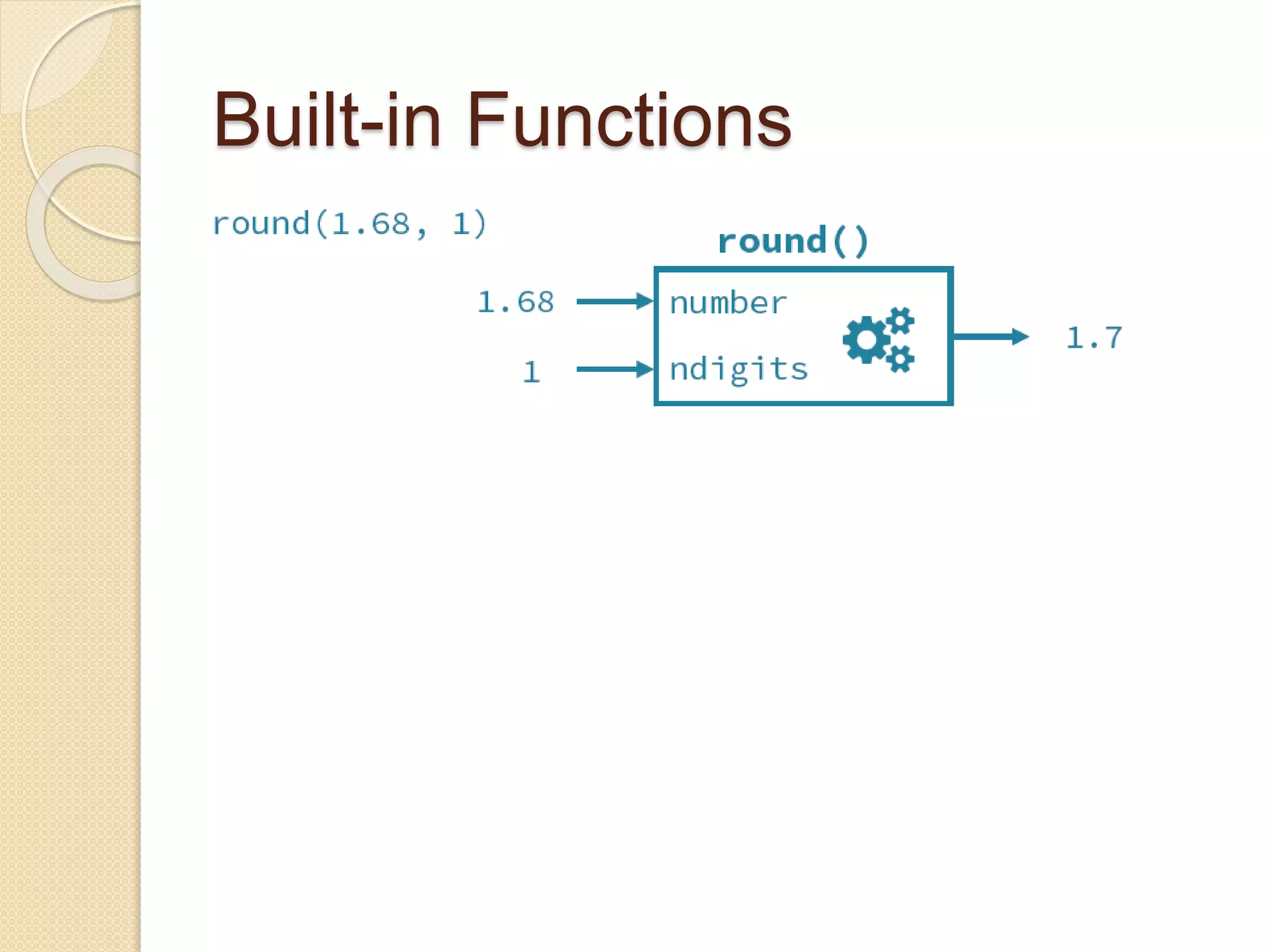
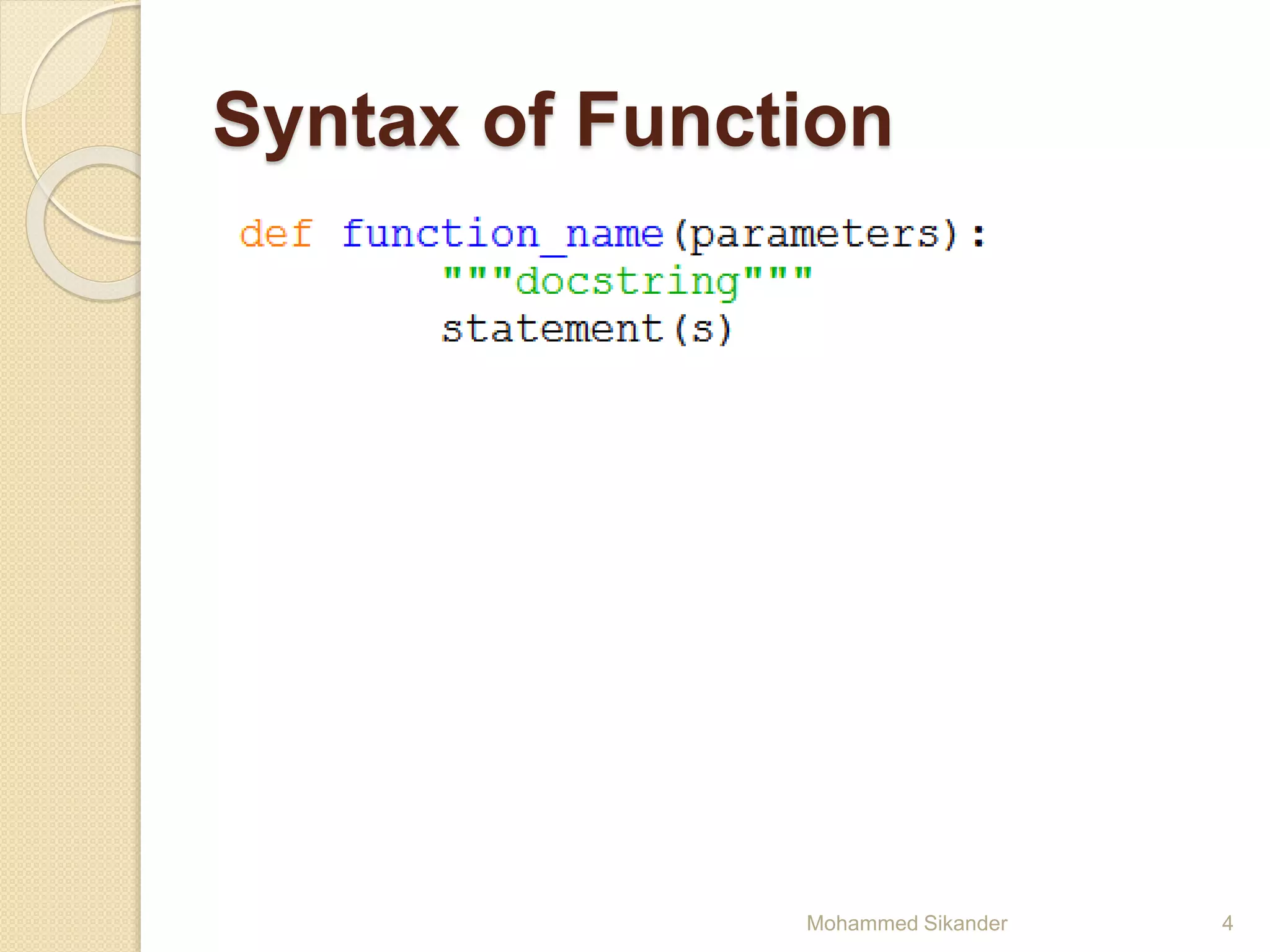
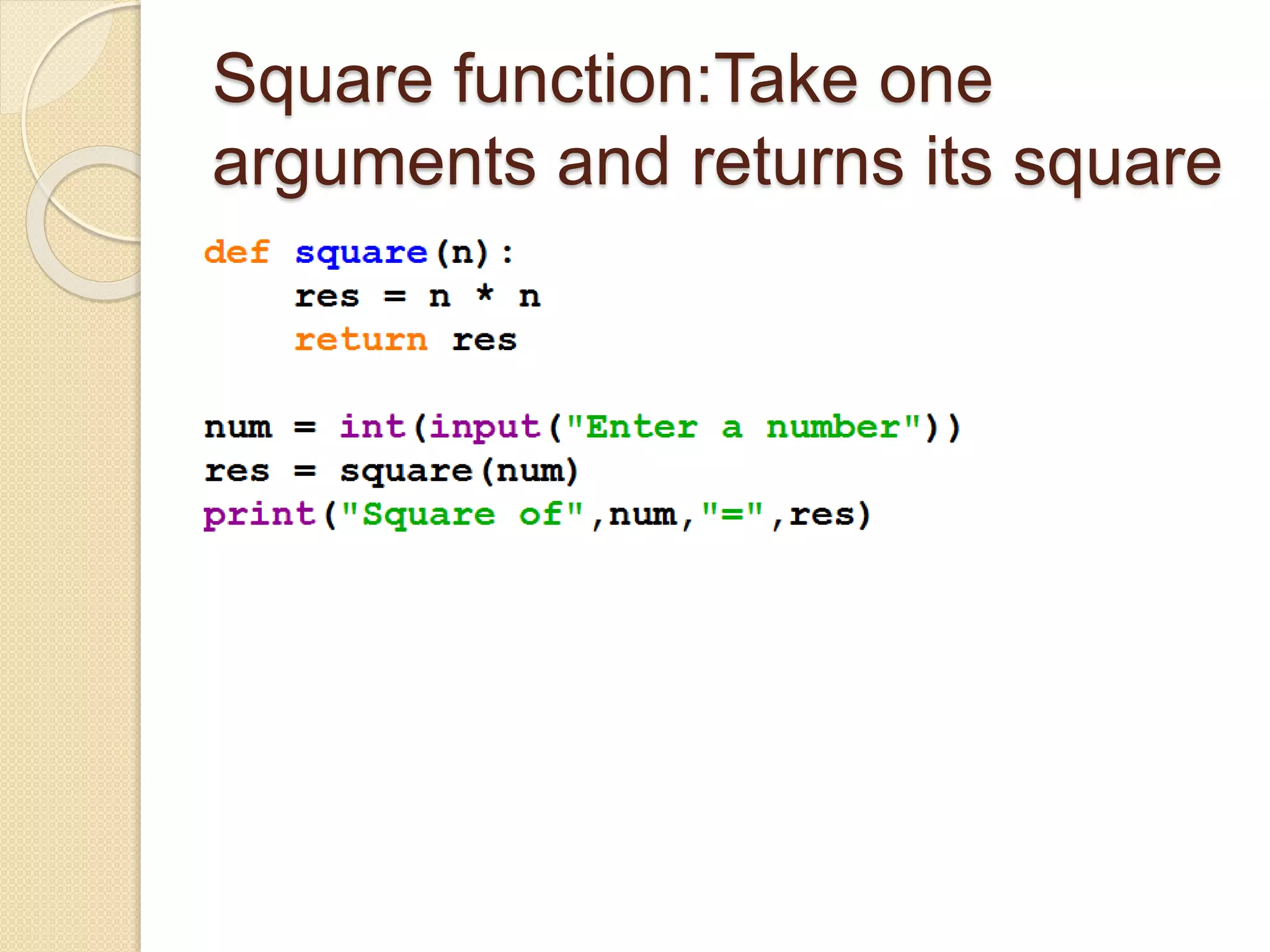
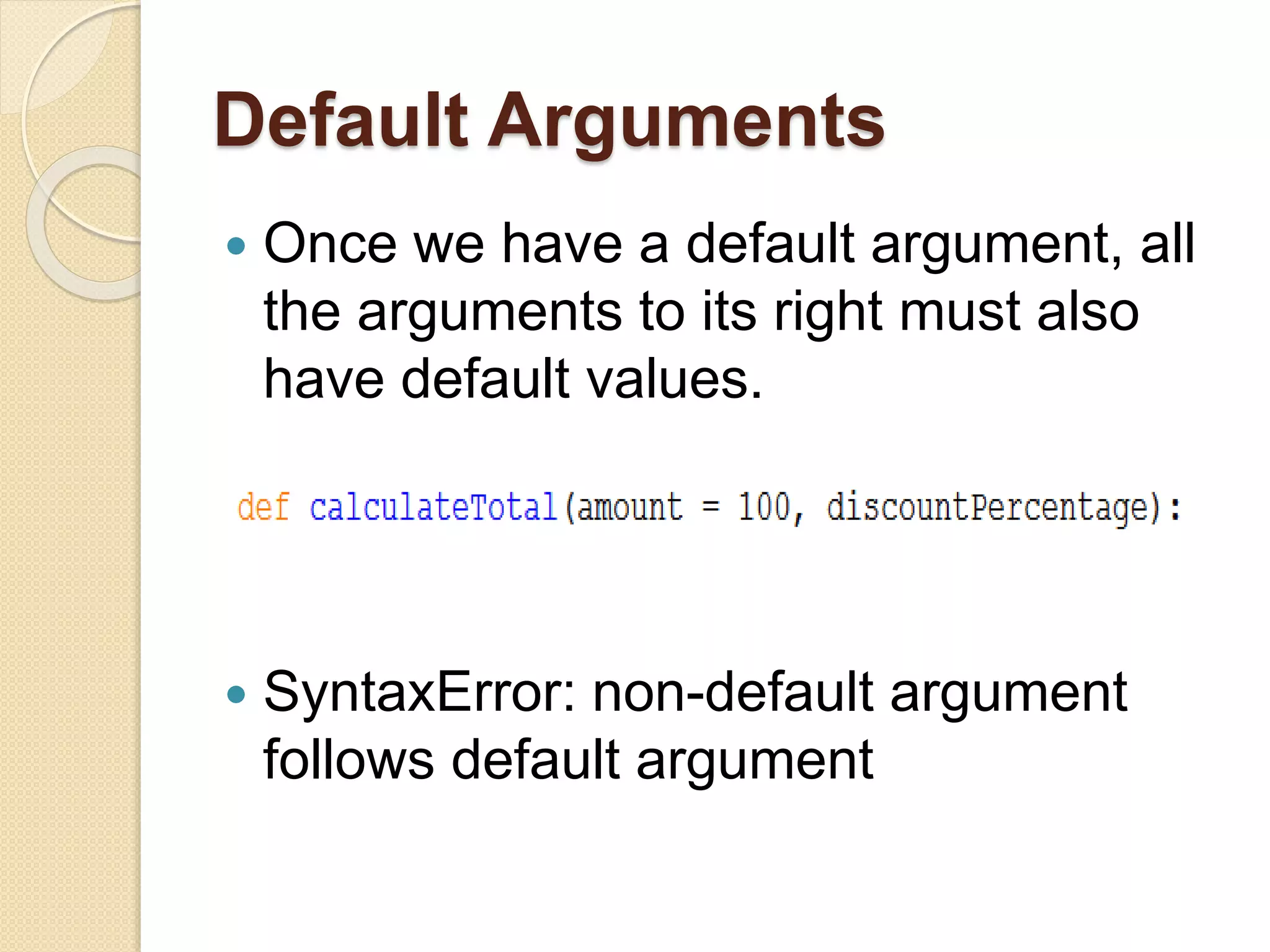
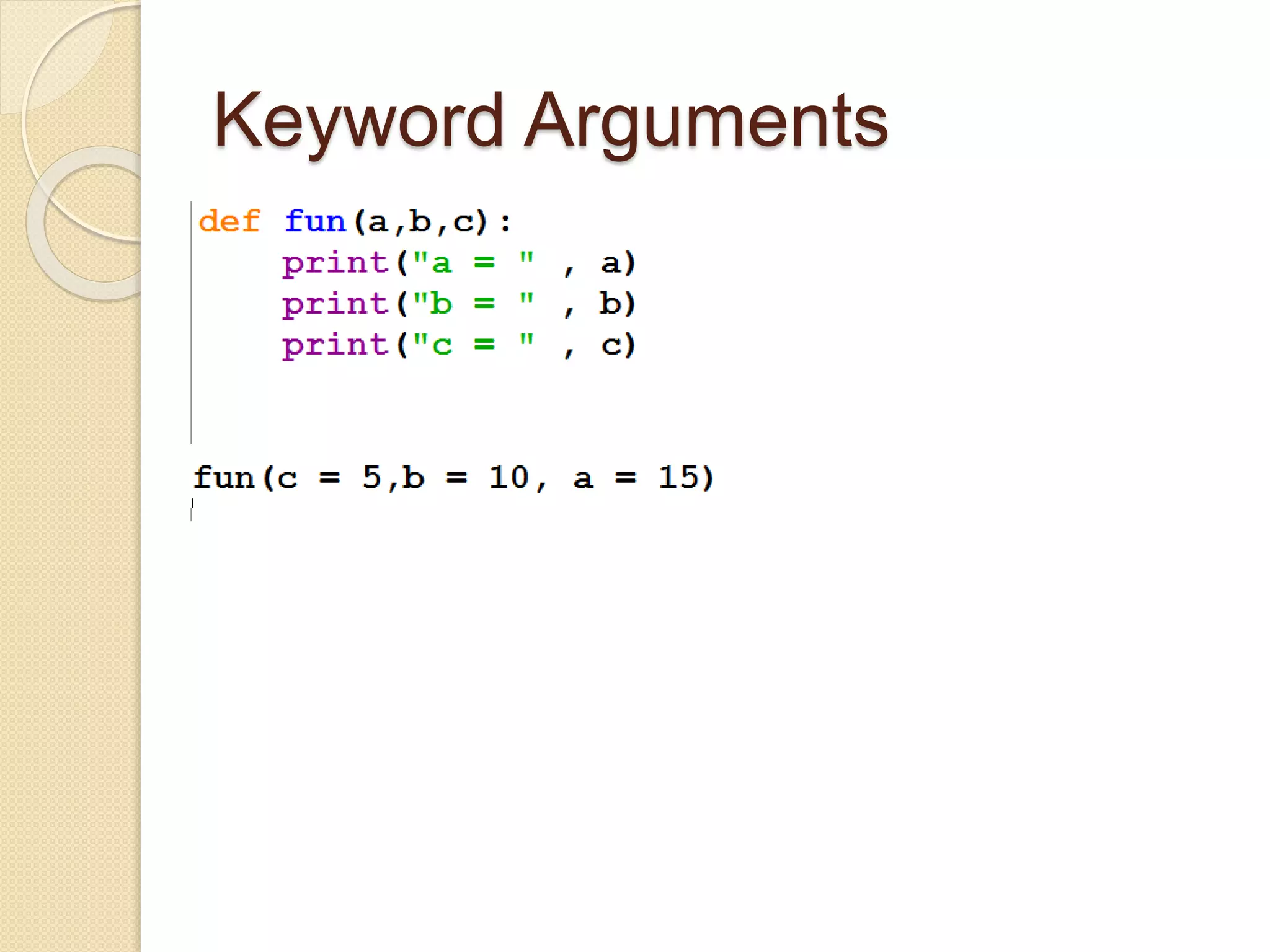
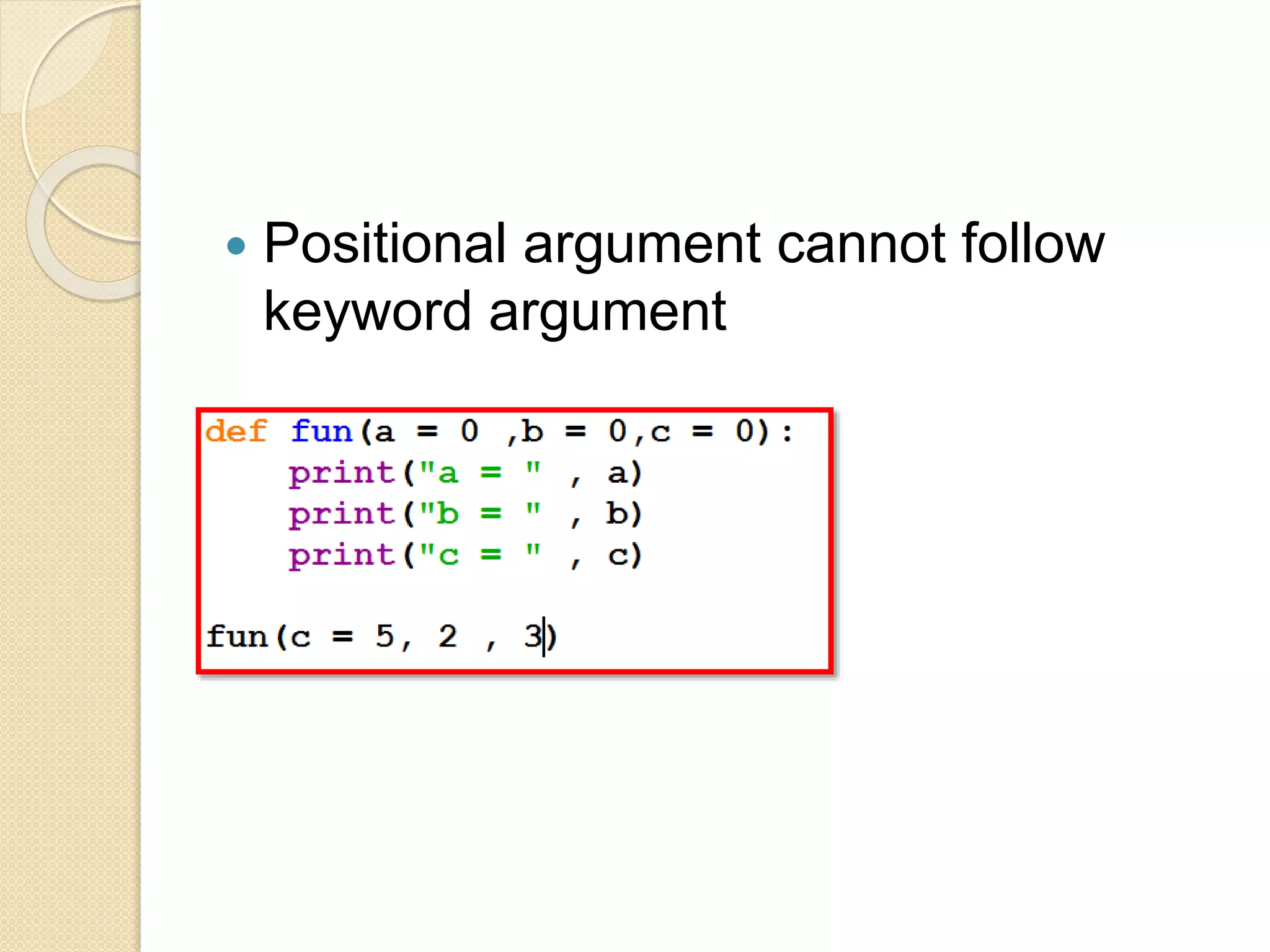
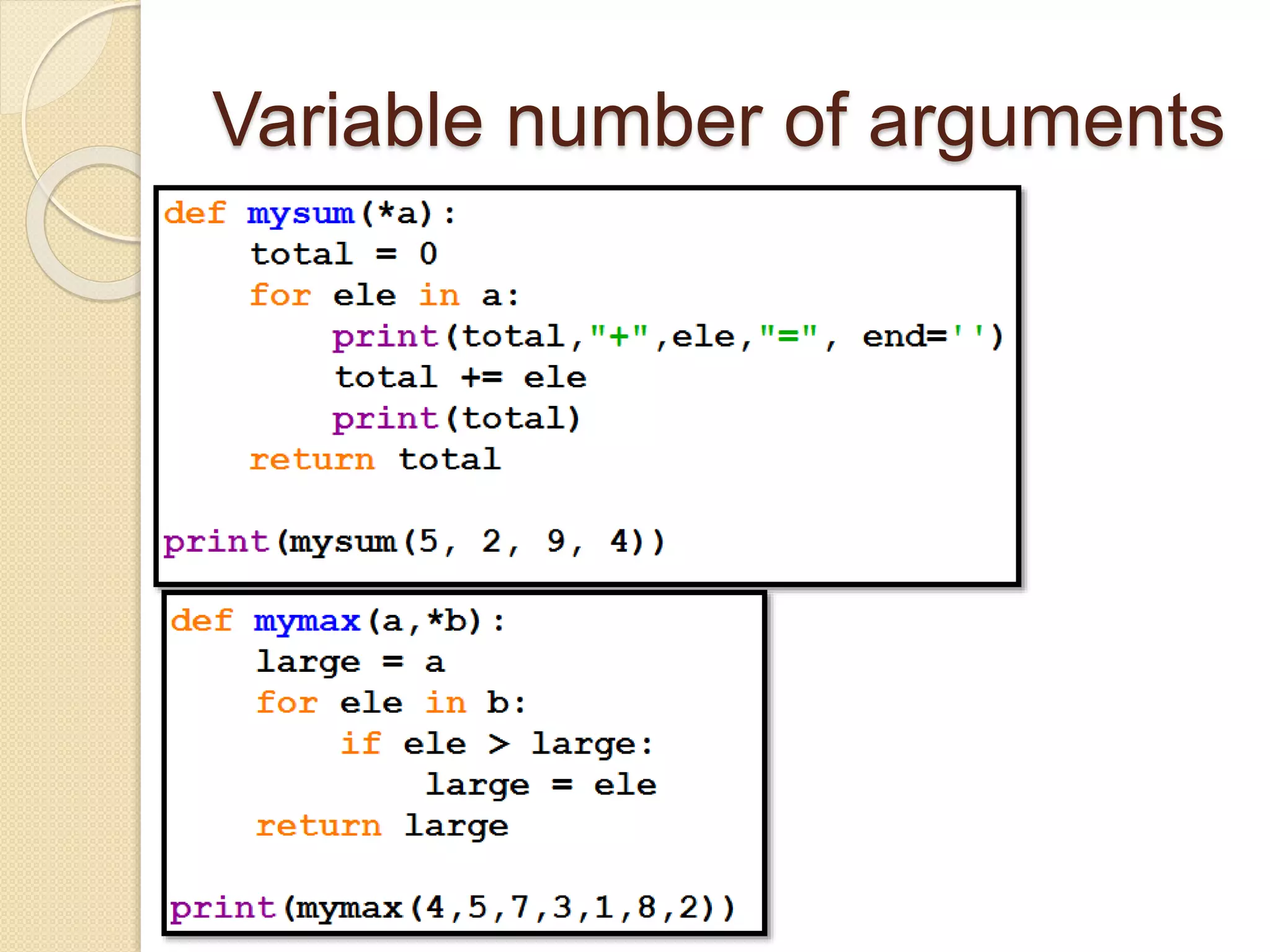
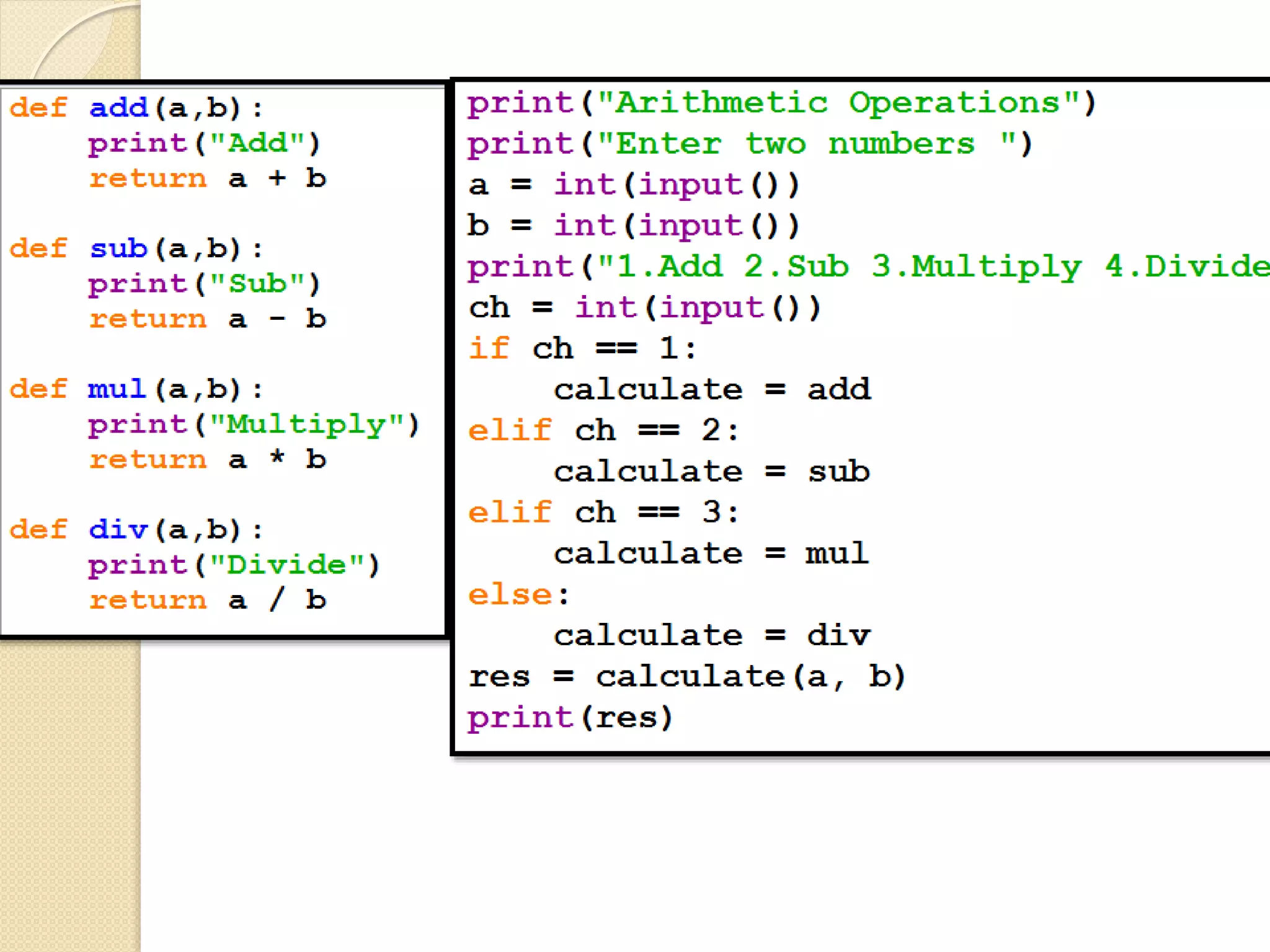
Python functions allow for reusable code through defining functions, passing arguments, returning values, and setting scopes. Functions can take positional or keyword arguments, as well as variable length arguments. Default arguments allow functions to specify default values for optional parameters. Functions are objects that can be assigned to variables and referenced later.