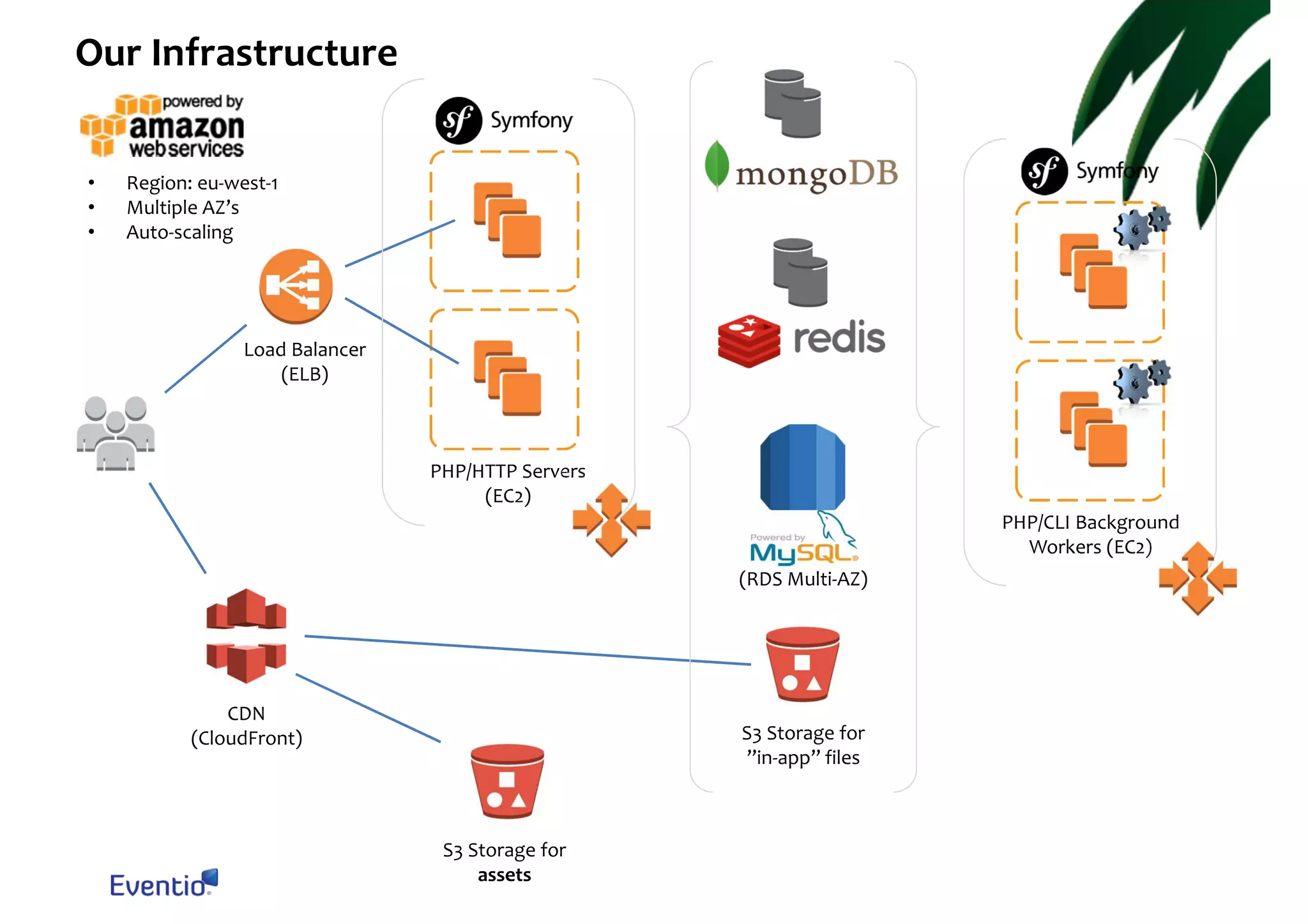
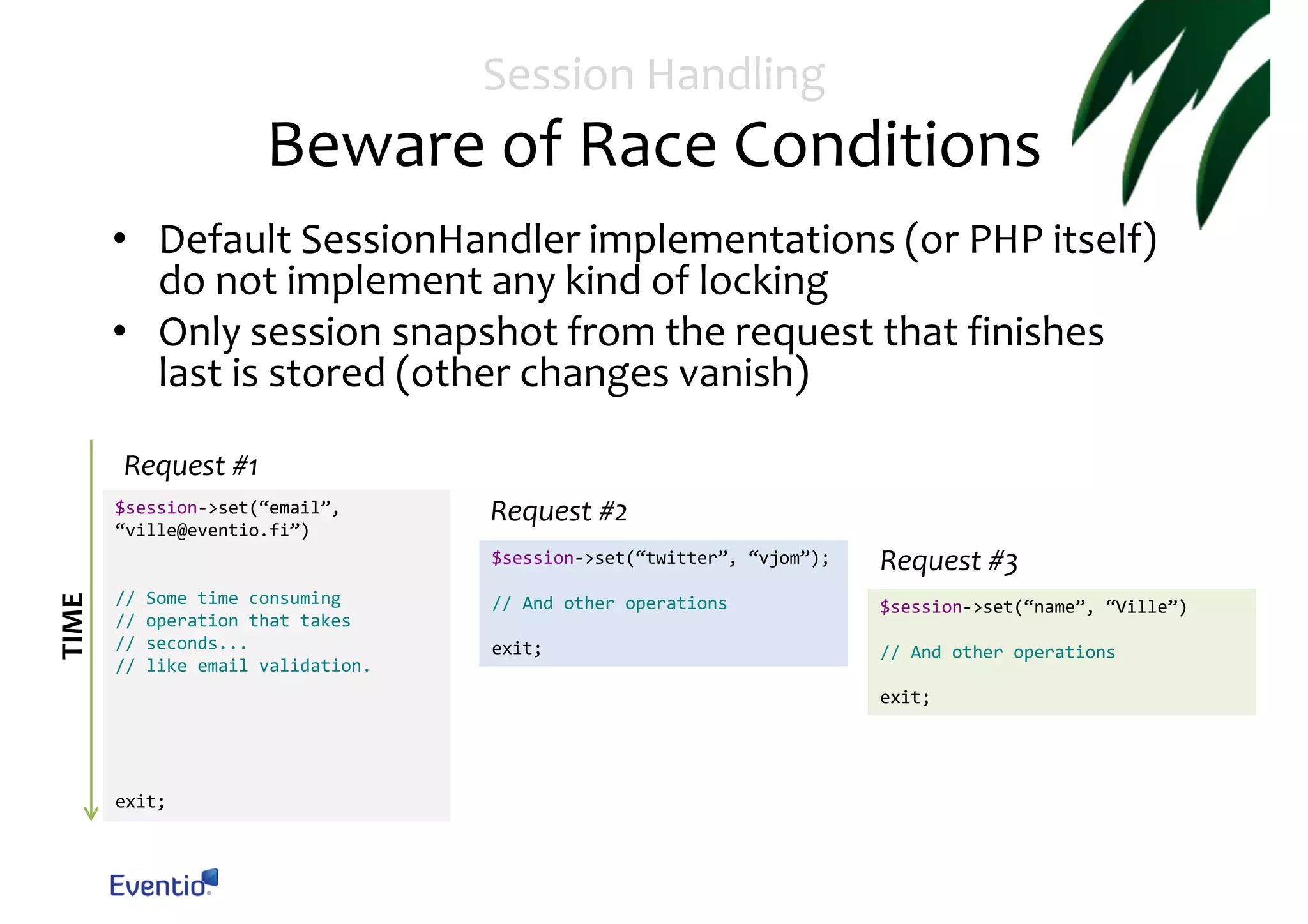
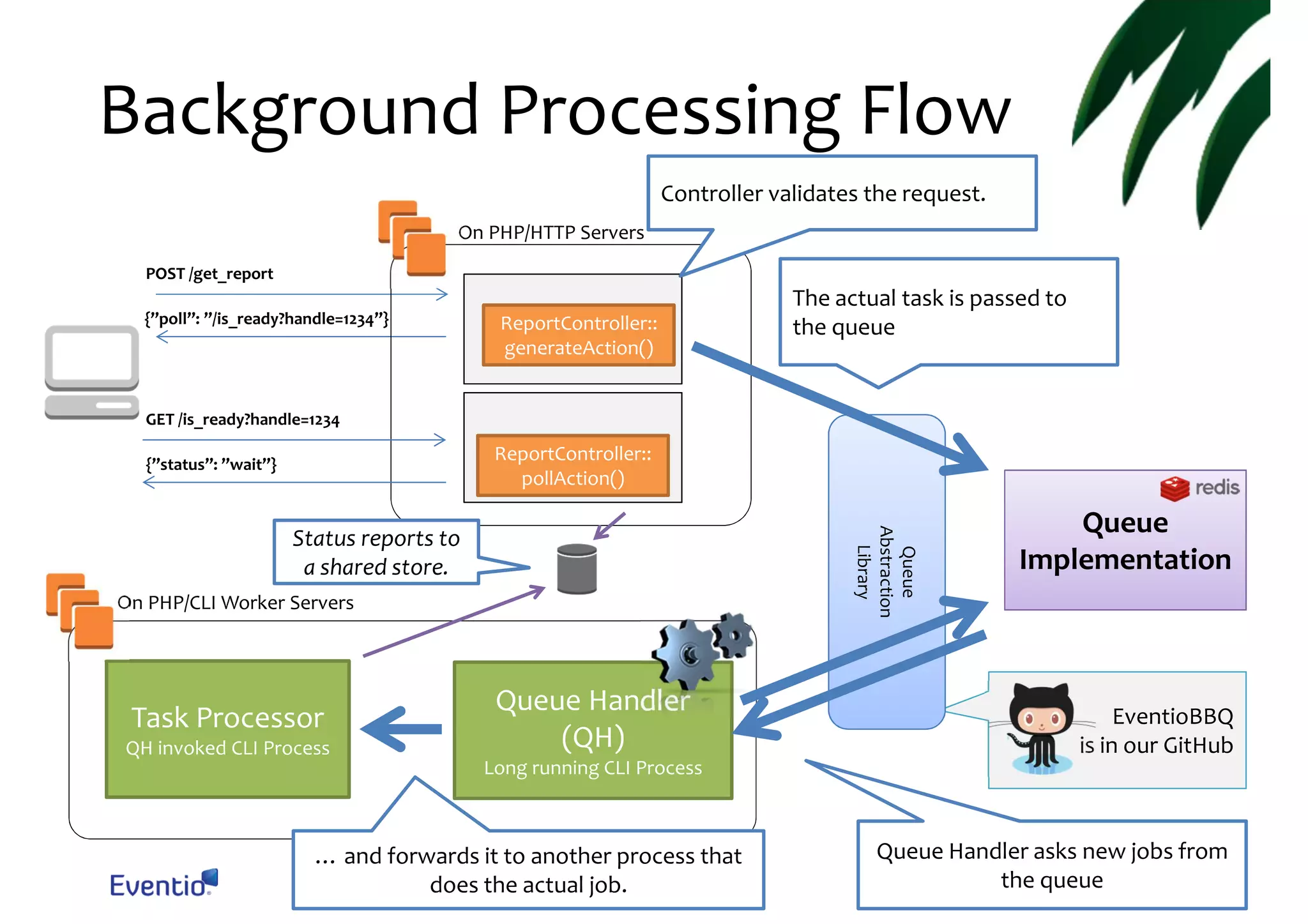
The document outlines best practices for running a scalable and reliable Symfony2 application, specifically for the Eventio platform. It details infrastructure setup, session handling, background processing, cron reliability, and asset deployment strategies using AWS services like S3 and Redis. Emphasis is placed on ensuring atomic session handling, preventing duplicate cron processes, and efficient asset management through version control.



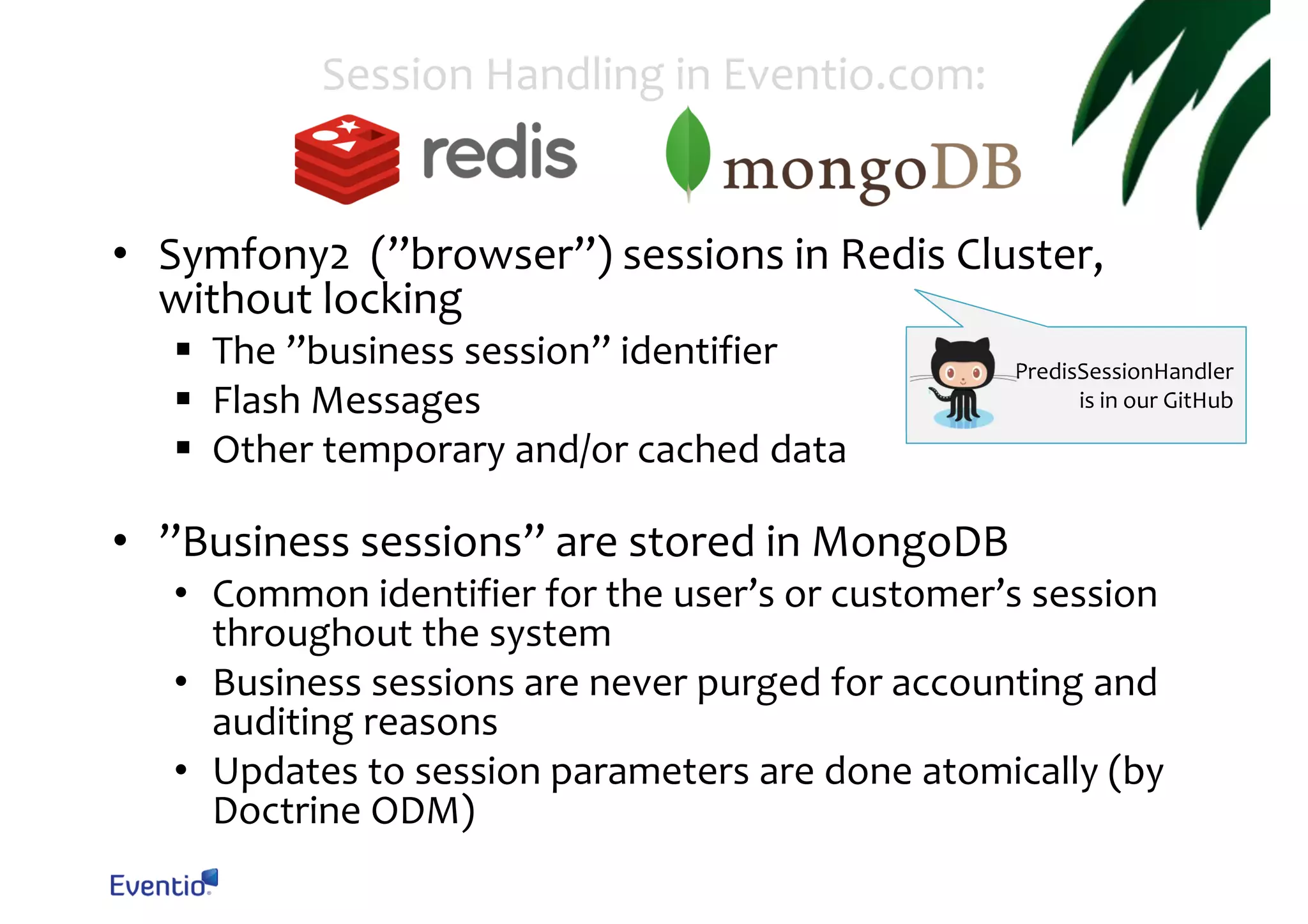
![Session Handling Store Sessions in Database • Replace NativeFileSessionHandler with an existing database handler or create your own config.yml: services: my.distributed.session_handler: class: MyDistributedSessionHandler arguments: [ . . . ] framework: session: handler_id: my.distributed.session_handle Symfony2 offers handlers for PDO, MongoDB and Memcached by default!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/running-20a-20scalable-20and-20reliable-20symfony2-20application-20in-20cloud-131123102414-phpapp01/75/Running-a-Scalable-And-Reliable-Symfony2-Application-in-Cloud-Symfony-Sweden-November-Camp-22-Nov-2013-5-2048.jpg)



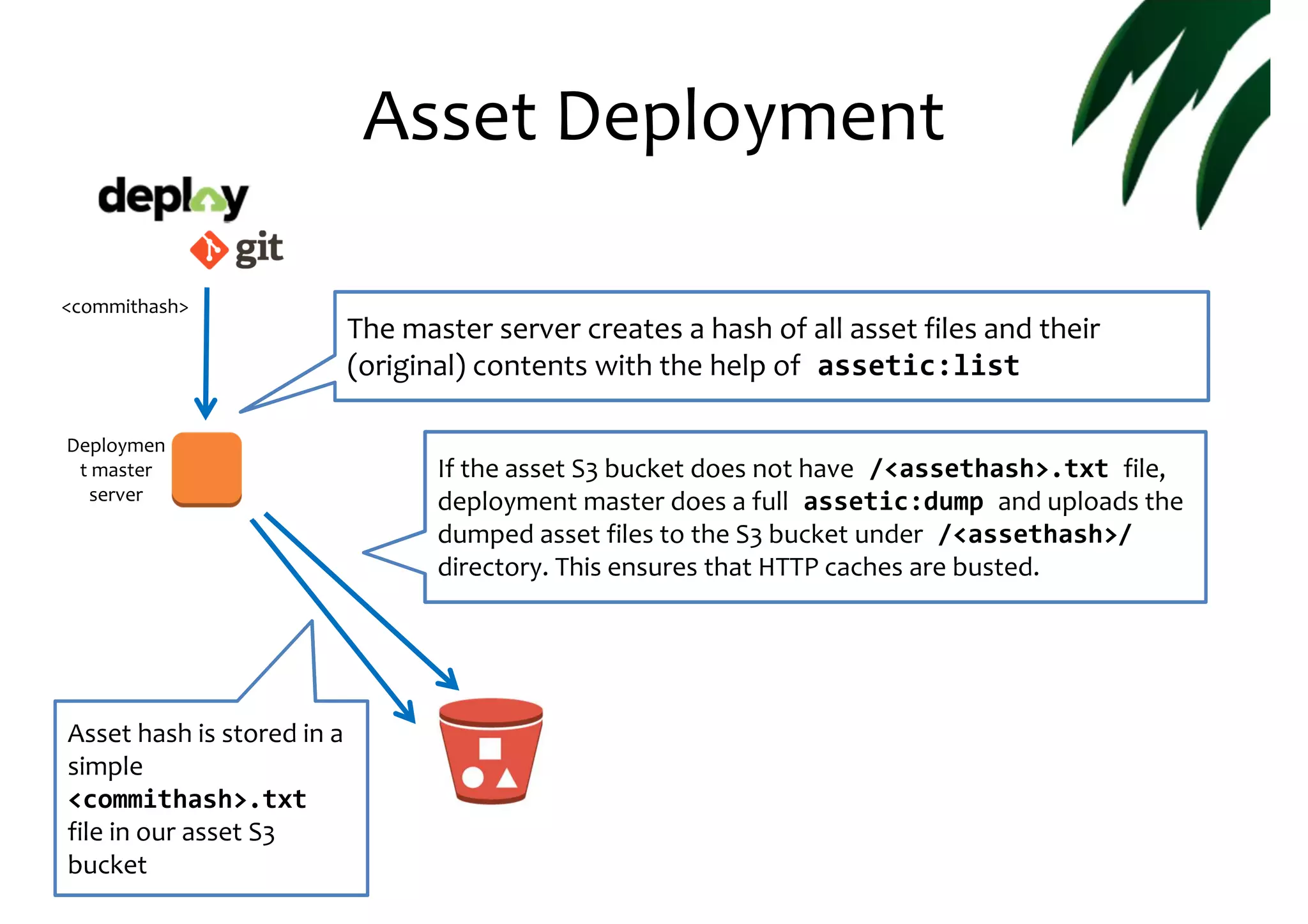
![Application deployments <commithash> Deploymen t master server • • • cache:clear Quick local & connectivity tests (Instance registration back to ELB) Instance is unregistered from the Load Balancer S3 bucket is queried for the <assethash> matching the current <commithash> … and added to the parameters.yml asset_hash: <assethash> config.yml: framework: templating: assets_base_urls: ["https://.../%asset_hash%"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/running-20a-20scalable-20and-20reliable-20symfony2-20application-20in-20cloud-131123102414-phpapp01/75/Running-a-Scalable-And-Reliable-Symfony2-Application-in-Cloud-Symfony-Sweden-November-Camp-22-Nov-2013-18-2048.jpg)
