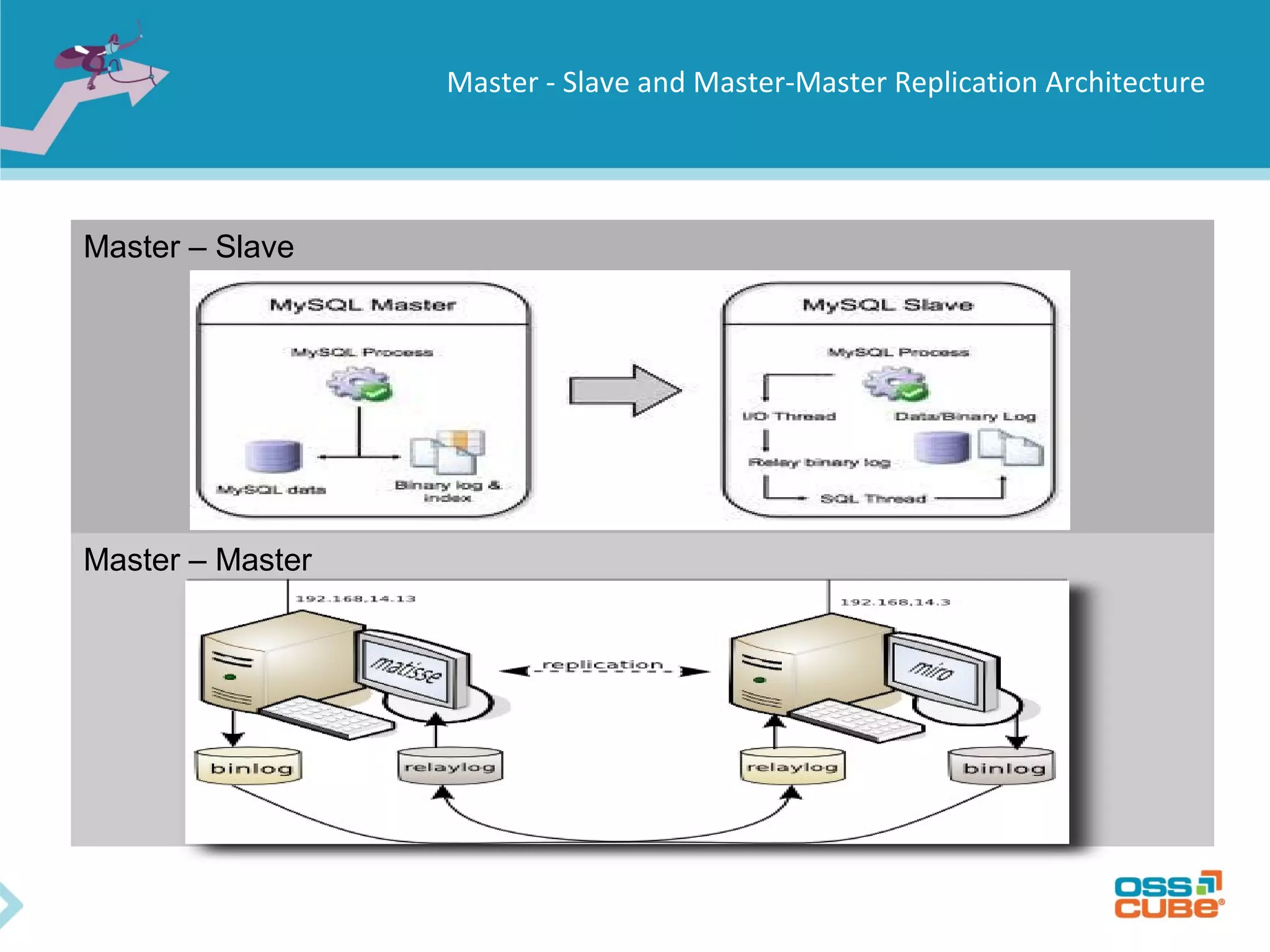
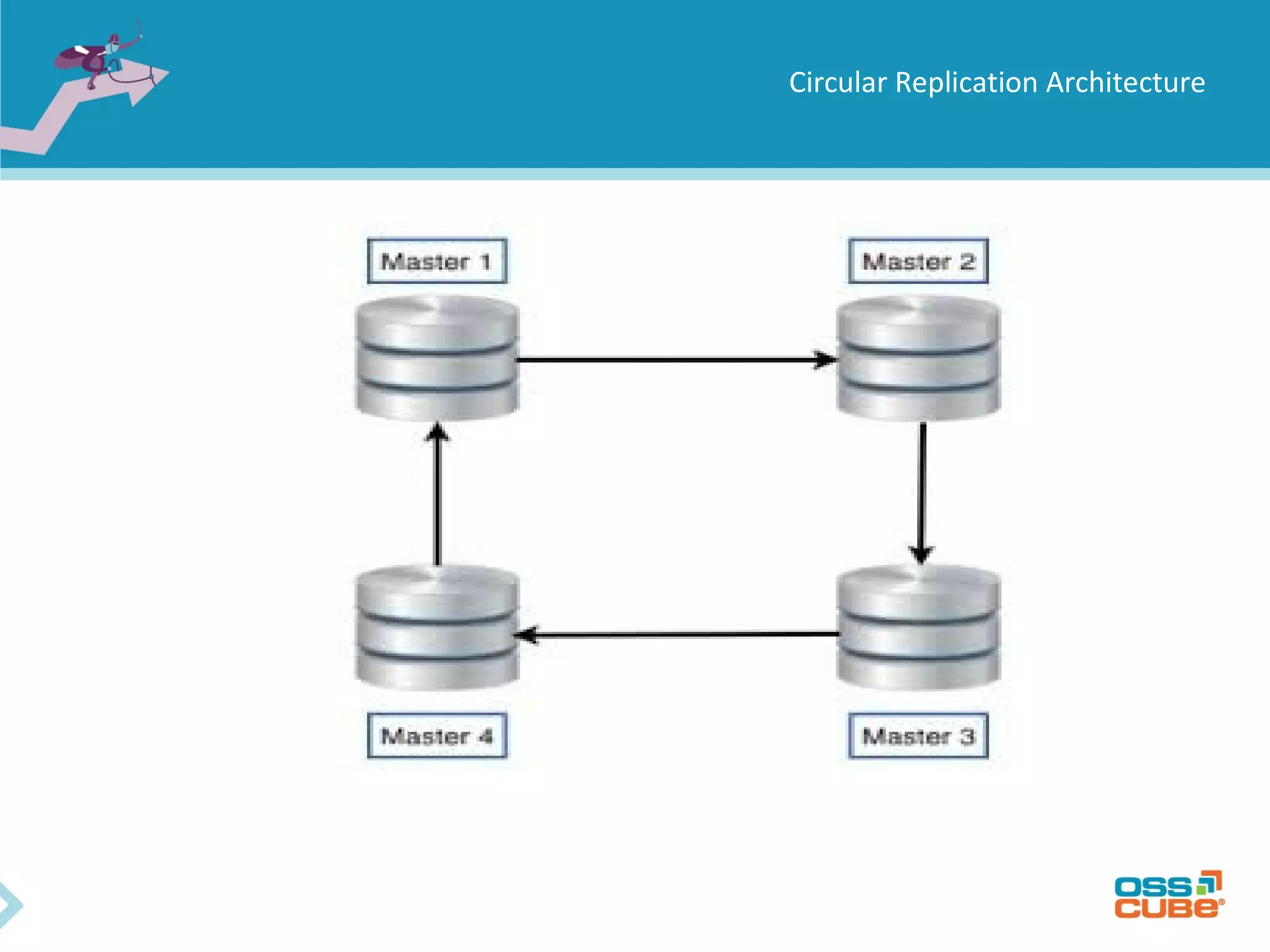
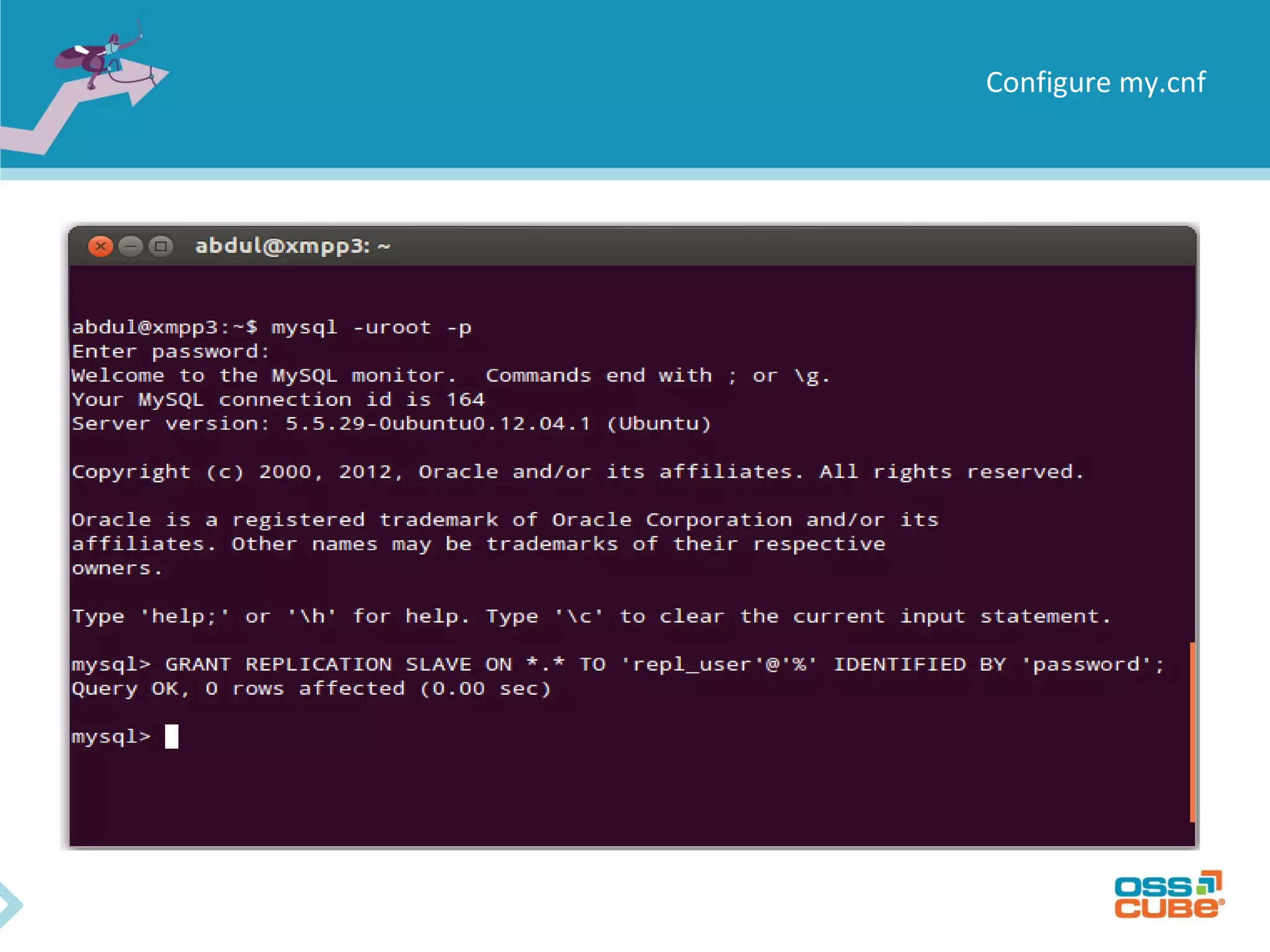
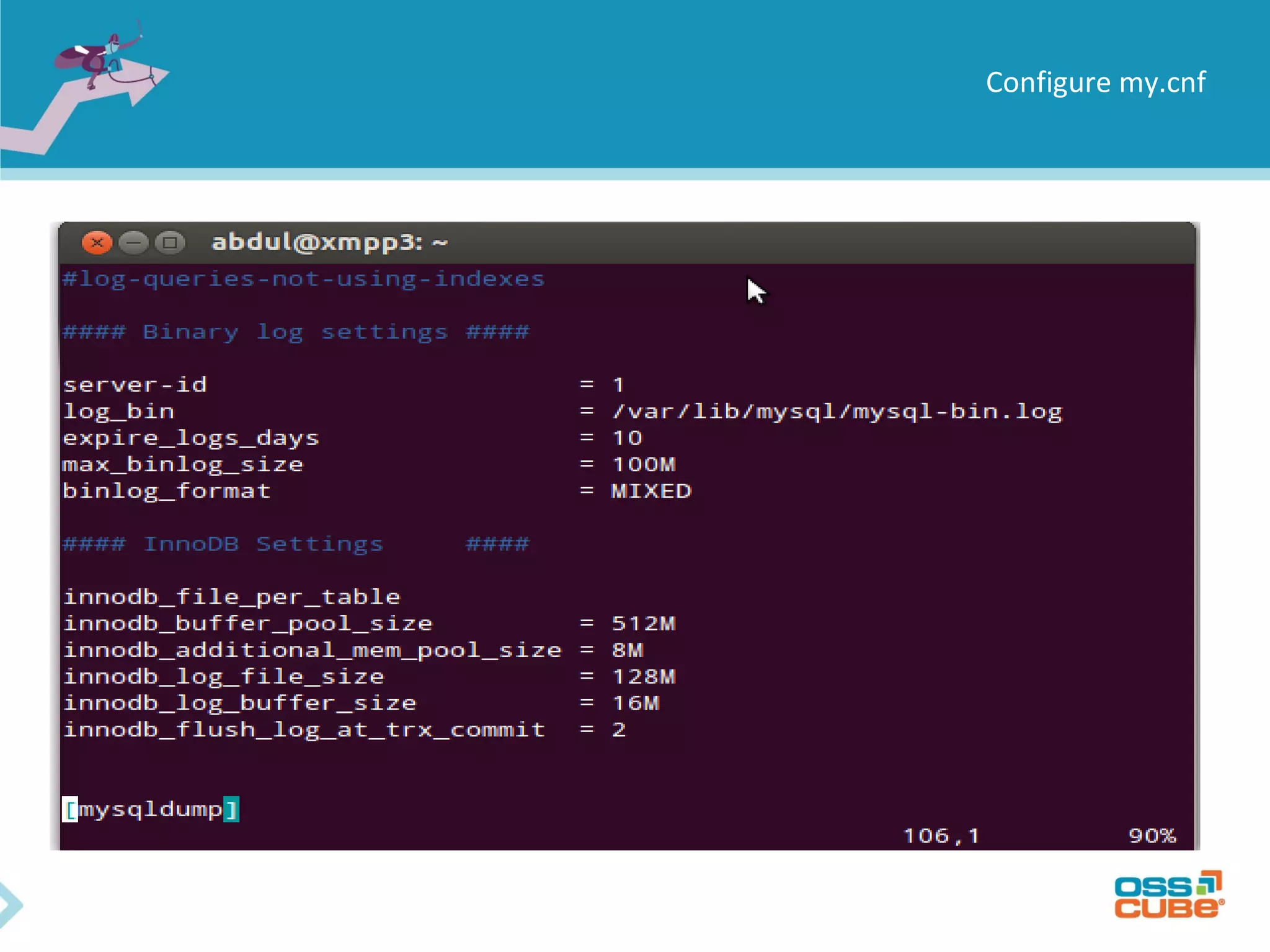
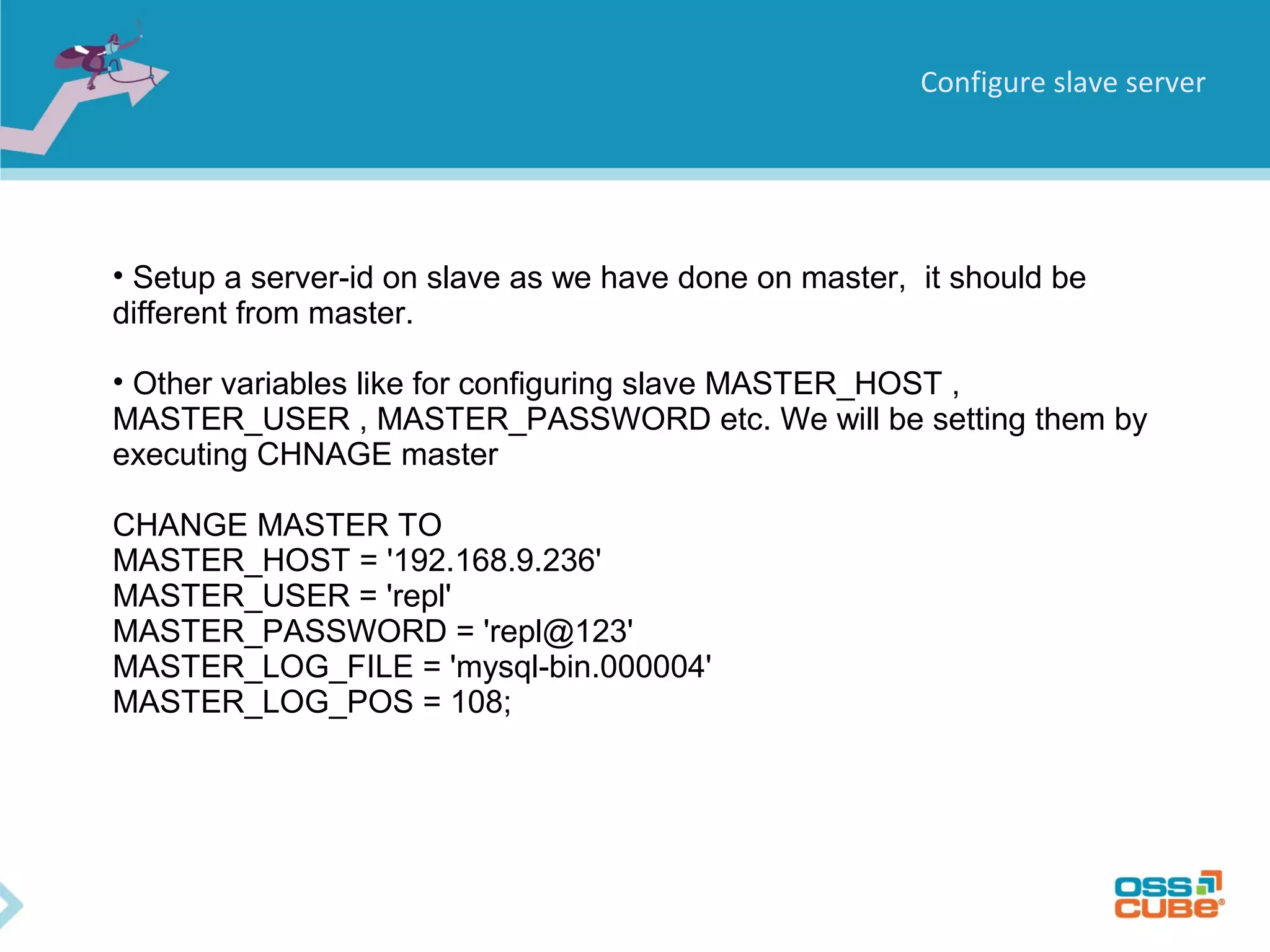
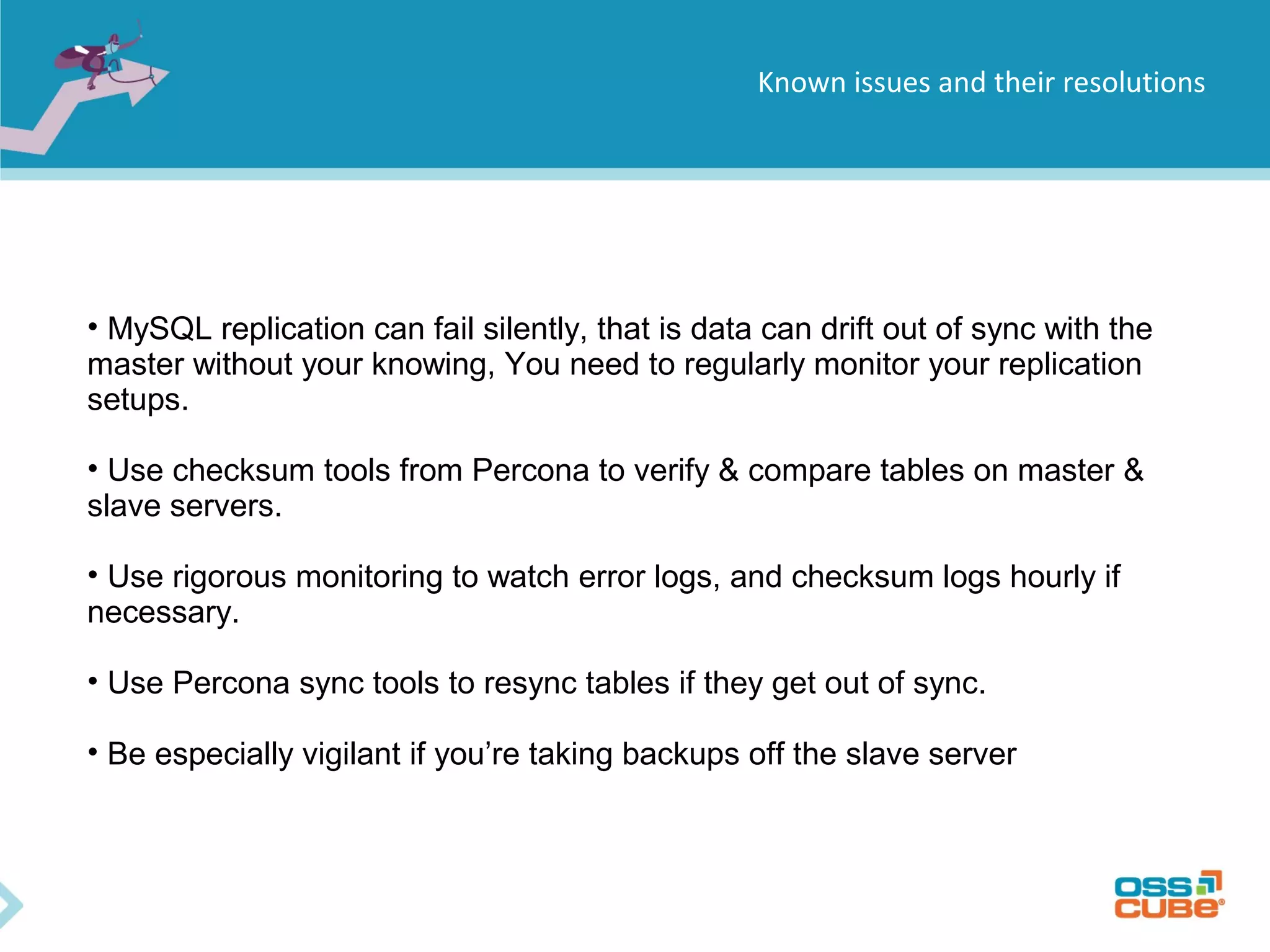
MySQL replication allows data to be replicated from a master database server to slave servers. It works by having the master write all data and schema changes to its binary log, which slaves then read from to apply the same changes locally. Replication can be used for backups, splitting read/write loads, and creating reporting systems on slaves. MySQL supports asynchronous replication where writes are considered complete once acknowledged locally, without waiting for confirmation from slaves. Setting up replication involves configuring replication users and server IDs, enabling binary logging on the master, restoring backups on slaves, and starting the replication process using CHANGE MASTER and START SLAVE commands. Regular monitoring is needed to check for data drift between master and slaves.