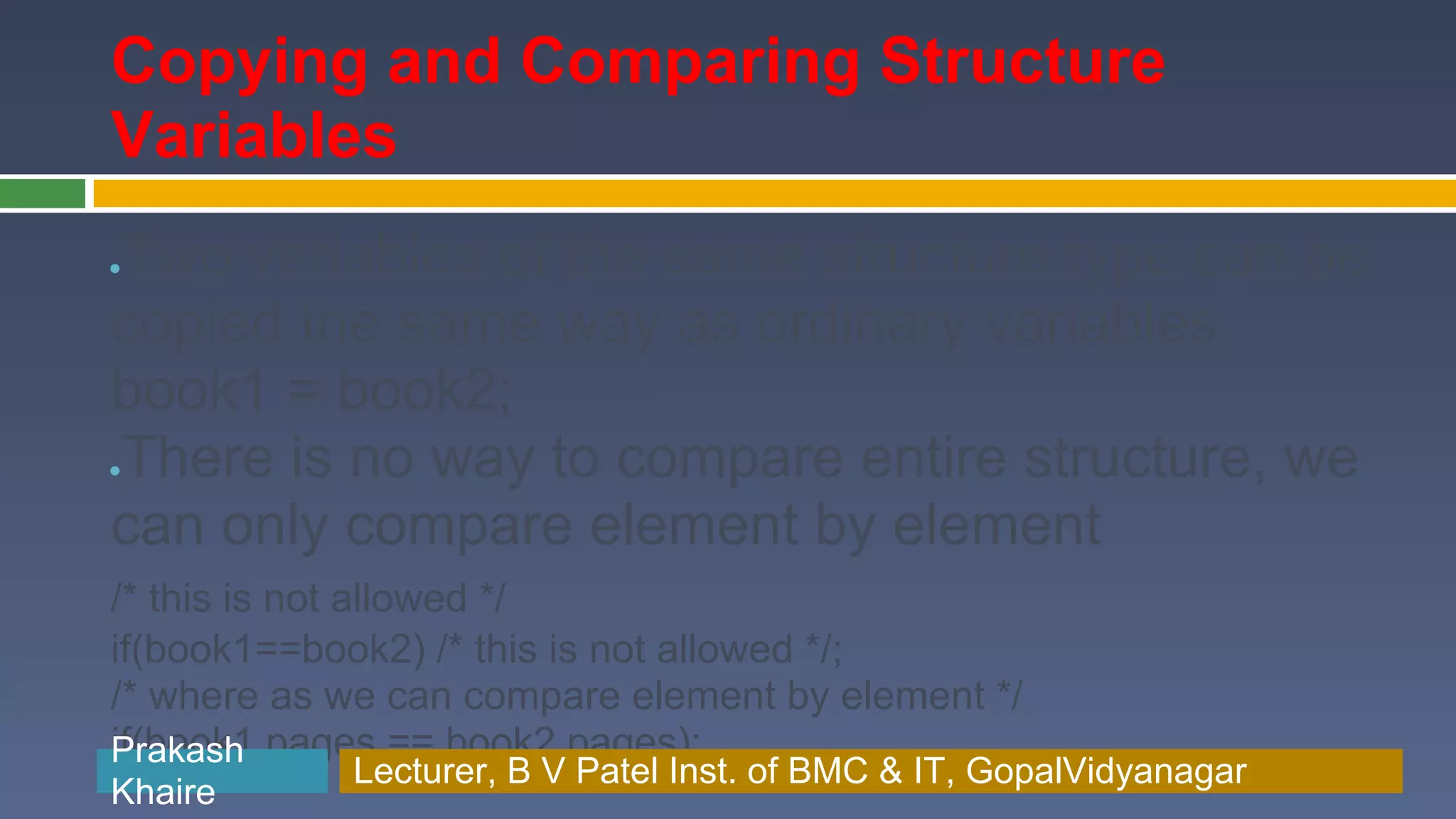
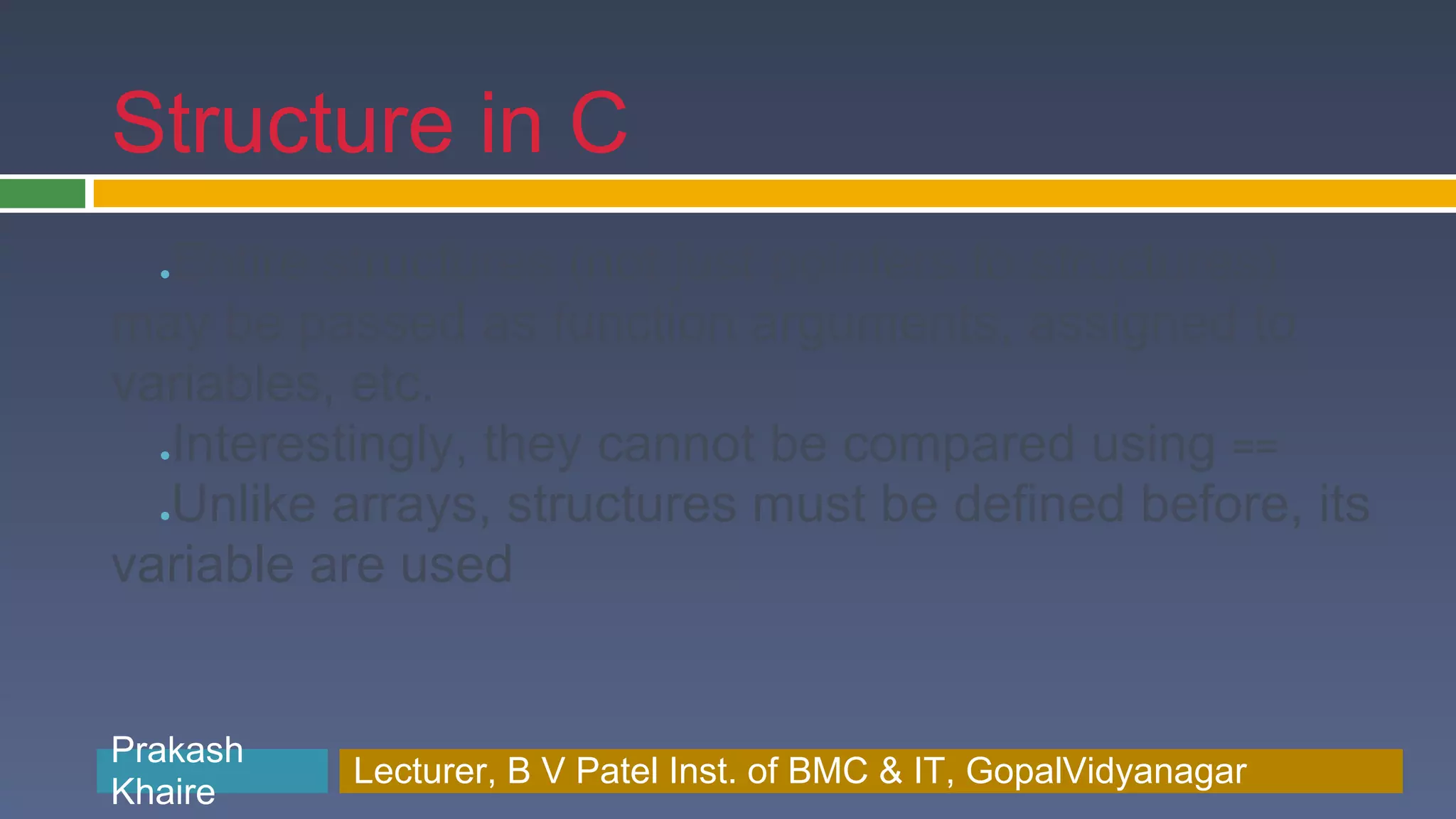
The document discusses structures in C programming. It defines a structure as a collection of variables of different data types grouped together under a single name. Structures allow programmers to create custom data types by combining existing types. The document provides examples of defining, declaring, initializing and accessing members of structures, and also discusses arrays of structures and nested structures.

![Definition - Structure ●A structure is collections of more than one variables with different data type like int, float & char Example : char name[25]; int sci, eng, maths; float per; Prakash Prakash Khaire Lecturer, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & BMC & IT, GopalVidyanagar Lecturer, B V Patel Inst. of IT, GopalVidyanagar Khaire](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture18-structureinc-ppt-120306025956-phpapp02/75/Lecture18-structurein-c-ppt-3-2048.jpg)
![Example struct book_bank void main() { { char title[20]; struct book_bank x,y, MyBooks[5]; int i,j; char author[15]; clrscr(); int pages; --------------- float price; --------------- --------------- }; getch(); } Prakash Prakash Khaire Lecturer, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & BMC & IT, GopalVidyanagar Lecturer, B V Patel Inst. of IT, GopalVidyanagar Khaire](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture18-structureinc-ppt-120306025956-phpapp02/75/Lecture18-structurein-c-ppt-5-2048.jpg)



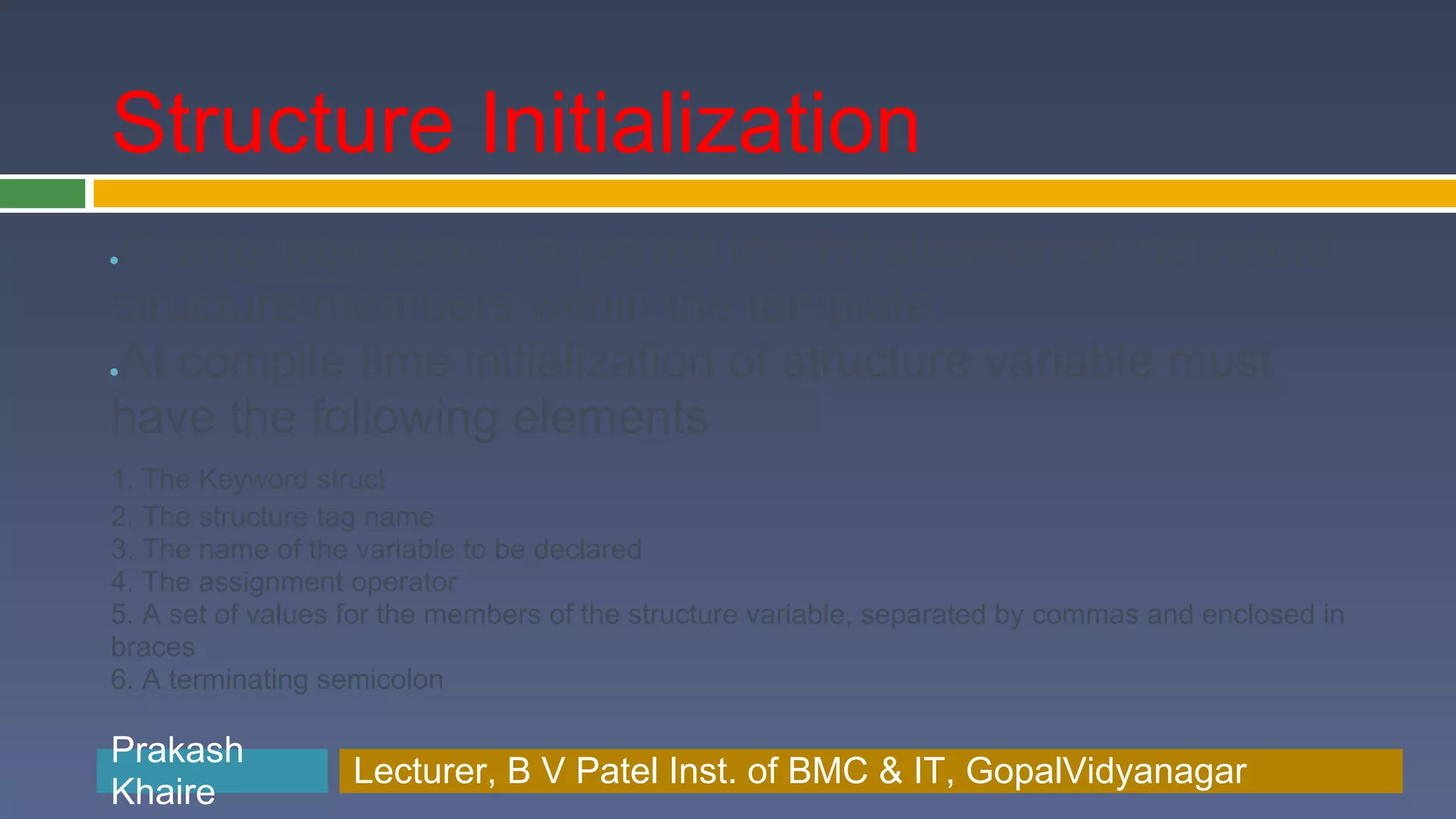
![Structure Initialization Like other data type we can initialize structure when we declare them ● A structure variable can be initialized at compile time struct book_bank { char title[20]; char author[15]; int pages; float price; } book1={“ANSI C”,”Balaguruswamy”,430,200.0}; or struct book_bank book1 = {“ANSI C”,”Balaguruswamy”,430,200.0}; Prakash Prakash Khaire Lecturer, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & BMC & IT, GopalVidyanagar Lecturer, B V Patel Inst. of IT, GopalVidyanagar Khaire](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture18-structureinc-ppt-120306025956-phpapp02/75/Lecture18-structurein-c-ppt-10-2048.jpg)

![Array of structure ●Like array of int, float or char, we can also have array of structure ●We can use single-dimensional or multi-dimensional arrays ●Example struct student { Subject contains three elements, char name[20]; subject[0], subject[1] and subject[2]. char city[15]; These elements can be accessed as int subject[3]; followed float per; stud[1].subject[2] }stud[10]; This will refer to the marks of third subject of second student Prakash Khaire Lecturer, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & IT, GopalVidyanagar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture18-structureinc-ppt-120306025956-phpapp02/75/Lecture18-structurein-c-ppt-15-2048.jpg)
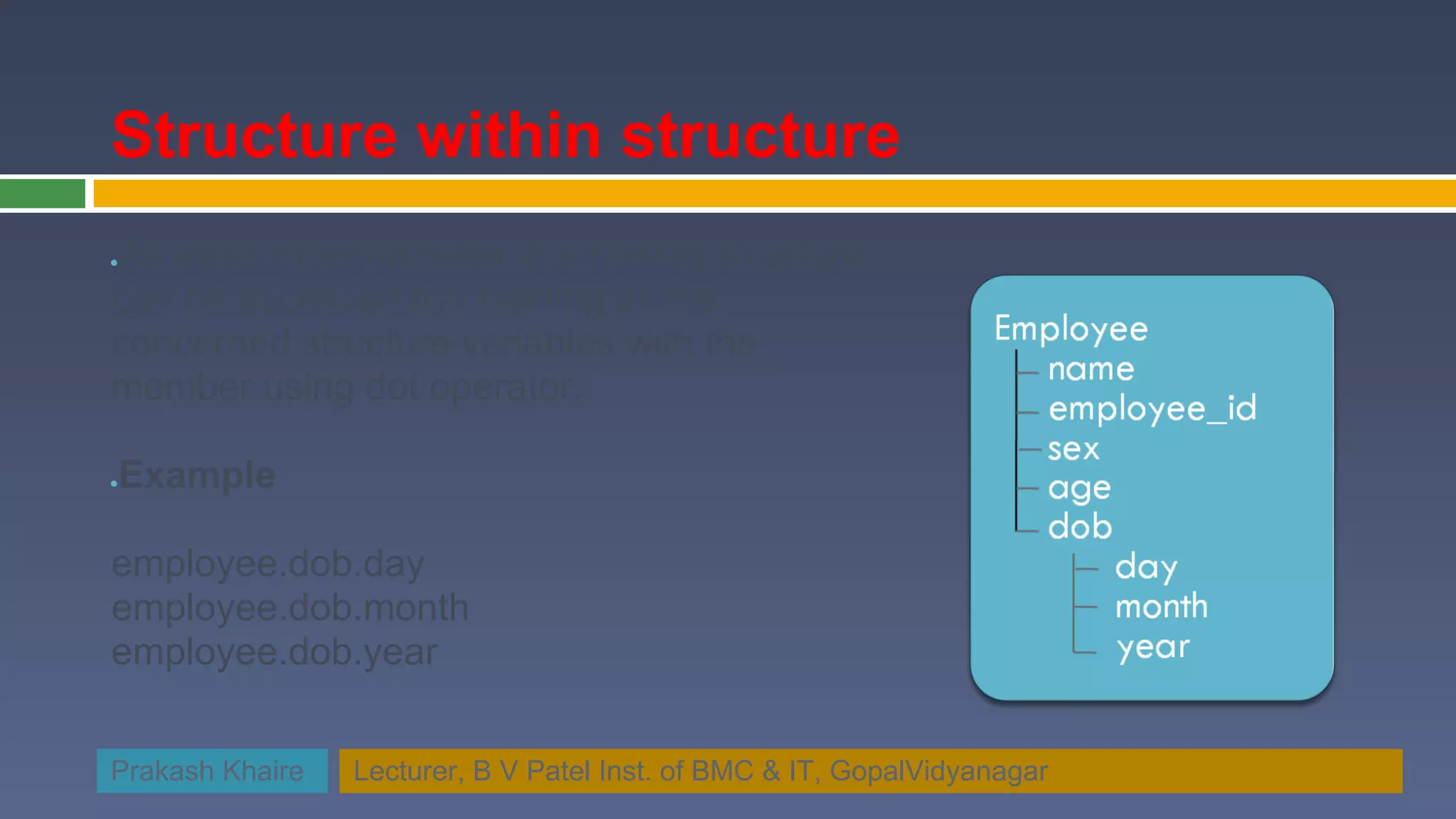
![Structures within structure Structure within structure is known as nested structure ● struct date struct company { // members of structure { int day; char name[20]; int month; long int employee_id; int year; char sex[5]; }; int age; struct company { struct char name[20]; { long int employee_id; int day; char sex[5]; int month; int age; int year; struct date dob; }dob; }; }employee; Prakash Khaire Lecturer, B V Patel Inst. of BMC & IT, GopalVidyanagar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture18-structureinc-ppt-120306025956-phpapp02/75/Lecture18-structurein-c-ppt-16-2048.jpg)