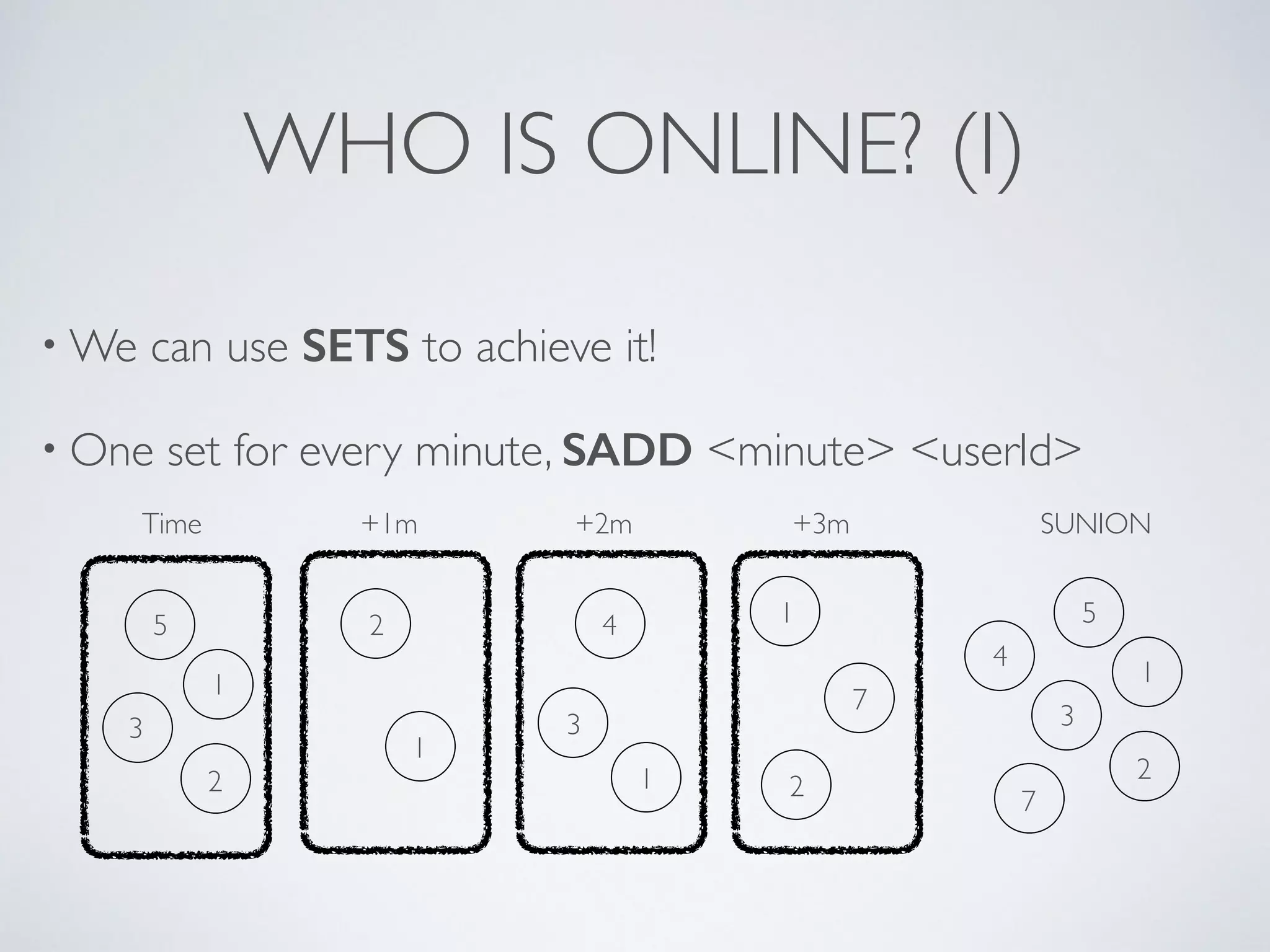
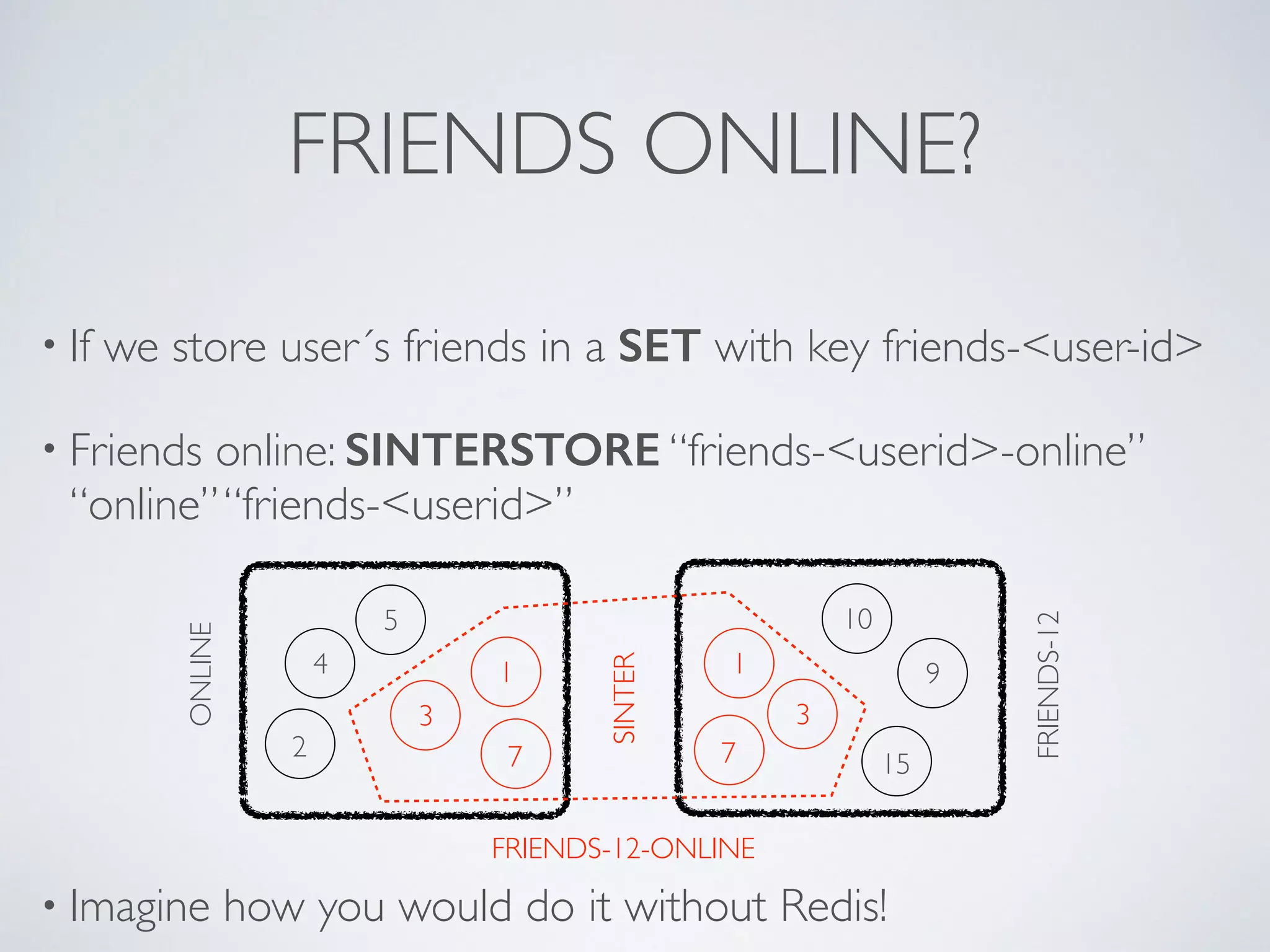
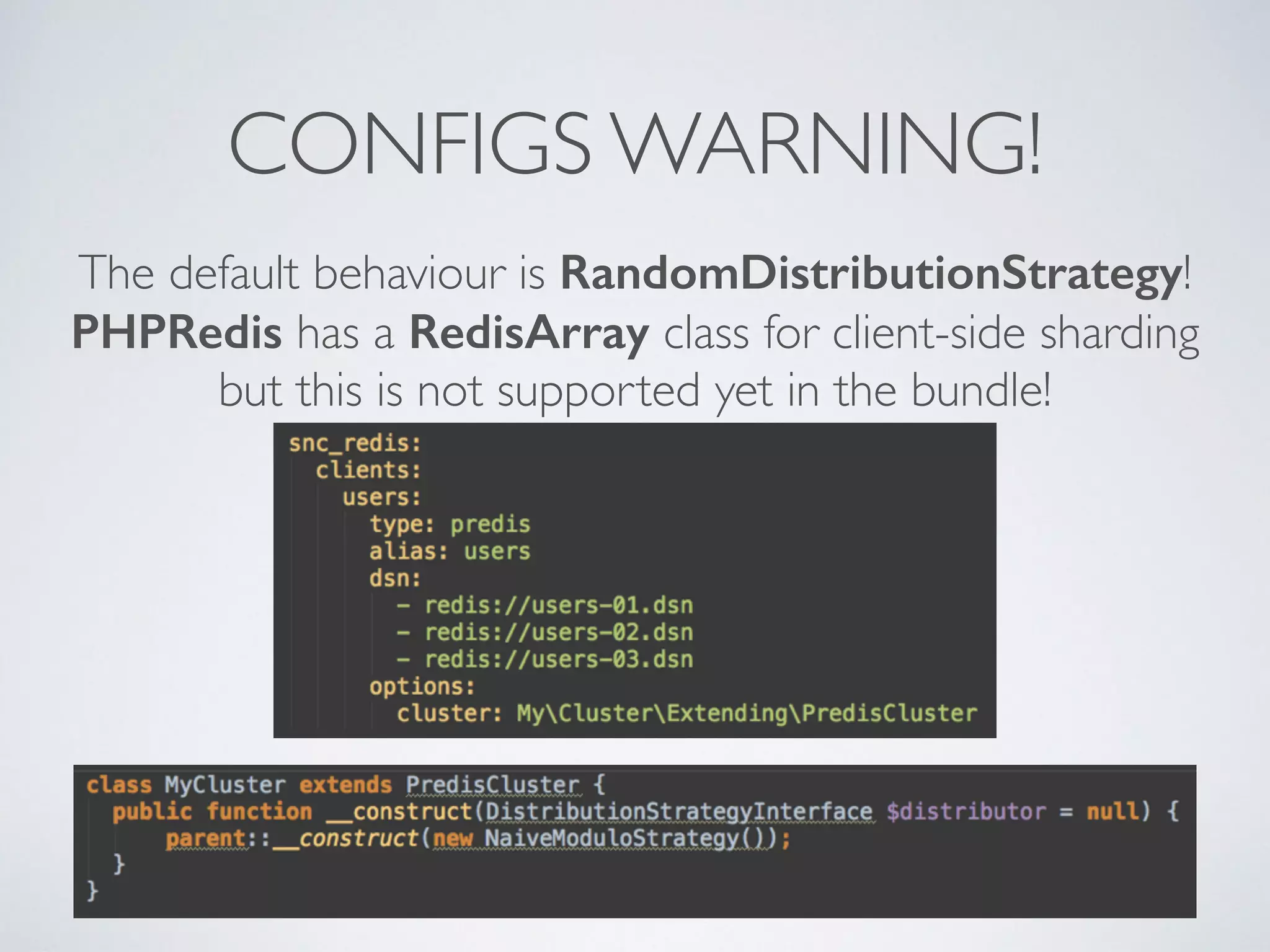
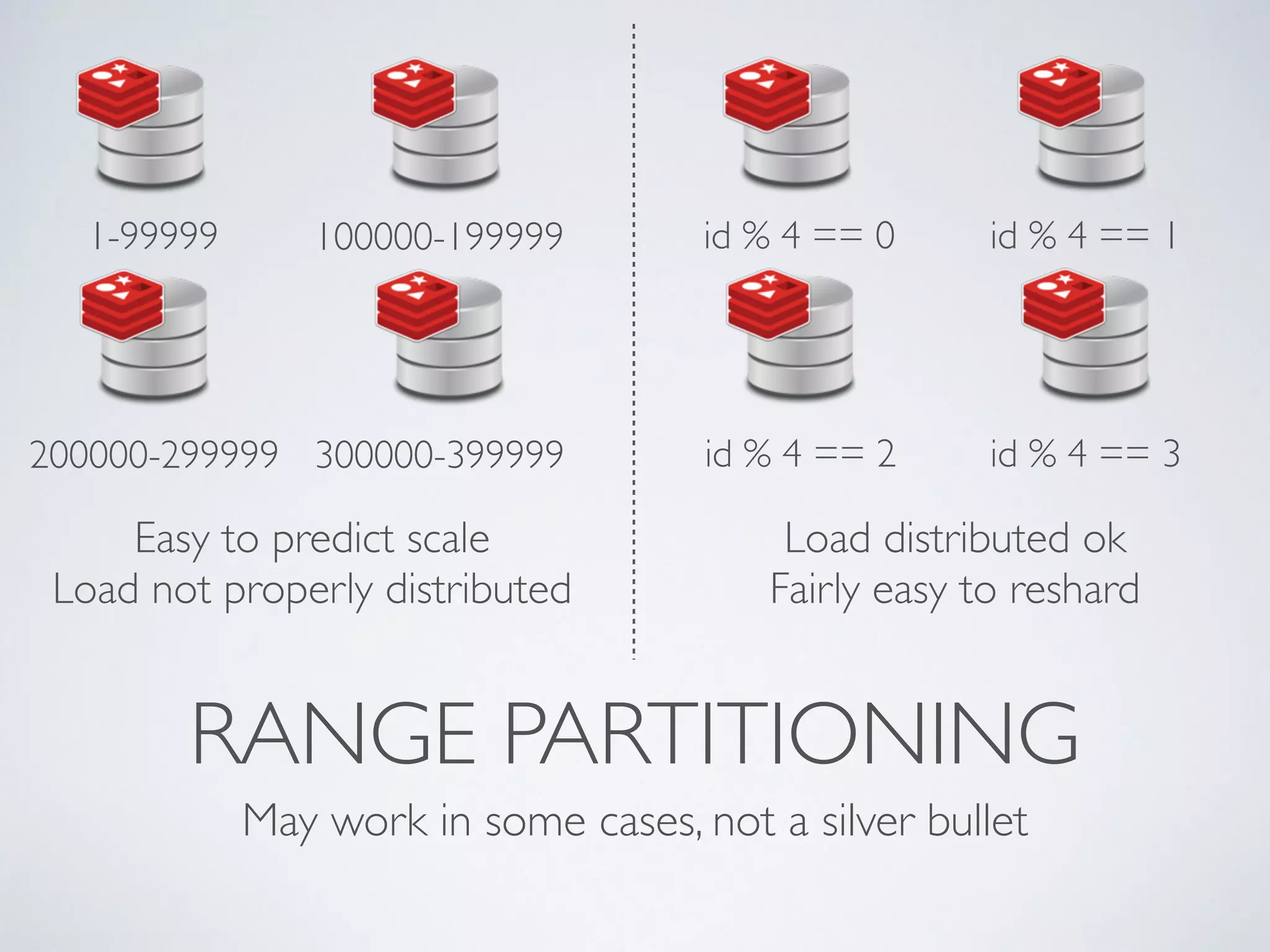
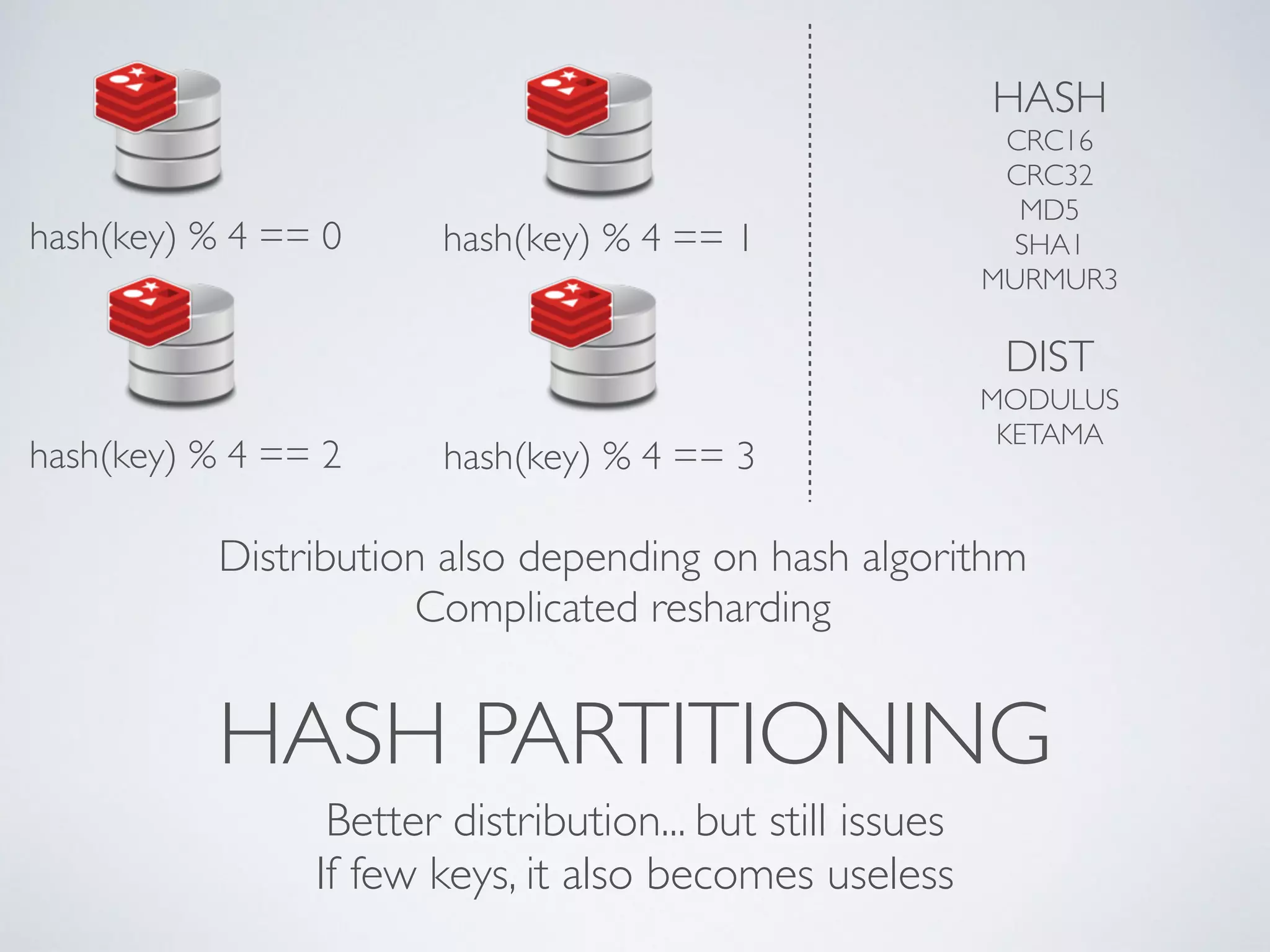
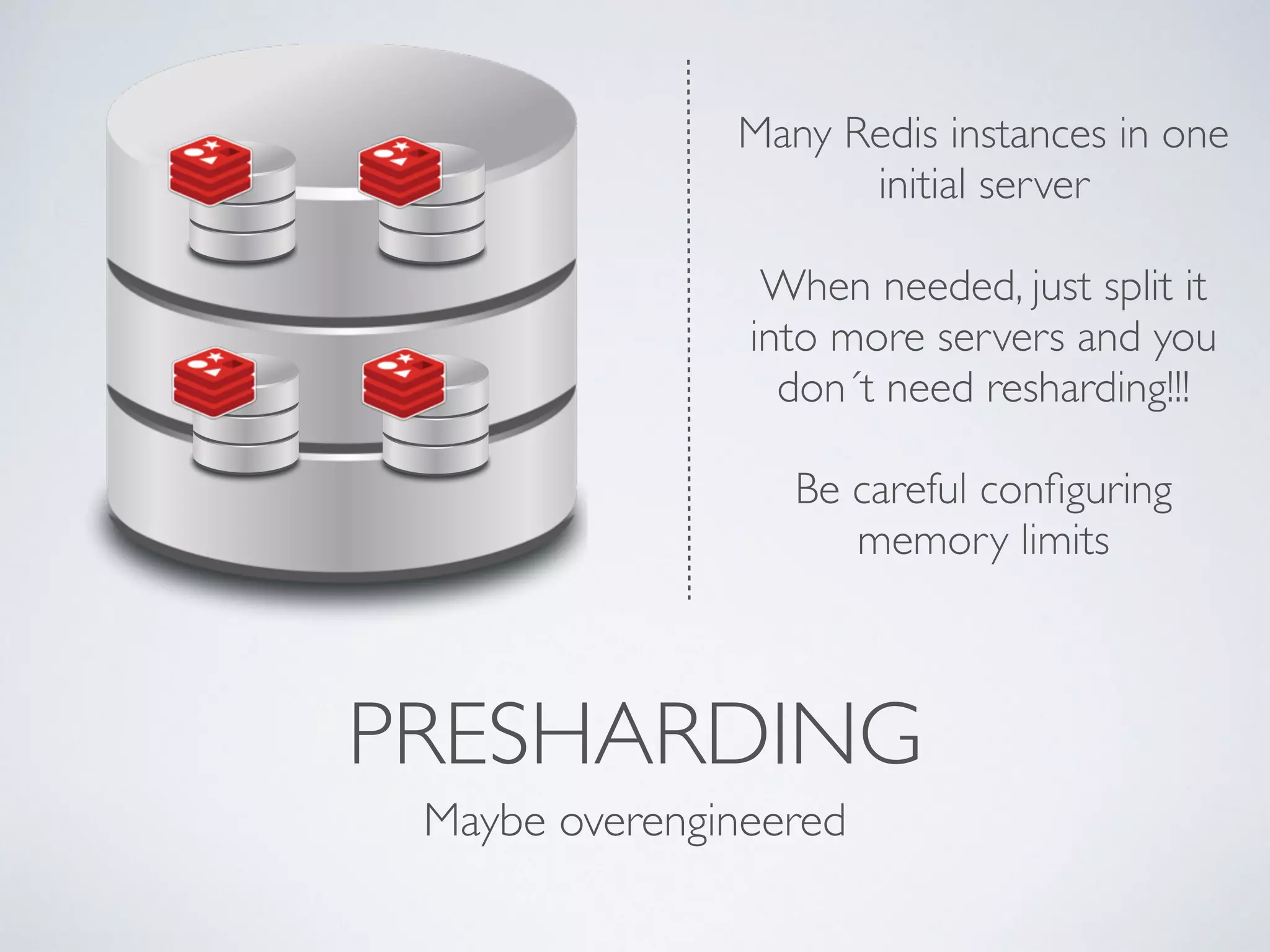
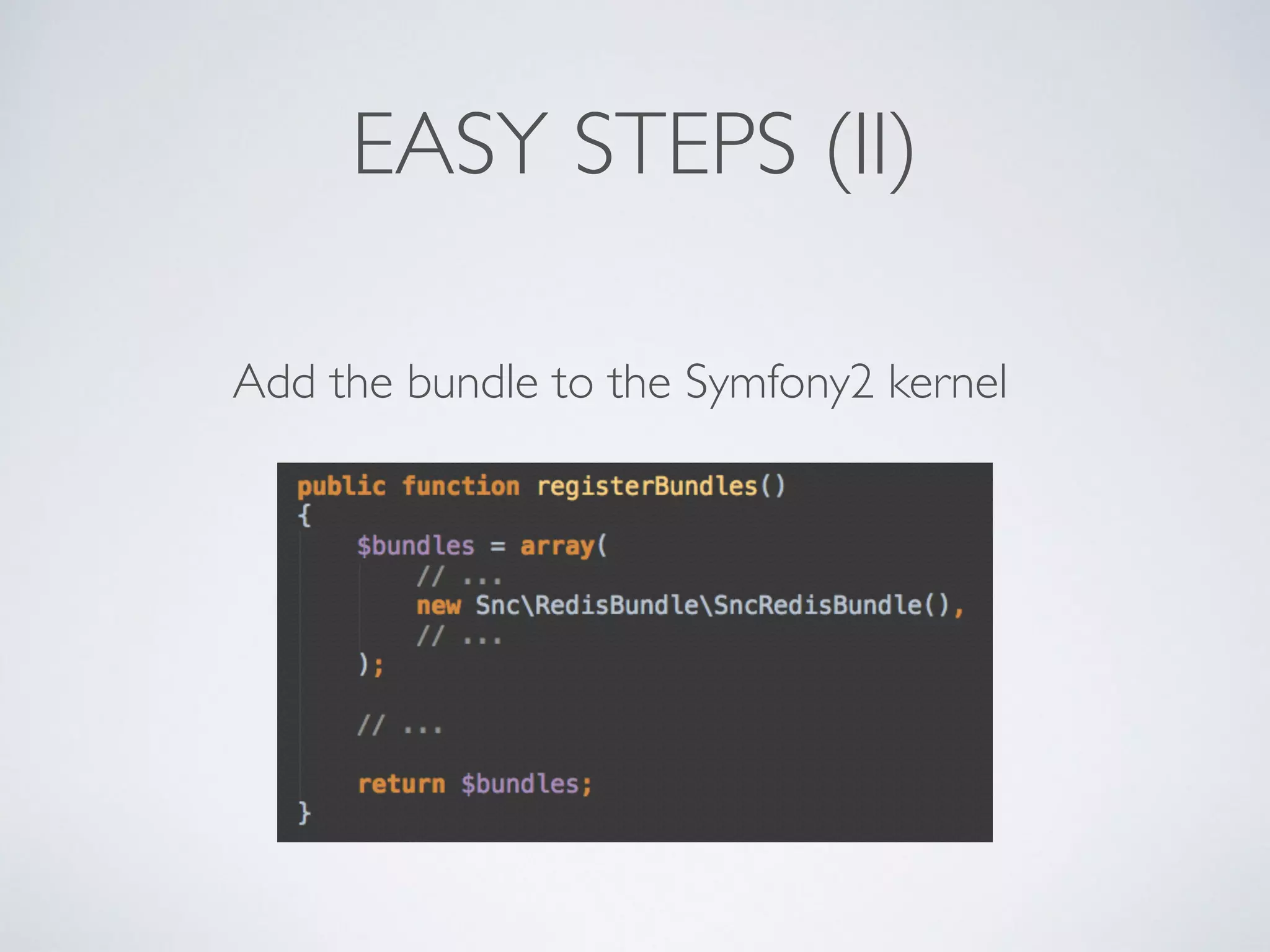
The document is a presentation by Ricard Clau on improving Symfony2 applications using Redis, an advanced in-memory key-value store. It covers Redis features, data types, commands, and practical implementations such as caching and real-time applications. Additionally, it discusses configurations, sharding, clustering, and when to use Redis versus other database solutions.















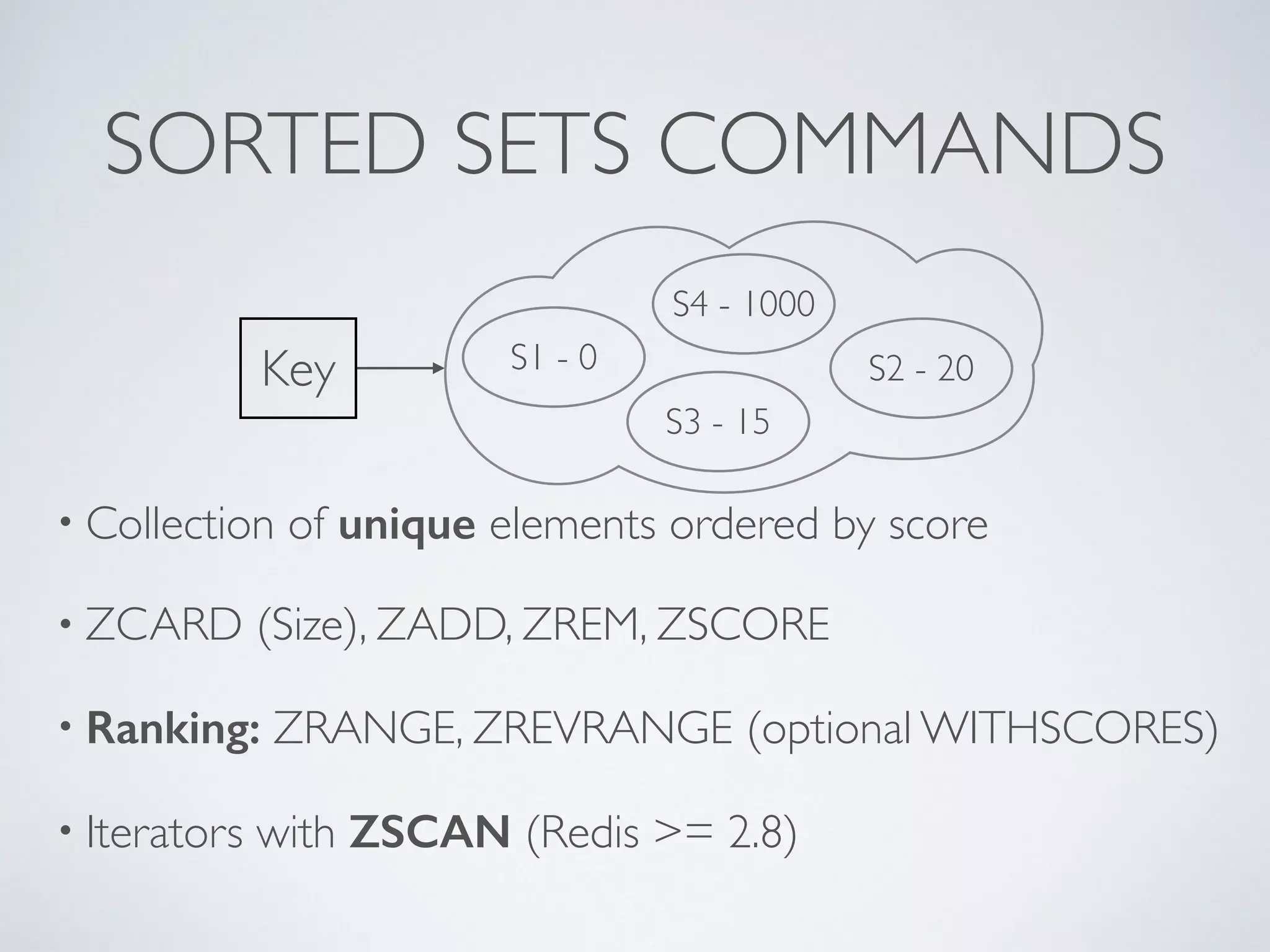






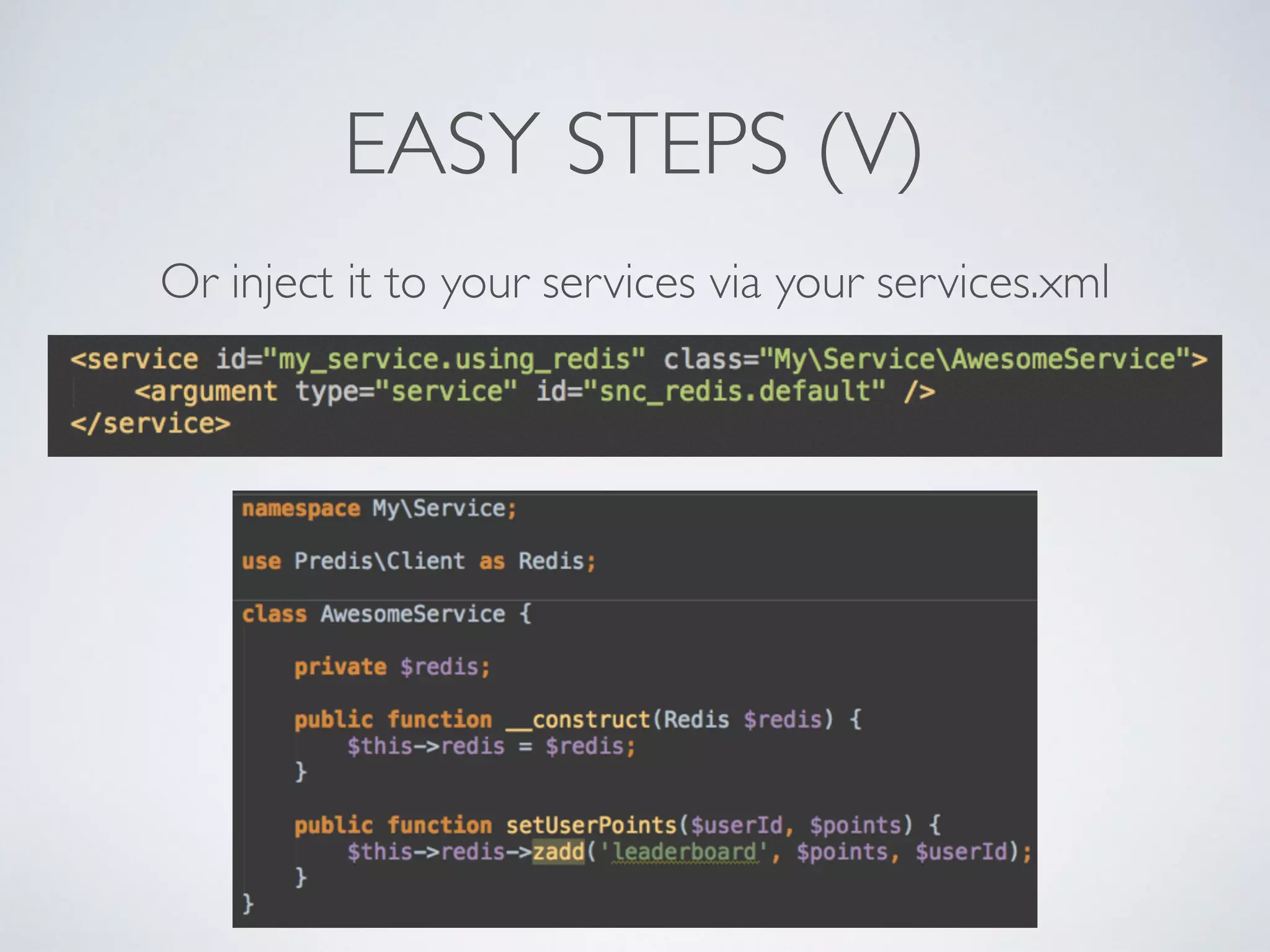
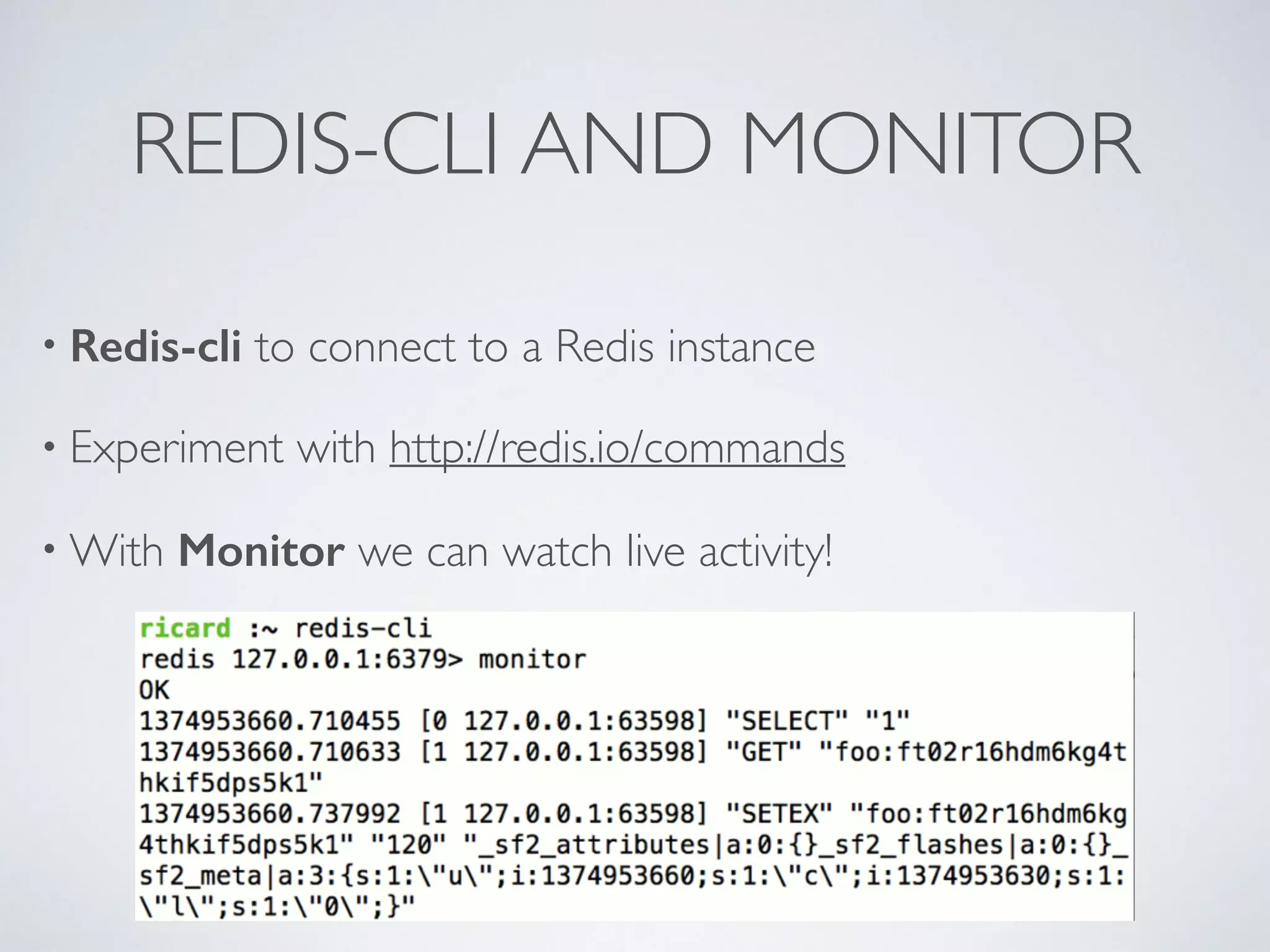



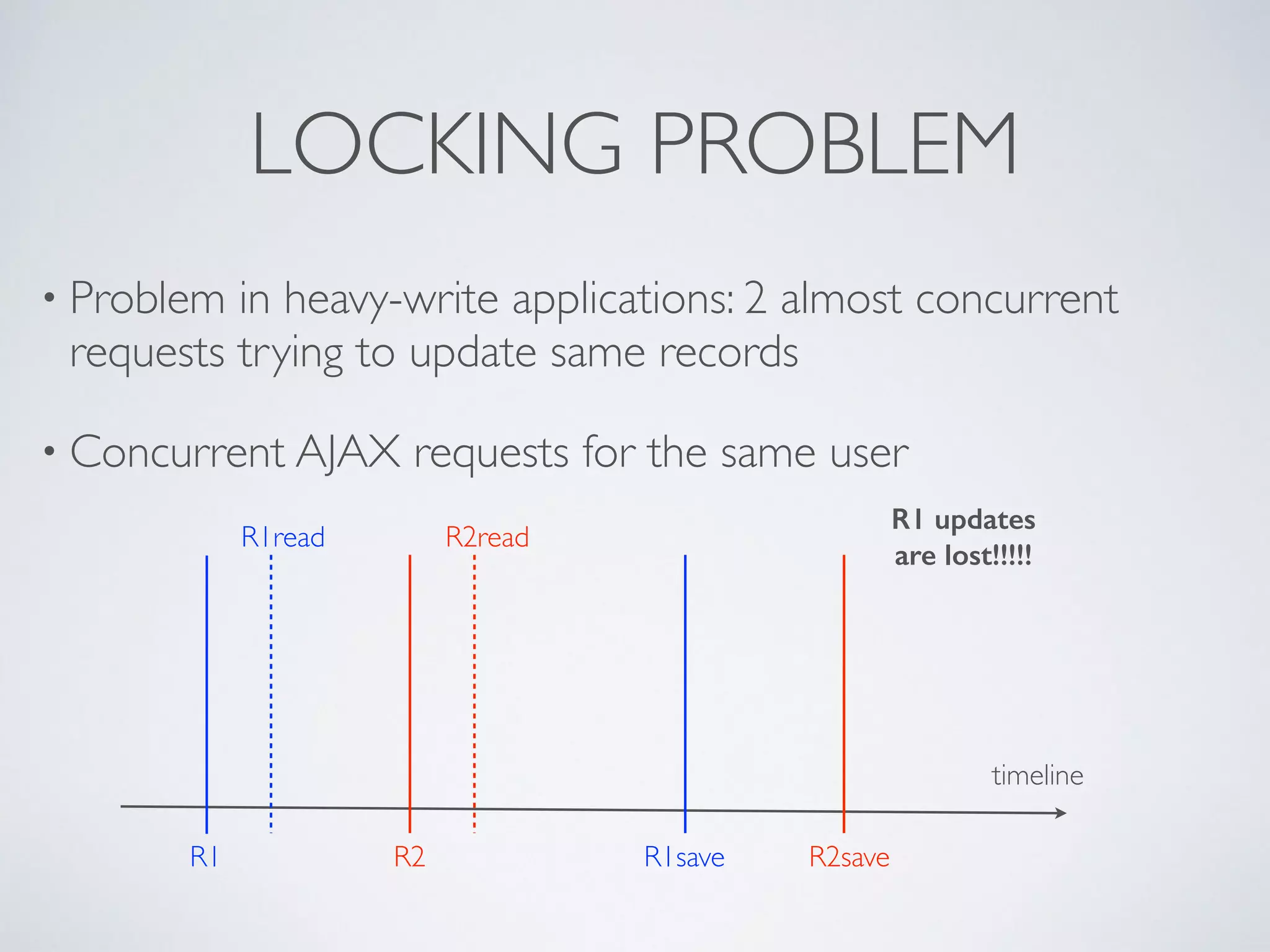

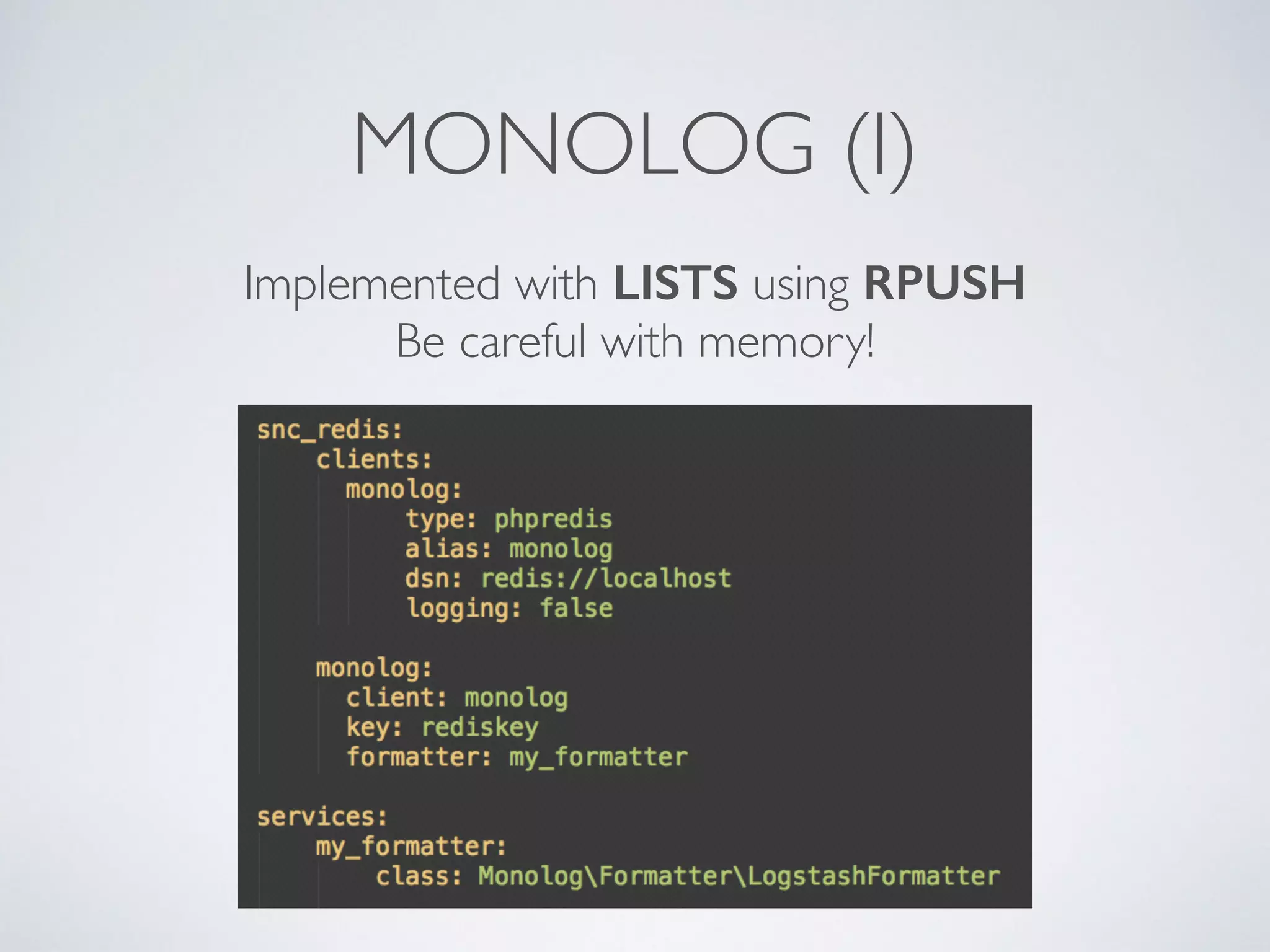





![LEADERBOARDS • Super-easy with Redis, heavy consuming with other systems • Each board with a single key, using sorted sets • ZINCRBY “rankXXX” <increment> <userId> • Top N ZREVRANGE “rankXXX” 0 N [WITHSCORES] • You can store several millions of members under 1 key](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/symfonylondon-redis-141016025650-conversion-gate01/75/Speed-up-your-Symfony2-application-and-build-awesome-features-with-Redis-37-2048.jpg)