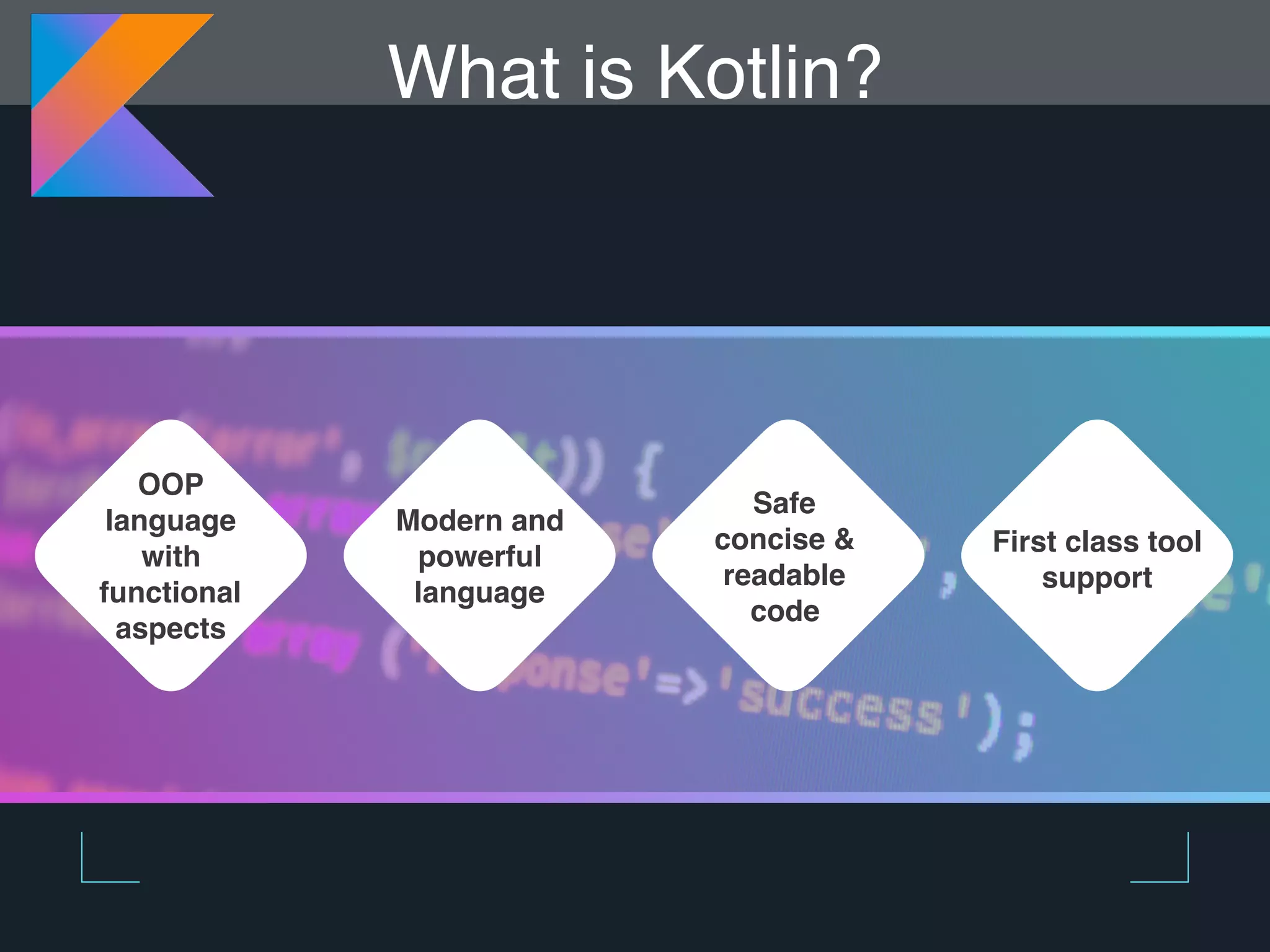
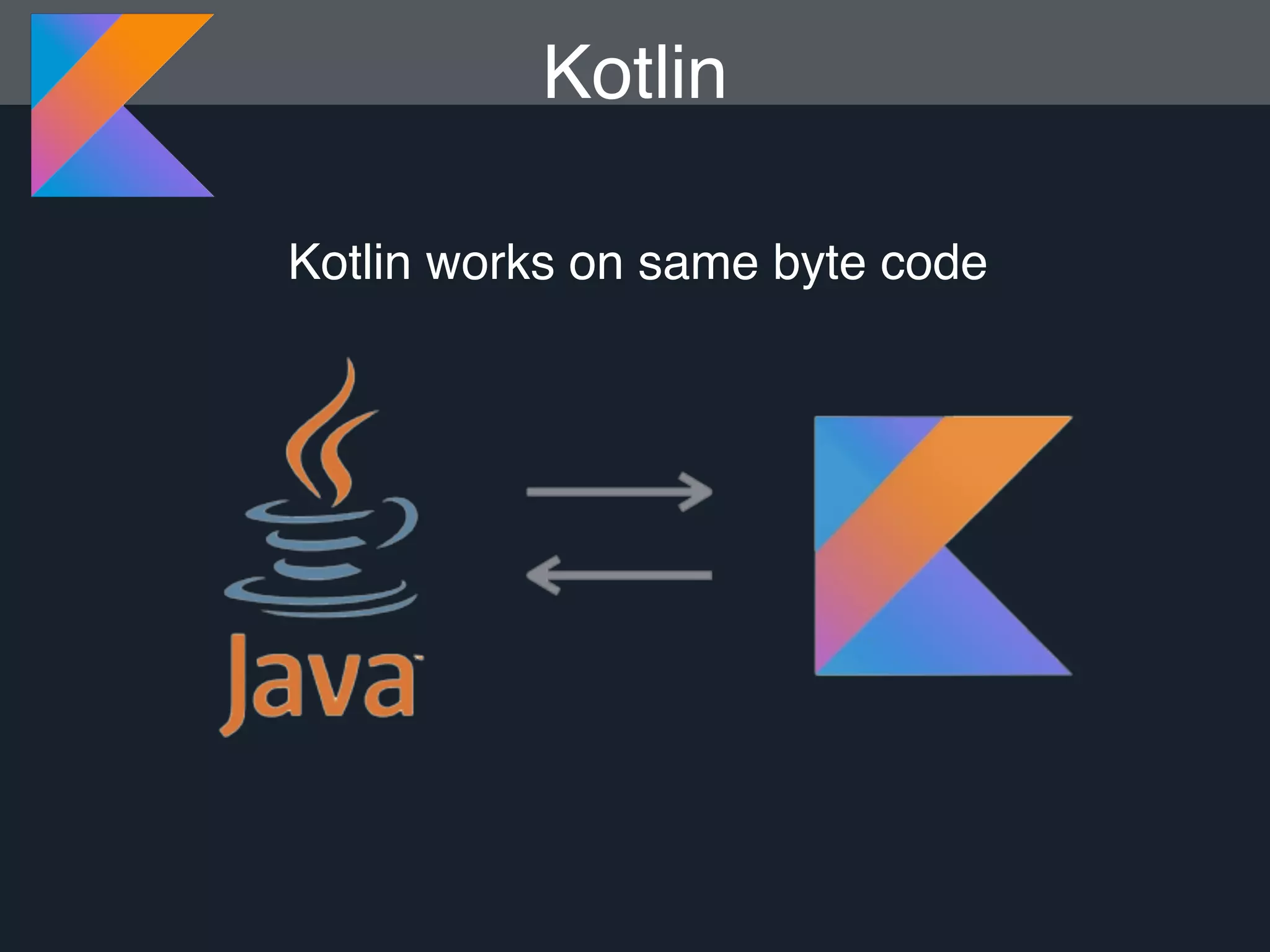
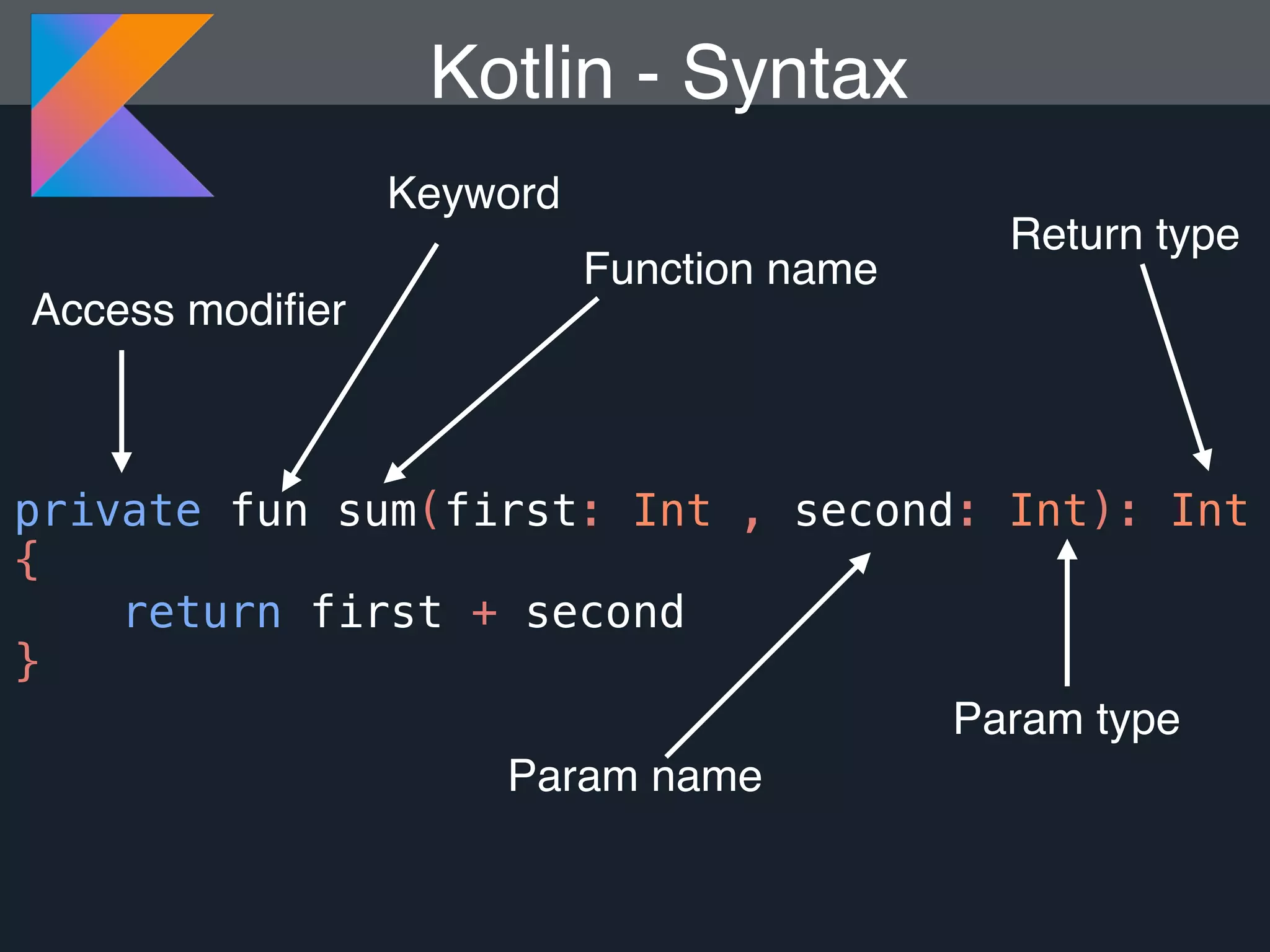
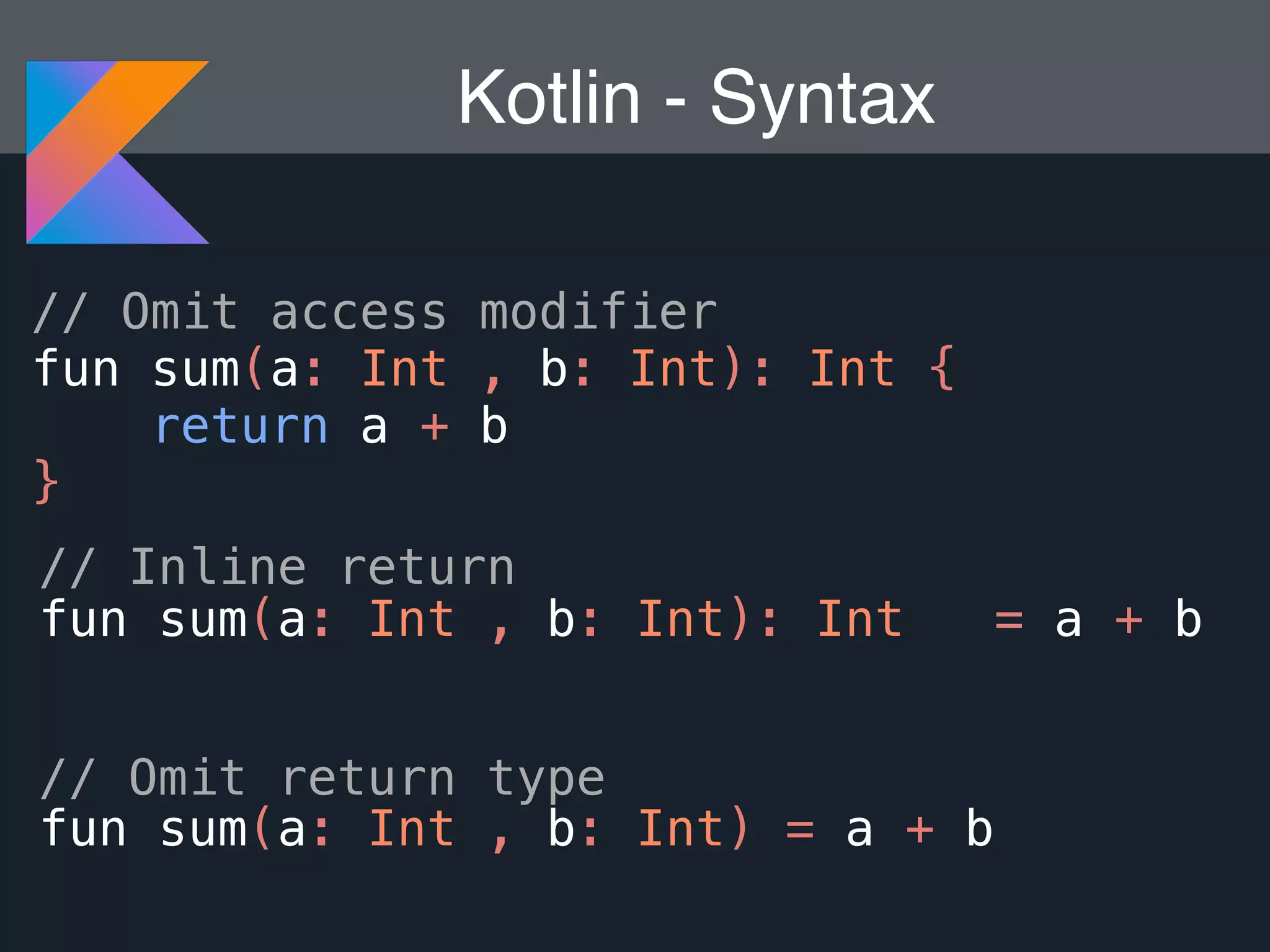
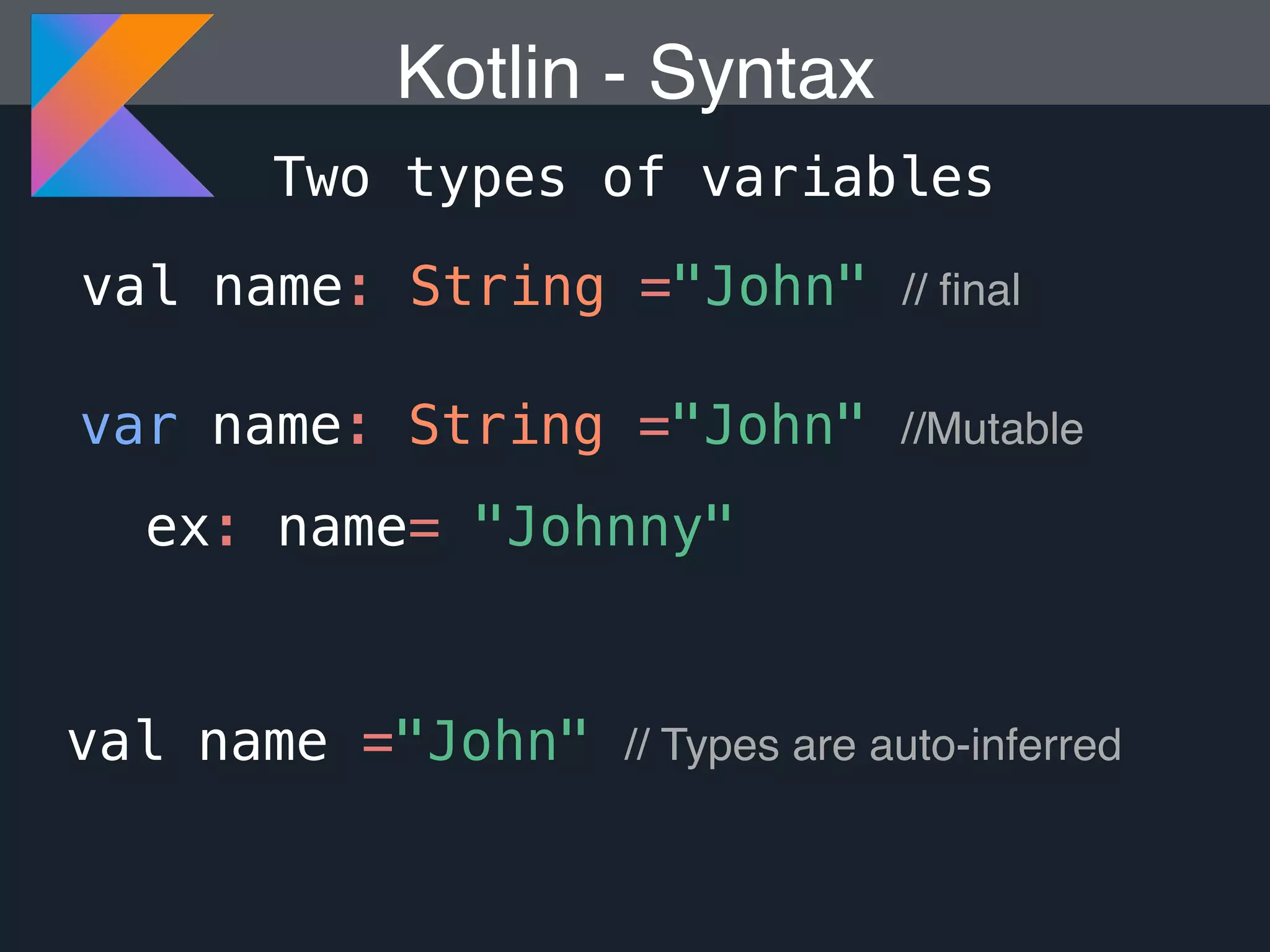
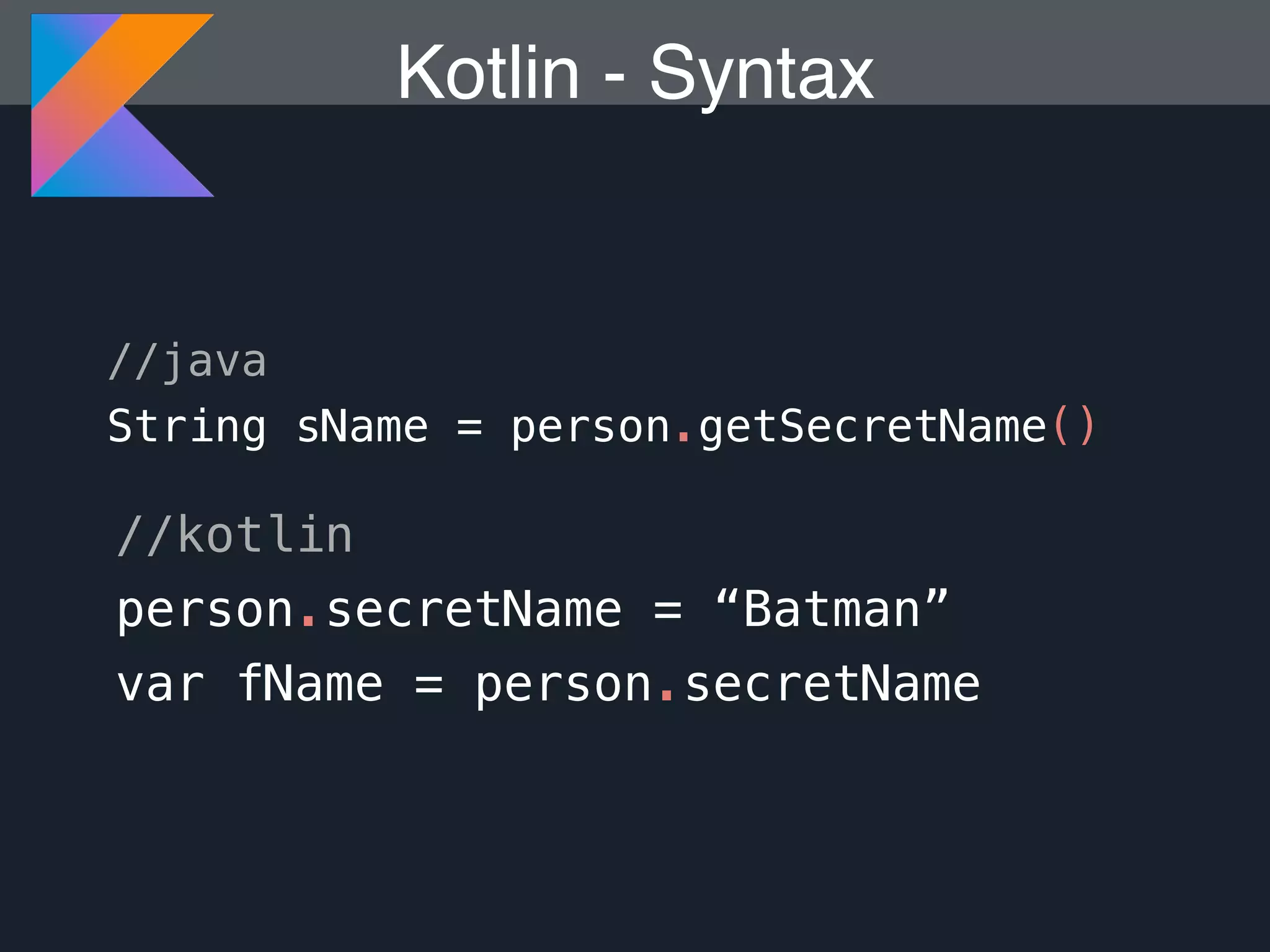
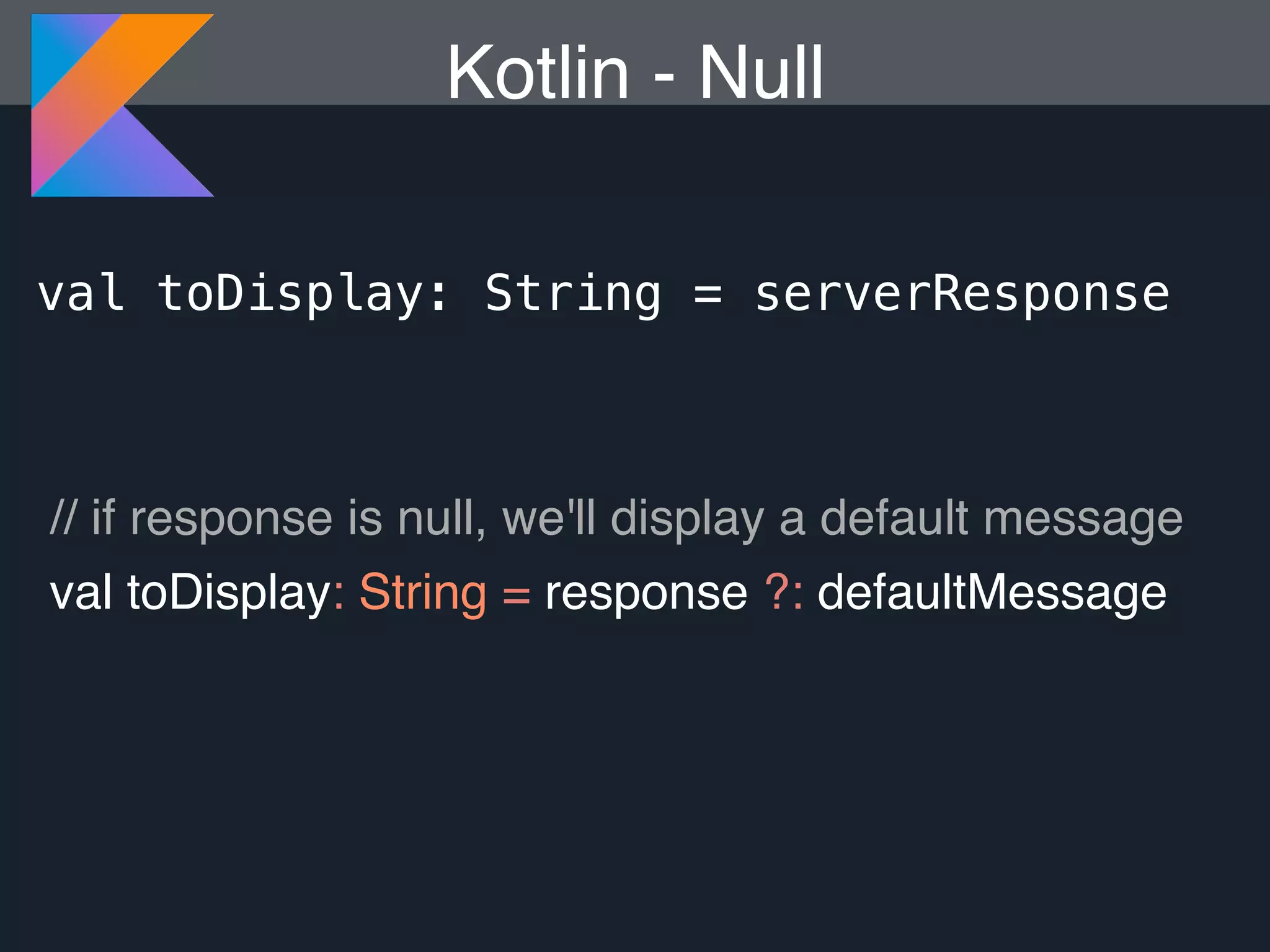
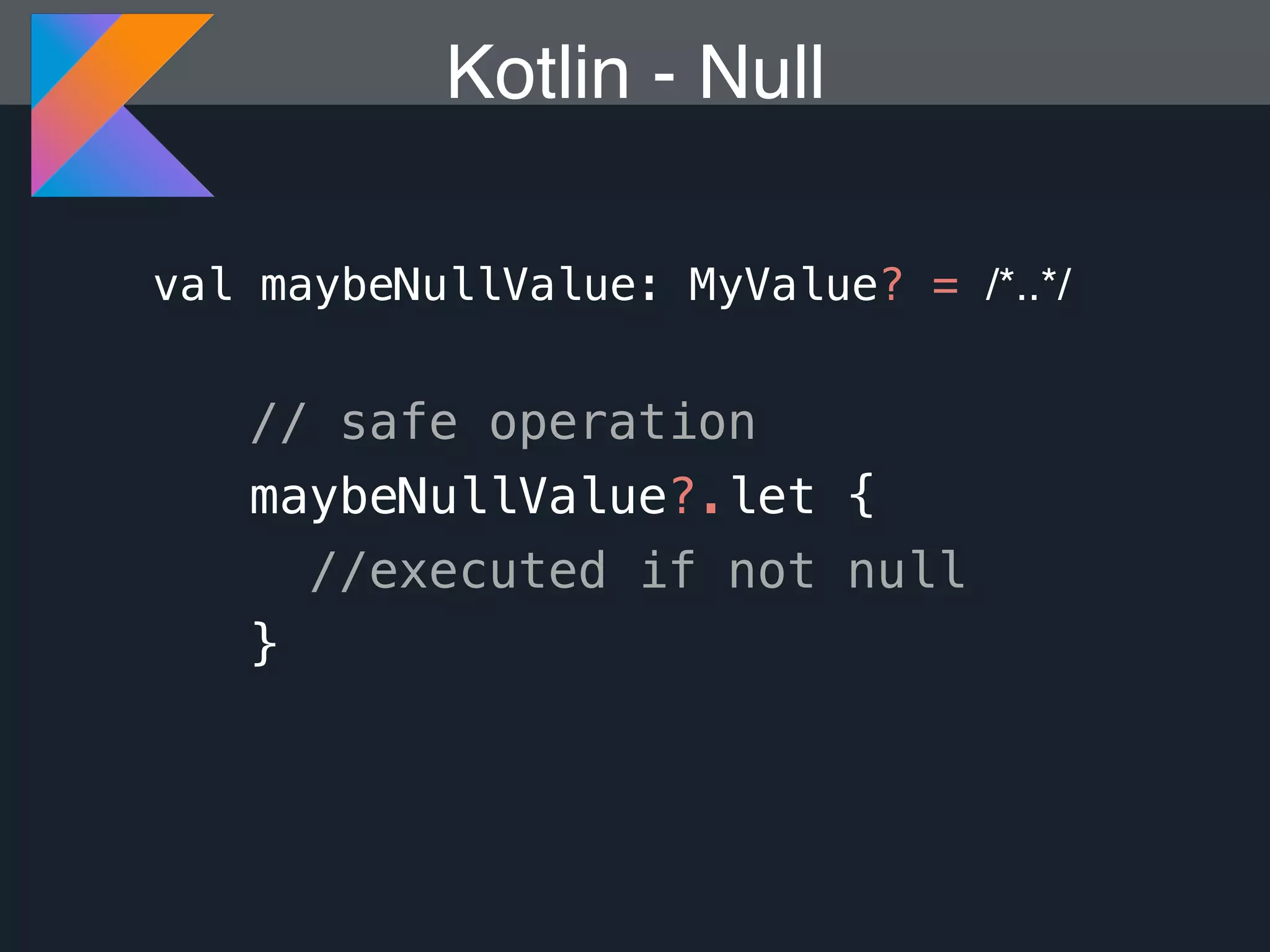
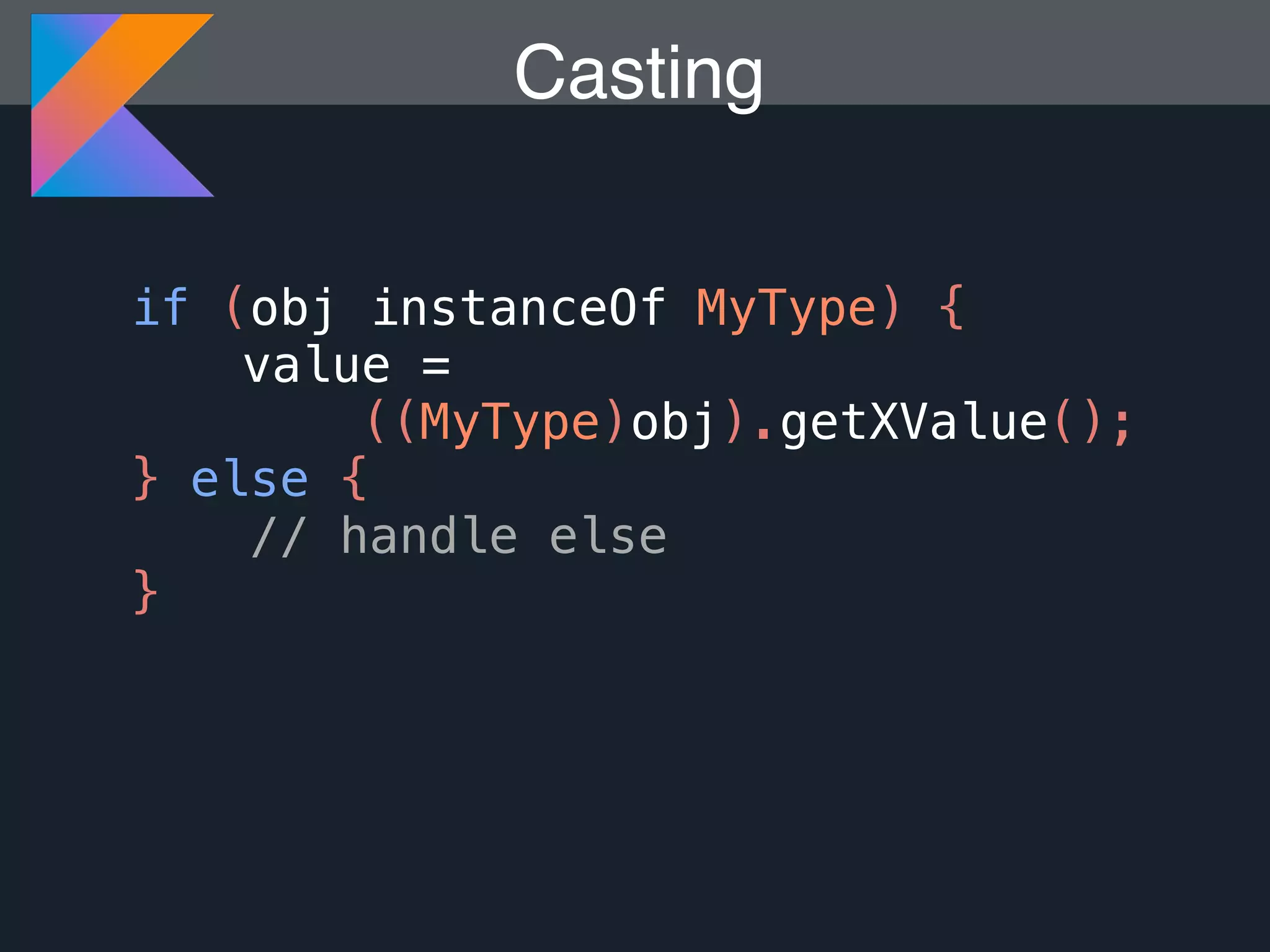
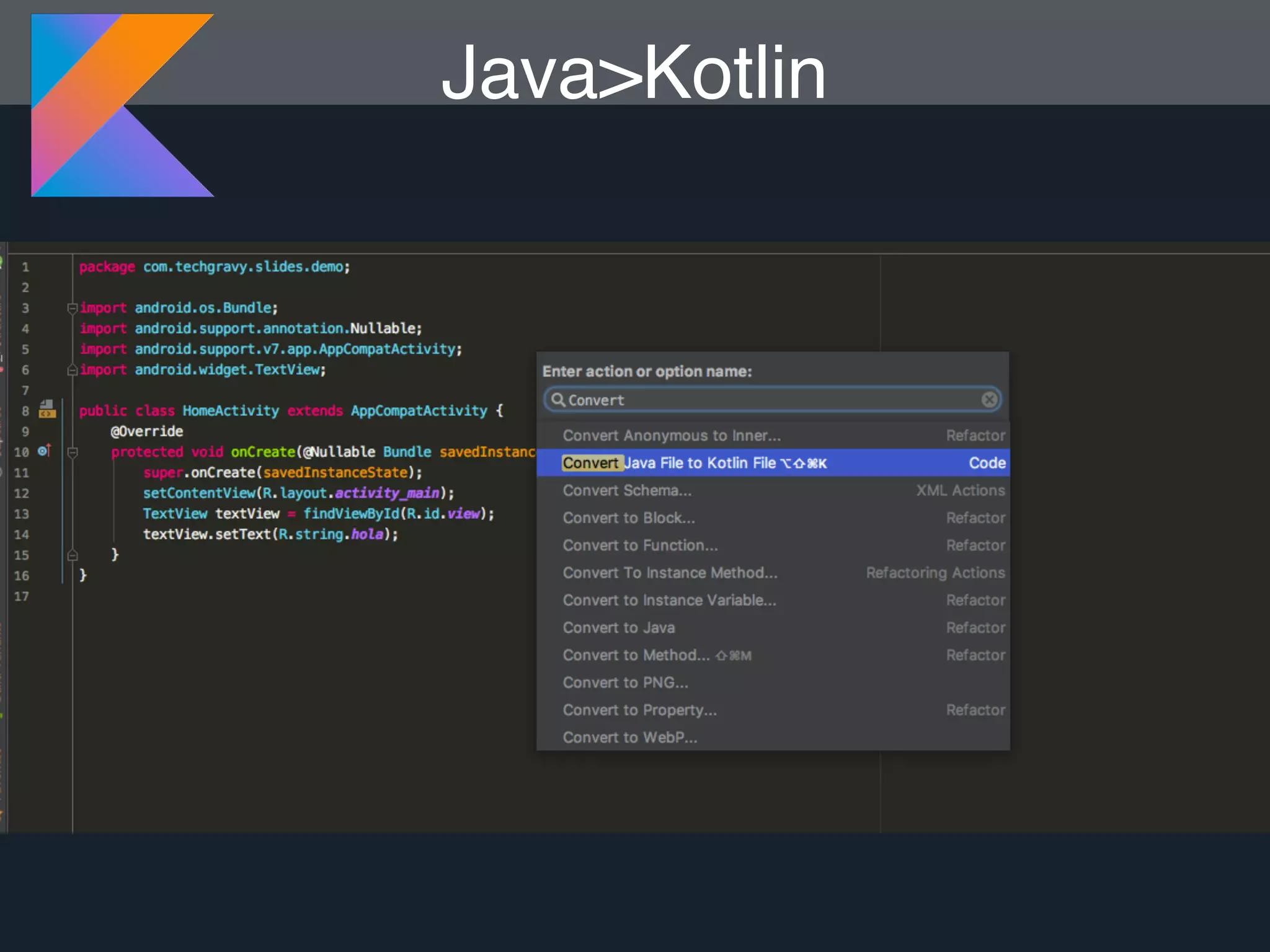
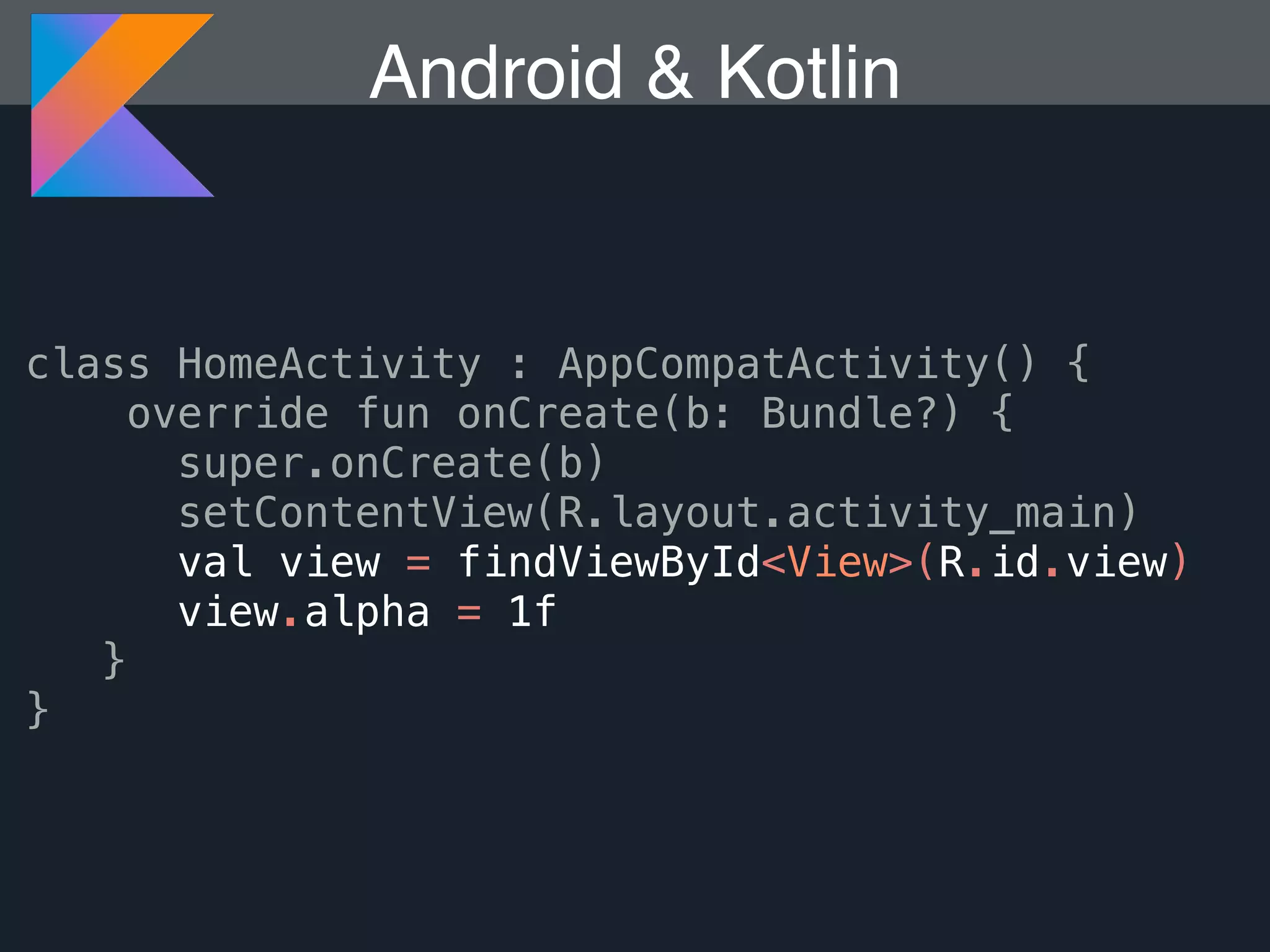
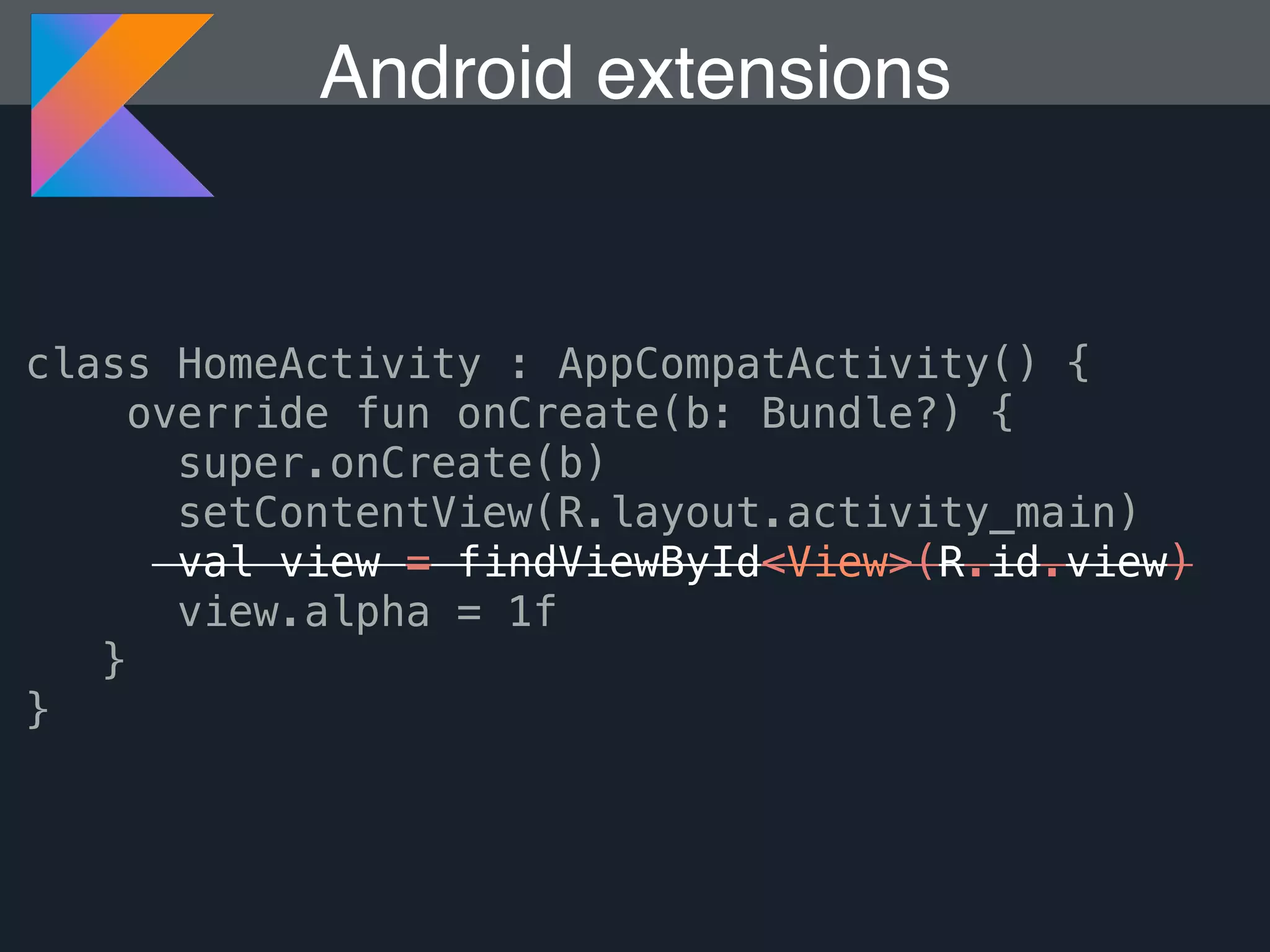
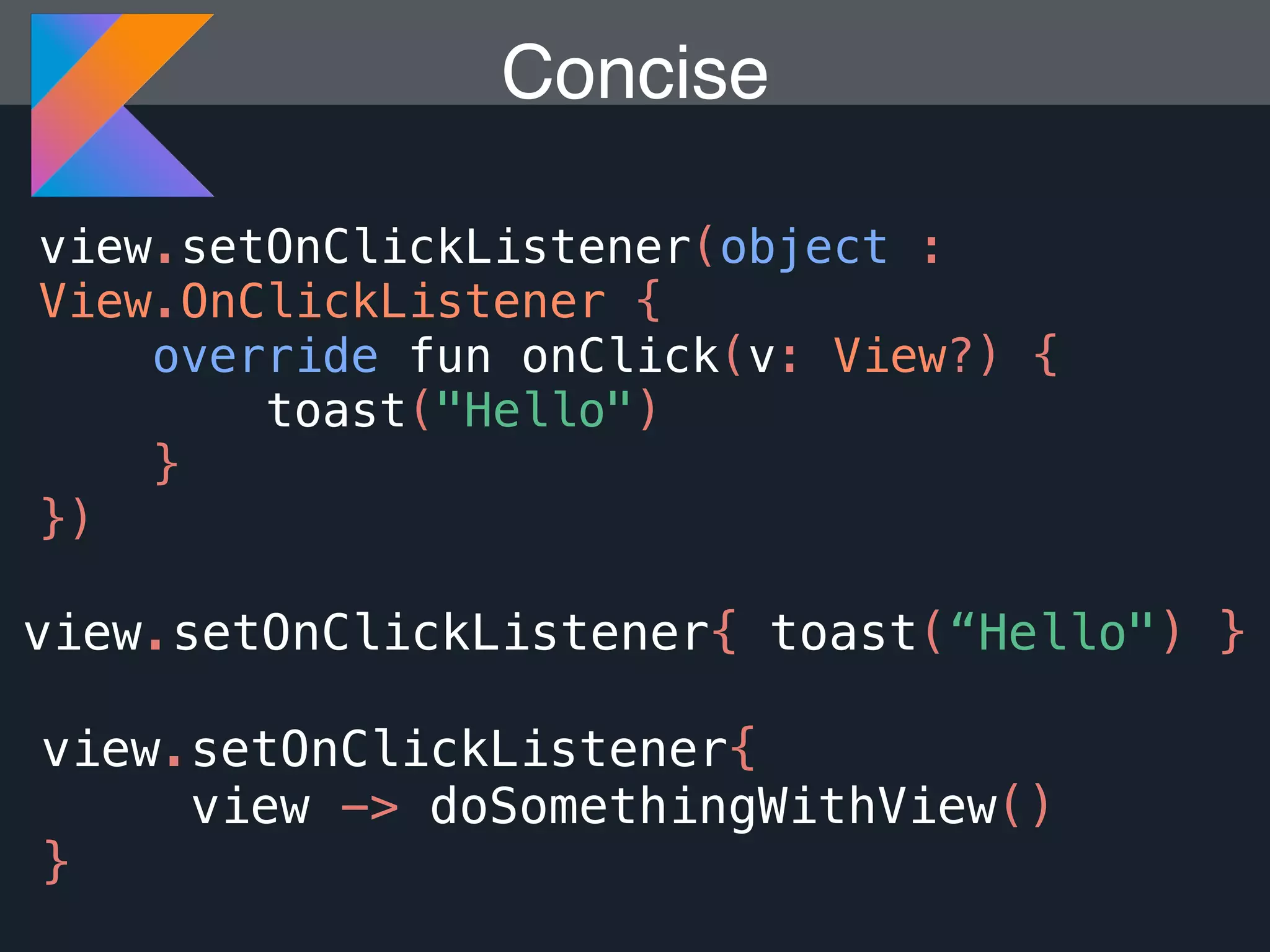
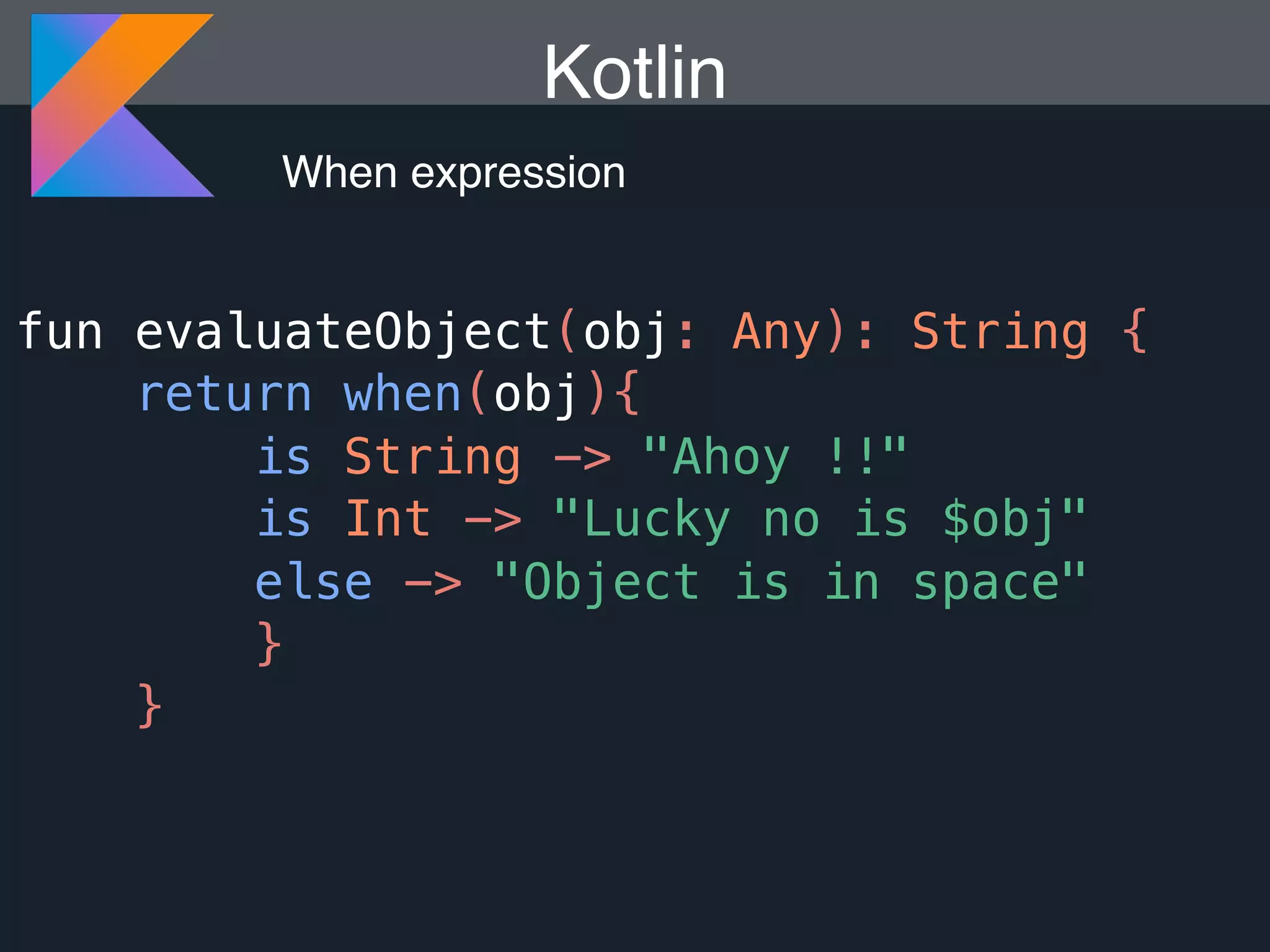
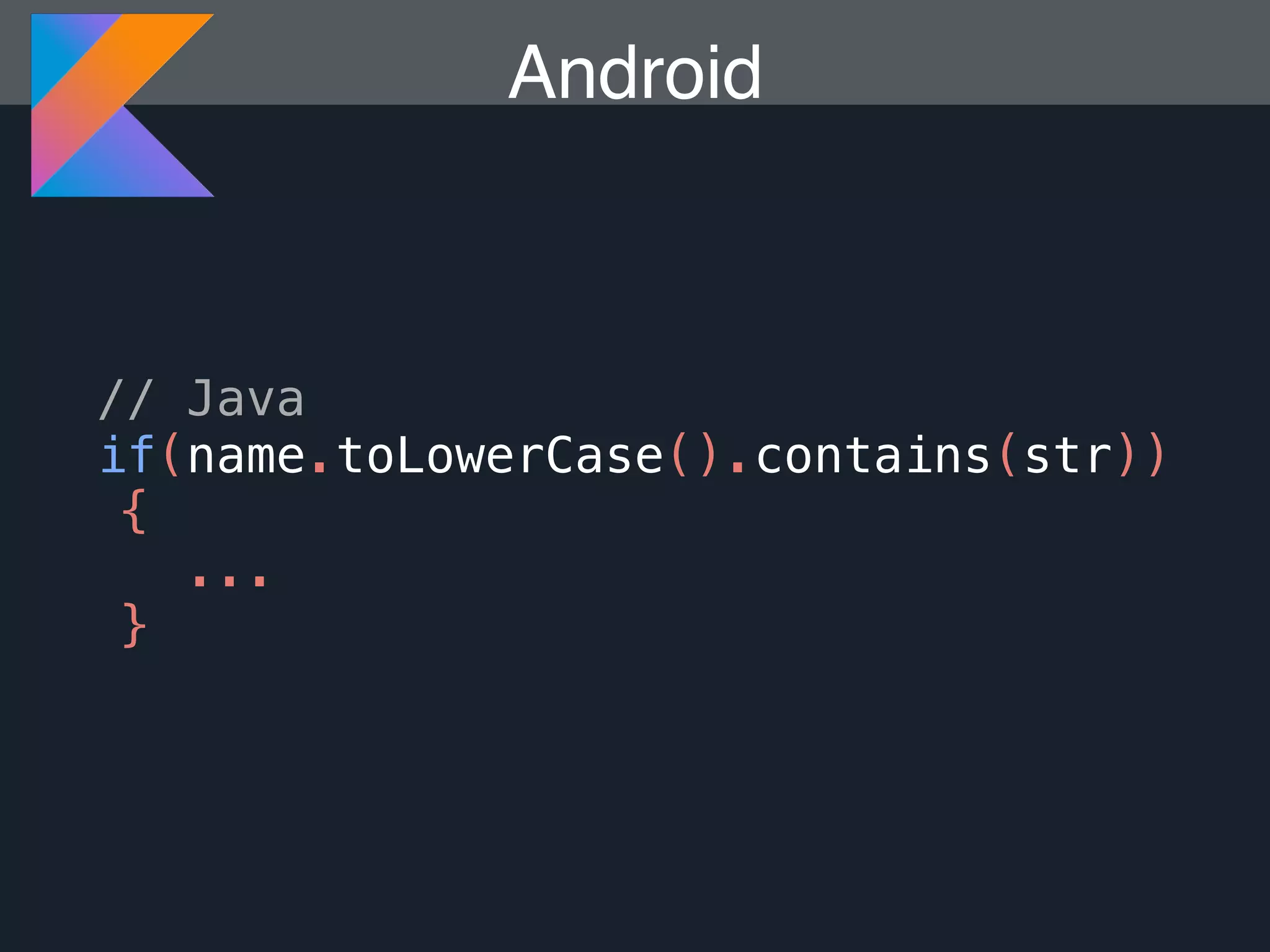
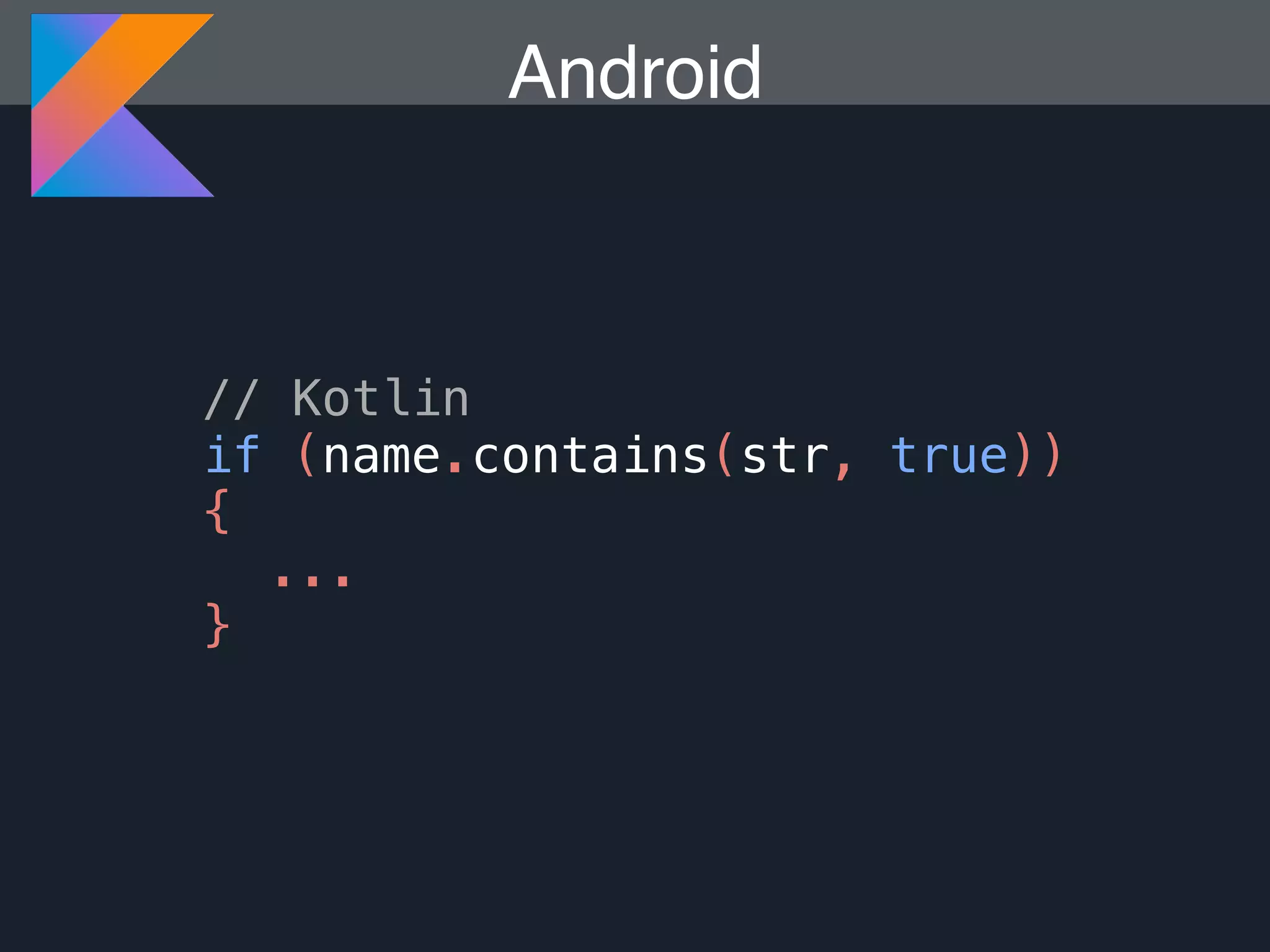
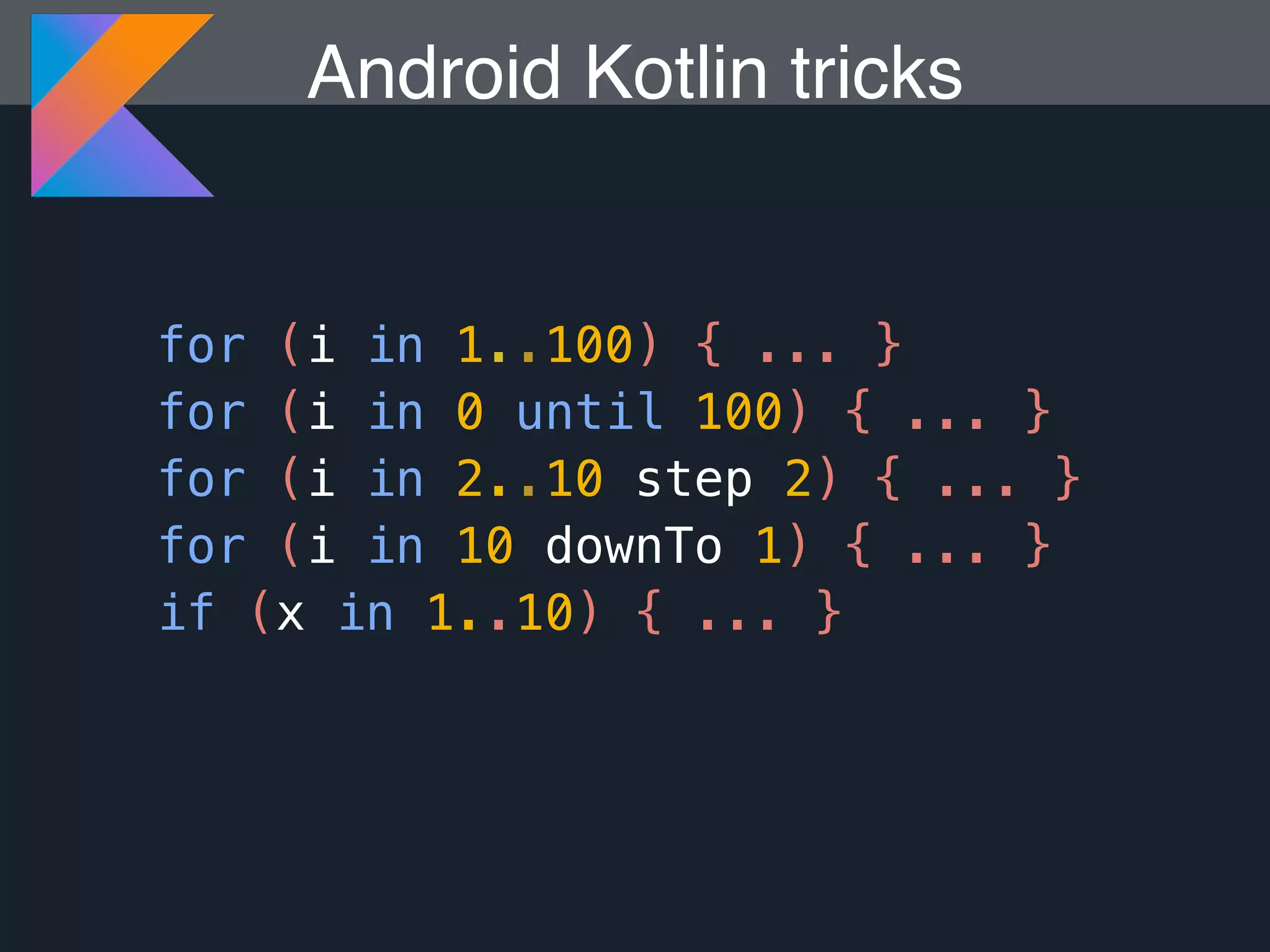
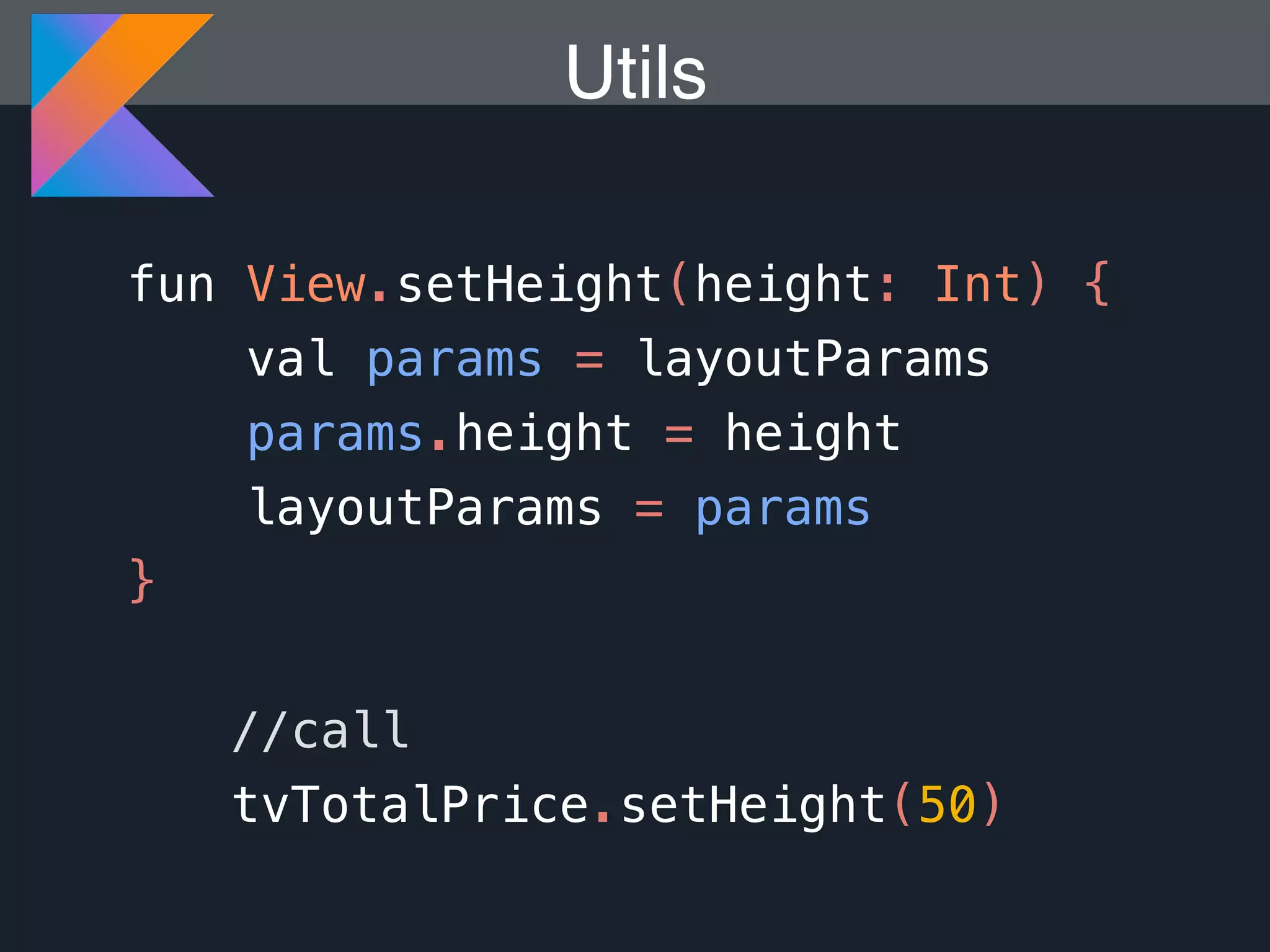
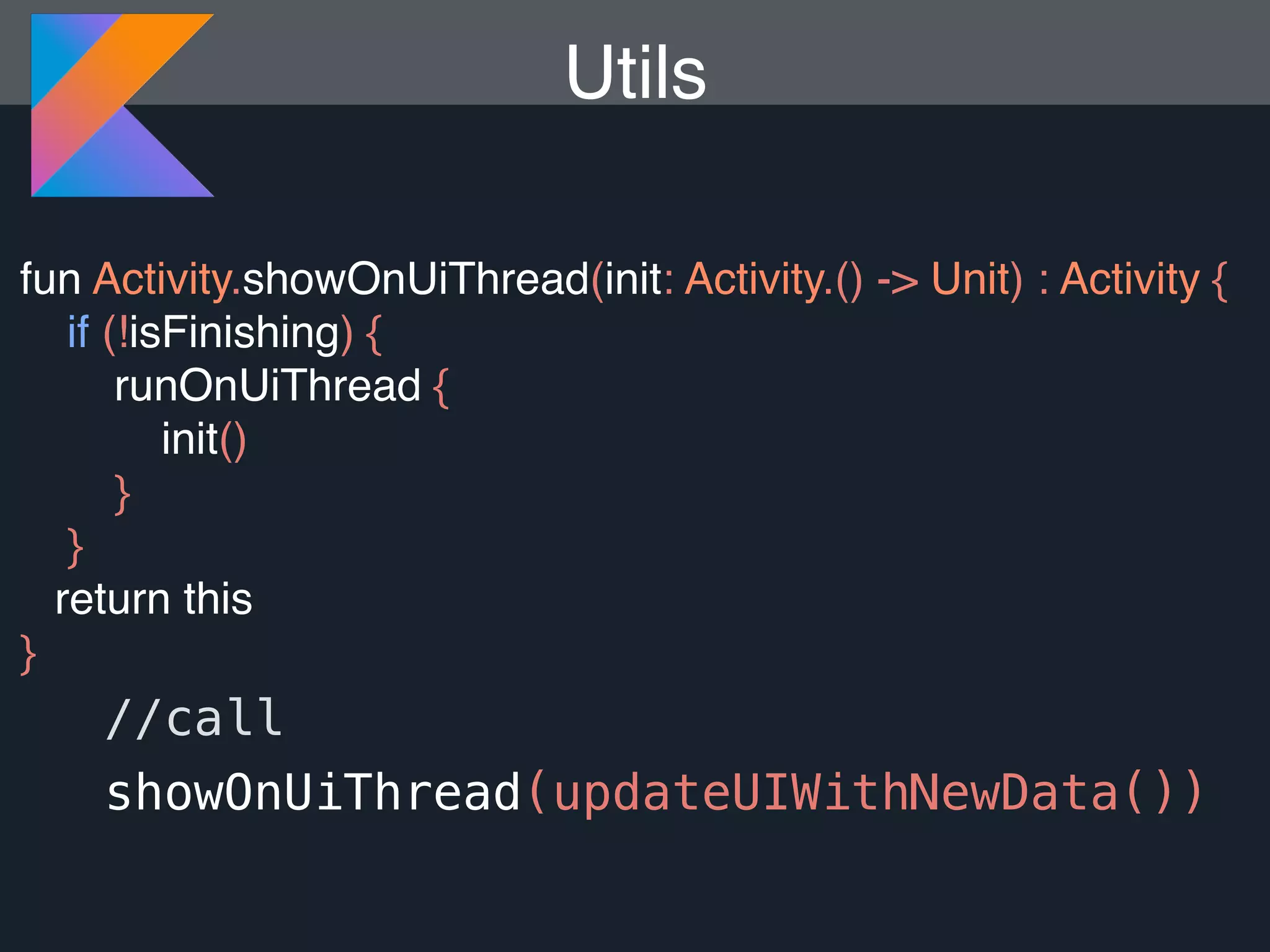
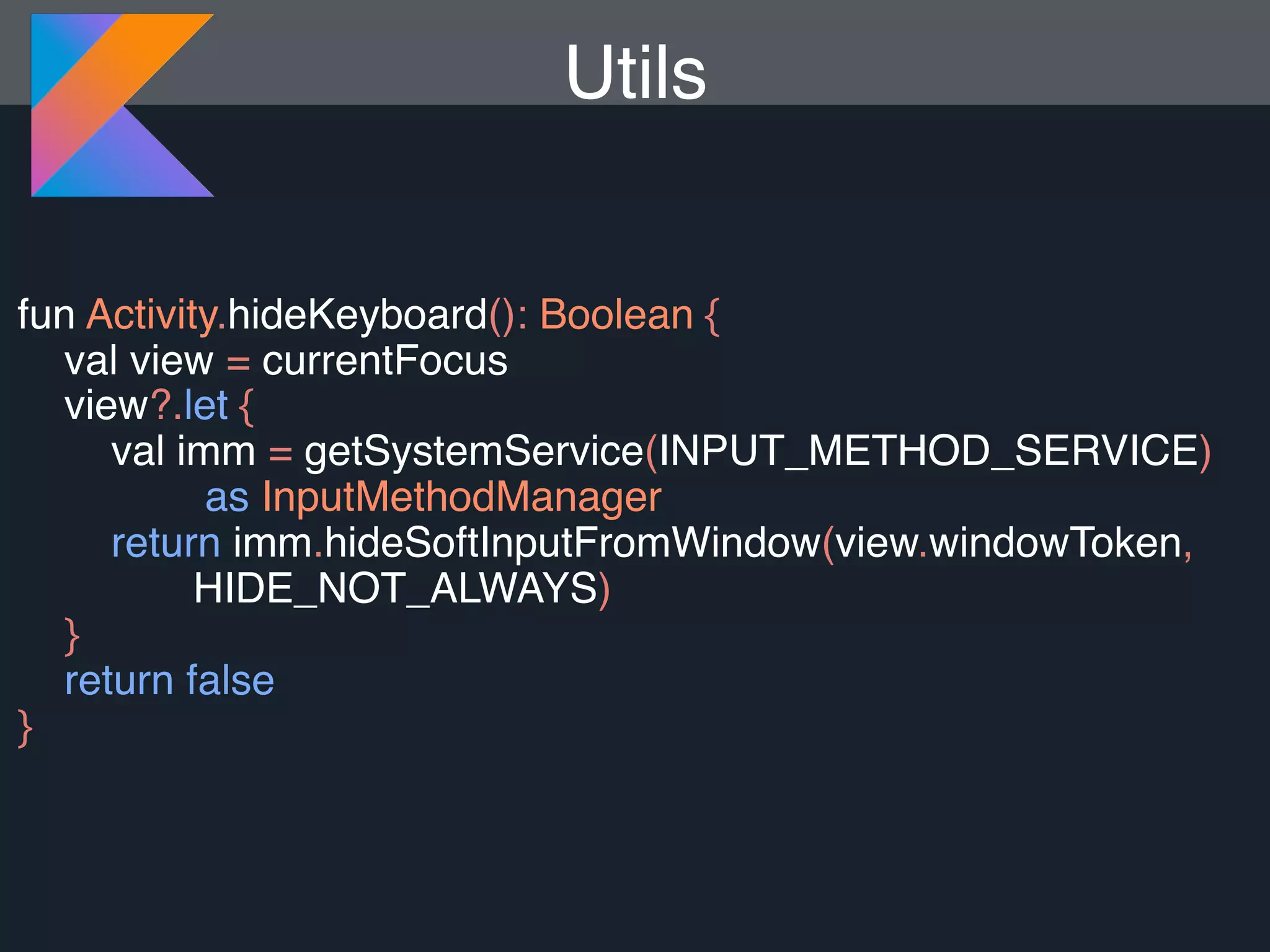
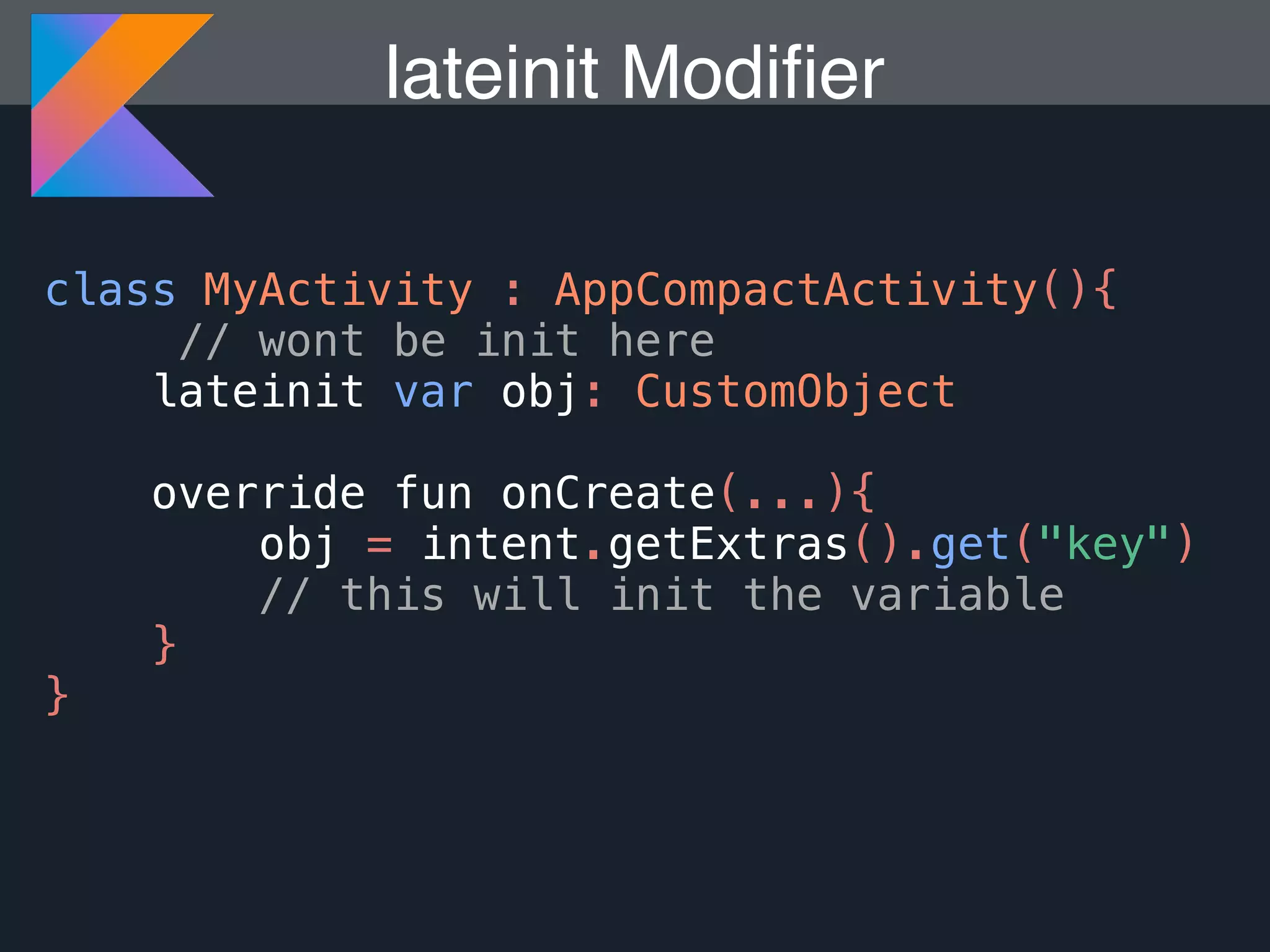
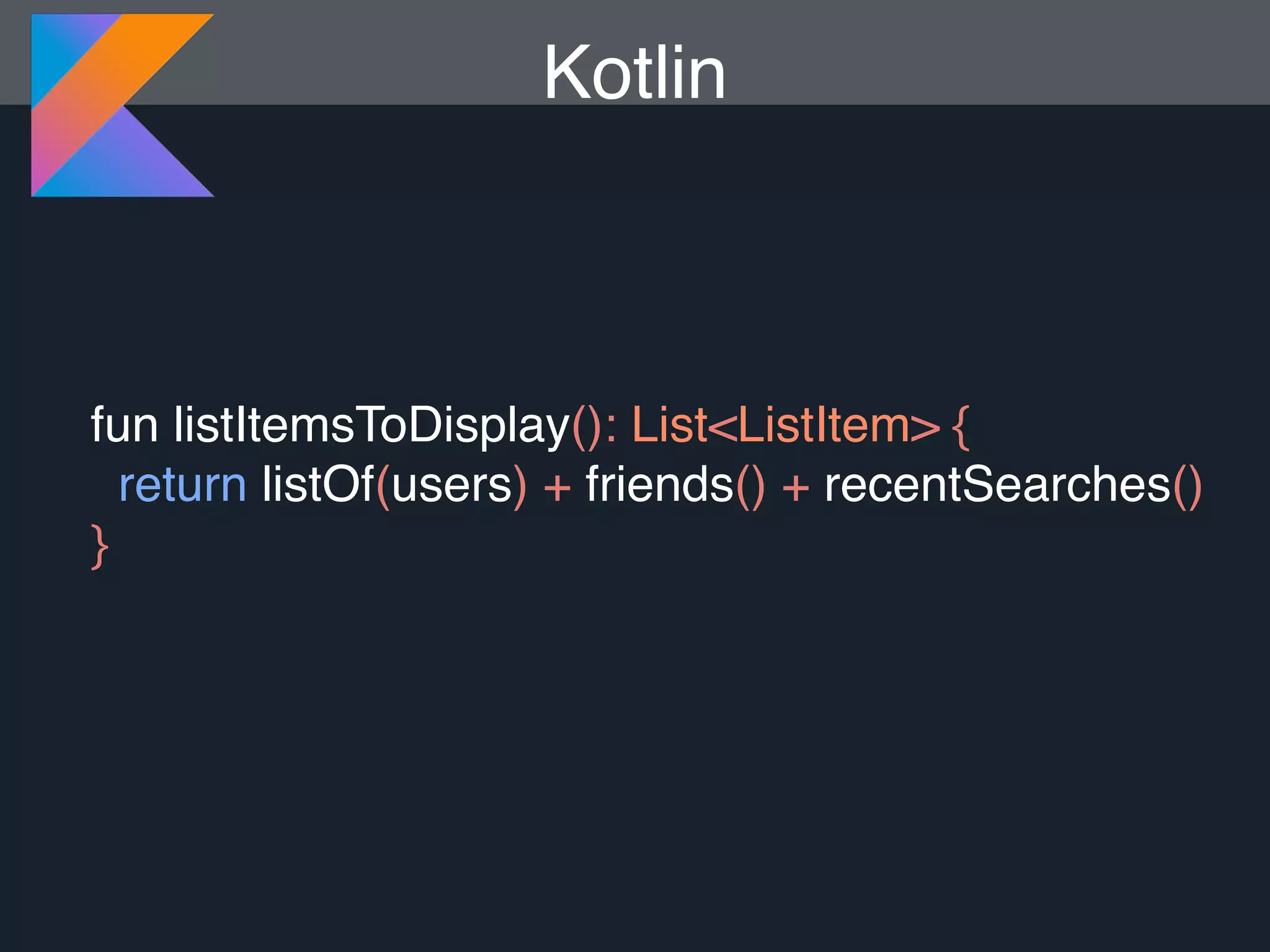
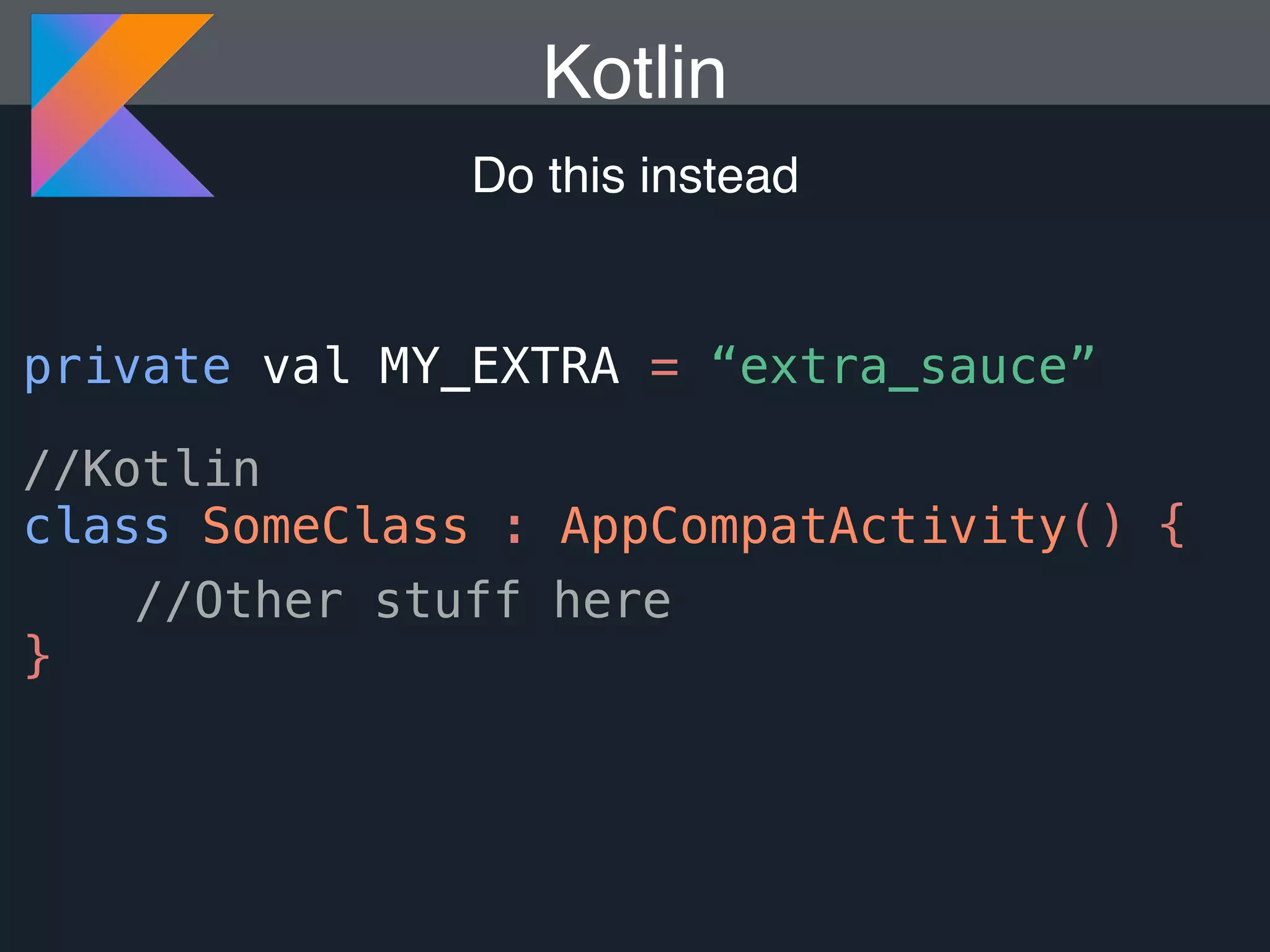
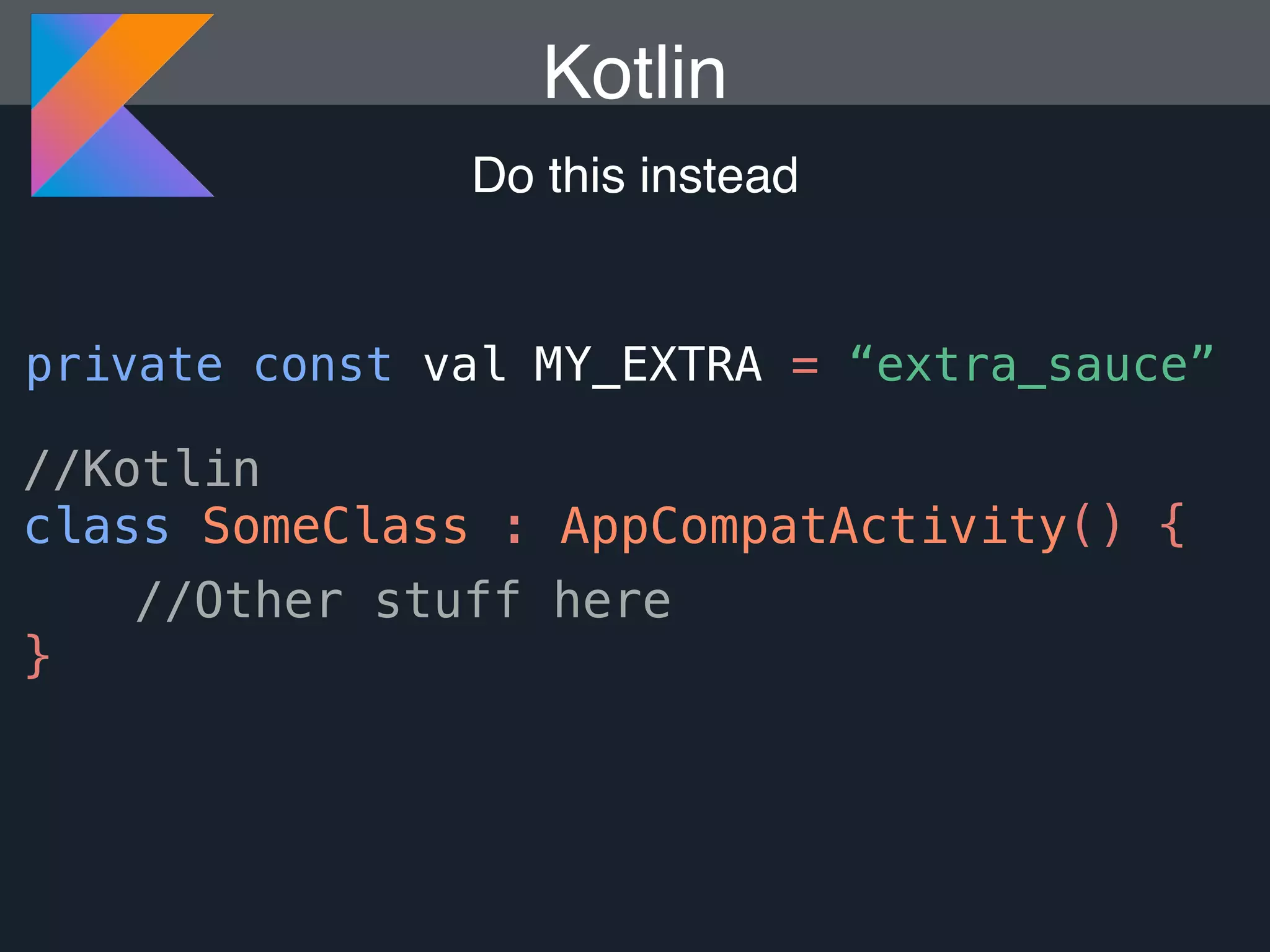
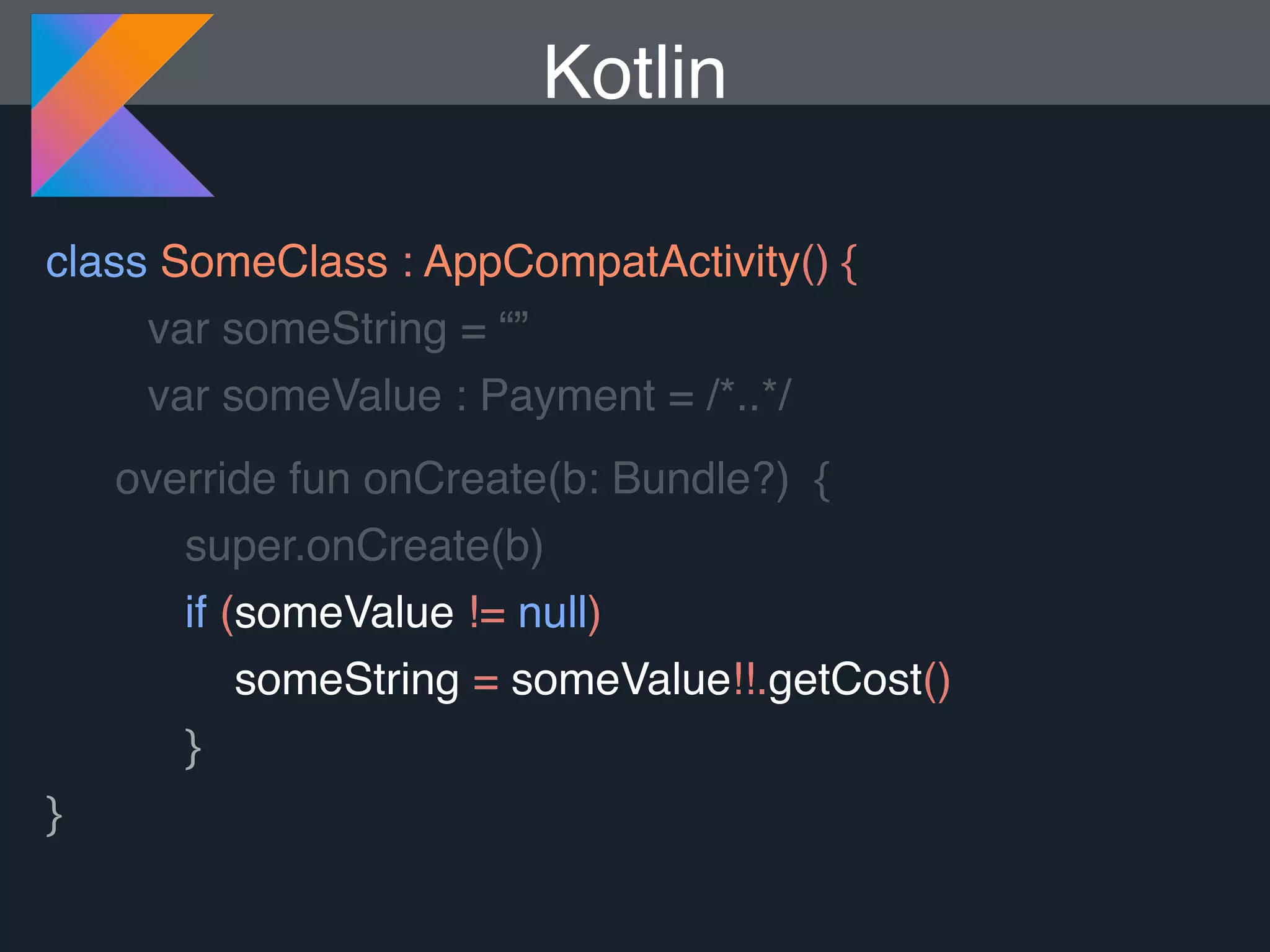
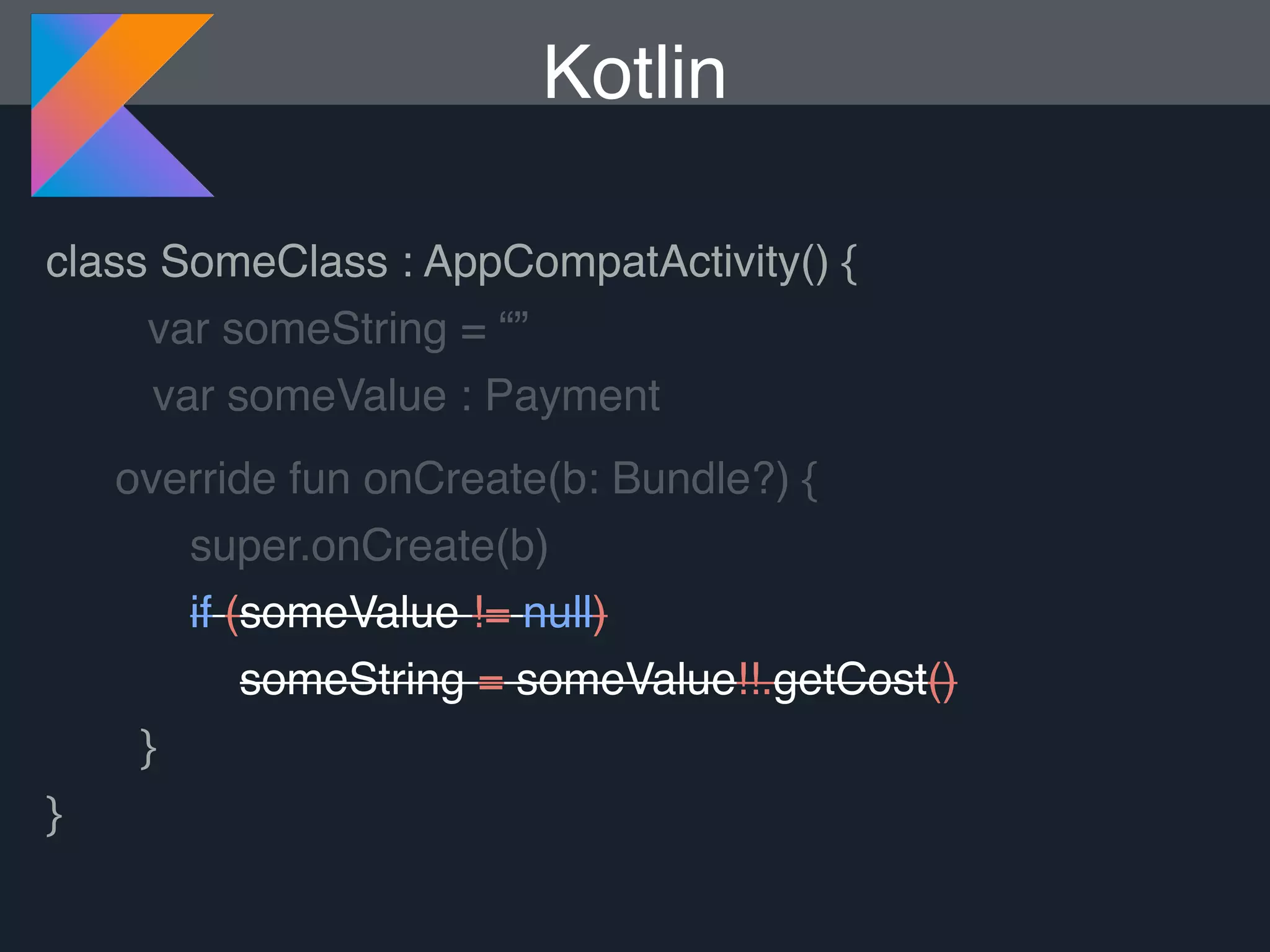
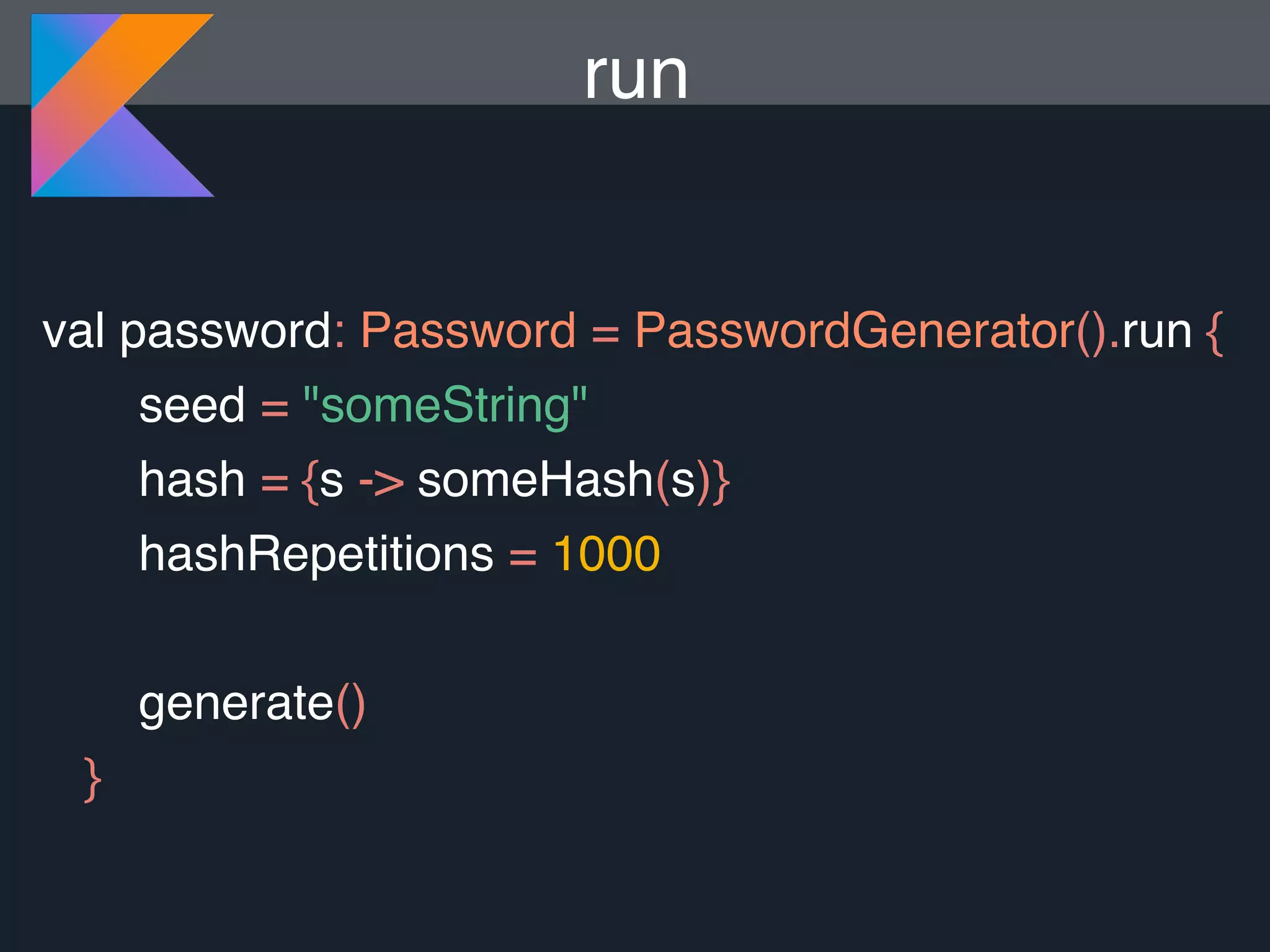
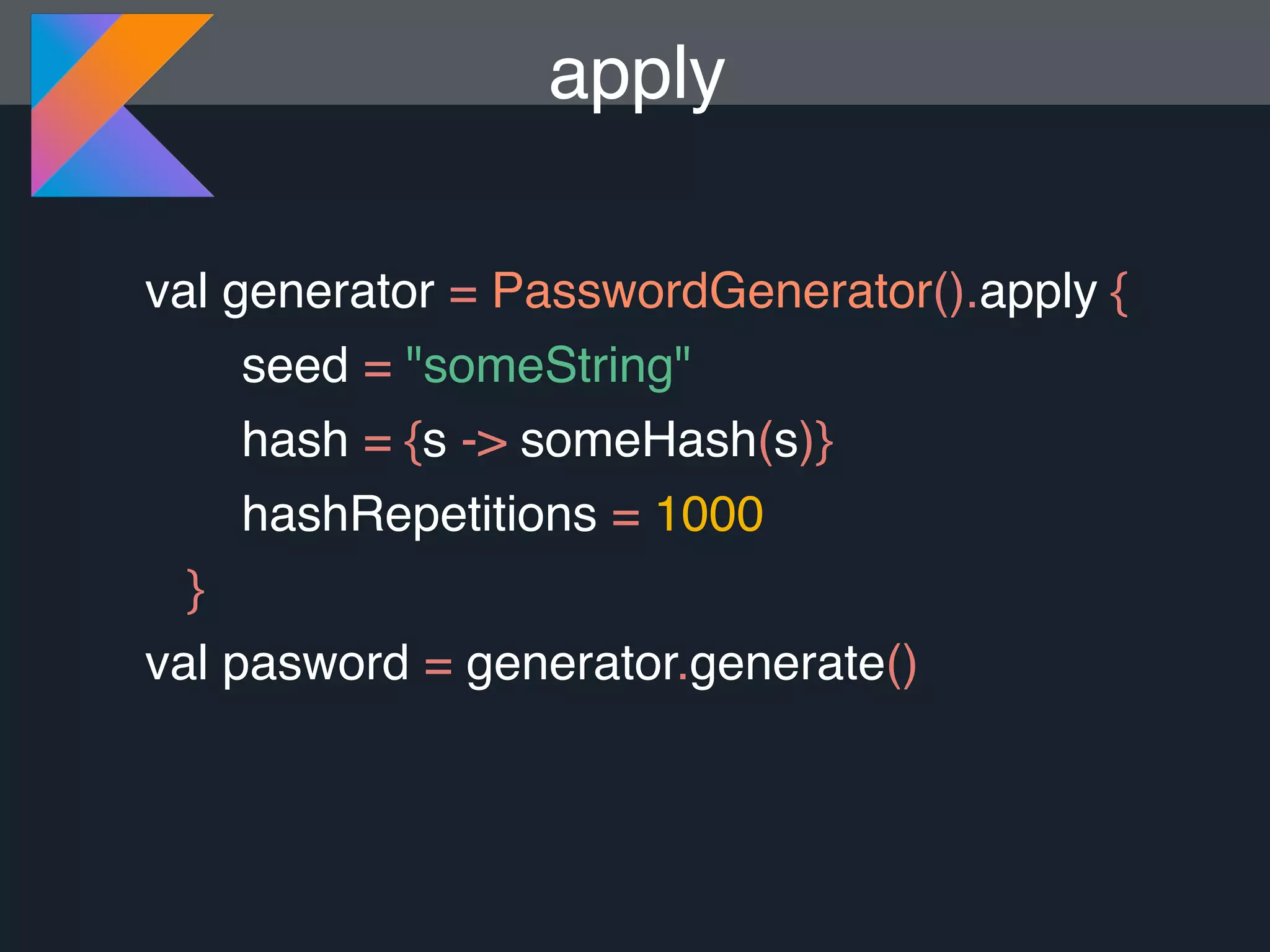
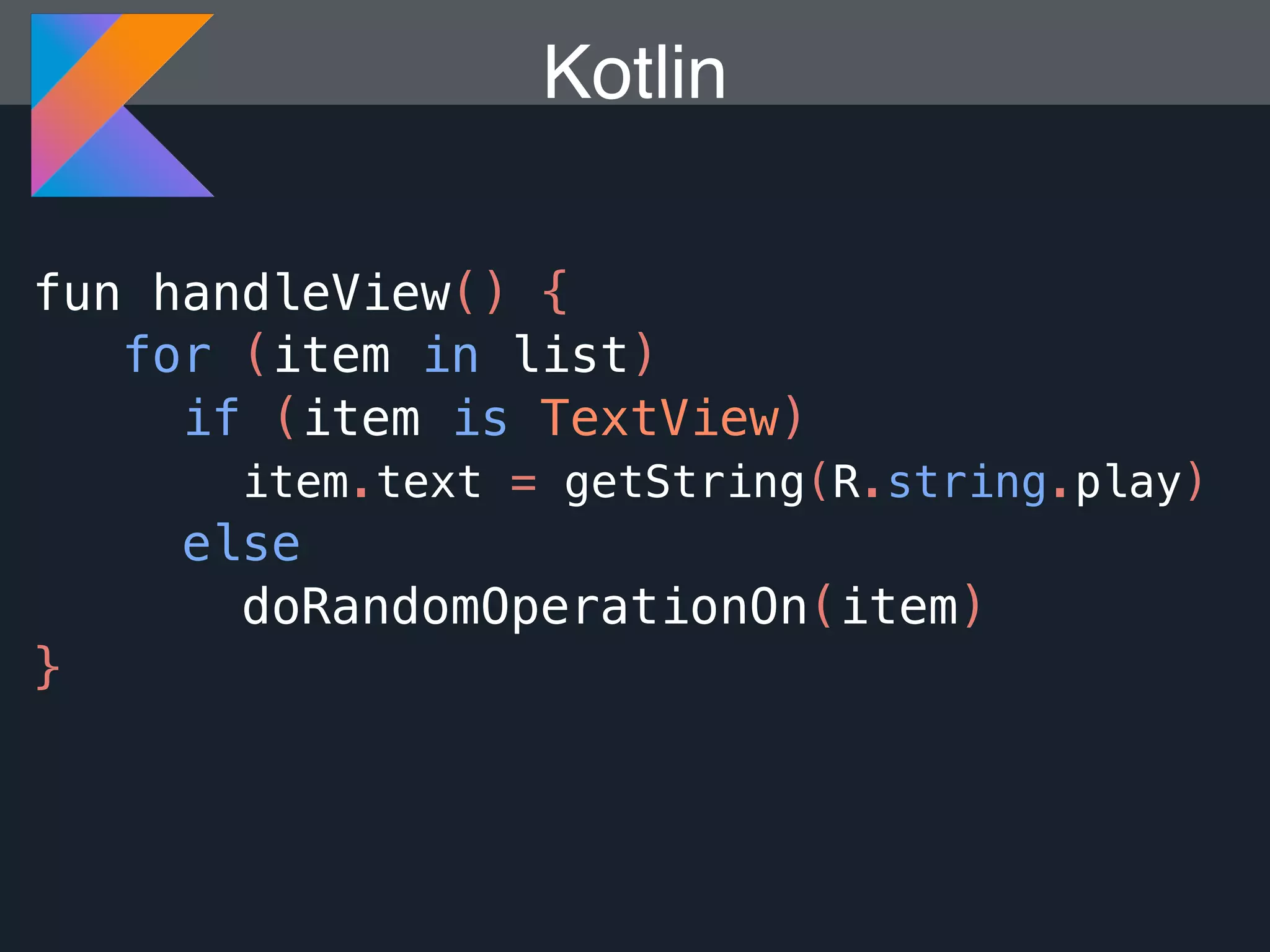
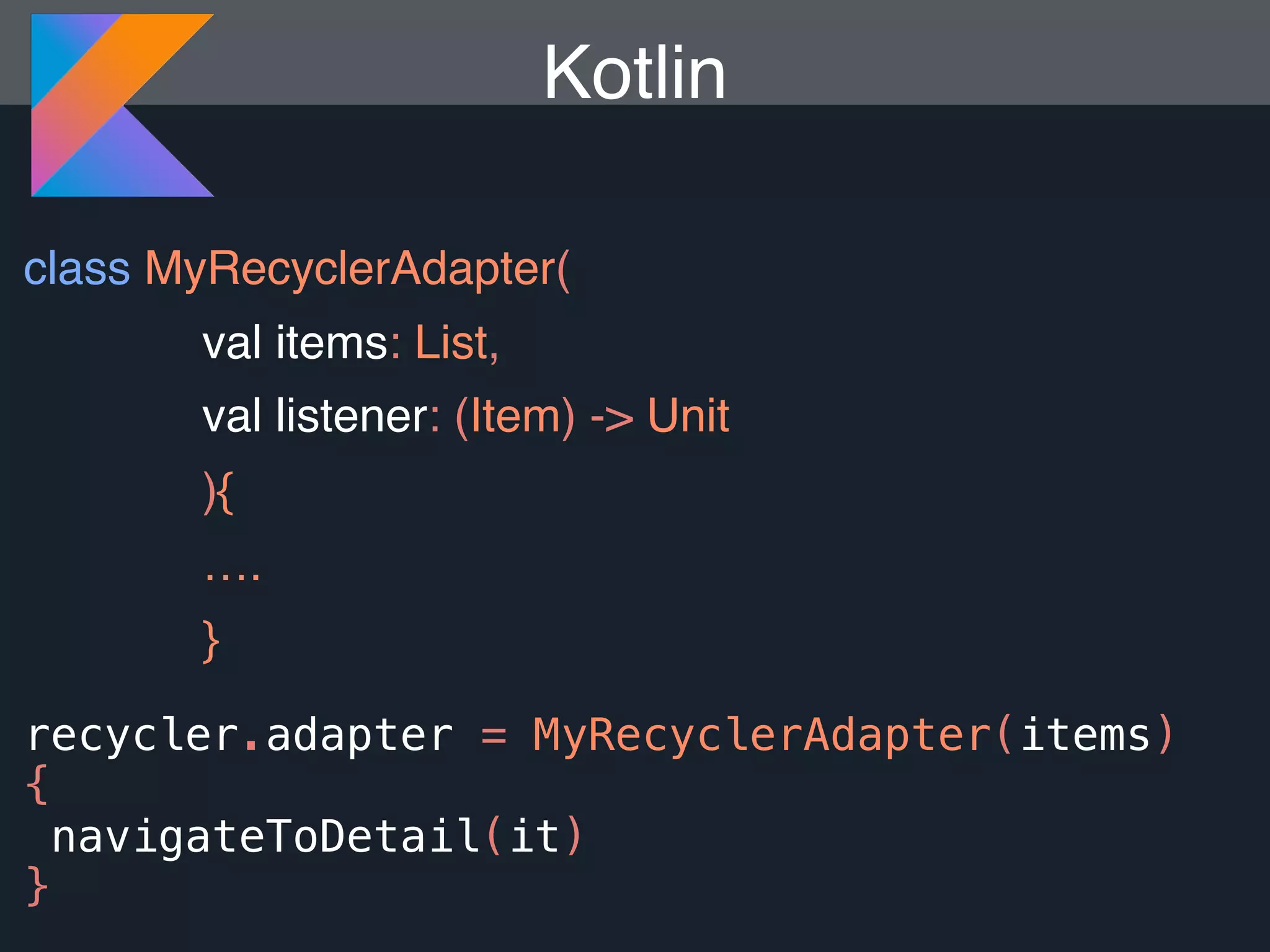
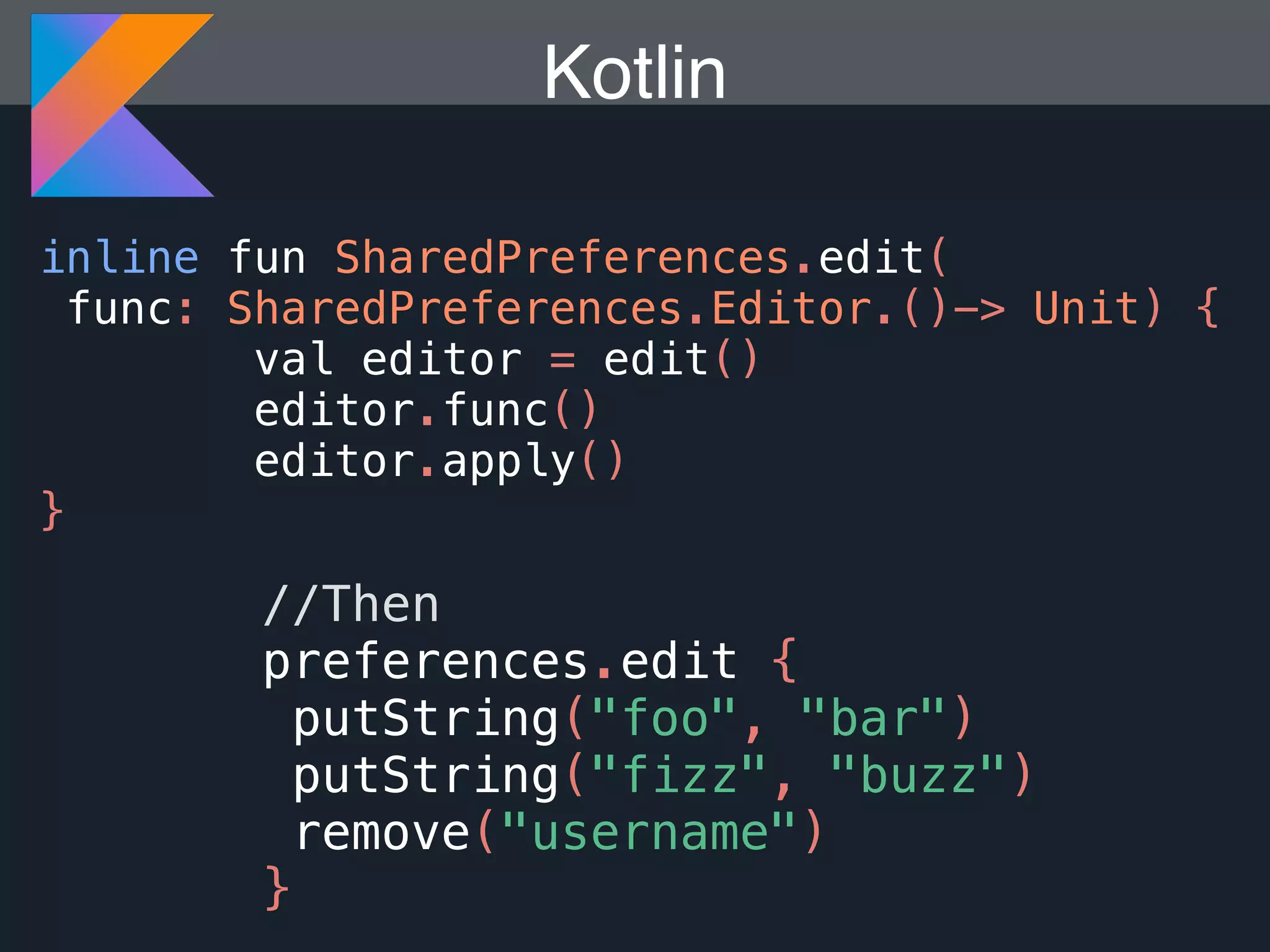
Kotlin is a statically typed programming language that is fully interoperable with Java and improves on Java in several ways such as null safety, concise syntax, and functional programming features. The document provides an overview of Kotlin and how it can help improve Android development by reducing code verbosity and allowing for more concise implementations of common patterns compared to Java. It also provides guidance on incrementally migrating existing Java/Android projects to Kotlin.