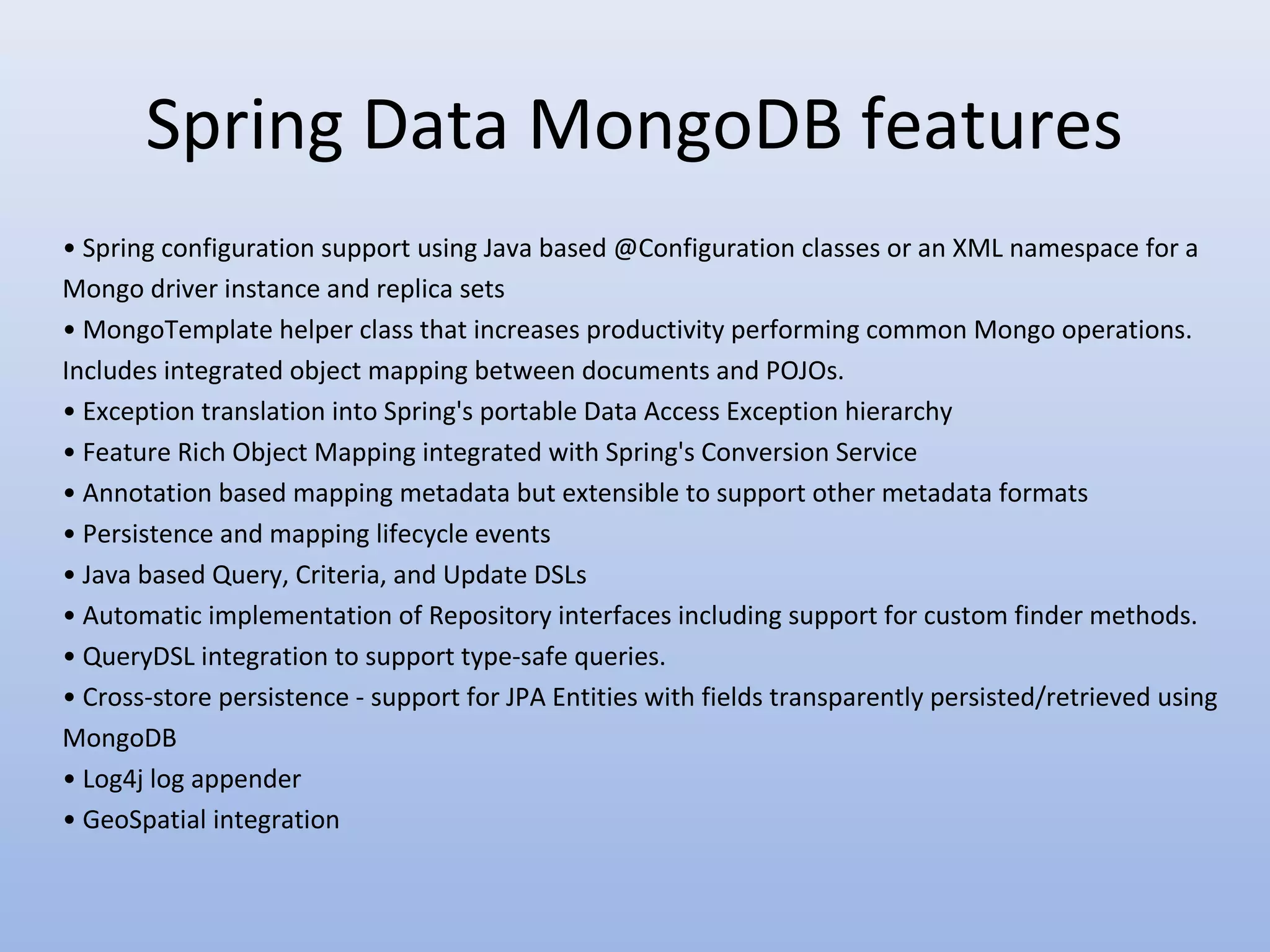
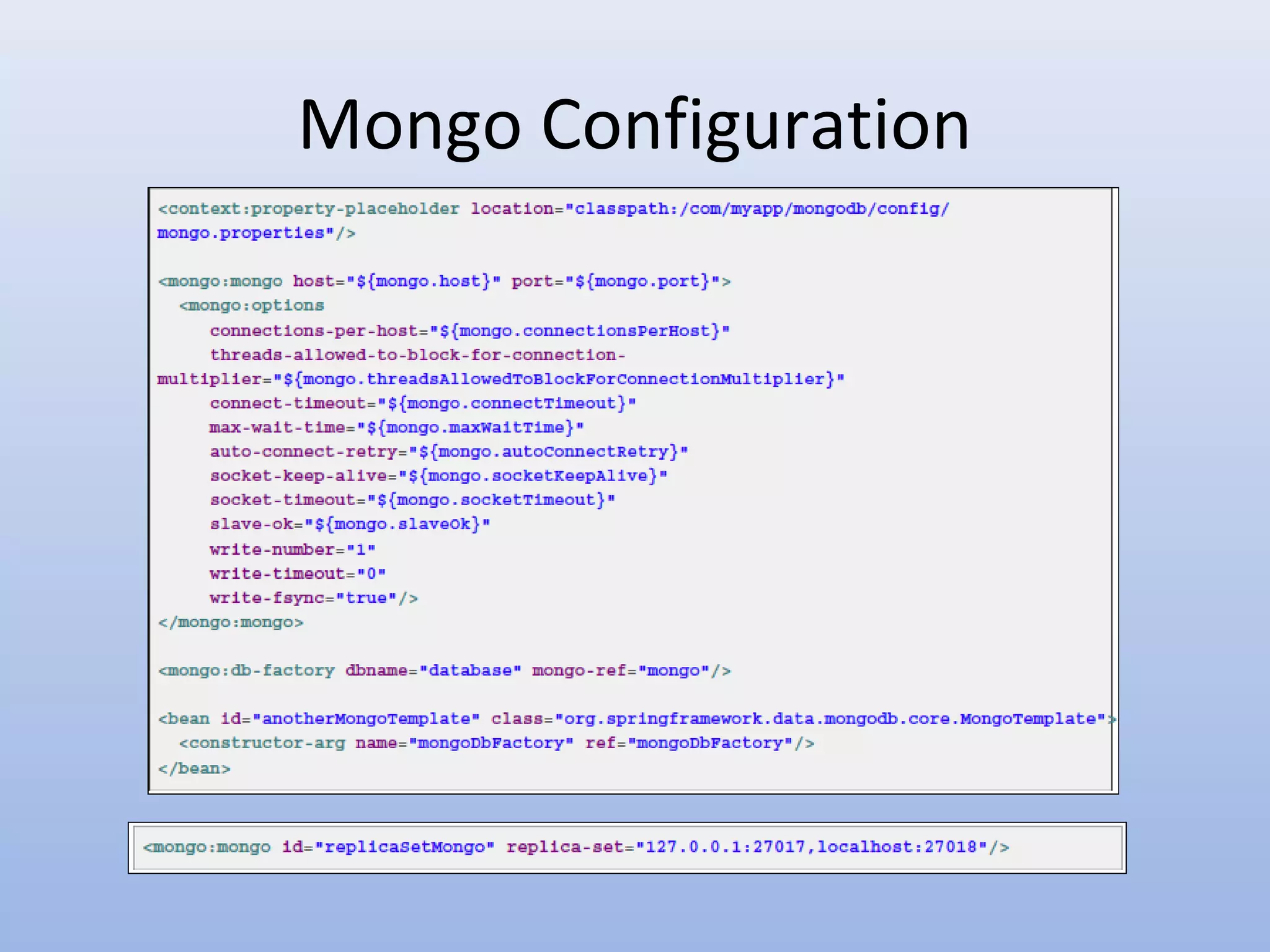
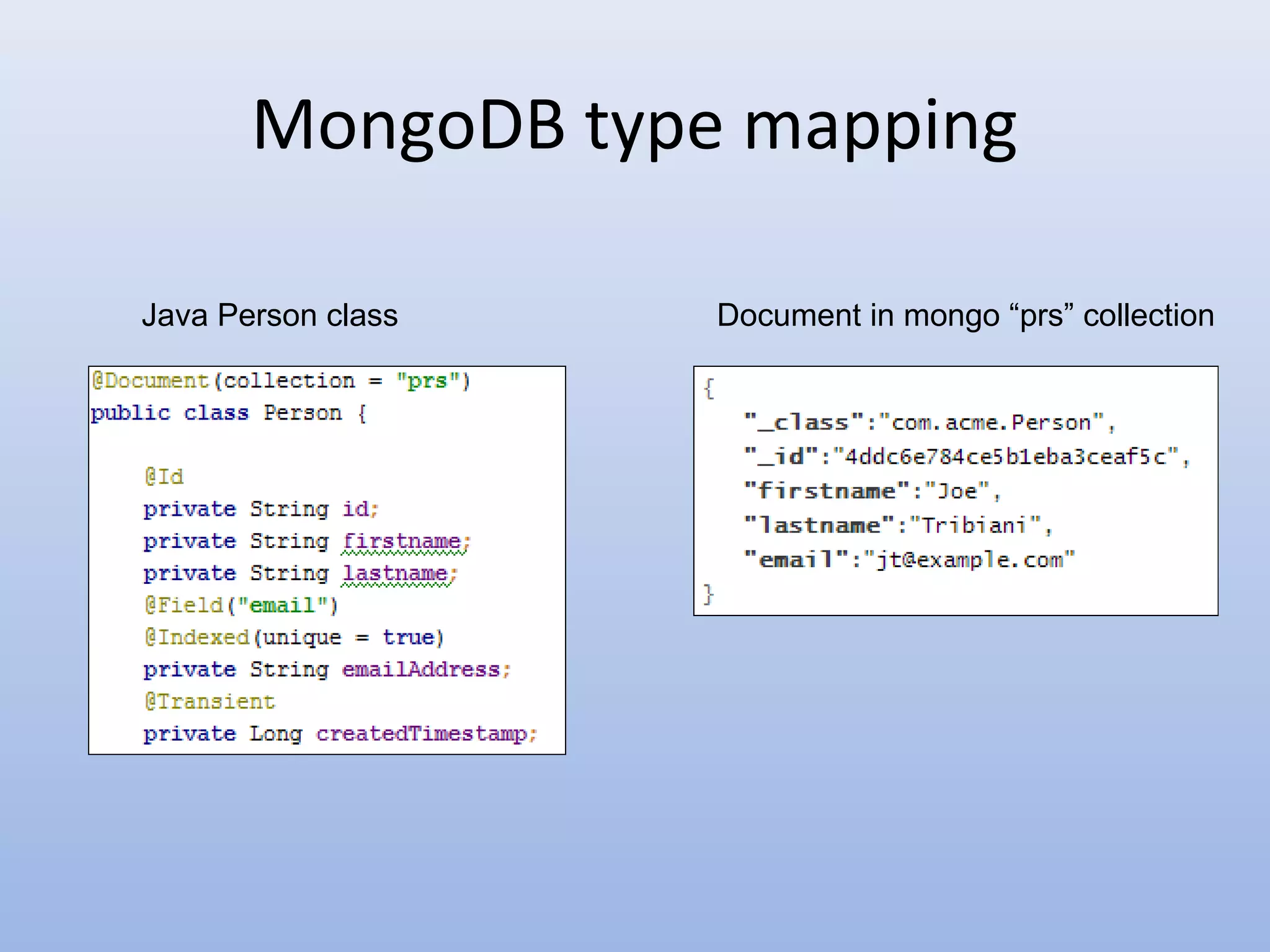
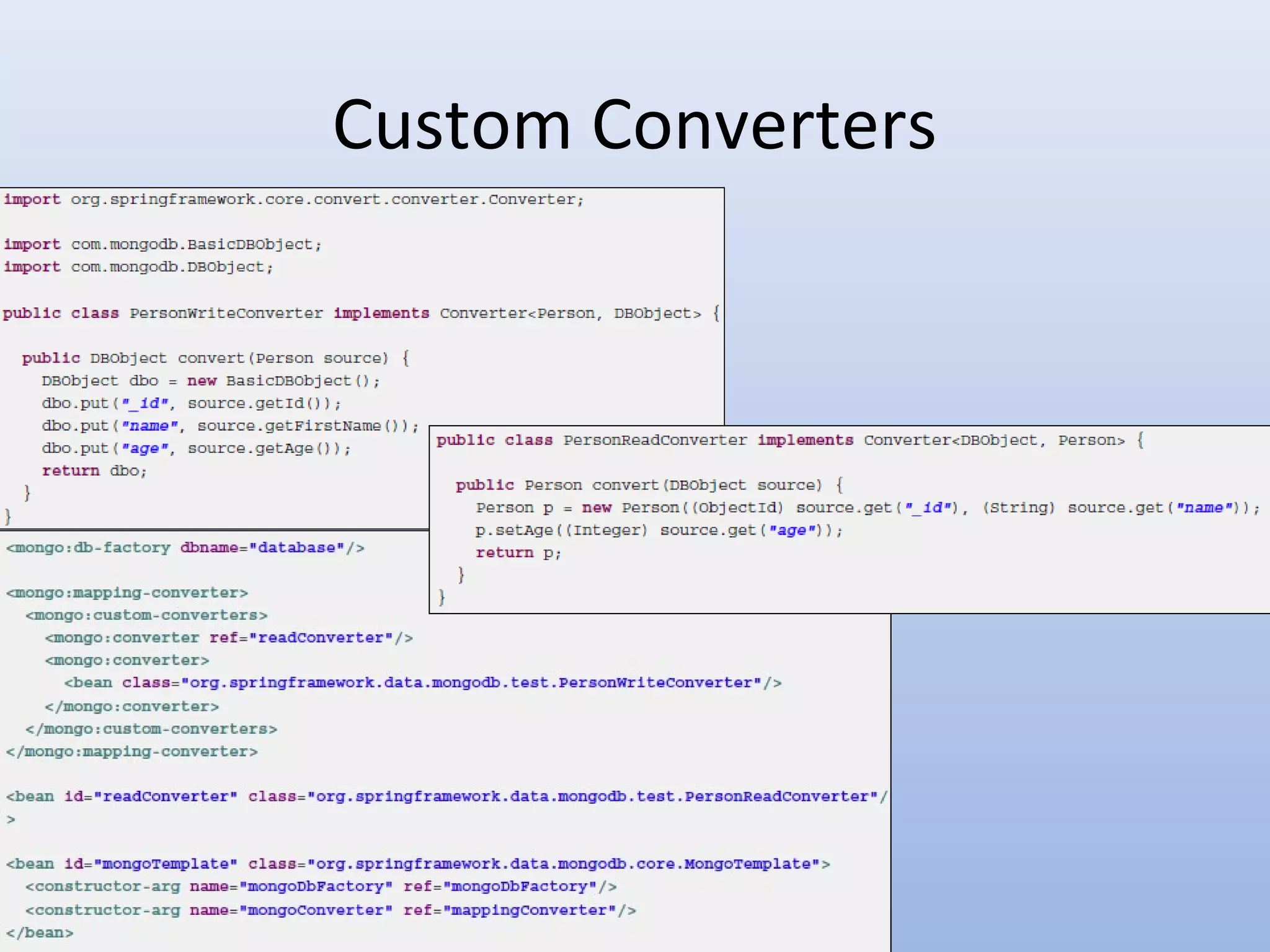
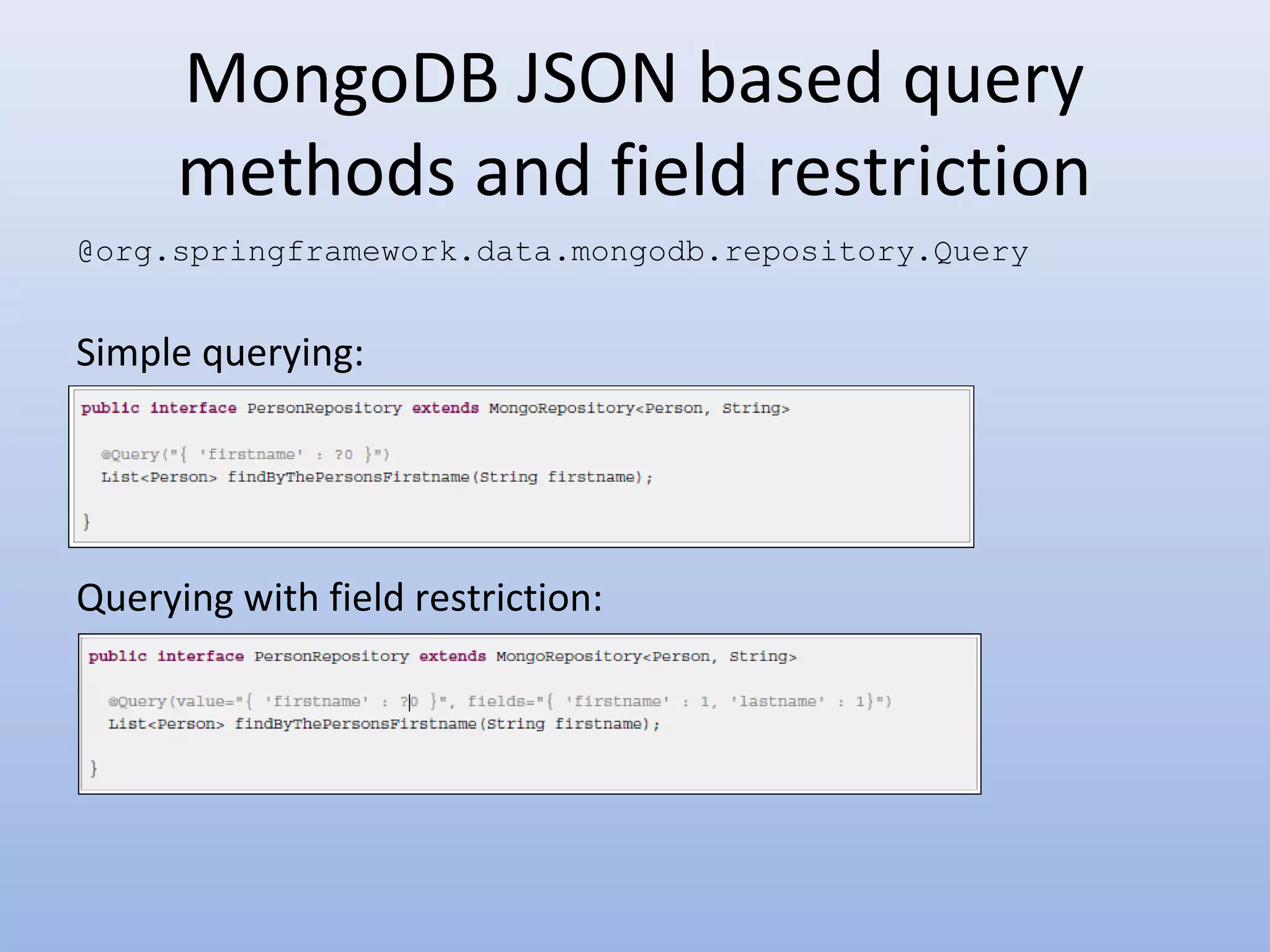
Spring Data provides a unified model for data access and management across different data access technologies such as relational, non-relational and cloud data stores. It includes utilities such as repository support, object mapping and templating to simplify data access layers. Spring Data MongoDB provides specific support for MongoDB including configuration, mapping, querying and integration with Spring MVC. It simplifies MongoDB access through MongoTemplate and provides a repository abstraction layer.