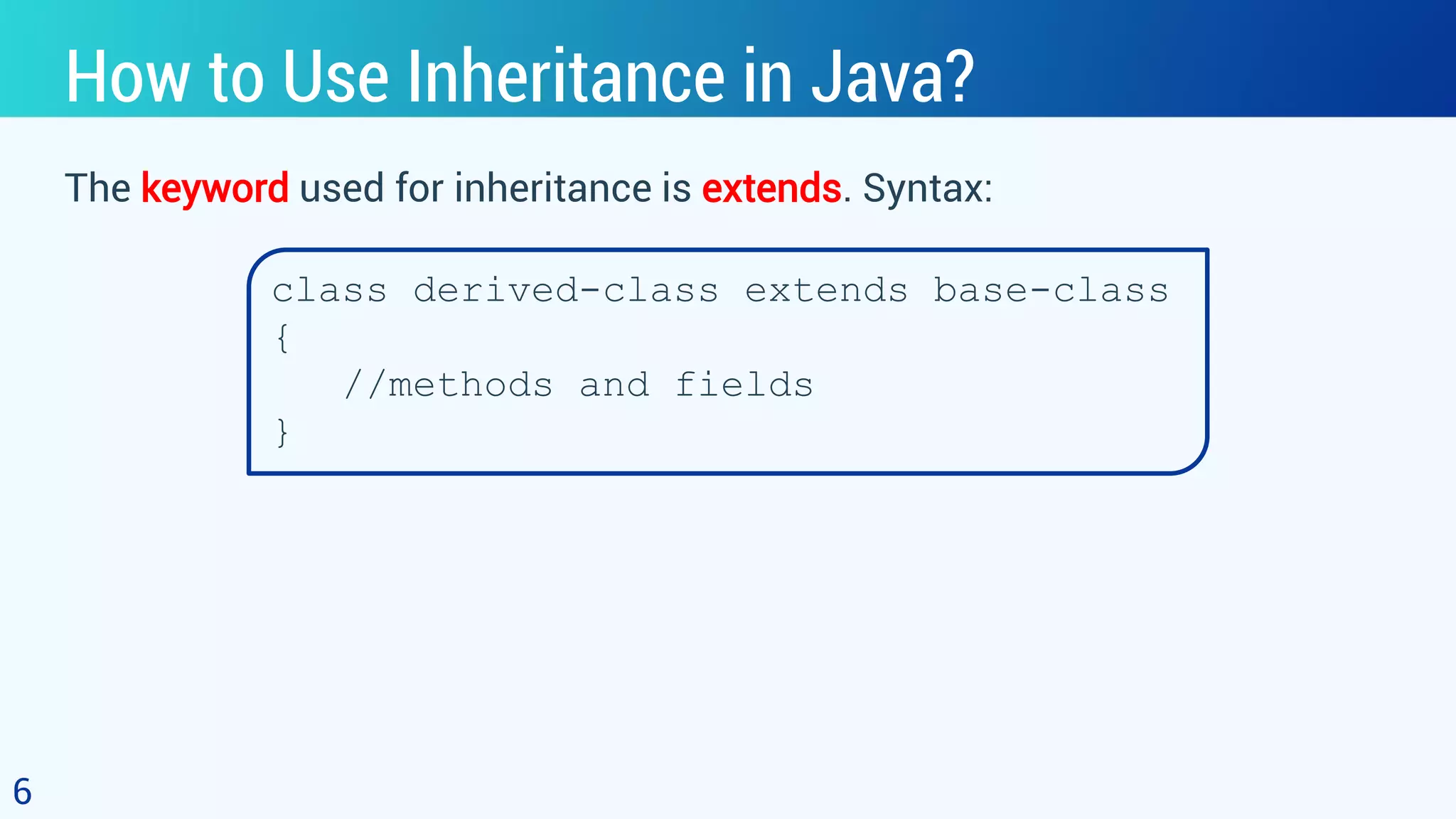
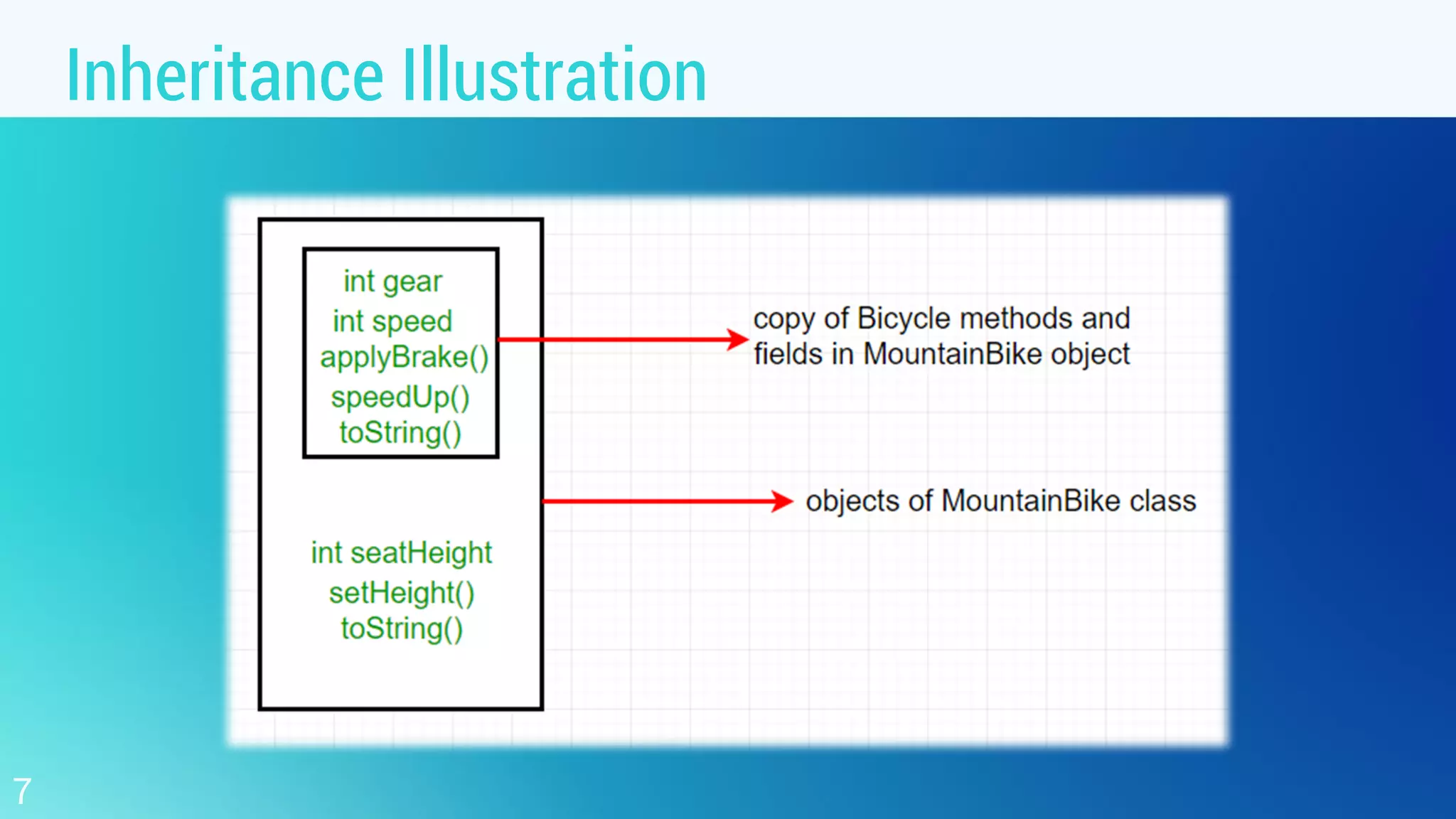
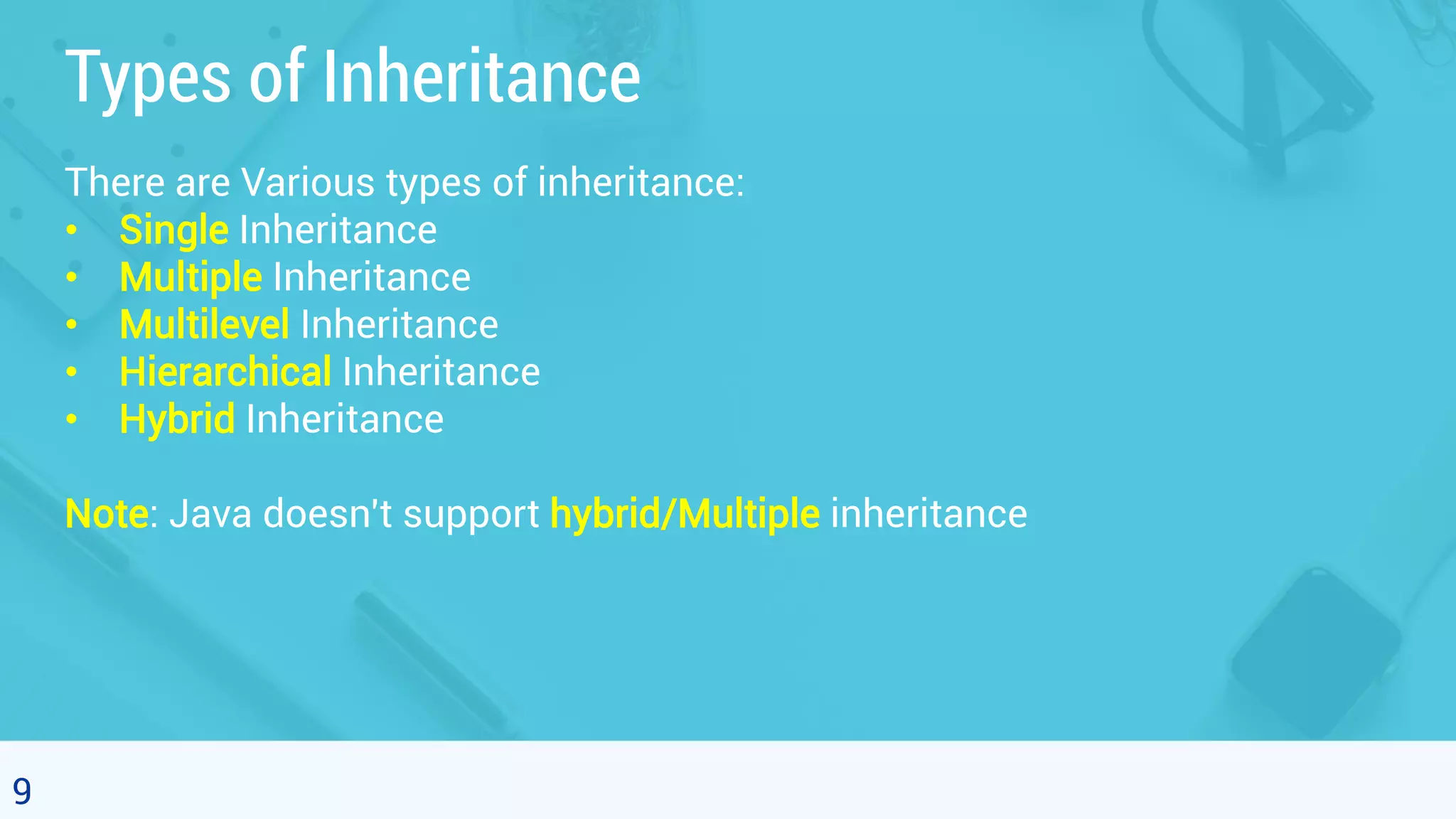
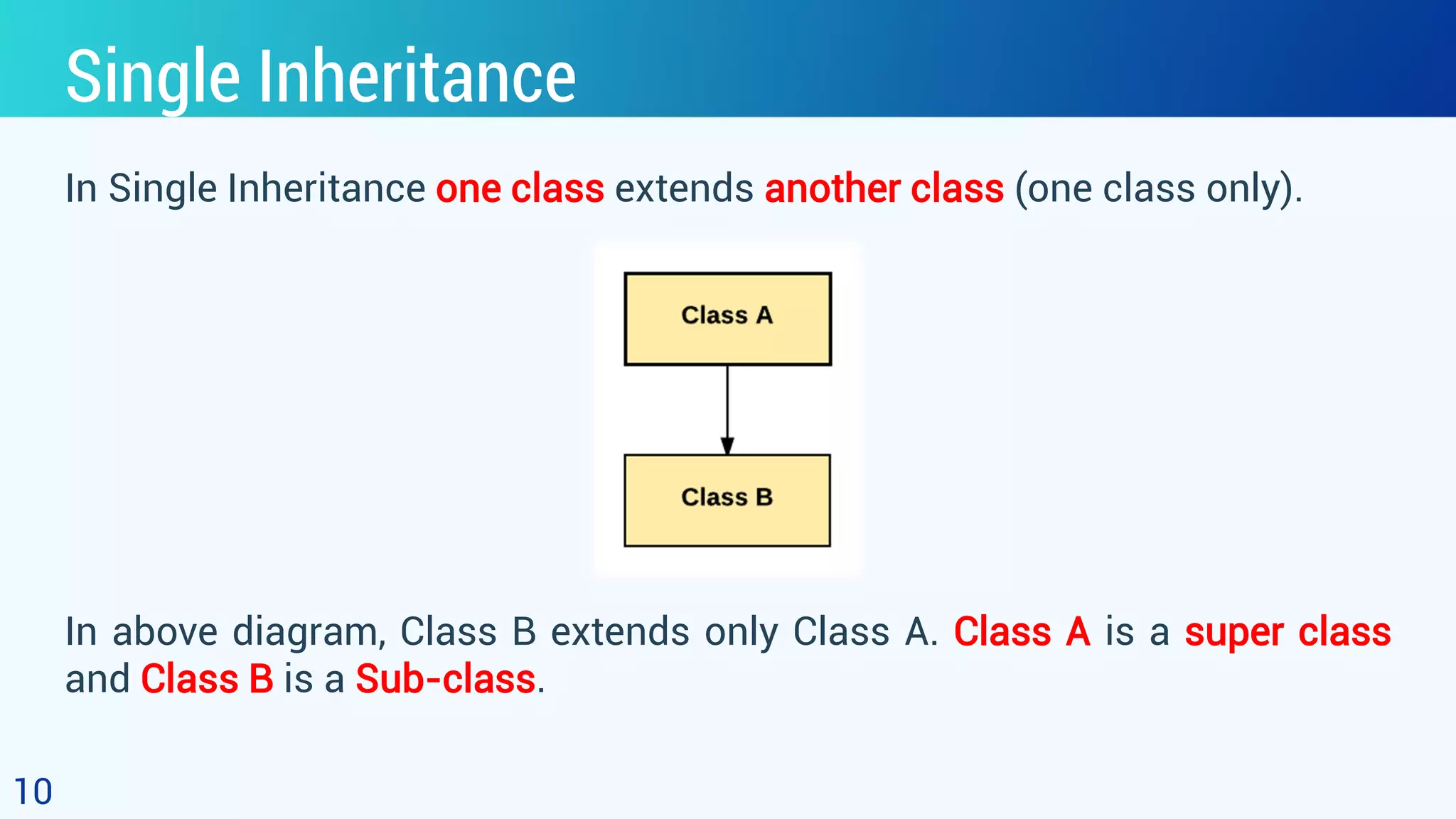
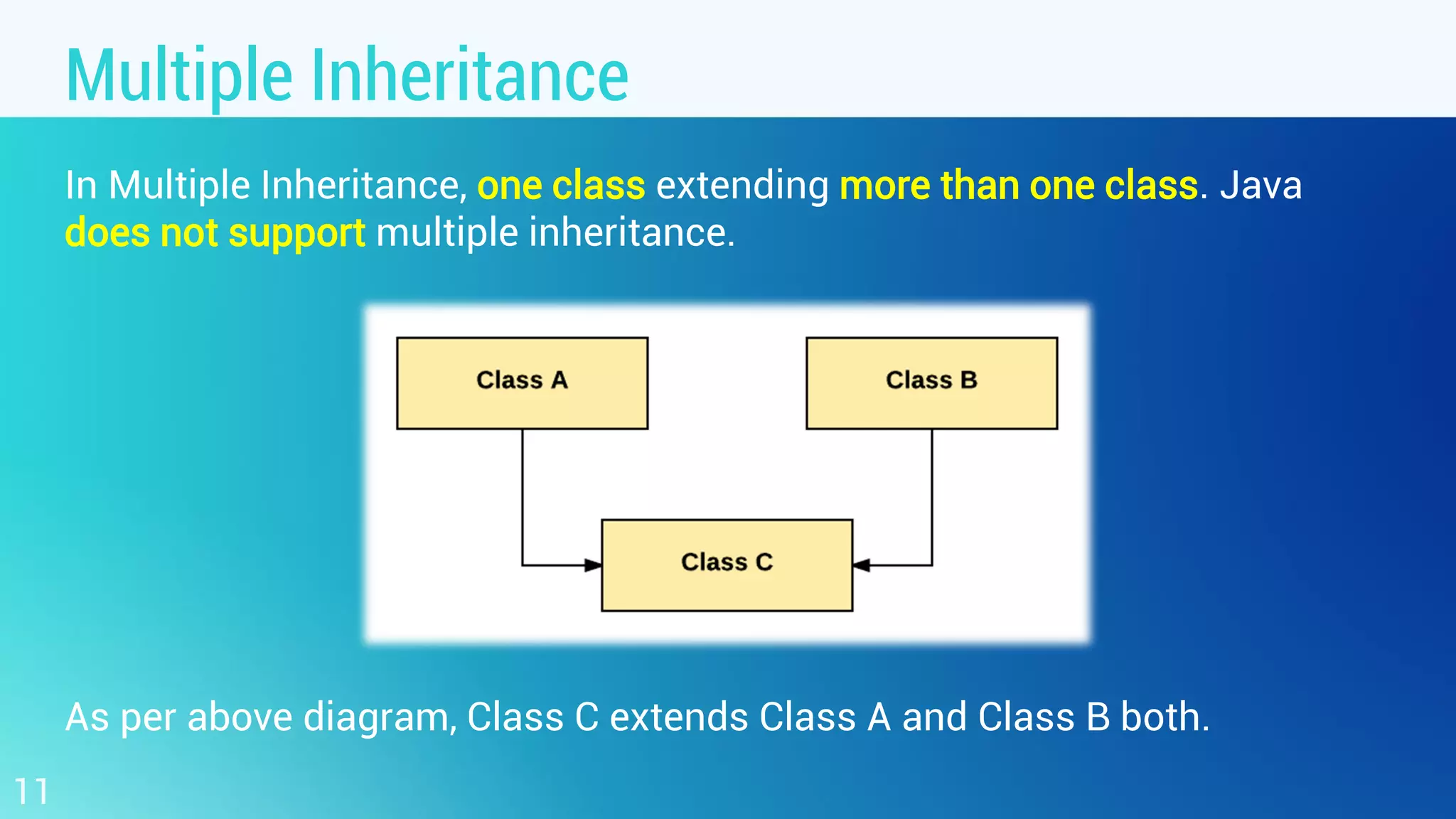
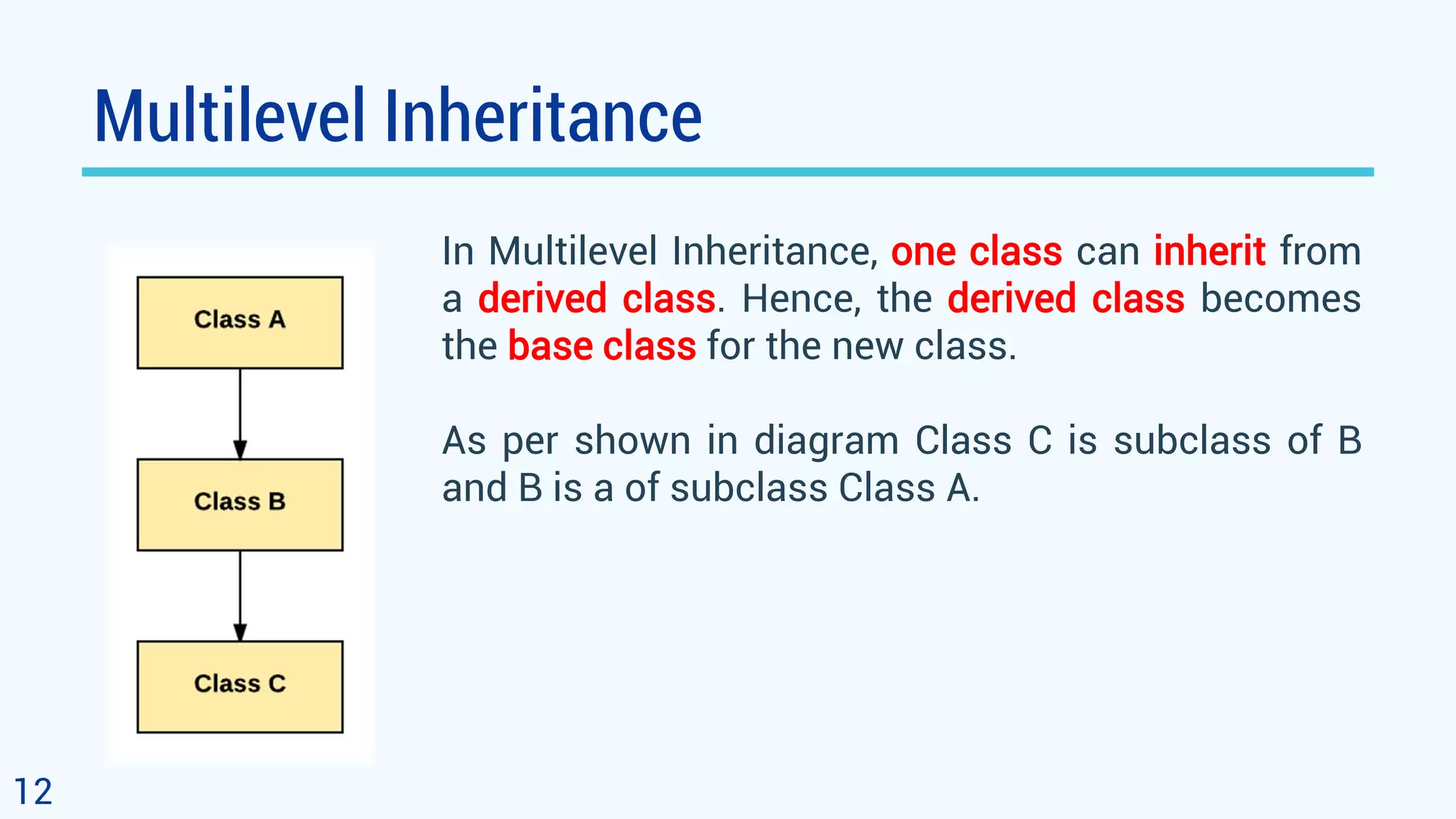
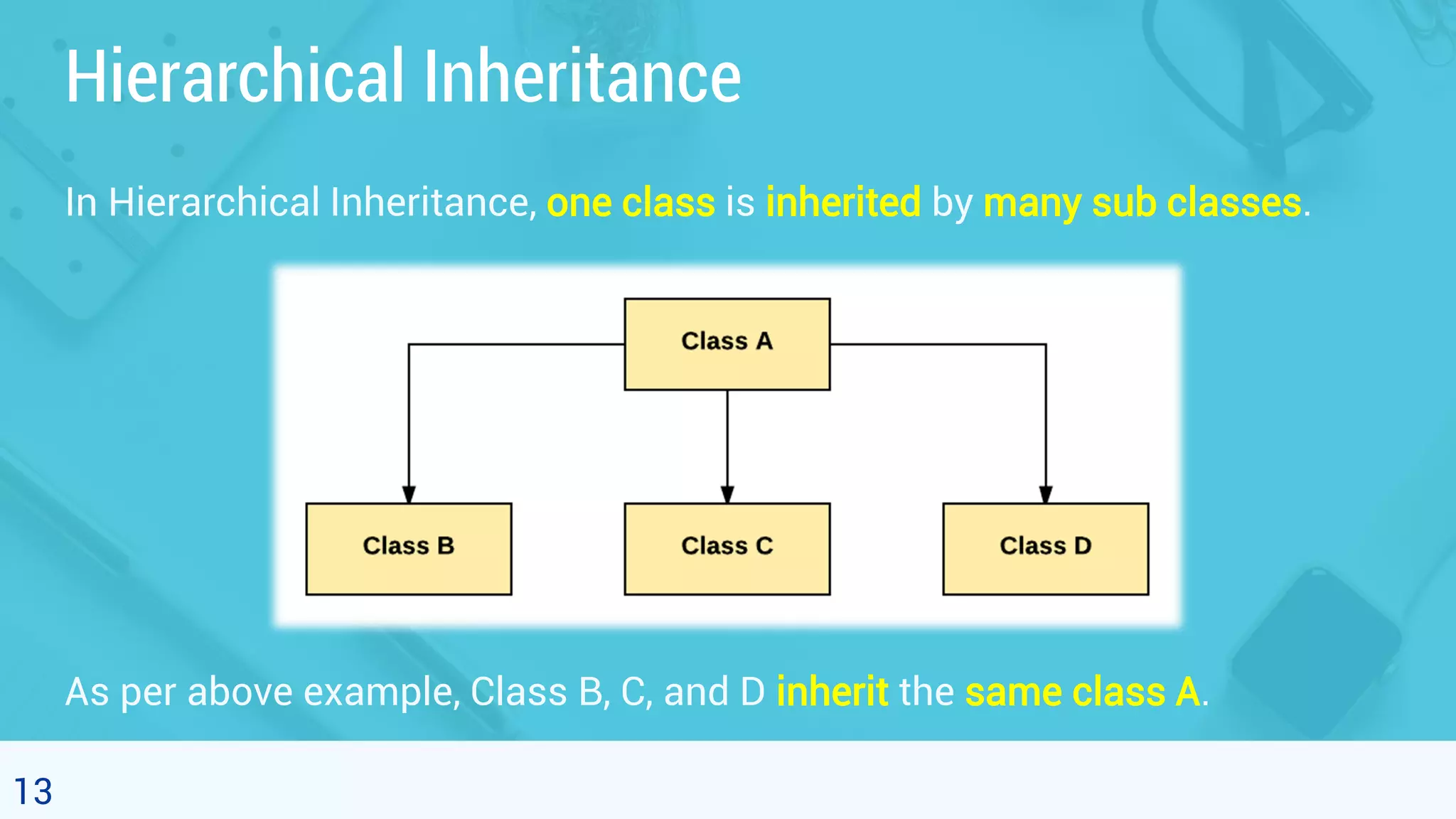
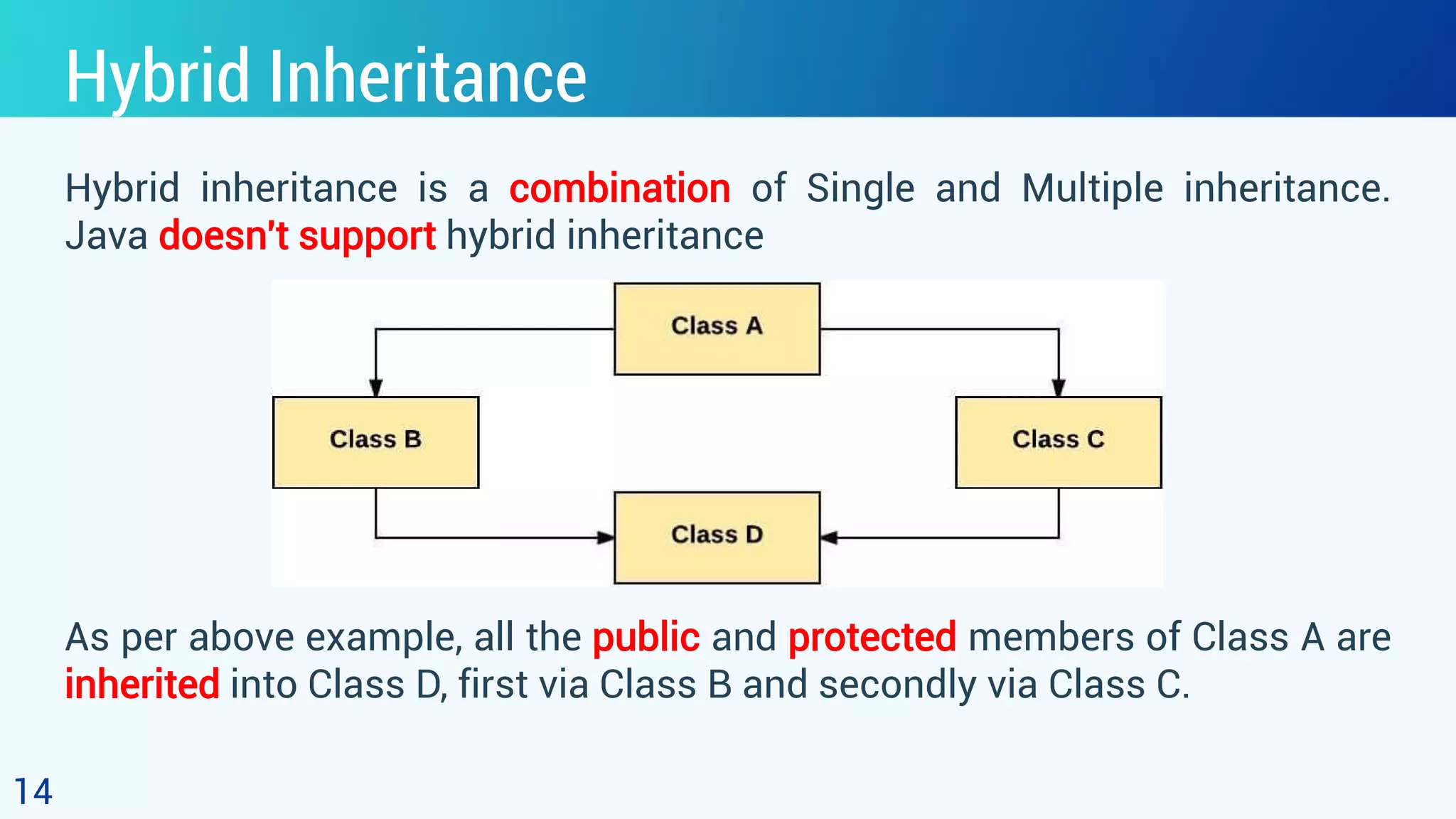
This document discusses object oriented programming and inheritance in Java. It defines inheritance as the mechanism in Java that allows one class to inherit the features of another class. It describes key terminology like superclass, subclass, reusability. It explains how to use the extends keyword in Java to create a subclass that inherits from a superclass. It provides examples of different types of inheritance like single, multilevel, hierarchical. It notes important facts like a subclass can only have one superclass and constructors are not inherited. Finally, it discusses how inheritance enables code reusability.