Downloaded 53 times


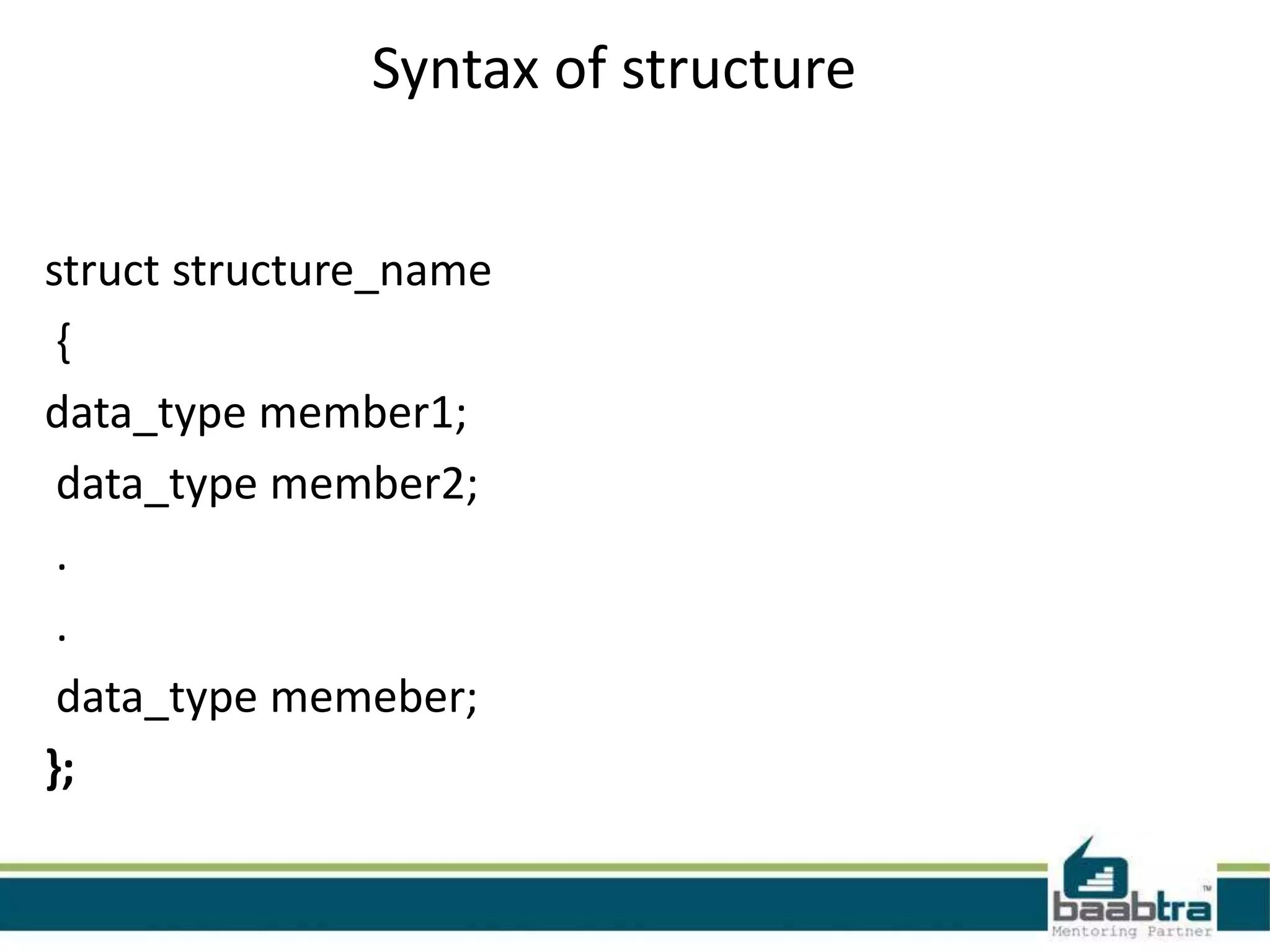
![EXAMPLE#include<stdio.h> struct student { char name[10]; int age; }; int main() { int n,i; struct student std[10]; printf("enter the no.of stusdent:"); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("enter the details of student%dn",i+1); printf("enter the namet"); scanf("%s",std[i].name); printf("enter the aget"); scanf("%d",&std[i].age); } printf("NAMEtAGEn"); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%st",std[i].name); printf("%dtn",std[i].age); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurespointersandstringsinc-140502225657-phpapp01/75/Structures-pointers-and-strings-in-c-Programming-8-2048.jpg)

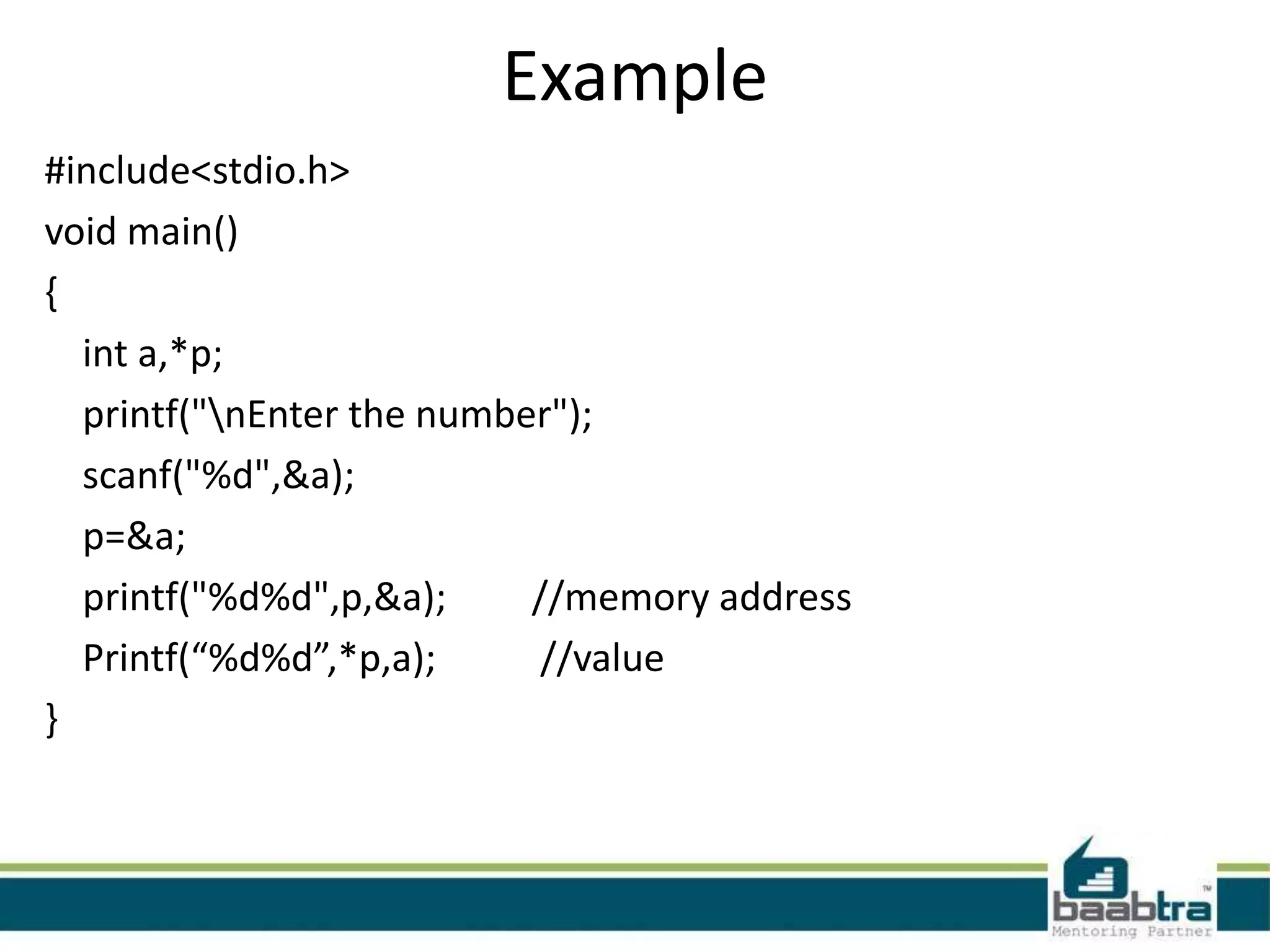

![Example #include<stdio.h> void main() { char a[7]="baabtra"; scanf("%s",&a); printf("%s",a); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurespointersandstringsinc-140502225657-phpapp01/75/Structures-pointers-and-strings-in-c-Programming-12-2048.jpg)
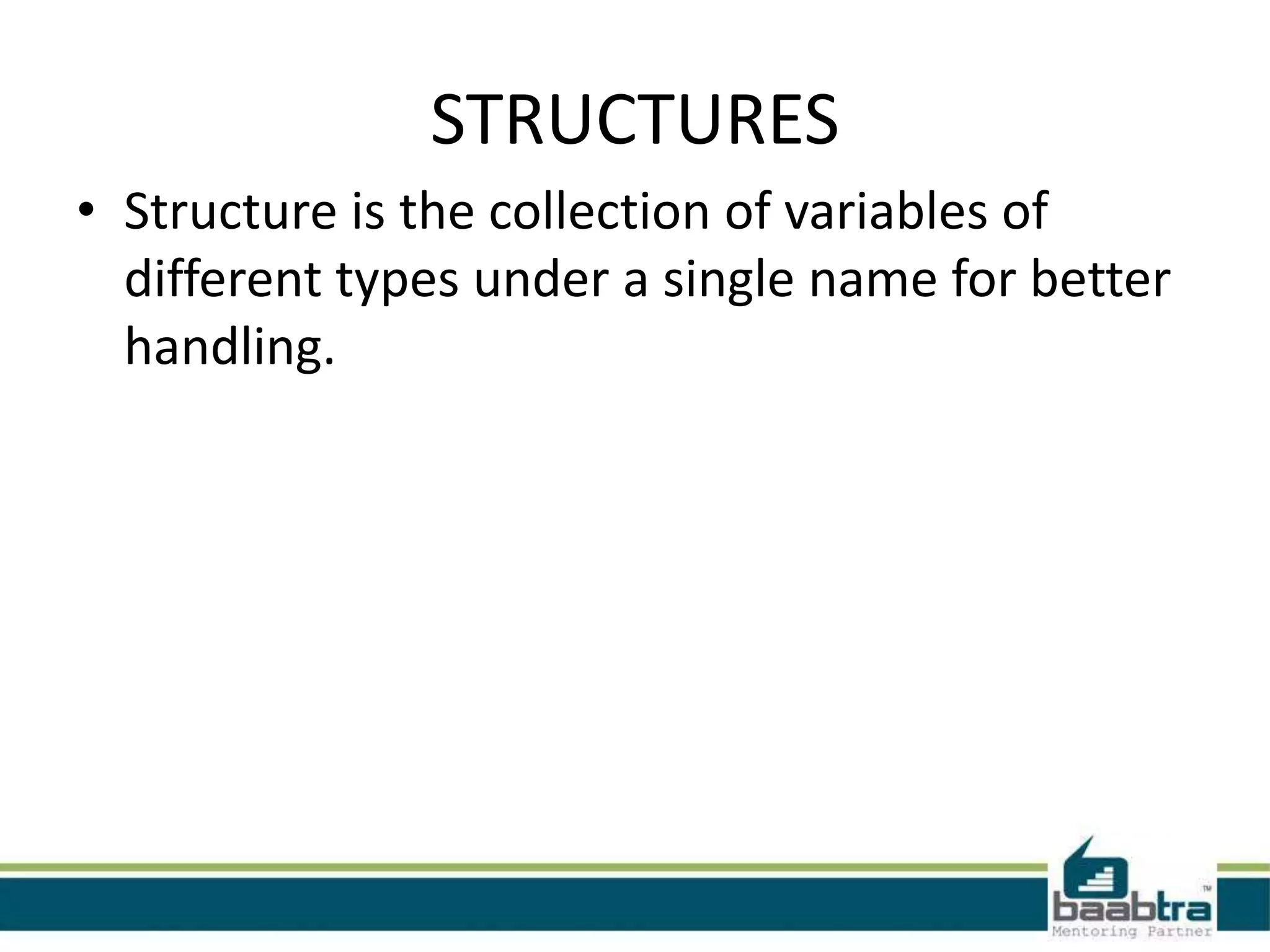
This document contains 3 summaries of technical topics: 1) Structures allow grouping of different data types under a single name for easier handling. 2) Pointers are variables that store memory addresses of other variables. They must be declared before use and are declared with a type and asterisk. 3) Strings in C are arrays of characters with a null character marking the end.







![EXAMPLE#include<stdio.h> struct student { char name[10]; int age; }; int main() { int n,i; struct student std[10]; printf("enter the no.of stusdent:"); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("enter the details of student%dn",i+1); printf("enter the namet"); scanf("%s",std[i].name); printf("enter the aget"); scanf("%d",&std[i].age); } printf("NAMEtAGEn"); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%st",std[i].name); printf("%dtn",std[i].age); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurespointersandstringsinc-140502225657-phpapp01/75/Structures-pointers-and-strings-in-c-Programming-8-2048.jpg)



![Example #include<stdio.h> void main() { char a[7]="baabtra"; scanf("%s",&a); printf("%s",a); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurespointersandstringsinc-140502225657-phpapp01/75/Structures-pointers-and-strings-in-c-Programming-12-2048.jpg)