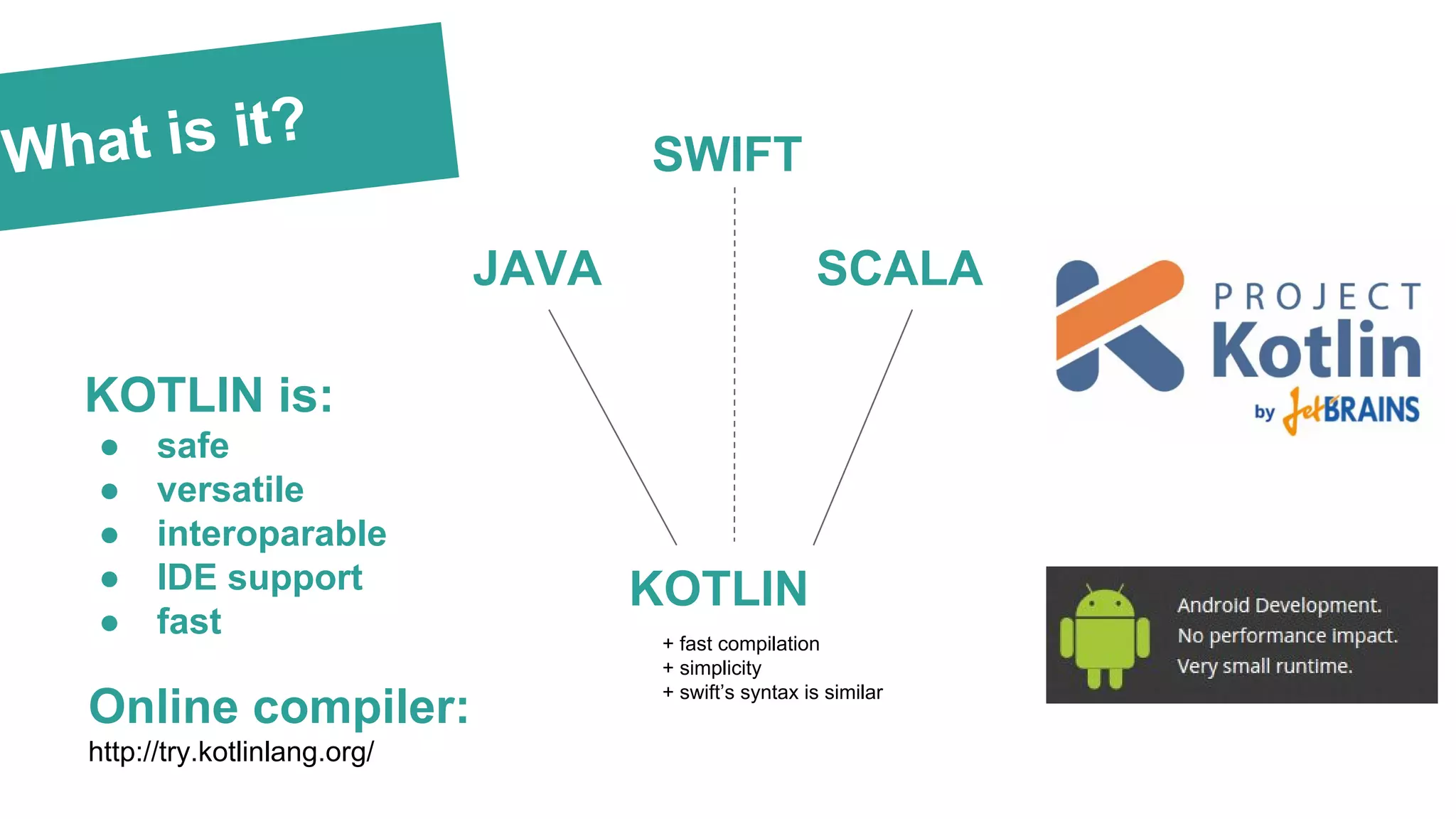
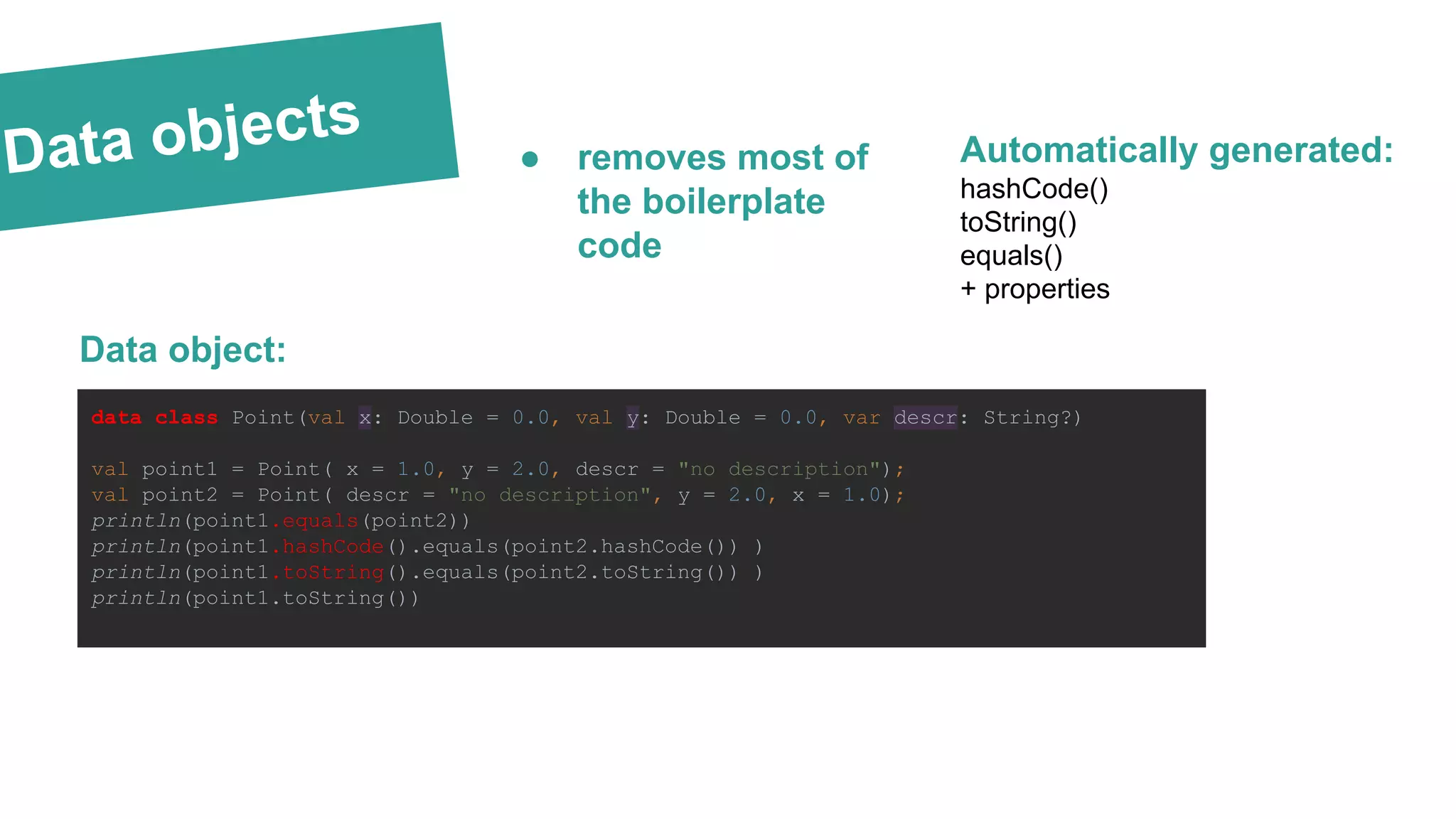
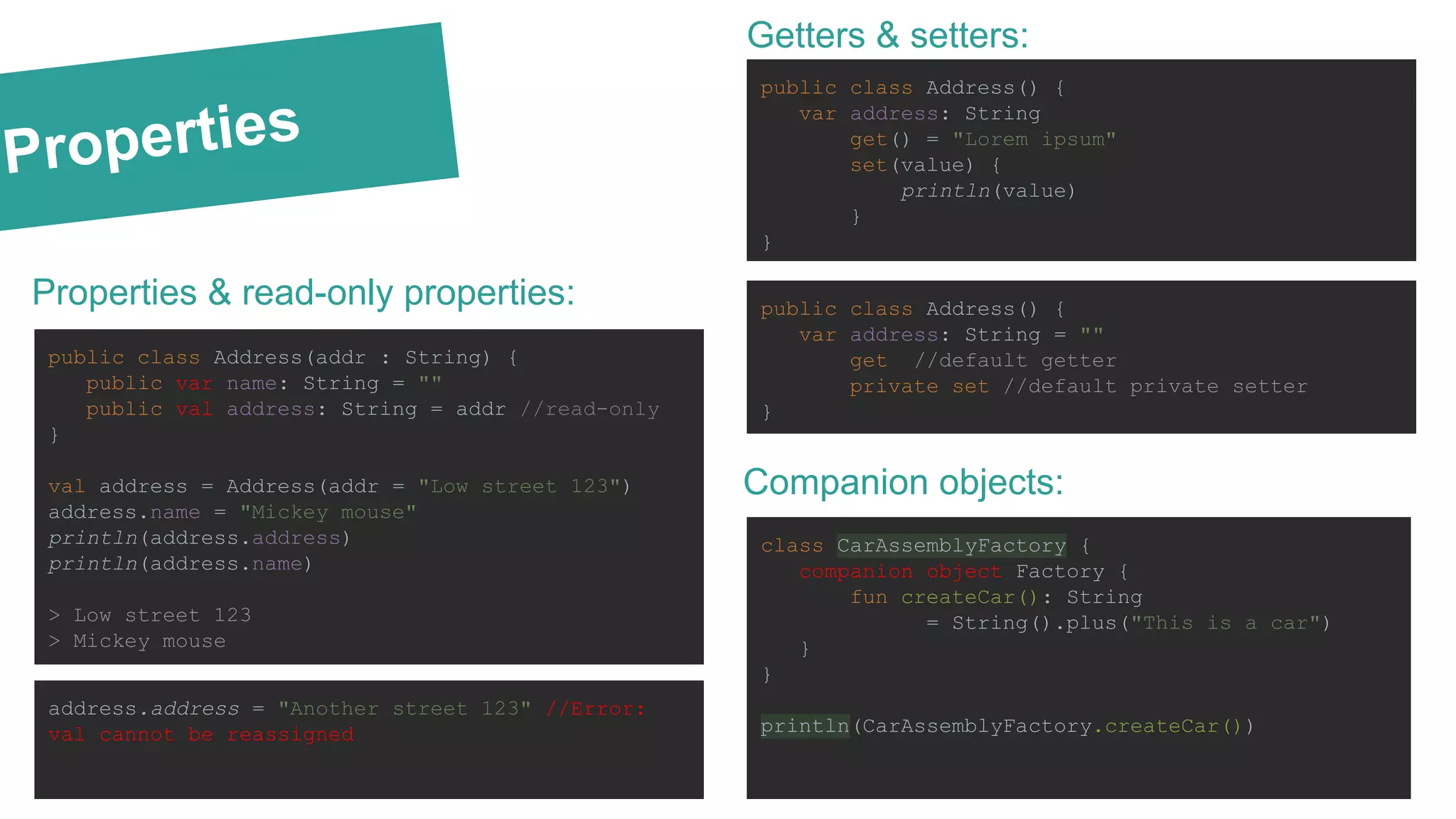
The document is an overview of Kotlin basics as it applies to Android development, covering required knowledge, language features, syntax comparisons with Java and Swift, and advantages such as null pointer safety and built-in lambdas. It includes practical examples, highlights the simplification of development through higher-order functions, and discusses Kotlin's interoperability with Java. The document also touches on the integration of Kotlin with Android tools and libraries, including Dagger 2 and Anko.















![Dagger 2 & KOTLIN @Module class AndroidModule(private val application: Application) { @Provides @Singleton fun provideLocationManager(): LocationManager { return application .getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE) as LocationManager } @Provides @Singleton @Named("something") fun provideSomething(): String { return "something" } } class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { @Inject lateinit var locationManager: LocationManager @field:[Inject Named("something")] lateinit var something: String override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) } } ● compatible with KOTLIN since M13 ● introduction of lateinit property Late-initialized property: e.g. for unit tests public class MyTest { lateinit var subject: TestSubject @SetUp fun setup() { subject = TestSubject() } @Test fun test() { subject.method() } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bkosarzyckikotlindeveloperstarterinandroidprojectslightningtalks-160212141725/75/Kotlin-Developer-Starter-in-Android-projects-20-2048.jpg)


![SWIFT var myVariable = 42 //Variable val explicitDouble: Double = 70.0 //Explicit Type Constant for (i in 1..5) { print(i) } //Inclusive Range Operator val a = "A"; val b = "B"; val str = "I have ${a + b} "; //String interpolation var shoppingList = arrayOf("catfish" , "water") //Array Creation var hashMap = hashMapOf("Malcolm" to "Captain" ); //Maps val emptyArray = arrayOf<String>() //Empty Typed Array interface Nameable { fun name(): String } //Interface val movie = obj as Movie //Downcasting fun Double.km() : Double = this * 1000; //Extension function KOTLIN SWIFT var myVariable = 42 //Variable let explicitDouble: Double = 70 //Explicit Type Constant for i in 1...5 { println( i) } //Inclusive Range Operator let a = "A"; let b = "B"; let str = "I have (a + b) " //String interpolation var shoppingList = [ "catfish" , "water"] //Array Creation var occupations = [ "Malcolm" : "Captain" ] //Maps let emptyArray = String[]() //Empty Typed Array protocol Nameable { func name() -> String } //Protocol (Interface) let movie = object as Movie //Downcasting extension Double { var km: Double { return self * 1_000.0 } } //Extension function ● Kotlin’s syntax is similar Swift](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bkosarzyckikotlindeveloperstarterinandroidprojectslightningtalks-160212141725/75/Kotlin-Developer-Starter-in-Android-projects-23-2048.jpg)

![Command line compiler Kotlin: class Capturing { fun run2(func: Runnable) { func.run() } } fun main(args: Array<String>) { Capturing().run2(Runnable { println("Hey! $args") }) } $ kotlinc Capturing.kt $ javap -p Compiled from "Capturing.kt" public final class Capturing { public final void run2(java.lang.Runnable); public Capturing(); } public final class CapturingKt { public static final void main(java.lang.String[]); } Java: ● Let us compare the resulting bytecode of kotlin and java compilation import java.util.Arrays; class Capturing { public static void main(final String... args) { run(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Hey! " + Arrays.toString(args)); } }); } private static void run(Runnable run) { run.run(); } } $ javac Capturing.java $ javap -p Capturing Compiled from "Capturing.java" class Capturing { Capturing(); public static void main(java.lang.String...); private static void run(java.lang.Runnable); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bkosarzyckikotlindeveloperstarterinandroidprojectslightningtalks-160212141725/75/Kotlin-Developer-Starter-in-Android-projects-25-2048.jpg)

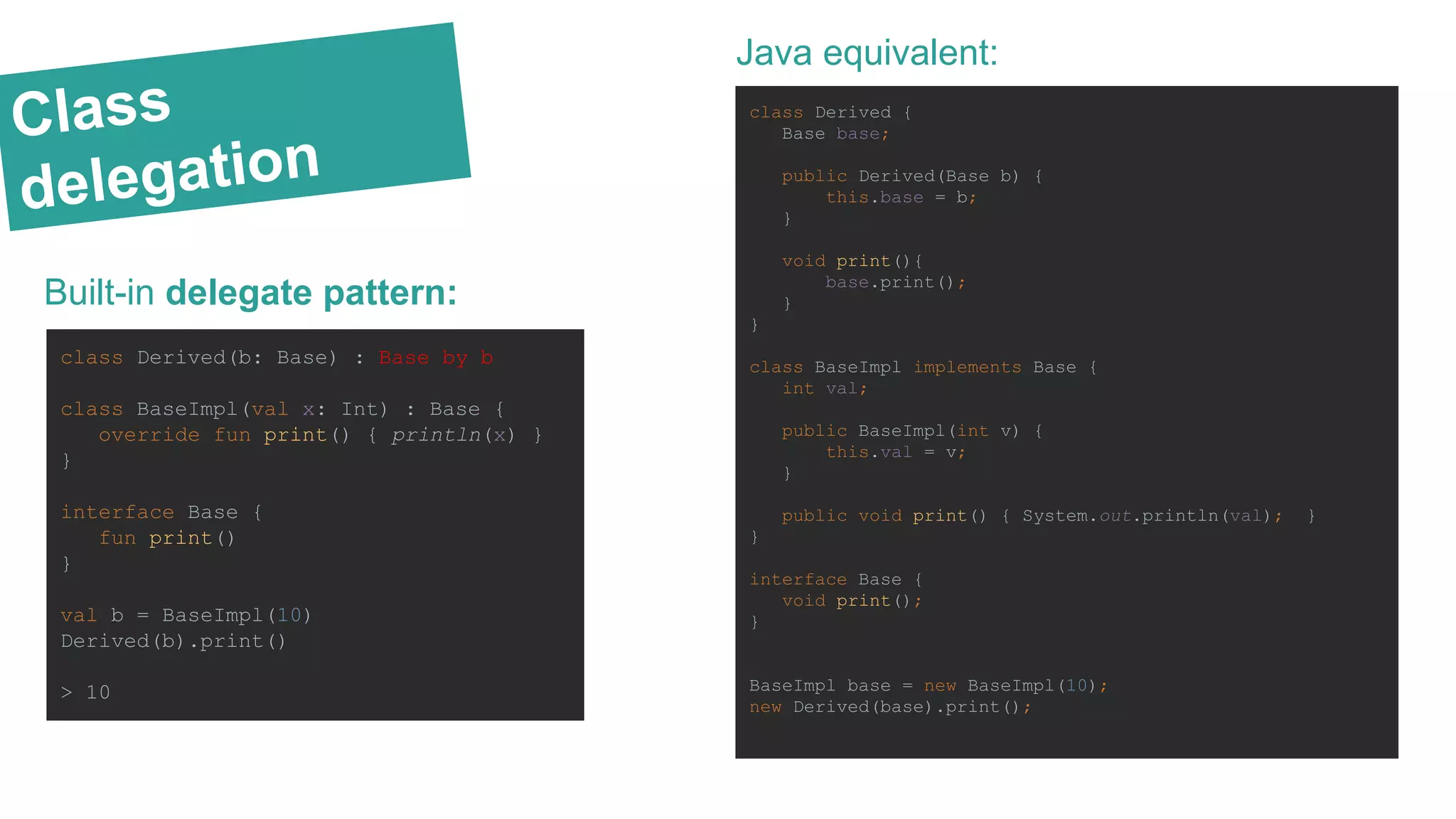
![Comparison KOTLIN WORSE THAN SCALA: BETTER THAN SCALA: ● no static members (BY DESIGN) - if you need something that is not attached to an instance of any class, you define it in a package ● no checked exceptions (BY DESIGN) no functions like: void copy(CharSequence csq) throws IOException ● primitive types that are not classes ● non-private fields (i.e. java’s public int field; ) - by design - in kotlin one should use properties instead of public fields IN JAVA NOT IN KOTLIN: ● Overridable type members ● Path-dependent types ● Macros ● Existential types ● Complicated logic for initialization of traits ● Custom symbolic operations ● Built-in XML ● Parallel collections ● Structural types ● Value types ● Yield operator ● Actors ● smart-casts ● first-class delegation (built-in delegate pattern) ● no overhead in extension functions (compared to implicit class in Scala [link]) ● no overhead in null-safety](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bkosarzyckikotlindeveloperstarterinandroidprojectslightningtalks-160212141725/75/Kotlin-Developer-Starter-in-Android-projects-27-2048.jpg)