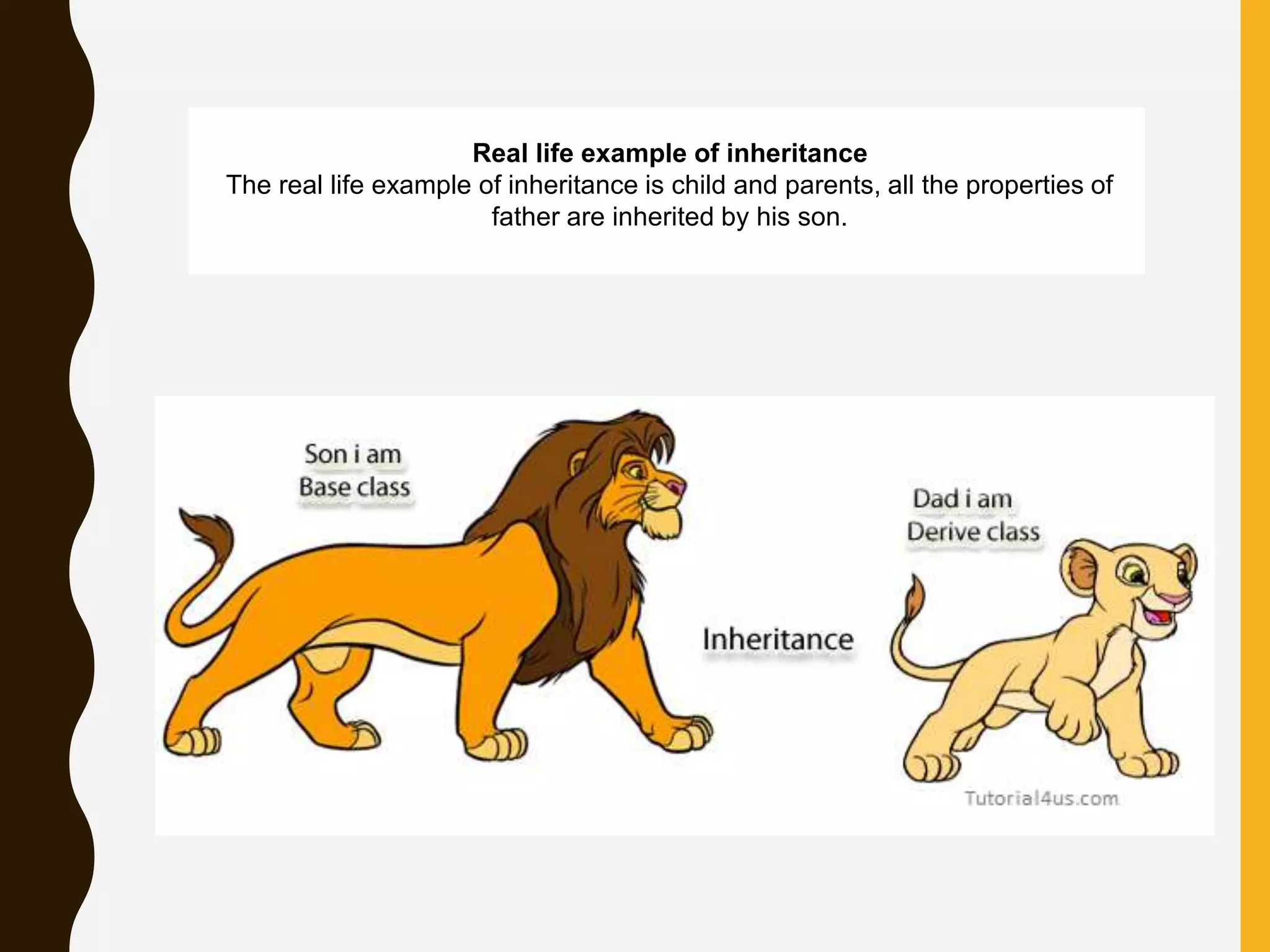
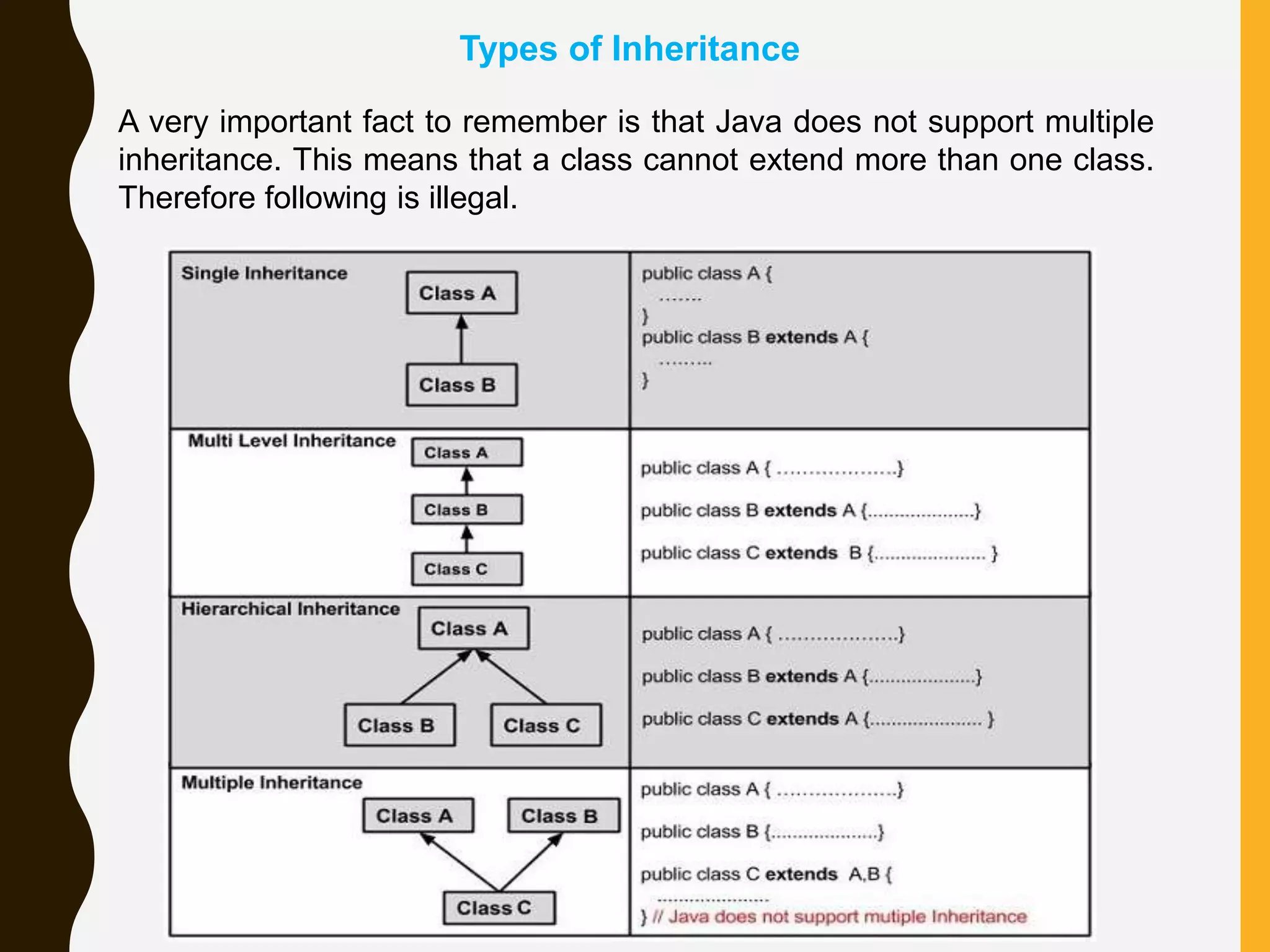
This document summarizes inheritance in Java. It defines inheritance as a class acquiring the properties of another class. The existing class is called the parent/superclass, while the derived class is the child/subclass. The child inherits characteristics from the parent like methods and data. Inheritance allows code reuse and minimizes duplicate code by moving common code to a superclass. However, it can increase program execution time and tightly couples classes, requiring changes to both if a method signature changes.




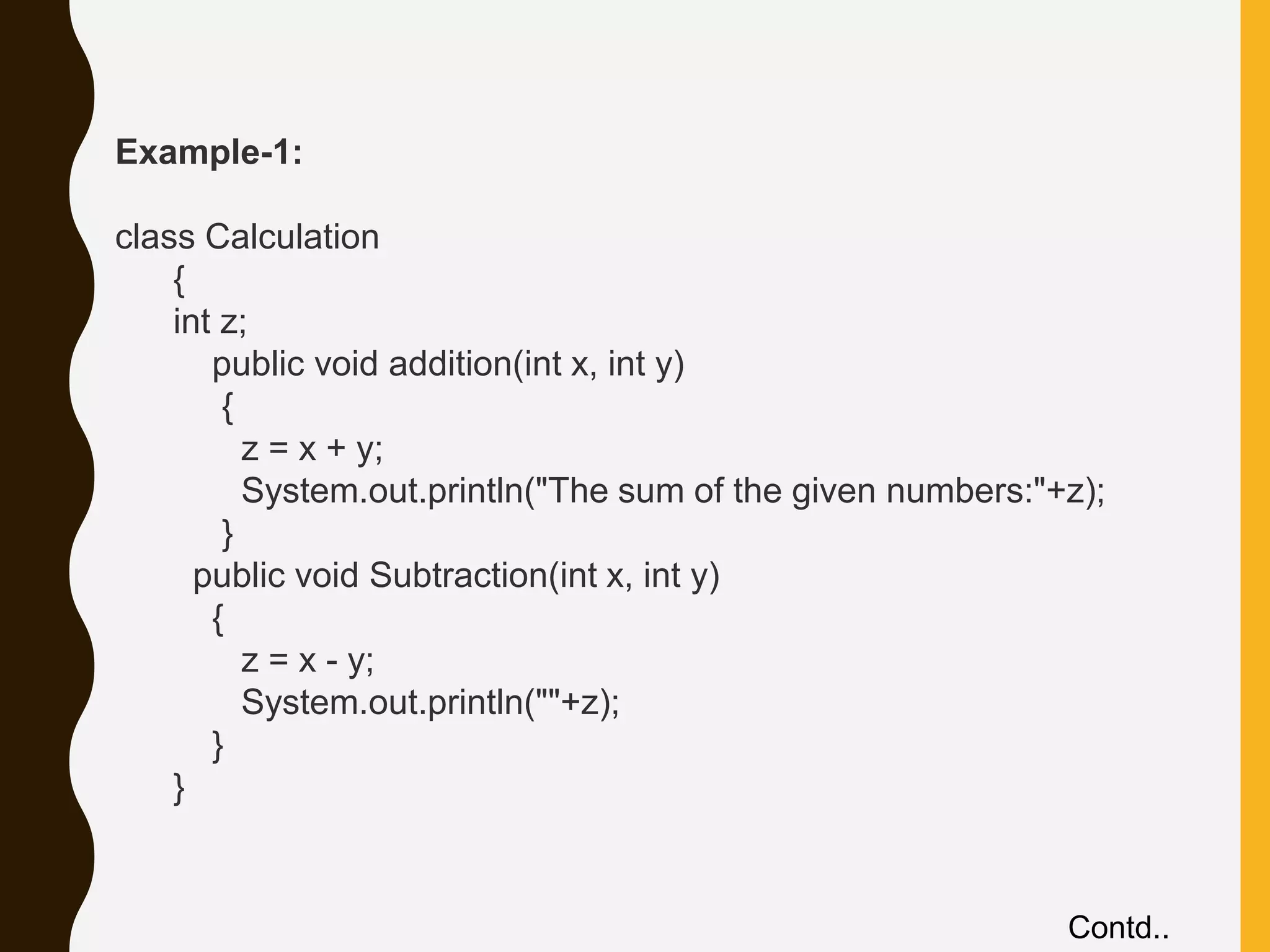
![public class MyCalculation extends Calculation { public void multiplication(int x, int y) { z = x * y; System.out.println("The product of the given numbers:"+z); } } class exe_calc { public static void main(String args[]) { int a = 20, b = 10; MyCalculation demo = new MyCalculation(); demo.addition(a, b); demo.Subtraction(a, b); demo.multiplication(a, b); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2javainheritance-210516072218/75/Java-Inheritance-9-2048.jpg)