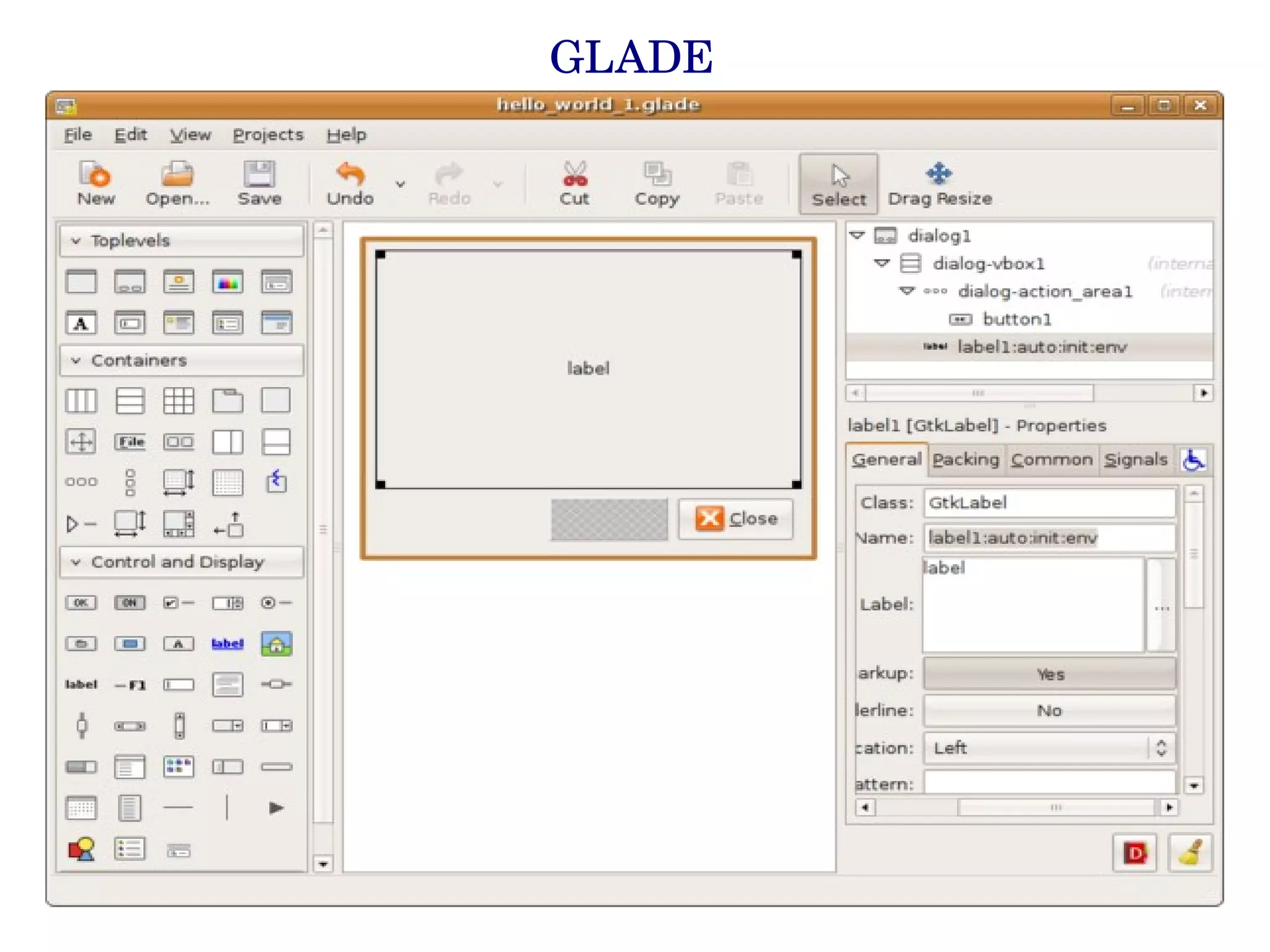
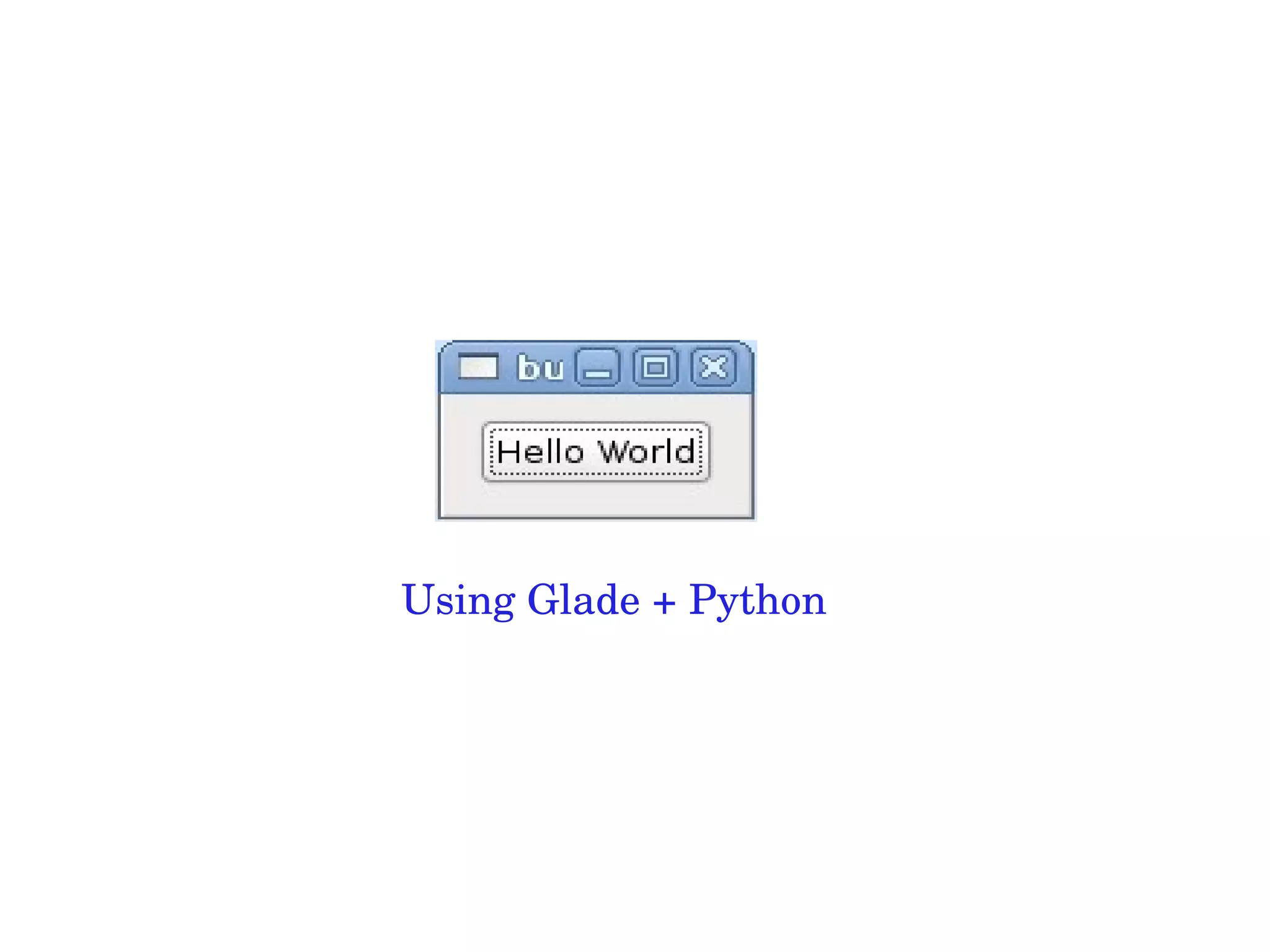
Python is a simple yet powerful programming language that can be used for a wide range of applications from web development to data science. It has an easy to read syntax and is easy to learn. Some key features of Python include being interpreted, having dynamic typing, automatic memory management, and being open source. Python can be used for tasks like text processing, system administration, GUI programming, web applications, databases, scientific computing, and more. It has a large standard library and can interface with other languages like C/C++ and Java.























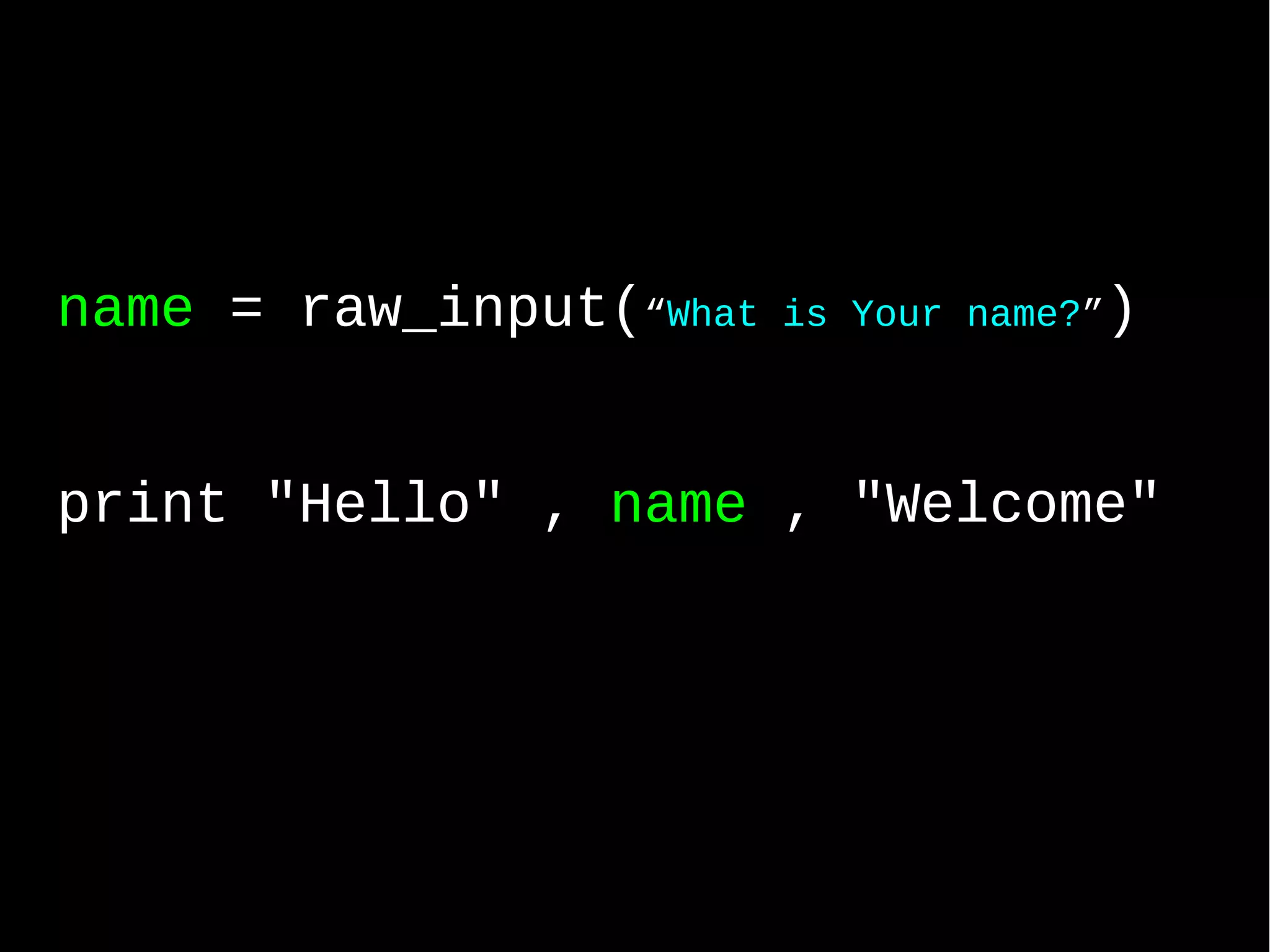











![List = Array numbers = [ "zero", "one", "two", "three", "FOUR" ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-42-2048.jpg)
![List = Array numbers = [ "zero", "one", "two", "three", "FOUR" ] numbers[0] >>> zero numbers[4] numbers[1] >>> FOUR >>> FOUR numbers[2] >>> three](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-43-2048.jpg)
![Multi Dimension List numbers = [ ["zero", "one"], ["two", "three", "FOUR" ] ] numbers[0] >>> ["zero", "one"] numbers[0][0] numbers[1][1] >>> zero >>> FOUR len(numbers) >>> 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-44-2048.jpg)
![Sort List primes = [ 11, 5, 7, 2, 13, 3 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-45-2048.jpg)
![Sort List primes = [ 11, 5, 7, 2, 13, 3 ] primes.sort()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-46-2048.jpg)
![Sort List primes = [ 11, 5, 7, 2, 13, 3 ] primes.sort() >>> [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-47-2048.jpg)
![Sort List names = [ "Shrini", "Bala", "Suresh", "Arul"] names.sort() >>> ["Arul", "Bala","Shrini","Suresh"] names.reverse() >>> ["Suresh","Shrini","Bala","Arul"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-48-2048.jpg)
![Mixed List names = [ "Shrini", 10, "Arul", 75.54] names[1]+10 >>> 20 names[2].upper() >>> ARUL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-49-2048.jpg)
![Append on List numbers = [ 1,3,5,7] numbers.append(9) >>> [1,3,5,7,9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-50-2048.jpg)



![name = 'Arul' name[0] >>>'A' myname = 'Arul' + 'alan' >>> 'Arulalan'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-54-2048.jpg)
![name = 'This is python string' name.split(' ') >>> ['This', 'is', 'python', 'string'] comma = 'Shrini,Arul,Suresh' comma.split(',') >>> ['Shrini', 'Arul', 'Suresh'] split](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-55-2048.jpg)
![li = ['a','b','c','d'] new = ''.join(li) >>> 'abcd' new.split('') >>> ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] join](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-56-2048.jpg)


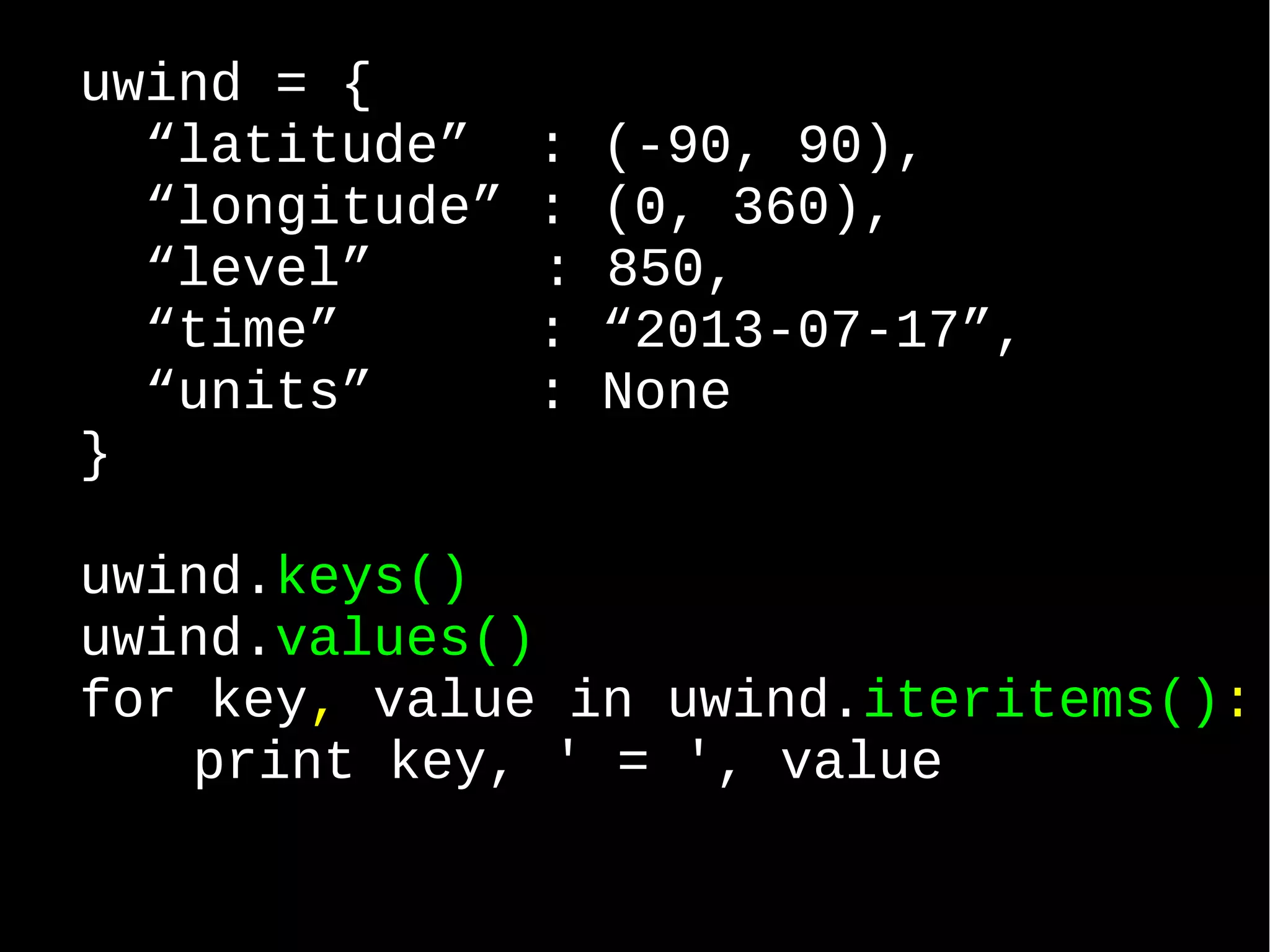
![menu = { “idly” : 2.50, “dosai” : 10.00, “coffee” : 5.00, “ice_cream” : 5.00, 100 : “Hundred” } >>> menu[“idly”] 2.50 >>> menu[100] ”Hundred” >>> menu.get(“tea”, None) None](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-an-introv2-130718042003-phpapp01/75/Python-an-intro-v2-59-2048.jpg)