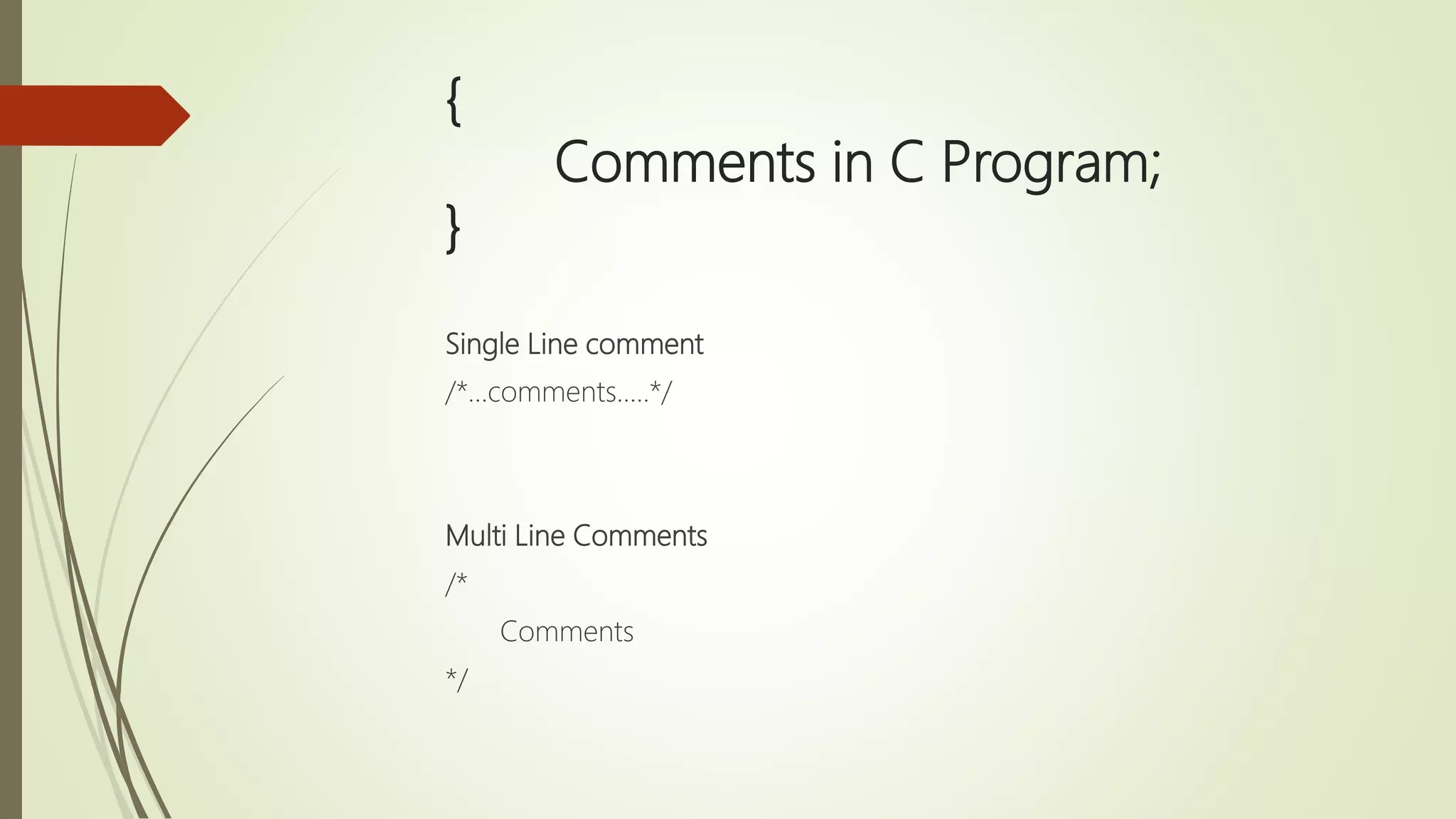
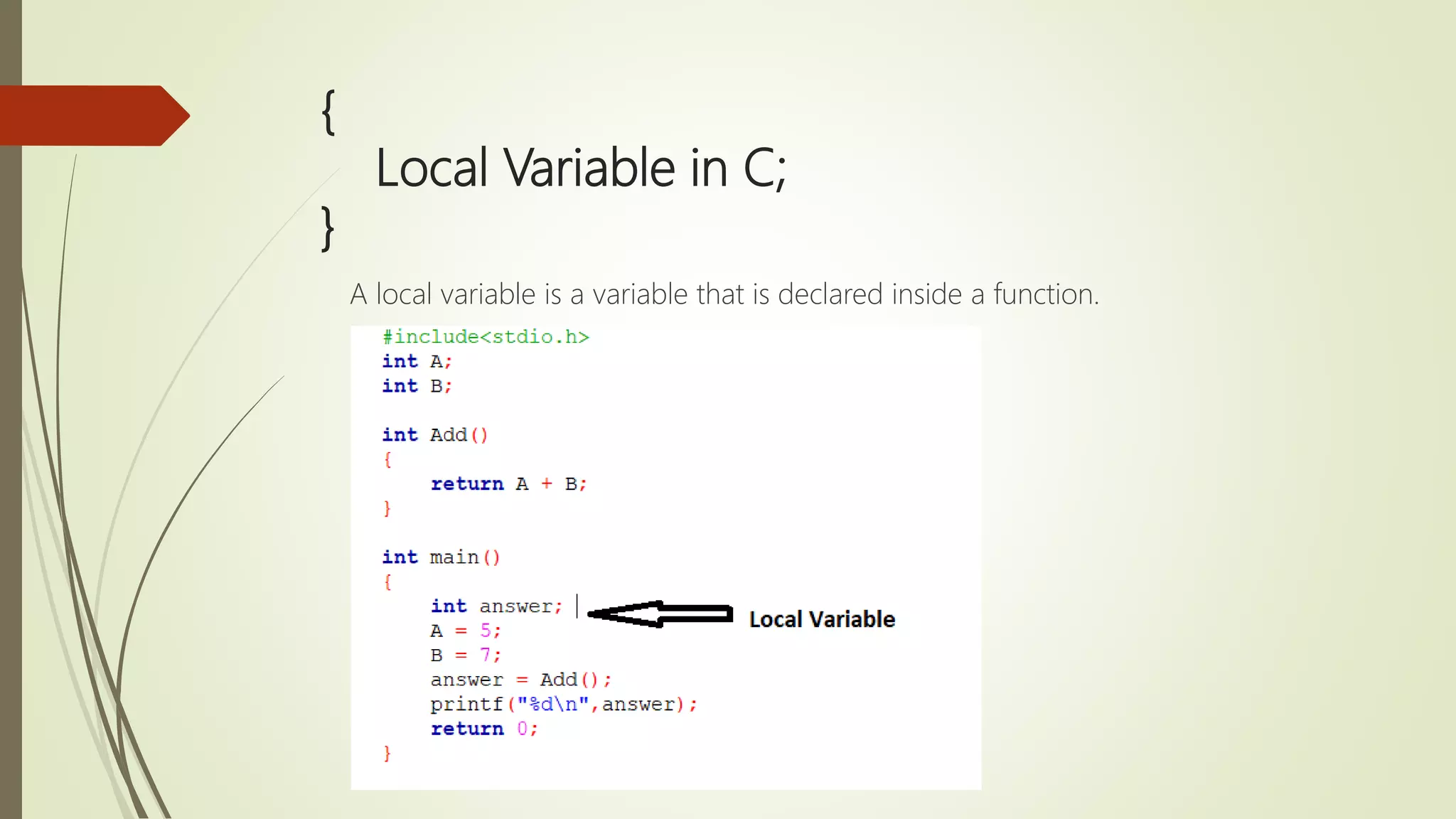
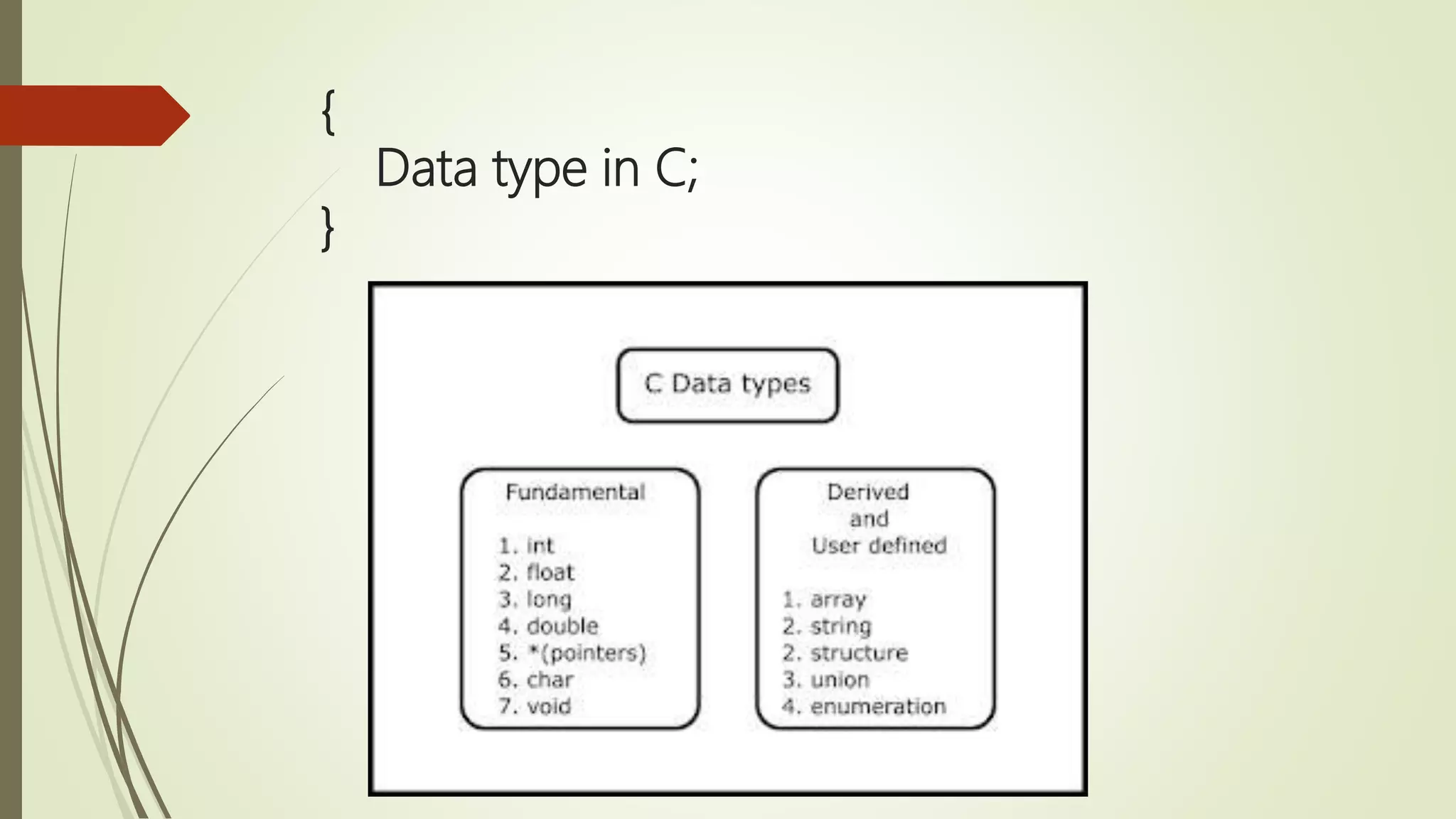
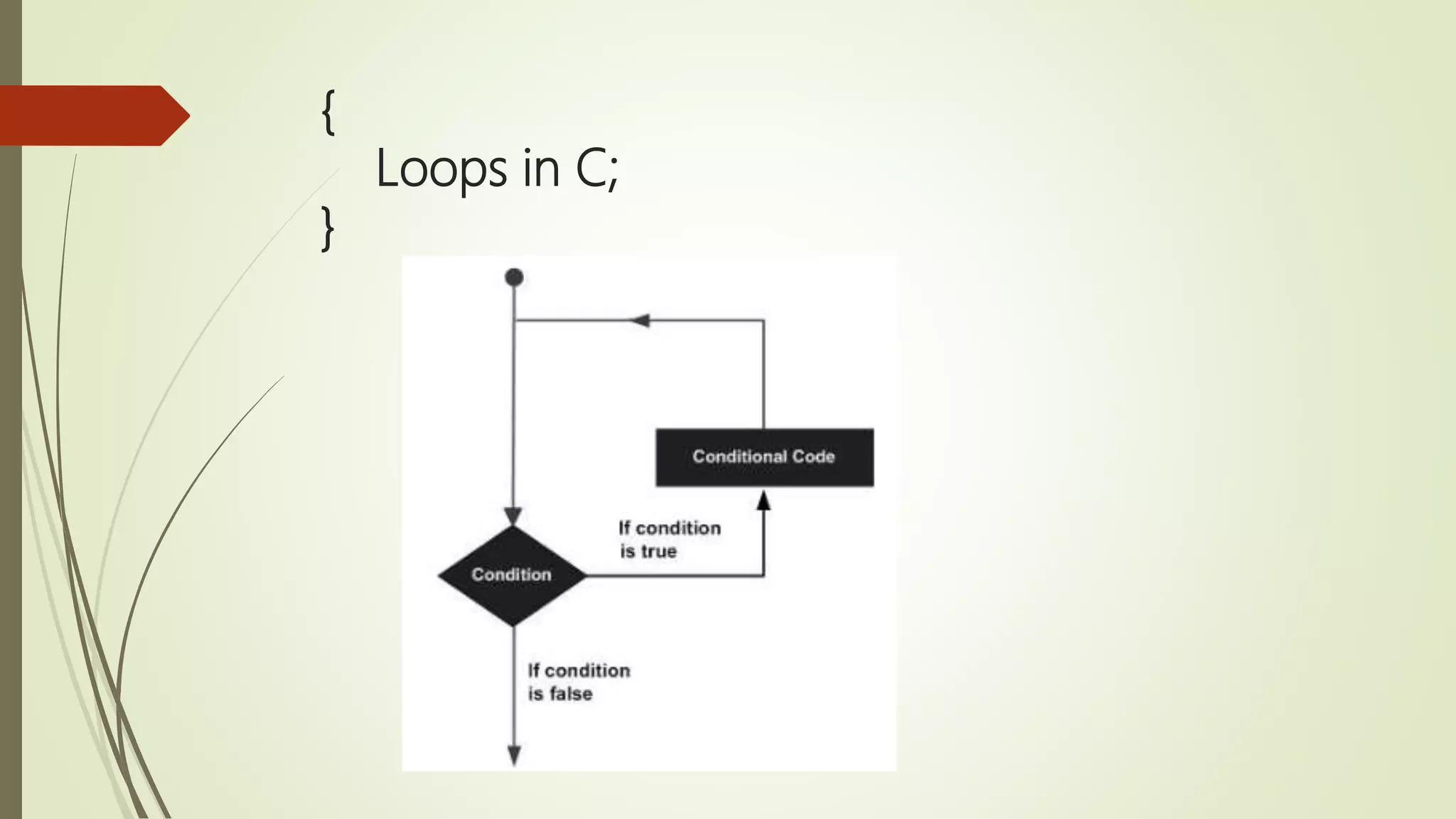
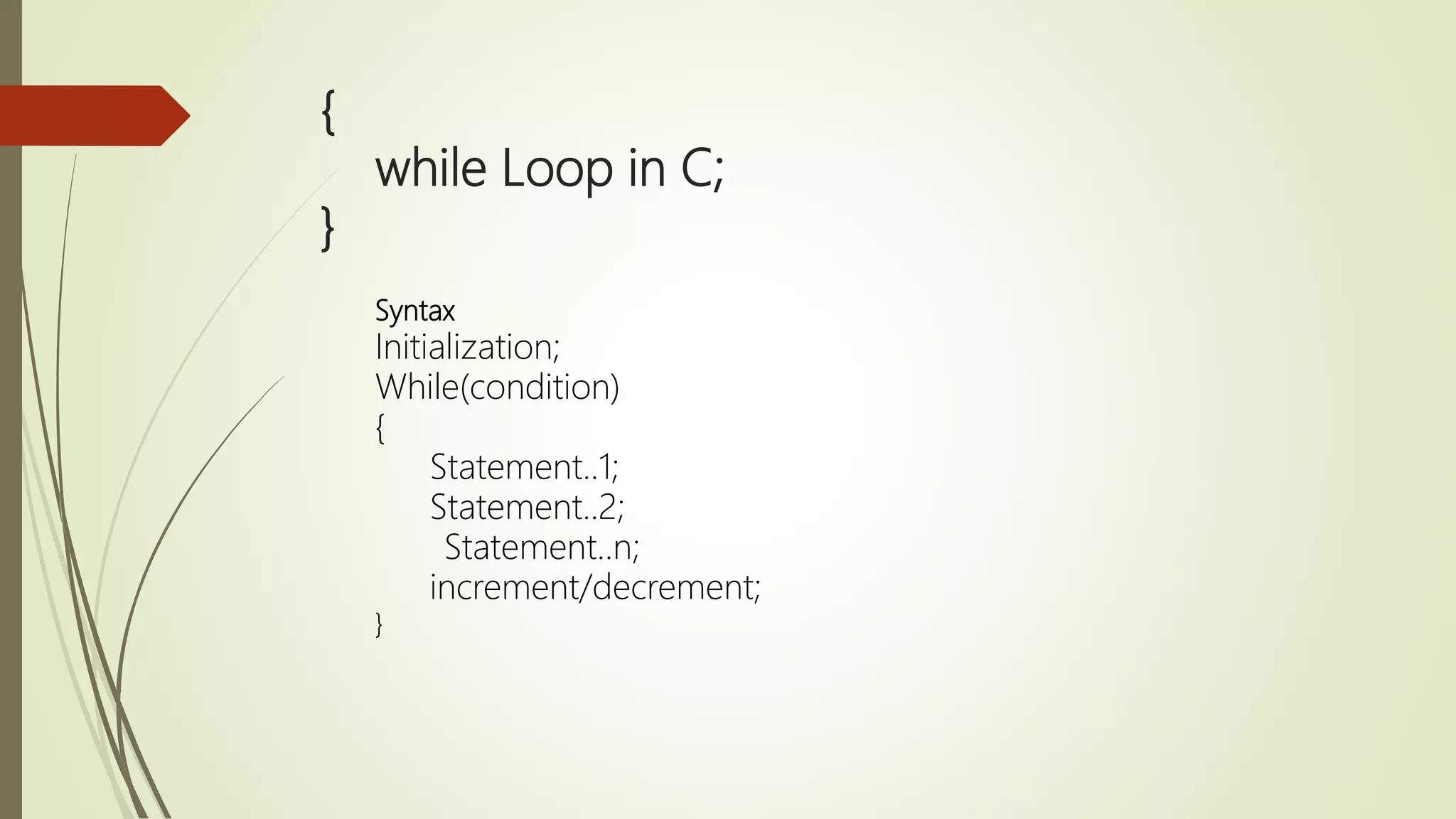
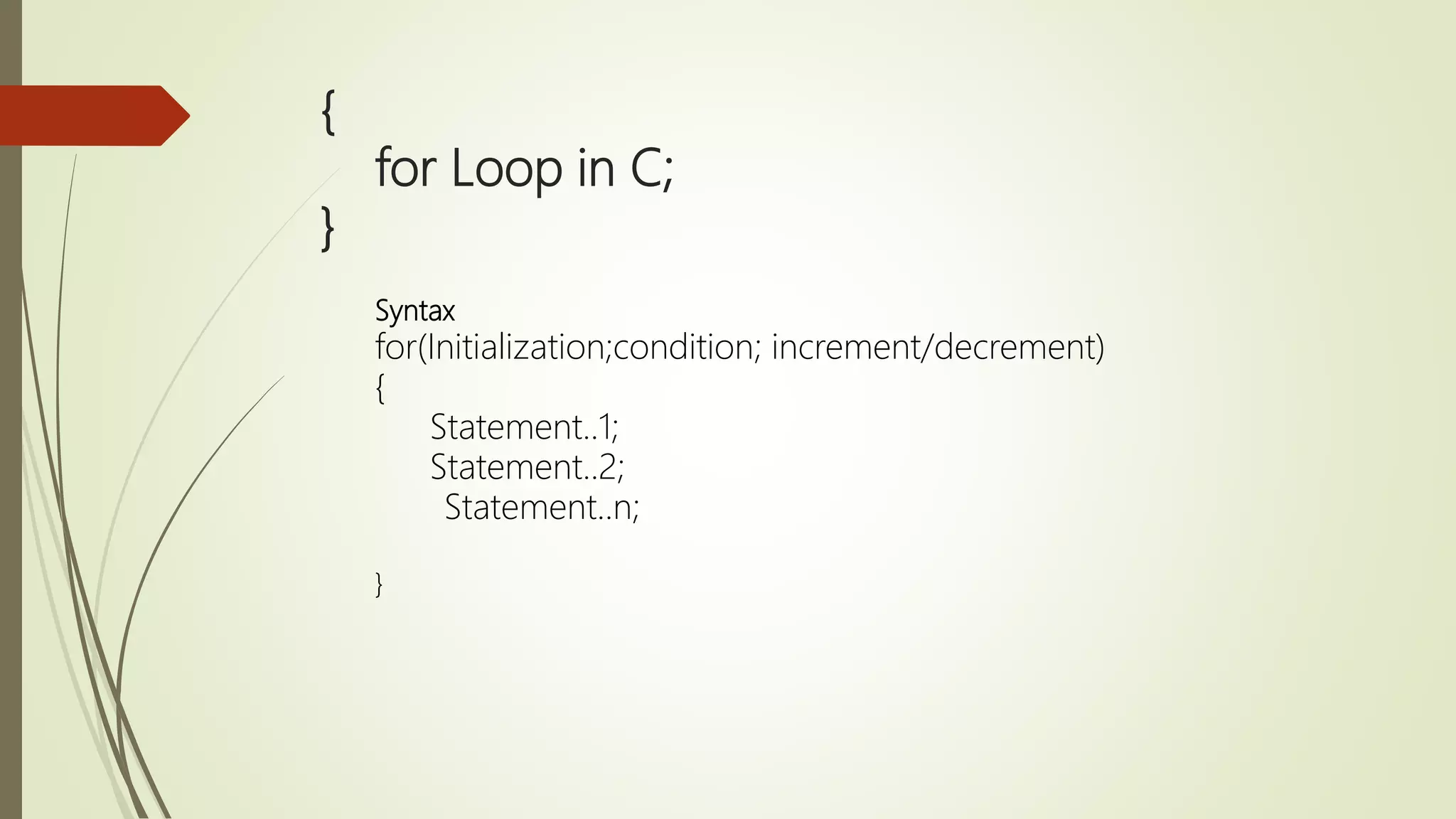
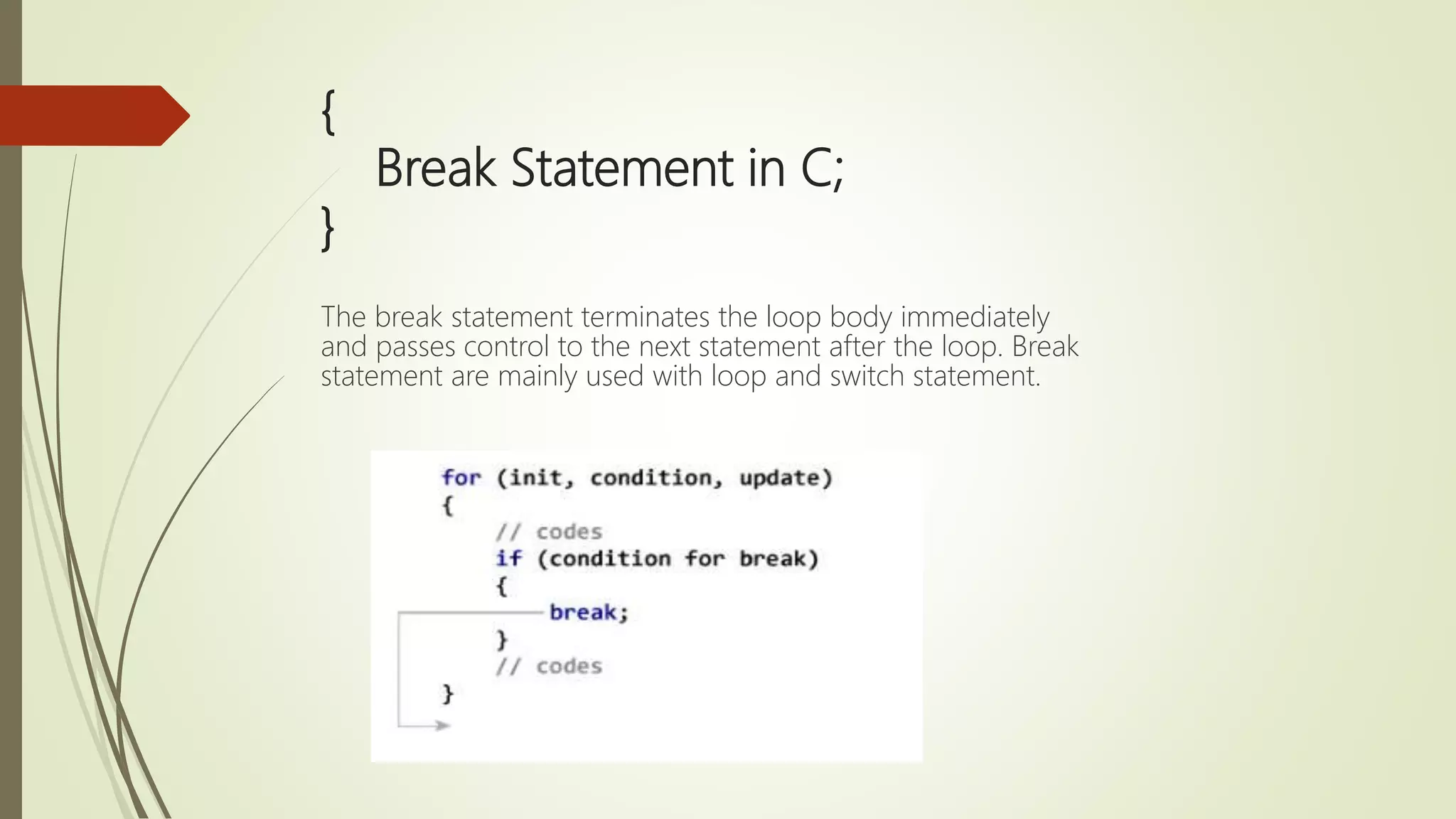
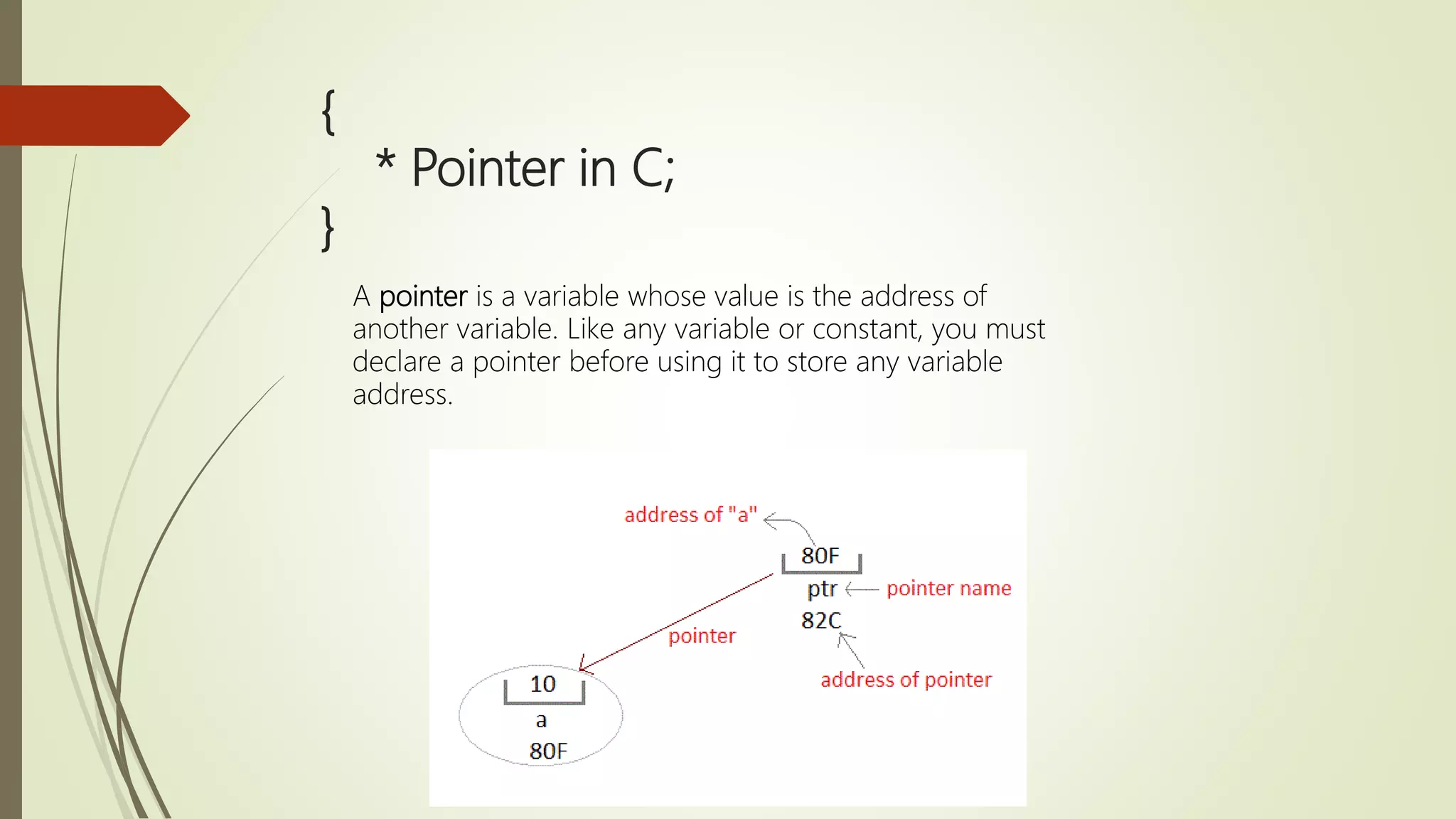
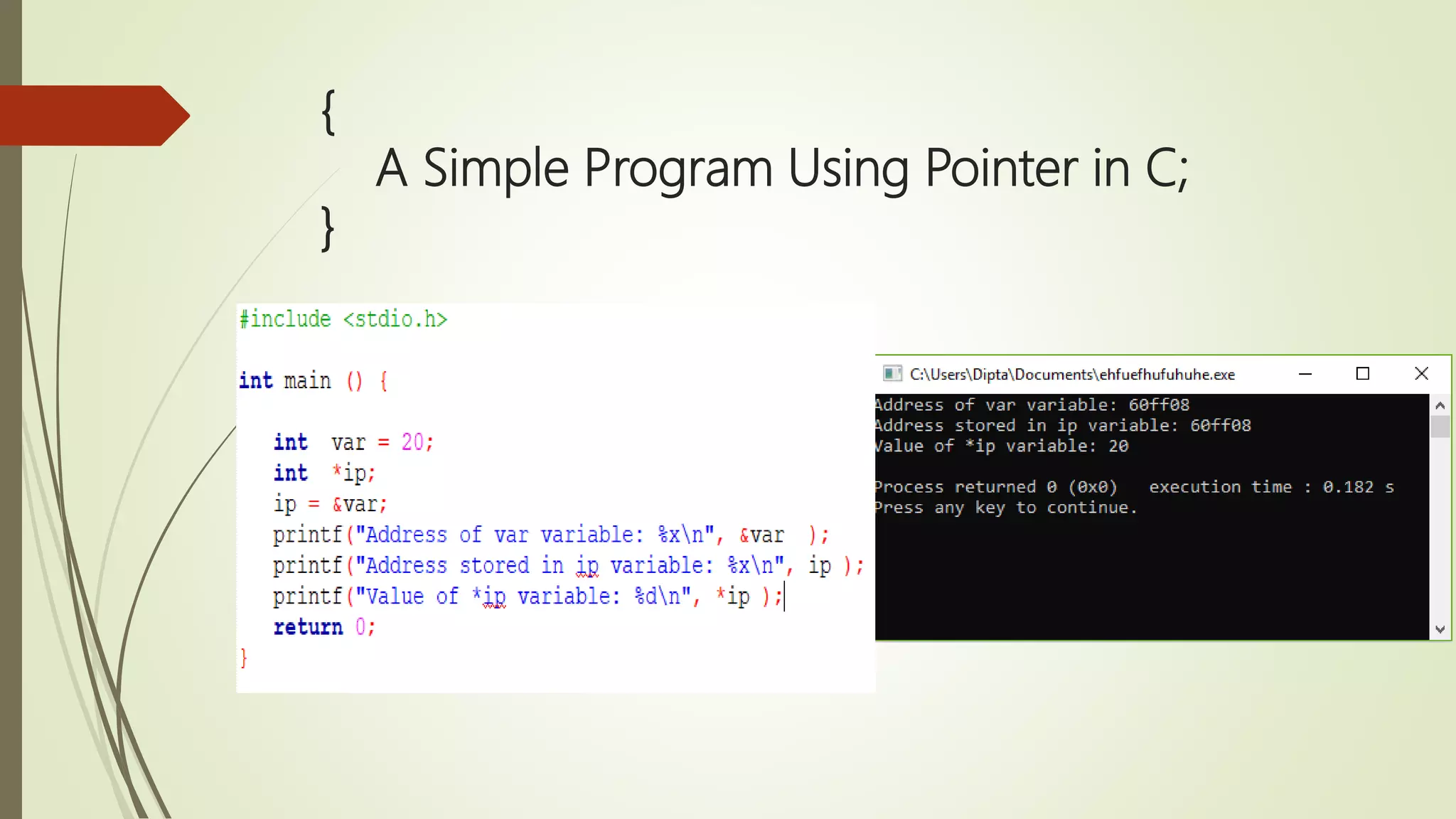
The document provides an overview of the C programming language, detailing its history, basic syntax, variable types, operators, decision-making statements, loops, functions, arrays, pointers, and file handling. It includes example codes for various concepts and syntax for declarations and operations. This serves as a foundational guide for understanding C programming.













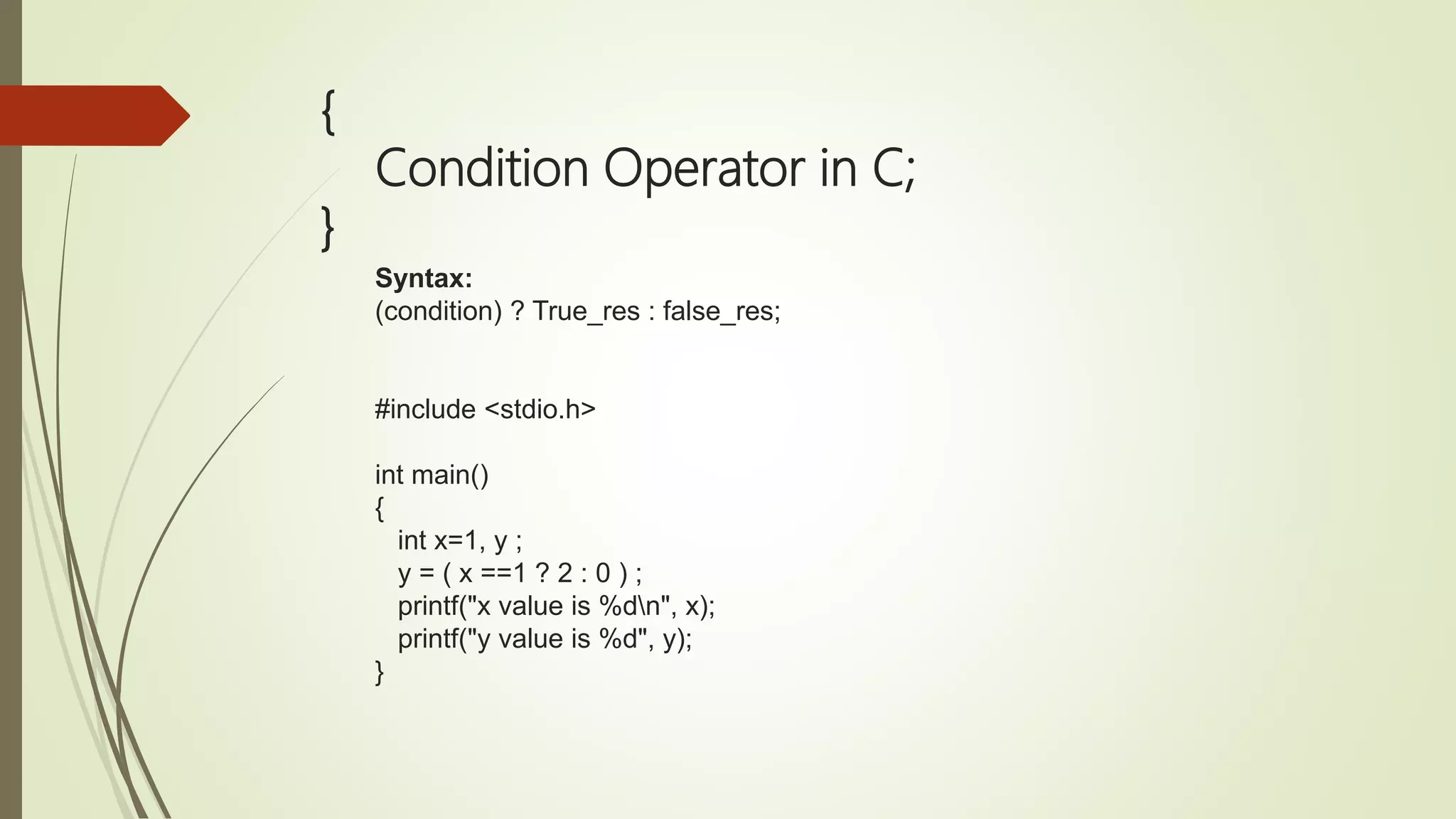

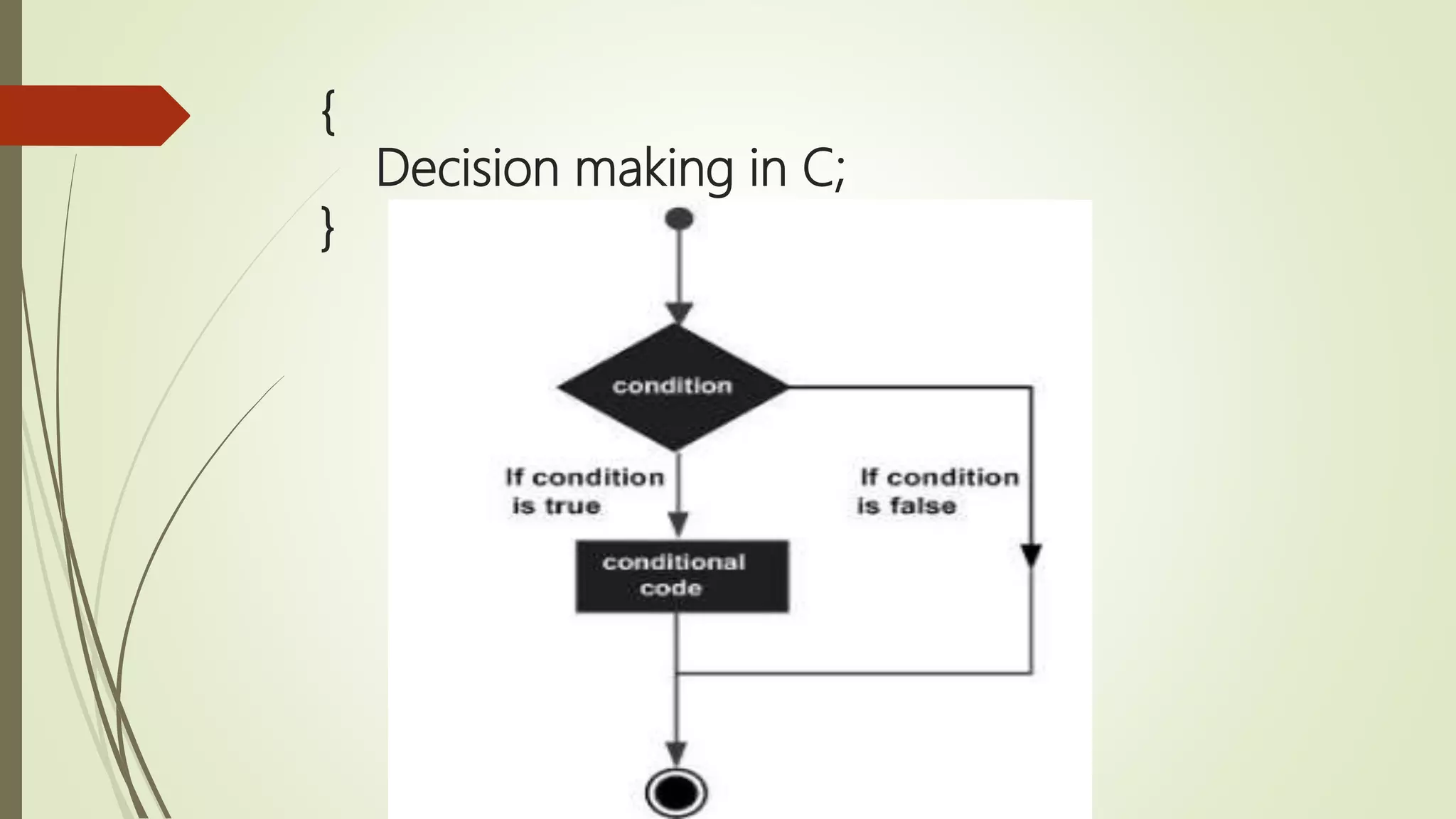

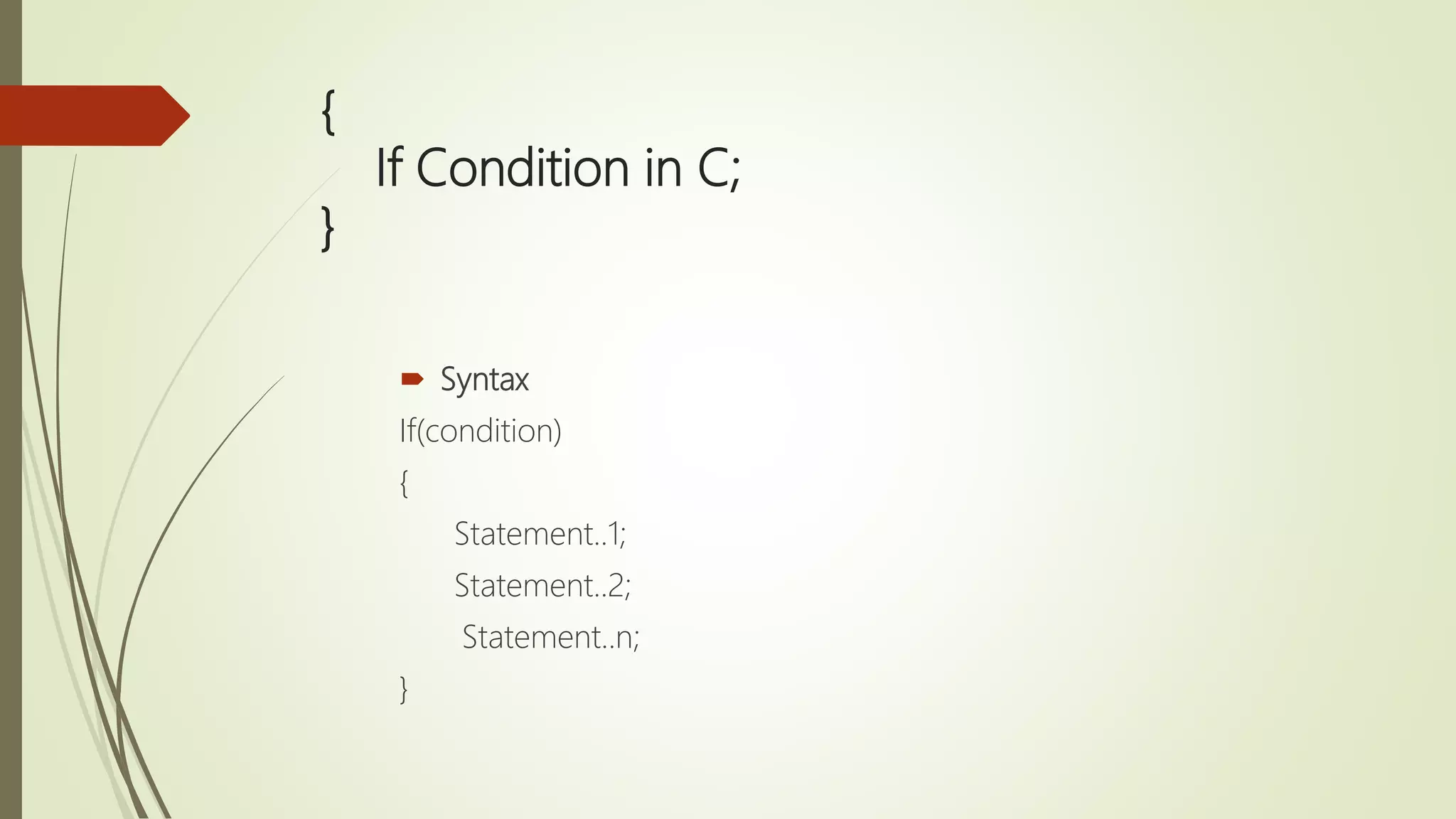




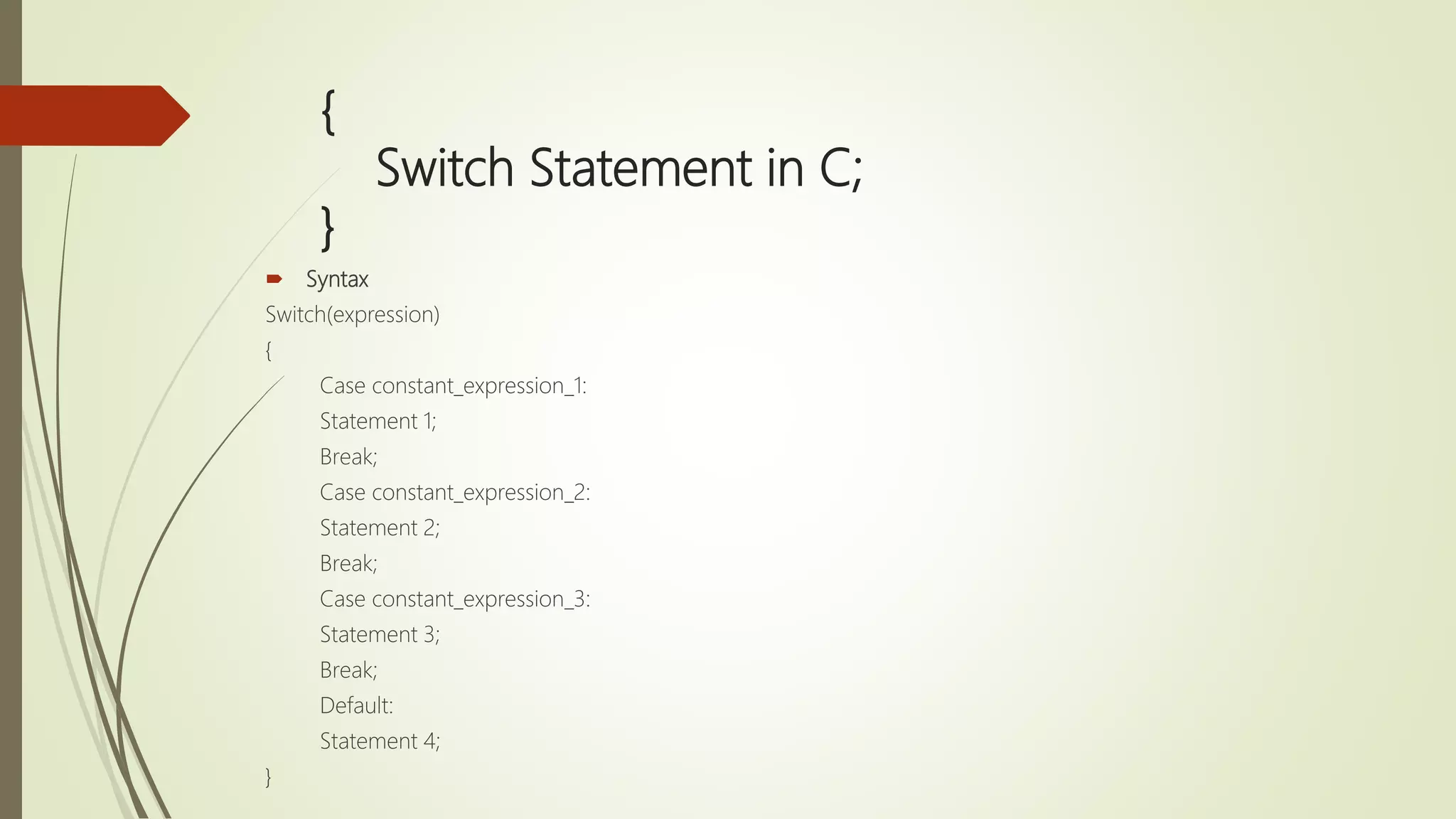







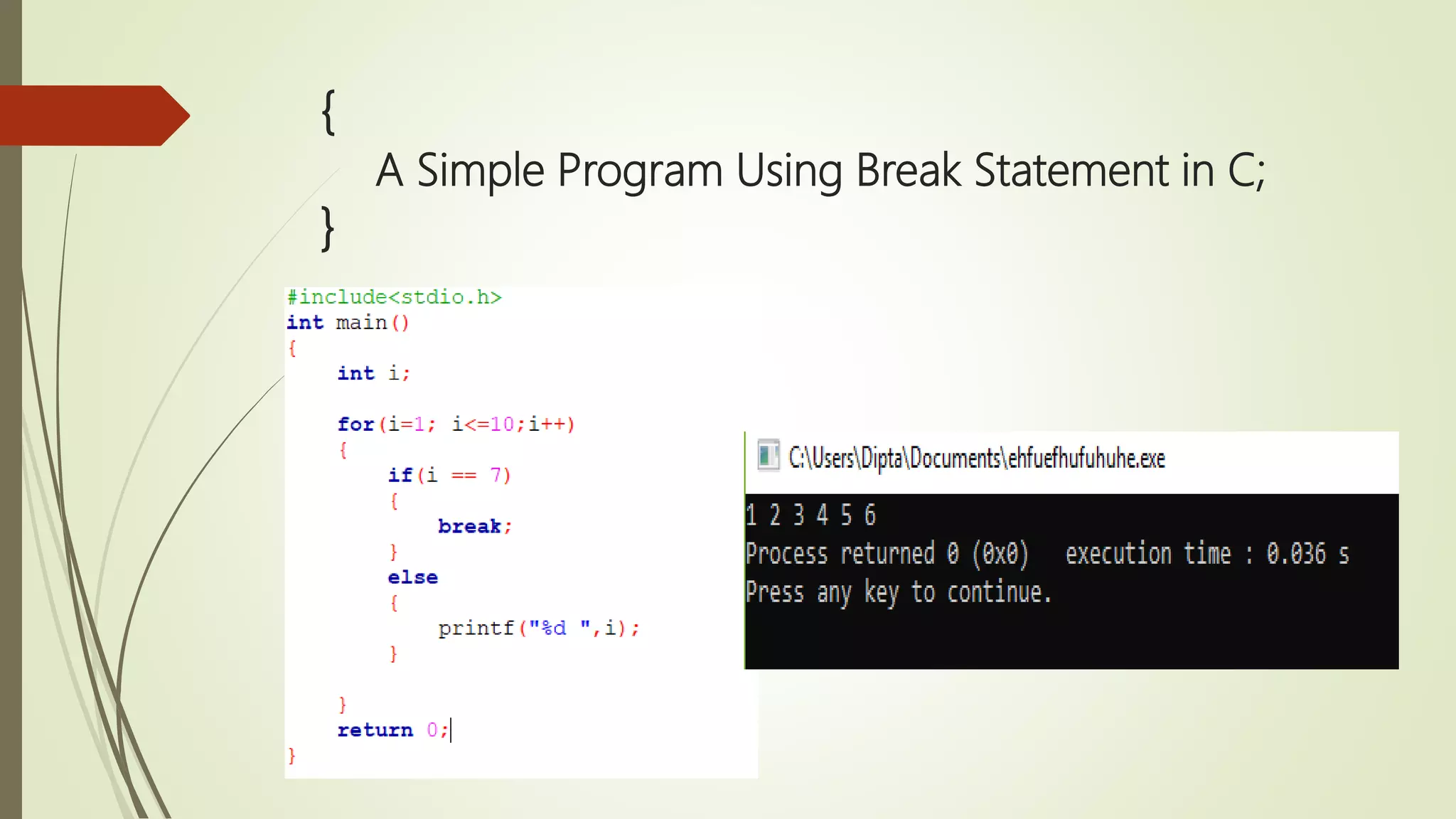
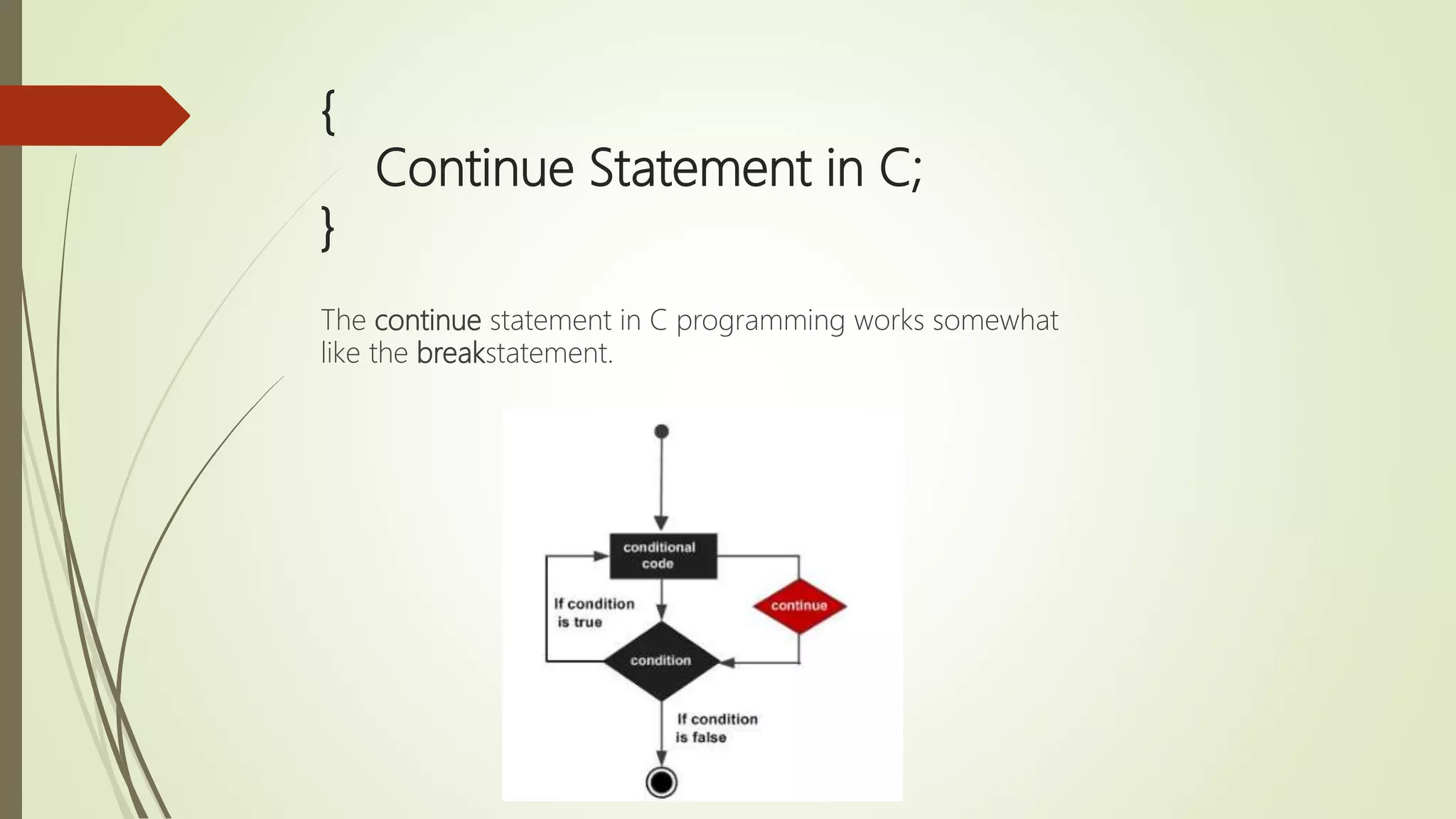
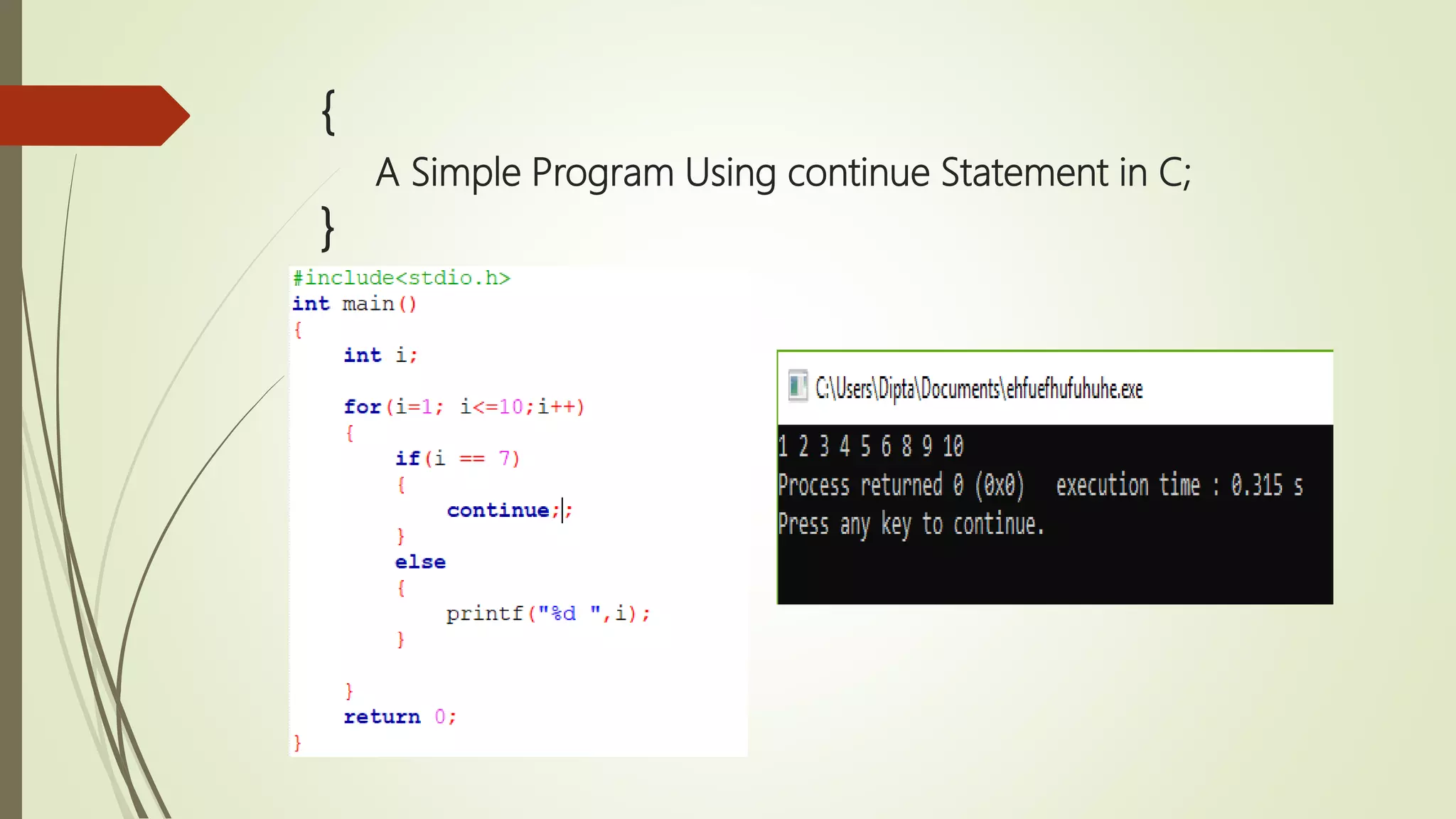



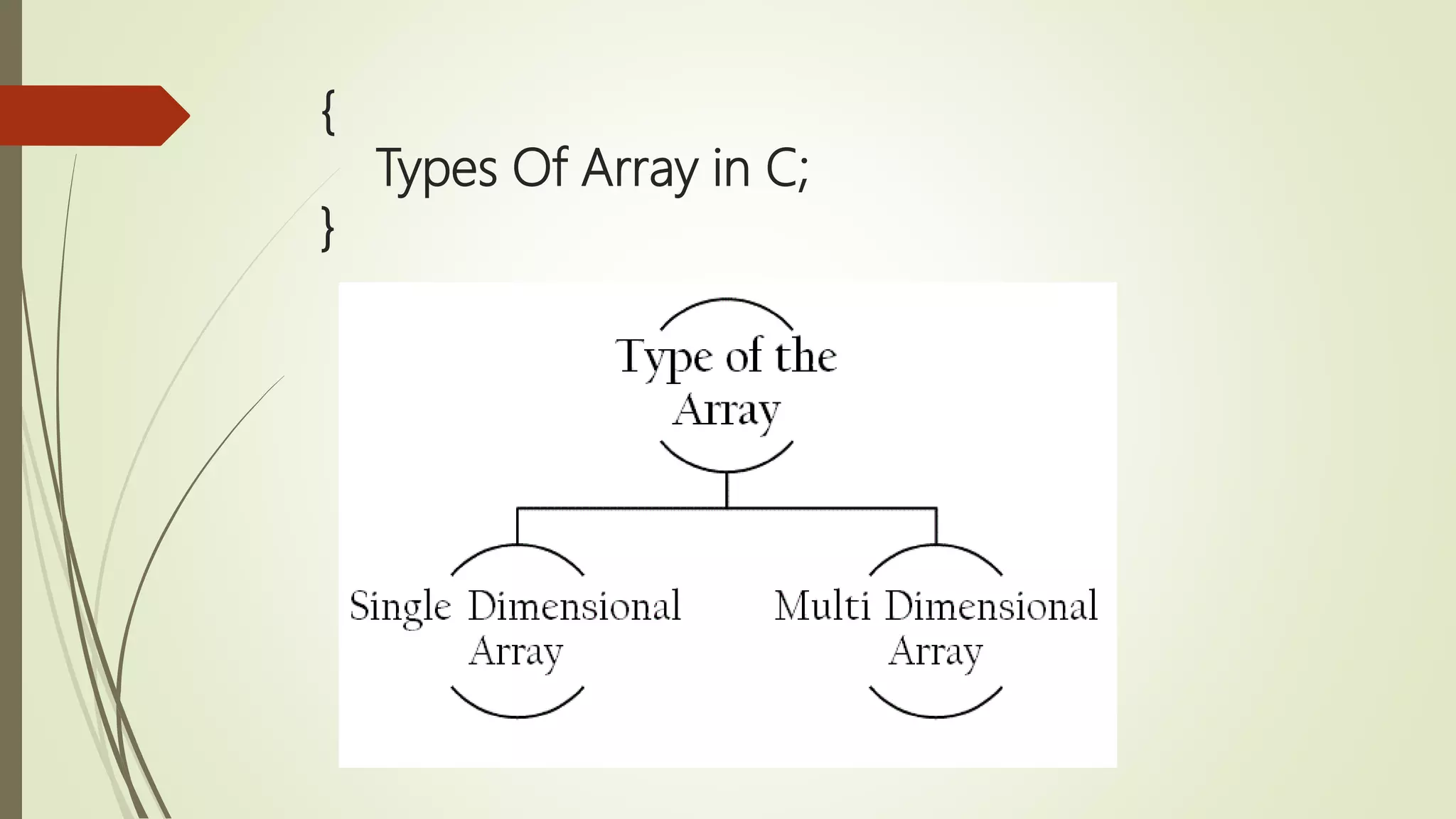
![{ Single Dimensional Array in C; } Syntax data_type array_name [size];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuptopointer-180804092048-190306091149/75/Programming-in-C-Presentation-upto-FILE-50-2048.jpg)
![{ Multi Dimensional Array in C; } Syntax data_type array_name [row_size][column_size];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuptopointer-180804092048-190306091149/75/Programming-in-C-Presentation-upto-FILE-51-2048.jpg)


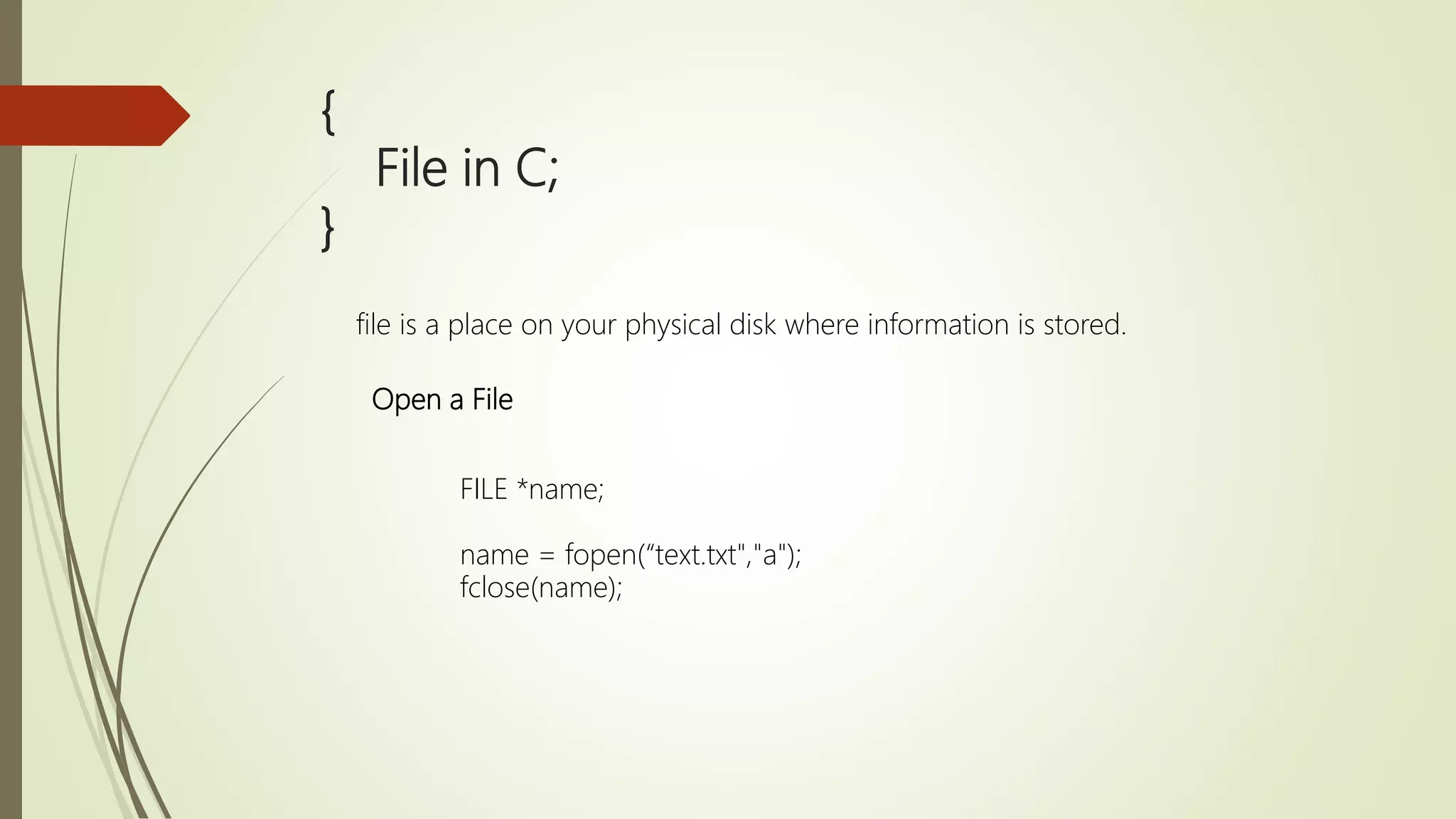

![{ File in C; } Read in a File FILE *name; name = fopen(“text.txt",“w"); Char buff[200]; If(name == NULL) { printf(“File Dose Not exist”); } else { while(fscanf(fp, "%s", buff)!=EOF){ printf("%s ", buff ); } fclose(name); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuptopointer-180804092048-190306091149/75/Programming-in-C-Presentation-upto-FILE-58-2048.jpg)
