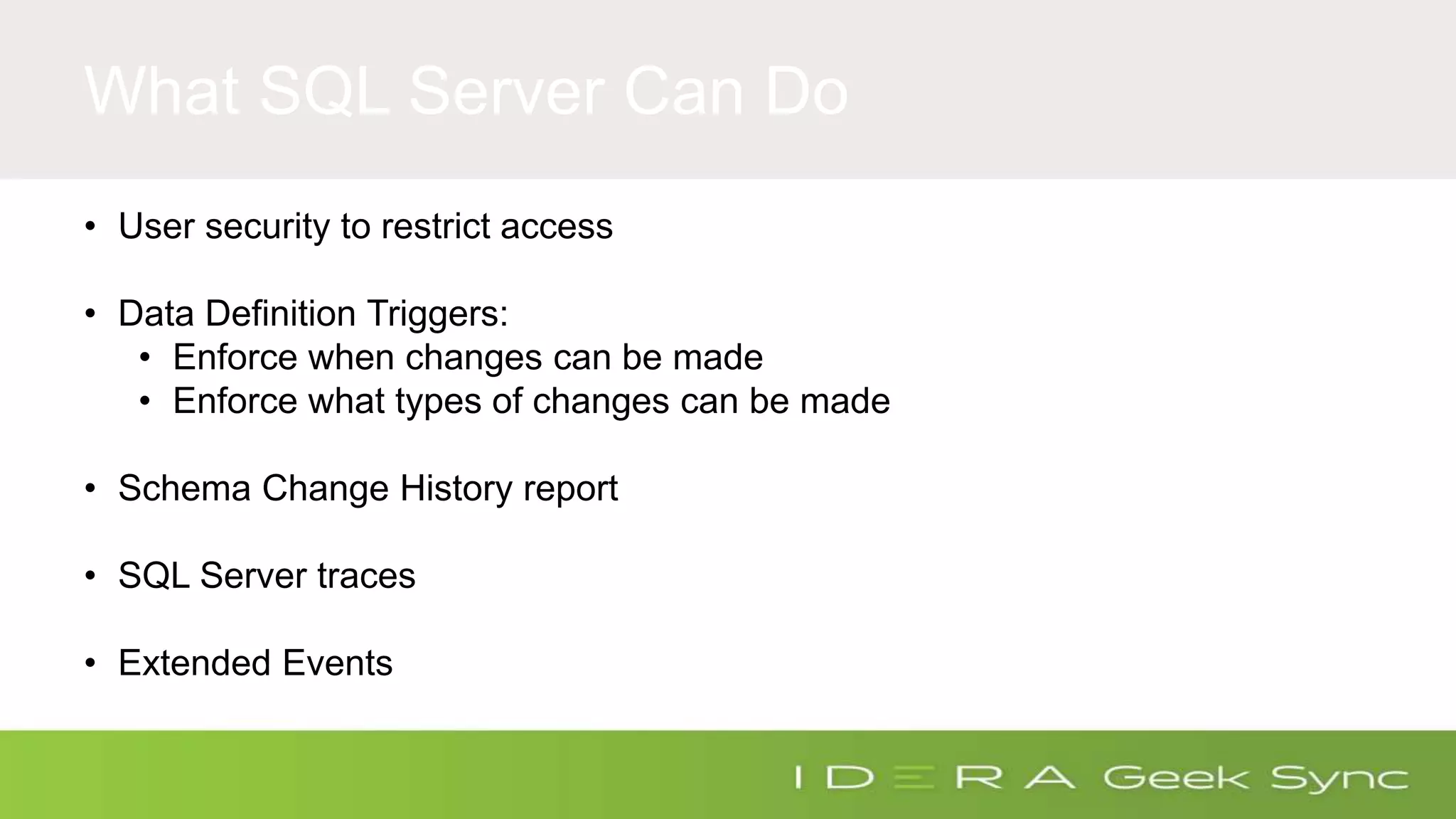
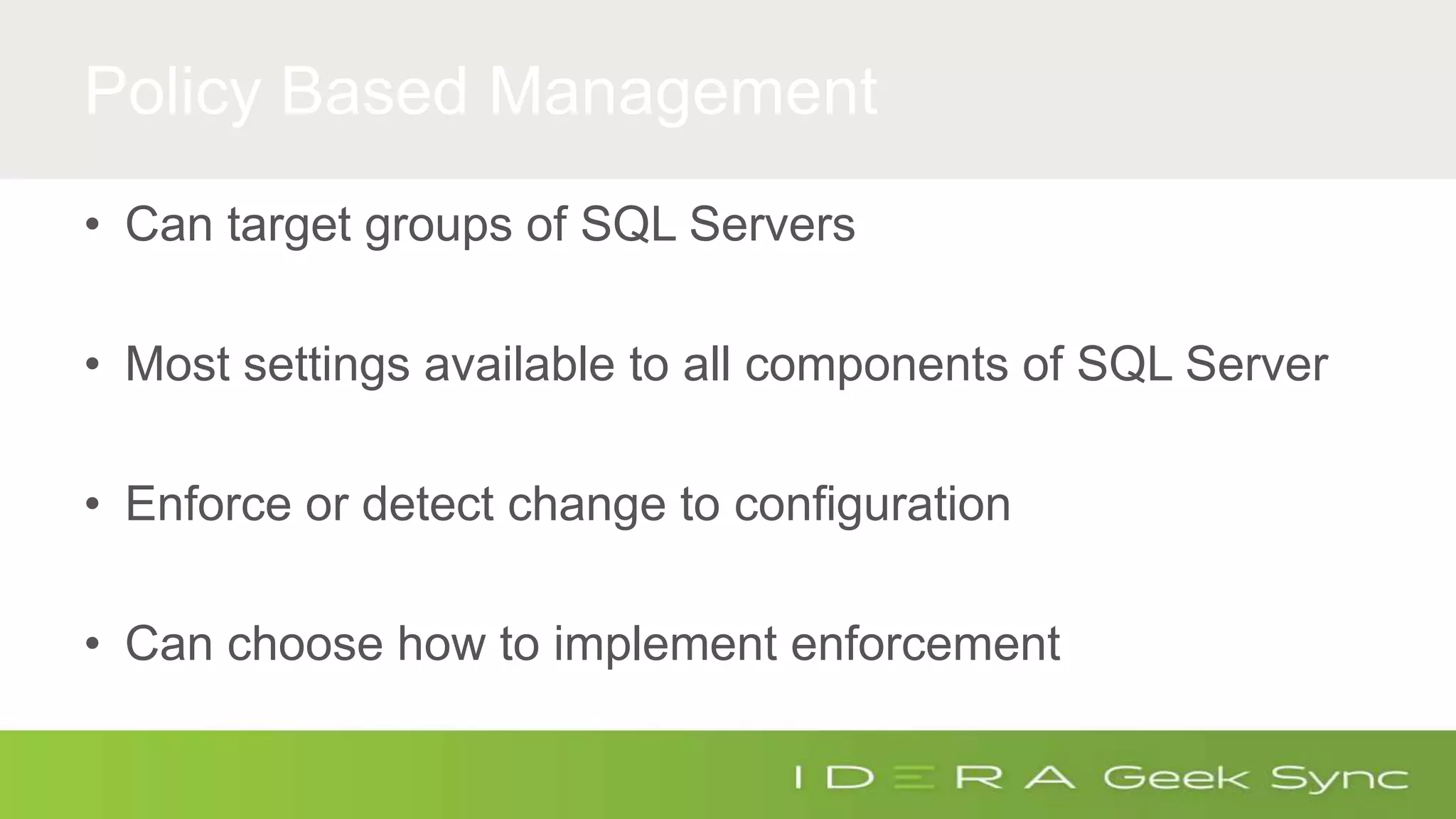
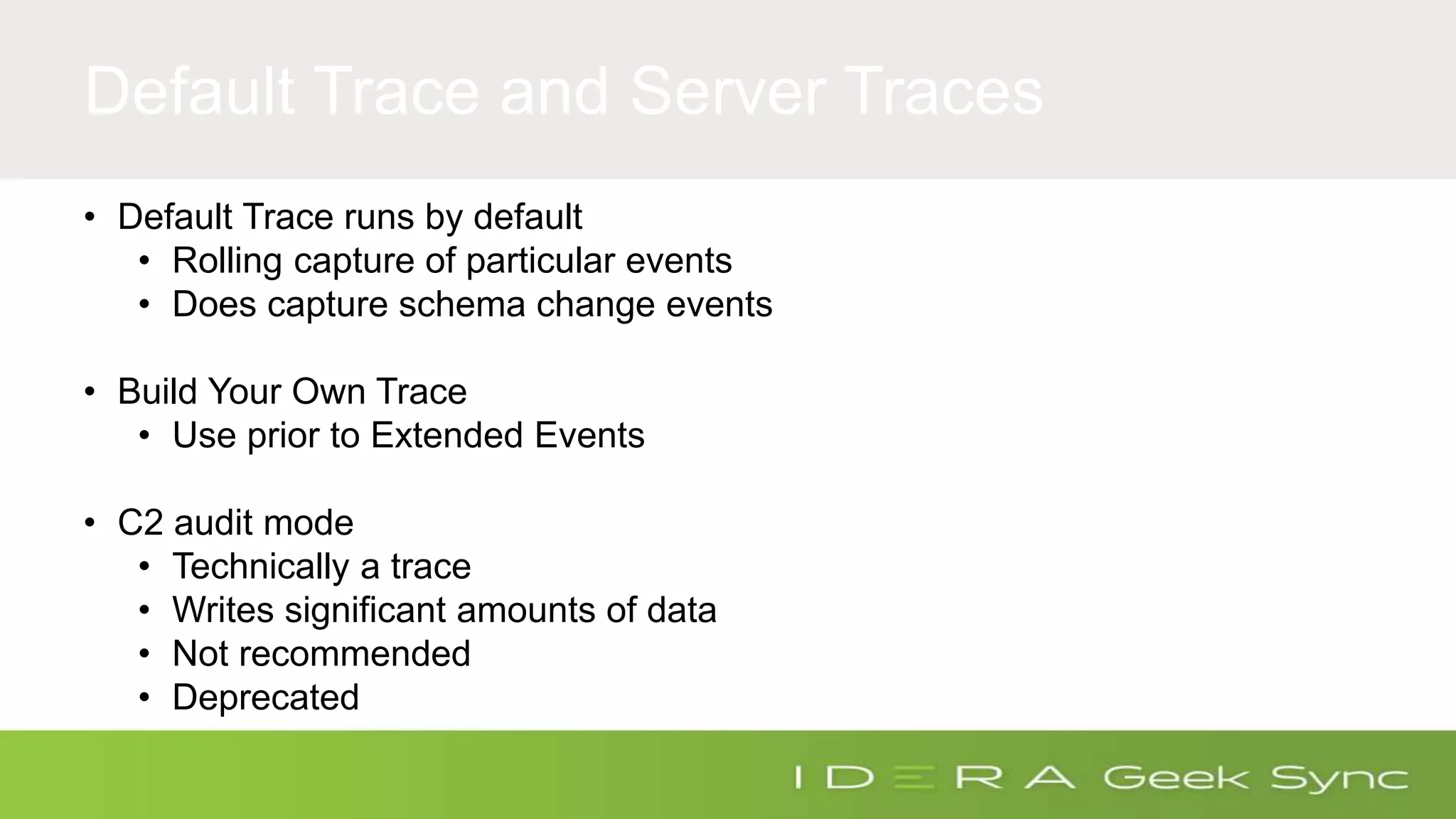
The document discusses how to ensure compliance with HIPAA regulations when handling electronic protected health information (ePHI) stored in SQL Server databases. It addresses five key questions around auditing access to ePHI, defining a secure SQL Server configuration baseline, implementing repeatable security processes, auditing permissions and changes in SQL Server, and maintaining ongoing compliance. The presenter provides recommendations for secure configurations, including role-based access control, encryption of data at rest and in transit, and auditing access through features like extended events and audit objects. Maintaining repeatable processes for security and change management is emphasized as important for compliance.