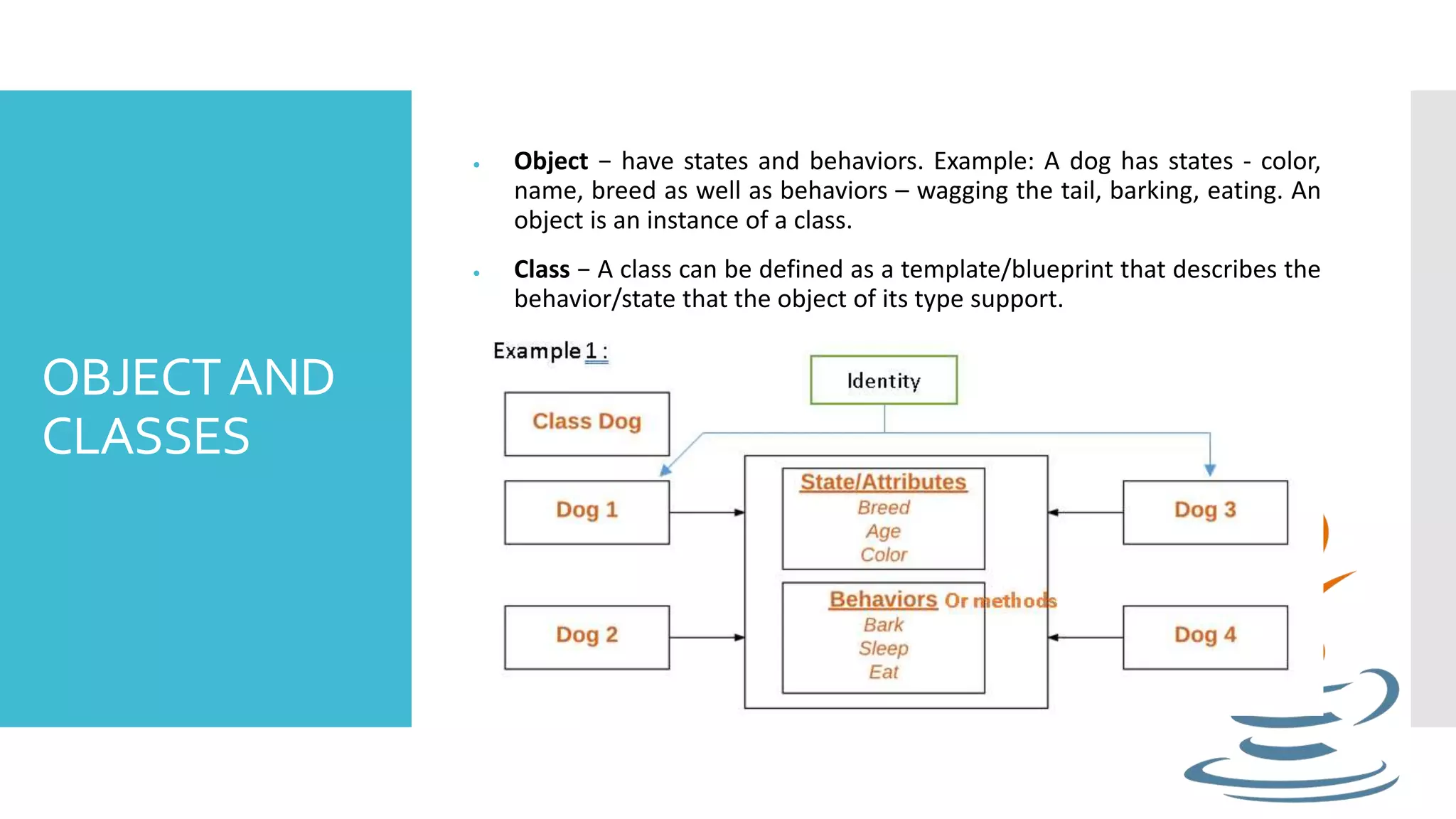
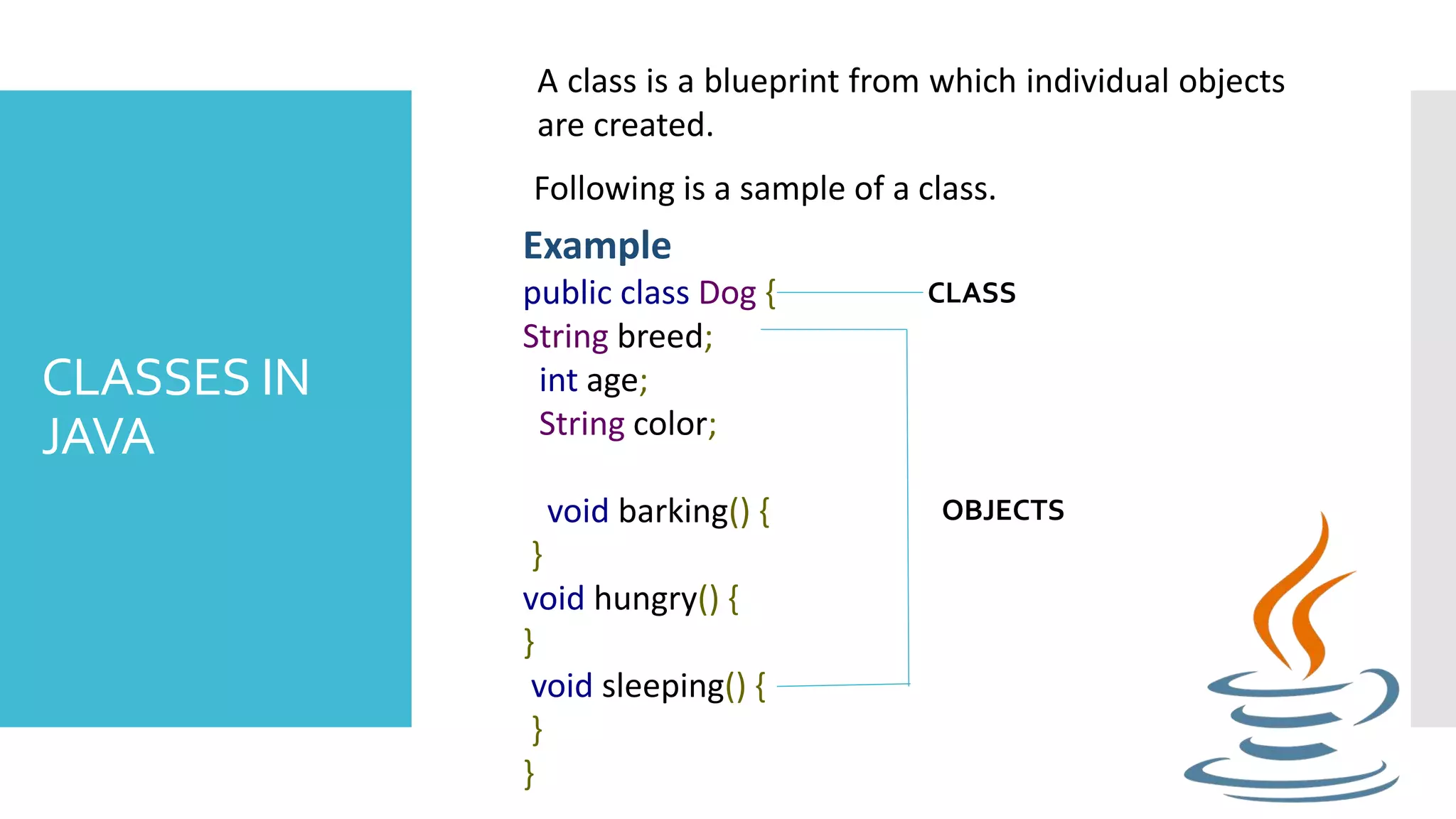
This document discusses objects and classes in Java. An object has states like attributes and behaviors like methods. A class defines a template for objects with the same attributes and behaviors. In Java, objects have fields to store state and methods to show behavior. A class defines the blueprint for objects, including variables and methods. Constructors are special methods that initialize new objects, and the new keyword is used to create objects from classes by allocating memory and calling a constructor.



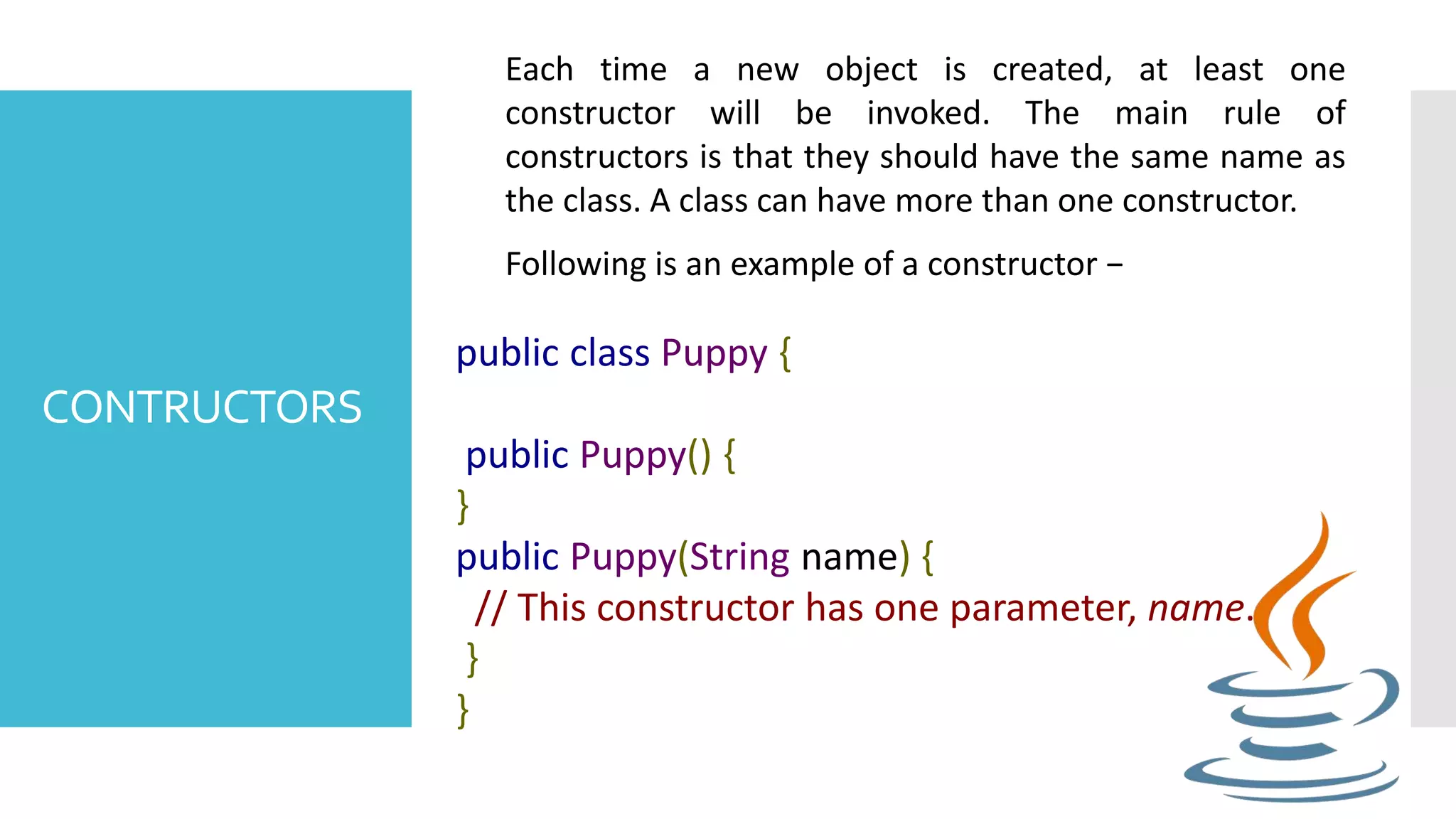

![EXAMPLE public class Puppy { public Puppy(String name) { // This constructor has one parameter, name. System.out.println("Passed Name is :" + name ); } public static void main(String []args) { // Following statement would create an object myPuppy Puppy myPuppy = new Puppy( "tommy" ); } } If we compile and run the above program, then it will produce the following result − Output Passed Name is :tommy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerprogramming2-chapter2-201020032839/75/Computer-programming-2-Lesson-3-8-2048.jpg)