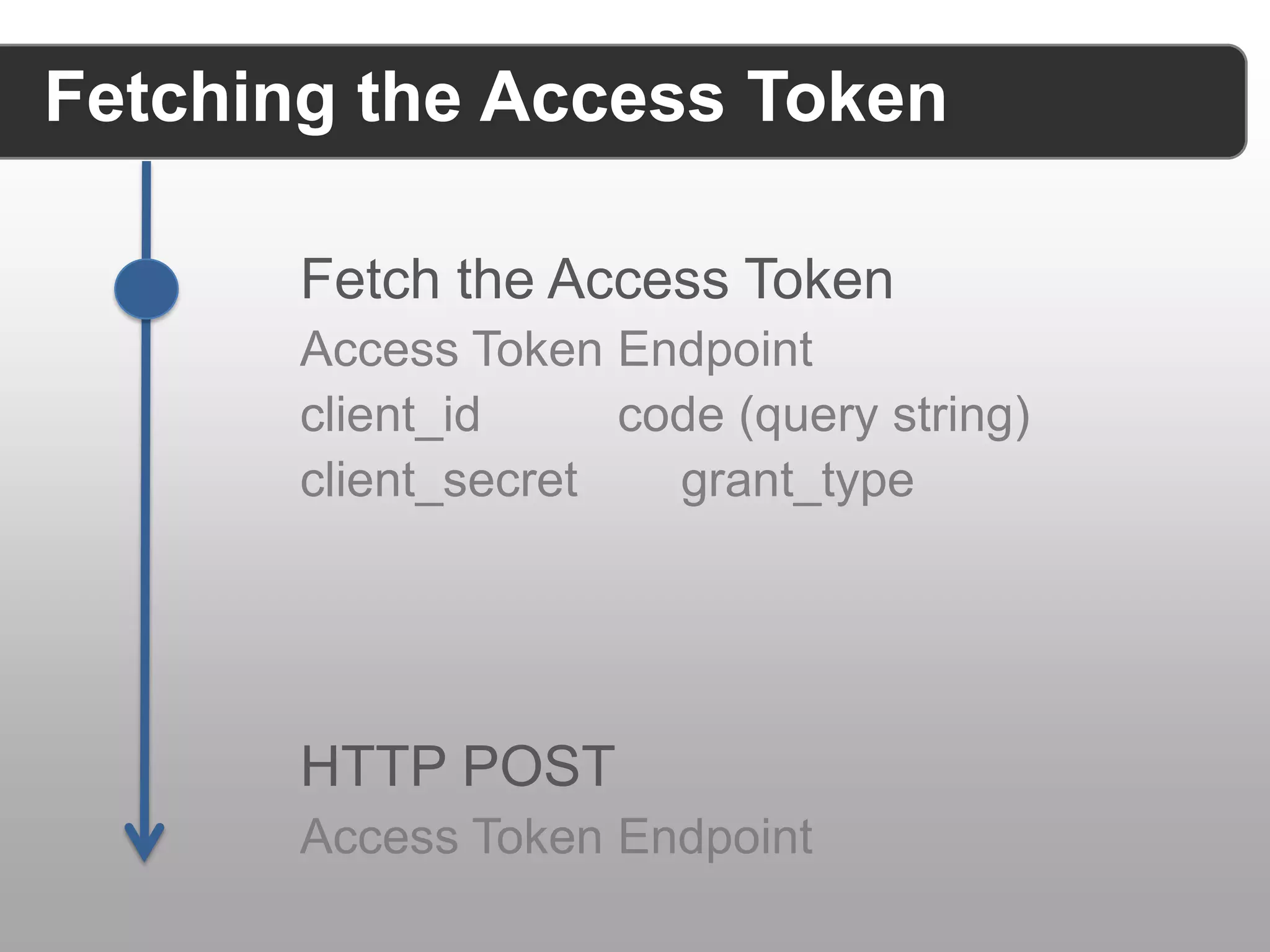
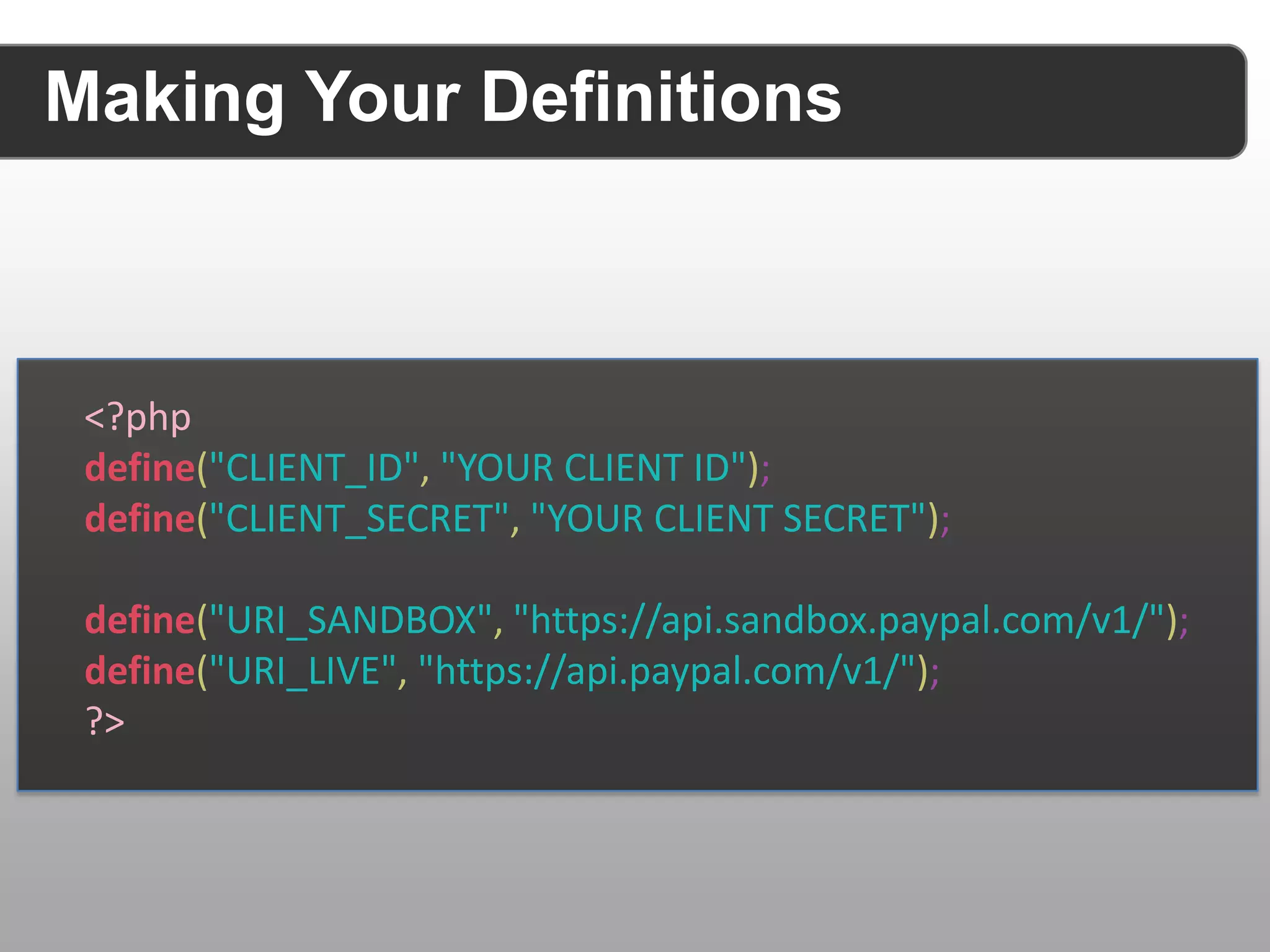
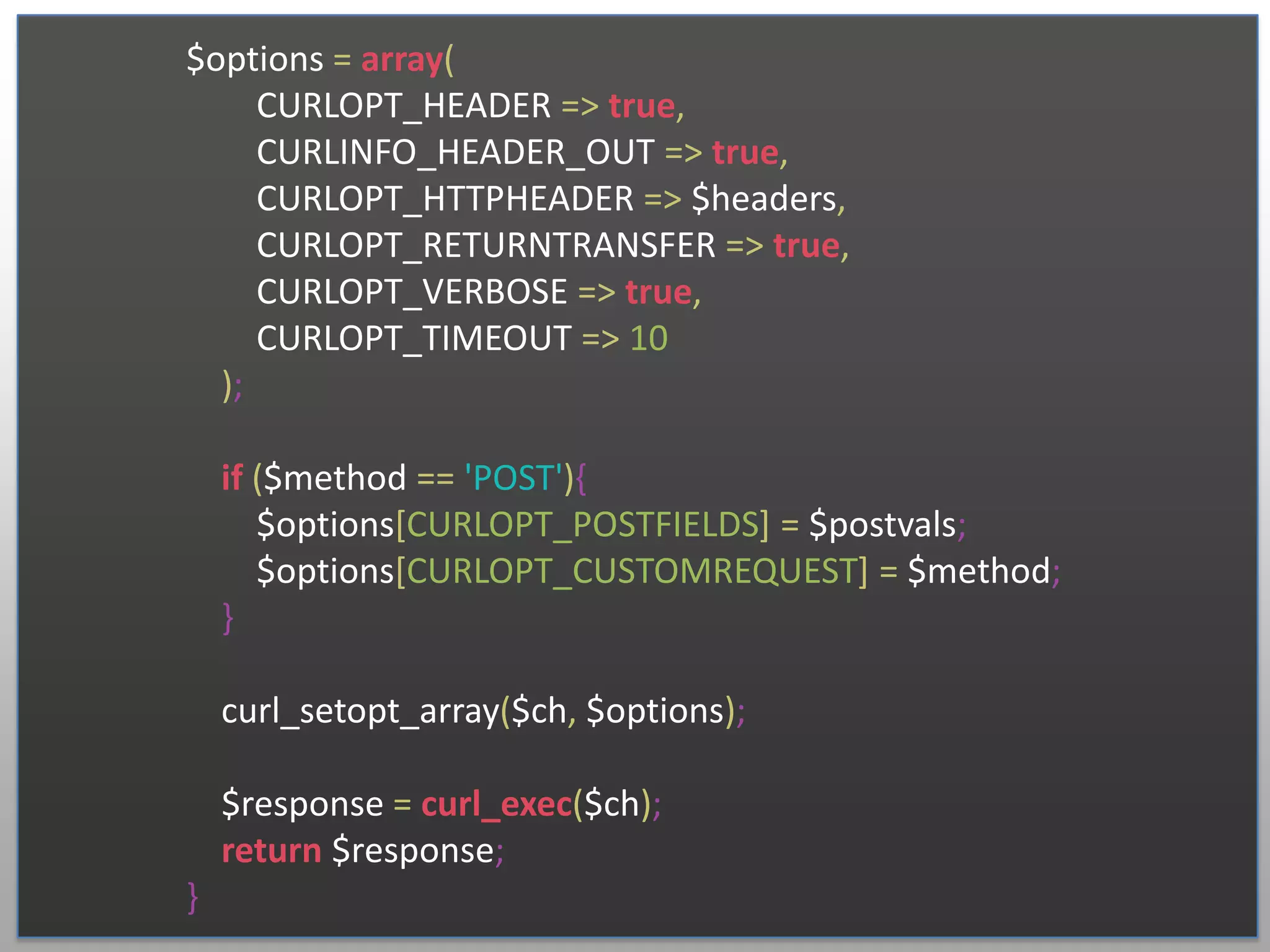
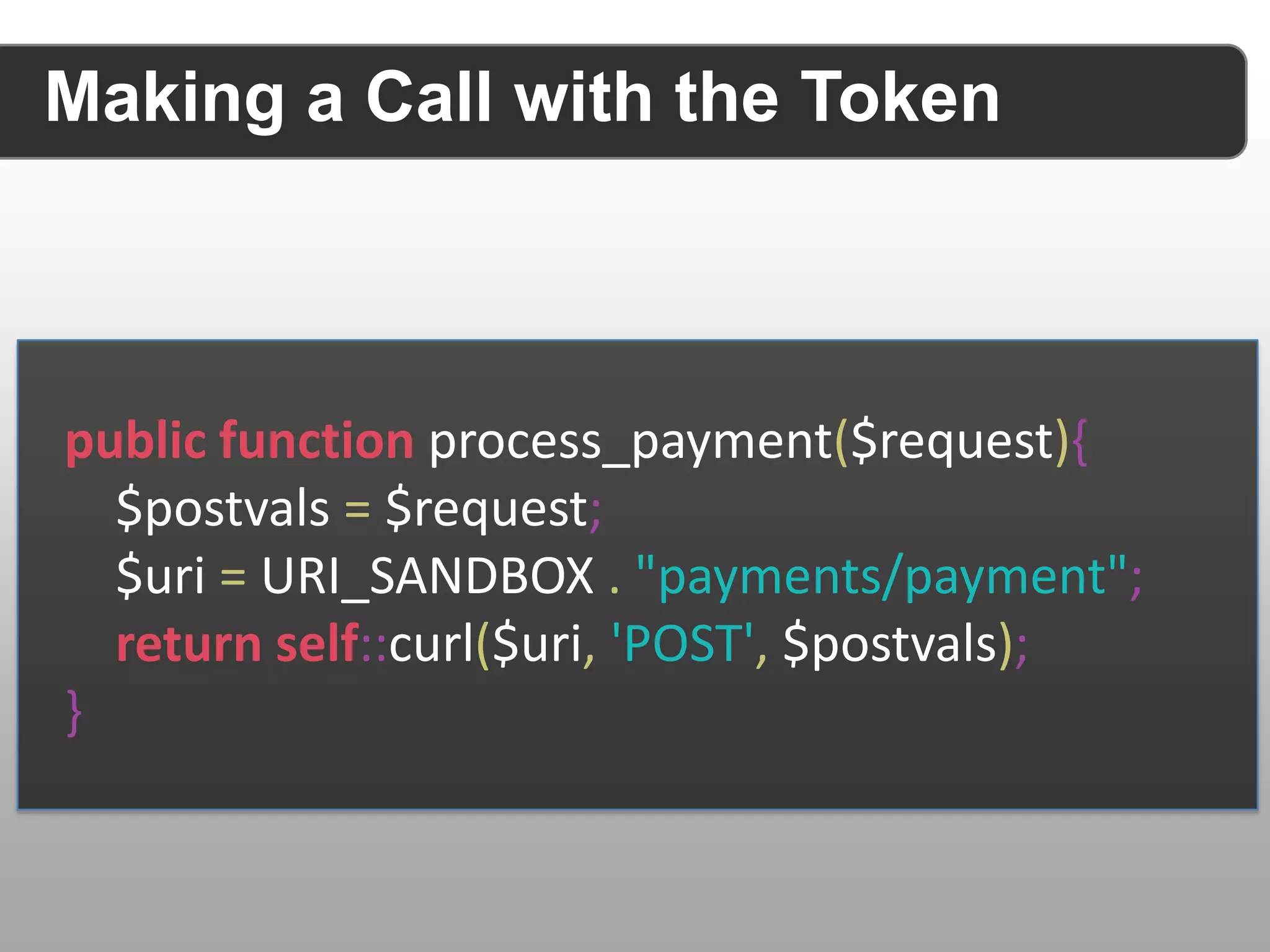
The document discusses securing RESTful APIs using OAuth 2 and OpenID Connect, highlighting the importance of authentication and authorization mechanisms for user data protection. It covers practical implementation details for fetching and using access tokens, along with various authorization flows and considerations for integrating these security standards without alienating developers. Additionally, it emphasizes the flexibility of REST and OAuth as specifications and provides resource links for further exploration.












!["links": [{ "href": "https://api.sandbox.paypal.com/v1/payments/ payment/PAY-6RV75EKEYSZ6Y", "rel": "self", "method": "GET" },{ "href": "https://www.sandbox.paypal.com/webscr? cmd=_express-checkout&token=EC-6019609", "rel": "approval_url", "method": "REDIRECT" },{ "href": "https://api.sandbox.paypal.com/v1/payments/ payment/PAY-6RV75EKEYSZ6Y/execute", "rel": "execute", "method": "POST" } ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2013octsvcodecampsecurerestapisoauth2-131002134922-phpapp01/75/Securing-RESTful-APIs-using-OAuth-2-and-OpenID-Connect-14-2048.jpg)