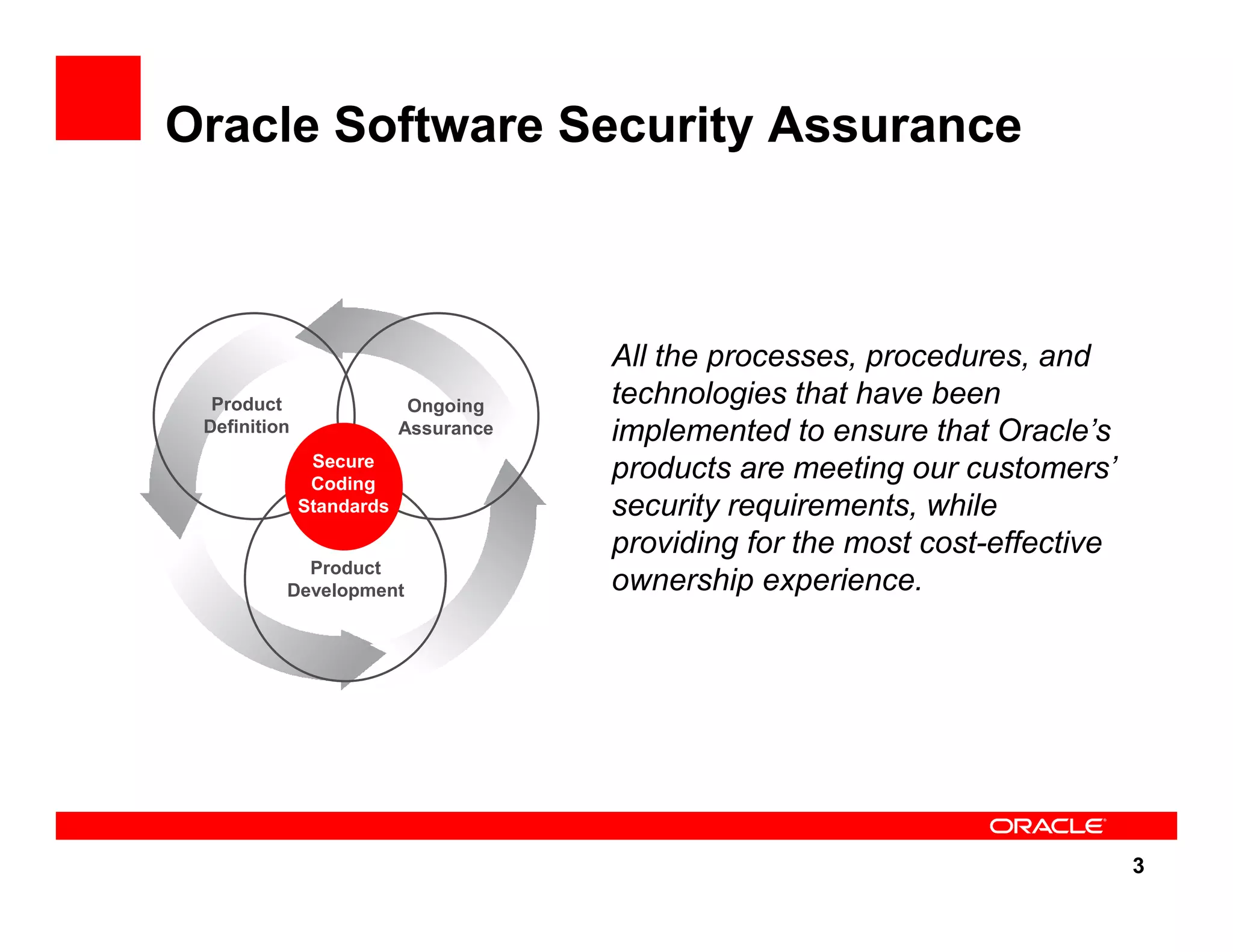
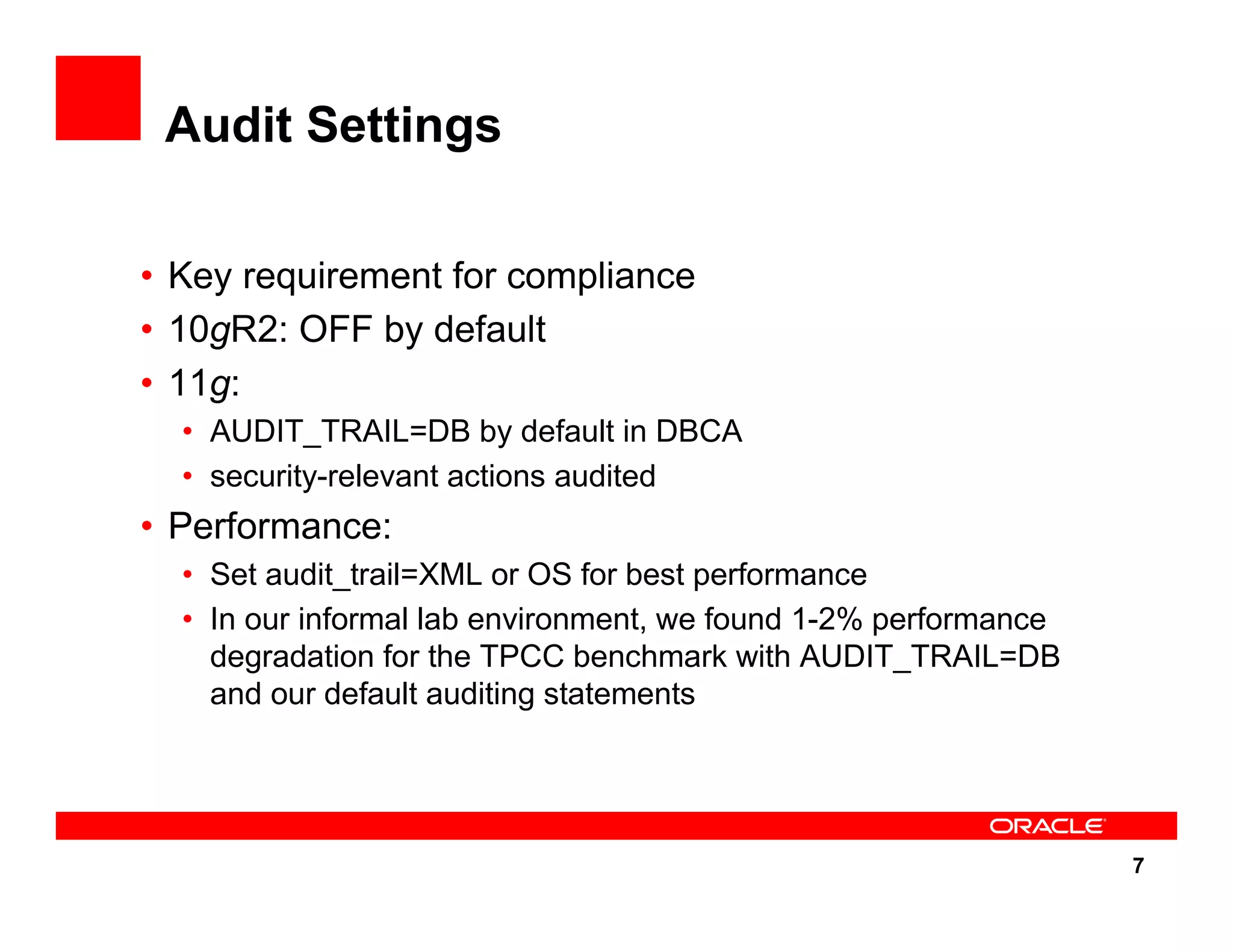
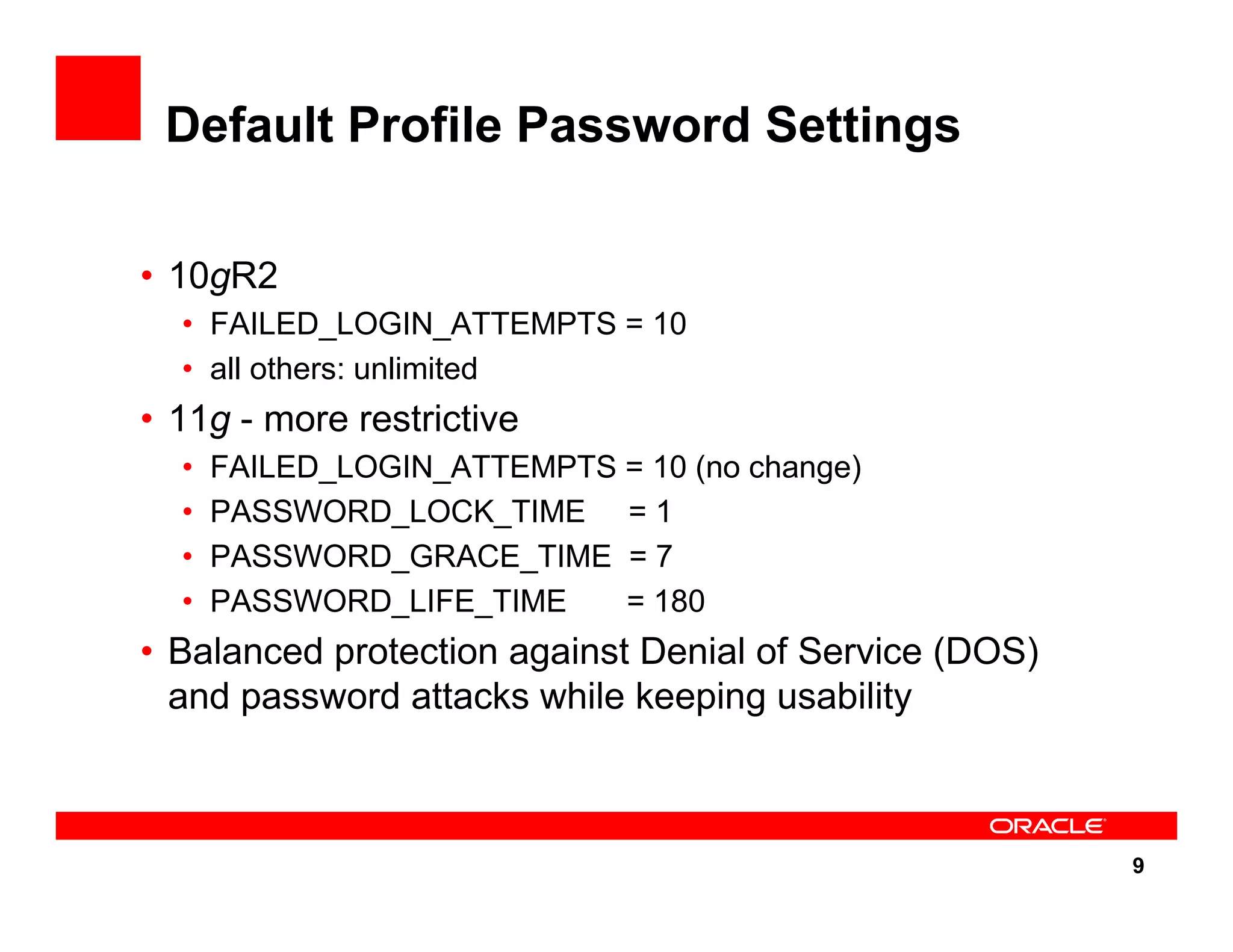
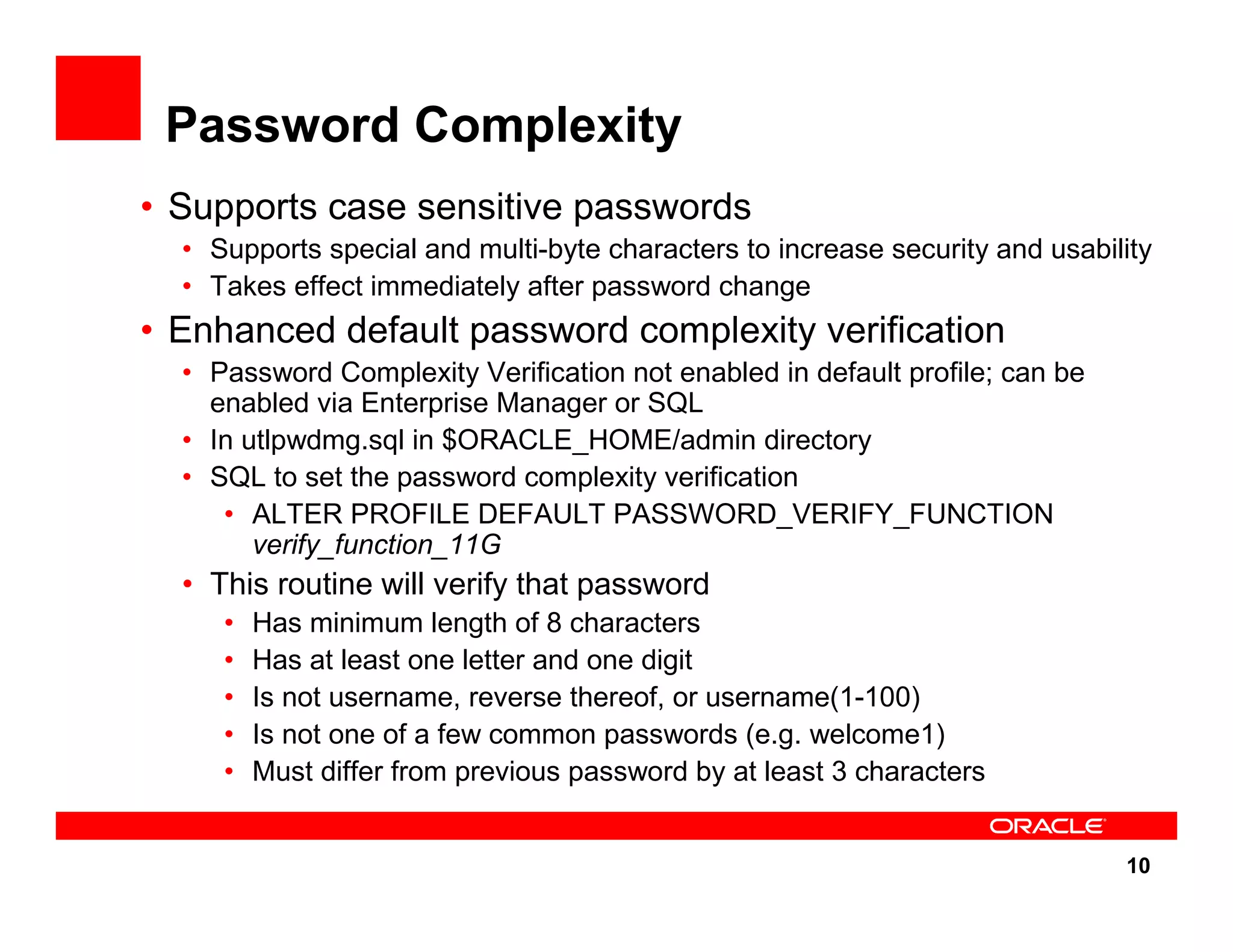
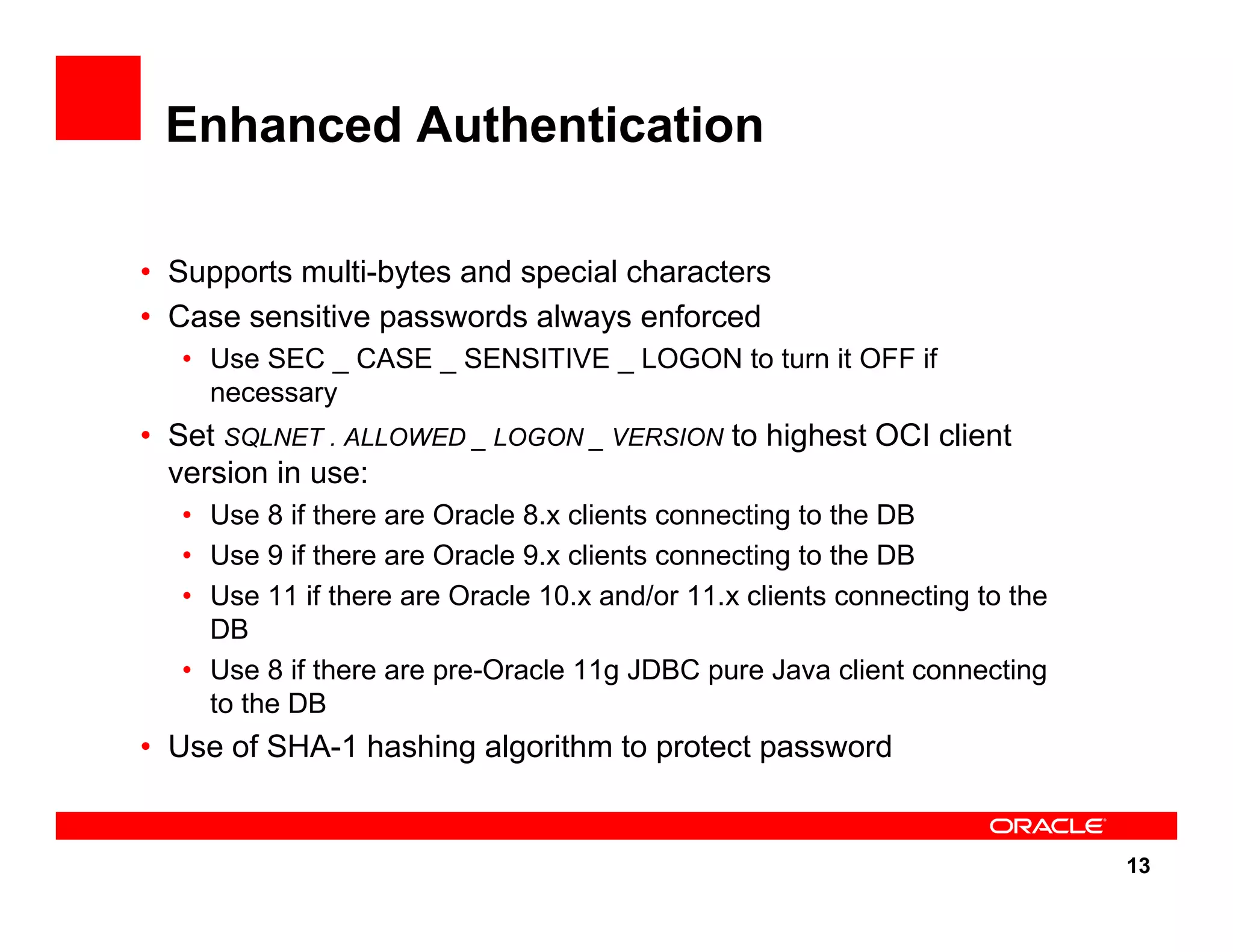
The document outlines the security enhancements introduced in Oracle Database 11g, focusing on secure configuration, enhanced password management, and improved access controls. Key features include mandatory password complexity, preconfigured audit settings, and enhanced security for external network service access. The document also emphasizes ongoing security assurance and the importance of adapting security settings to organizational needs.