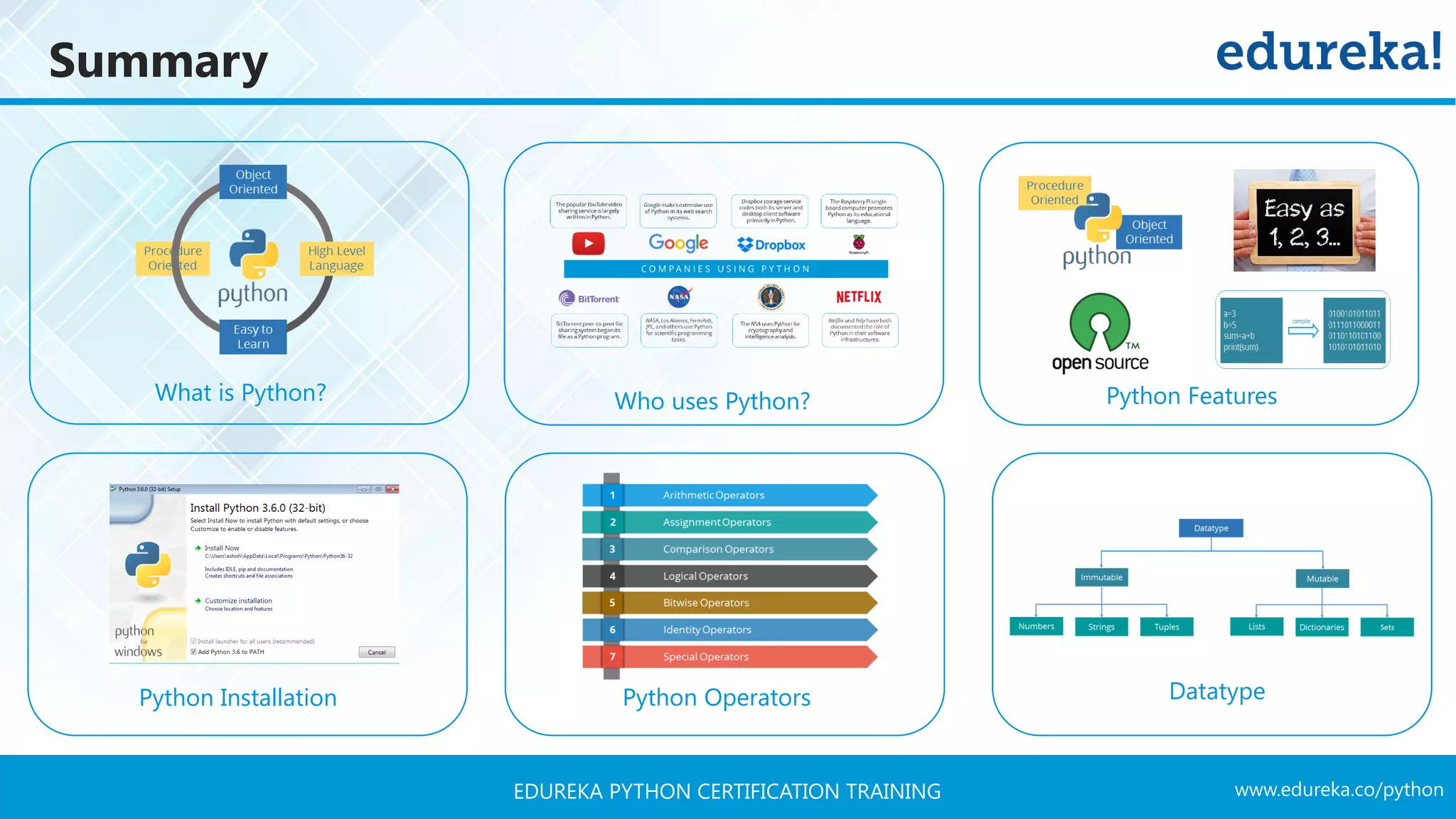
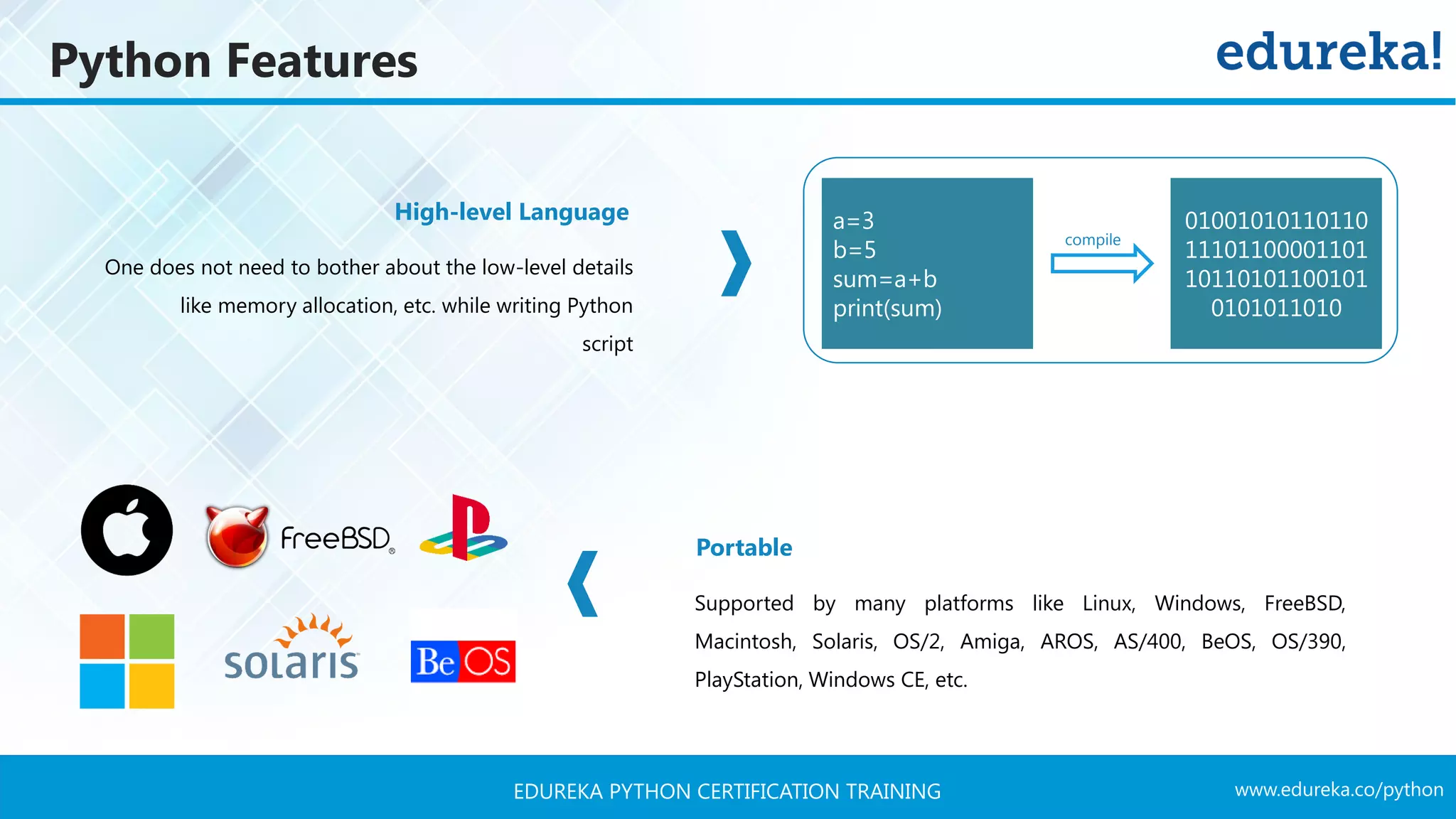
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Python programming, covering its introduction, features, and various data types such as strings, lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets. It highlights Python's ease of use, portability, and support for multiple programming paradigms, along with practical examples of operators and methods. Additionally, it includes installation steps and identifies notable companies and applications that utilize Python.
















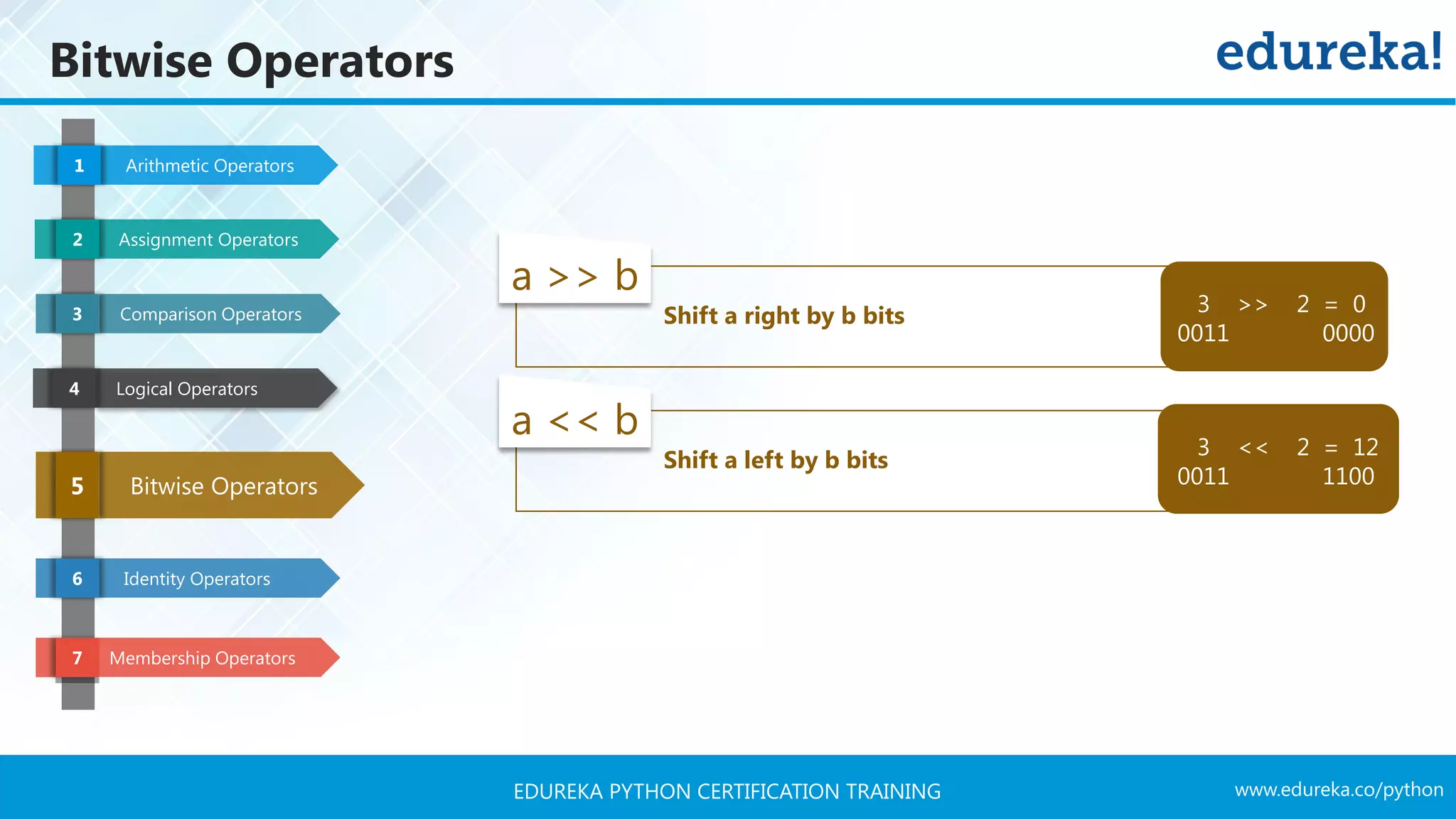

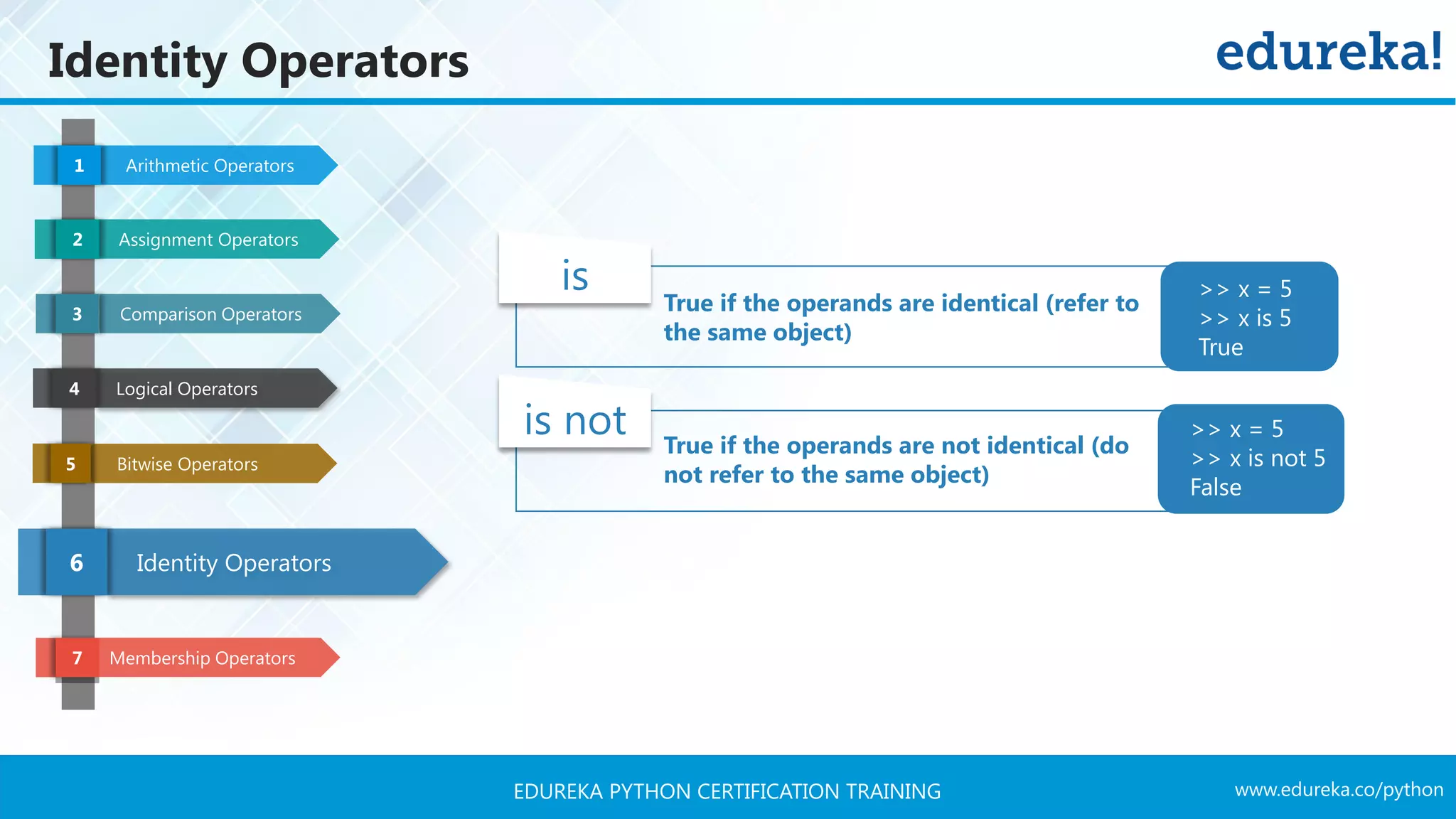

![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Membership Operators Arithmetic Operators1 Assignment Operators2 Comparison Operators3 Logical Operators4 Bitwise Operators5 Identity Operators6 Membership Operators7 is True if the operands are identical (refer to the same object) is not True if the operands are not identical (do not refer to the same object) >> 3 in x True >> 3 not in x False X = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-35-2048.jpg)
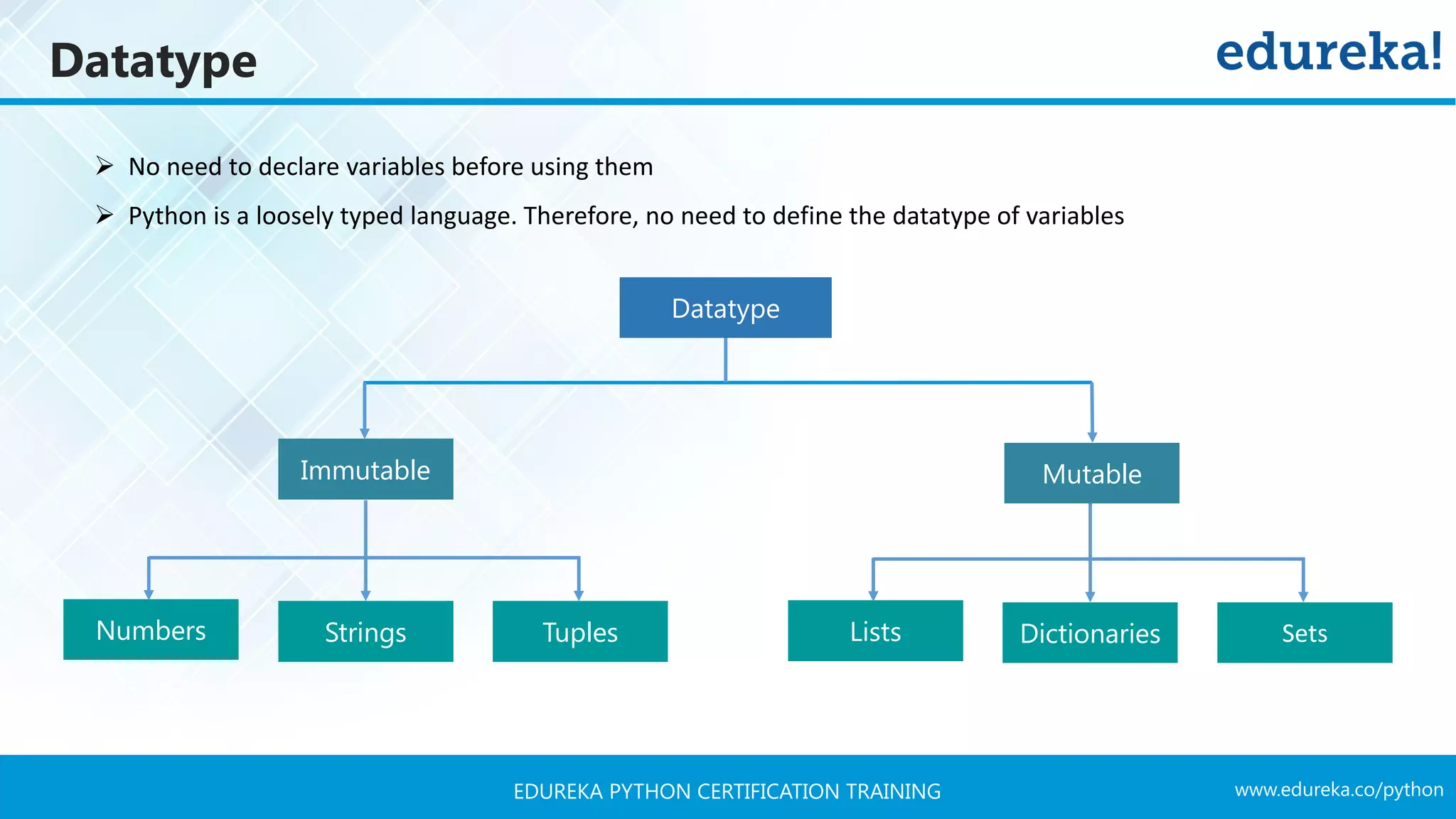

![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Sequence Operations: ➢ Concatenation: ➢ Repetition ➢ Slicing ➢ Indexing ‘Python’ ‘Tutorial’ ‘Edureka Tutorial’ ‘Edureka’ 2 ‘EdurekaEdureka’ ** string1 = ‘Edureka’ string1[2:7] ‘ureka’ string1 = ‘Edureka’ string1[-1] + string[1] ‘da’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-40-2048.jpg)
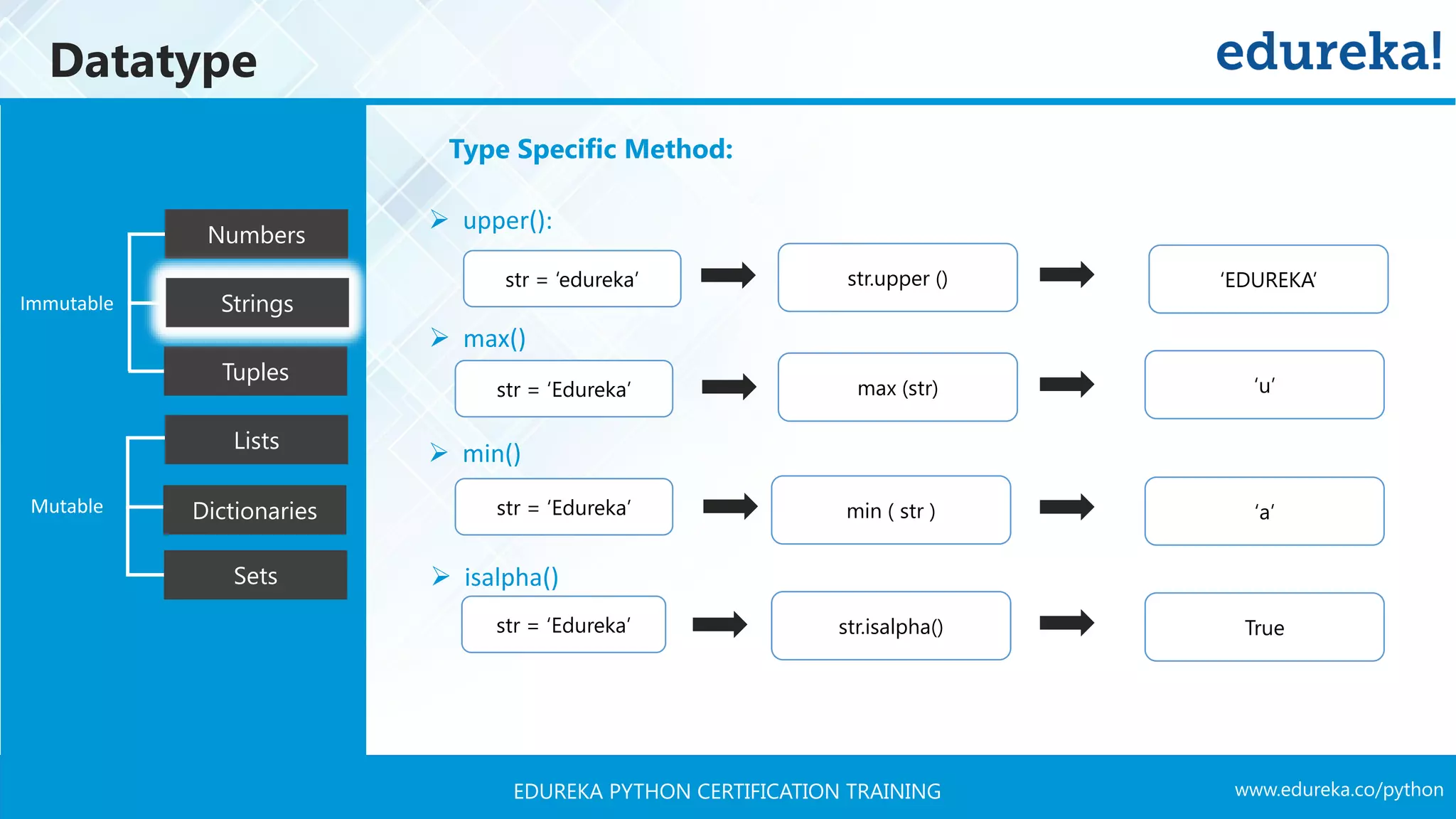
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Type Specific Method: ➢ find(): ➢ replace() ➢ split() ➢ count() str = ‘Edureka’ str.find ( ‘ureka’ ) ‘ureka’ str = ‘Edureka’ str.replace ( ‘Ed’,’E’ ) ‘Eureka’ str = ‘E, d, u, r, e, k, a’ s.split ( ‘,’ ) [‘E’, ‘d’, ‘u’, ‘r’, ‘e’, ‘k’, ‘a’] str = ‘Edureka’ str.count(‘e’, beg=2, end=6) 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-41-2048.jpg)

![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Sequence Operations: ➢ Concatenation: ➢ Repetition ➢ Slicing ➢ Indexing tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup +( ‘d’ ) ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ , ‘d’ ) tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup[1:2] ( ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup[0] ‘a’ tup = ( ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ) tup * 2 (‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ , ‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-44-2048.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ A list is a sequence of mutable Python objects like floating number, string literals, etc. ➢ The lists can be modified ➢ Tuples are defined using square braces myList = [ ‘Edureka’ , 2.4, 5, ‘Python’ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-45-2048.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Sequence Operations: ➢ Concatenation: ➢ Repetition ➢ Slicing ➢ Indexing [ ‘1’ , ‘b’ , 2.5 ] ‘d’ [ 1 , ‘b’ , 2.5 , ‘d’ ] [ ‘a’ , ‘b’ , 2.5 ] 2 [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘a’ , ‘b’ ] ** list = [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’ ,’d’] list[1:3] ( ‘b’ , ‘c’, ‘d’ ) list = [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’] list[0] ‘a’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-46-2048.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable Type Specific Method ➢ append(value) ➢ extend(list) ➢ insert(index, value) ➢ pop() list = [1, ‘a’, 2.5] List.append (‘d’ ) [ 1 , ‘a’ , 2.5 , ‘d’ ] list = [1, ‘a’, 2.5] list.extend ( [‘c’, ‘d’] ) [1 , ‘a’ , 2.5 , ‘c’, ‘d’] list = [1, ‘a’, 2.5] List.insert(2,’b’) [1, ’a’, ‘b’ , 2.5 ] list = [‘a’ , ‘b’ , ‘c’] List.pop() [ ‘a’, ‘b’ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-47-2048.jpg)

![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ empty dictionary ➢ dictionary with integer keys ➢ dictionary with mixed keys ➢ from sequence having each item as a pair myDict = {} myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict = {'name': 'John', 1: [2, 4, 3]} myDict = dict([(1,'apple'), (2,'ball')]) Dictionary Examples](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-49-2048.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ Accessing Dictionary ➢ len() ➢ key() ➢ values() myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict [1] ‘apple’ len(myDict) 2 myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict.key() [1, 2] myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict.values() [‘apple’, ‘ball’] Dictionary Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-50-2048.jpg)
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Datatype Tuples Numbers Strings Lists Dictionaries Sets Mutable Immutable ➢ items() ➢ get() ➢ update() ➢ pop() myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict.items() [(1, ‘apple’), (2, ball)] myDict.get(1) ‘apple’ myDict = {1: ‘a', 2: ‘b'} myDict.update(3: ’c’) {1: ’a’, 2: ‘b’, 3: ‘c’} myDict = {1: 'apple', 2: 'ball'} myDict. pop(2) {1: ‘apple’} Dictionary Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-51-2048.jpg)


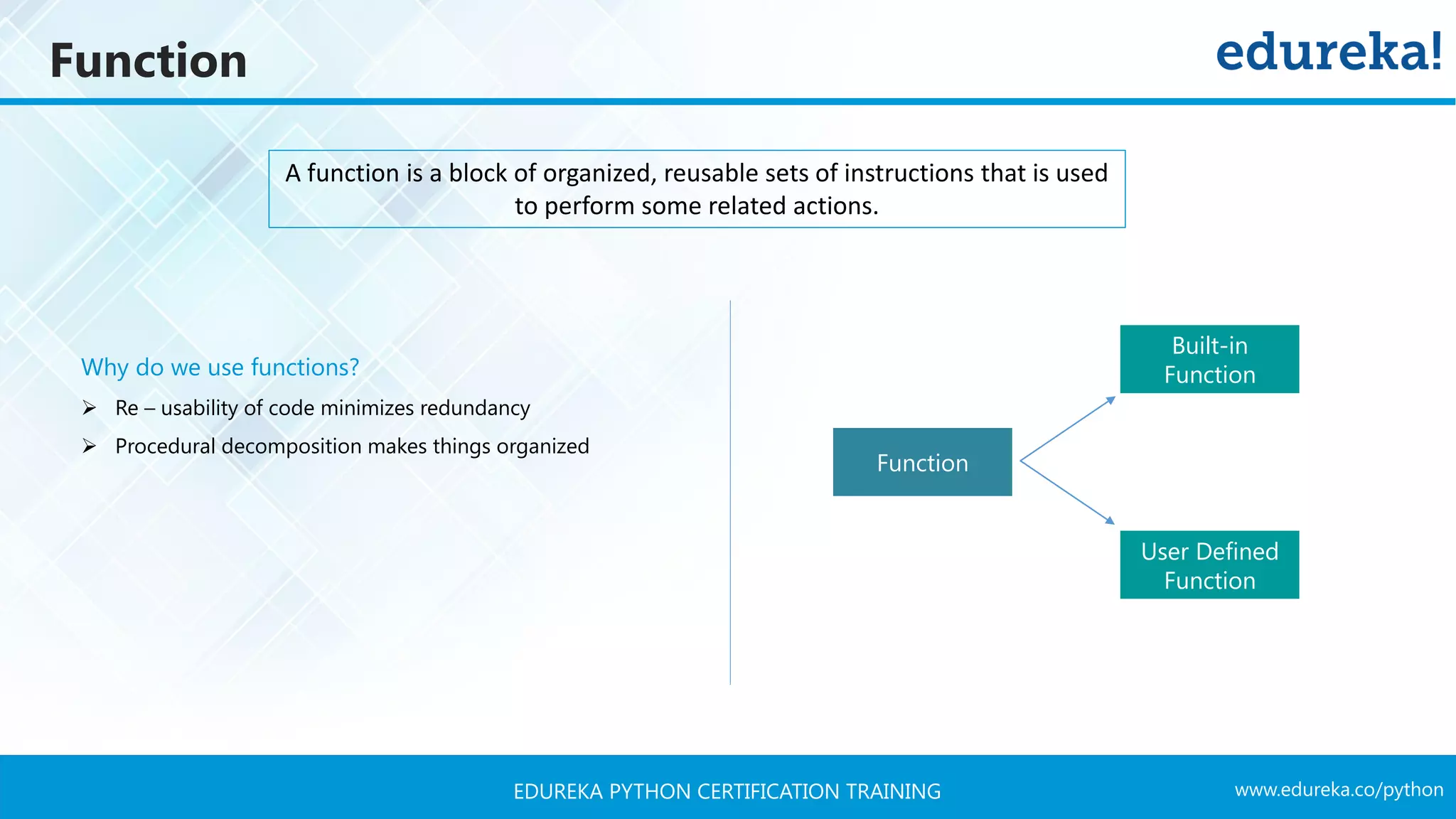
![www.edureka.co/pythonEDUREKA PYTHON CERTIFICATION TRAINING Function User Defined Function Syntax: def func_name (arg1, arg2, arg3, ….): statements… return [expression] Example: def add ( a, b ) sum = a + b return sum adding two number defining function Input variable print variable output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythontutorial-edureka-170424101234/75/Python-Tutorial-Python-Tutorial-for-Beginners-Python-Training-Edureka-65-2048.jpg)