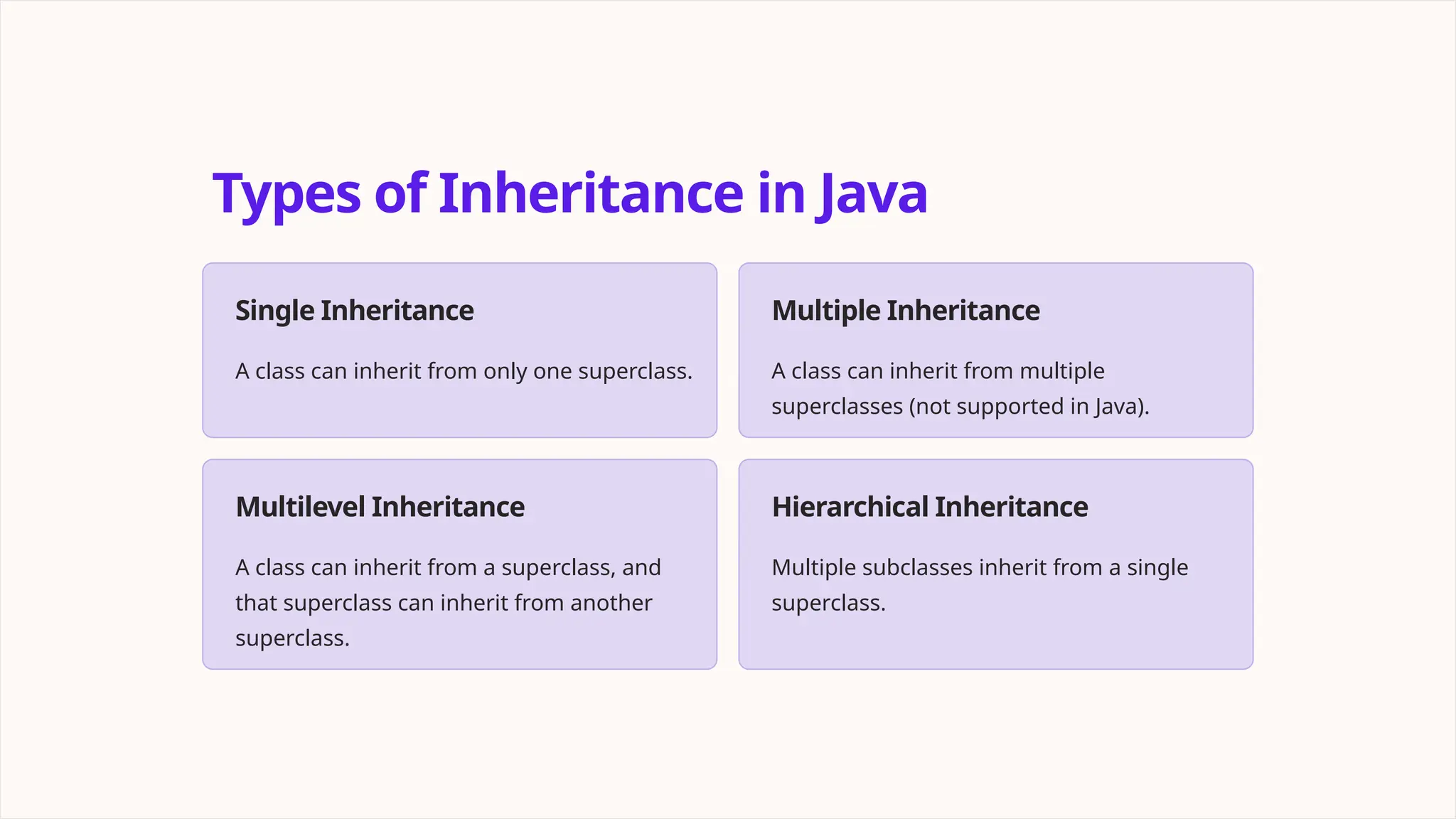
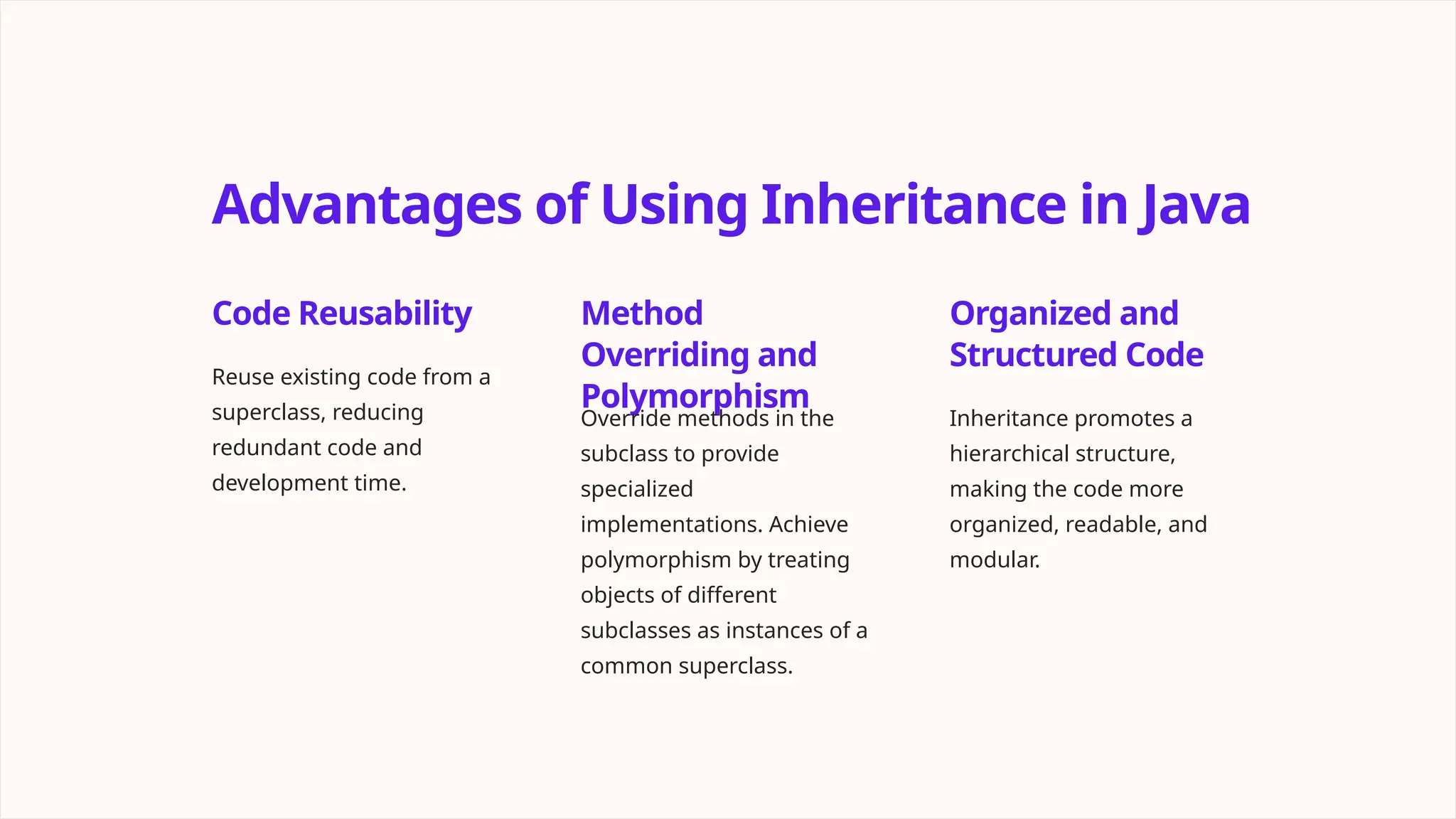
Inheritance in Java is a fundamental concept that allows classes to inherit properties and methods from other classes, promoting code reuse and establishing a hierarchy of classes. It includes types such as single, multilevel, and hierarchical inheritance, and offers advantages like code reusability and organized code. Best practices involve understanding class relationships, avoiding deep hierarchies, and using abstract classes and interfaces while being cautious of common misconceptions.