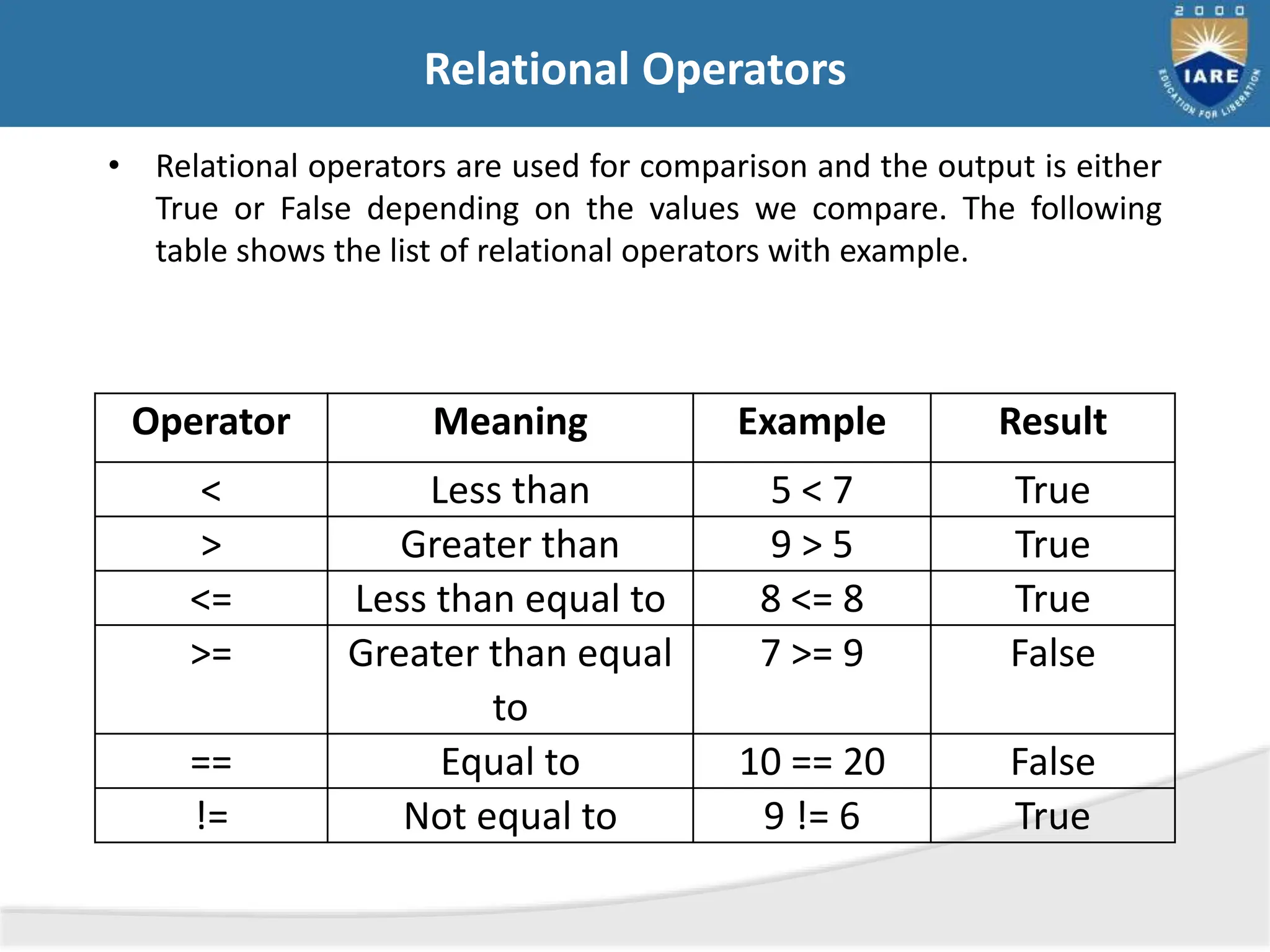
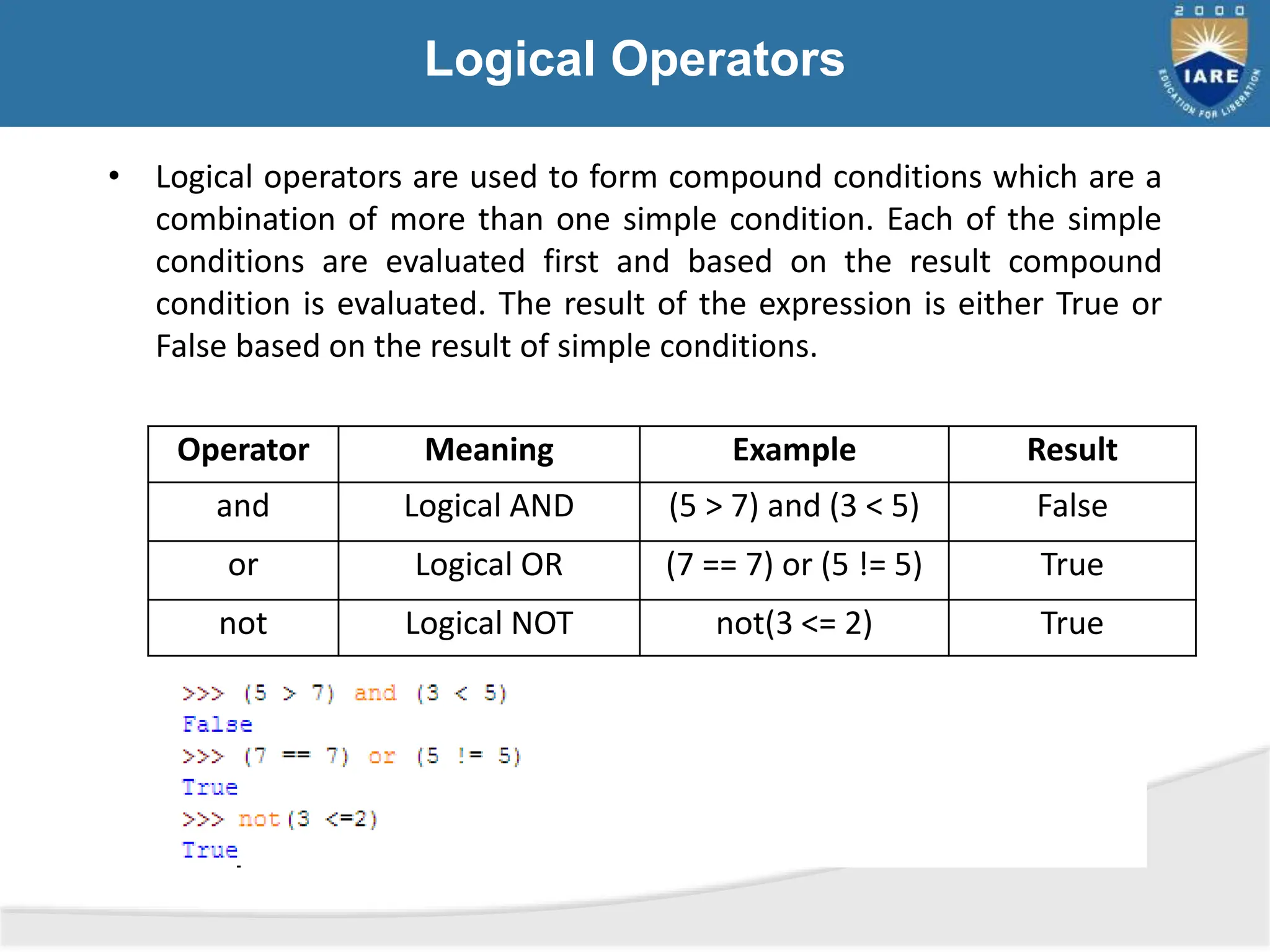
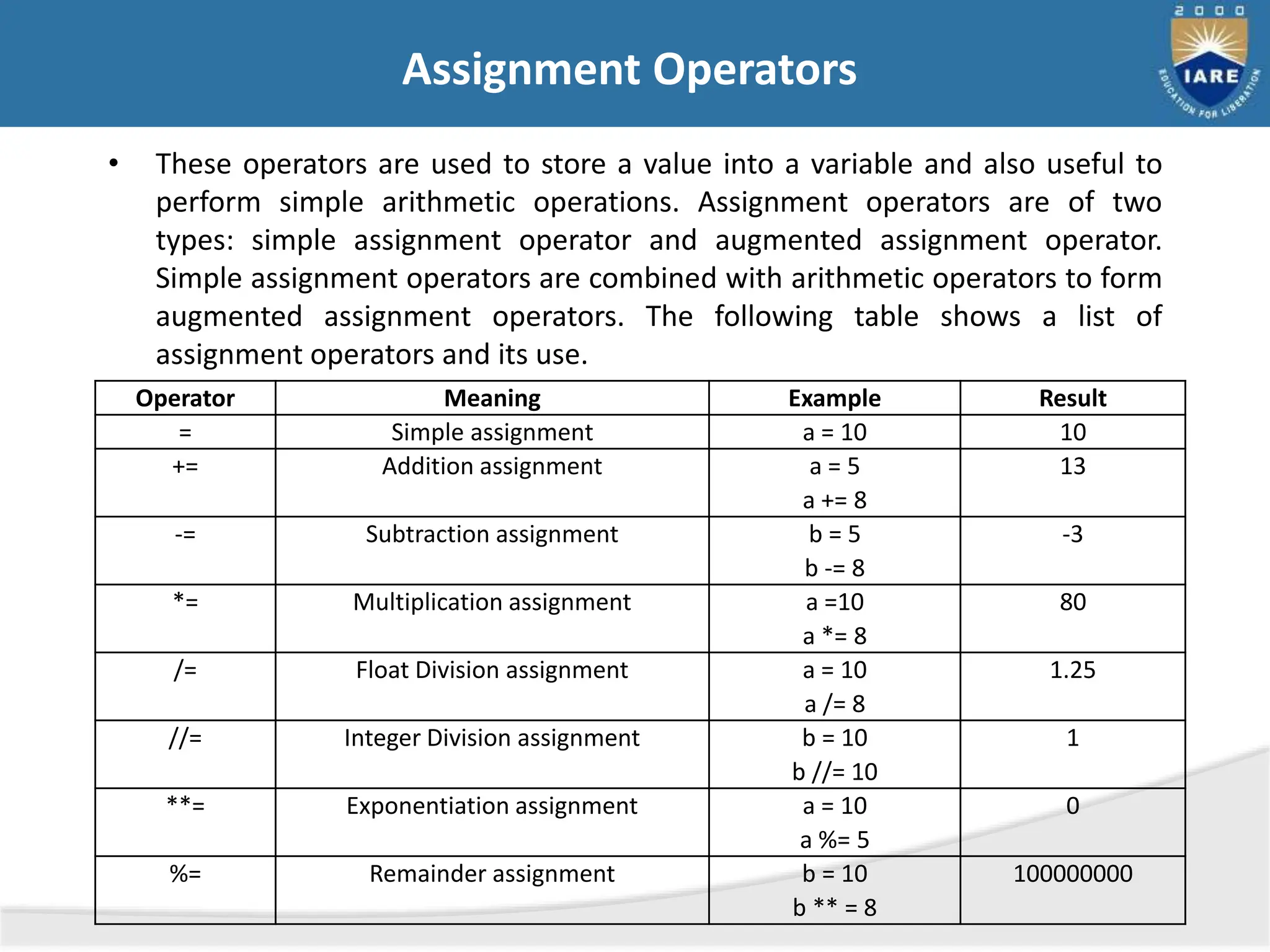
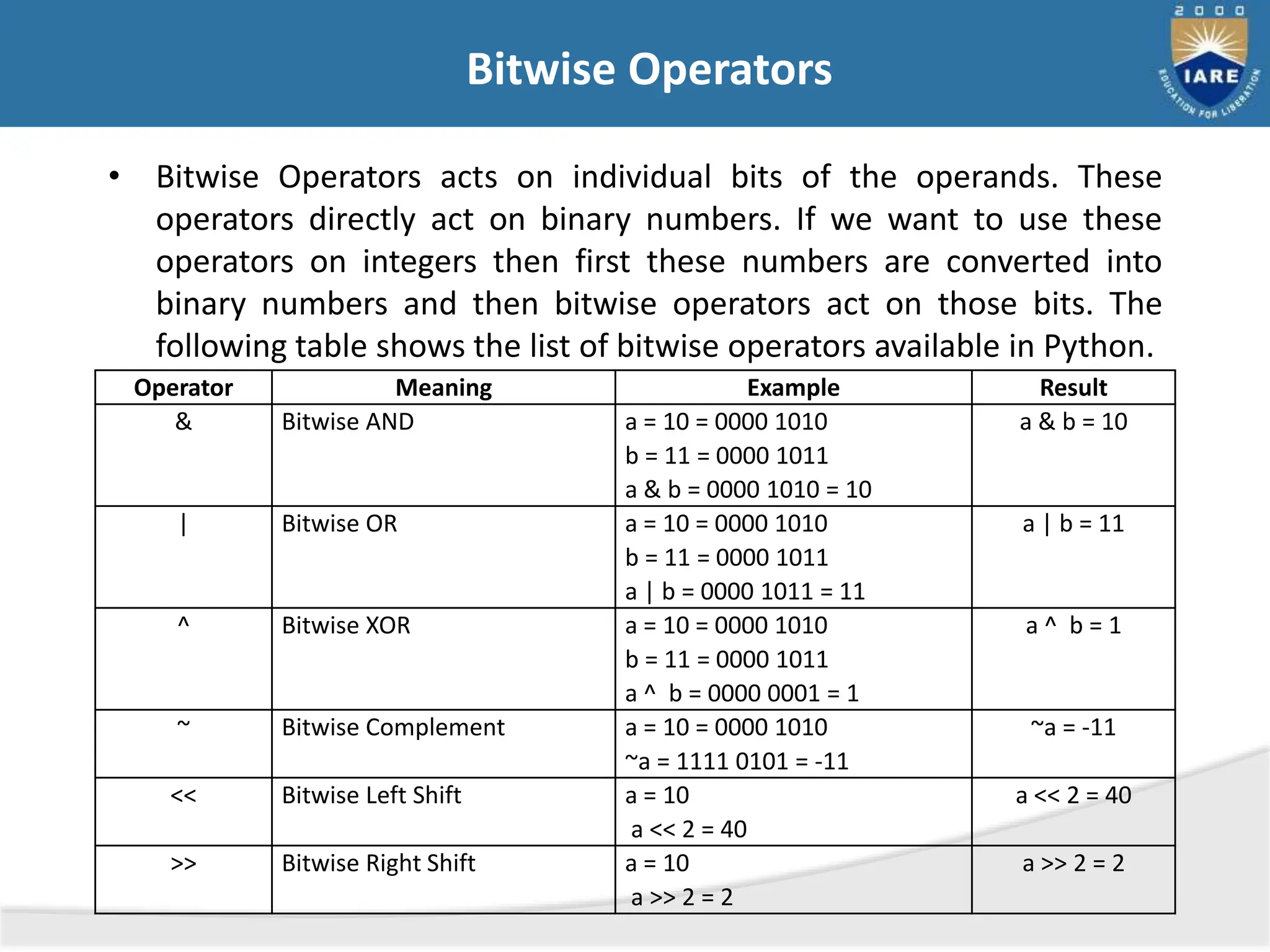
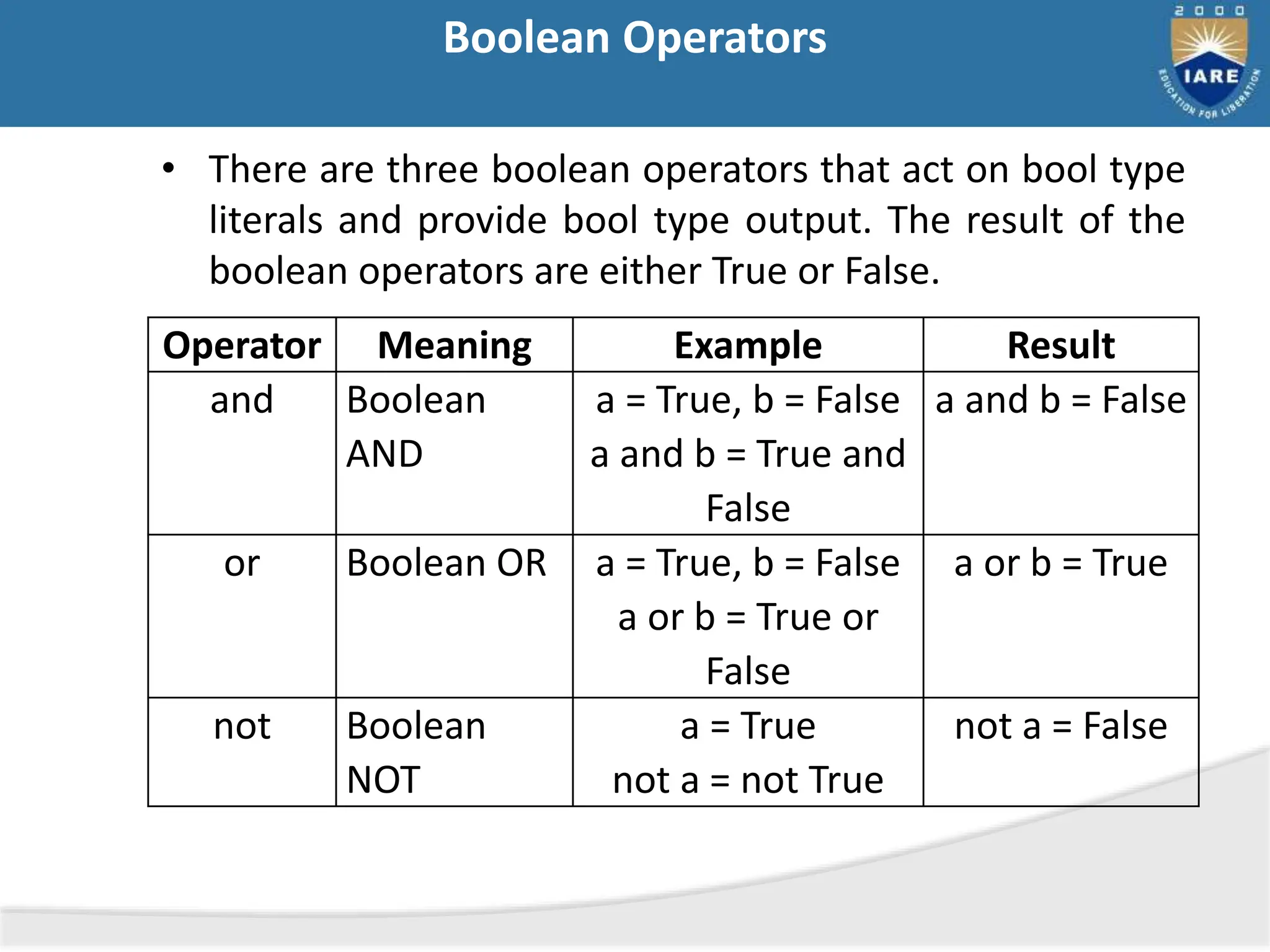
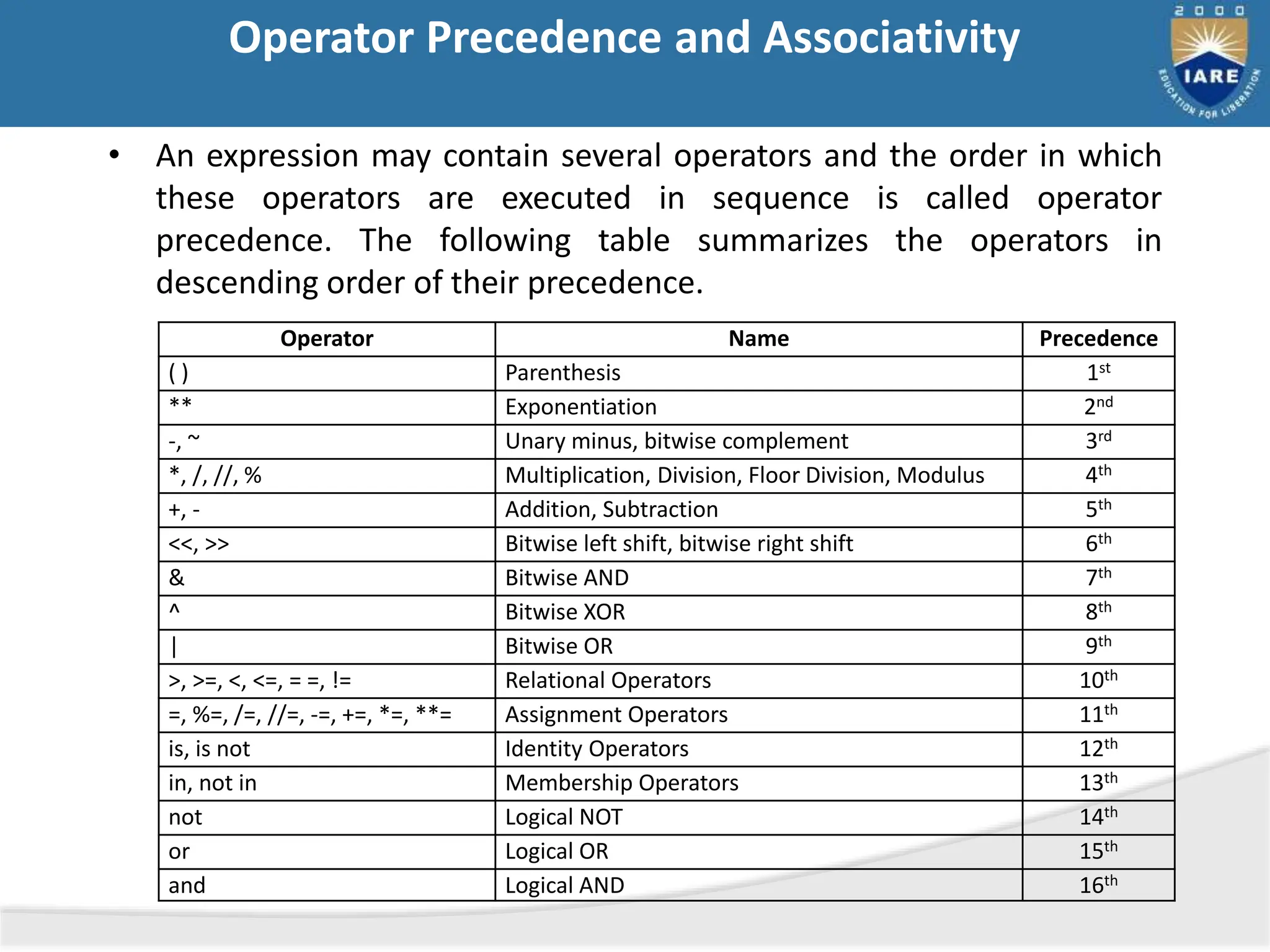
The document details various types of operators in Python, categorizing them into arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, bitwise, boolean, membership, and identity operators. It explains their functions with examples, operator precedence, and the use of comments for better code readability. Additionally, the document covers basic input and output operations necessary for data processing.

![Arithmetic Operators • These operators perform basic arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc. and these operators are binary operators that means these operators acts on two operands. And there are 7 binary arithmetic operators available in Python. Operator Meaning Example Result + Addition 10 + 7 12 - Subtraction 10.0 - 1.5 8.5 * Multiplication 30 * 3 900 / Float Division 5 / 2 2.5 // Integer Division 5 // 2 2 ** Exponentiation 3 ** 2 9 % Remainder 10 % 3 1 Operator Priority Parenthesis (( ), [ ]) First Exponentiation (**) Second Multiplication (*), Division (/, //), Modulus (%) Third Addition (+), Subtraction (-) Fourth Assignment Fifth](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsinpython-240511093649-fe31fe50/75/Operators-in-Python-Arithmetic-Operators-2-2048.jpg)