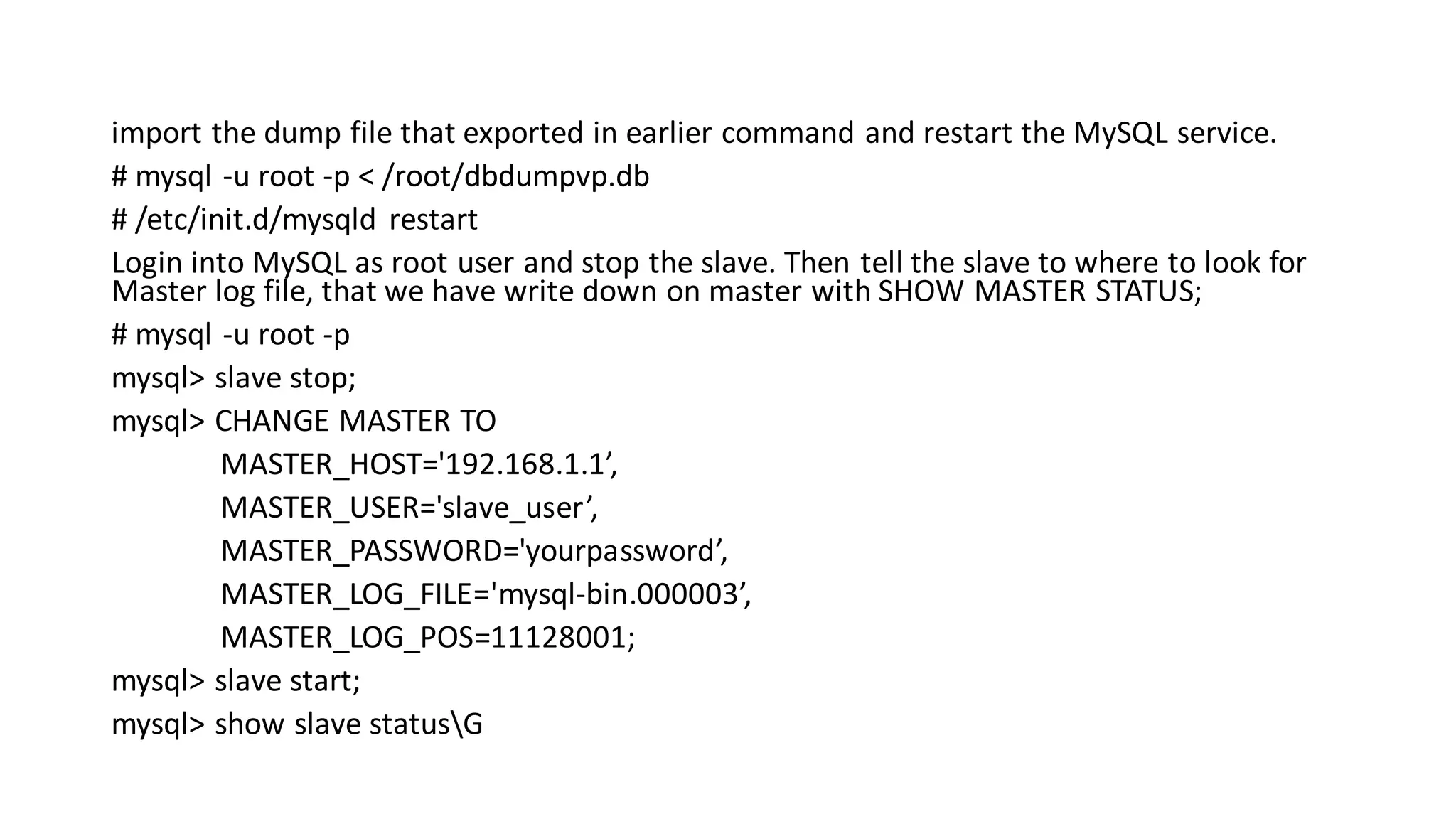
This document describes how to configure MySQL database replication between a master and slave server. The key steps are: 1. Configure the master server by editing its configuration file to enable binary logging and set the server ID. Create a replication user and grant privileges. 2. Export the databases from the master using mysqldump. 3. Configure the slave server by editing its configuration file to point to the master server. Import the database dump. Start replication on the slave. 4. Verify replication is working by inserting data on the master and checking it is replicated to the slave.