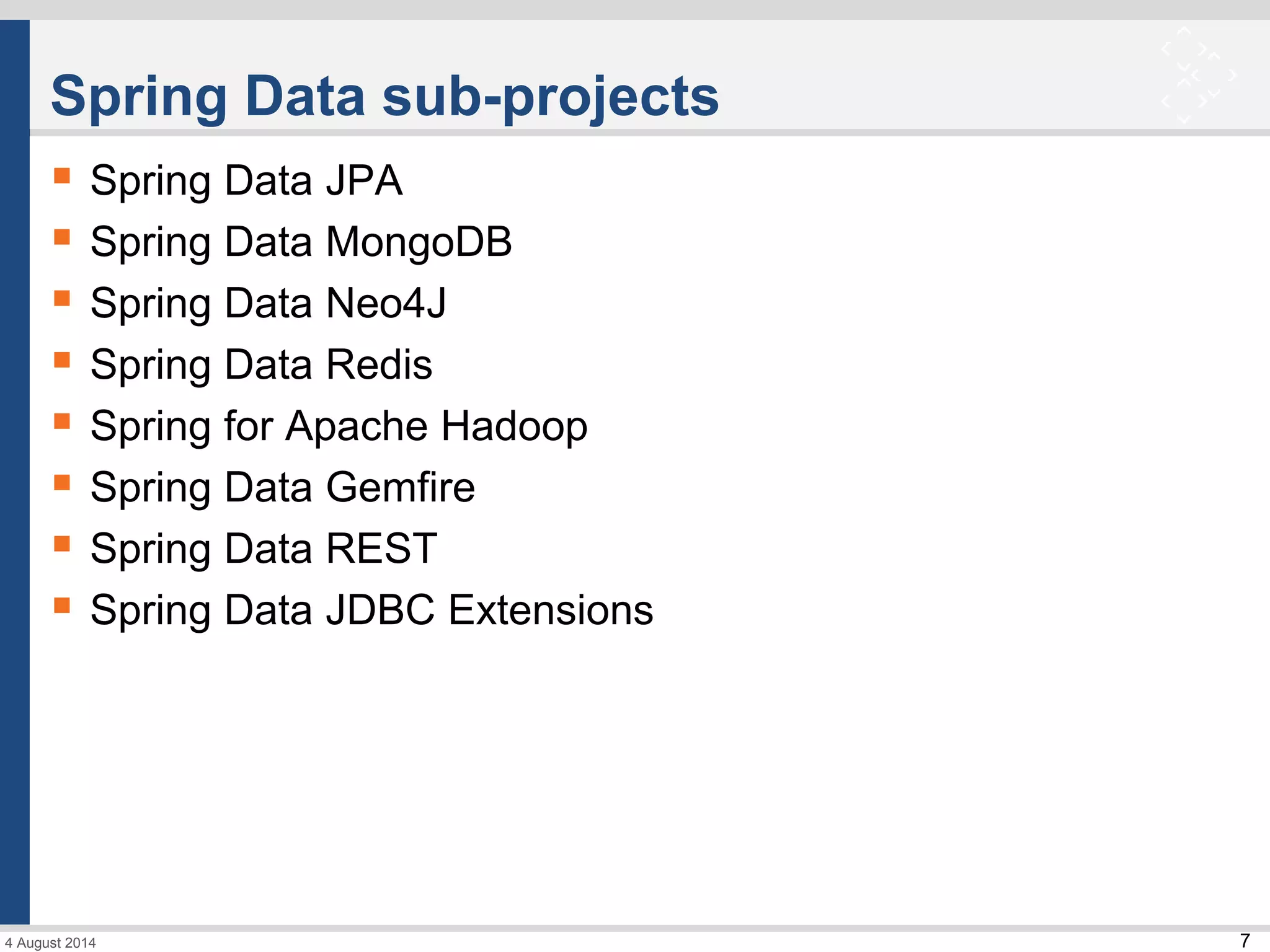
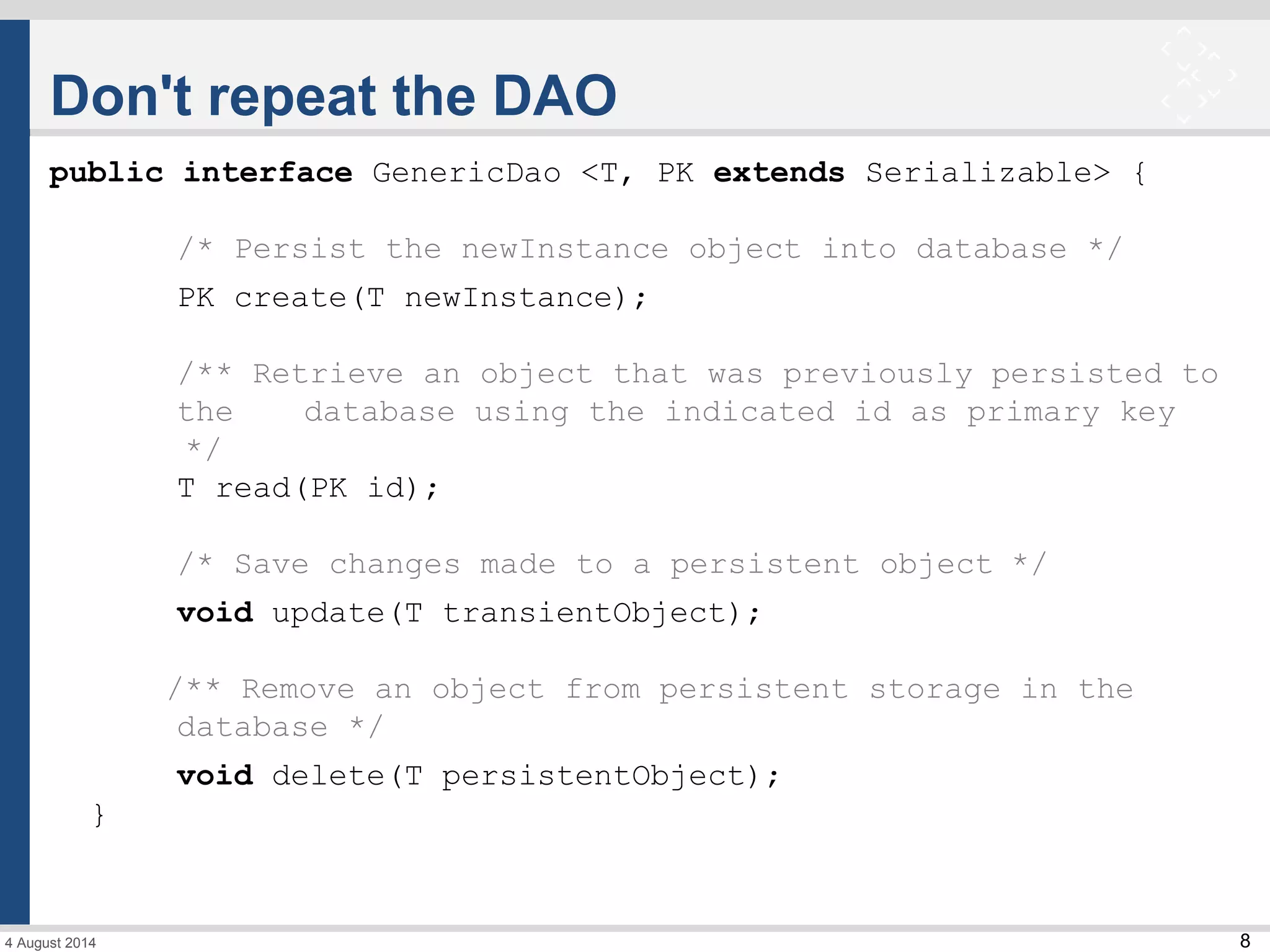
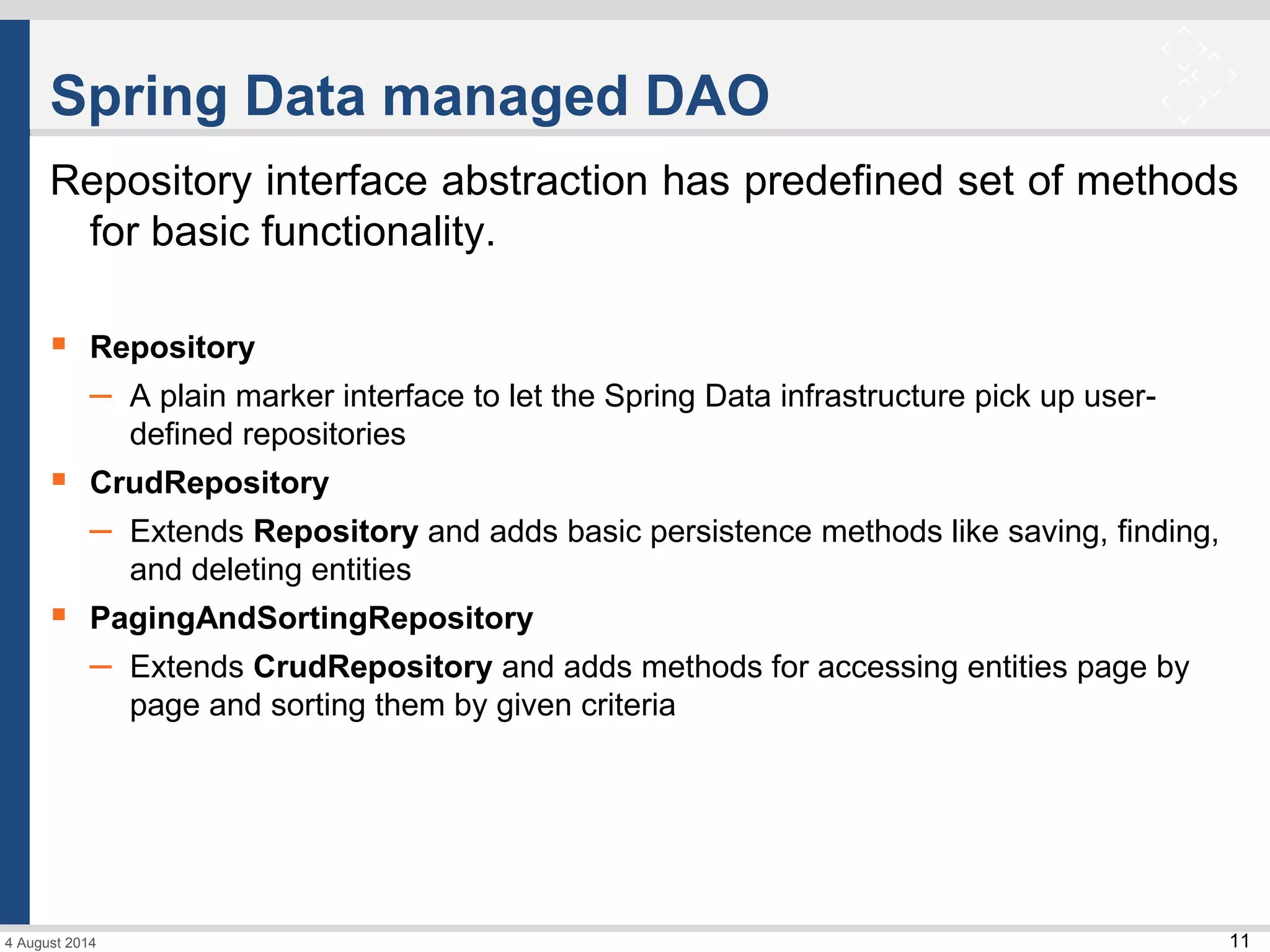
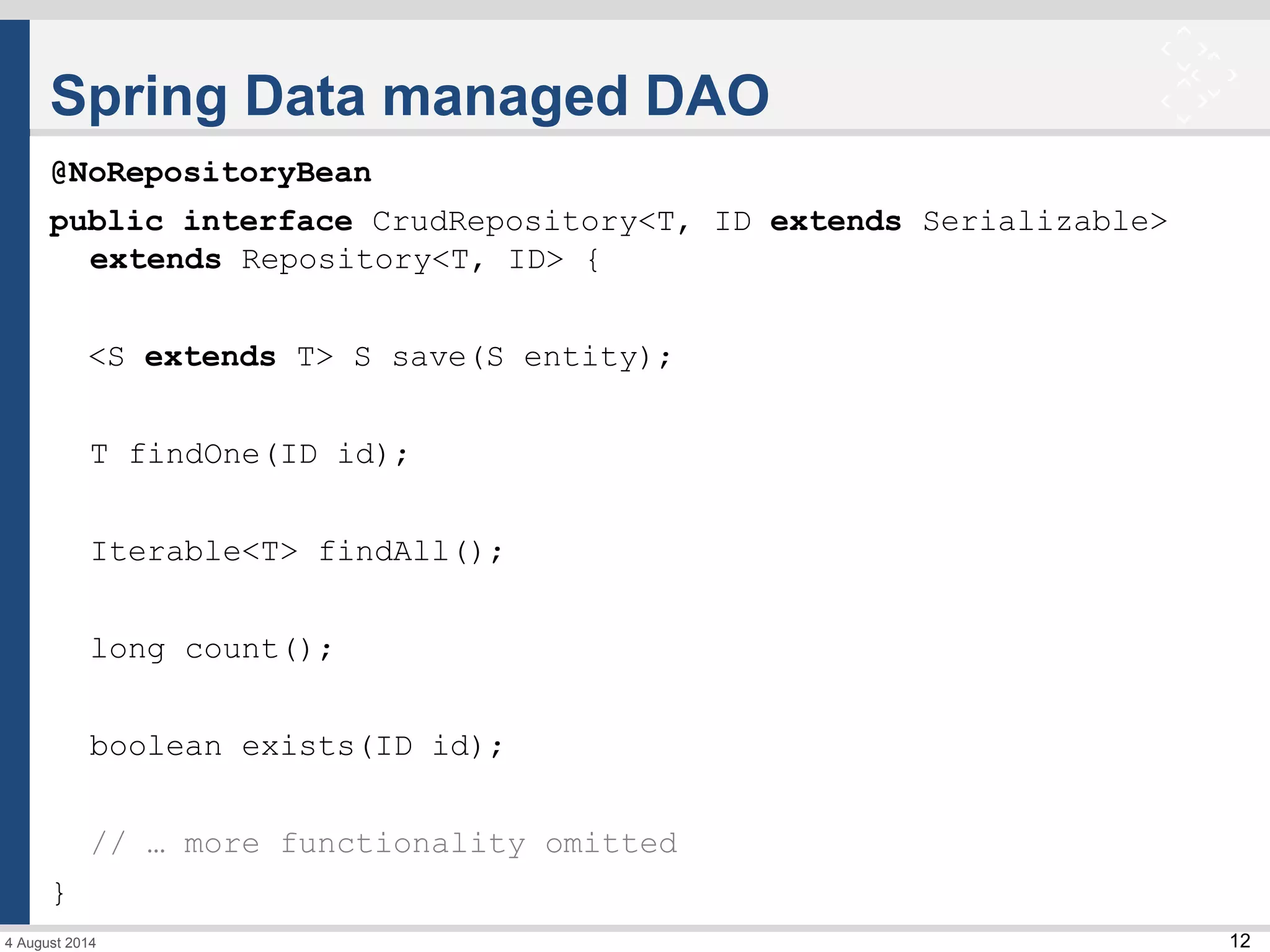
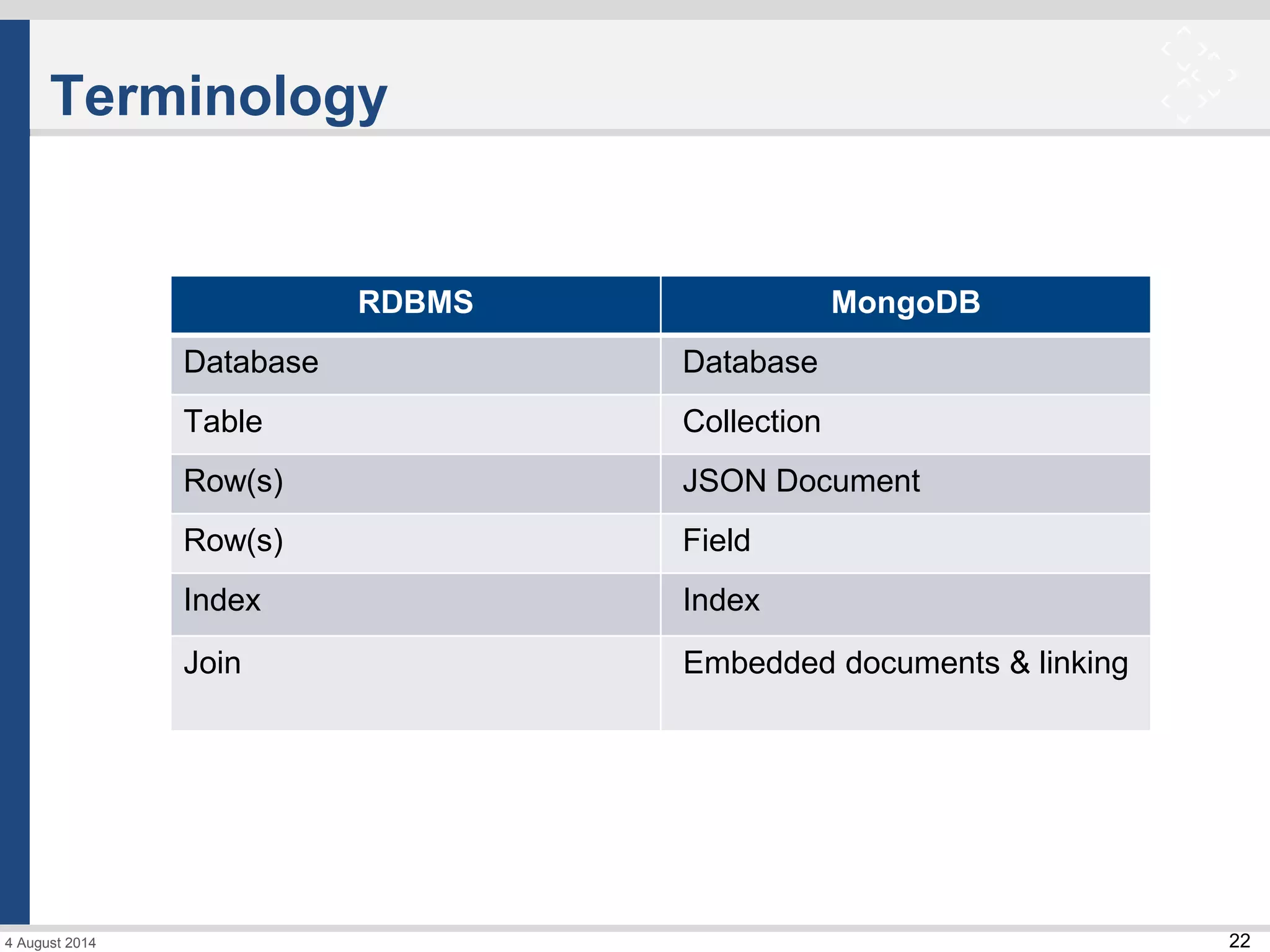
The document discusses Spring Data and its subprojects for working with different data stores. It focuses on Spring Data JPA for working with relational databases and object-relational mapping. Key features include repository interfaces that provide common CRUD methods and the ability to write queries. It also covers Spring Data MongoDB for working with MongoDB databases, including mapping of domain objects, repositories, and JSON-based queries. Both modules aim to reduce boilerplate code and provide consistent programming models across data stores.










![23 Document data model 4 August 2014 Document data model { _id: ObjectID('4bd9e8e17cefd644108961bb'), name: “The Godfather”, details: { isbn: “0451217403”, author: “Mario Puzo” }, price: 100.00, category: [ new ObjectID('4bf9bec50e32f82523389314')], comments: [ { user: “Don Corleone”, text: “Perfect!”, } ] } Schemaless { _id: ObjectID('4bf9bec50e32f82523389315'), name: “Lvivske”, price: 5.50, category: [ new ObjectID('4bf9bec50e32f82523389316')] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springdatatretyakov-140804090407-phpapp02/75/Spring-Data-JPA-and-MongoDB-23-2048.jpg)