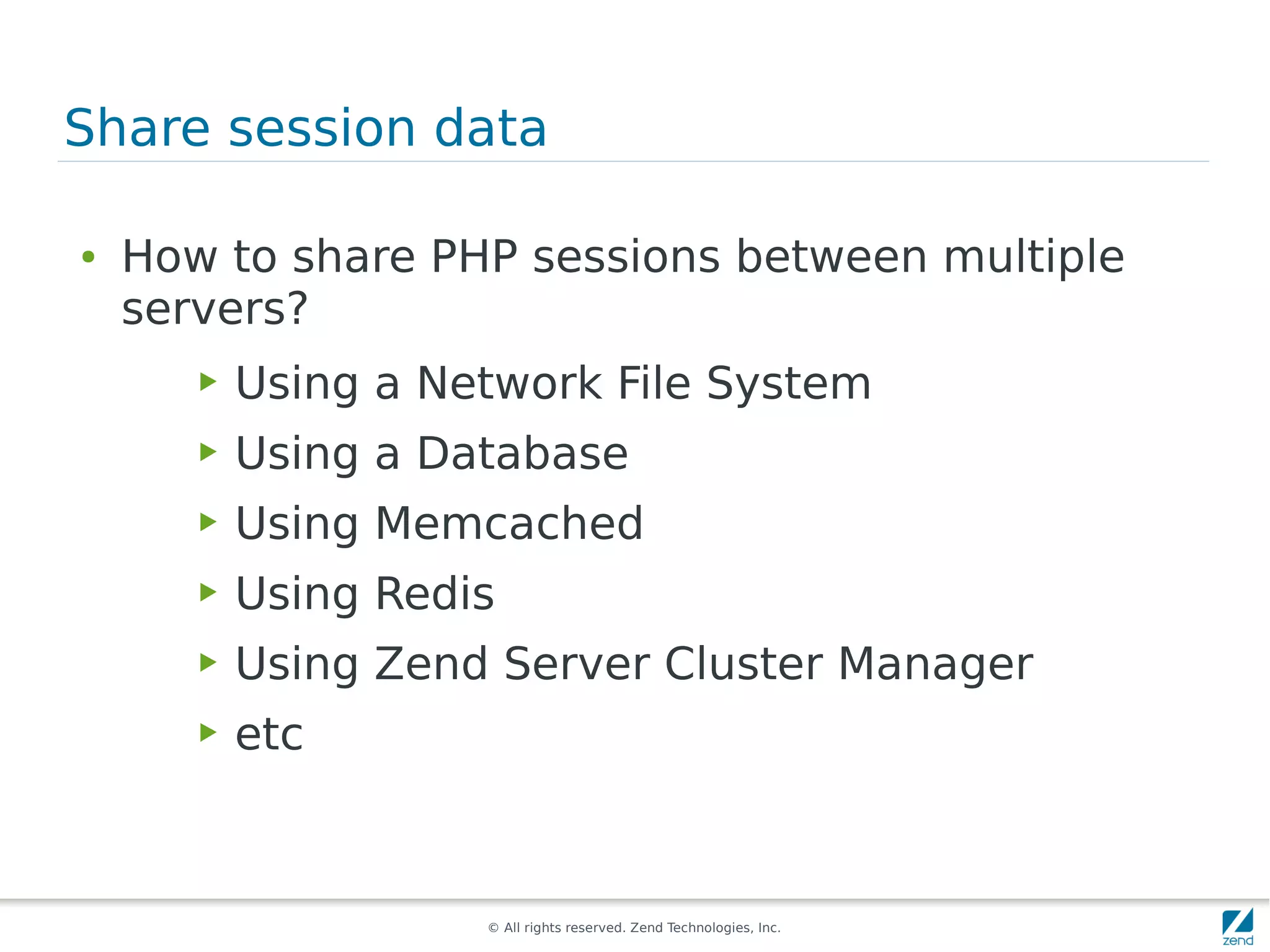
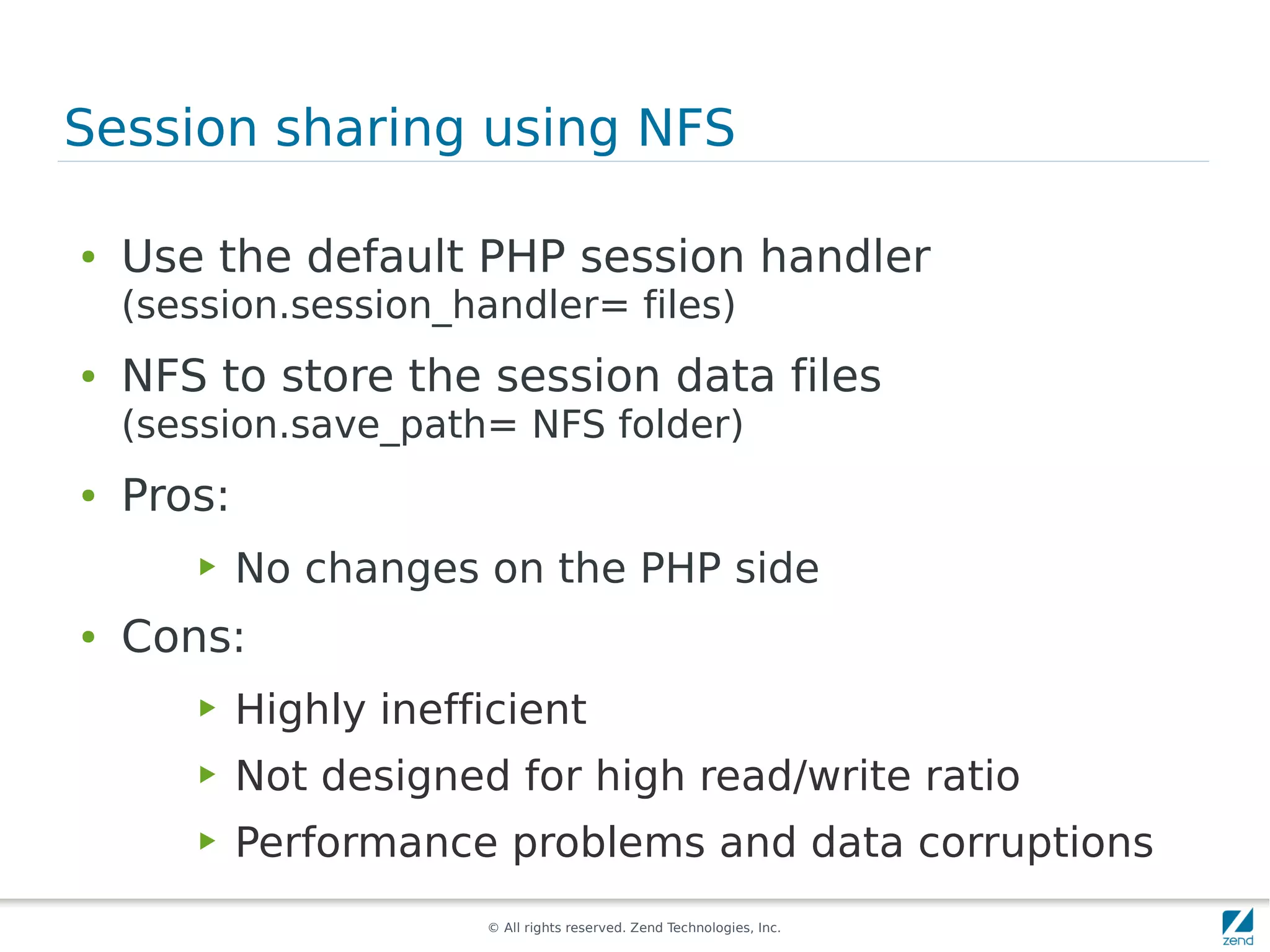
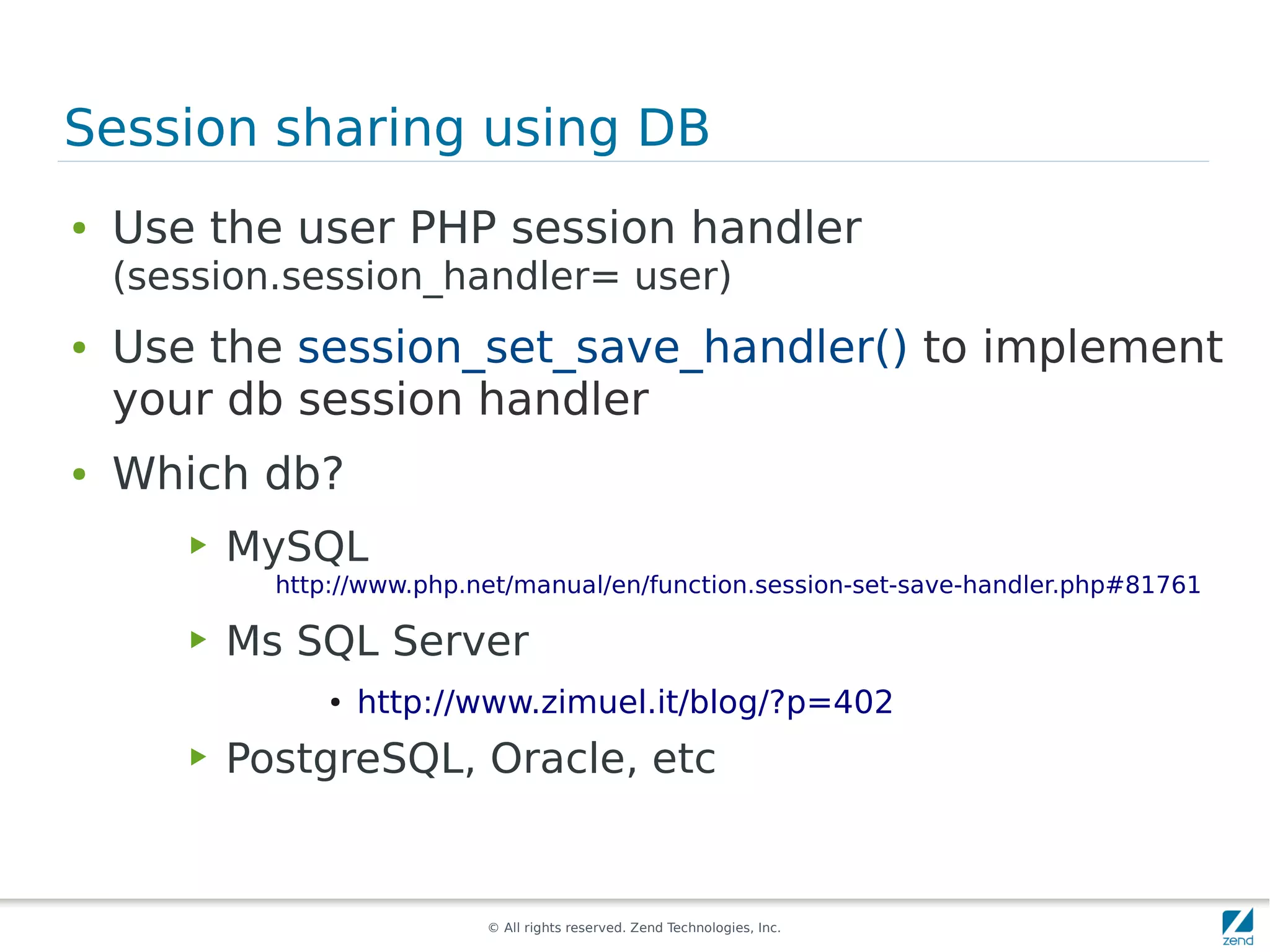
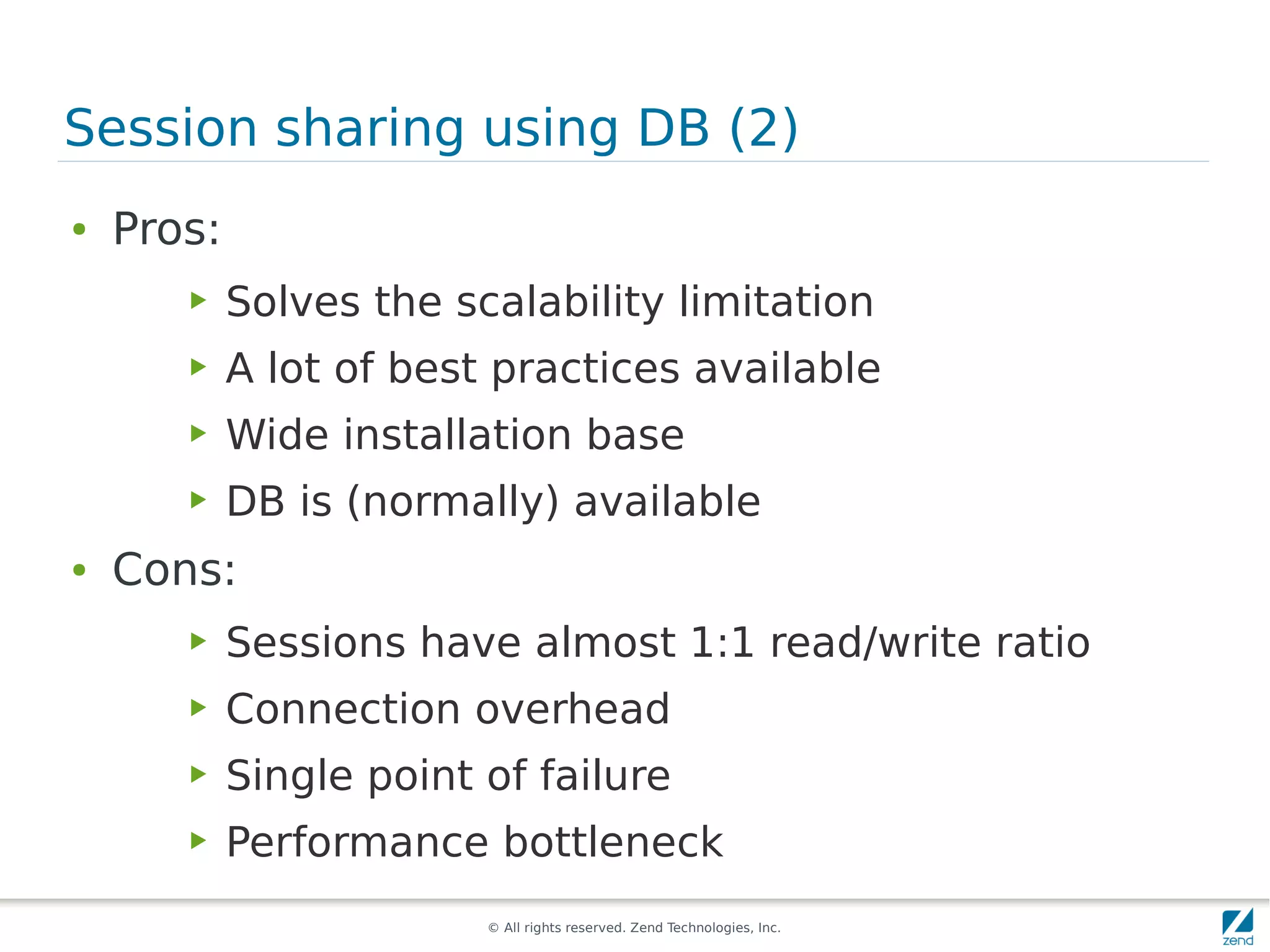
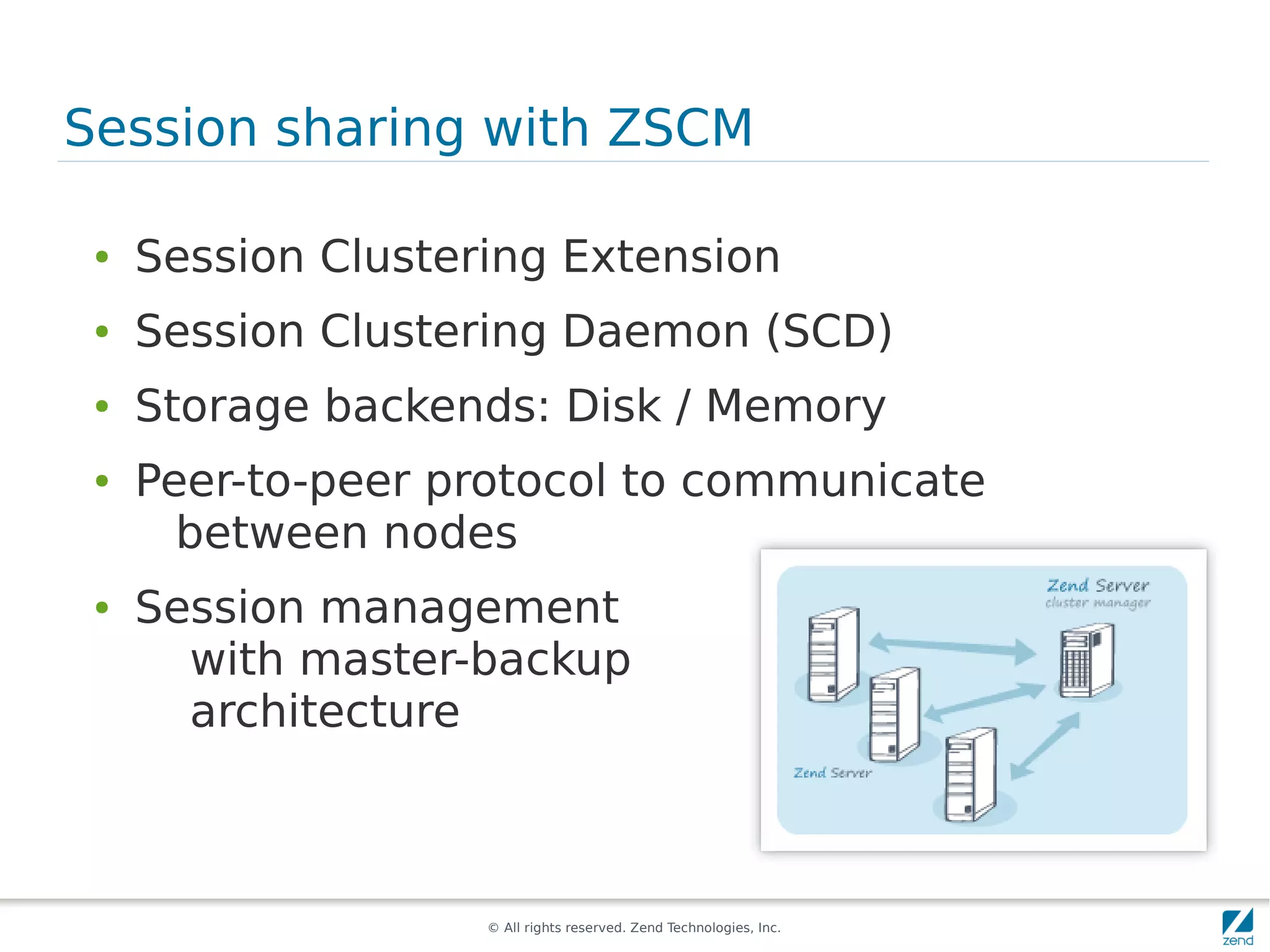
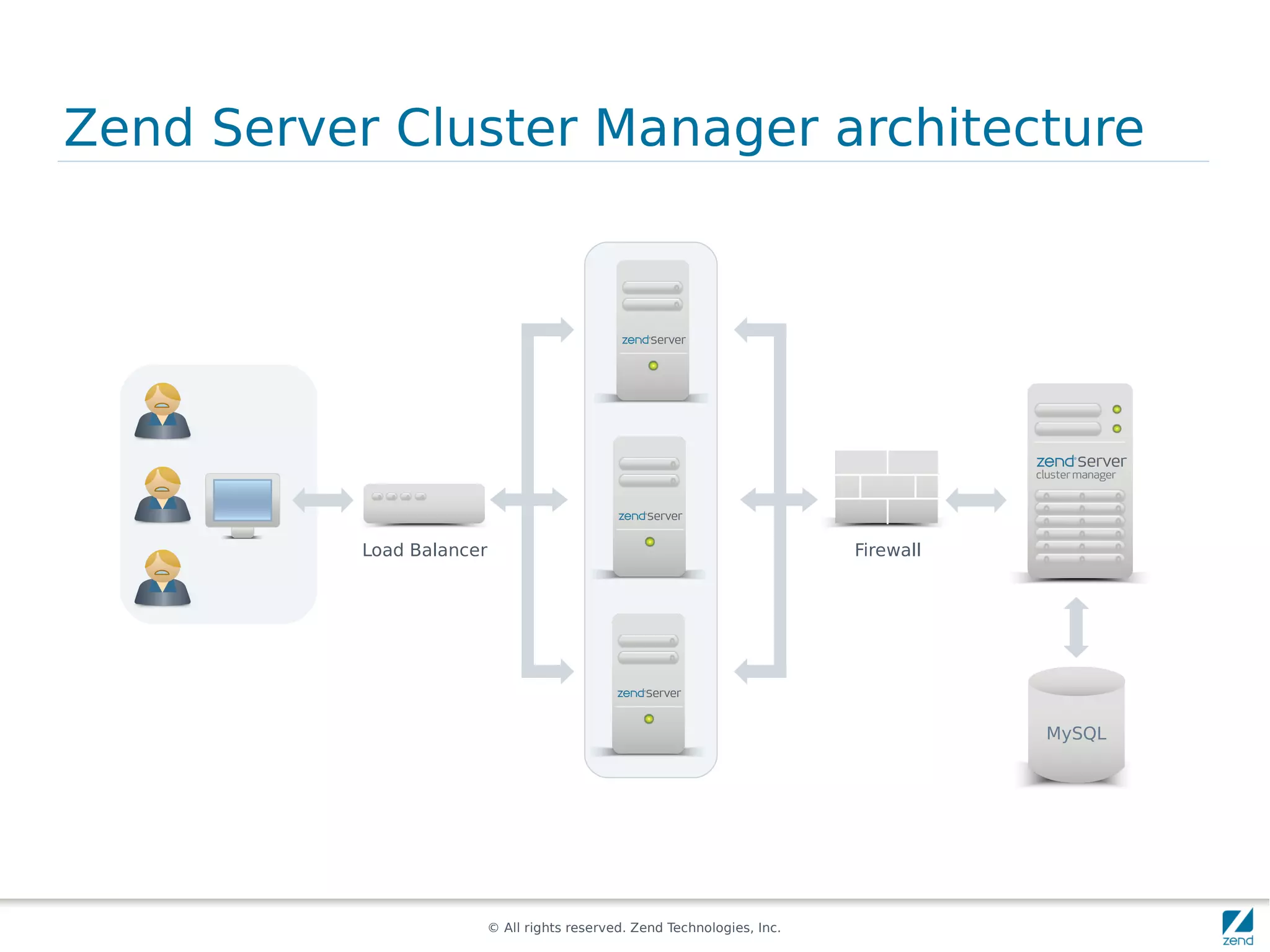
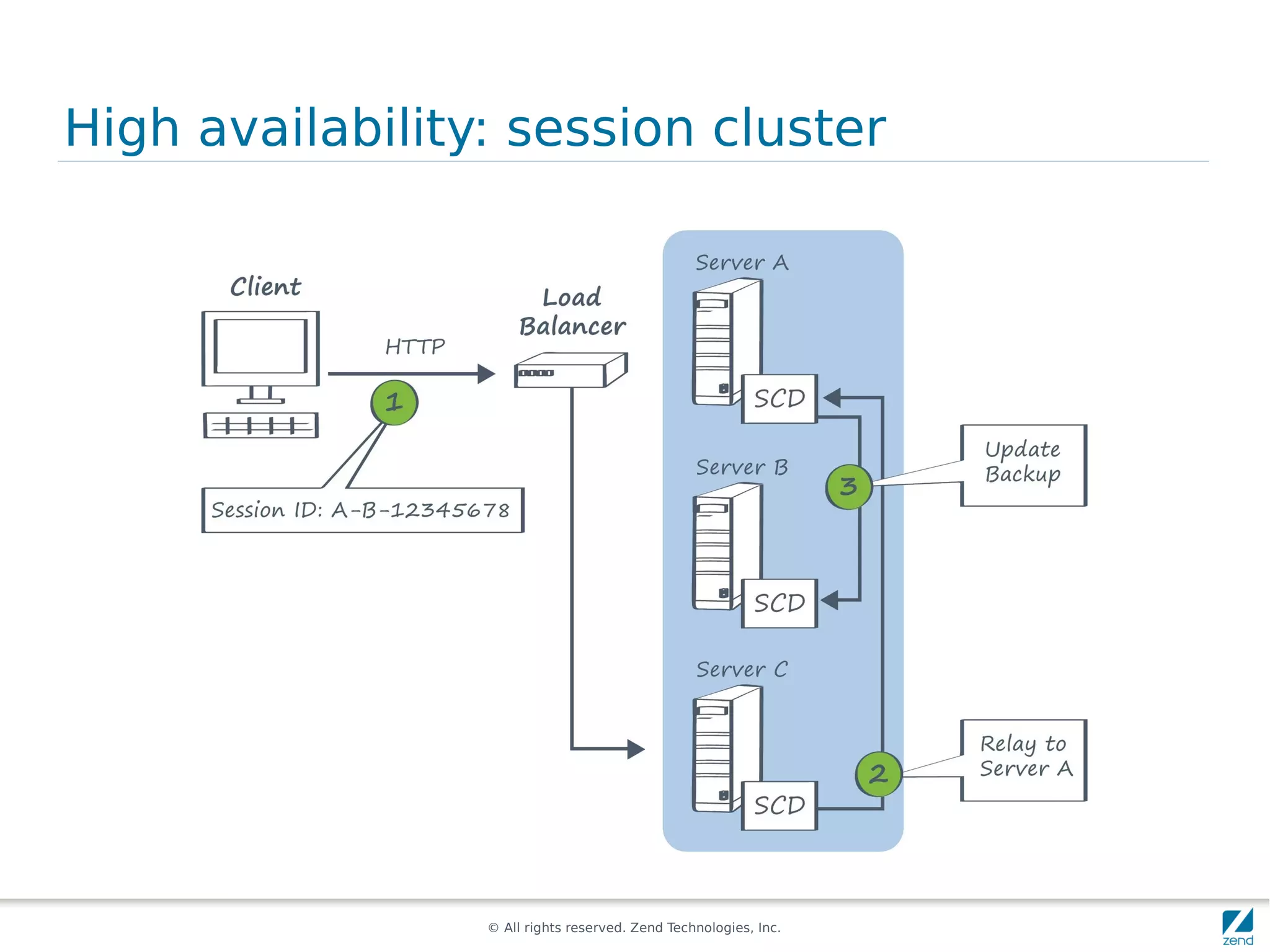
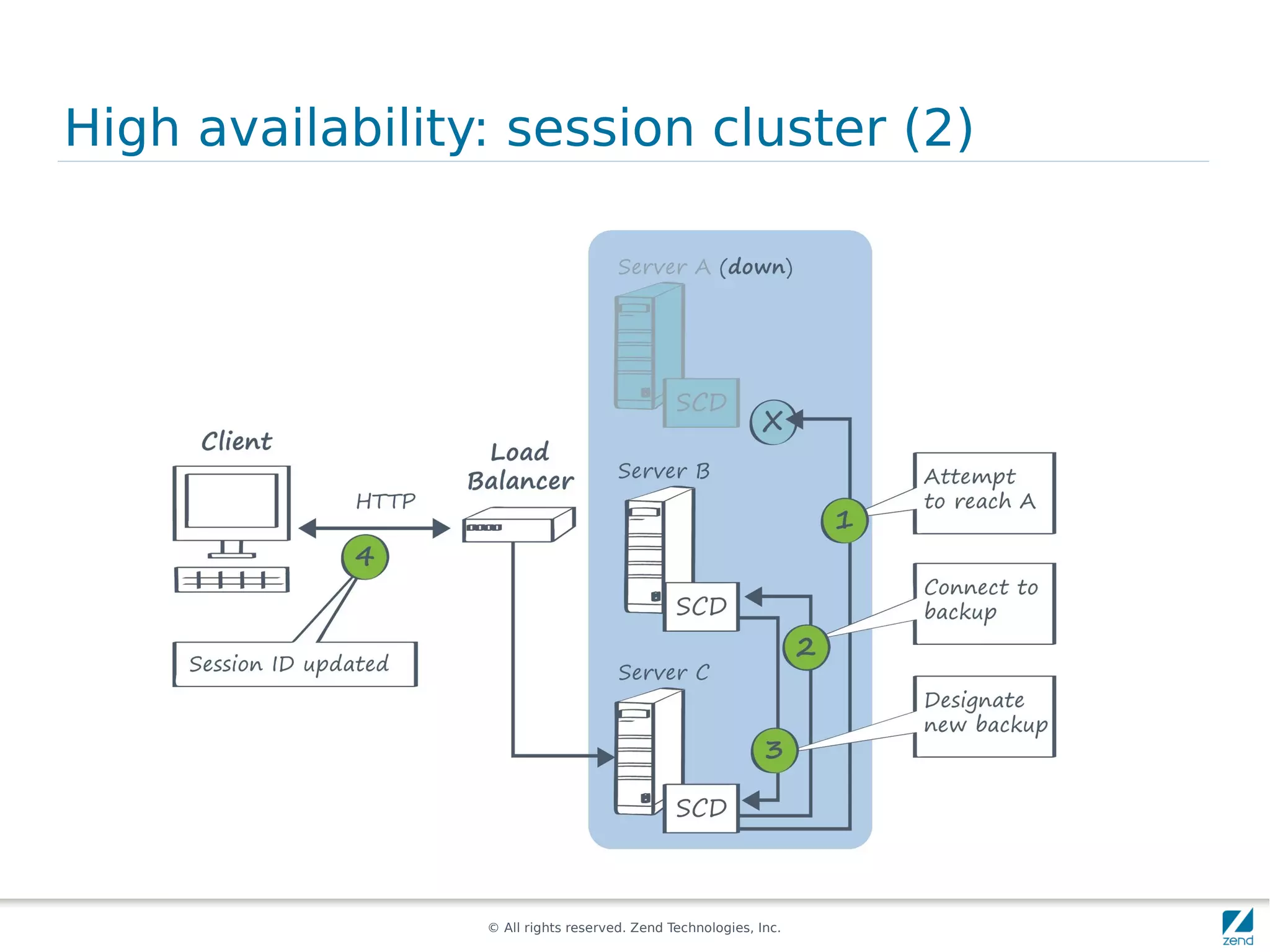
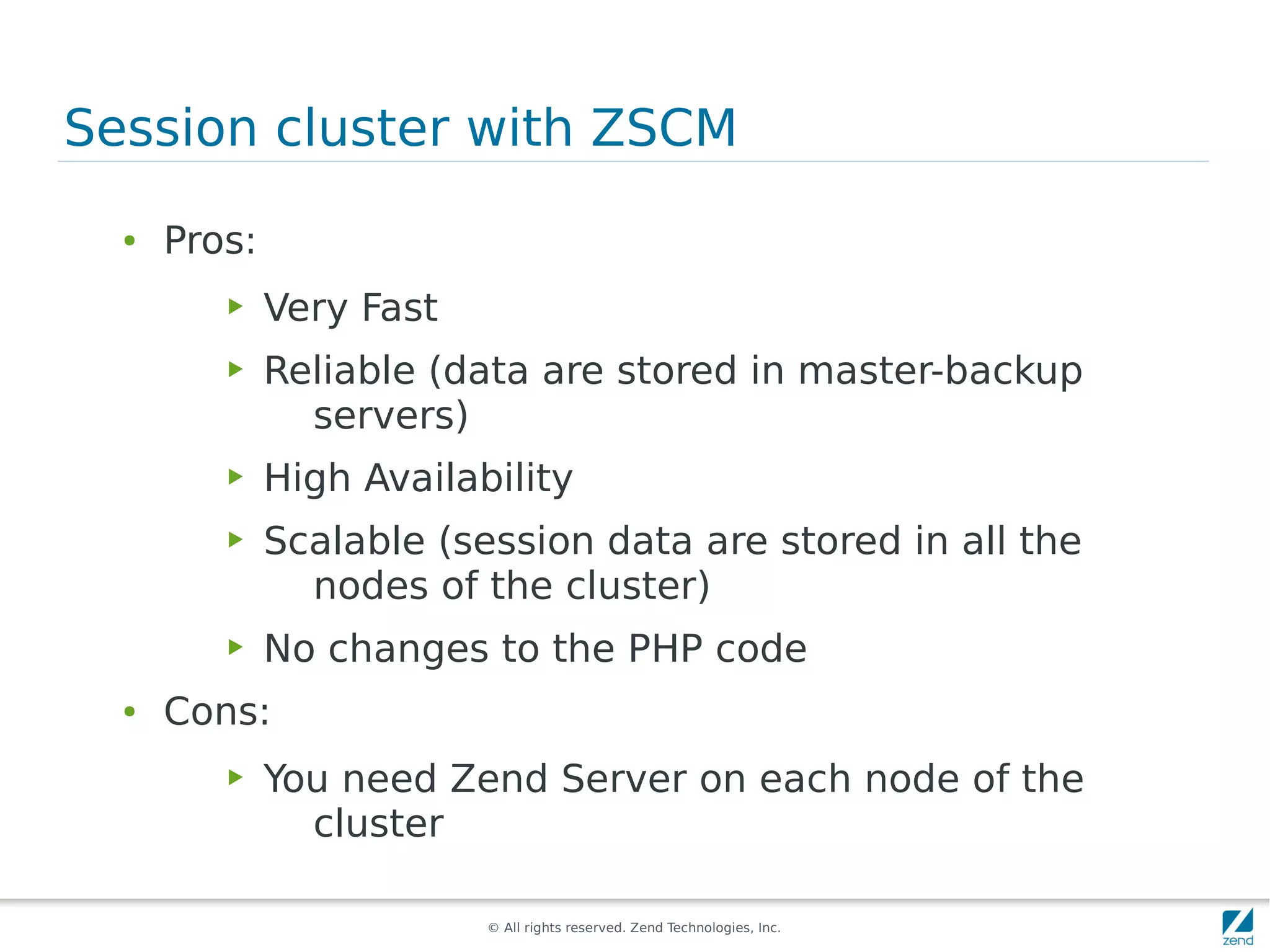
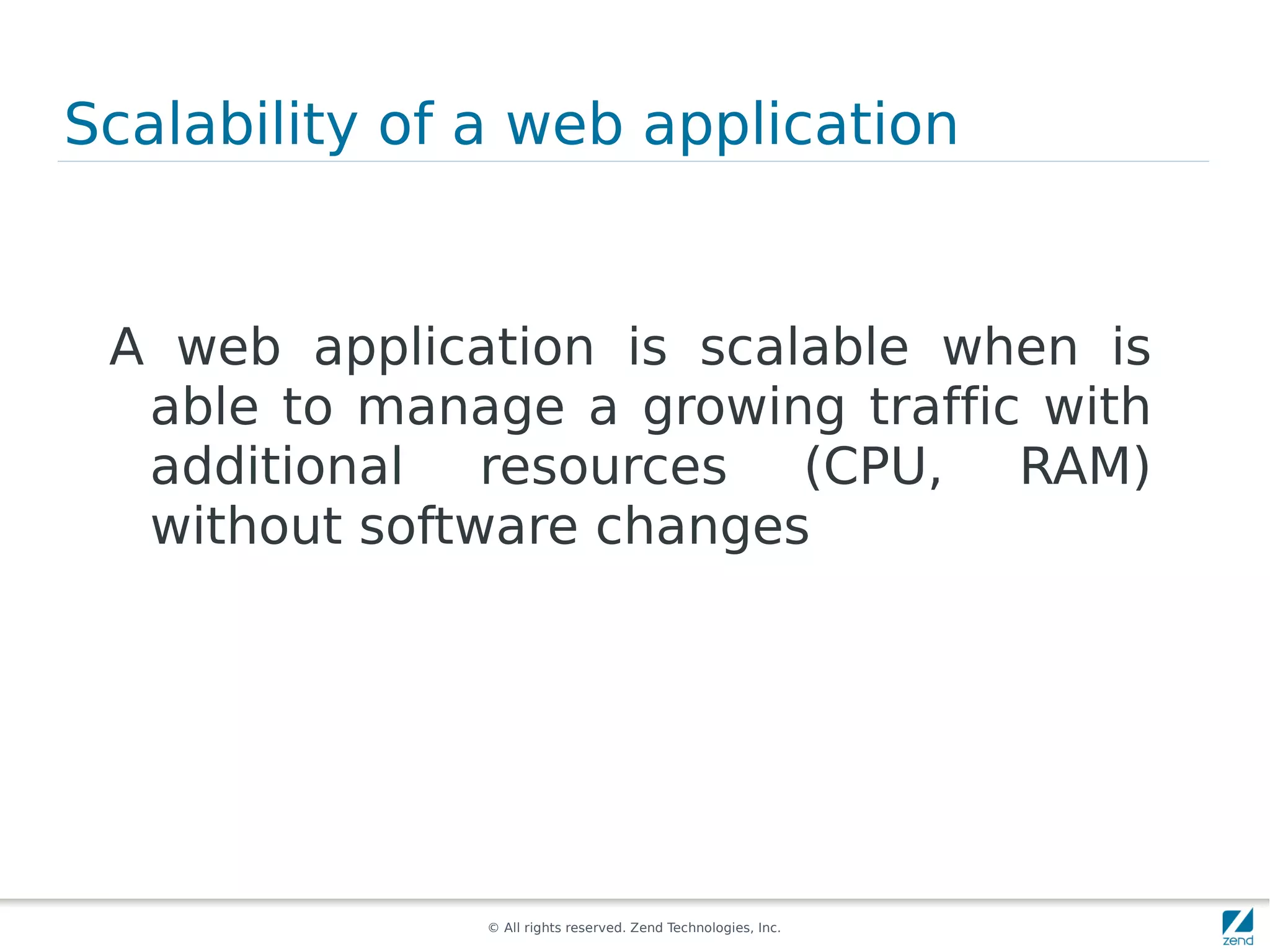
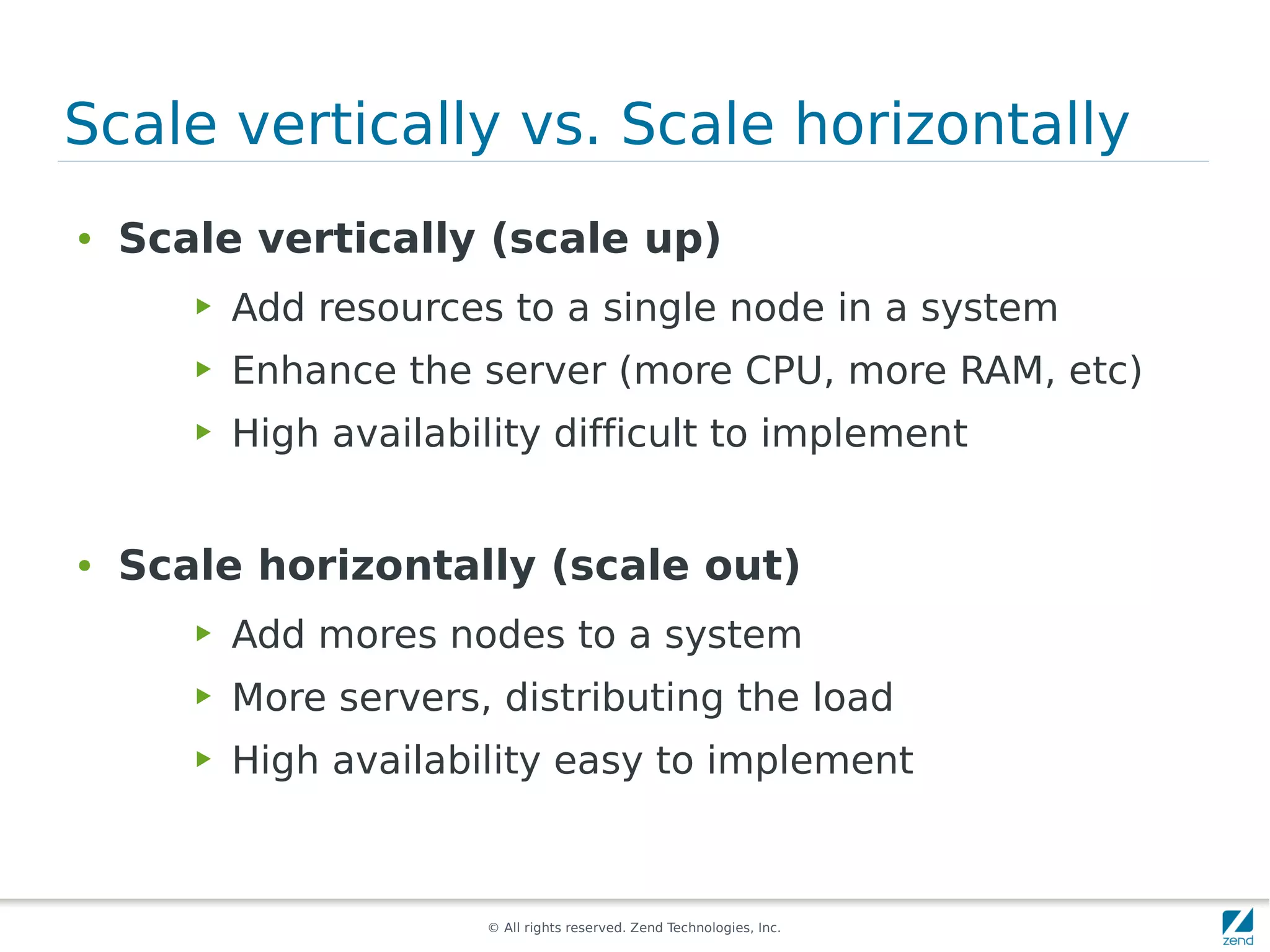
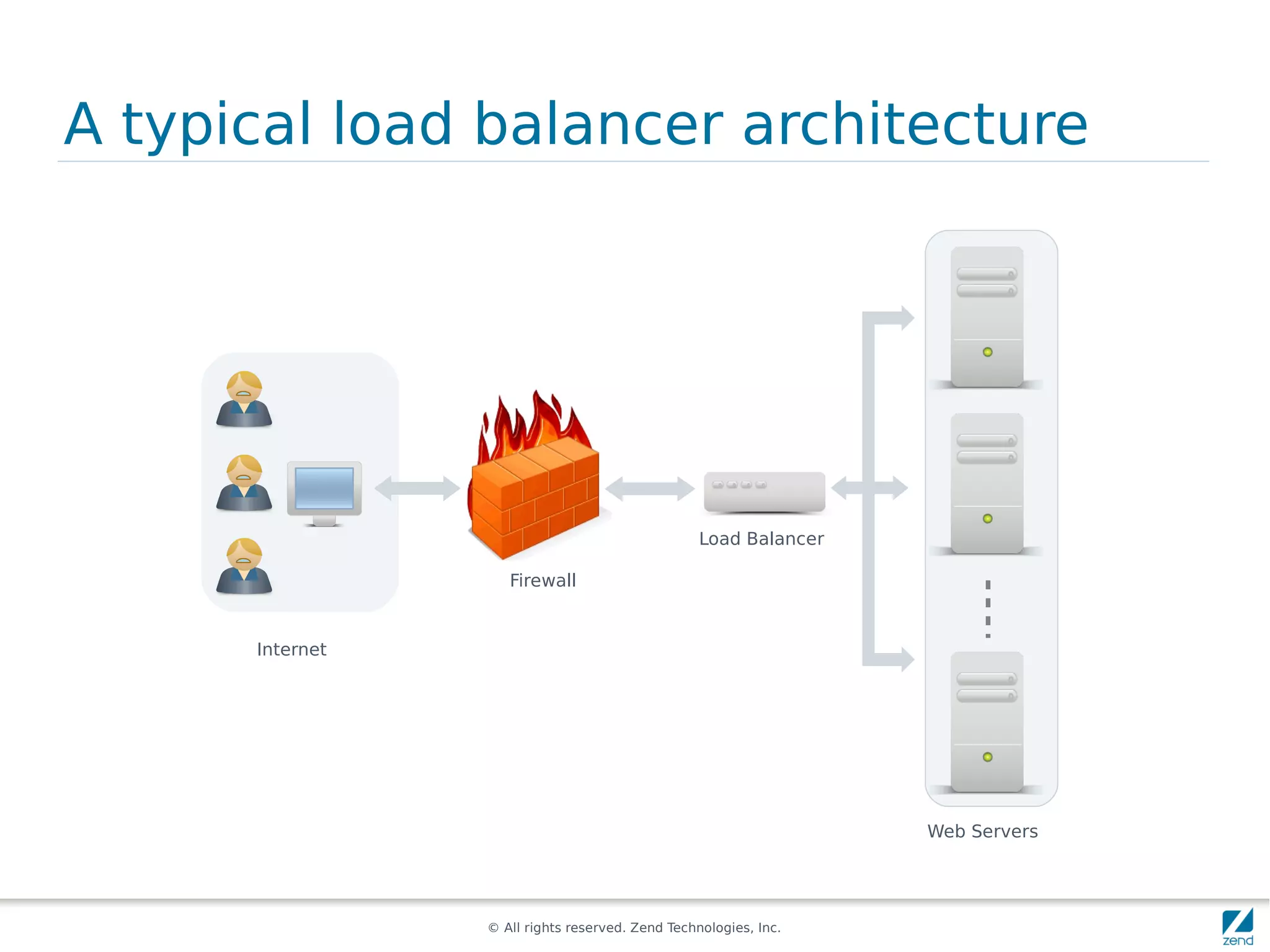
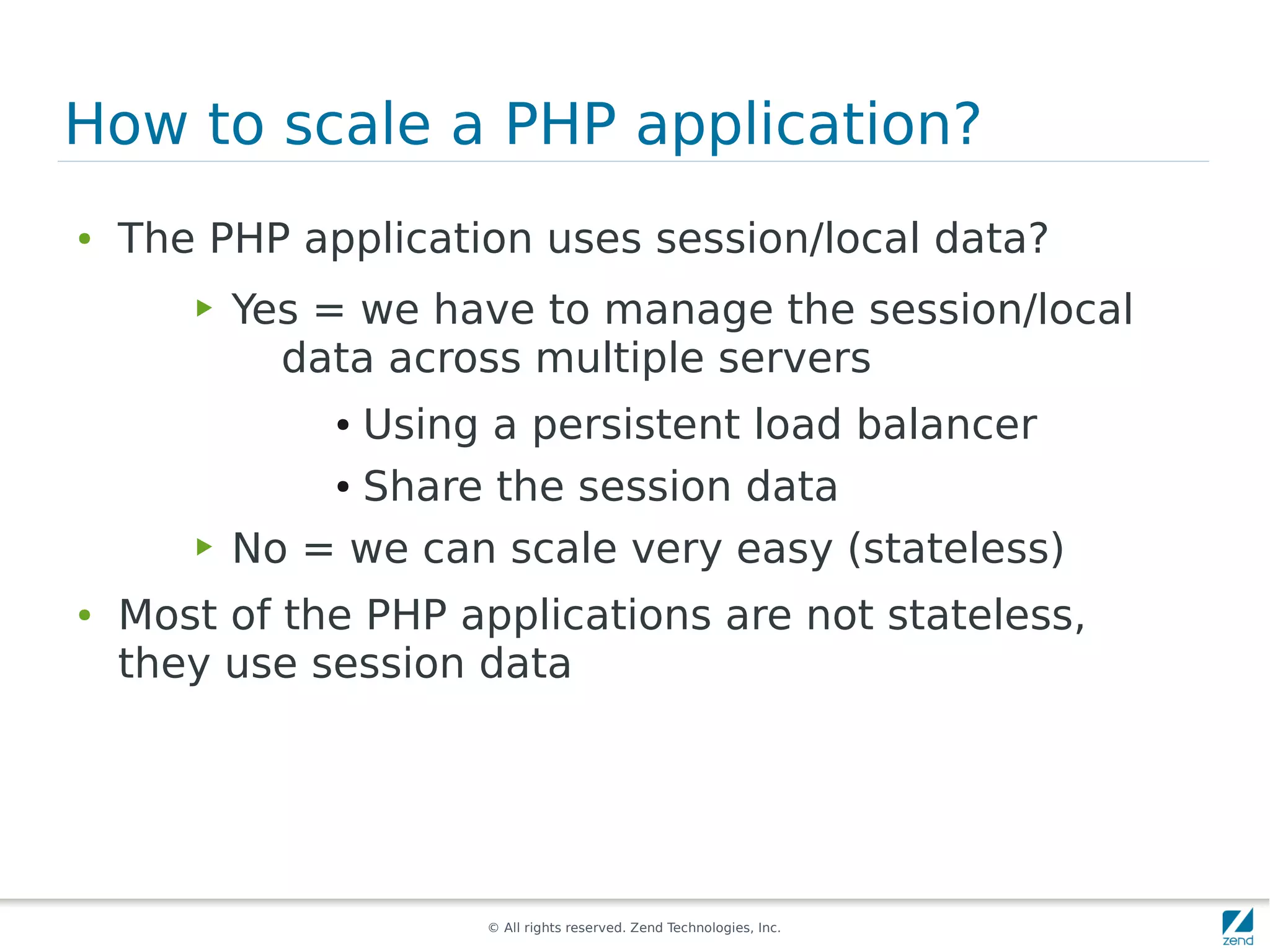
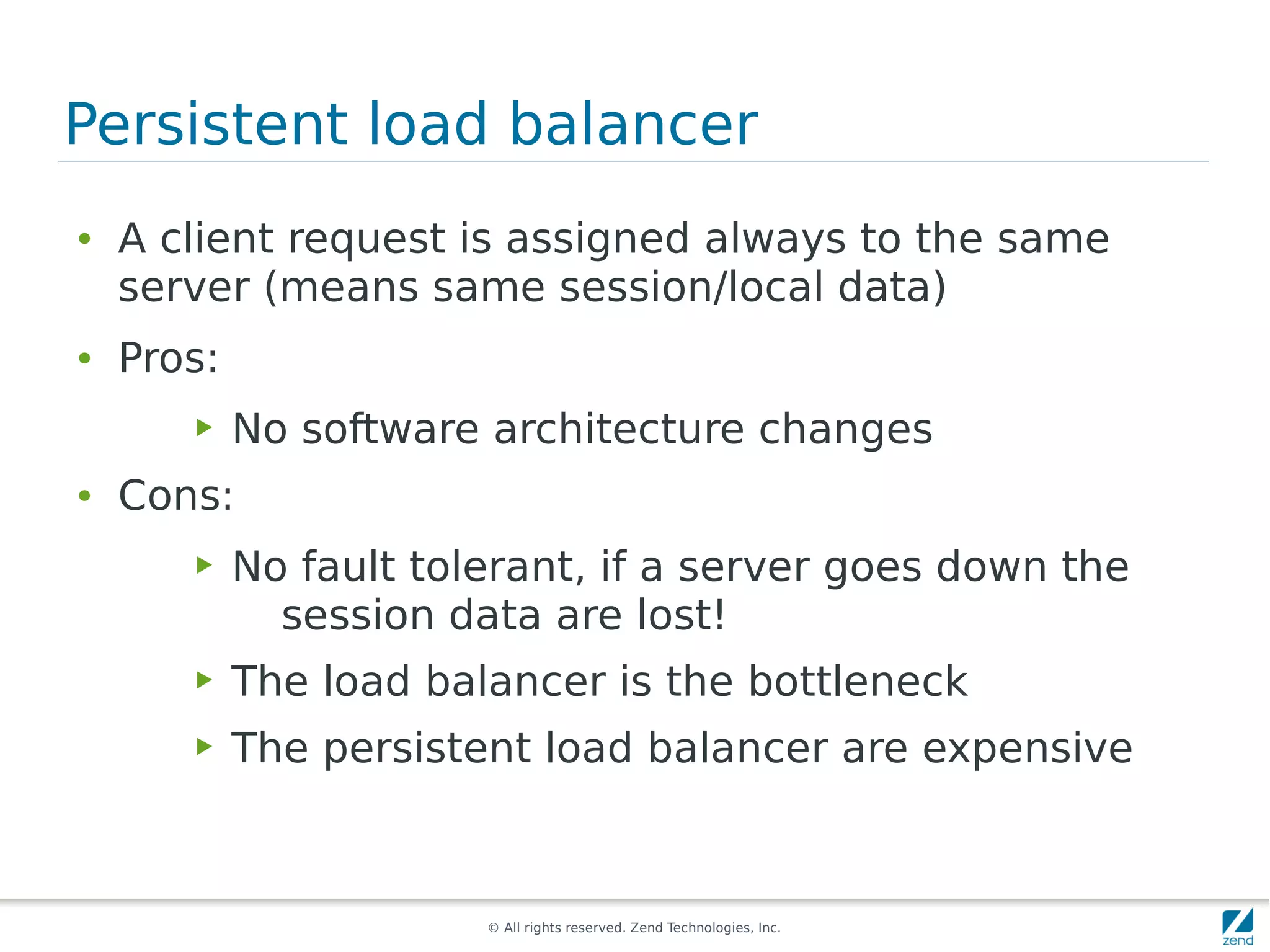
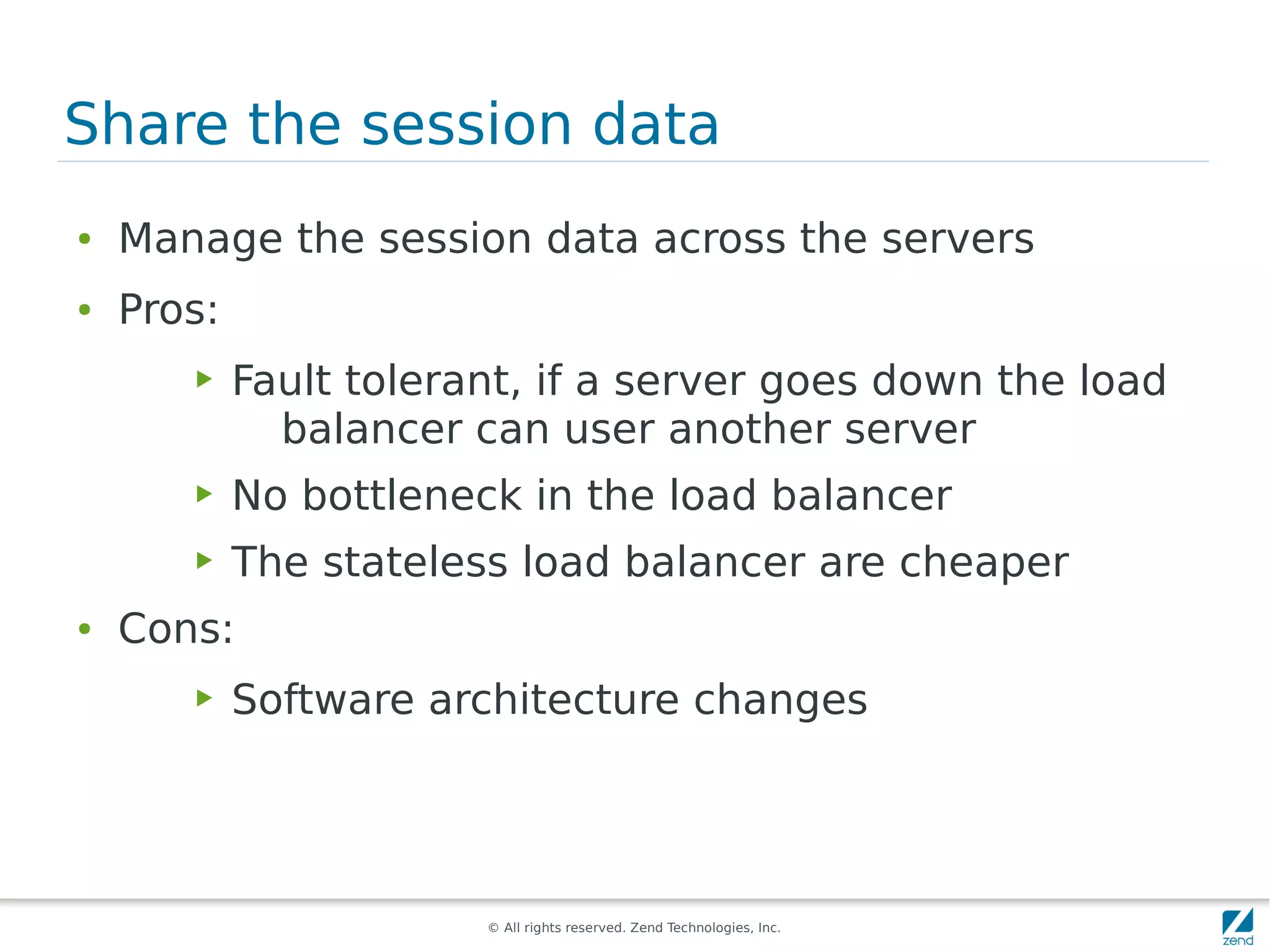
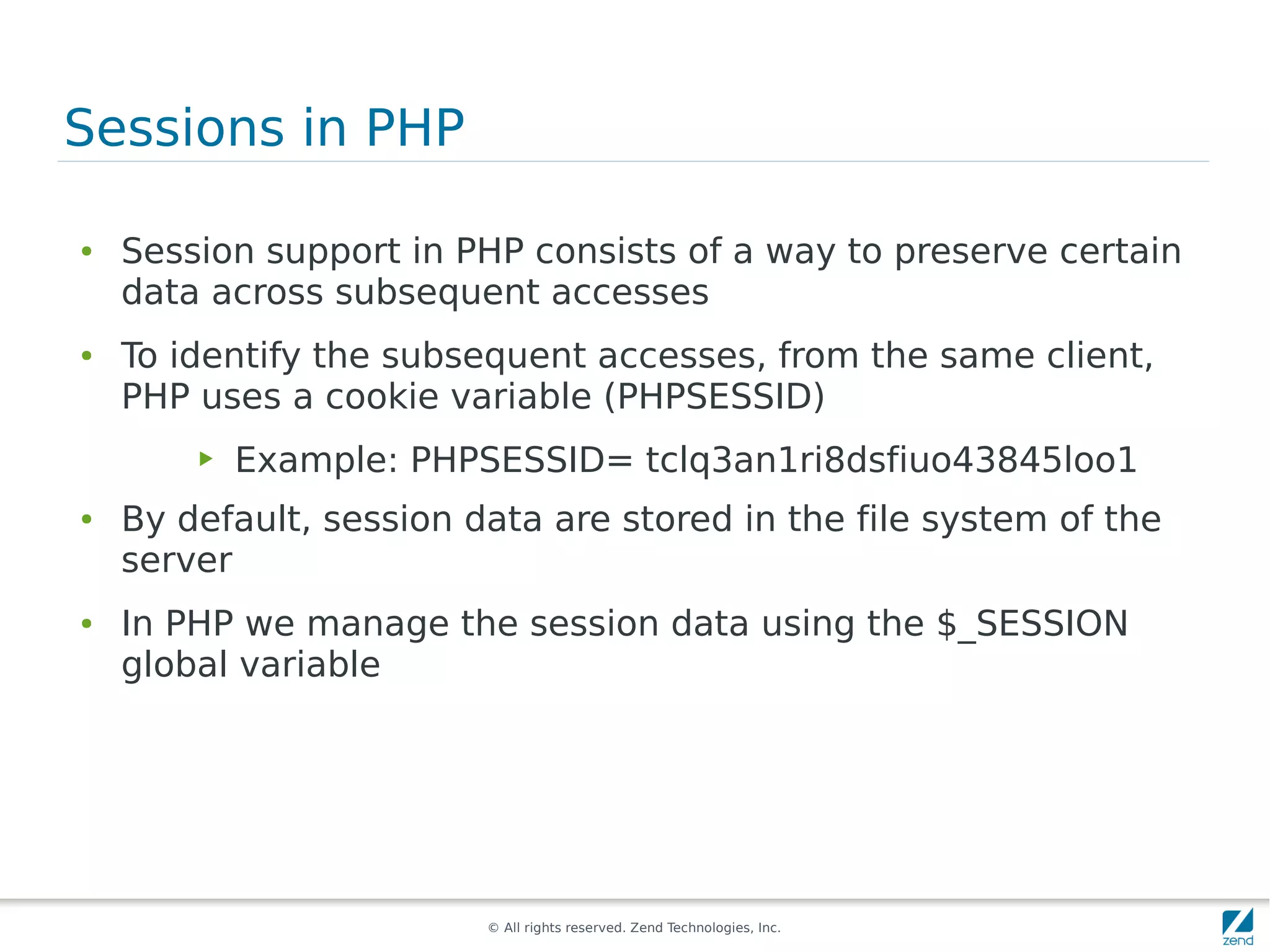
The document discusses strategies for scaling PHP applications, emphasizing the importance of managing session data for scalability. It highlights the differences between vertical and horizontal scaling, along with various methods for session management, including using databases, memcached, and Redis. Additionally, it outlines the benefits and drawbacks of each method and introduces Zend Server and its cluster manager for high availability and performance.






![© All rights reserved. Zend Technologies, Inc. Example (PHP sessions using files) ● <?php session_start(); $_SESSION['user']= 'enrico'; ● In session folder (for instance, /tmp) the PHP creates a file named sess_fvi9r84f14sjel8r28o6aqspr2 (where fvi9r84f14sjel8r28o6aqspr2 is PHPSESSID) that contains: user|s:6:"enrico";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/howtoscalephpapplications-101030051510-phpapp02/75/How-to-scale-PHP-applications-17-2048.jpg)