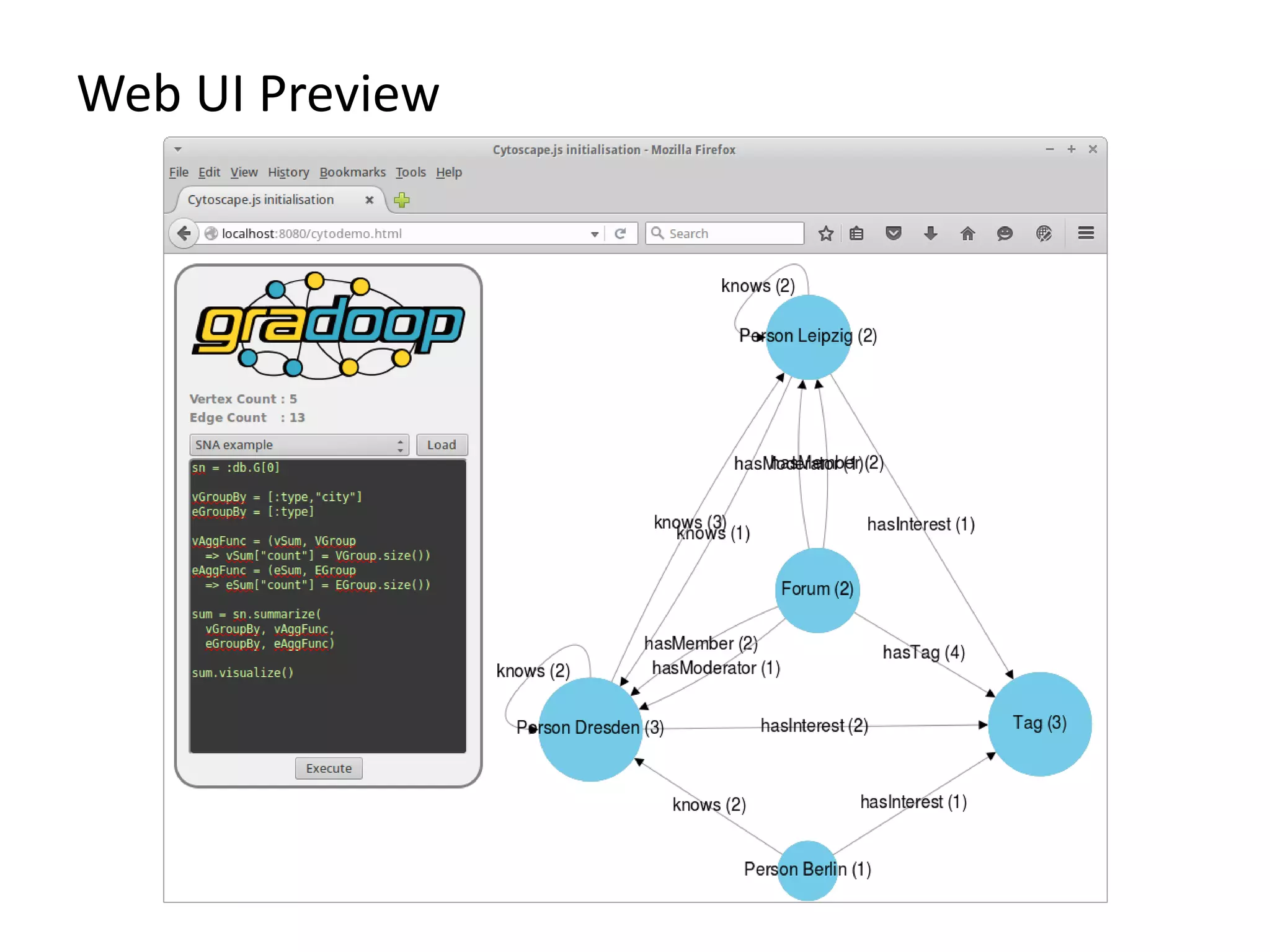
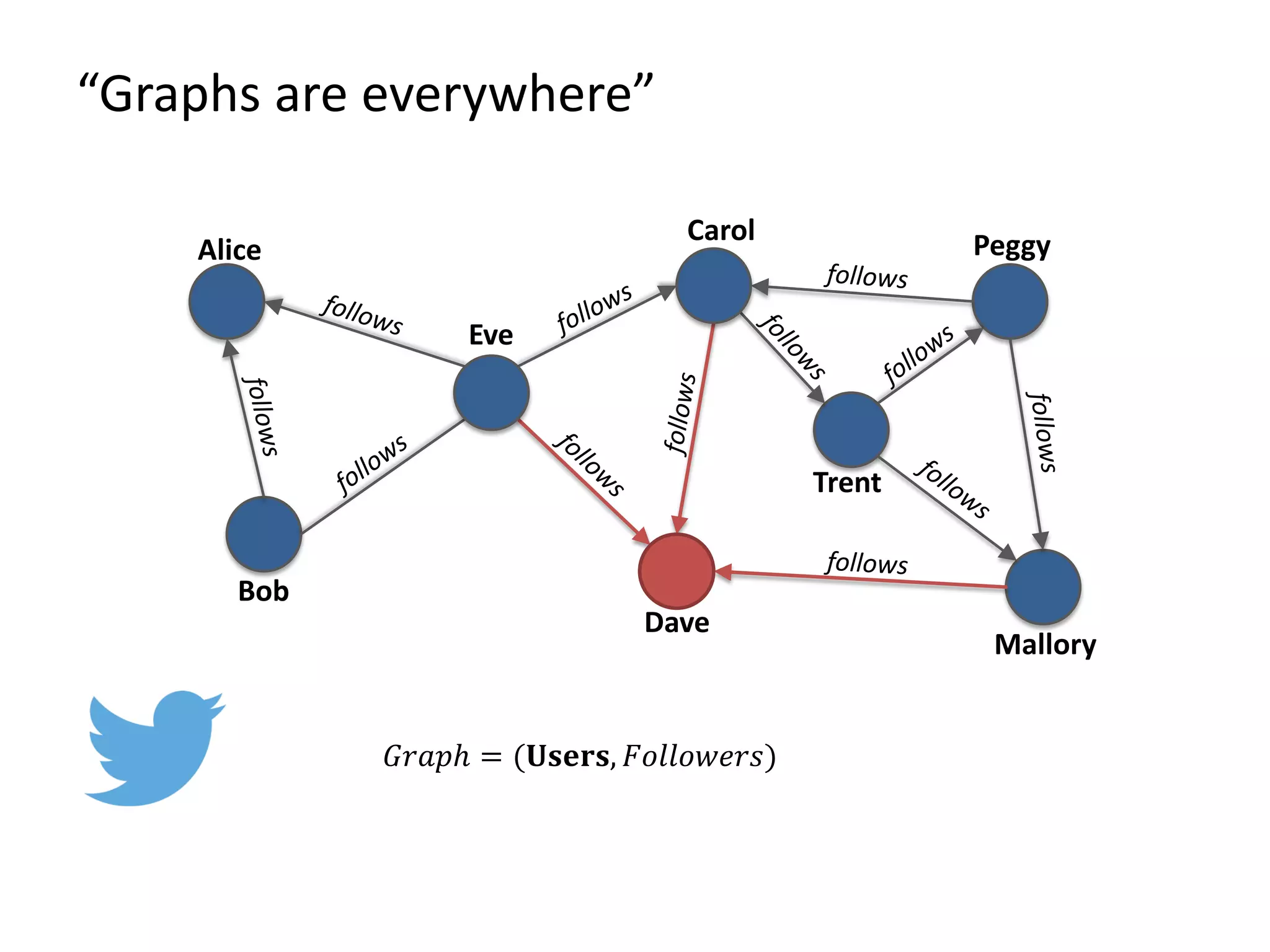
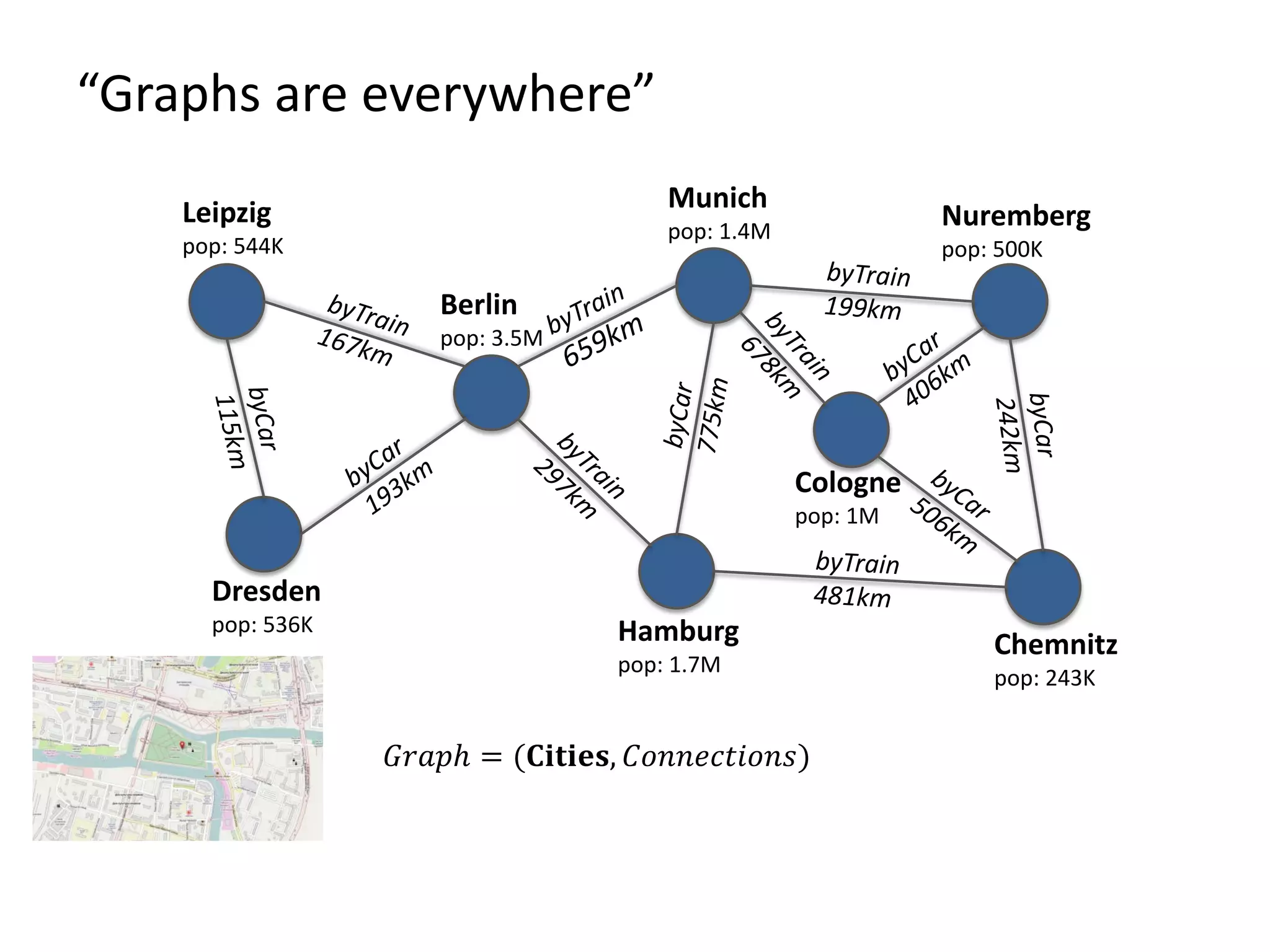
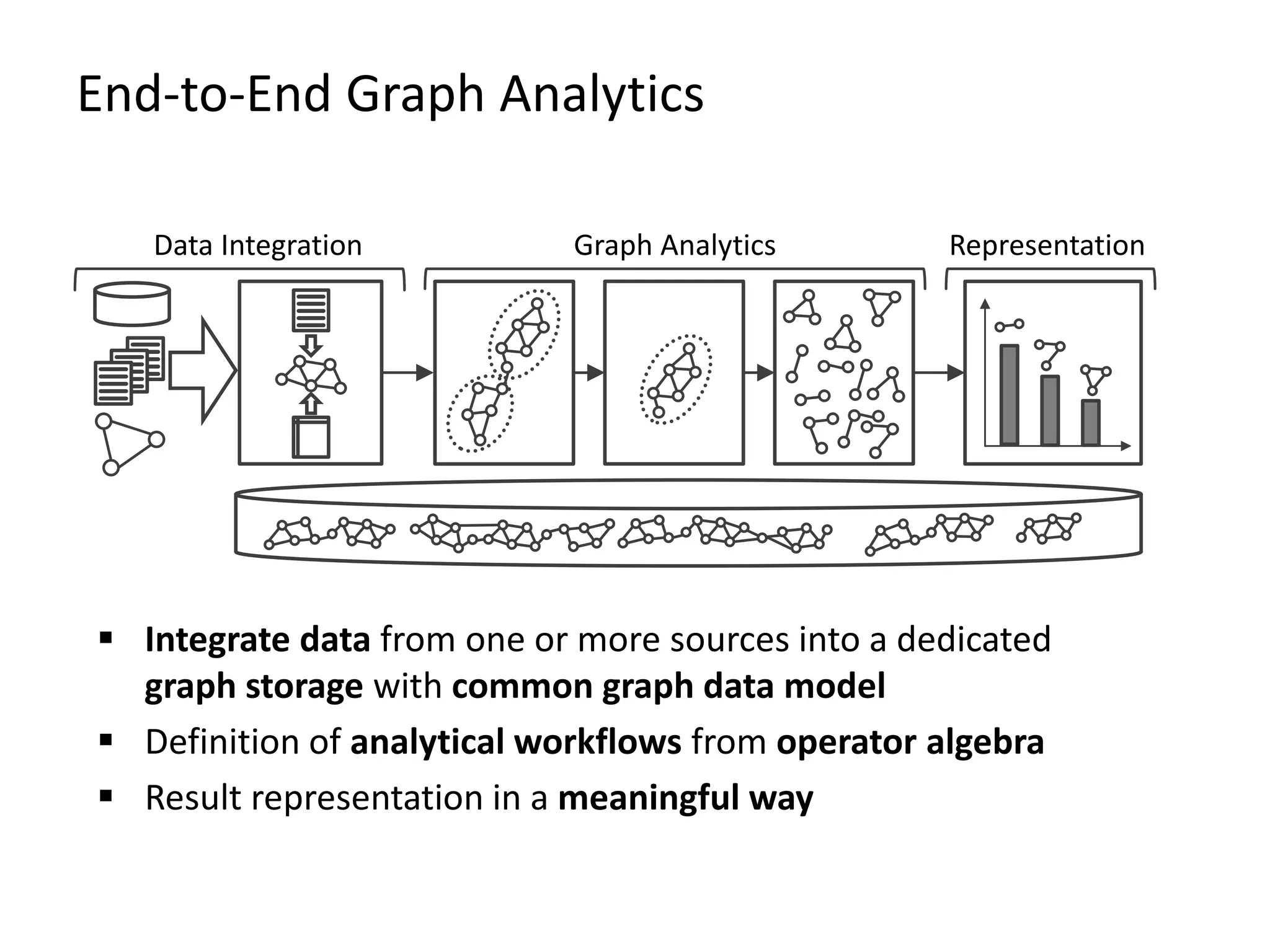
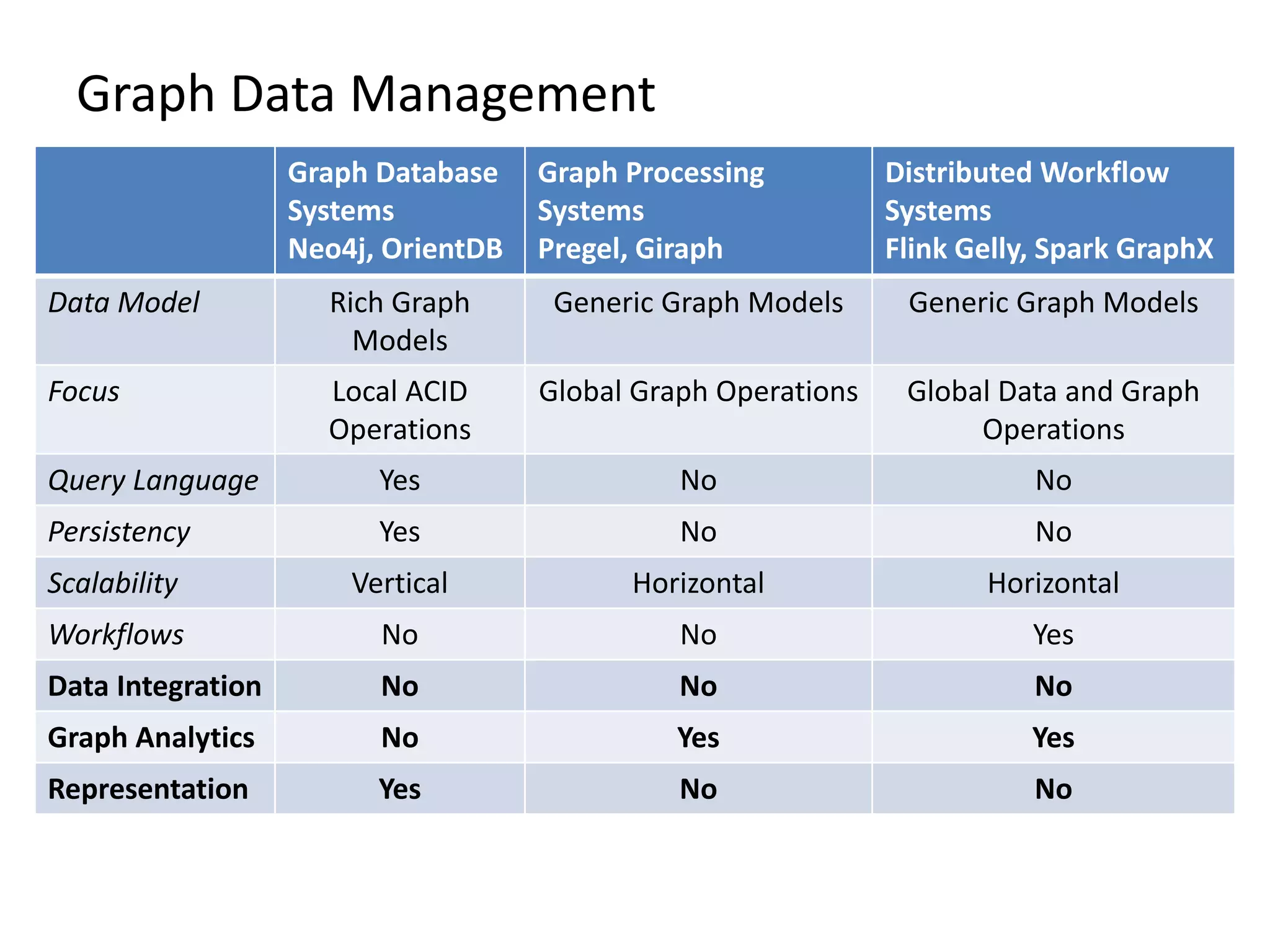
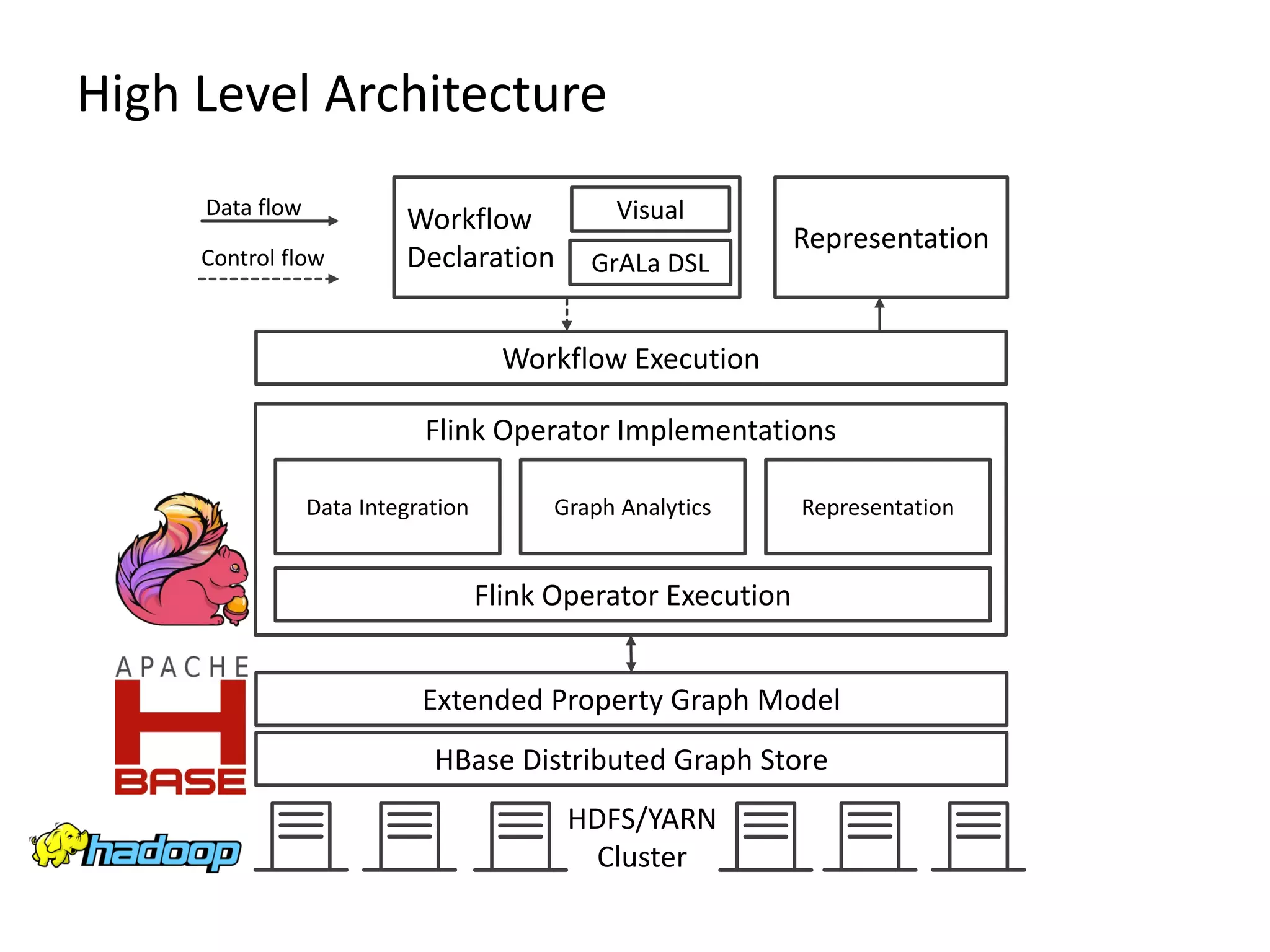
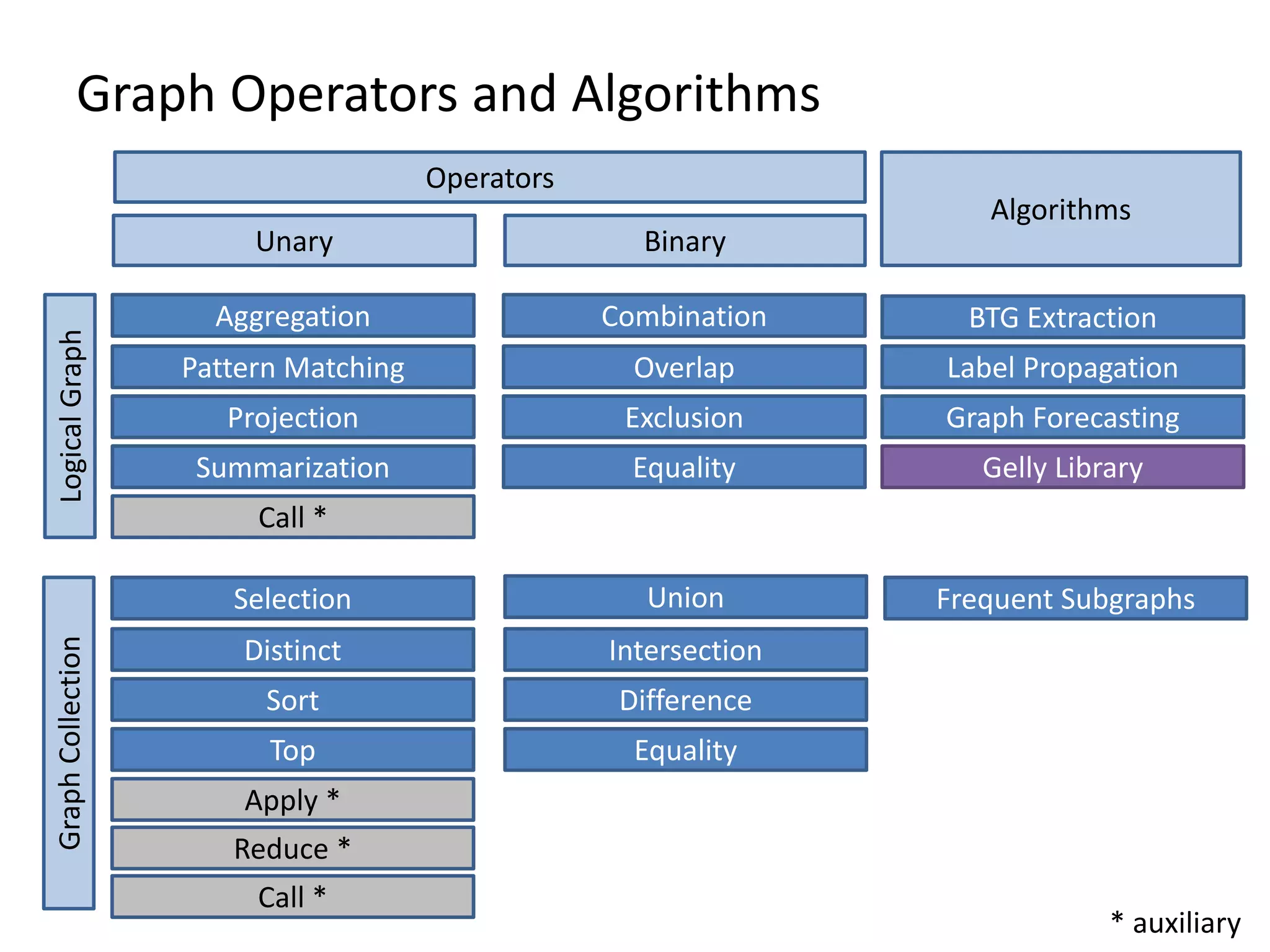
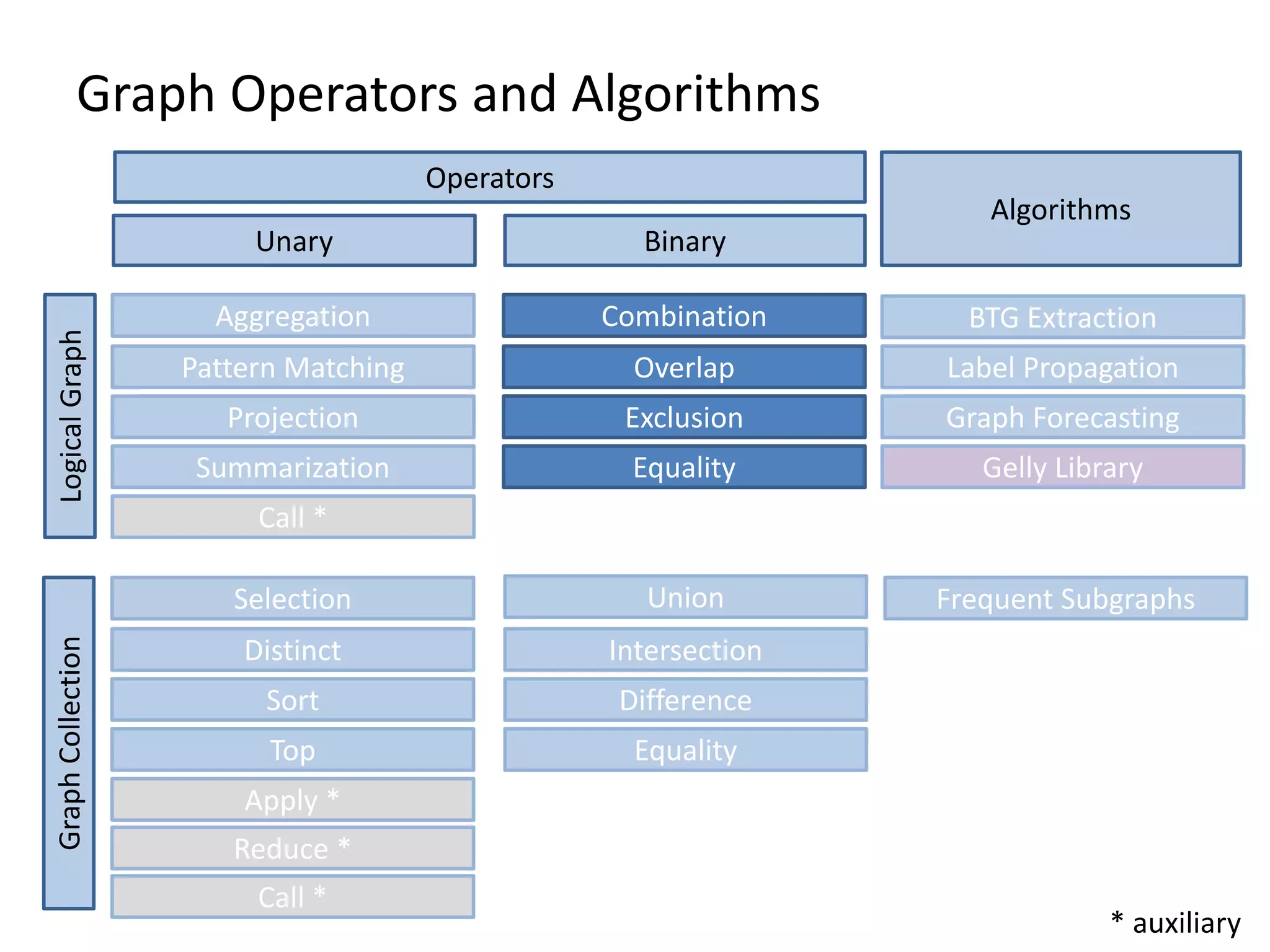
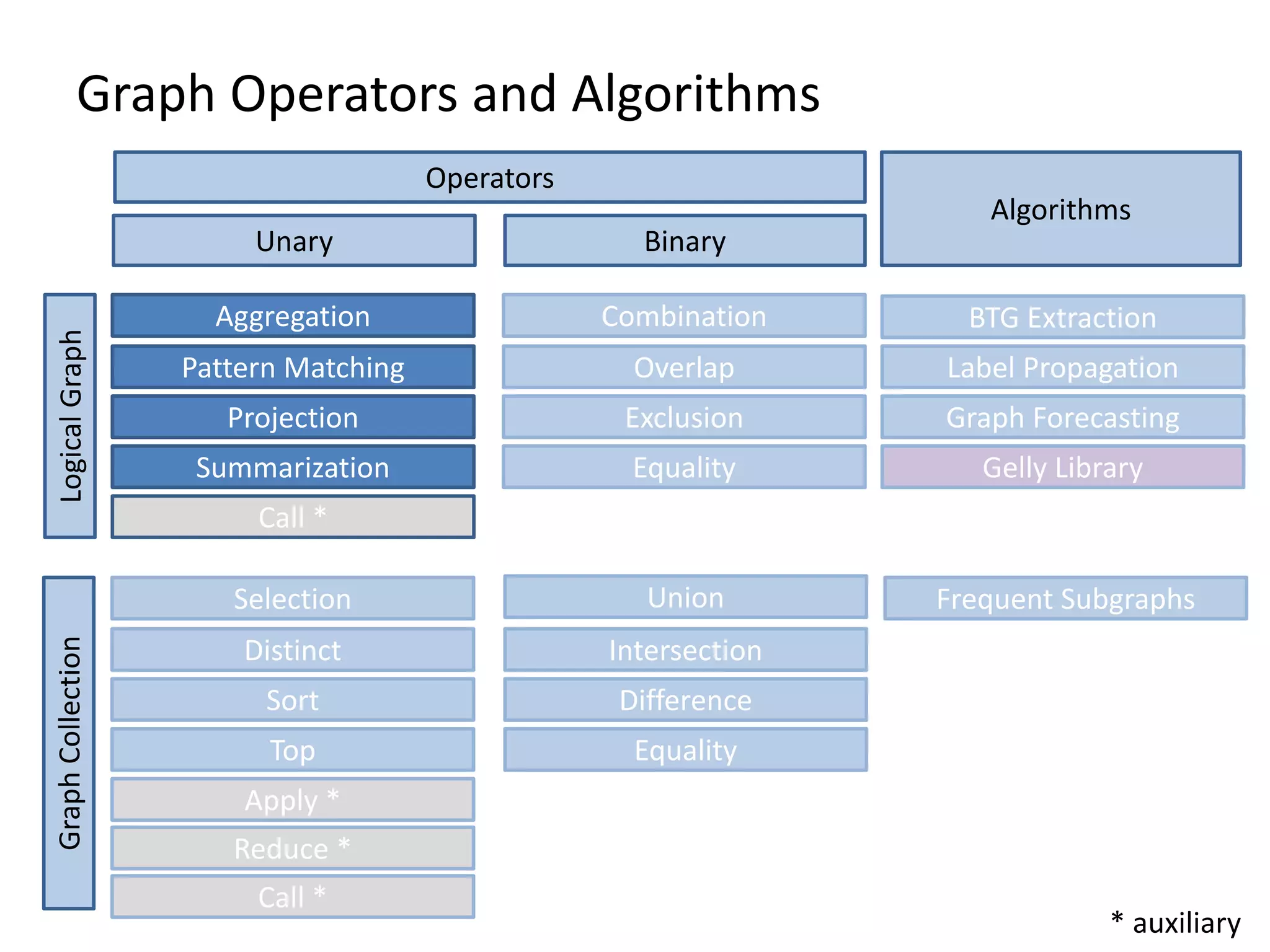
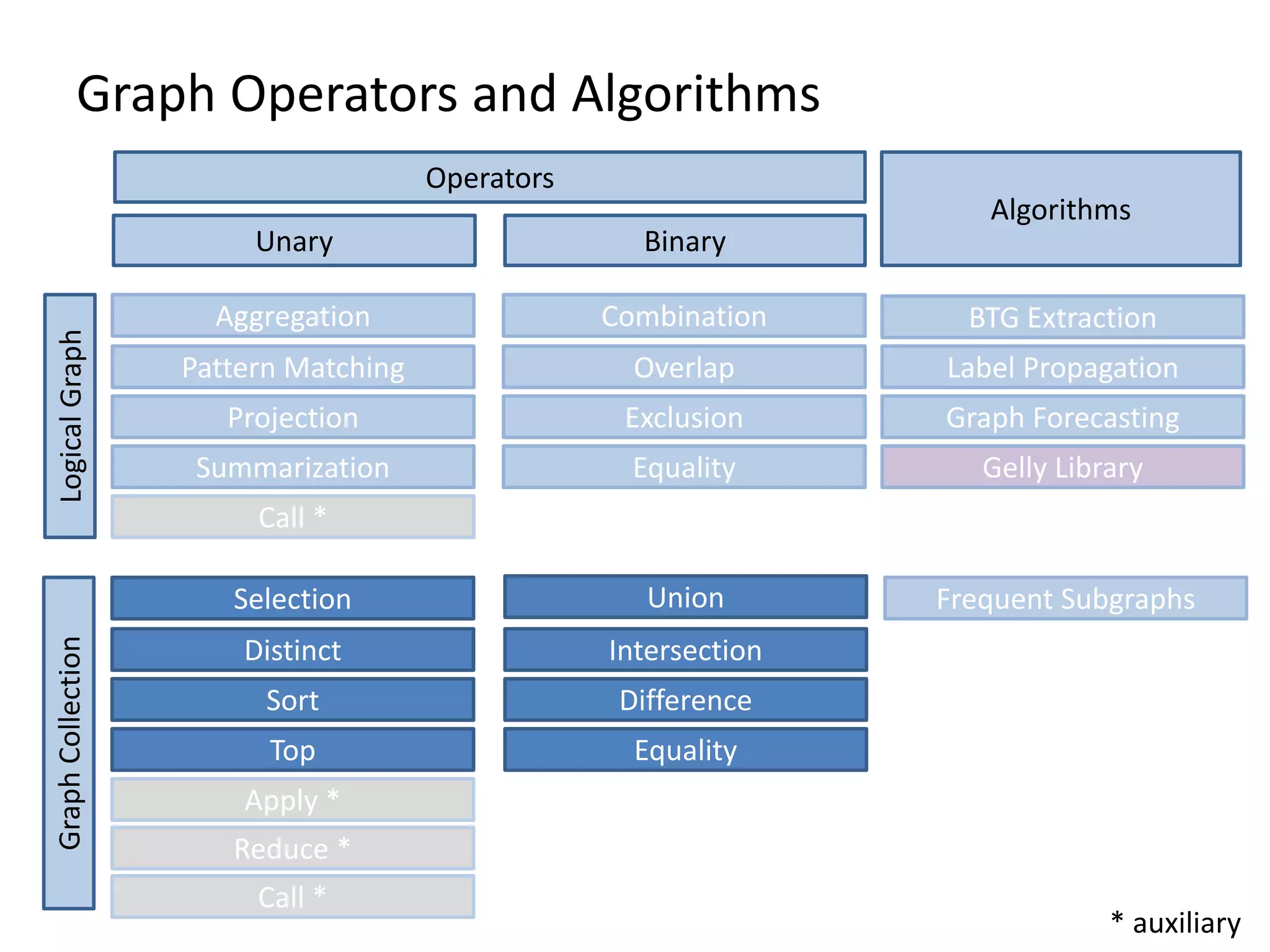
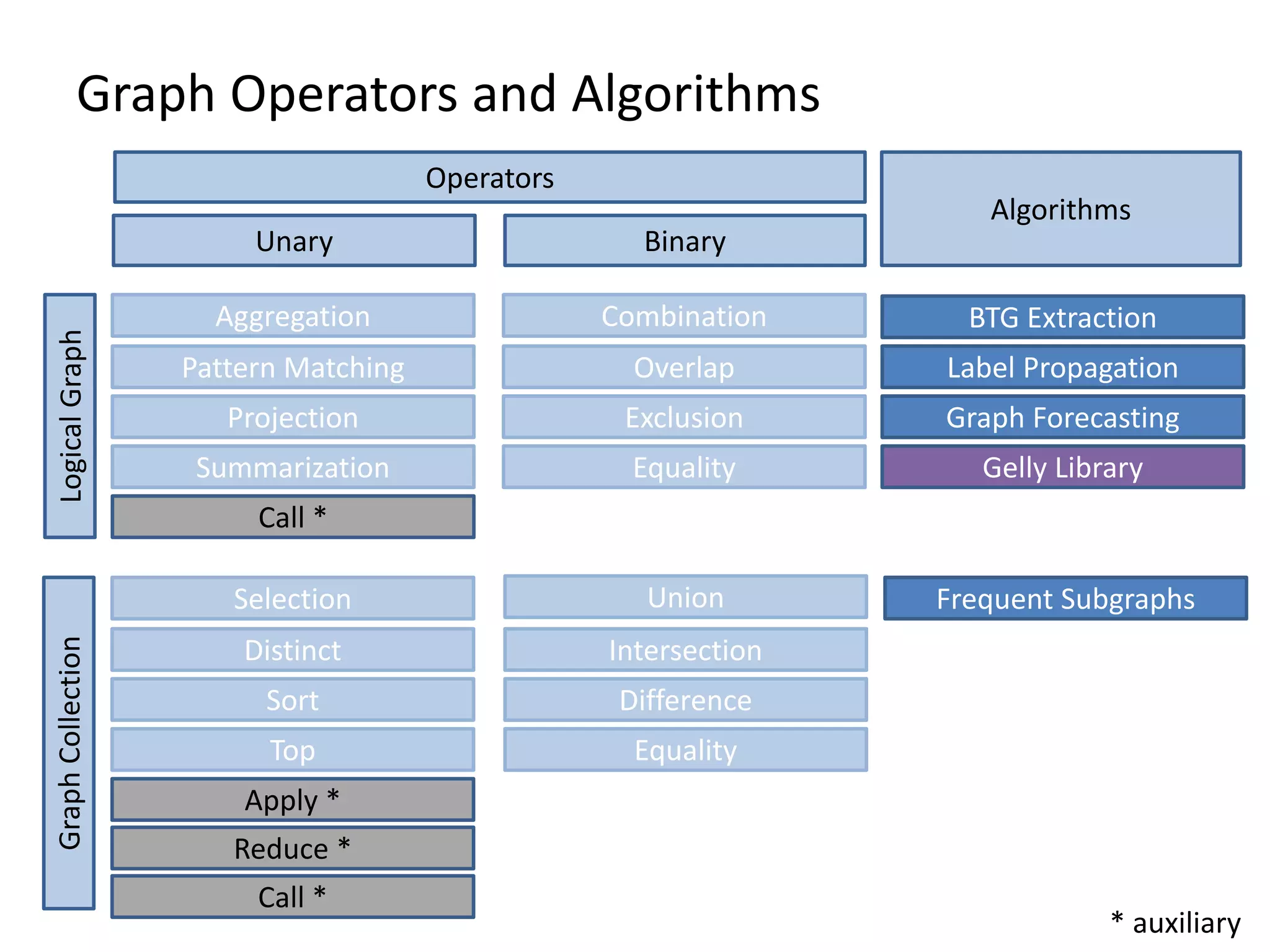
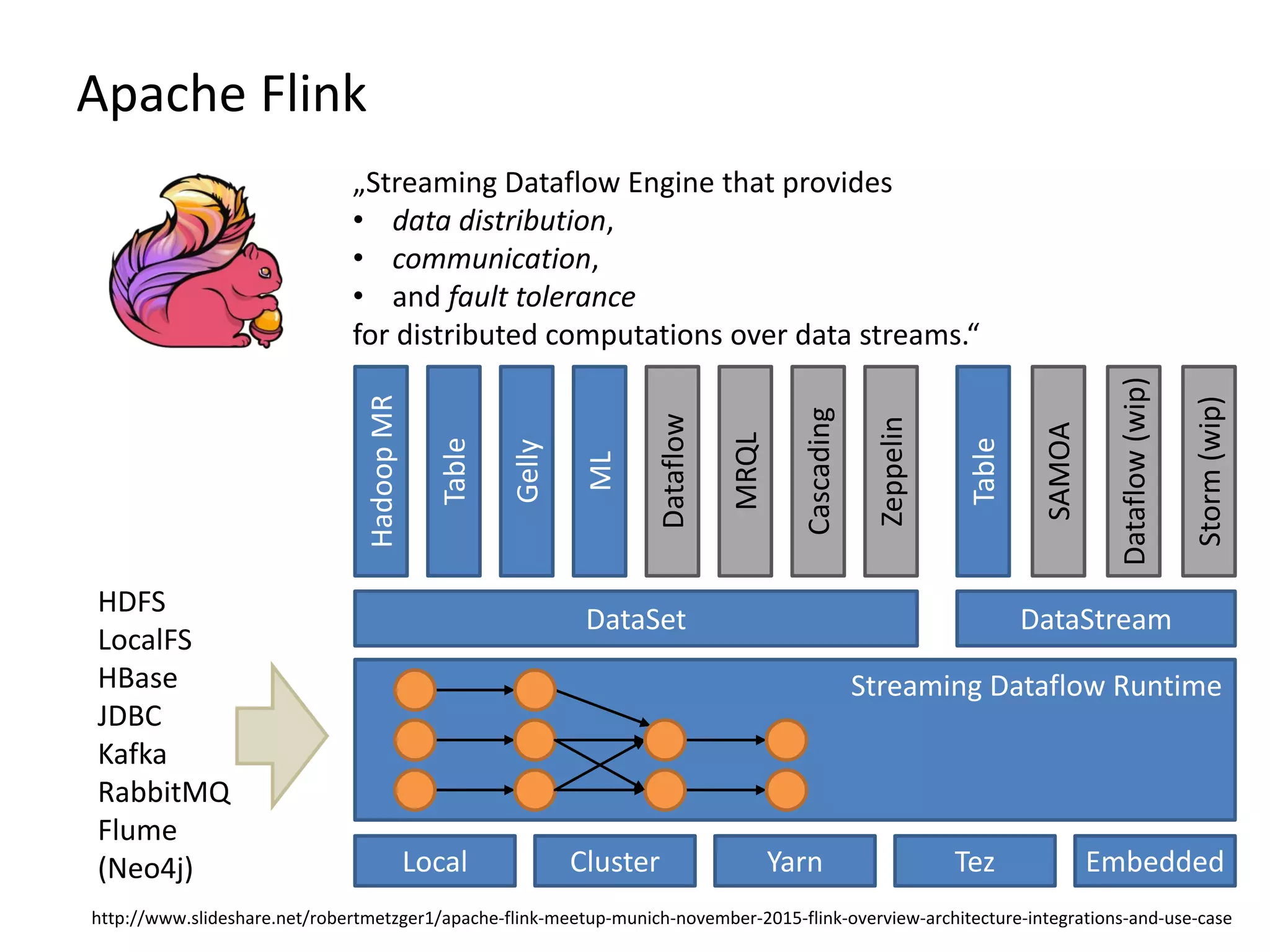
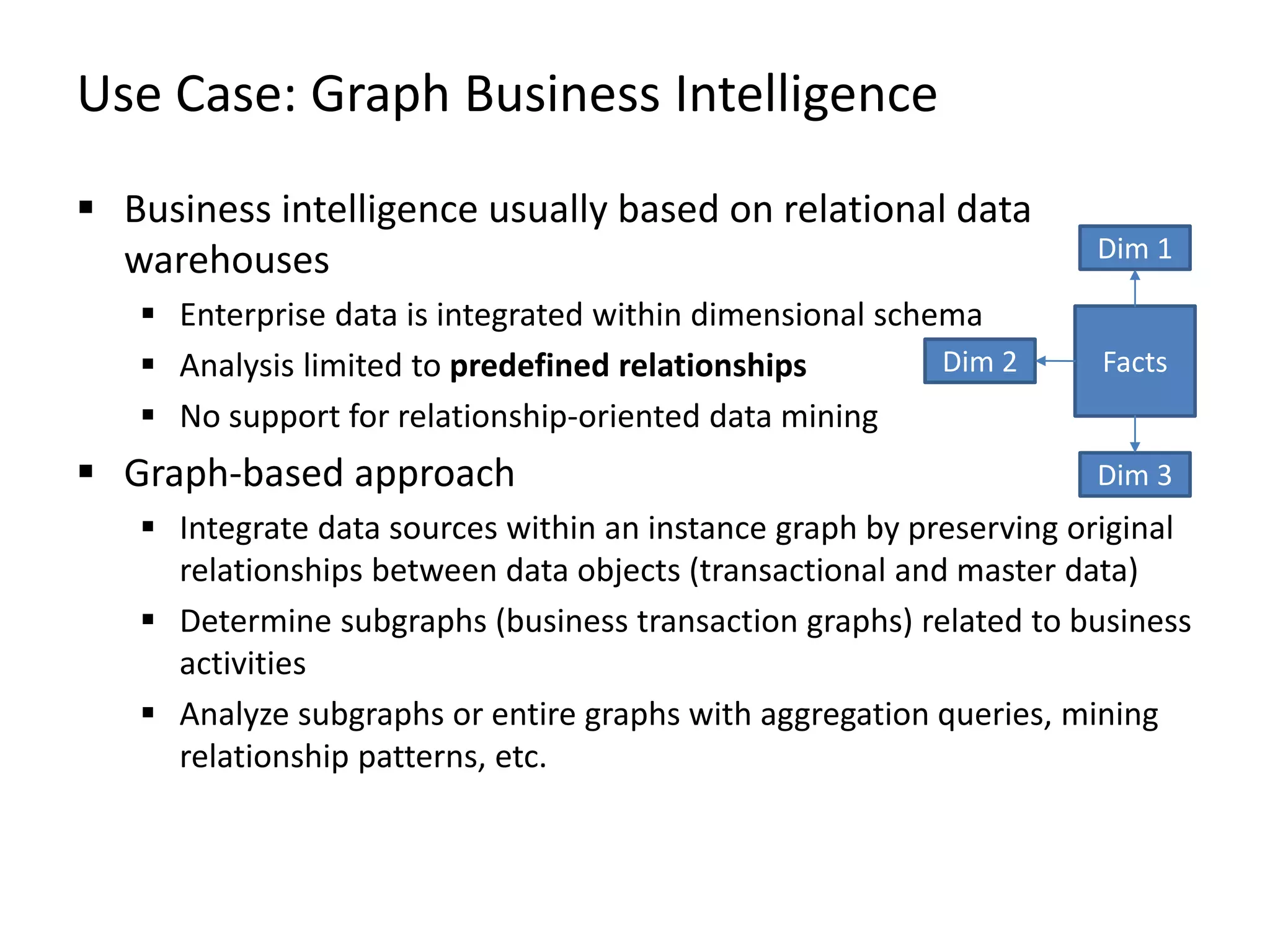
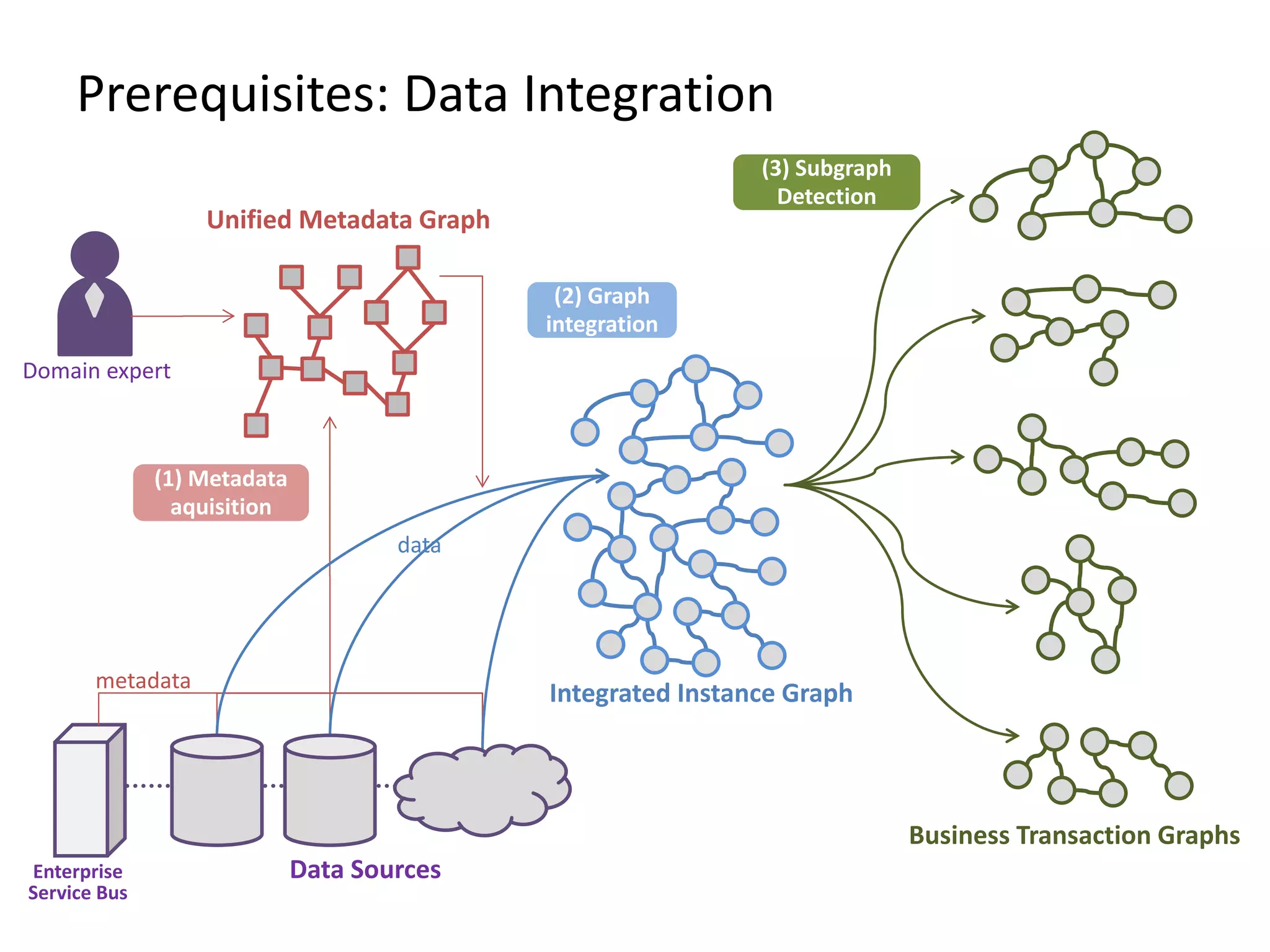
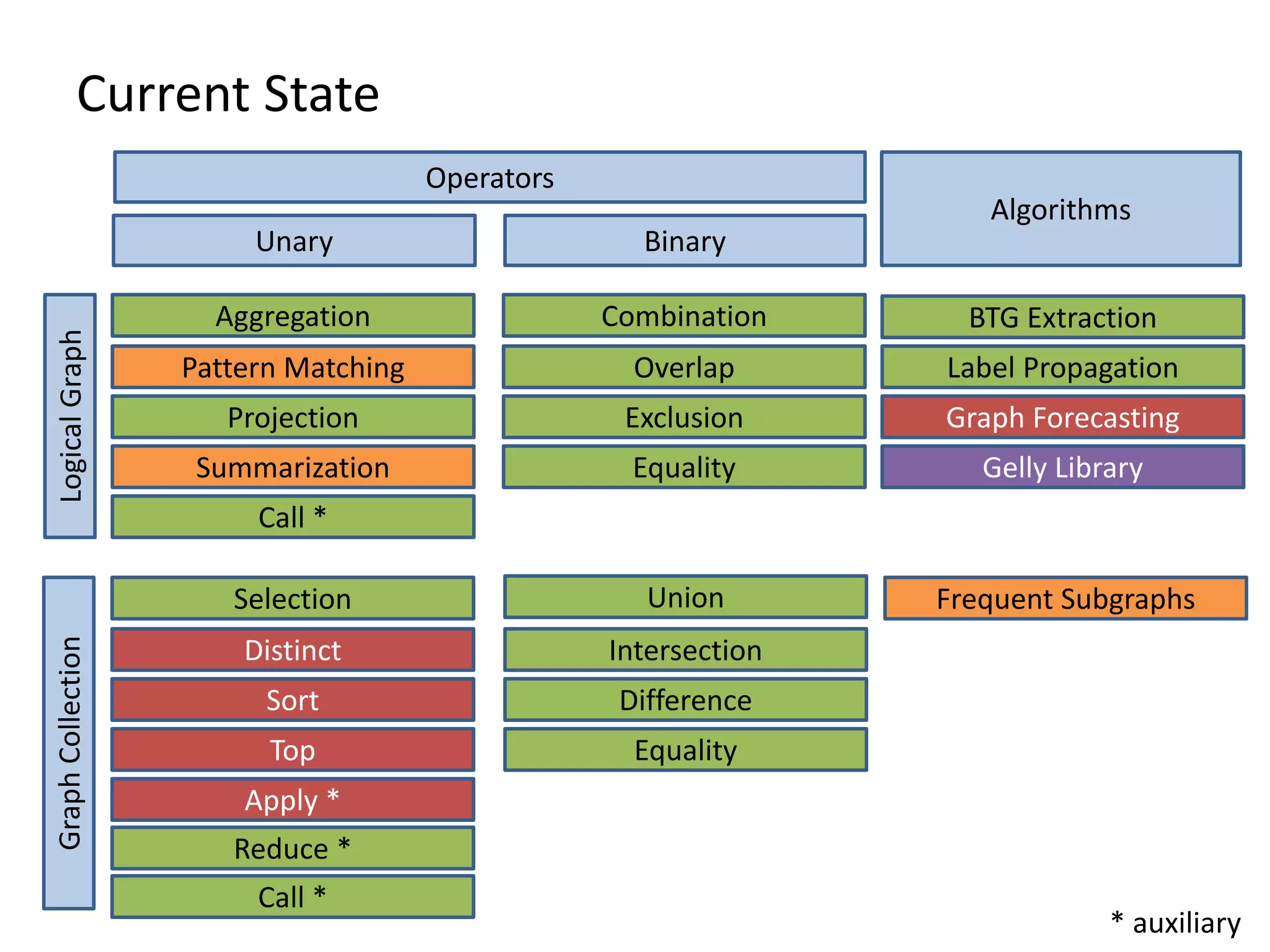
The document discusses Gradoop, a scalable graph analytics framework built on Apache Flink, designed to manage and analyze large-scale graph data. It highlights the architecture, extended property graph model (EPGM), and various graph processing techniques including data integration, analytical workflows, and operators. The presentation also touches on real-world applications and the platform's current state and future work prospects.






![[1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 Extended Property Graph Model [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-19-2048.jpg)
![[2] Community | interest : Graphs | vertexCount : 4 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 Extended Property Graph Model [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-20-2048.jpg)
![Combination 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) [2] Community | interest : Graphs| vertexCount : 4 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 DB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-23-2048.jpg)
![[0] Community | interest : Graphs| vertexCount : 4 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-24-2048.jpg)
![[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination + Summarization [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) 2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”} 3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL} 4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|) 5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|) 6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc, edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-26-2048.jpg)
![[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination + Summarization [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) 2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”} 3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL} 4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|) 5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|) 6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc, edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc) [5] [11] Person city : Leipzig count : 2 [12] Person city : Dresden count : 3 [13] Person city : Berlin count : 1 24 25 26 27 28 knows count : 3 knows count : 1 knows count : 2 knows count : 2 knows count : 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-27-2048.jpg)
![[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination + Summarization + Aggregation [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) 2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”} 3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL} 4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|) 5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|) 6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc, edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc) 7: aggFunc = (Graph g => |g.E|) 8: aggGraph = sumGraph.aggregate(“edgeCount”, aggFunc) [5] [11] Person city : Leipzig count : 2 [12] Person city : Dresden count : 3 [13] Person city : Berlin count : 1 24 25 26 27 28 knows count : 3 knows count : 1 knows count : 2 knows count : 2 knows count : 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-28-2048.jpg)
![[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag DB Combination + Summarization + Aggregation [4] [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 1: personGraph = db.G[0].combine(db.G[1]).combine(db.G[2]) 2: vertexGroupingKeys = {:LABEL, “city”} 3: edgeGroupingKeys = {:LABEL} 4: vertexAggFunc = (Vertex vSum, Set vertices => vSum[“count”] = |vertices|) 5: edgeAggFunc = (Edge eSum, Set edges => eSum[“count”] = |edges|) 6: sumGraph = personGraph.summarize(vertexGroupingKeys, vertexAggFunc, edgeGroupingKeys, edgeAggFunc) 7: aggFunc = (Graph g => |g.E|) 8: aggGraph = sumGraph.aggregate(“edgeCount”, aggFunc) [5] edgeCount : 5 [11] Person city : Leipzig count : 2 [12] Person city : Dresden count : 3 [13] Person city : Berlin count : 1 24 25 26 27 28 knows count : 3 knows count : 1 knows count : 2 knows count : 2 knows count : 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-29-2048.jpg)
![Selection 1: resultColl = db.G[0,1,2].select((Graph g => g[“vertexCount”] > 3)) [2] Community | interest : Graphs | vertexCount : 4 [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 DB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-31-2048.jpg)
![Selection 1: resultColl = db.G[0,1,2].select((Graph g => g[“vertexCount”] > 3)) [1] Community | interest : Hadoop| vertexCount : 3[0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [0] Tag name : Databases [1] Tag name : Graphs [2] Tag name : Hadoop [3] Forum title : Graph Databases [4] Forum title : Graph Processing [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en [10] Person name : Frank gender : m city : Berlin age : 23 IP: 169.32.1.3 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasInterest hasModeratorhasModerator hasMember hasMember hasMember hasMember hasTag hasTaghasTag hasTag knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013 DB [2] Community | interest : Graphs | vertexCount : 4 [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 0 1 2 3 4 5 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-32-2048.jpg)

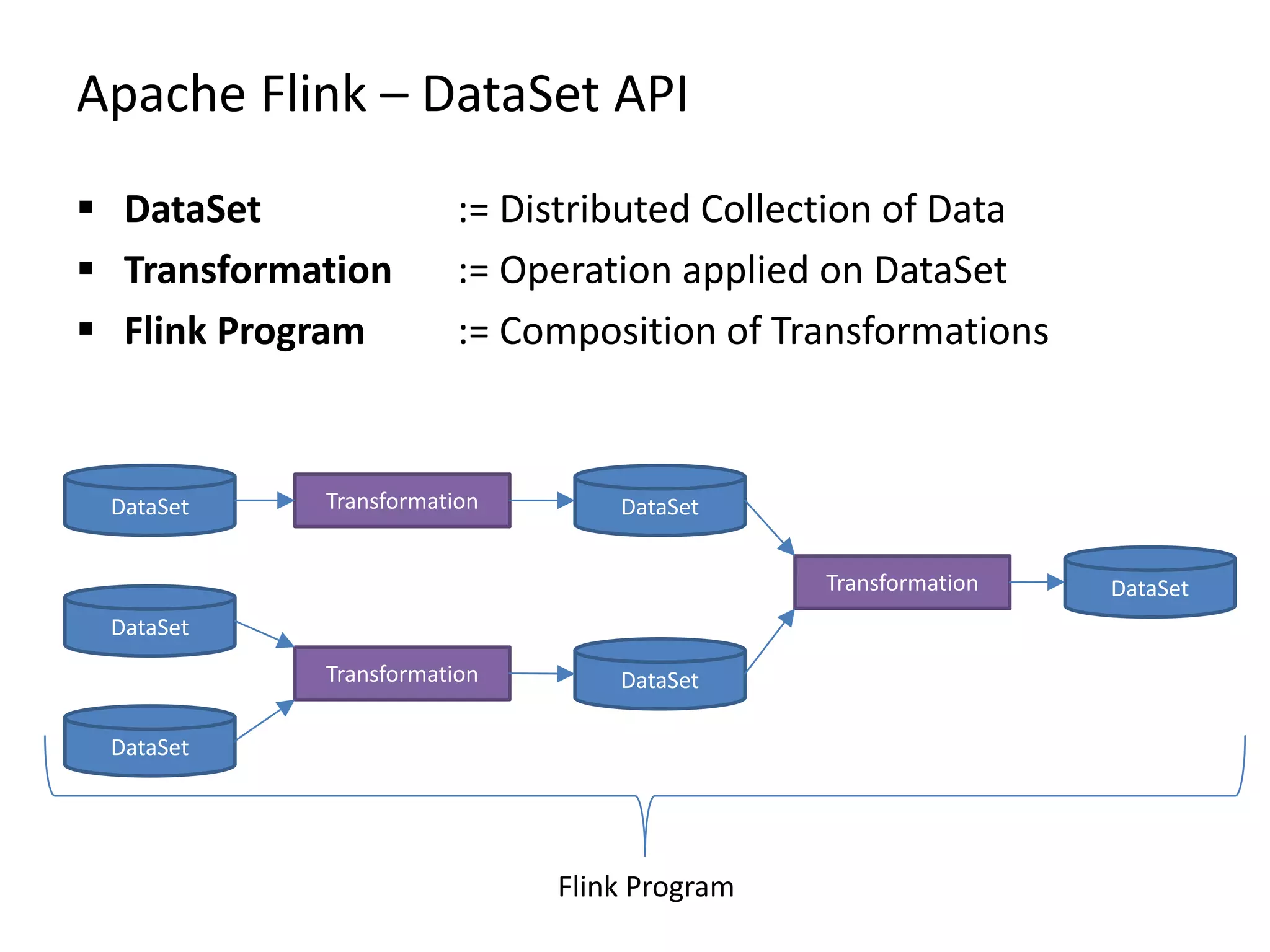

![The „Hello World“ of Big Data – Word Count 1: ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); 2: 3: DataSet<String> text = env.fromElements( // or env.readTextFile(„hdfs://…“) 4: „He who controls the past controls the future.“, 5: „He who controls the present controls the past.“); 6: 7: DataSet<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordCounts = text 8: .flatMap(new LineSplitter()) // splits the line and outputs (word, 1) tuples 9: .groupBy(0) 10: .sum(1); 11: 12: wordCounts.print(); // trigger execution flatMap „He who controls the past controls the future.“ „He who controls the present controls the past.“ (He,1) (who,1) (controls,1) (the,1) (past,1) // ... groupBy(0) [(He,1),(He,1)] [(who,1),(who,1)] [(future,1)] [(past,1),(past,1)] [(present,1)] // ... sum(1) (He,2) (who,2) (future,1) (past,2) (present,1) // ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-38-2048.jpg)

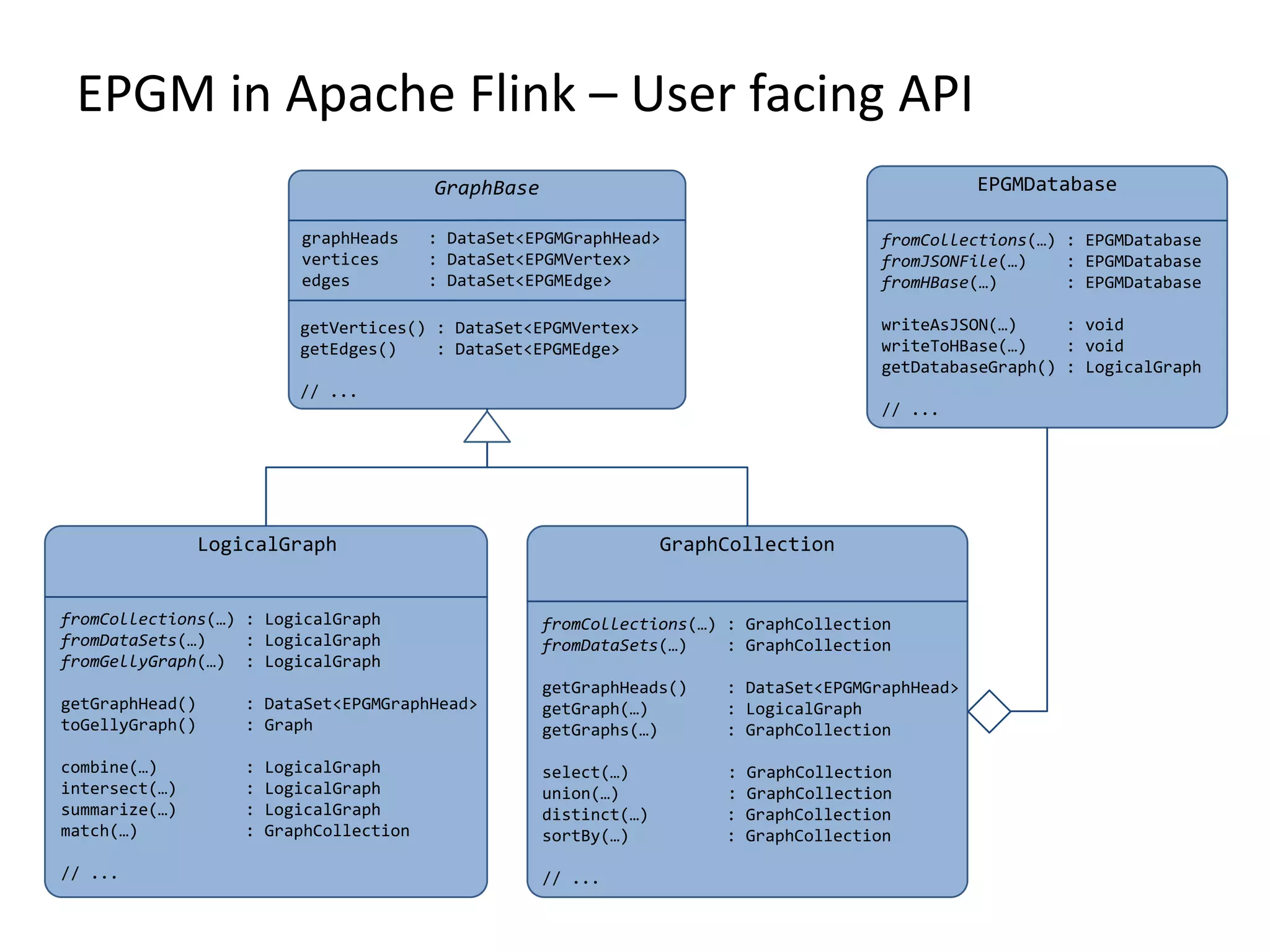
![EPGM in Apache Flink – DataSets Id Label Properties Graphs Id Label Properties SourceId TargetId Graphs EPGMGraphHead EPGMVertex EPGMEdge Id Label Properties POJO POJO POJO DataSet<EPGMGraphHead> DataSet<EPGMVertex> DataSet<EPGMEdge> Id Label Properties Graphs EPGMVertex GradoopId := UUID 128-bit String PropertyList := List<Property> Property := (String, PropertyValue) PropertyValue := byte[] GradoopIdSet := Set<GradoopId> (55421132-f45b-40f0-8f6a-50ea13dbf2ea:Person{gender=f,city=Leipzig,name=Alice,age=20} @ [c2c0f288-9f27-4e55-b1c6-7a35e0eabe36, 77b710f9-07c2-49ab-b4bf-51e1a3138822])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-41-2048.jpg)
![EPGM in Apache Flink – Exclusion // input: firstGraph (G[0]), secondGraph (G[2]) 1: DataSet<GradoopId> graphId = secondGraph.getGraphHead() 2: .map(new Id<G>()); 3: 4: DataSet<V> newVertices = firstGraph.getVertices() 5: .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<V>()) 6: .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID); 7: 8: DataSet<E> newEdges = firstGraph.getEdges() 9: .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<E>()) 10: .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID) 11: .join(newVertices) 12: .where(new SourceId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>()) 13: .with(new LeftSide<E, V>()) 14: .join(newVertices) 15: .where(new TargetId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>()) 16: .with(new LeftSide<E, V>()); db.G[0].exclude(db.G[2]) [2] Community | interest : Graphs| vertexCount : 4 [0] Community | interest : Databases | vertexCount : 3 [5] Person name : Alice gender : f city : Leipzig age : 23 [6] Person name : Bob gender : m city : Leipzig age : 30 [7] Person name : Carol gender : f city : Dresden age : 30 [8] Person name : Dave gender : m city : Dresden age : 42 [9] Person name : Eve gender : f city : Dresden age : 35 speaks : en 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2013 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2014 knows since : 2015 knows since : 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-42-2048.jpg)
![EPGM in Apache Flink – Exclusion Id Label Properties 2 Community interest: Graphs vertexCount: 4 graphId = secondGraph.getGraphHead() Id 2 newVertices = firstGraph.getVertices() Id Label Properties Graphs 5 Person name: Alice gender: f … [0, 2] 6 Person name: Bob gender: m … [0, 2] 9 Person name: Eve gender: f … [0] Id Label Properties Graphs 9 Person name: Eve gender: f … [0] .map(new Id<G>()); .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<V>()) .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-43-2048.jpg)
![EPGM in Apache Flink – Exclusion newEdges = firstGraph.getEdges() Id Label SourceId TargetId Properties Graphs 0 knows 5 6 since: 2014 [0, 2] 1 knows 6 5 since: 2014 [0, 2] 6 knows 9 5 since: 2013 [0] 7 knows 9 6 since: 2015 [0] Id Label SourceId TargetId Properties Graphs 6 knows 9 5 since: 2013 [0] 7 knows 9 6 since: 2015 [0] Id Label SourceId TargetId … Id Label … 6 knows 9 5 … 9 Person … 7 knows 9 6 … 9 Person … Id Label SourceId TargetId … 6 knows 9 5 … 7 knows 9 6 … Id Label SourceId TargetId … Id Label … Id Label SourceId TargetId ….with(new LeftSide<E, V>()); .join(newVertices) .where(new TargetId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>()) .with(new LeftSide<E, V>()) .join(newVertices) .where(new SourceId<E>().equalTo(new Id<V>()) .filter(new NotInGraphBroadCast<E>()) .withBroadcastSet(graphId, GRAPH_ID)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-44-2048.jpg)

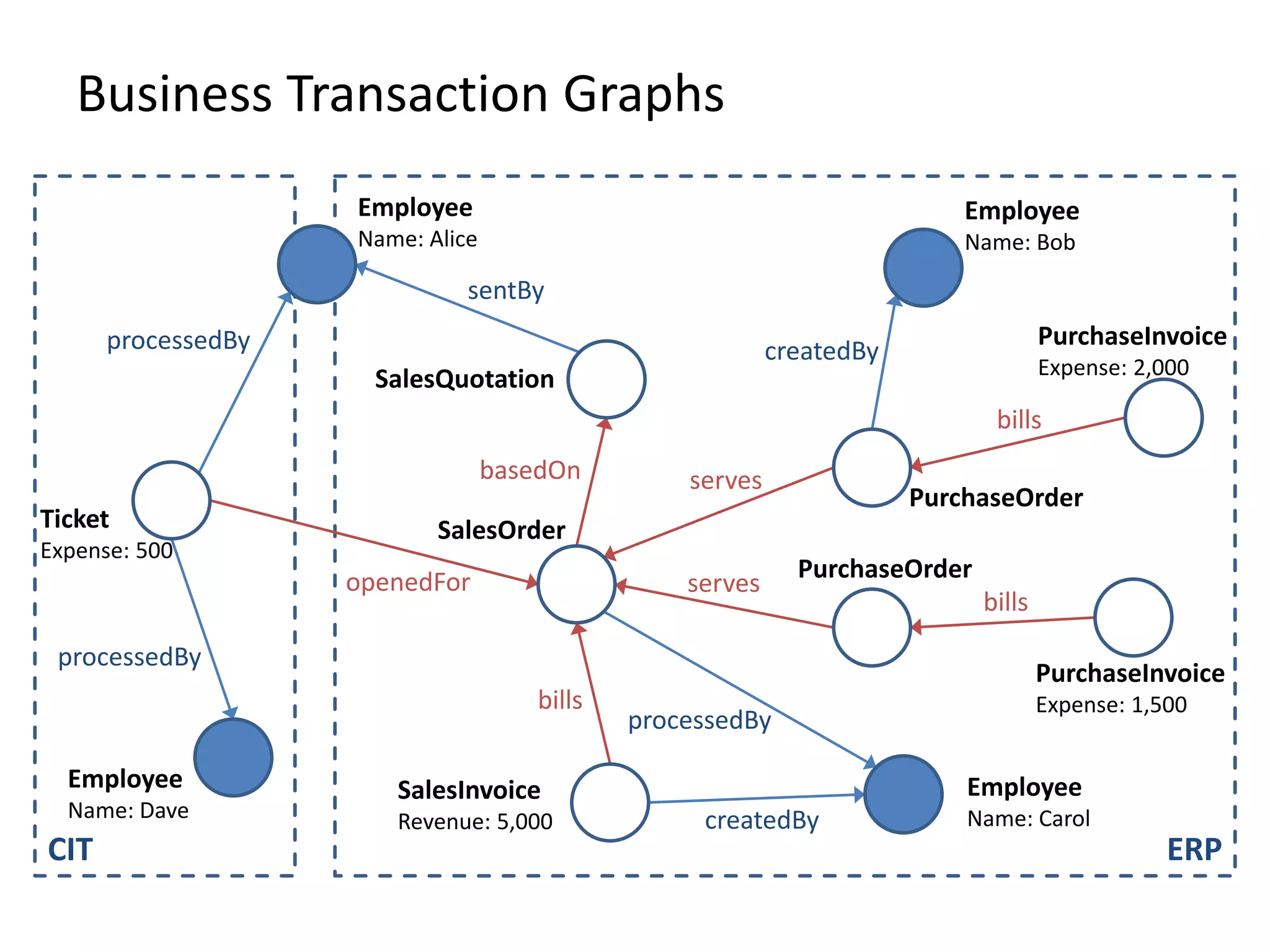
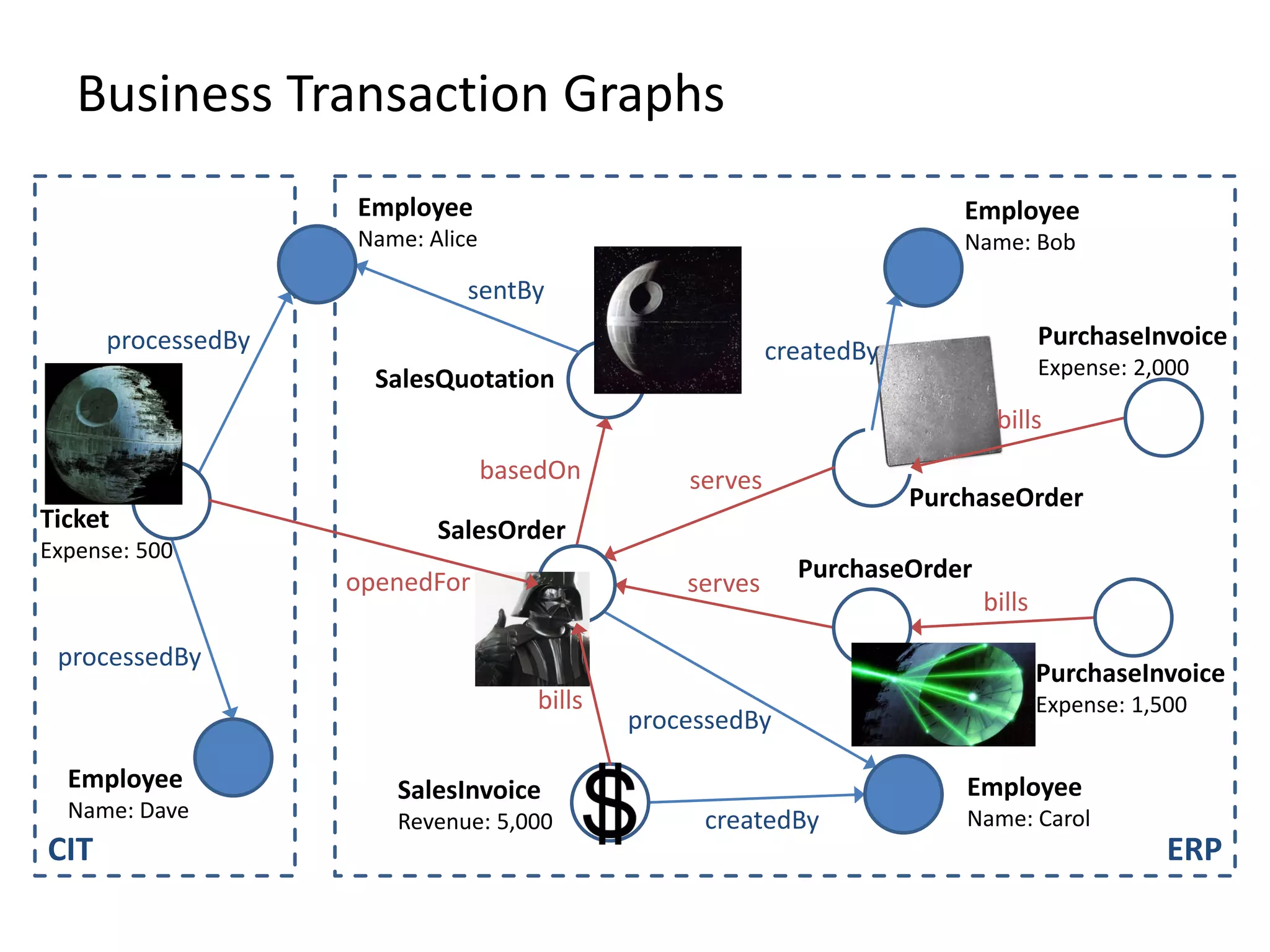
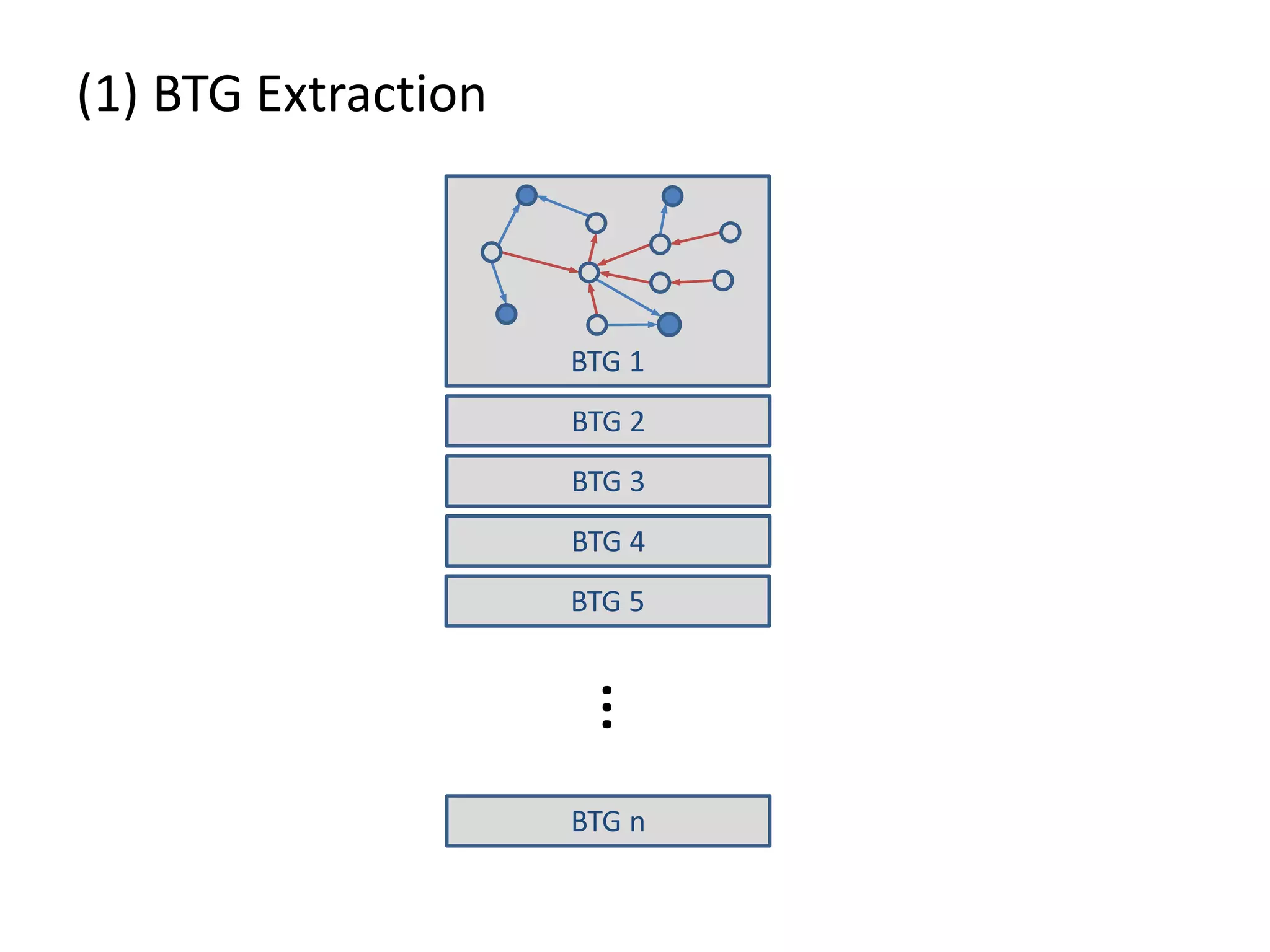

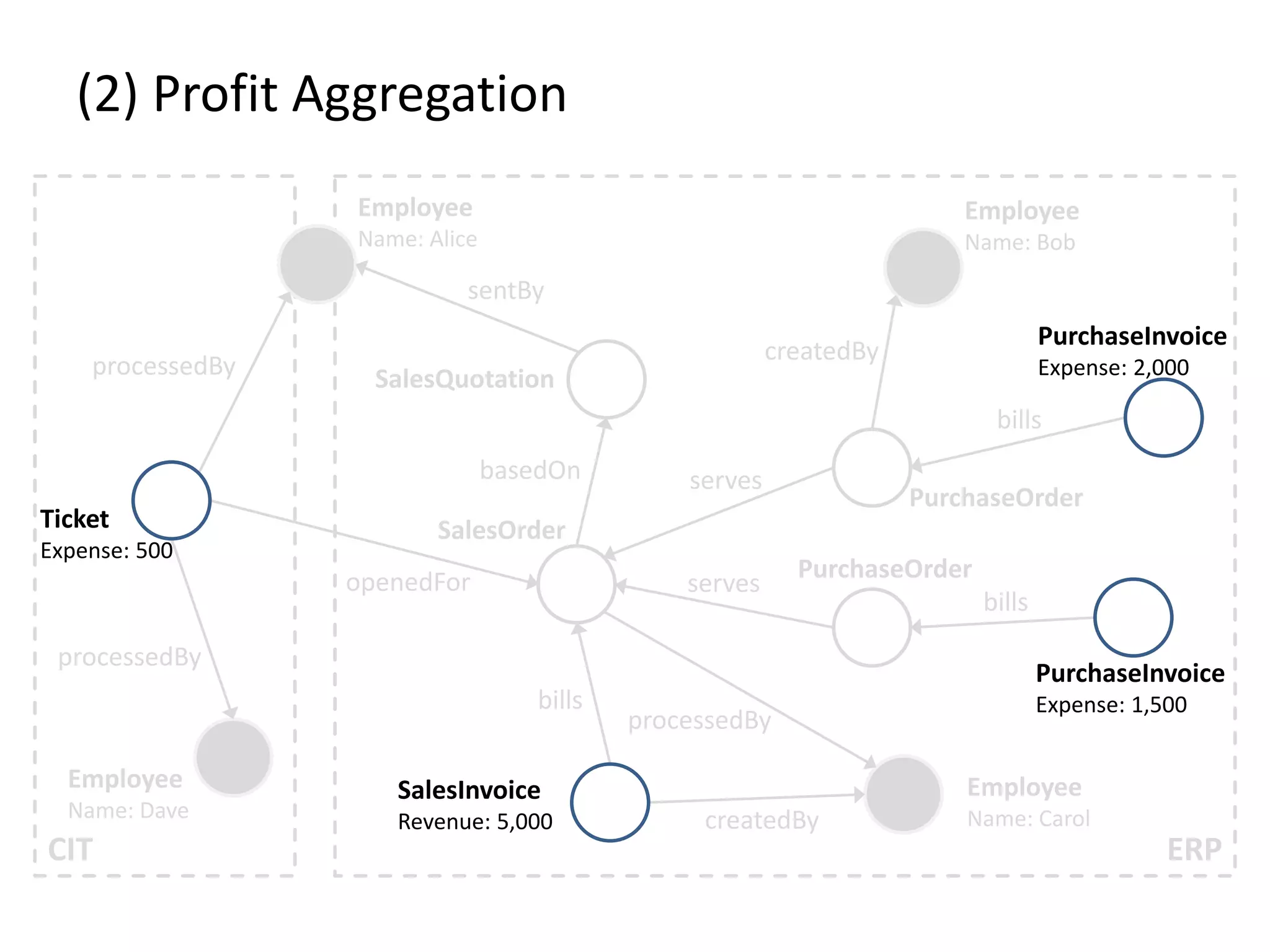

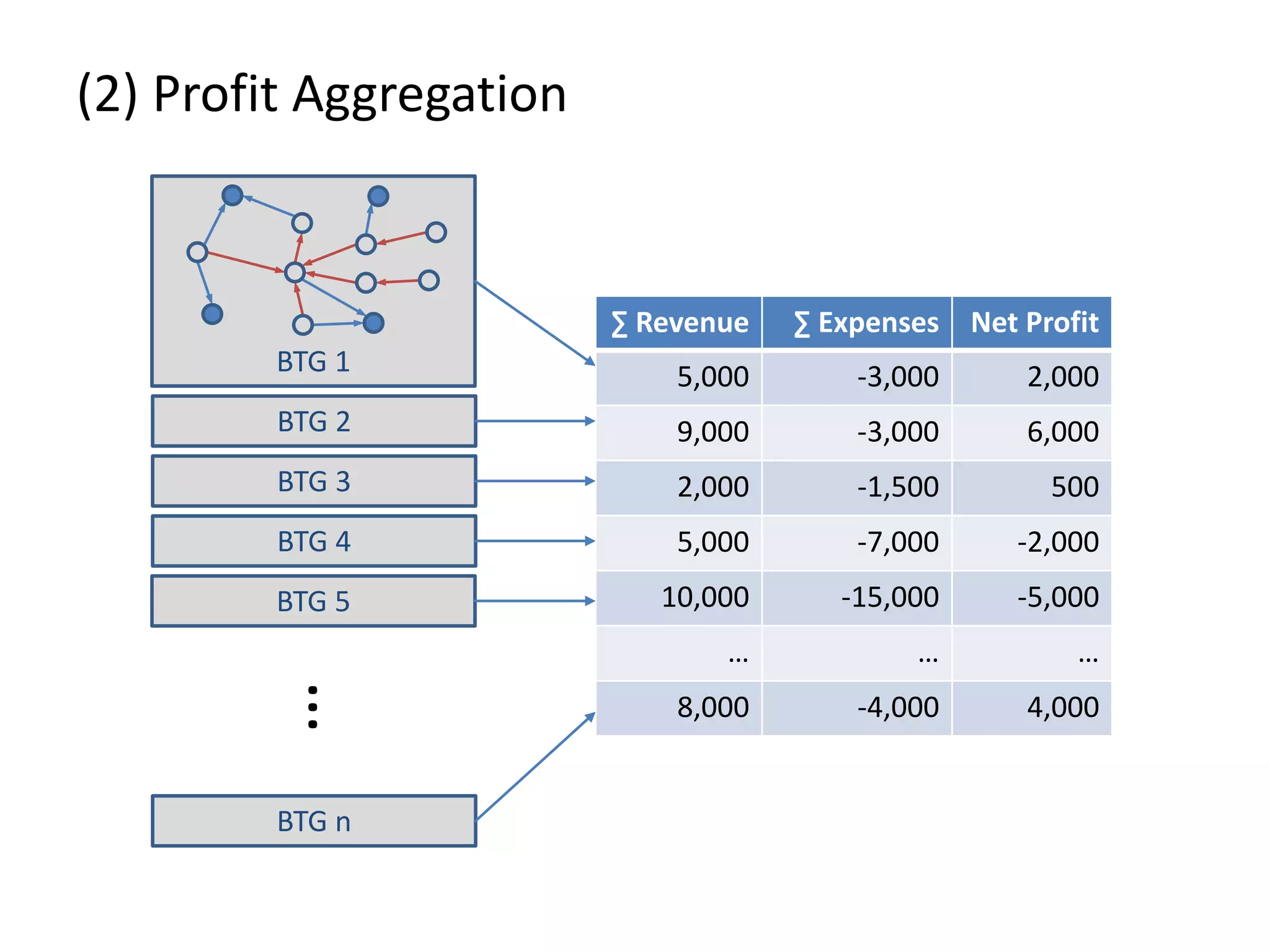

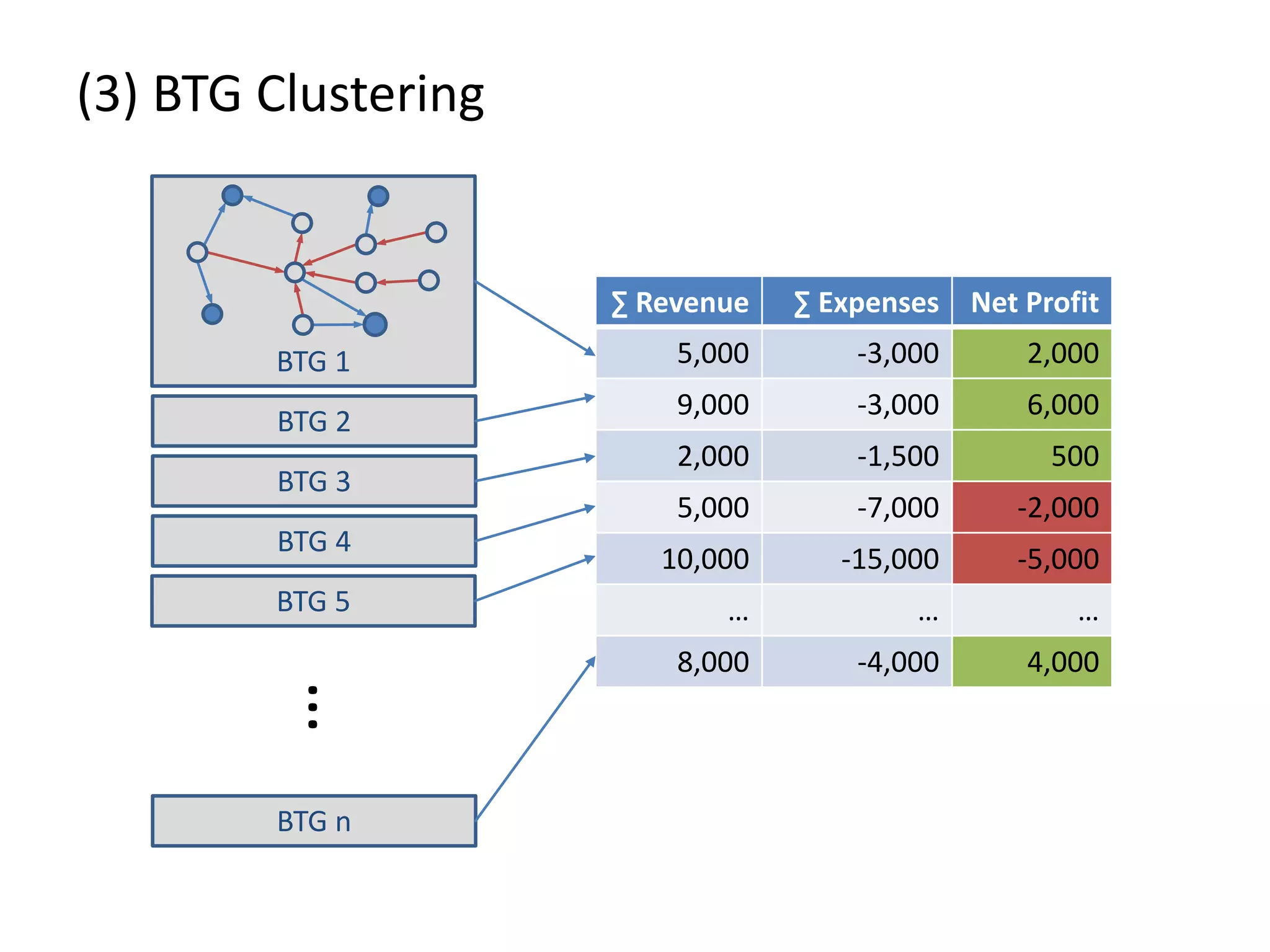
![(3) BTG Clustering // select profit and loss clusters profitBtgs = btgs.select( Graph g => g[“Profit”] >= 0 ) lossBtgs = btgs.difference(profitBtgs)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-61-2048.jpg)
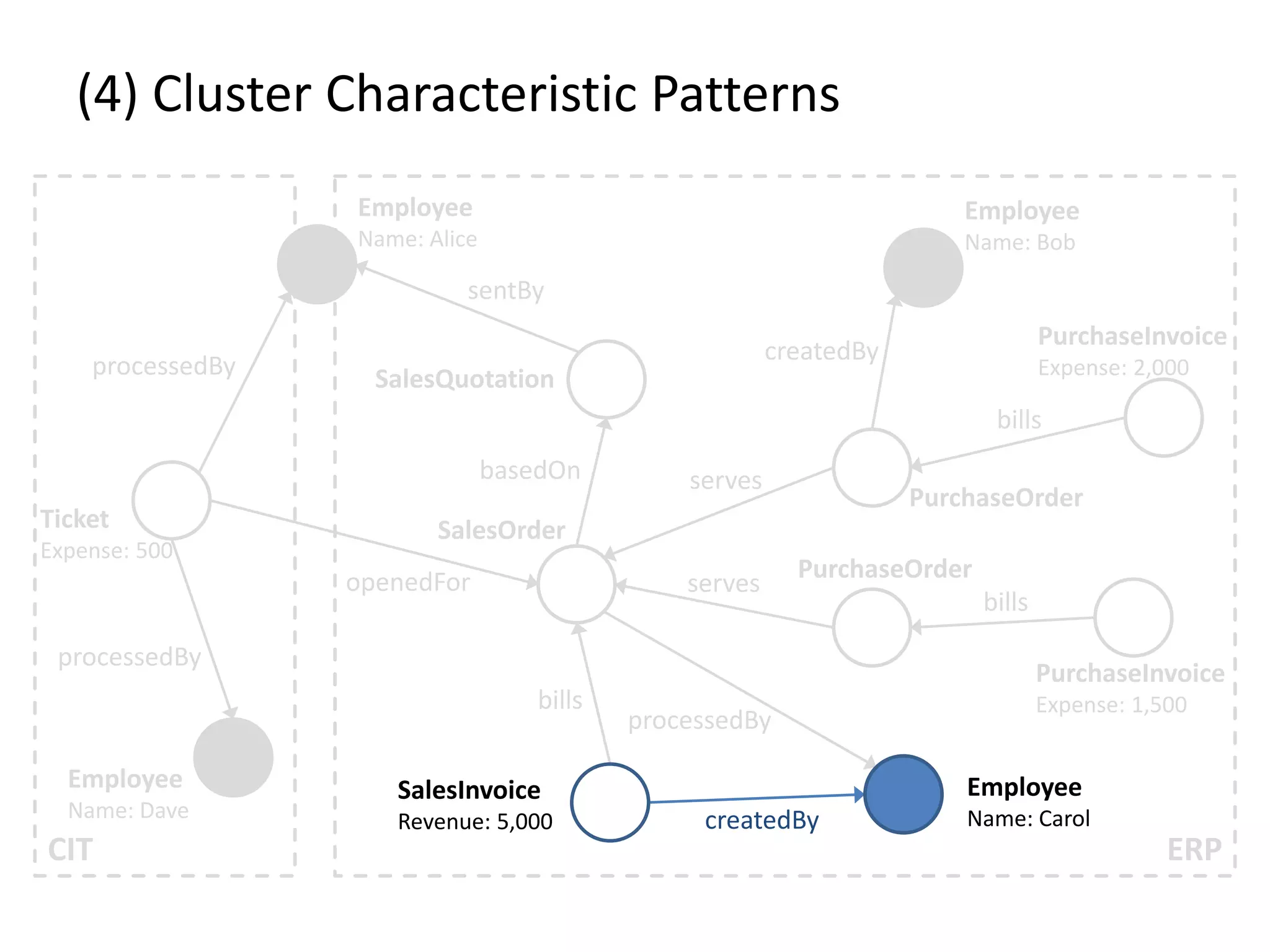
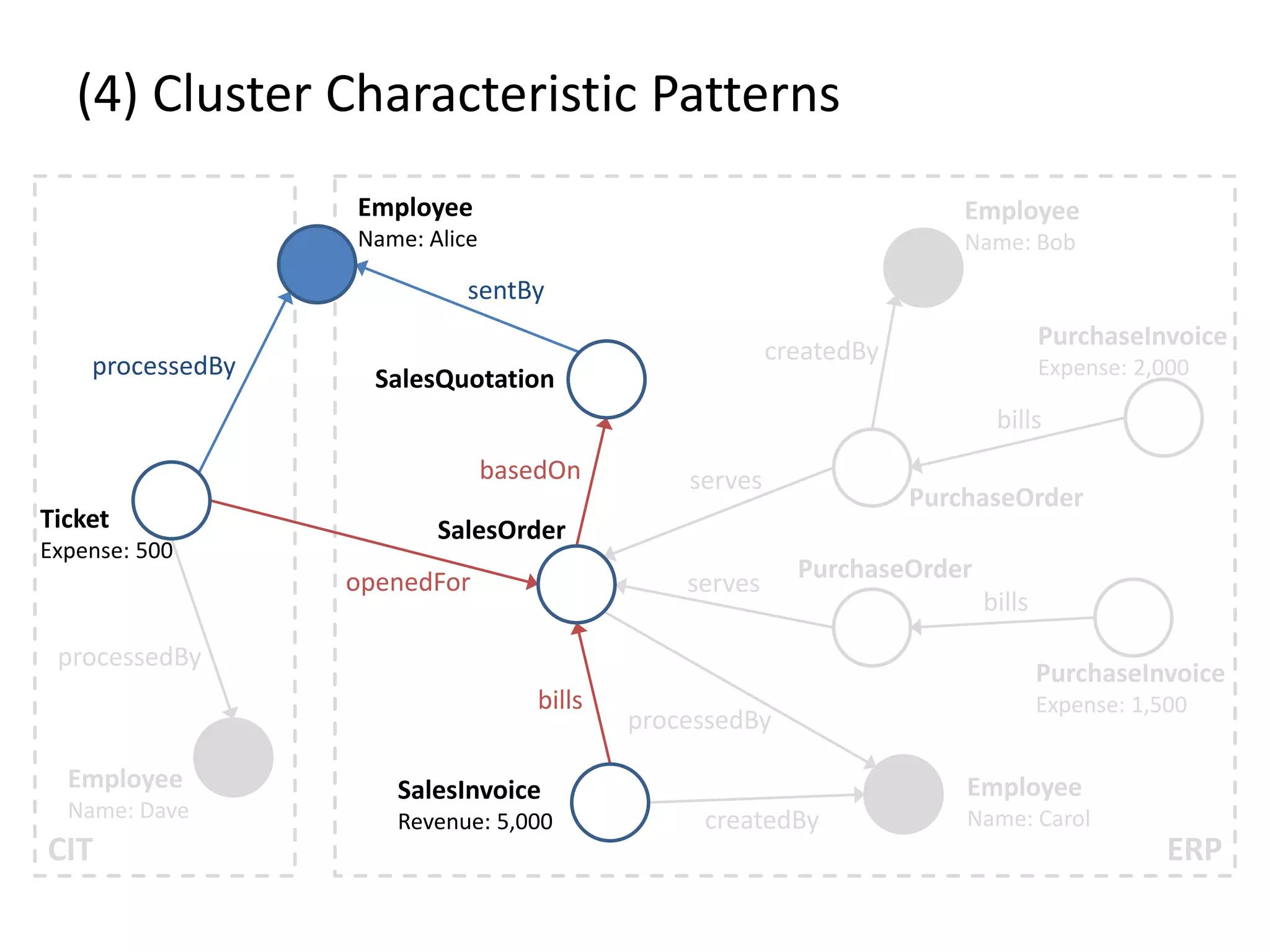
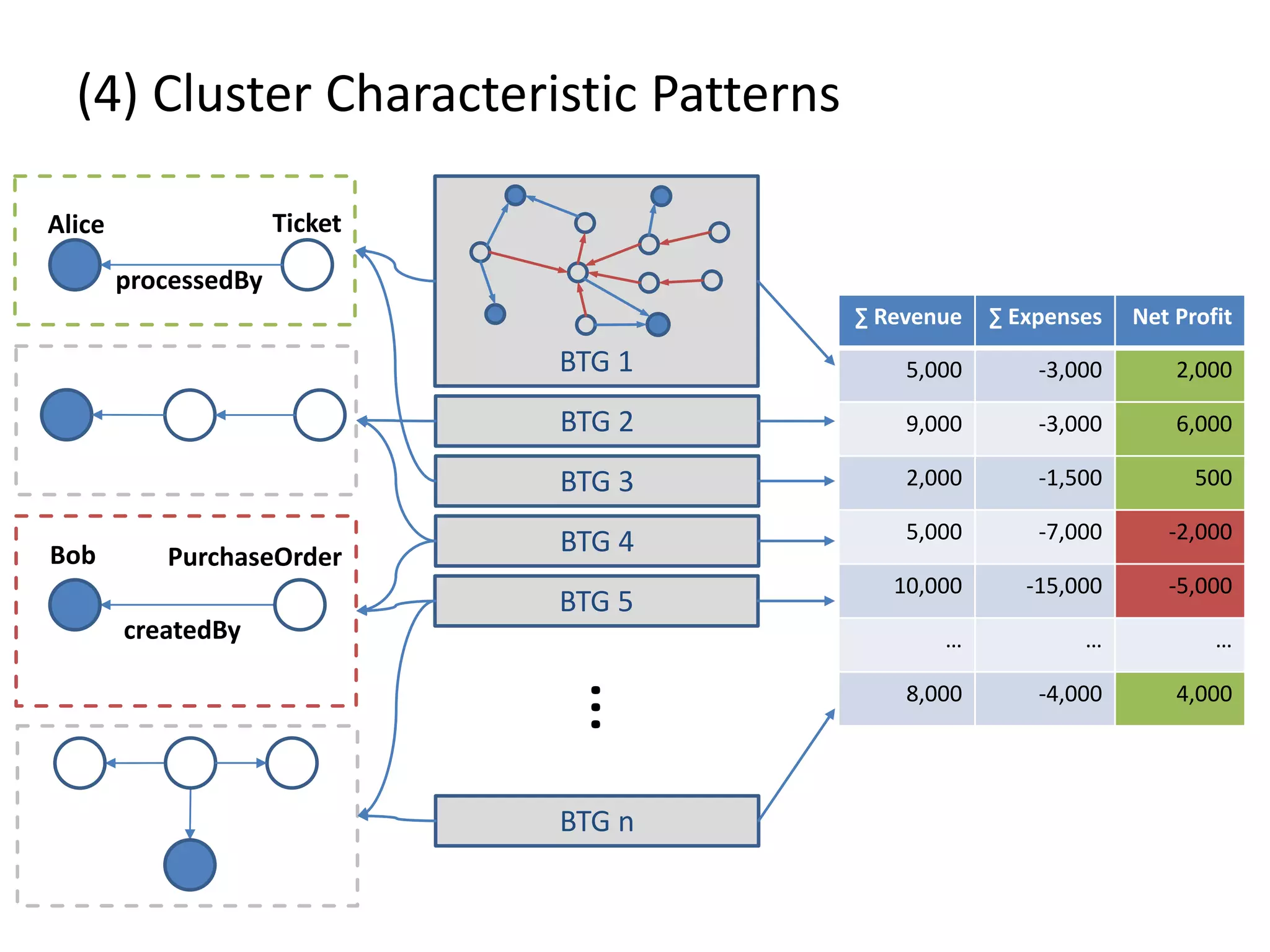
![(4) Cluster Characteristic Patterns // select profit and loss clusters profitBtgs = btgs.select( Graph g => g[“Profit”] >= 0 ) lossBtgs = btgs.difference(profitBtgs) // apply magic profitFreqPats = profitBtgs.callForCollection( :FrequentSubgraphs , {“Threshold”:0.7} ) lossFreqPats = lossBtgs.callForCollection( :FrequentSubgraphs , {“Threshold”:0.7} ) // determine cluster characteristic patterns trivialPats = profitFreqPats.intersect(lossFreqPats) profitCharPatterns = profitFreqPats.difference(trivialPats) lossCharPatterns = lossFreqPats.difference(trivialPats)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-65-2048.jpg)
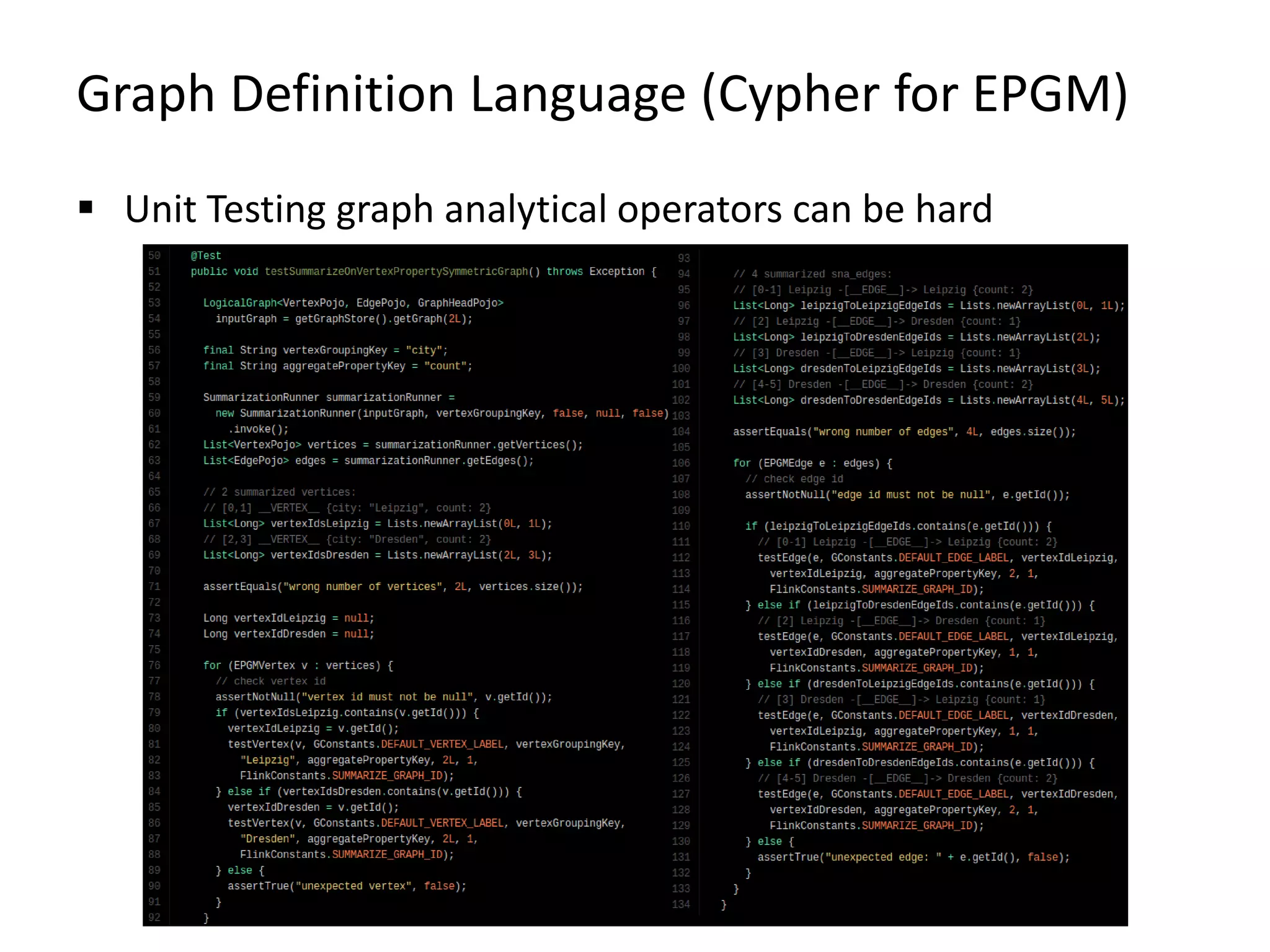


![Graph Definition Language (Cypher for EPGM) FlinkAsciiGraphLoader Creates LogicalGraphs and GraphCollections based on ASCII graph Based on Cypher: https://github.com/s1ck/gdl Define vertices (alice:User {name = "Alice", age = 23}) Define edges (alice)-[e1:knows {since = 2014}]->(bob) Define paths (alice)-->(bob)<--(eve)-->(carol)-->(alice) Define graphs g1:Community {title = "Graphs", memberCount = 3}[ (alice:User)-[:knows]->(bob:User) (bob)-[e:knows]->(eve:User) (eve) ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-70-2048.jpg)




![Benchmark Preview 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1 2 4 8 16 Time [s] # Worker Summarization (Vertex and Edge Labels) 16x Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2430 v2 @ 2.50GHz (12 Cores), 48 GB RAM Hadoop 2.5.2, Flink 0.9.0 slots (per node) 12 jobmanager.heap.mb 2048 taskmanager.heap.mb 40960 Foodbroker Graph (https://github.com/dbs-leipzig/foodbroker) Generates BI process data 858,624,267 Vertices, 4,406,445,007 Edges, 663GB Payload](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationfinalweb-151211075326/75/Meetup-Big-Data-User-Group-Dresden-Gradoop-Scalable-Graph-Analytics-with-Apache-Flink-77-2048.jpg)