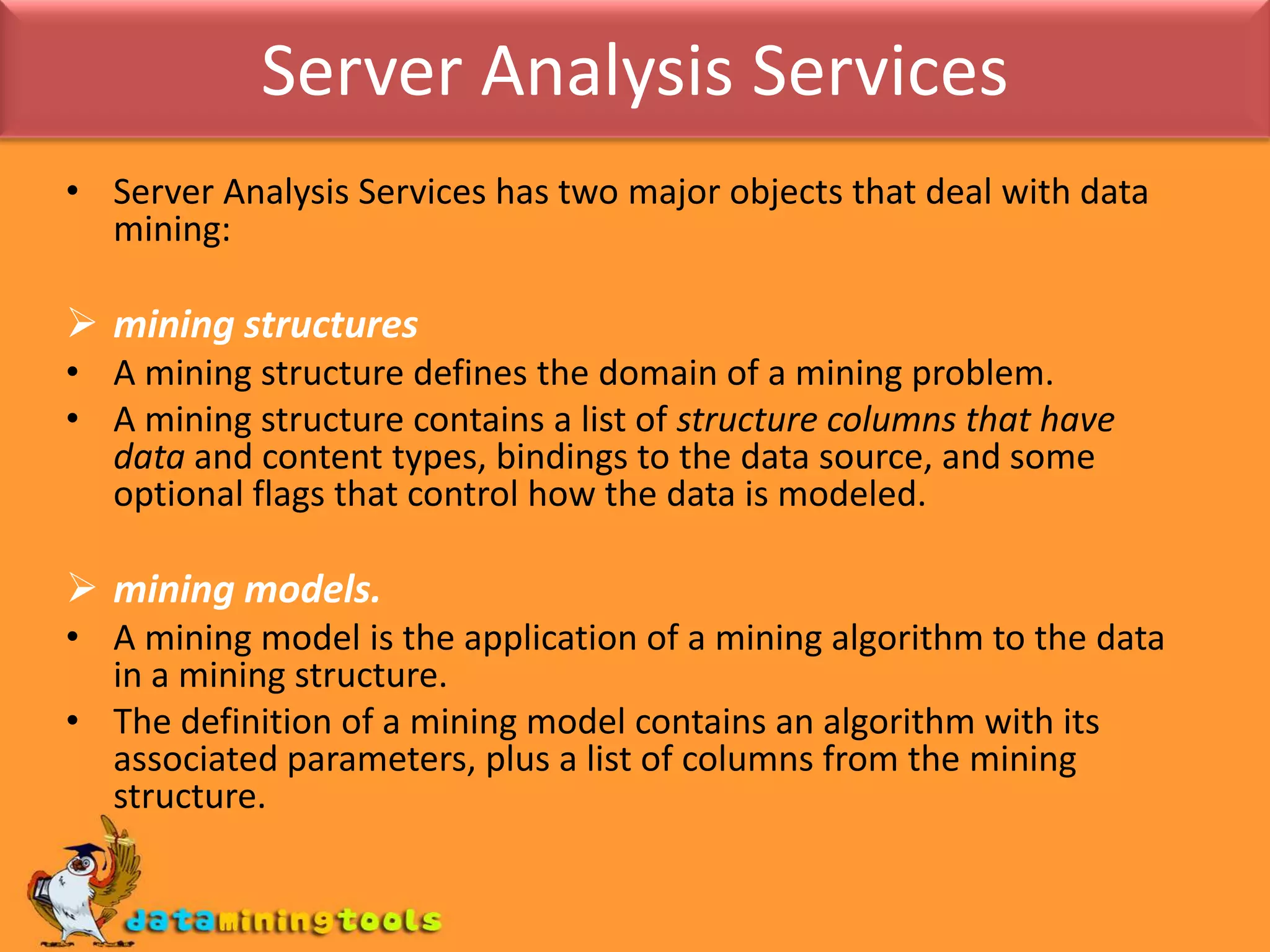
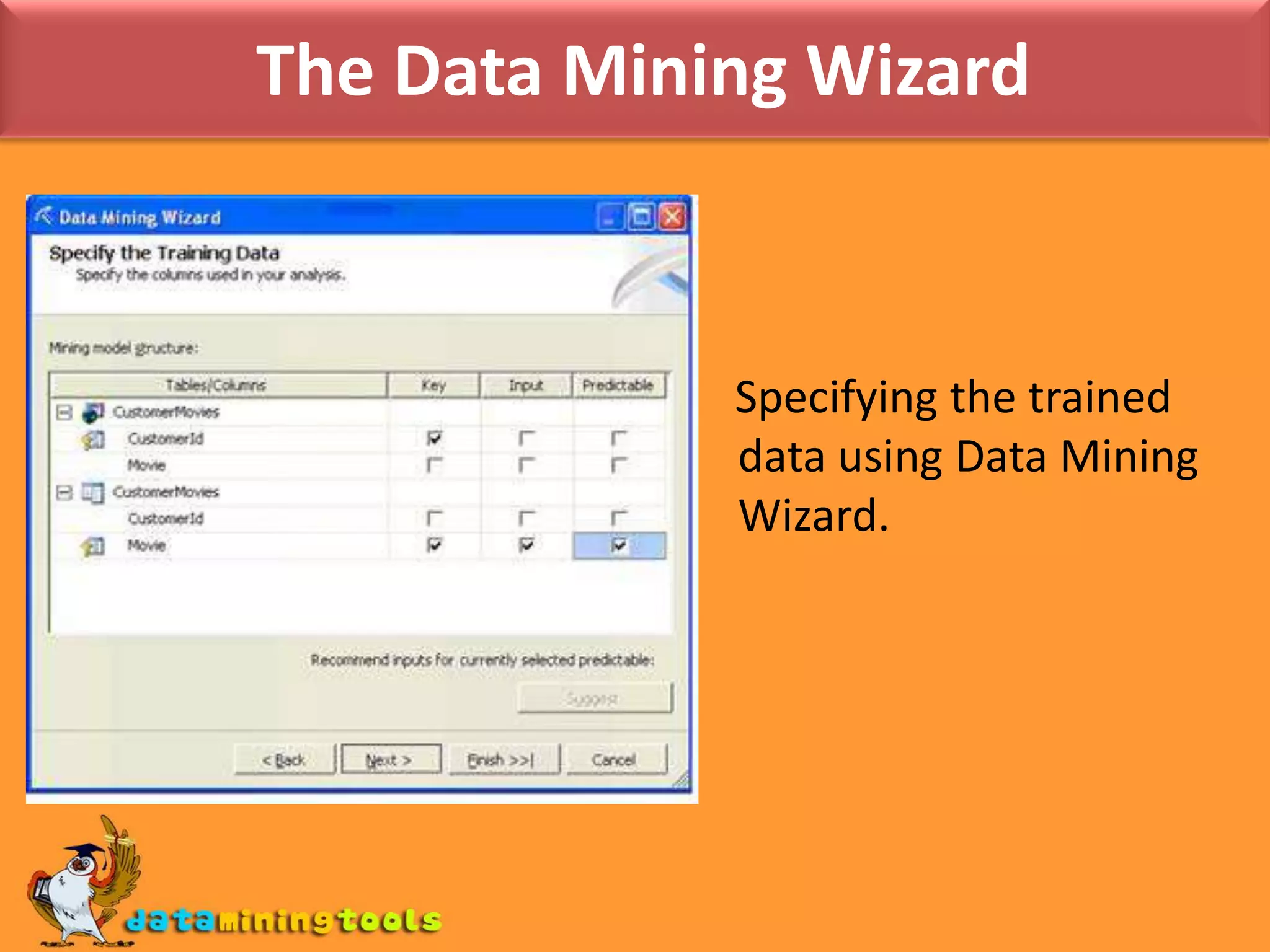
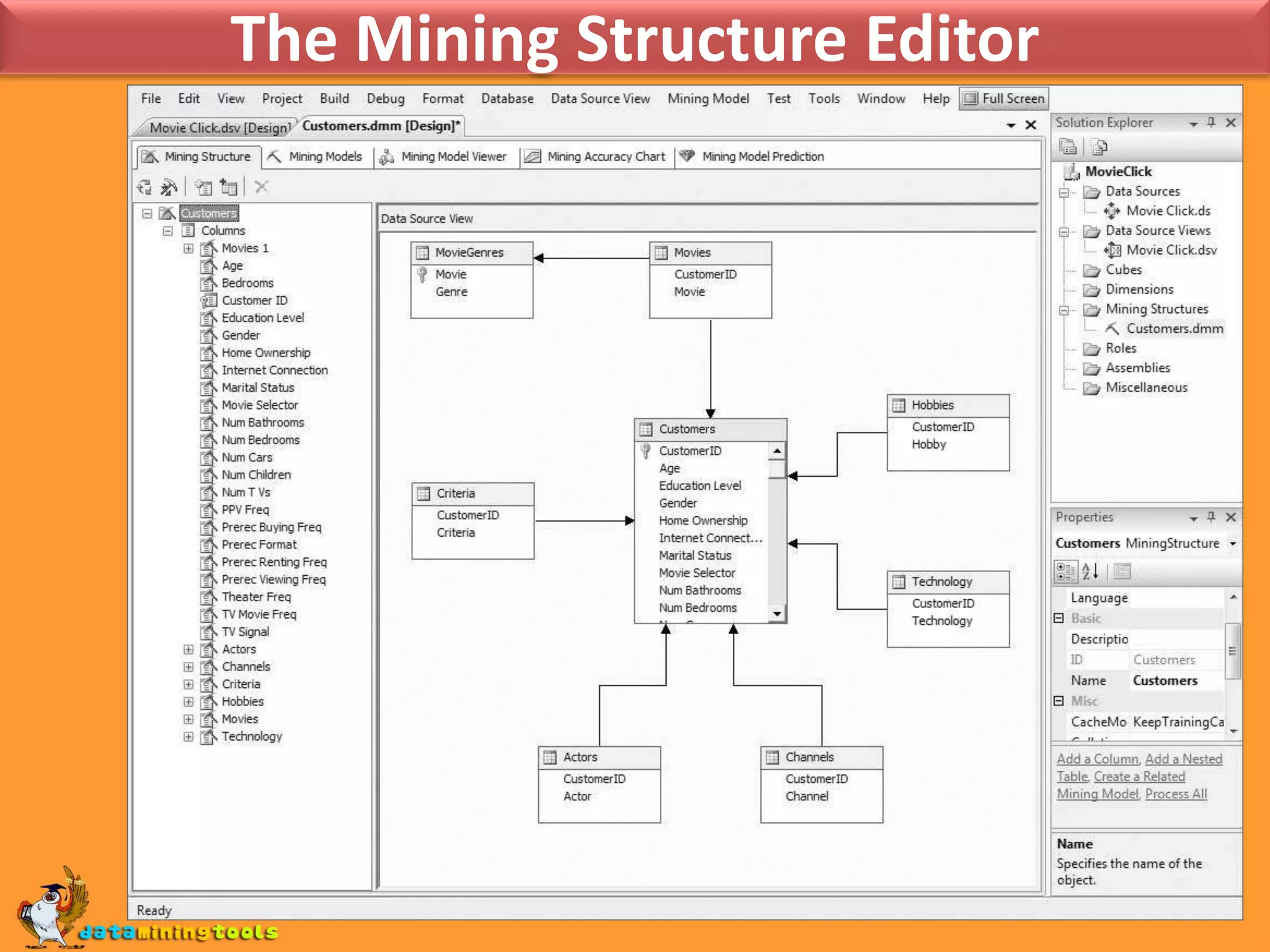
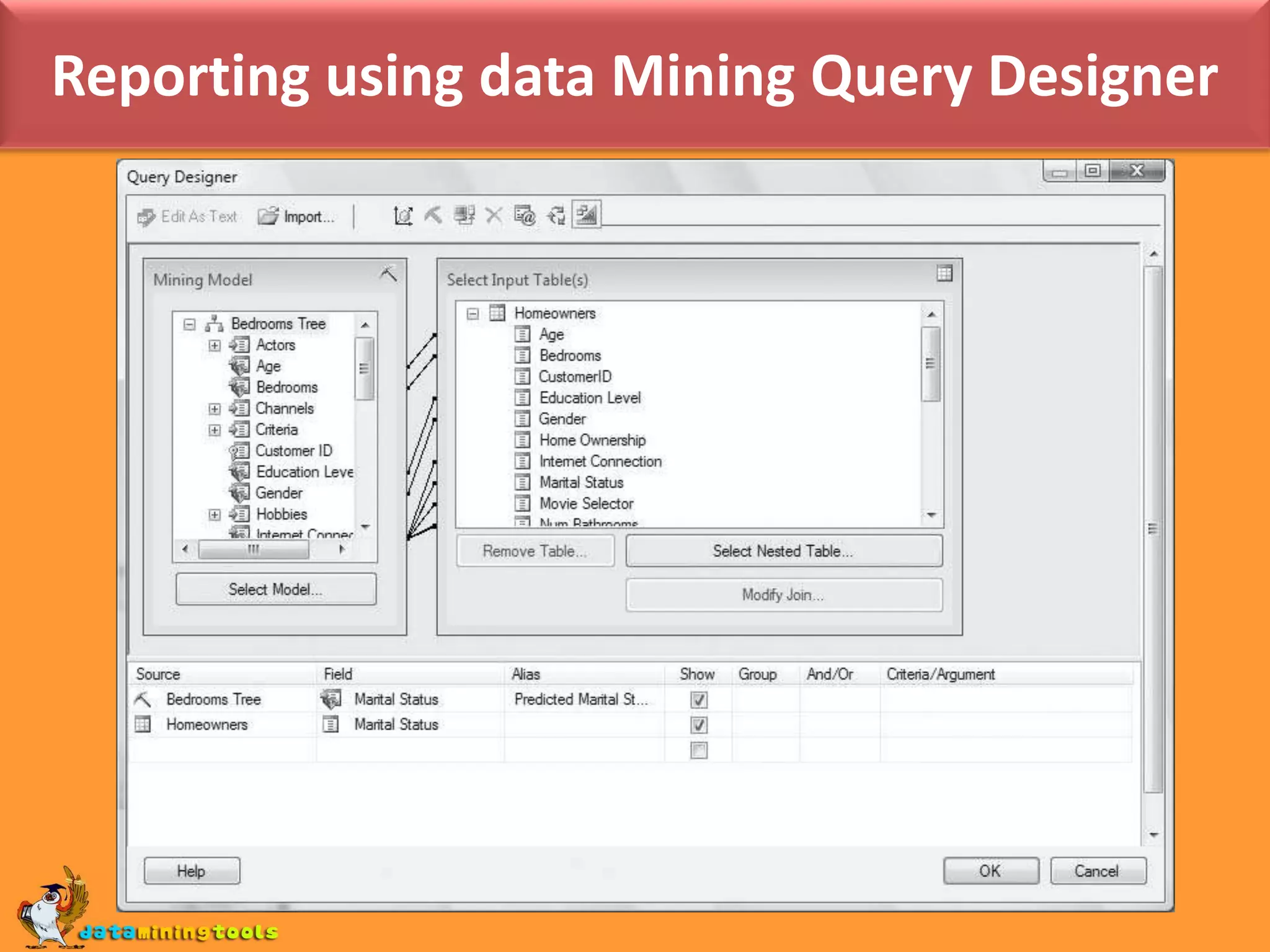
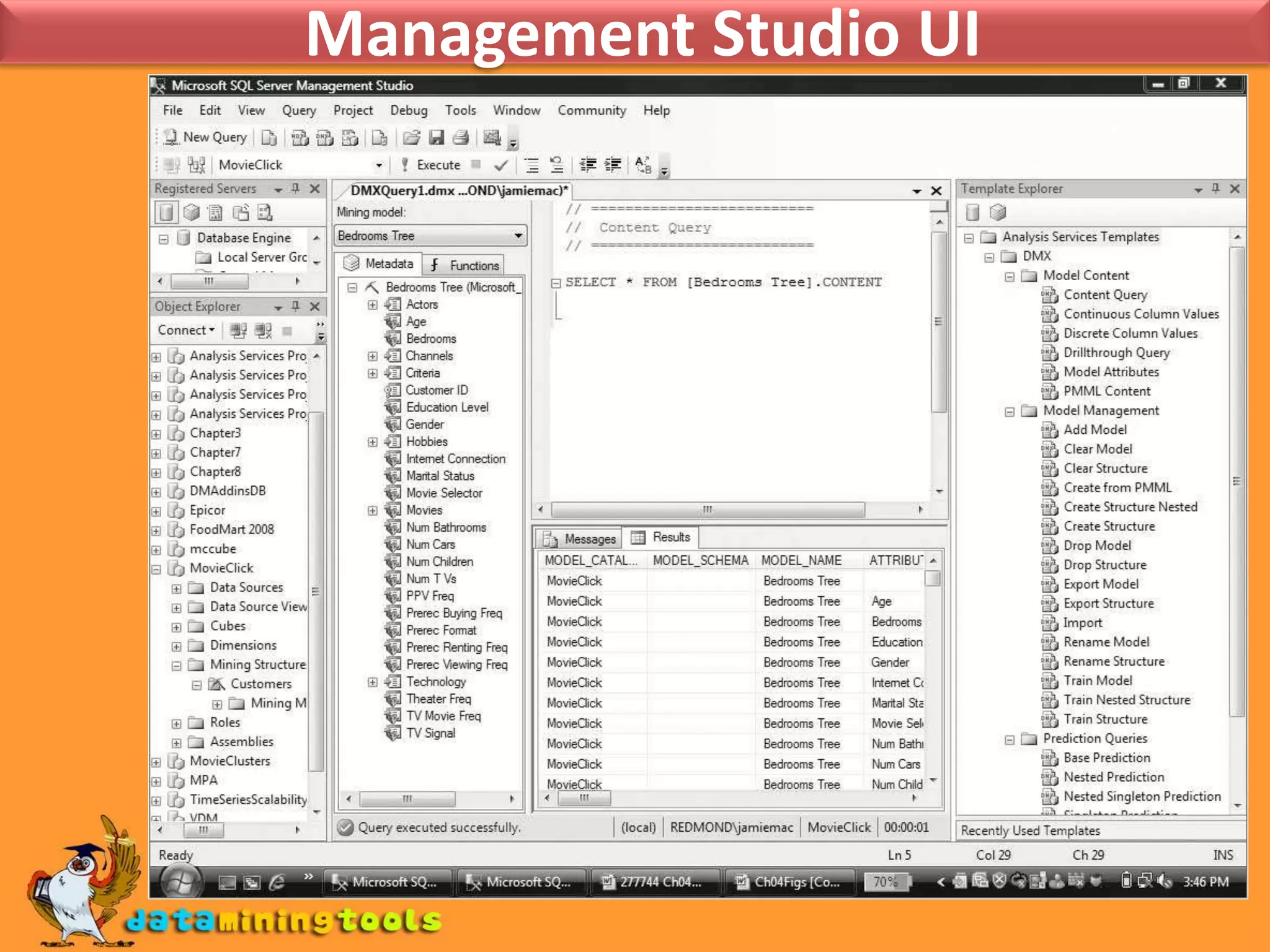
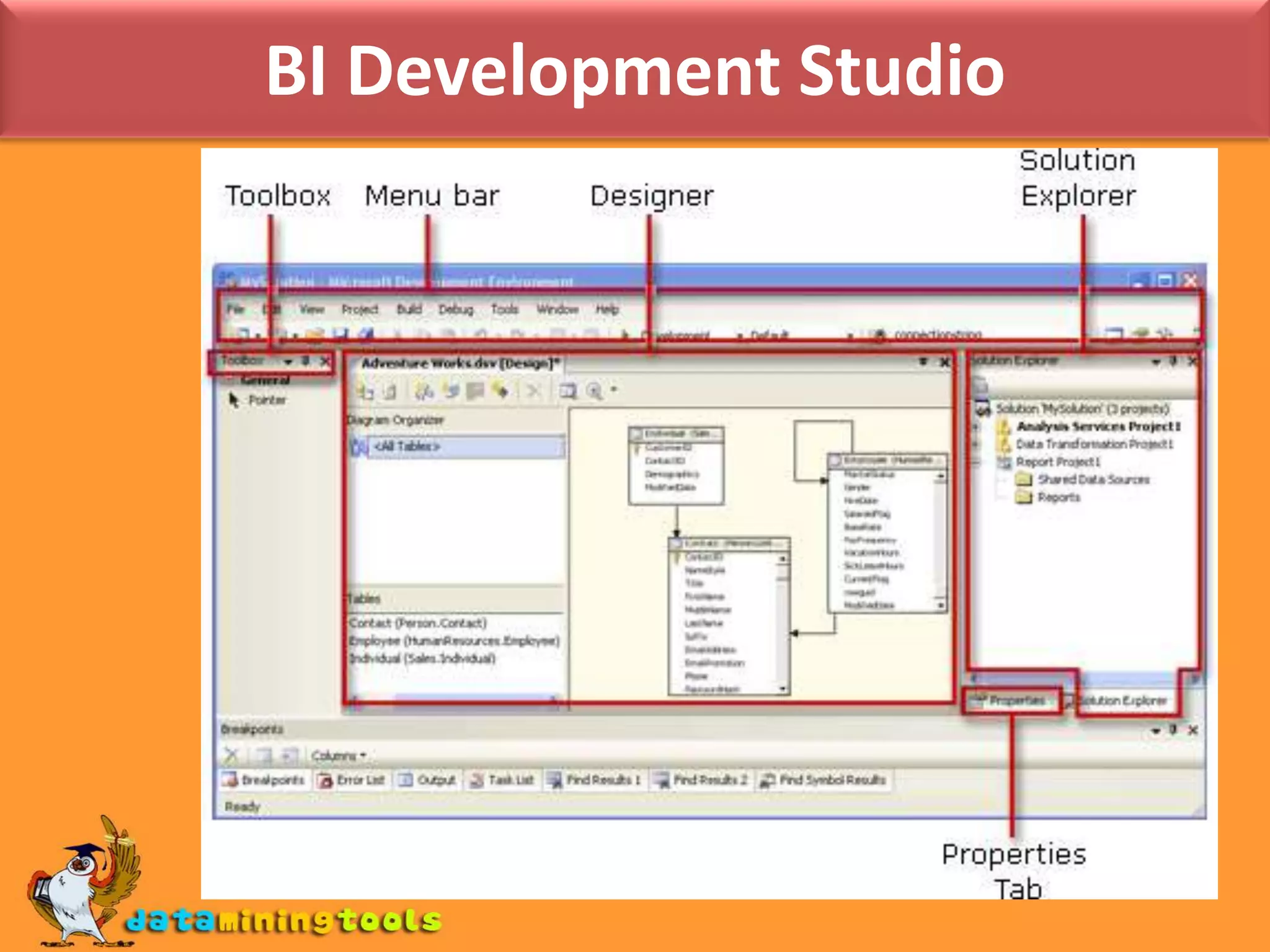
This document provides an overview of using various Microsoft tools for data mining, including: 1. Business Intelligence Development Studio (BI Dev Studio) which is used to develop data mining models and contains tools like Solution Explorer and Designers. 2. Creating data sources and data source views (DSVs) to connect to and organize data for modeling. 3. Using the Data Mining Wizard to create mining structures and models by selecting algorithms, data, and columns. 4. Refining models using the Data Mining Designer and tools like the Mining Structure Editor. 5. Generating reports on model results using SQL Server Reporting Services. 6. Managing databases and servers using SQL Server





![Compositing expressions : The hypothesis you want to test depends on a variable that is a combination of two of the variables you already have. EX: It may not be interesting that a person is married or has children, but the combination of the two may provide valuable information. A composite expression for this situation could look like this:[Marital Status] + ‘ ‘ + [Has Children]CASE expressions :CASE expressions are an extremely flexible wayto create meaningful variables for data mining. The CASE expression allows you to assign results based on the evaluation of one or more conditions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingthedataminingtools-100712054006-phpapp01/75/MS-SQL-SERVER-Using-the-data-mining-tools-16-2048.jpg)