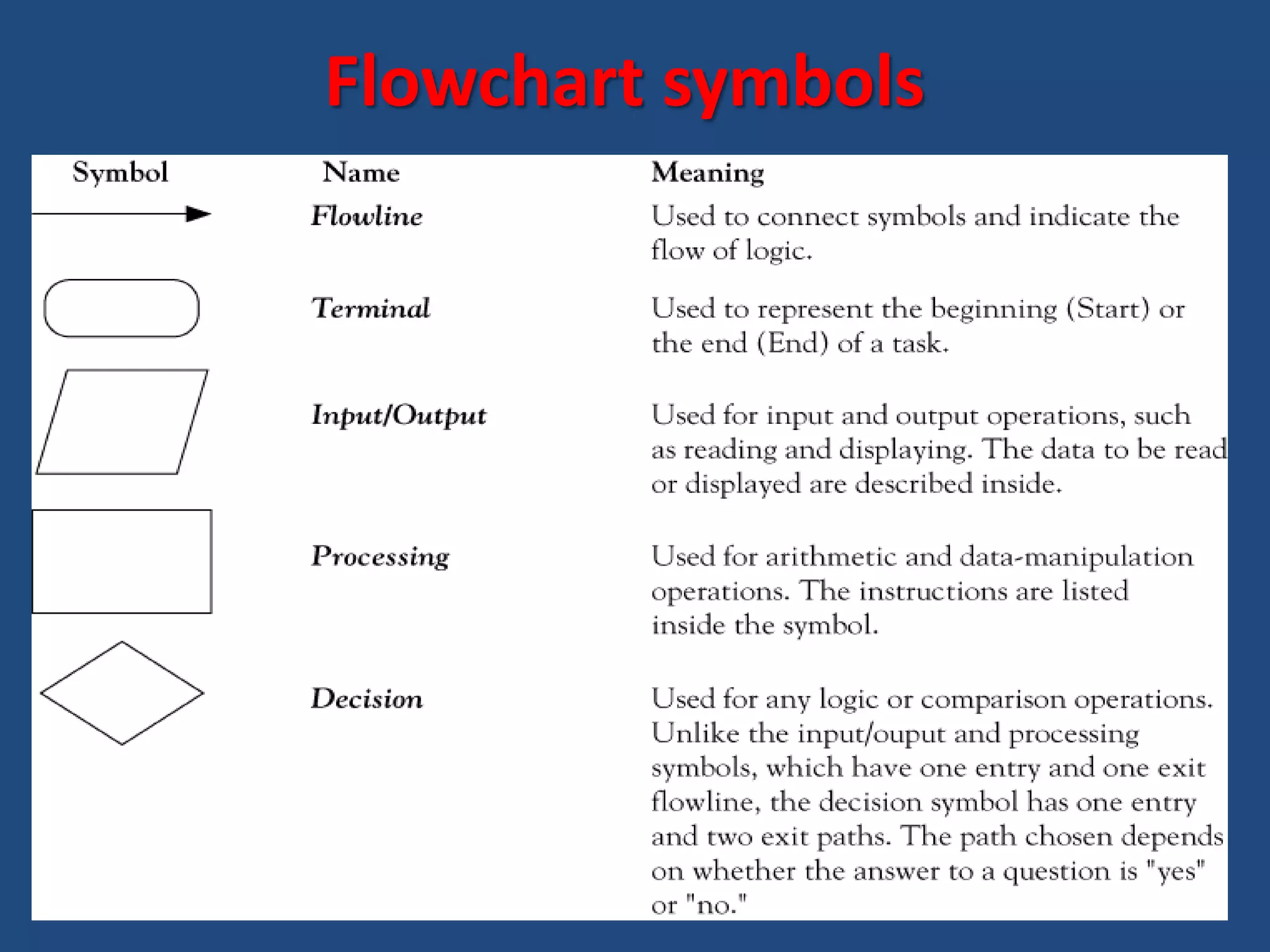
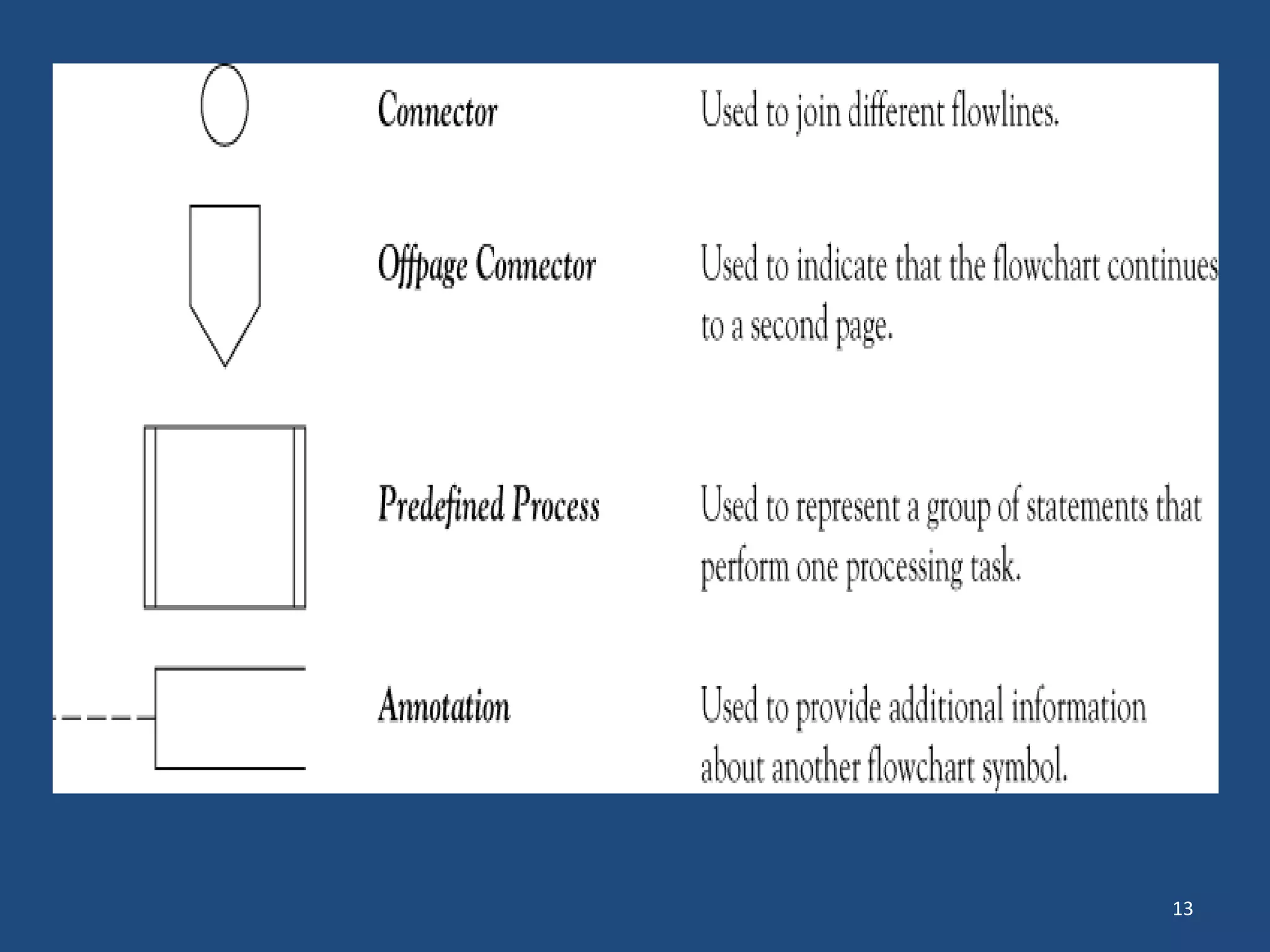
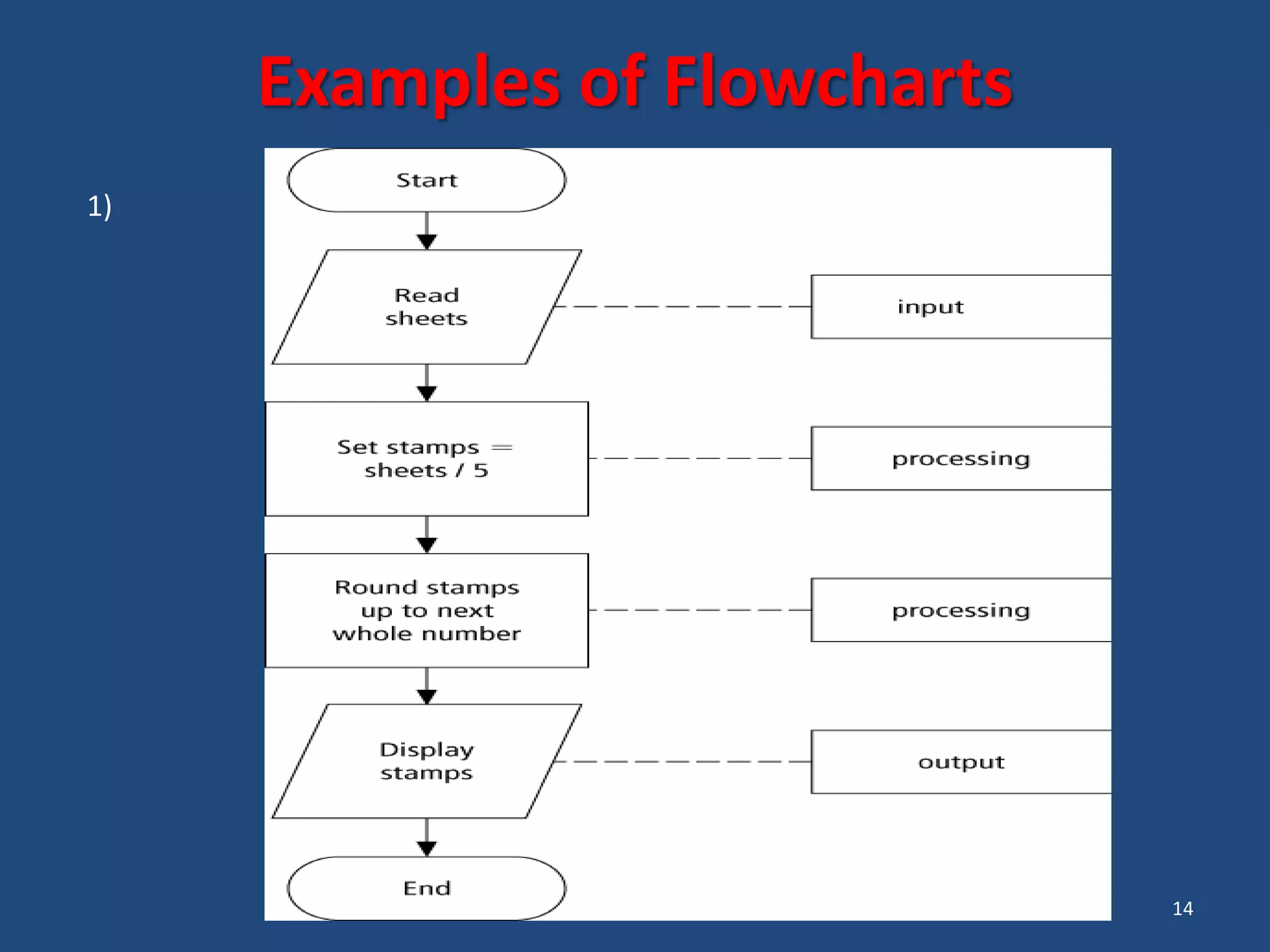
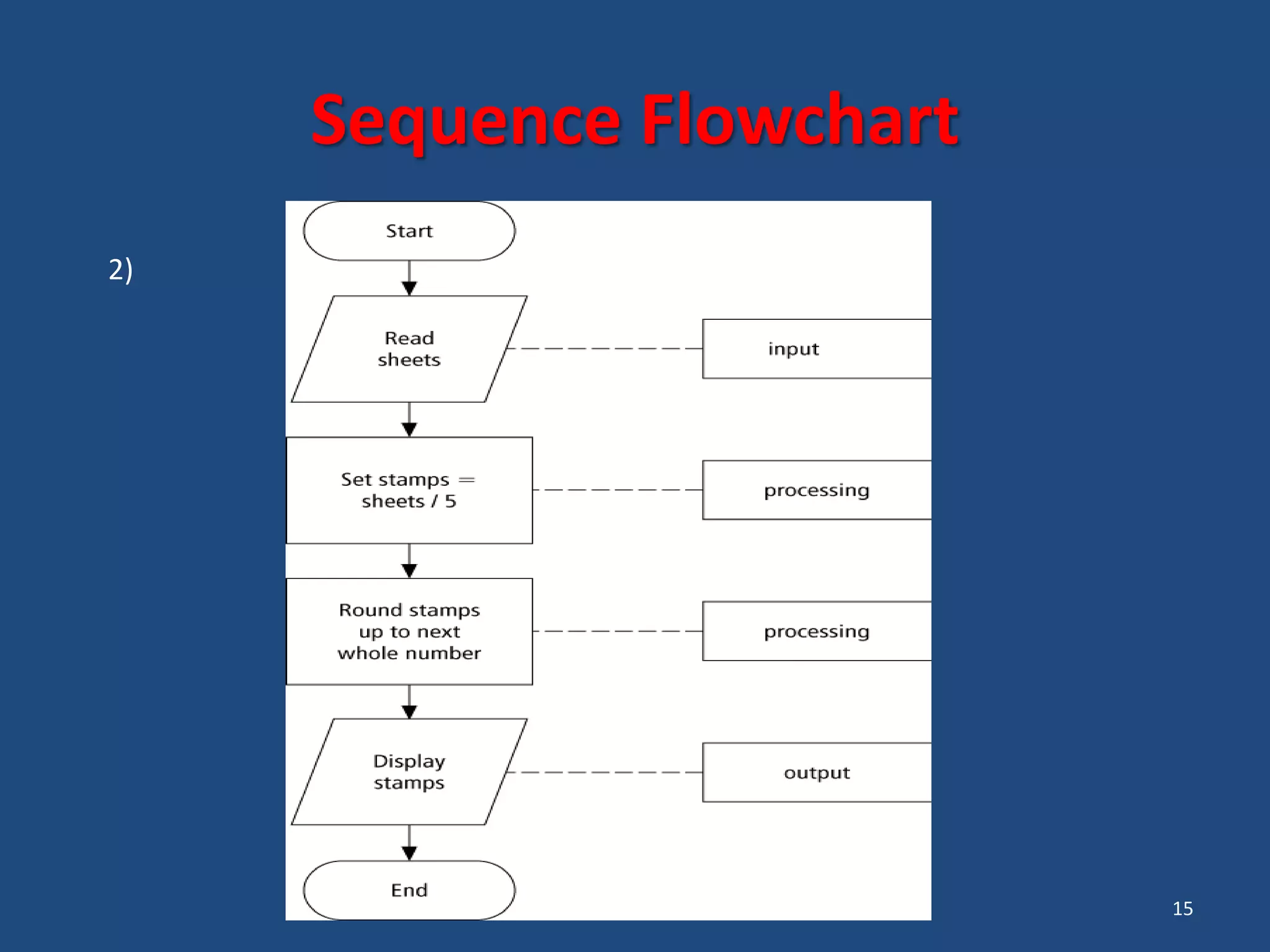
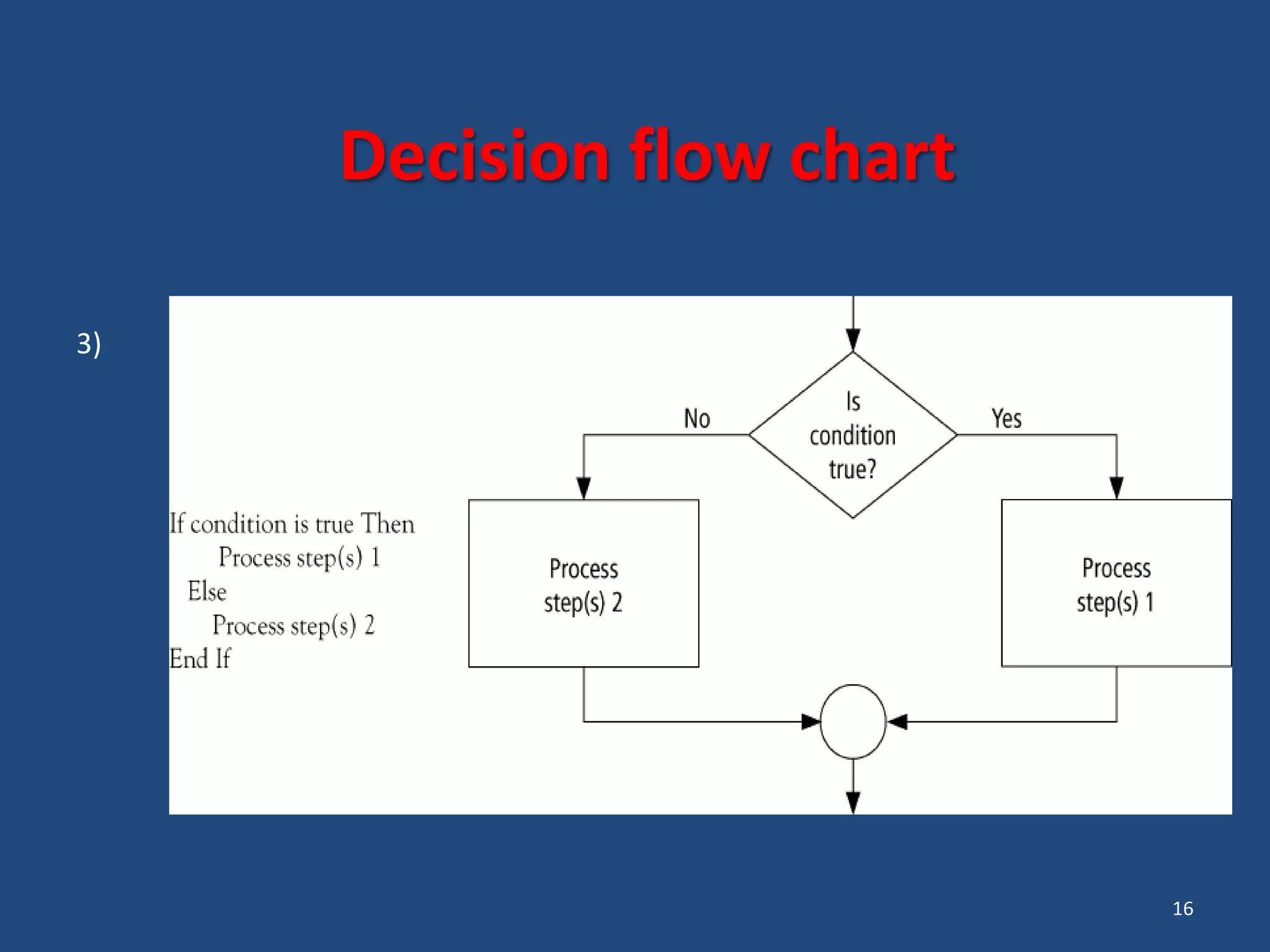
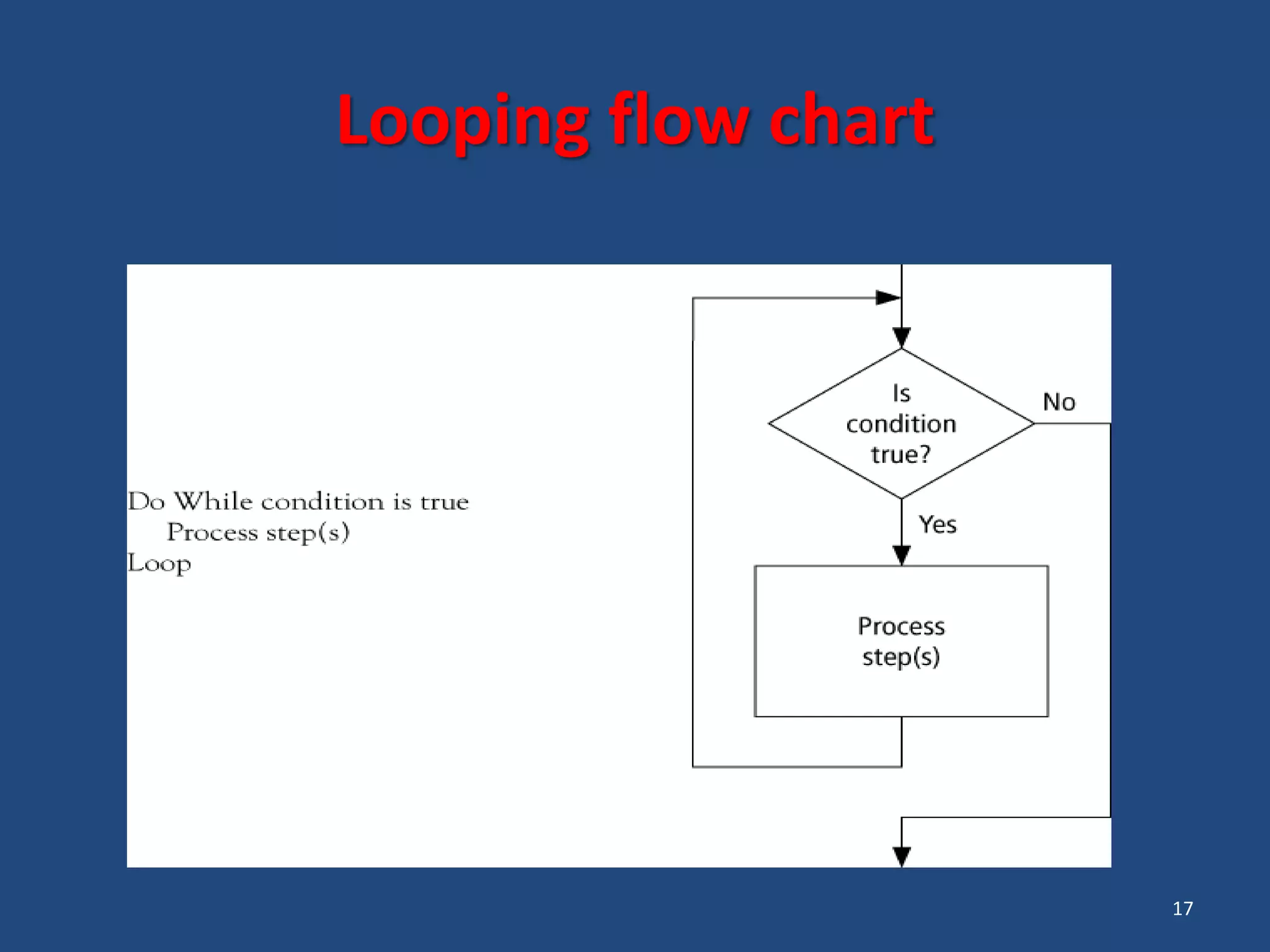
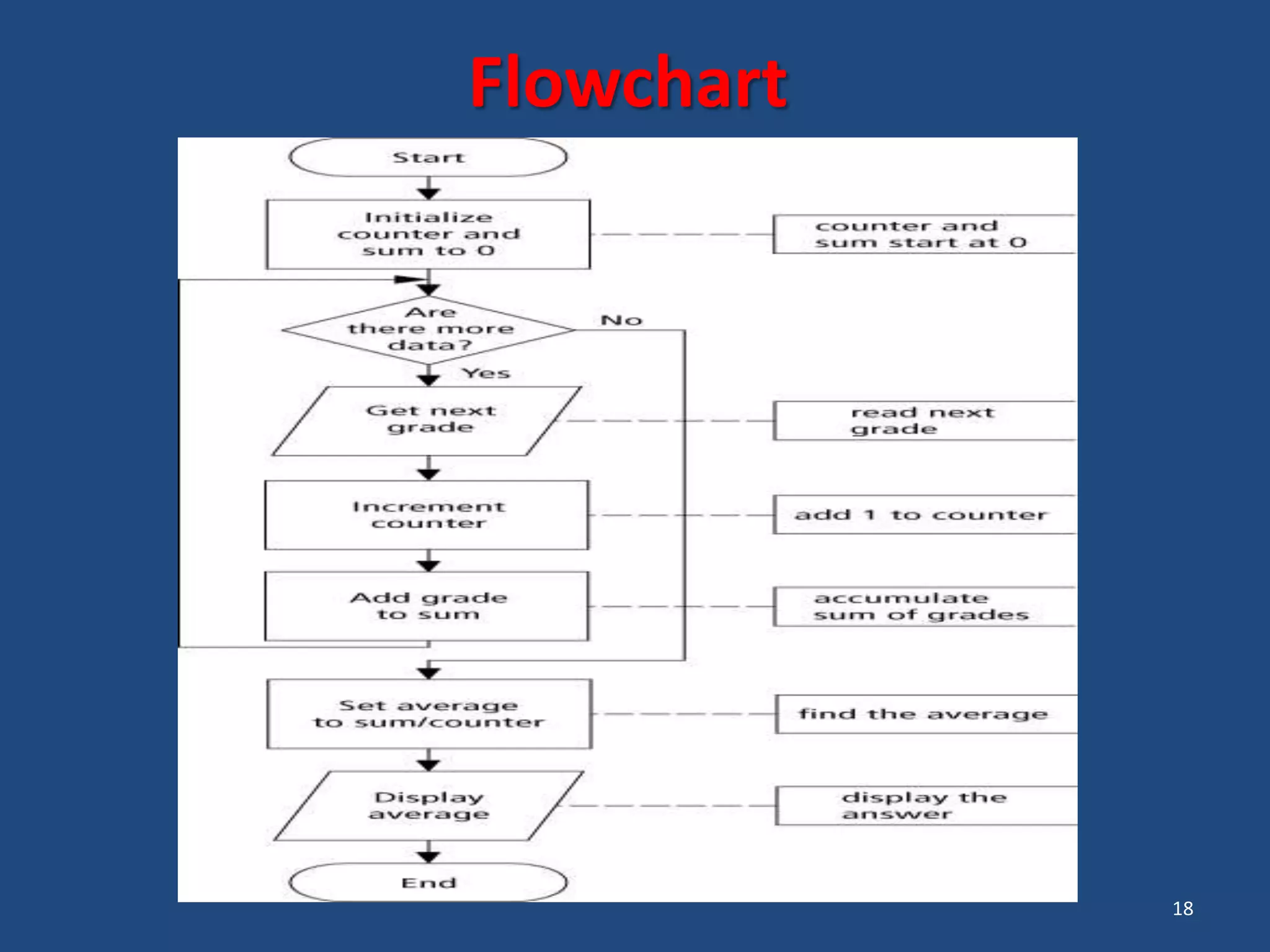
The document discusses different types of programming languages and software. It describes low-level languages like machine language and assembly language, and high-level languages used for scientific and business applications. It also defines algorithms, flowcharts, compilers, interpreters, and system and application software.