The document is a comprehensive guide on creating stored procedures and functions in PL/SQL. It explains the definitions, syntax, creation process, and differences between procedures and functions, providing examples for clarity. Additionally, it discusses how to delete a procedure and outlines the role of arguments in procedures.

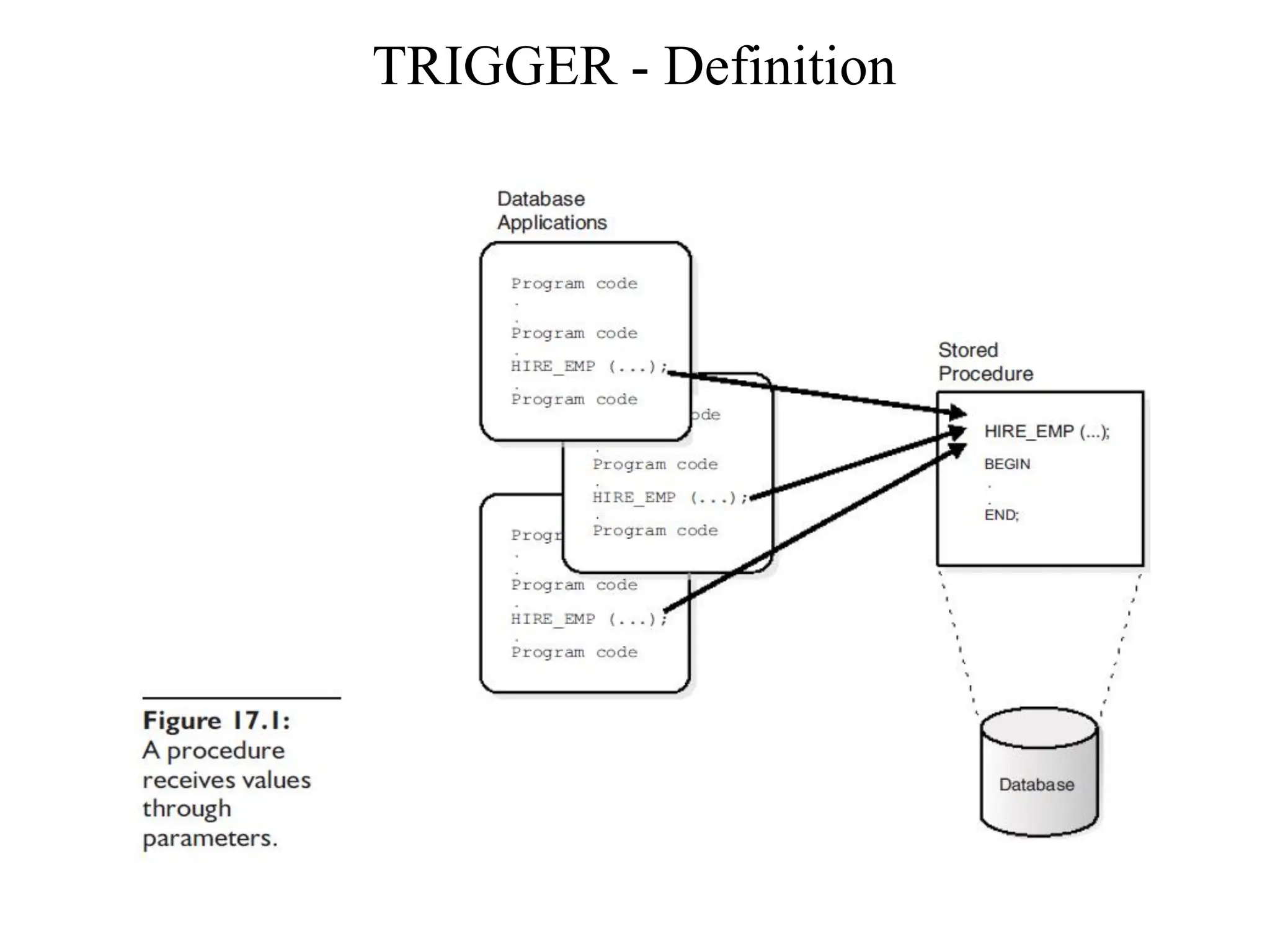
![Creating a Stored Procedure ➢ A stored procedure has two parts: a specification section and the procedure body. The CREATE PROCEDURE command is responsible for the creation of procedures. ➢ Syntax: CREATE [OR REPLACE] PROCEDURE [schema.] procedure [ (argument [IN | OUT | IN OUT] datatype [, argument [IN | OUT | IN OUT] datatype] ...)] {IS|AS} {pl/sql_subprogram_body | external_body}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecturenotesunit5chapter17storedprocedures-240807171319-7a17e7ea/75/Lecture-Notes-Unit5-chapter17-Stored-procedures-and-functions-4-2048.jpg)





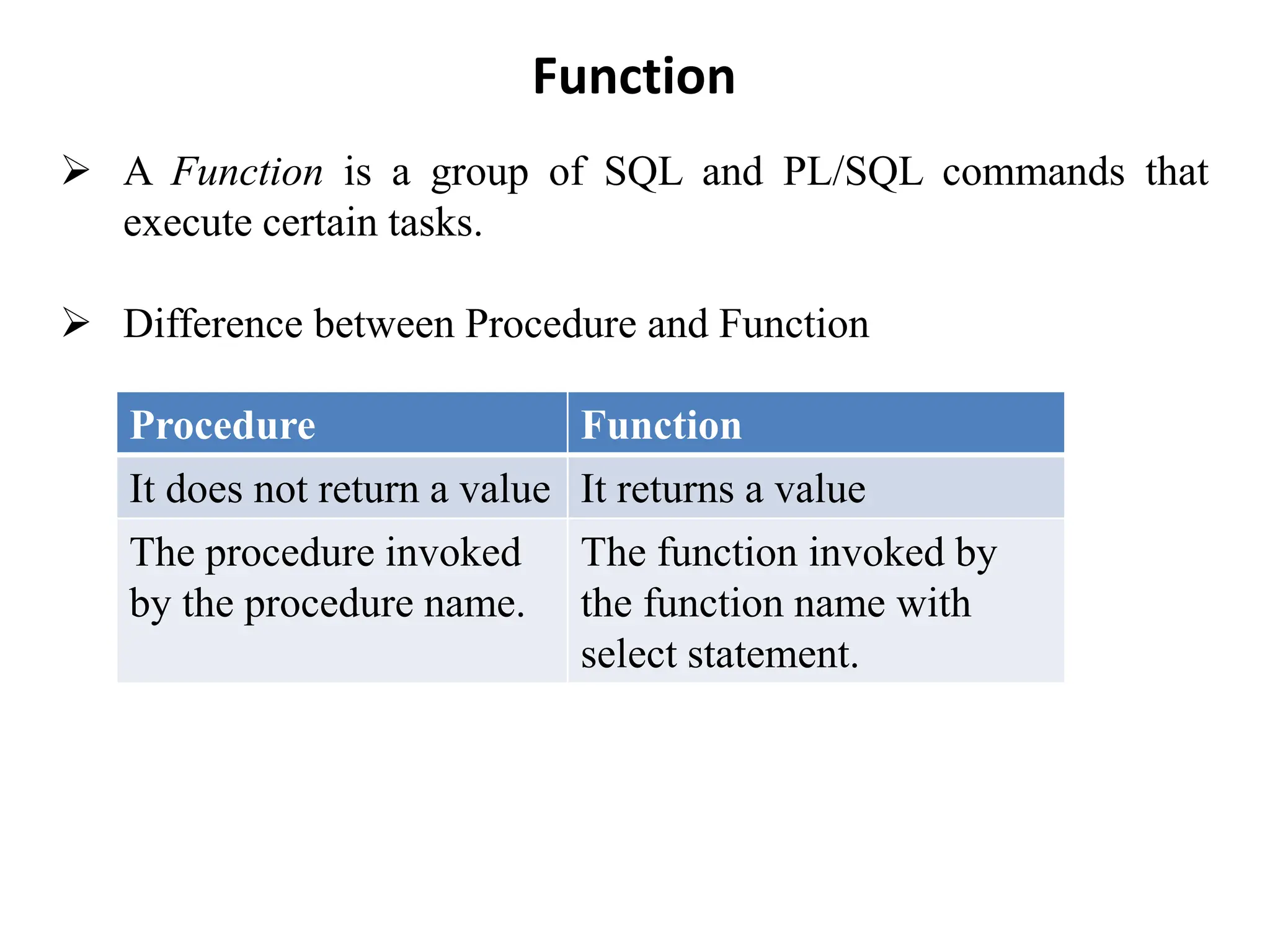
![Creating a Function ➢ The CREATE FUNCTION command creates a function as an isolated schema object. You can also create a function as part of a package. Syntax: CREATE [OR REPLACE] FUNCTION [schema.]function [(argument [IN | OUT | IN OUT] datatype [, argument [IN | OUT | IN OUT] datatype] ...)] RETURN datatype {IS | AS} pl/sql_subprogram_body](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecturenotesunit5chapter17storedprocedures-240807171319-7a17e7ea/75/Lecture-Notes-Unit5-chapter17-Stored-procedures-and-functions-11-2048.jpg)
