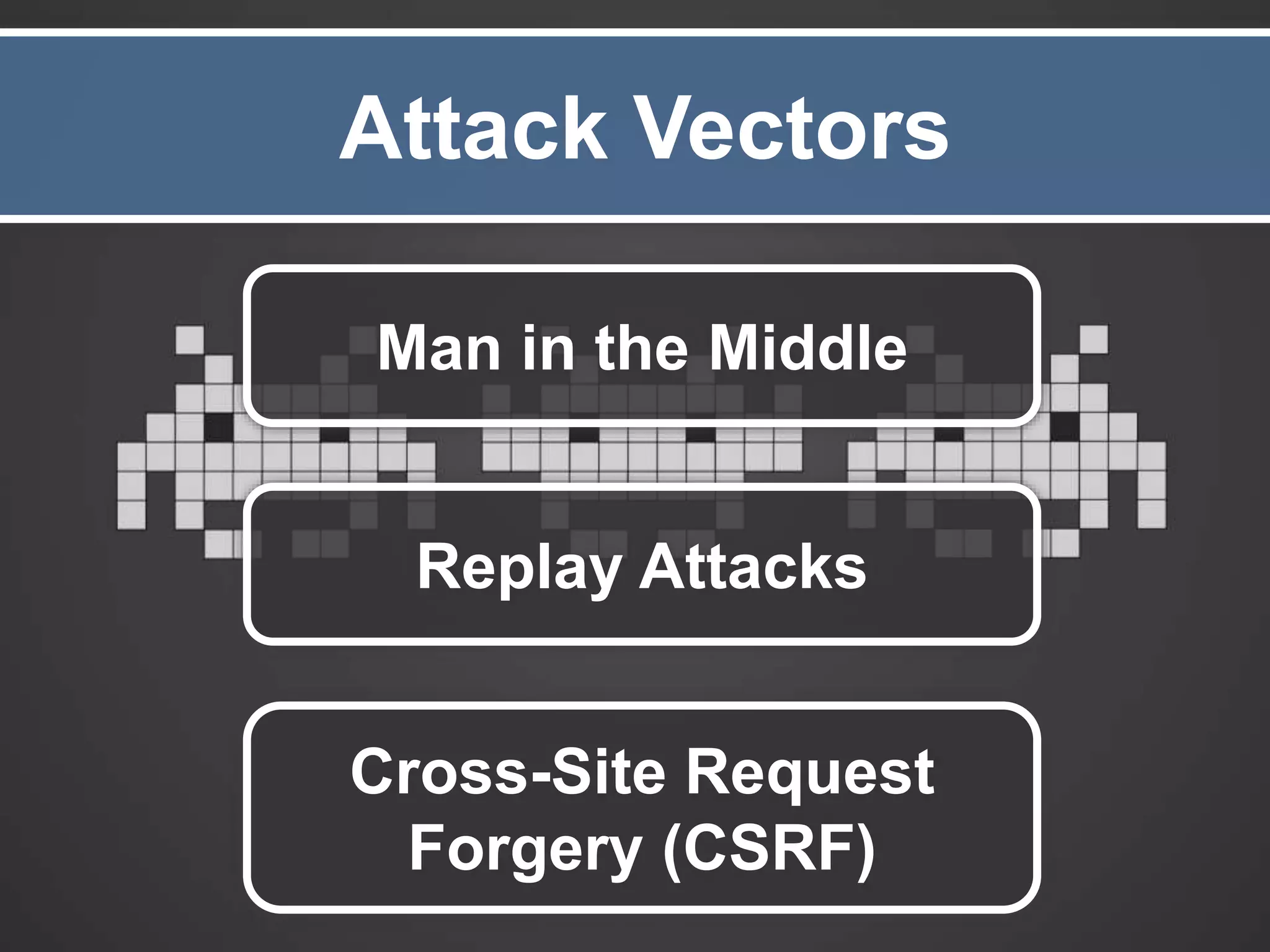
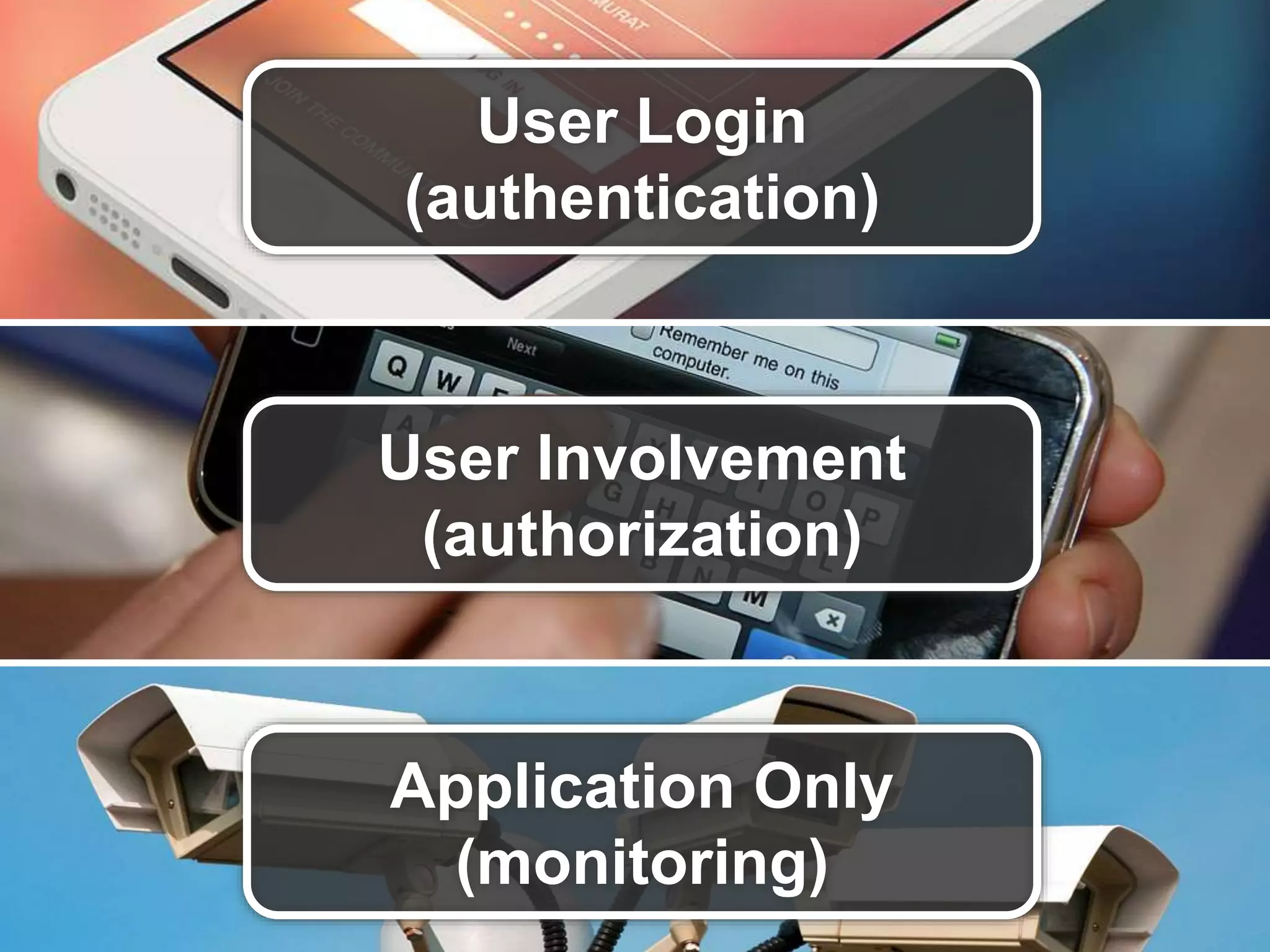
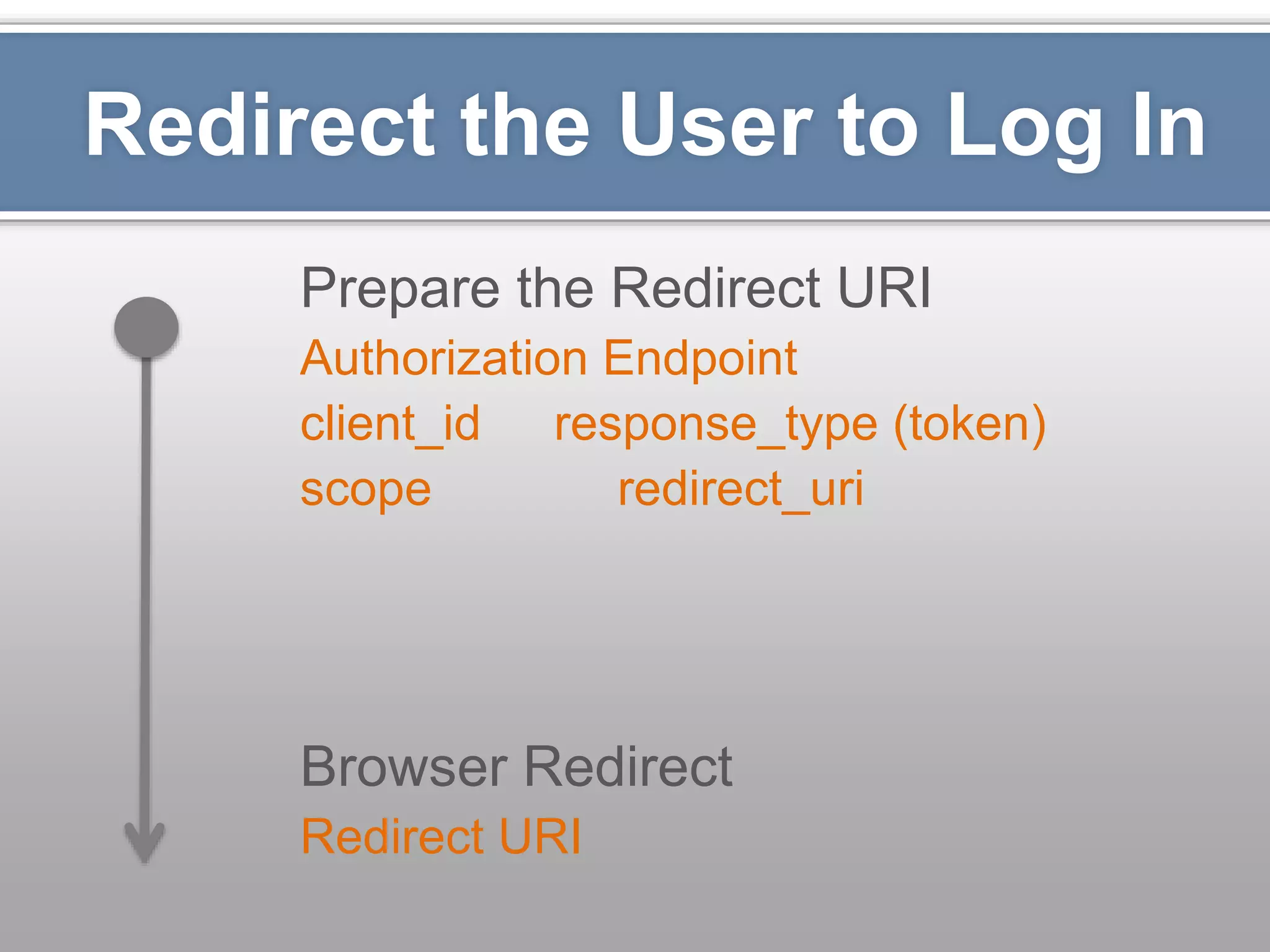
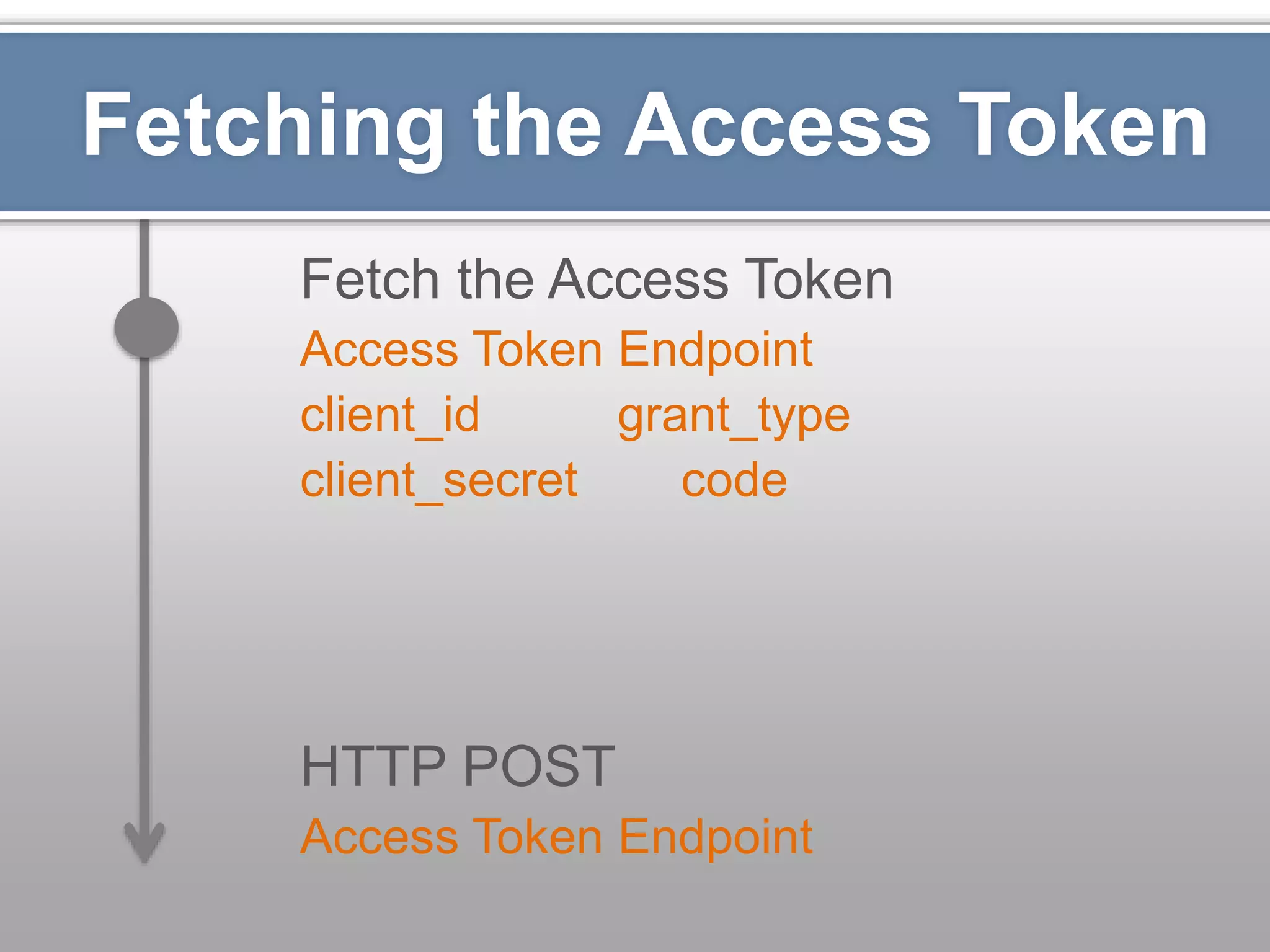
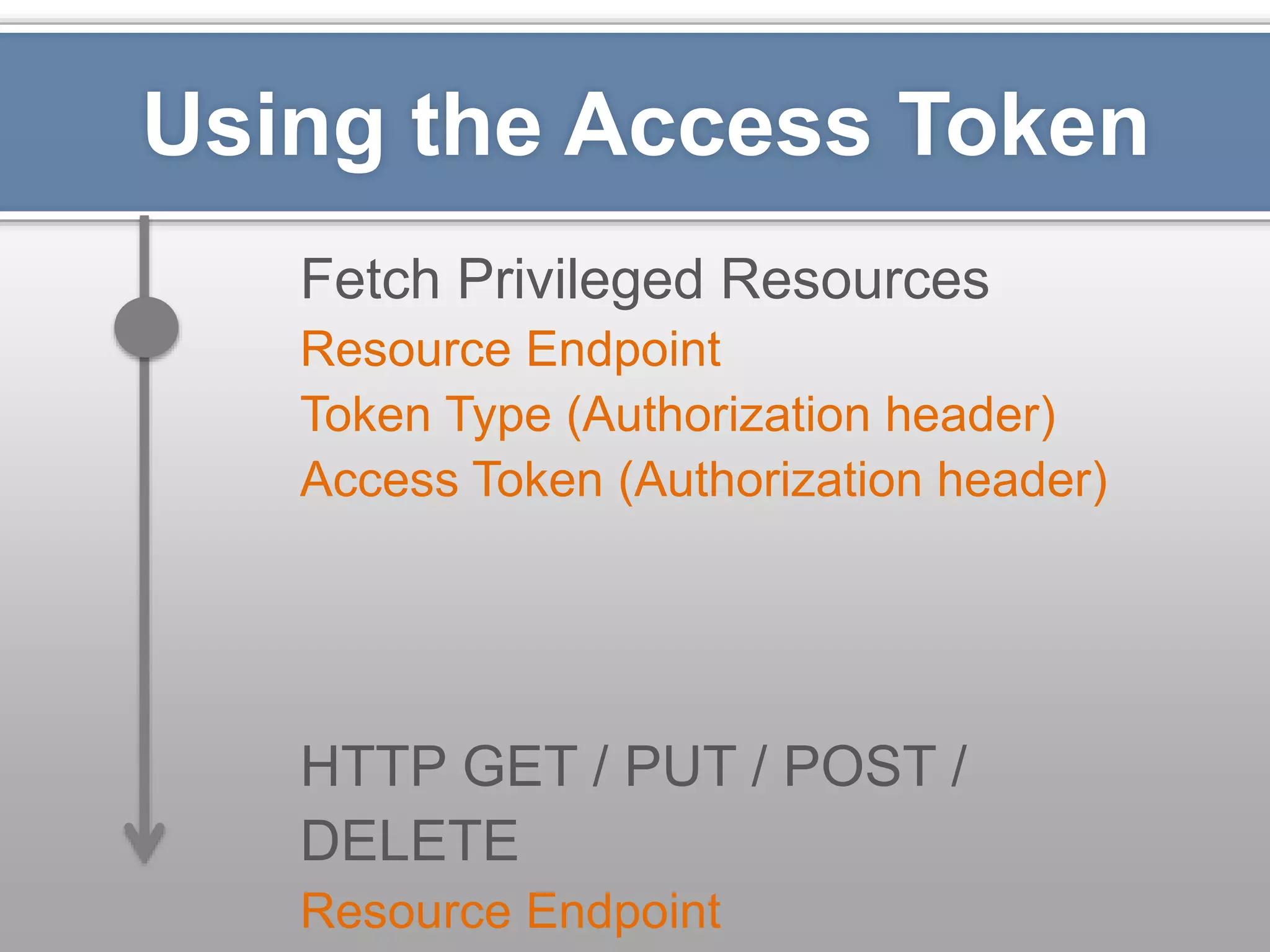
The document outlines the importance of securing RESTful APIs using OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect, highlighting the risks related to poor password choices among users. It details key components of API requests, authentication methods, attack vectors, and practical implementation steps for accessing secure resources. The conclusion emphasizes that REST and OAuth are specifications rather than strict rules, and encourages developers to adopt open-source tools and security measures without compromising usability.













![How Requests are Made curl -v https://api.sandbox.paypal.com/v1/payments/payme nt -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d '{ "intent": "sale", "payer": { ... }, "transactions": [{ "amount": { ... } }] }'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014febconfoooauthopenidconnect2-140226220910-phpapp02/75/Securing-RESTful-APIs-using-OAuth-2-and-OpenID-Connect-14-2048.jpg)
![How Auth is Added in curl -v https://api.sandbox.paypal.com/v1/payments/payment -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer {accessToken}" -d '{ "intent": "sale", "payer": { ... }, "transactions": [{ "amount": { ... } }] }'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014febconfoooauthopenidconnect2-140226220910-phpapp02/75/Securing-RESTful-APIs-using-OAuth-2-and-OpenID-Connect-15-2048.jpg)