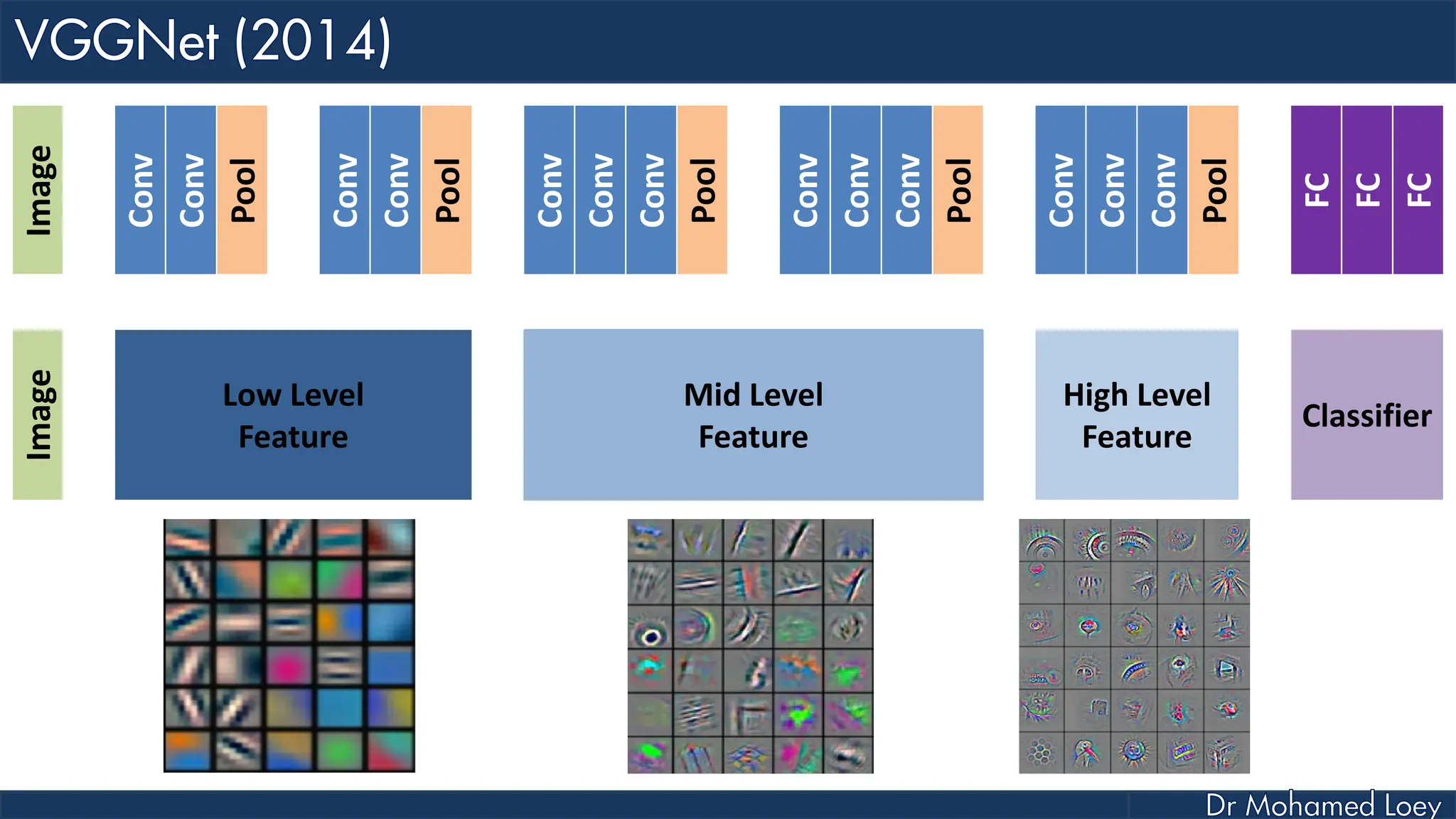
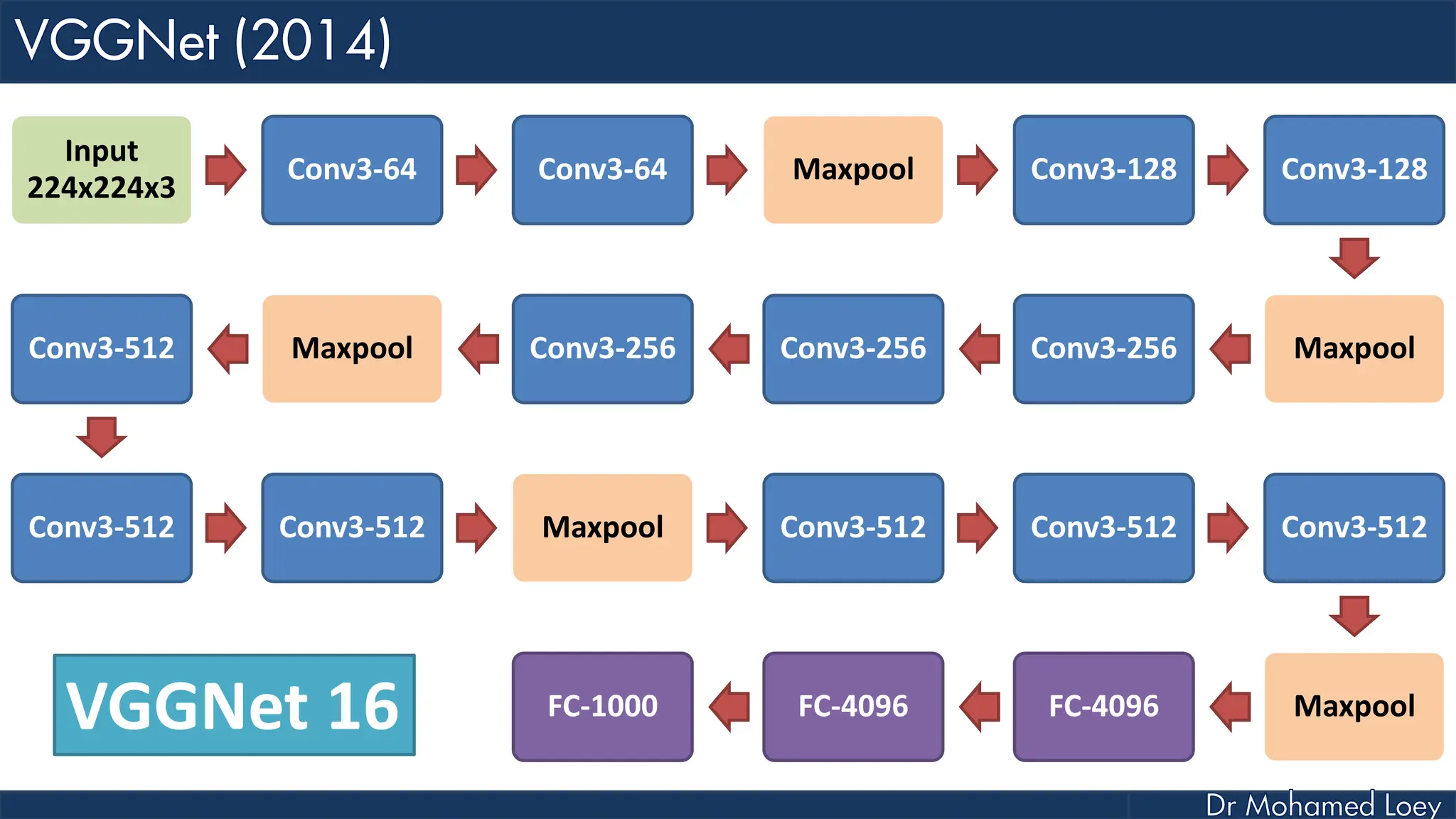
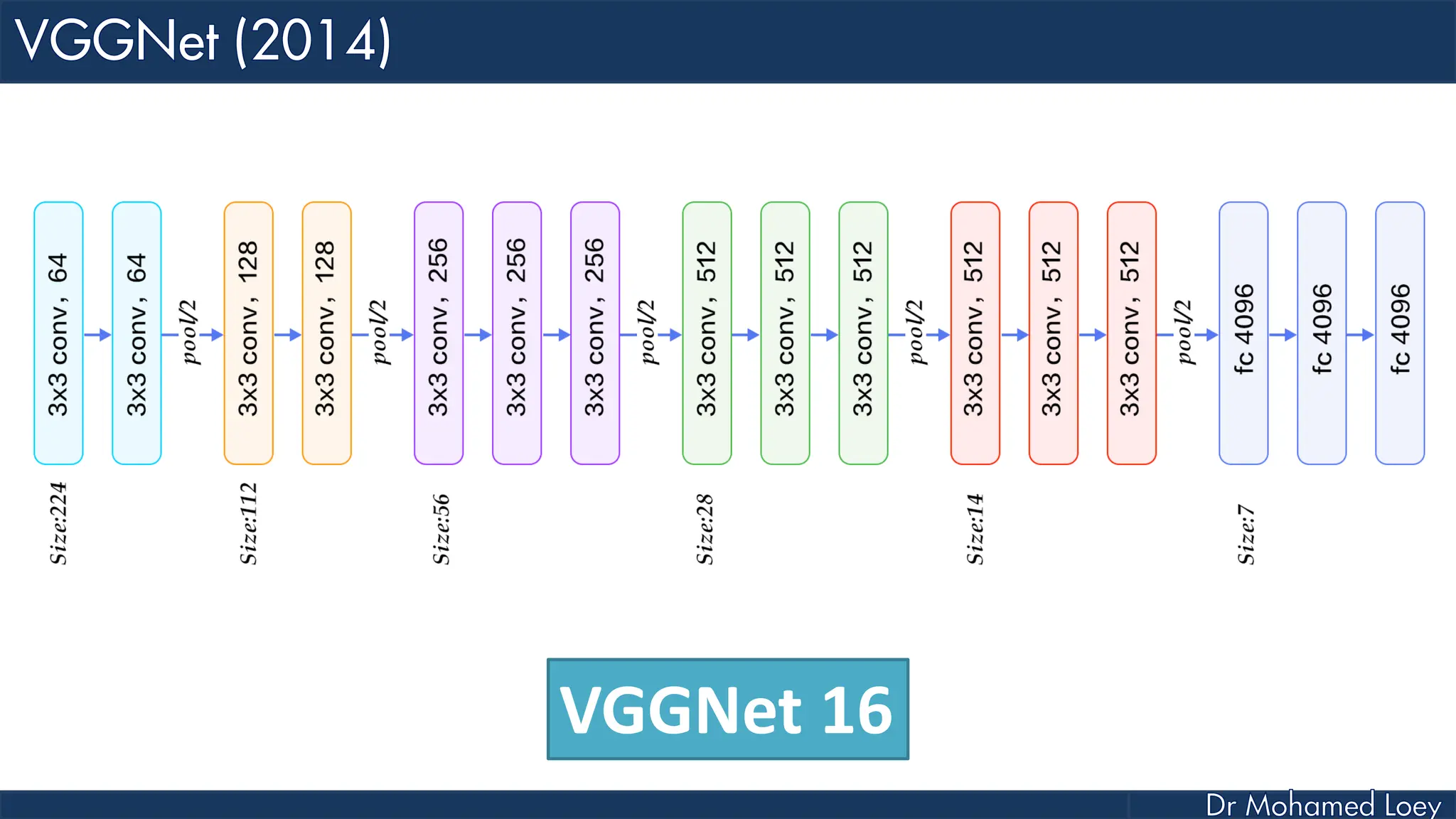
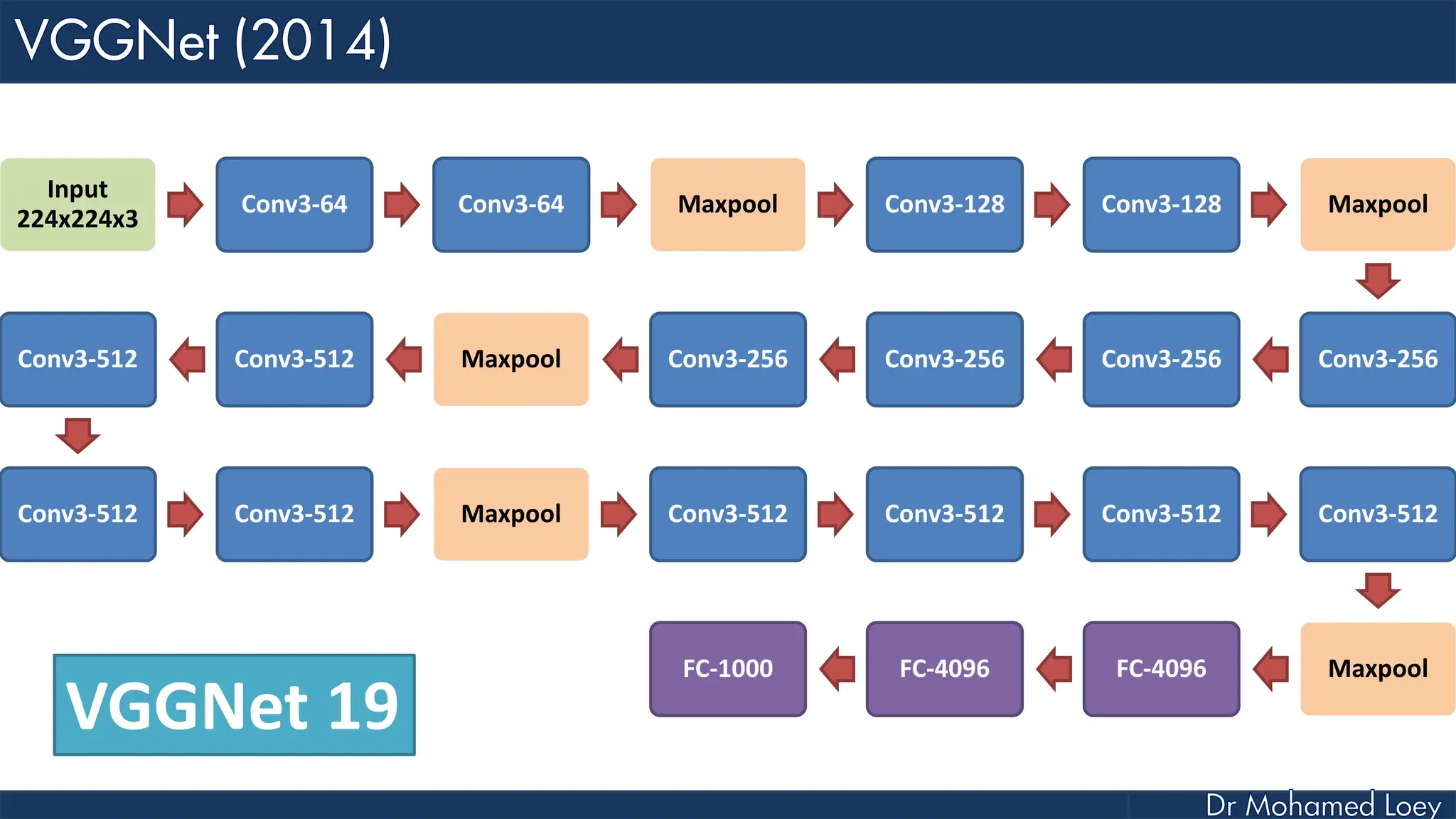
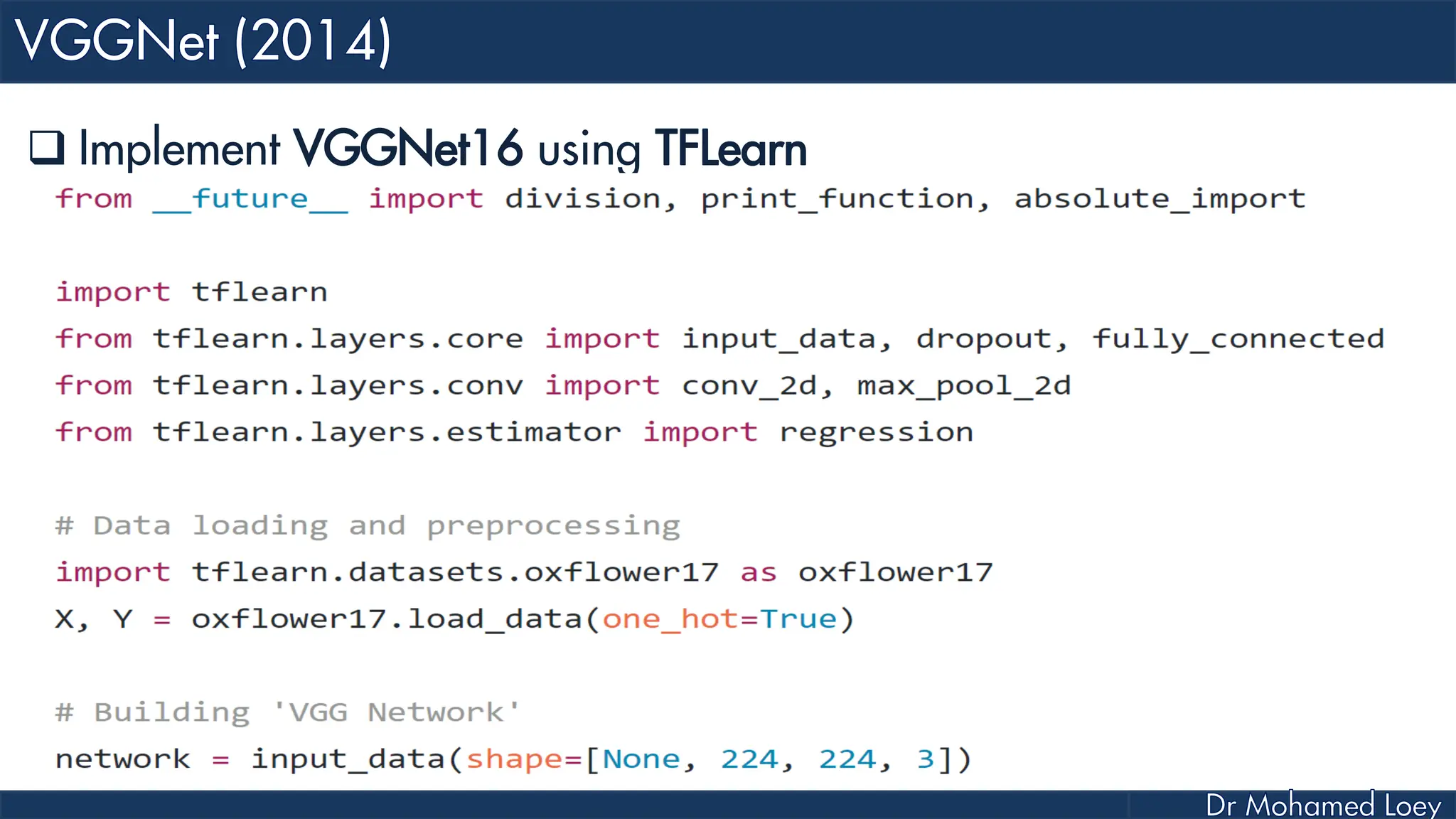
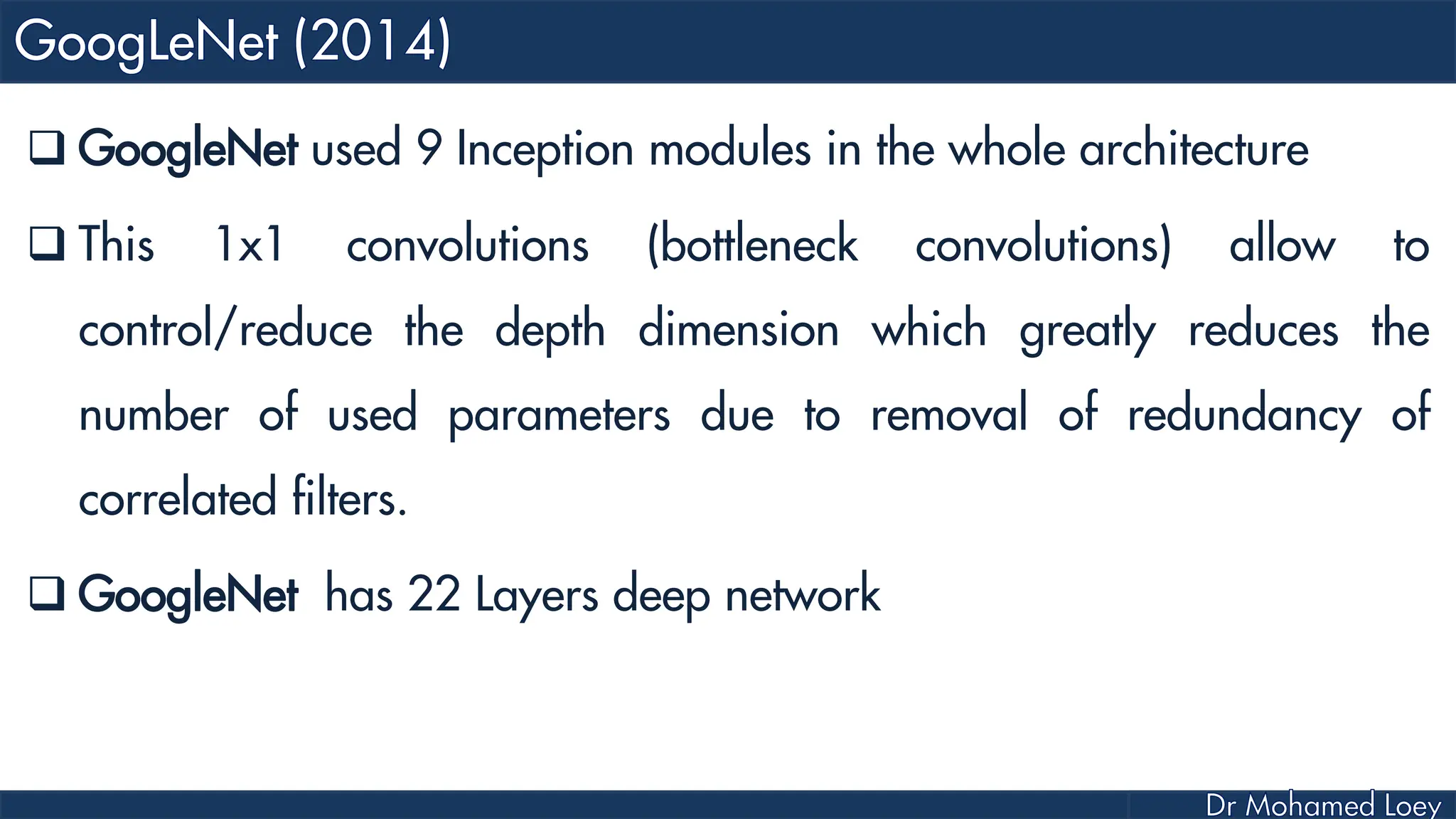
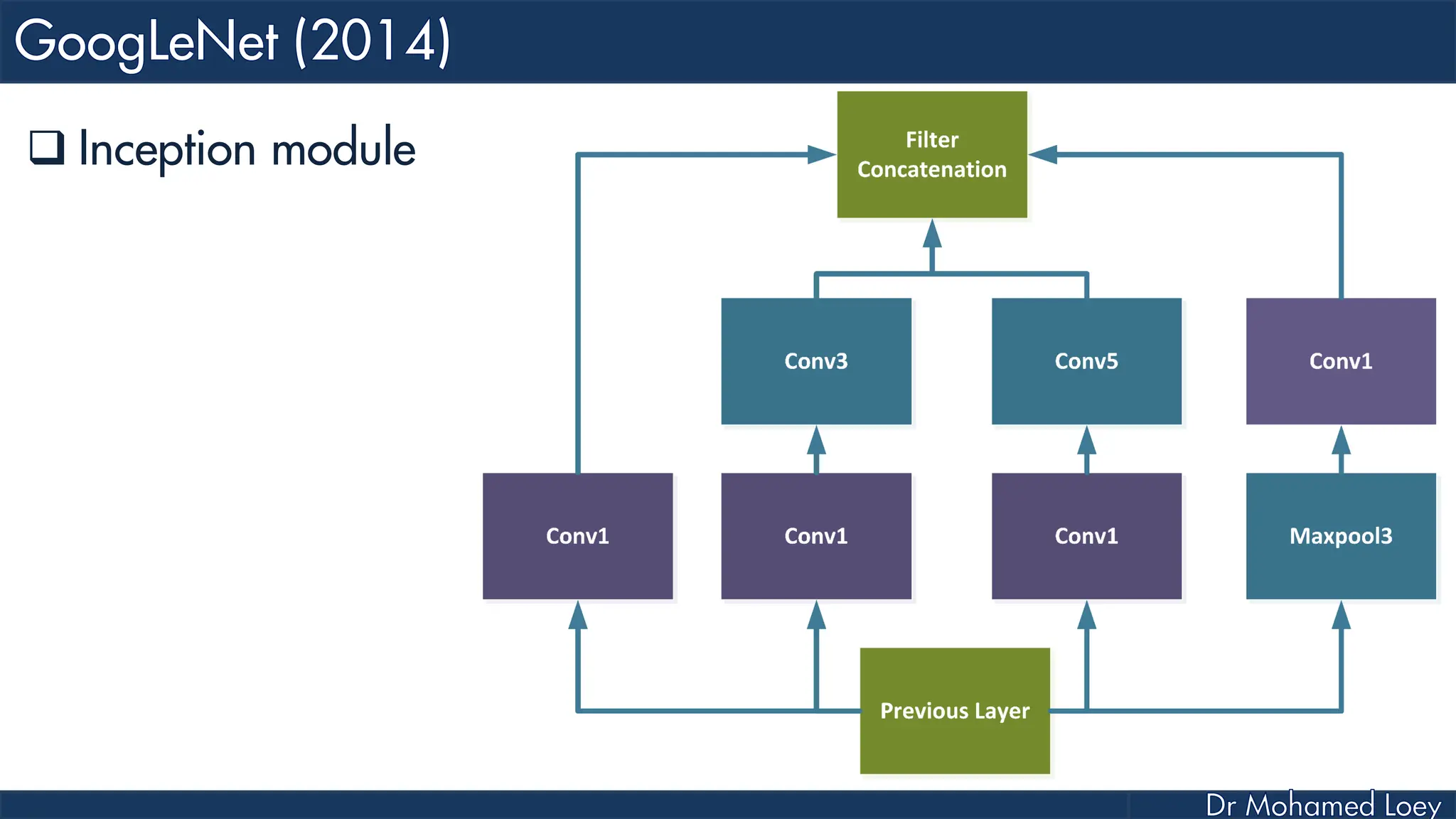
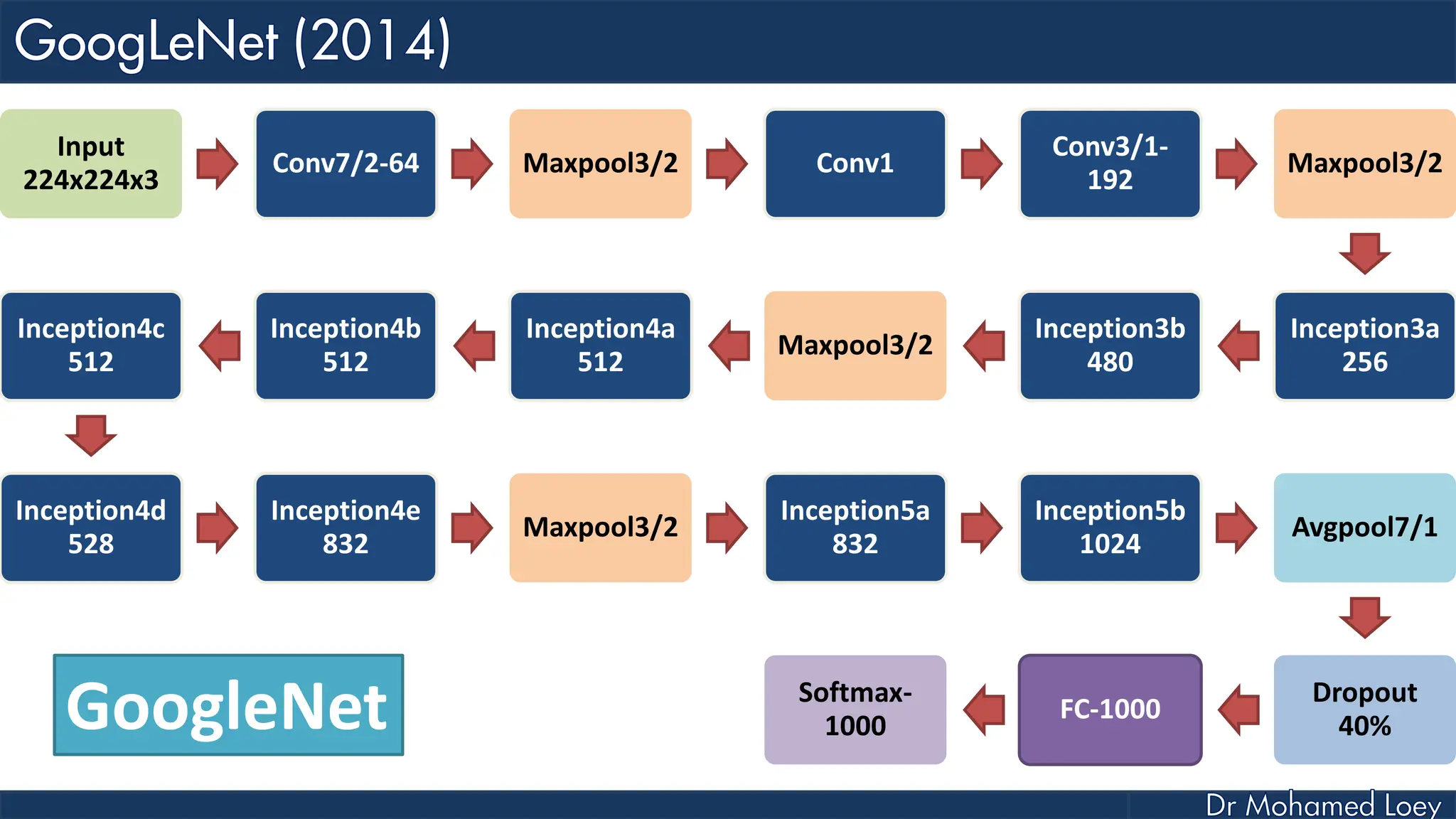
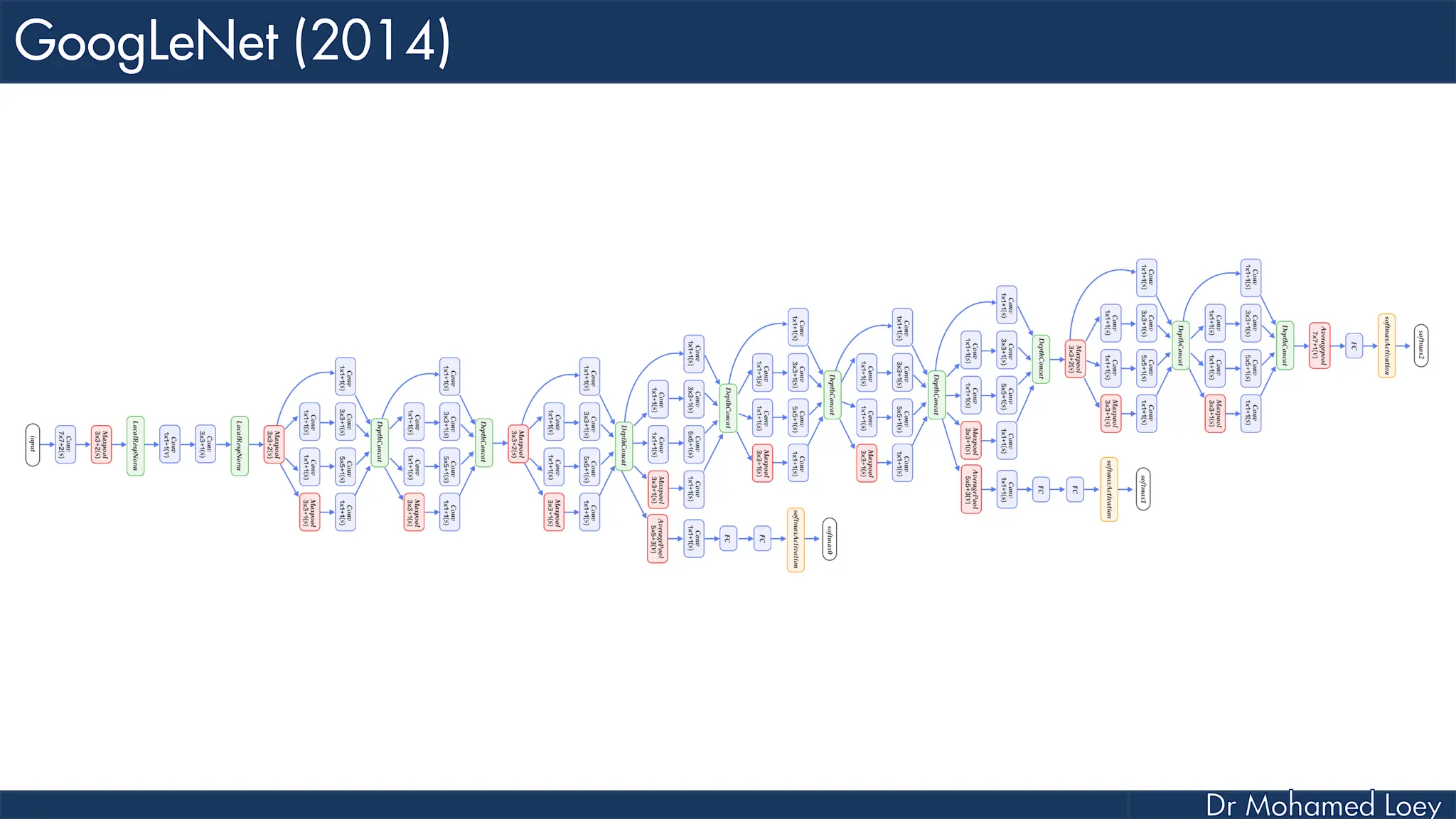
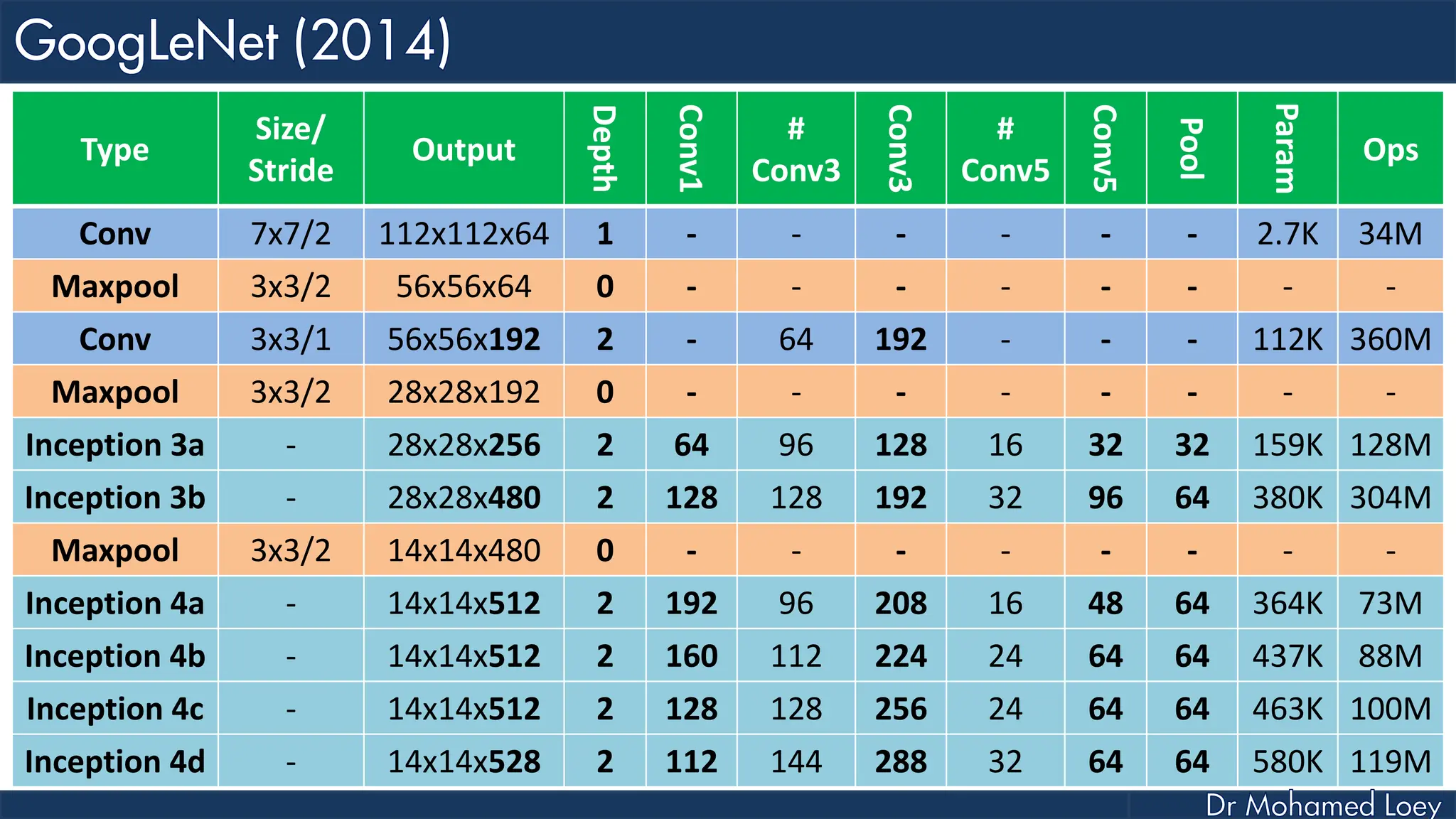
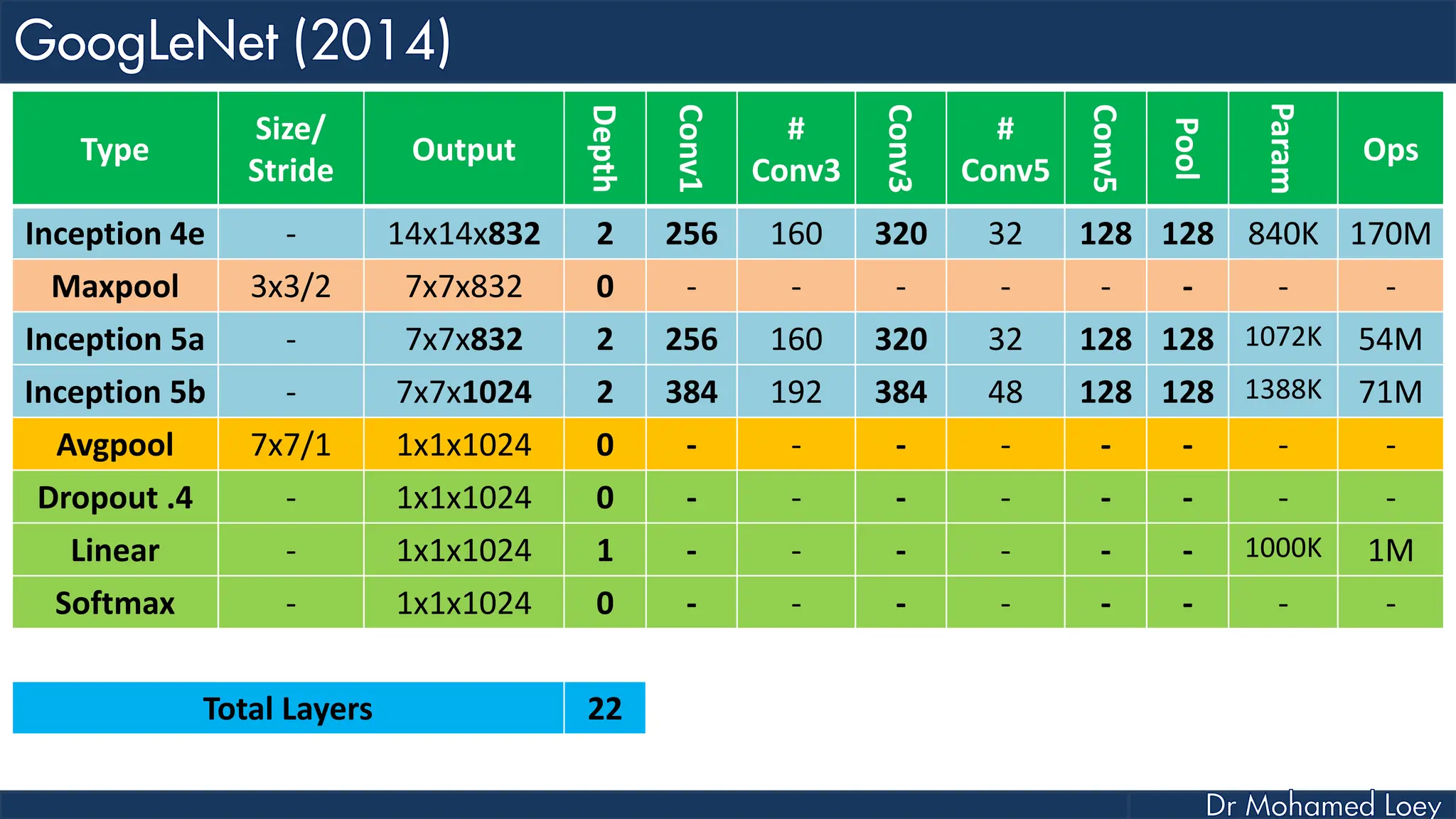
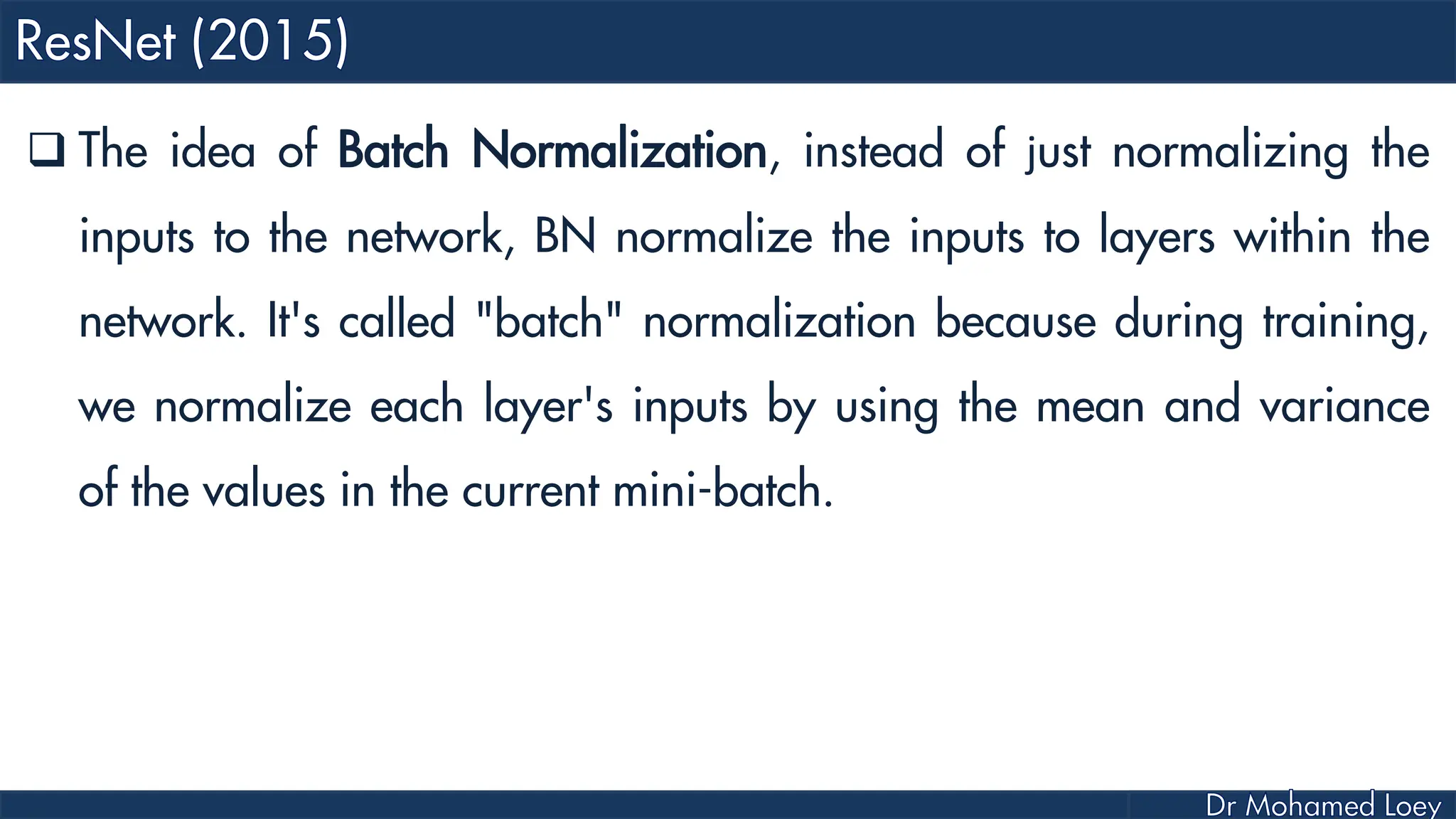
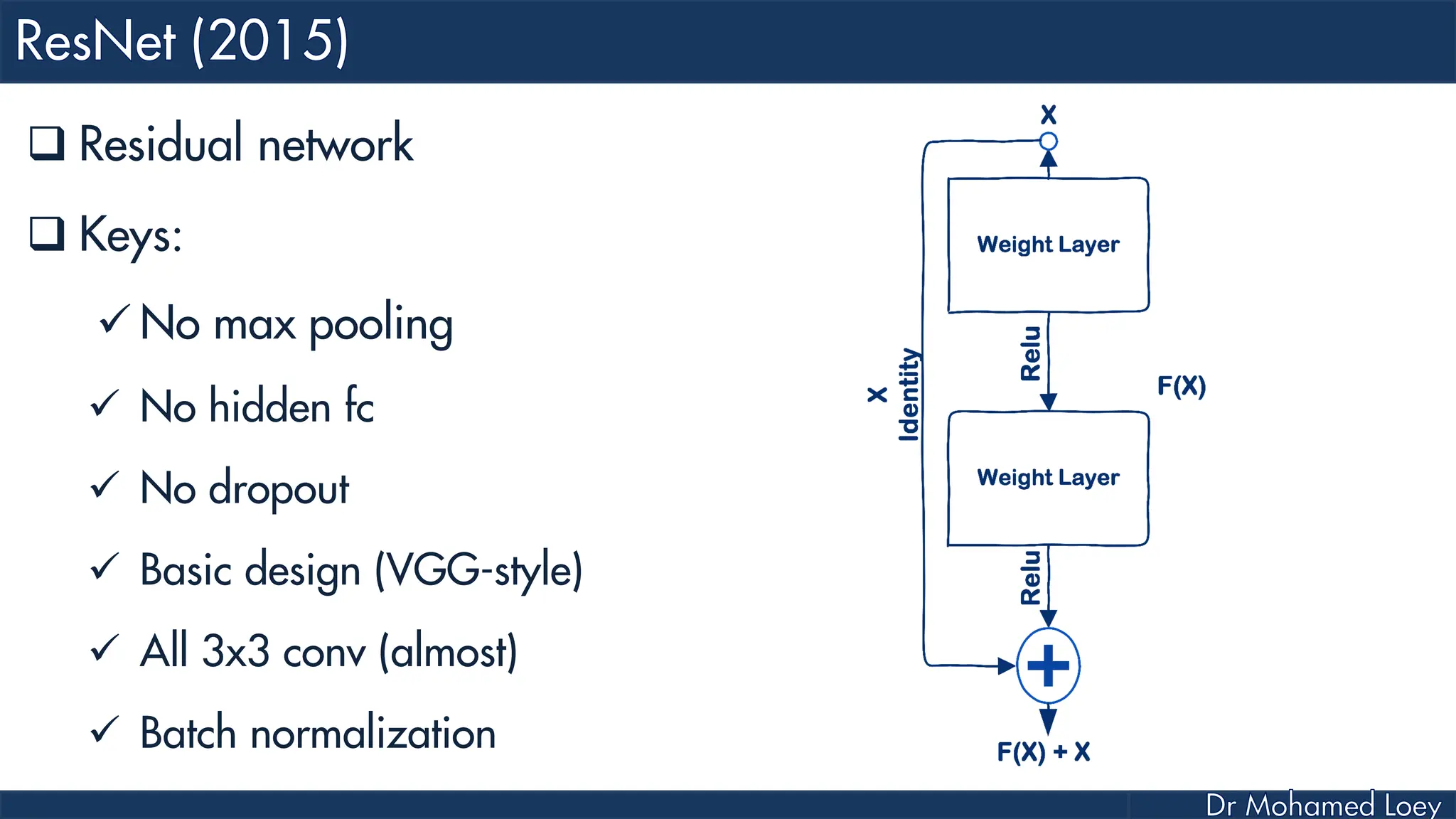
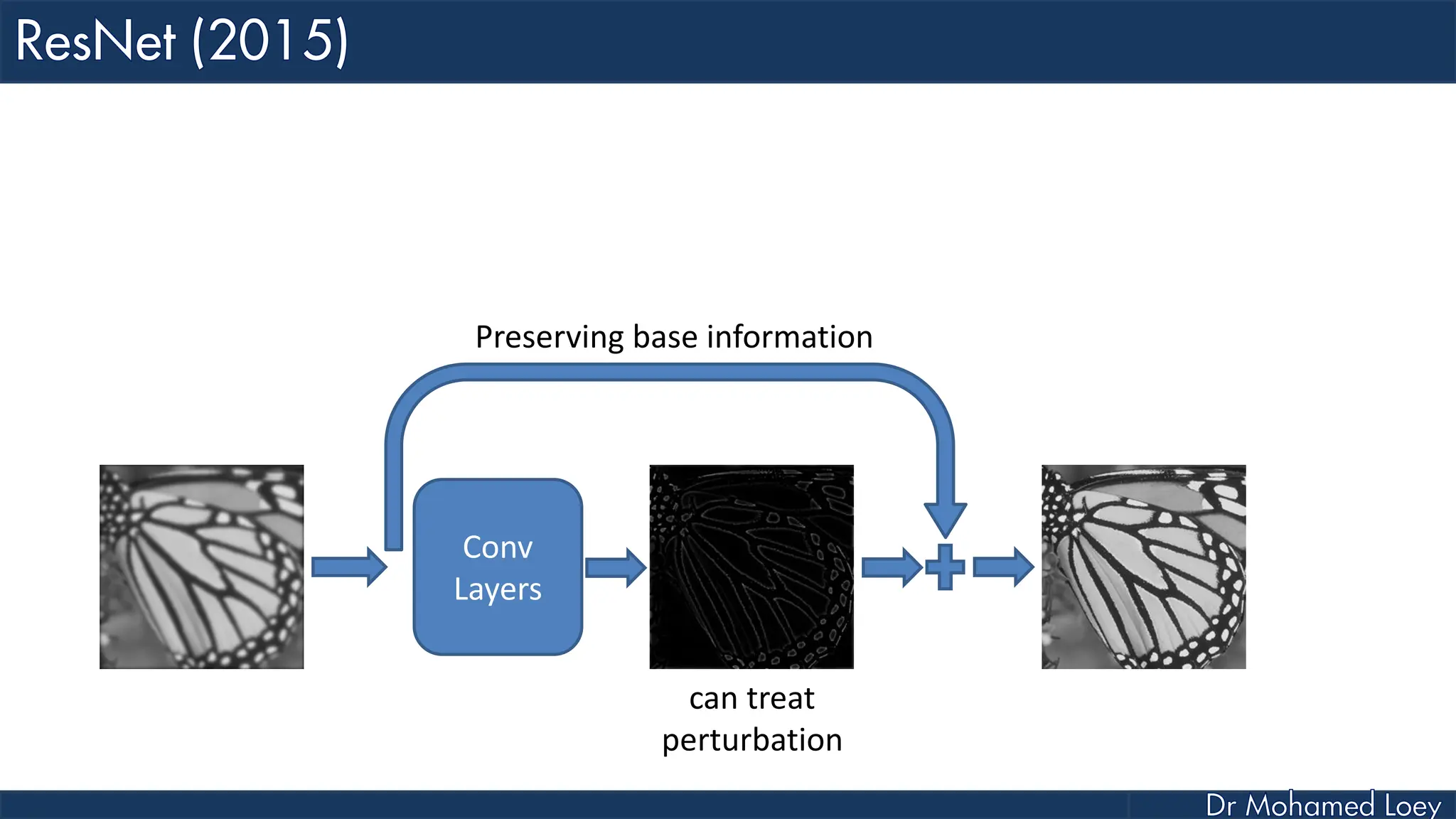
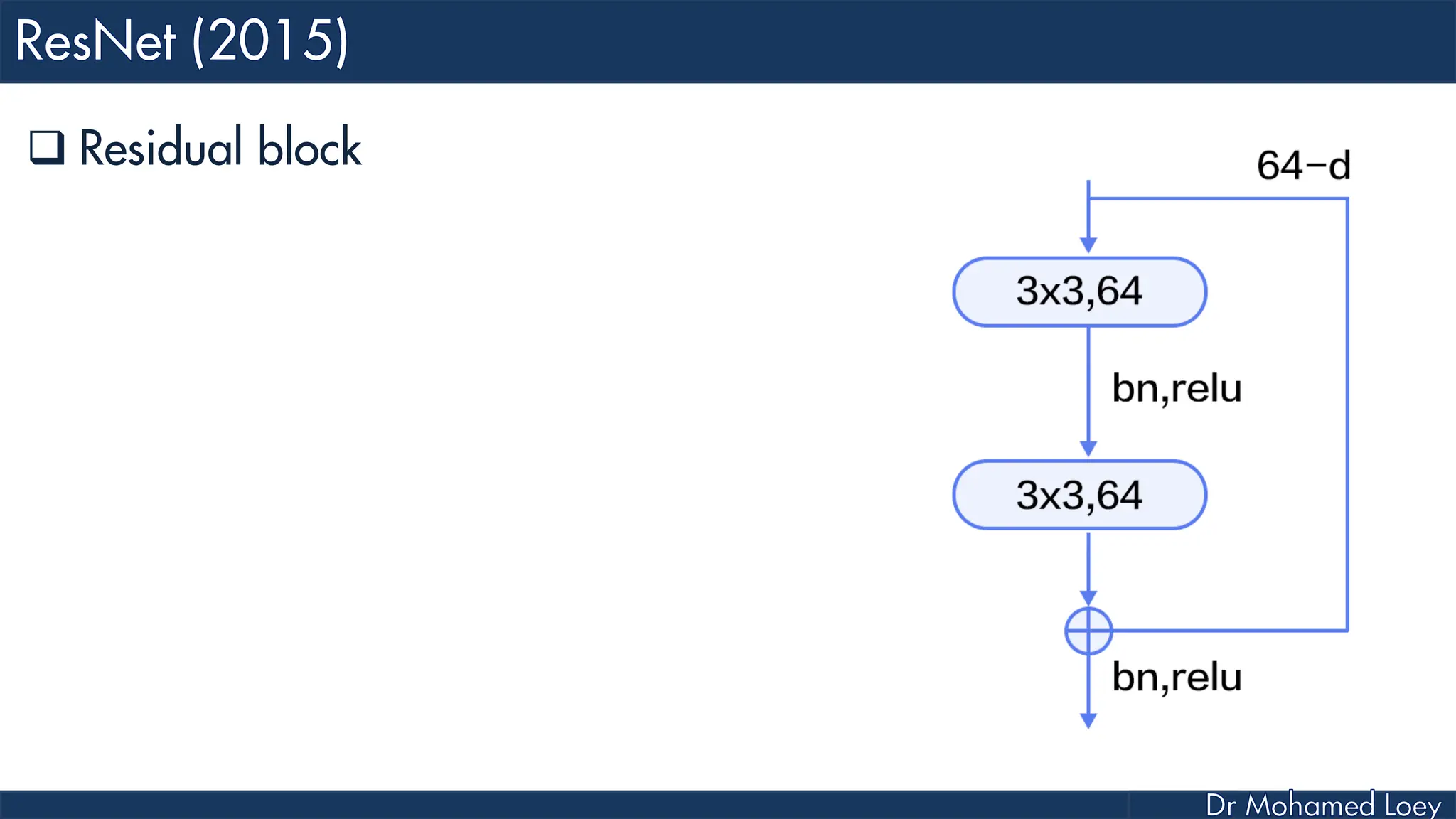
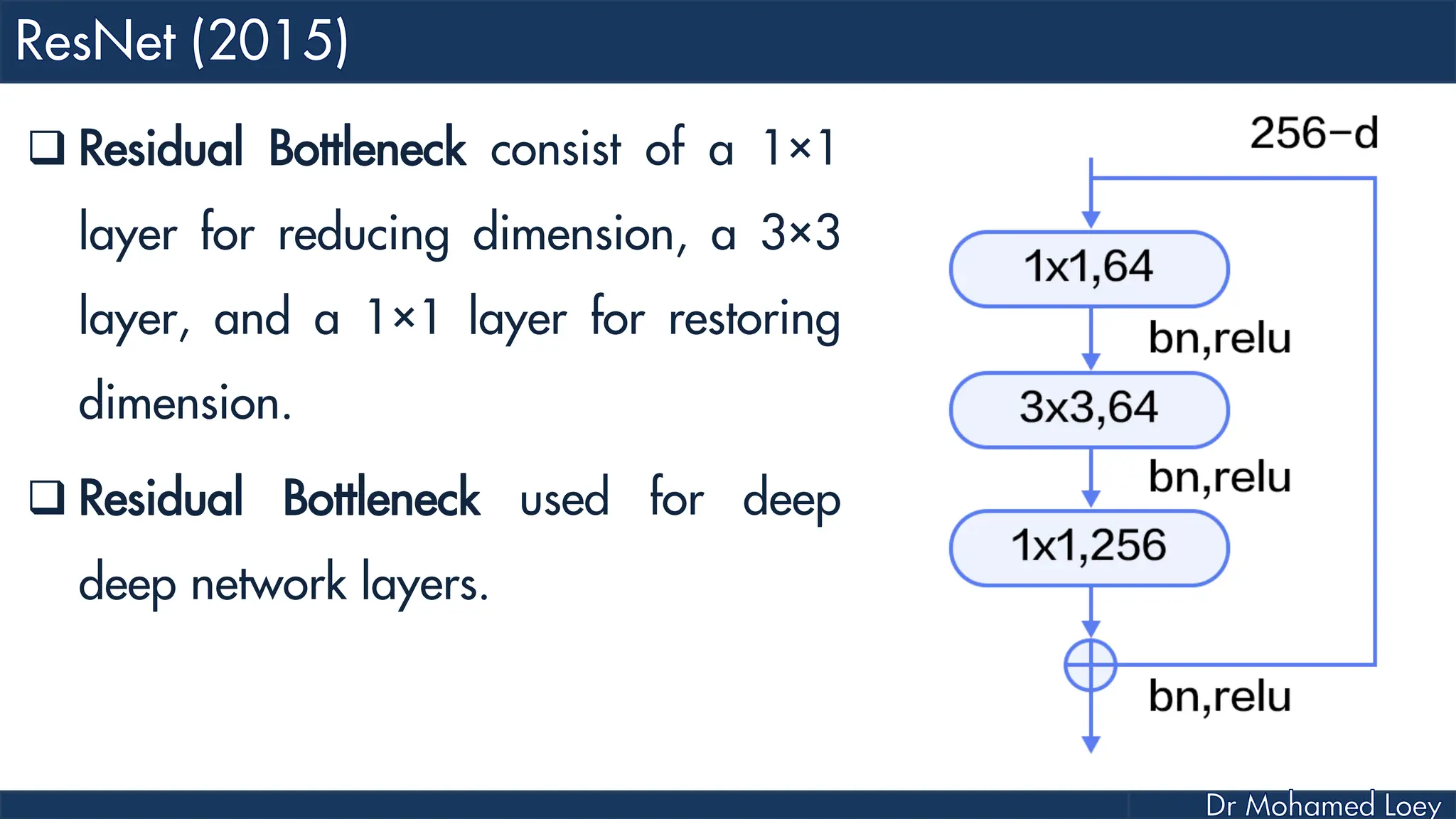
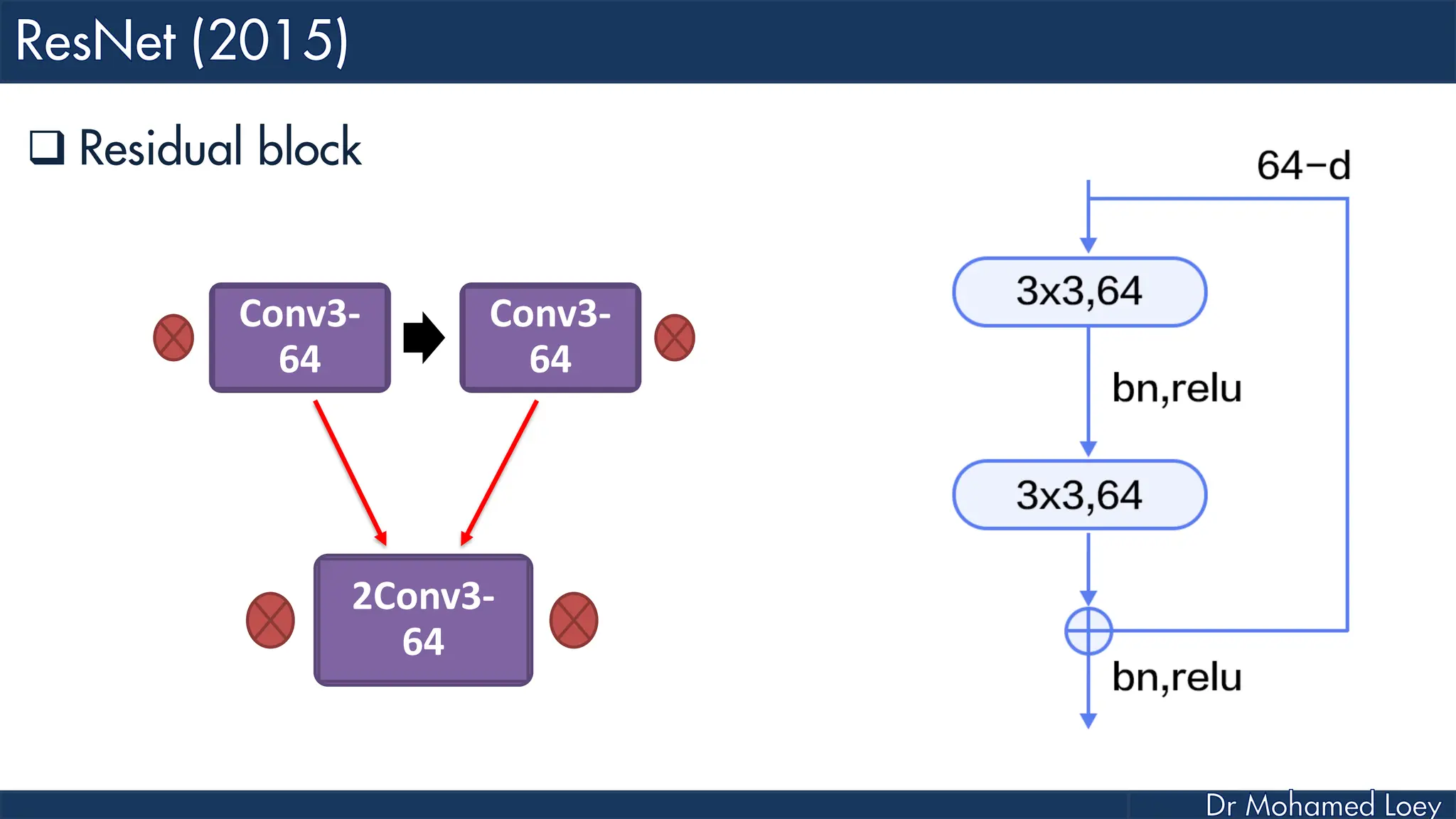
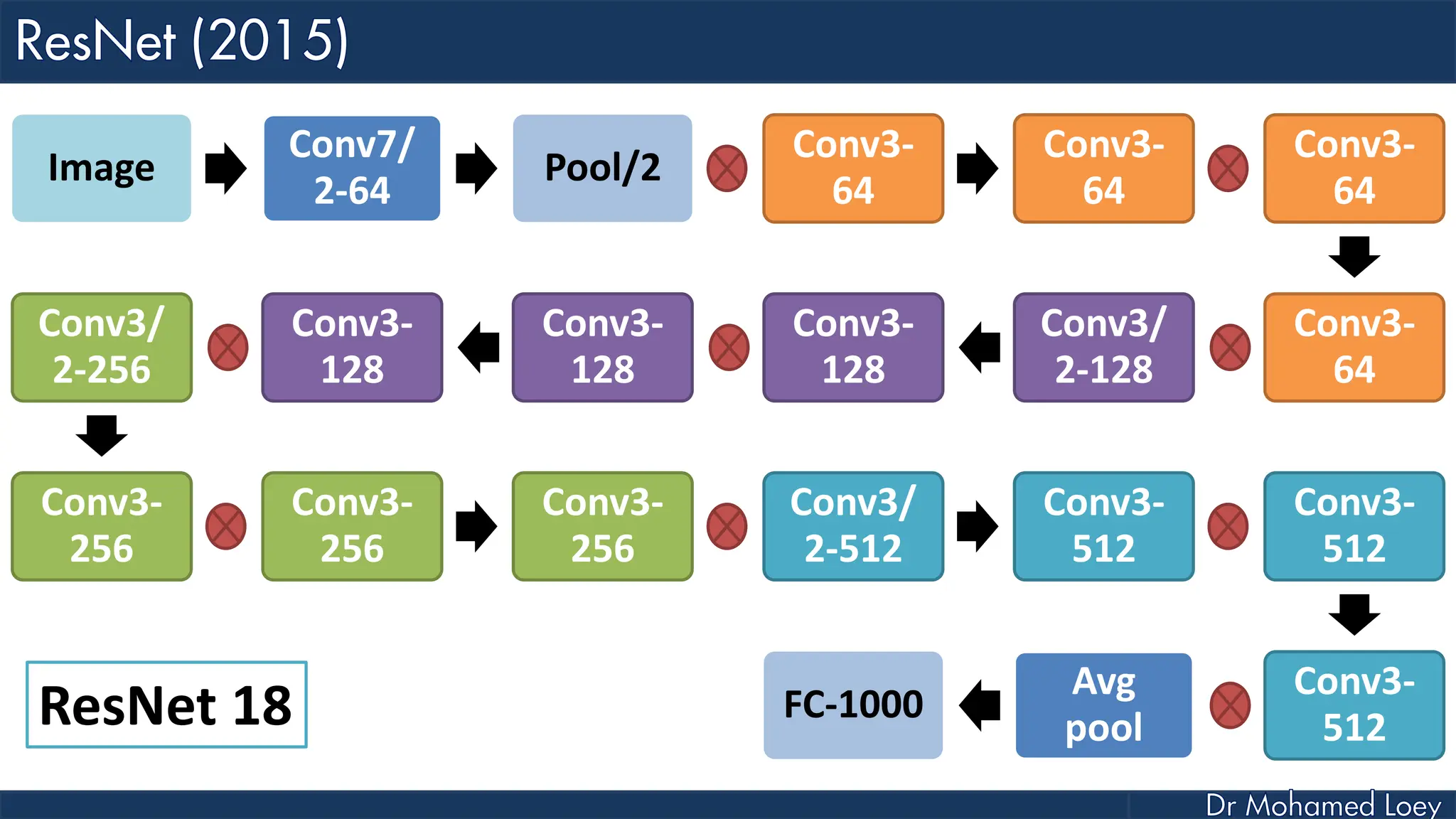
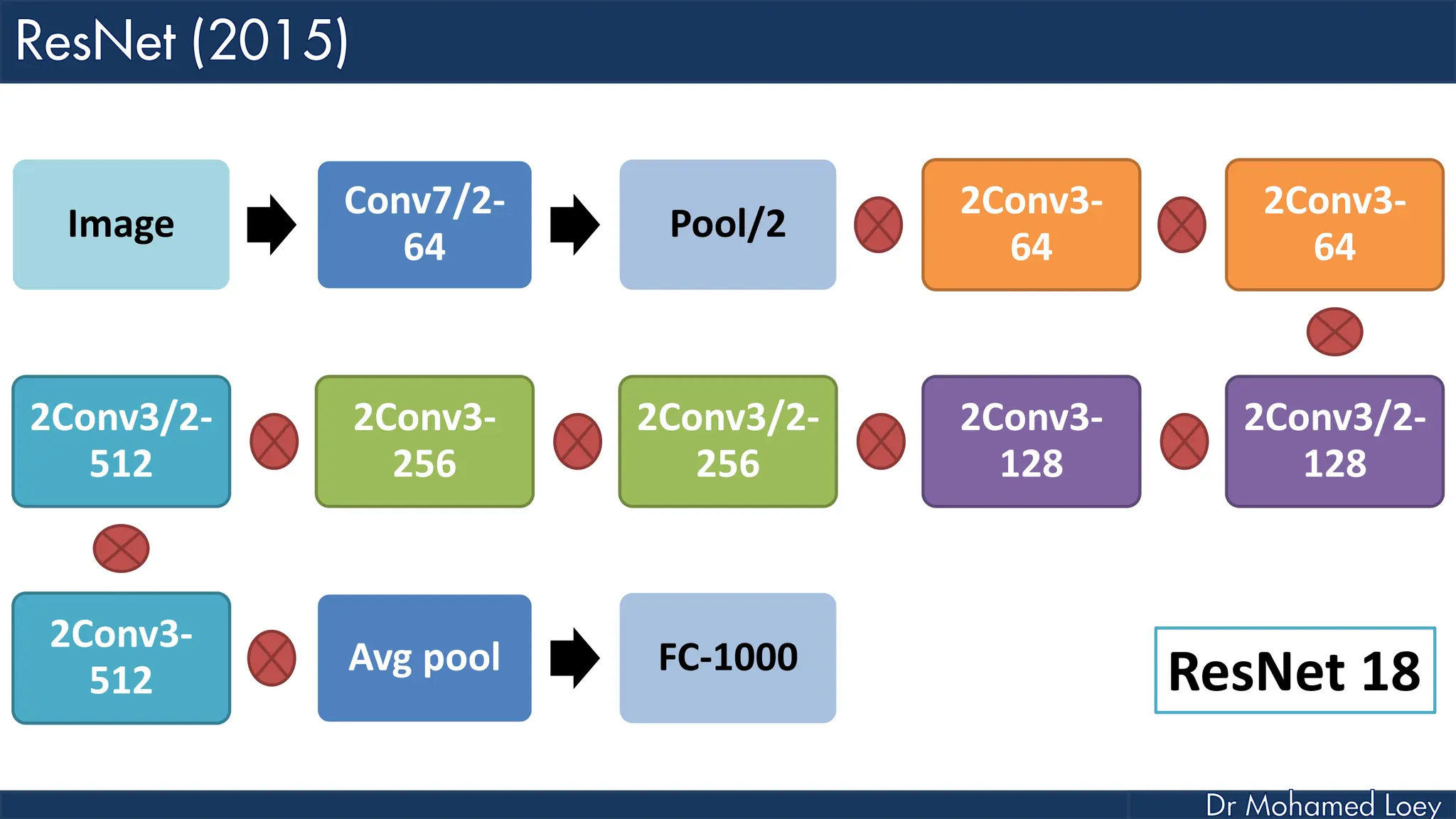
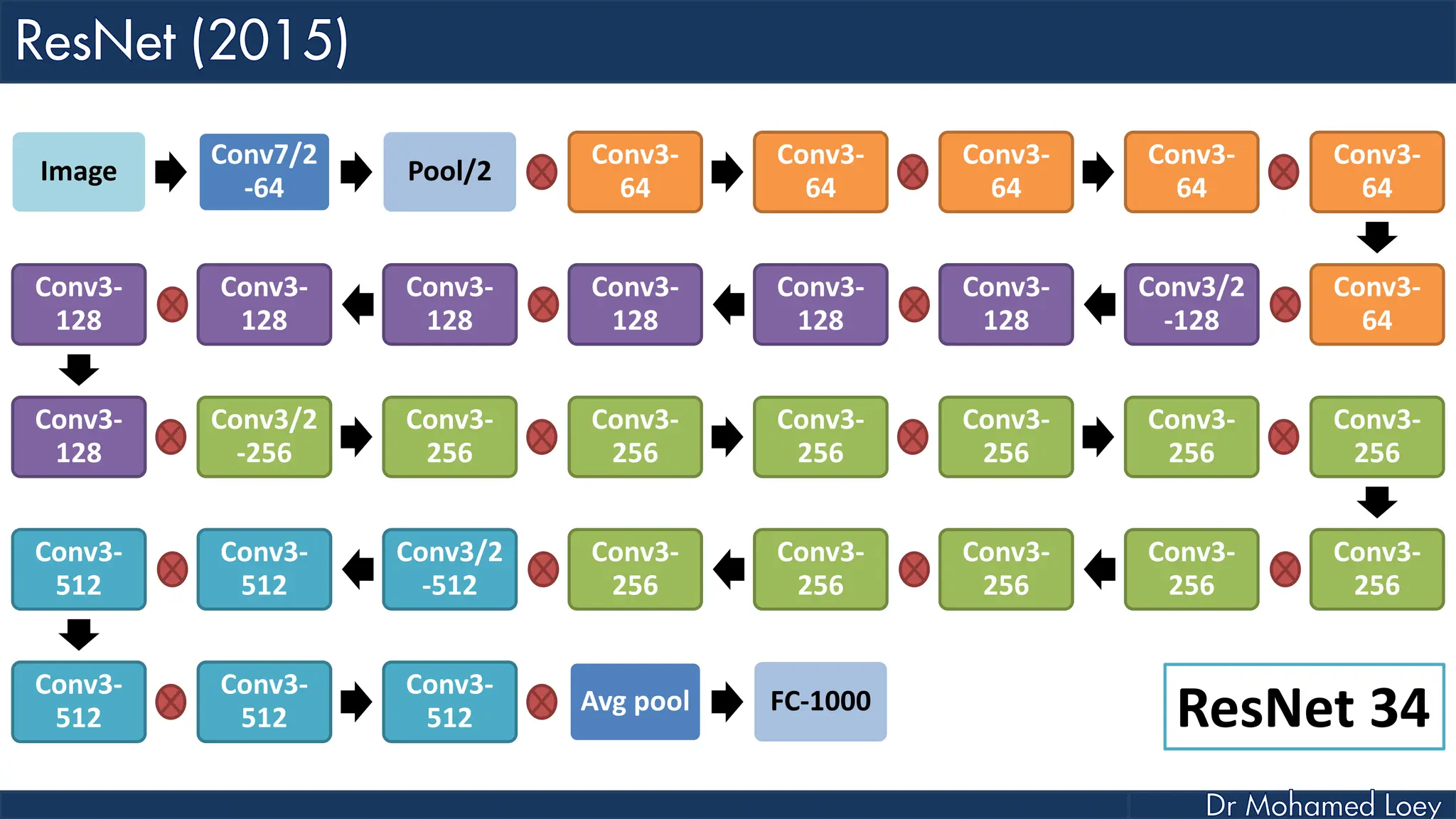
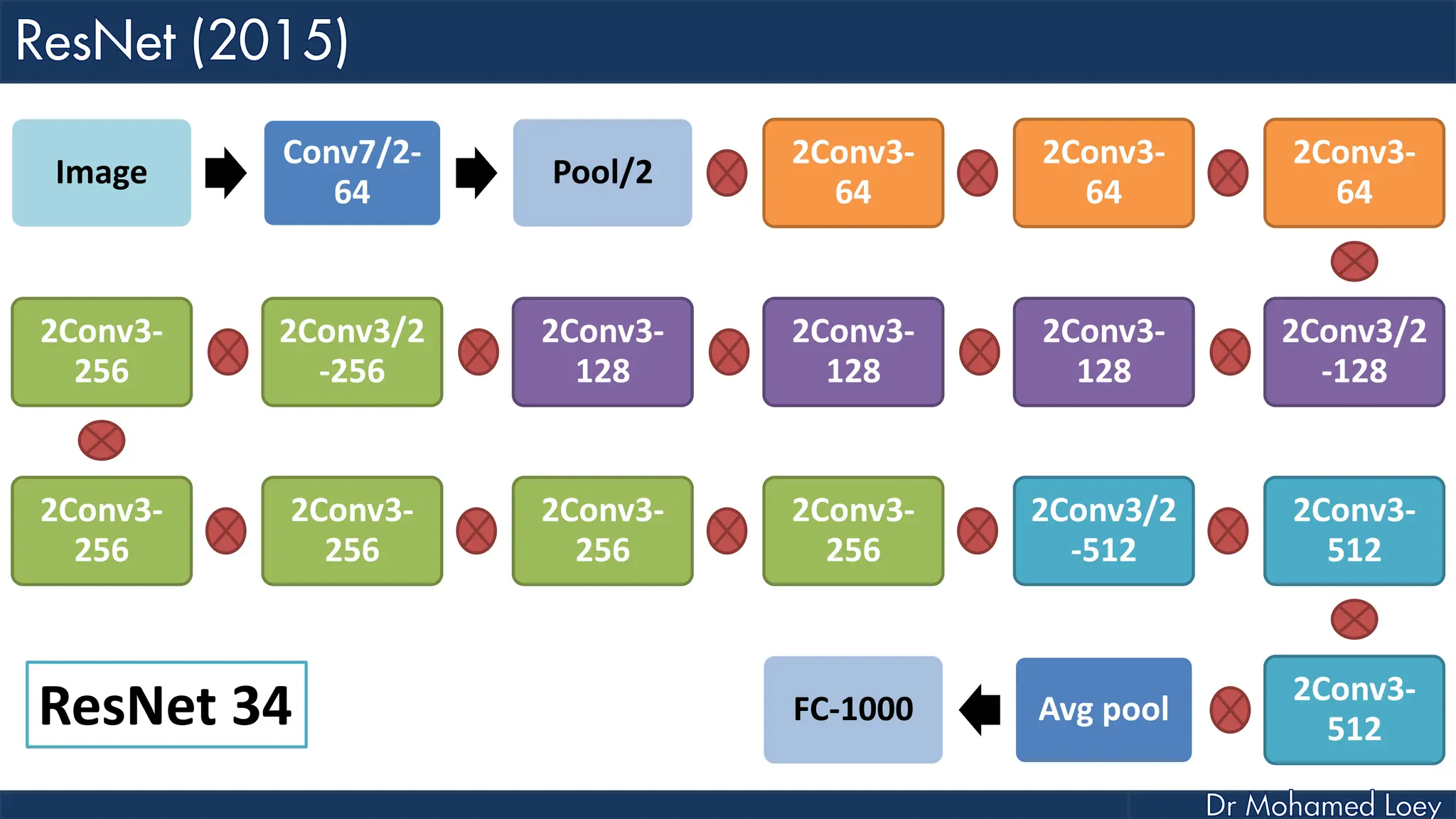
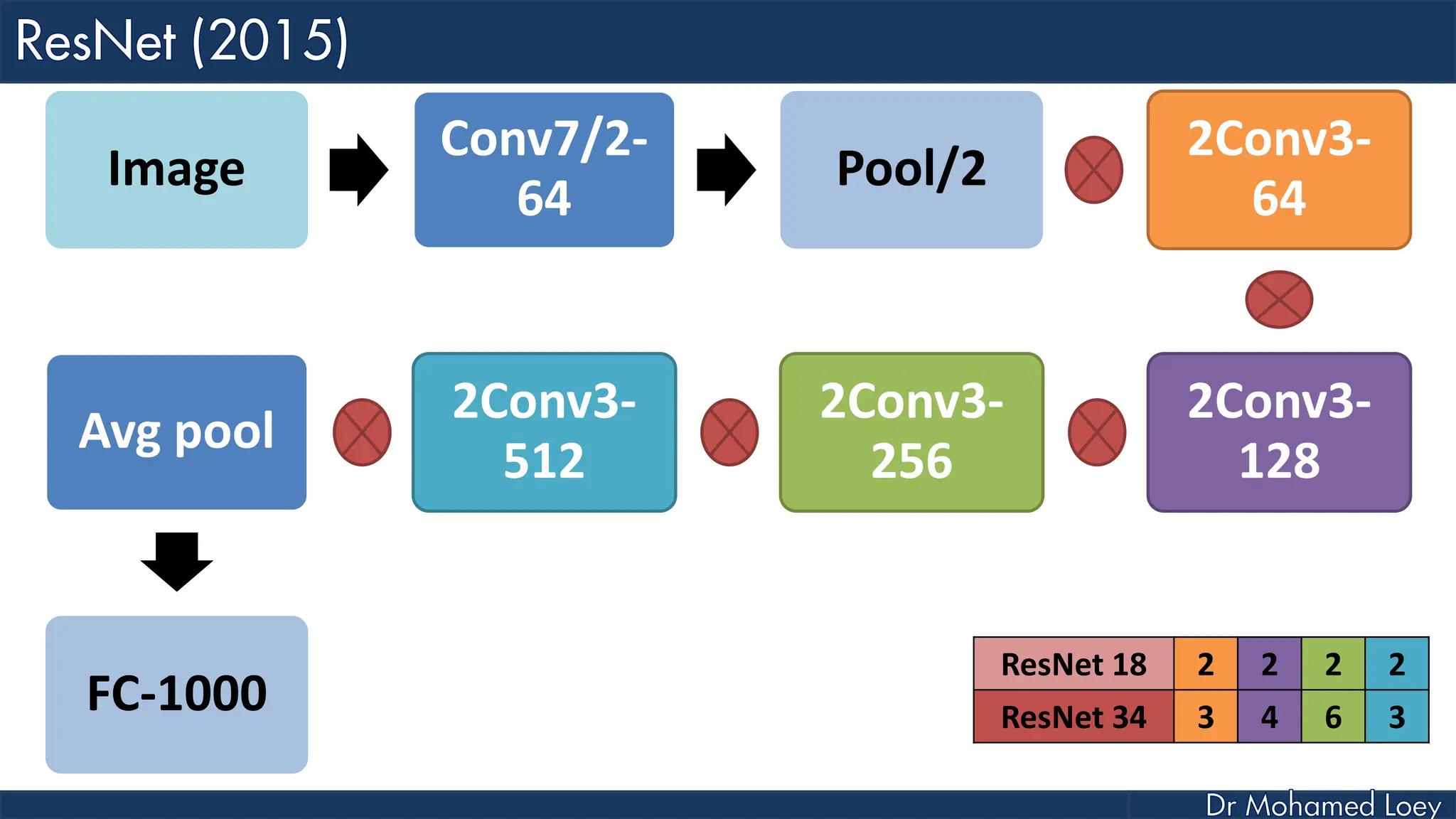
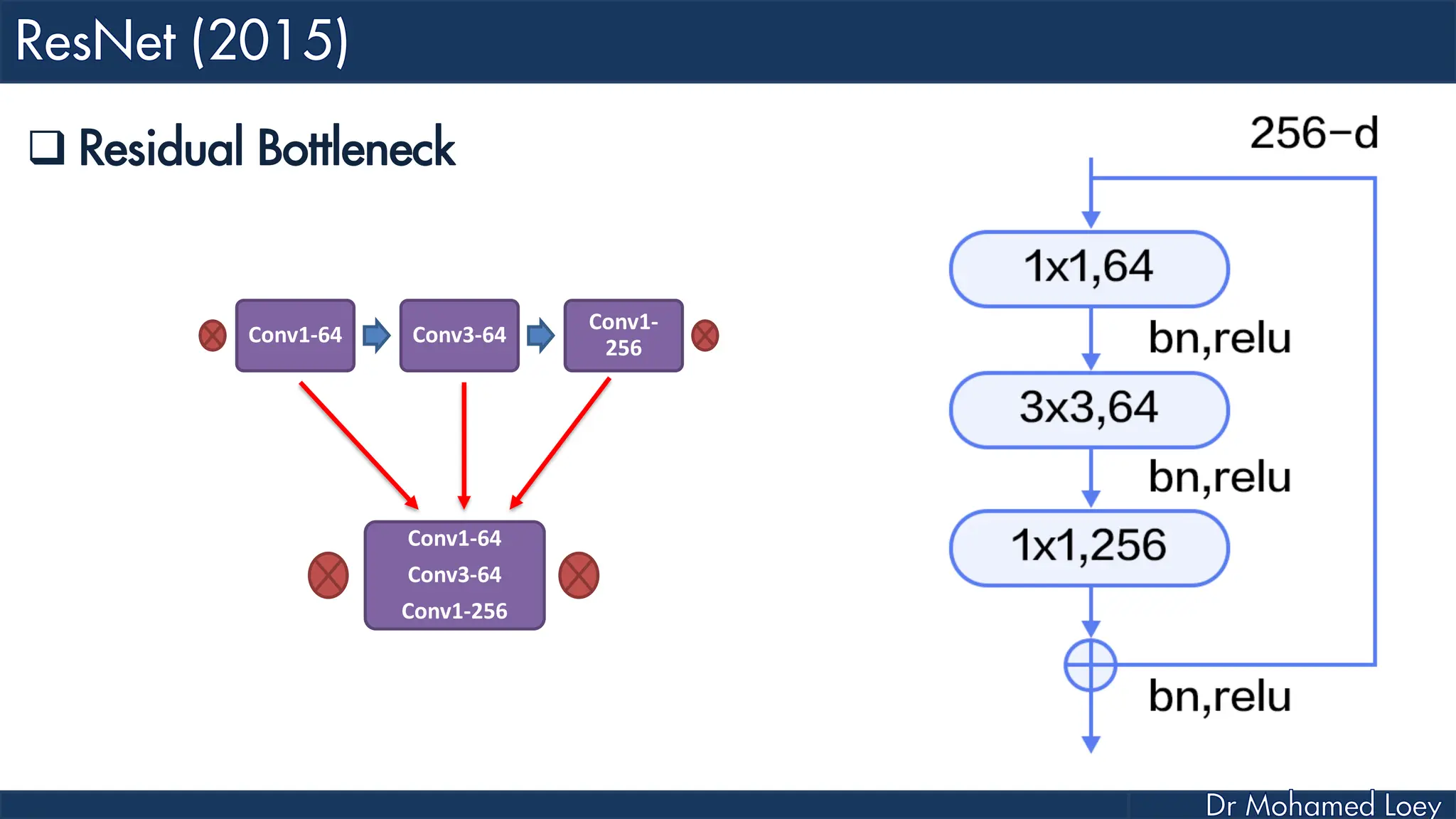
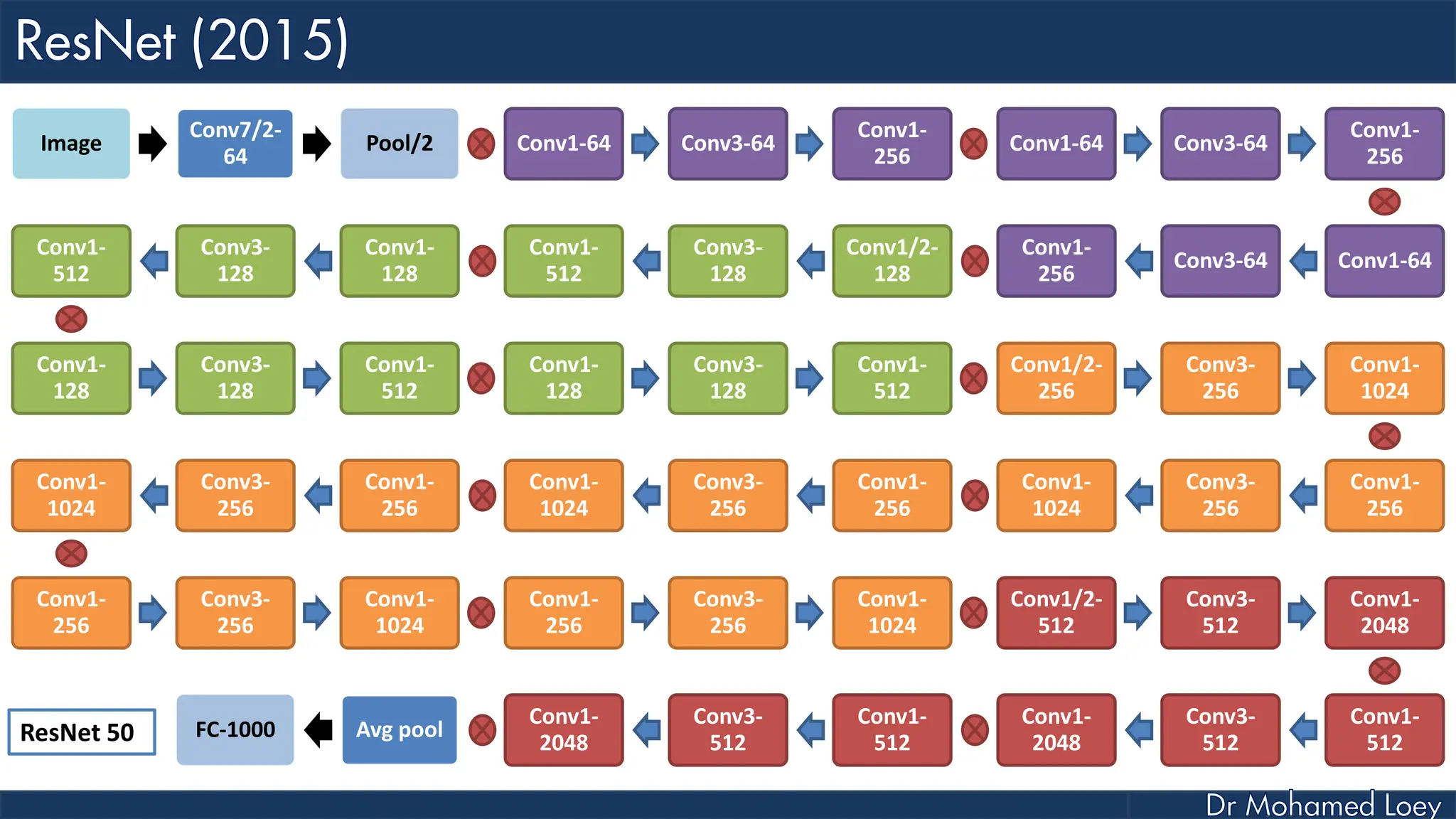
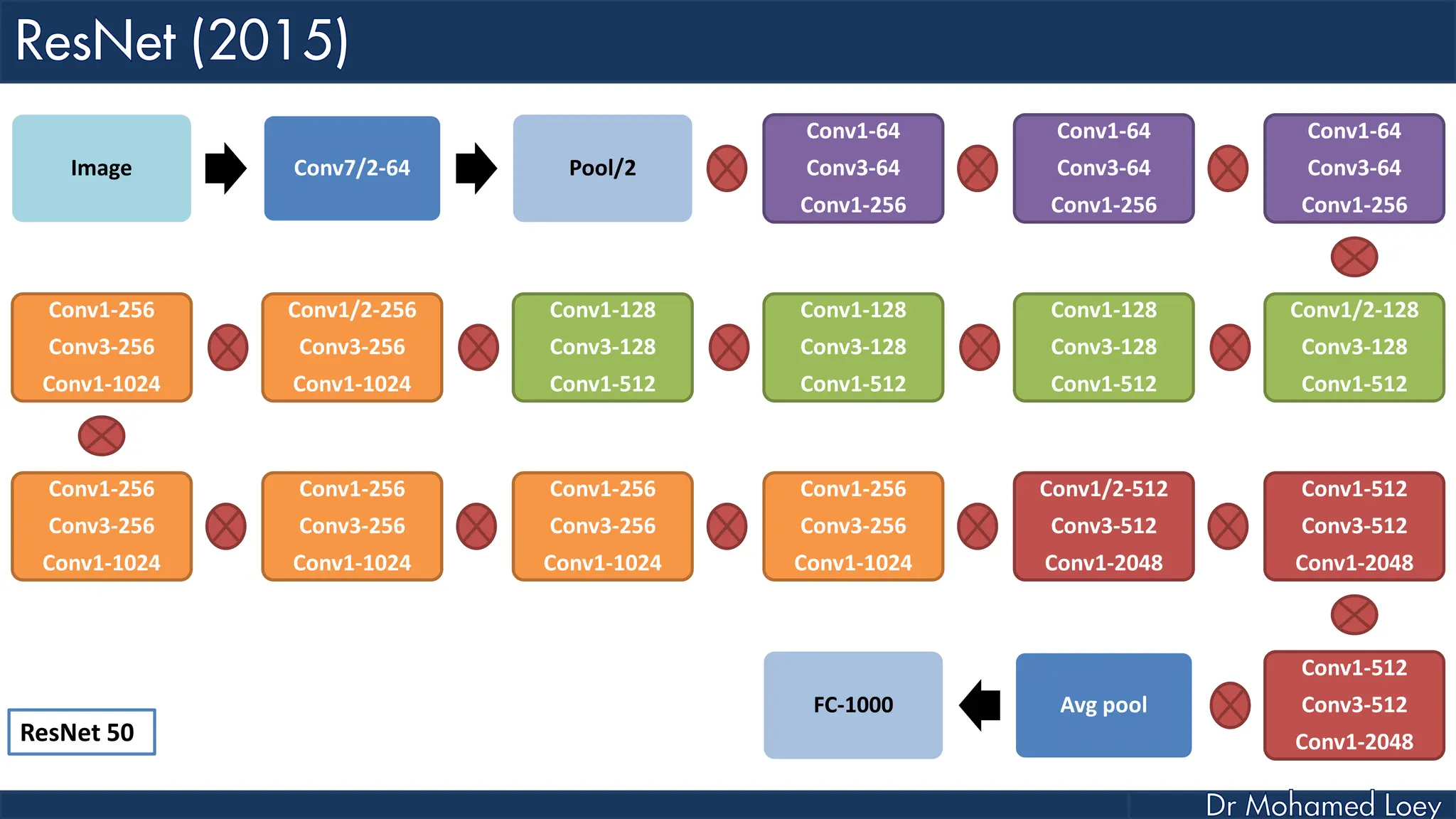
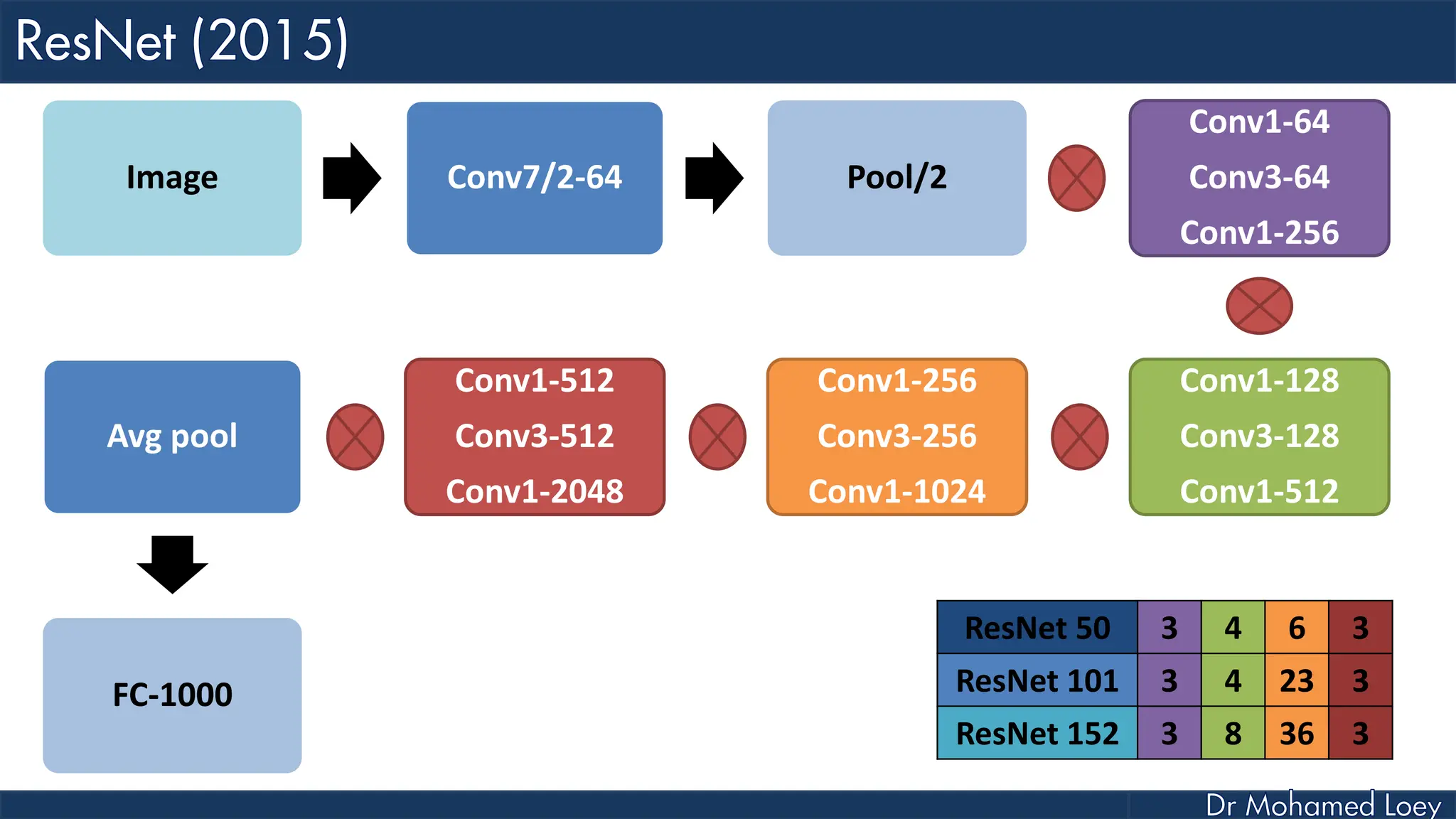
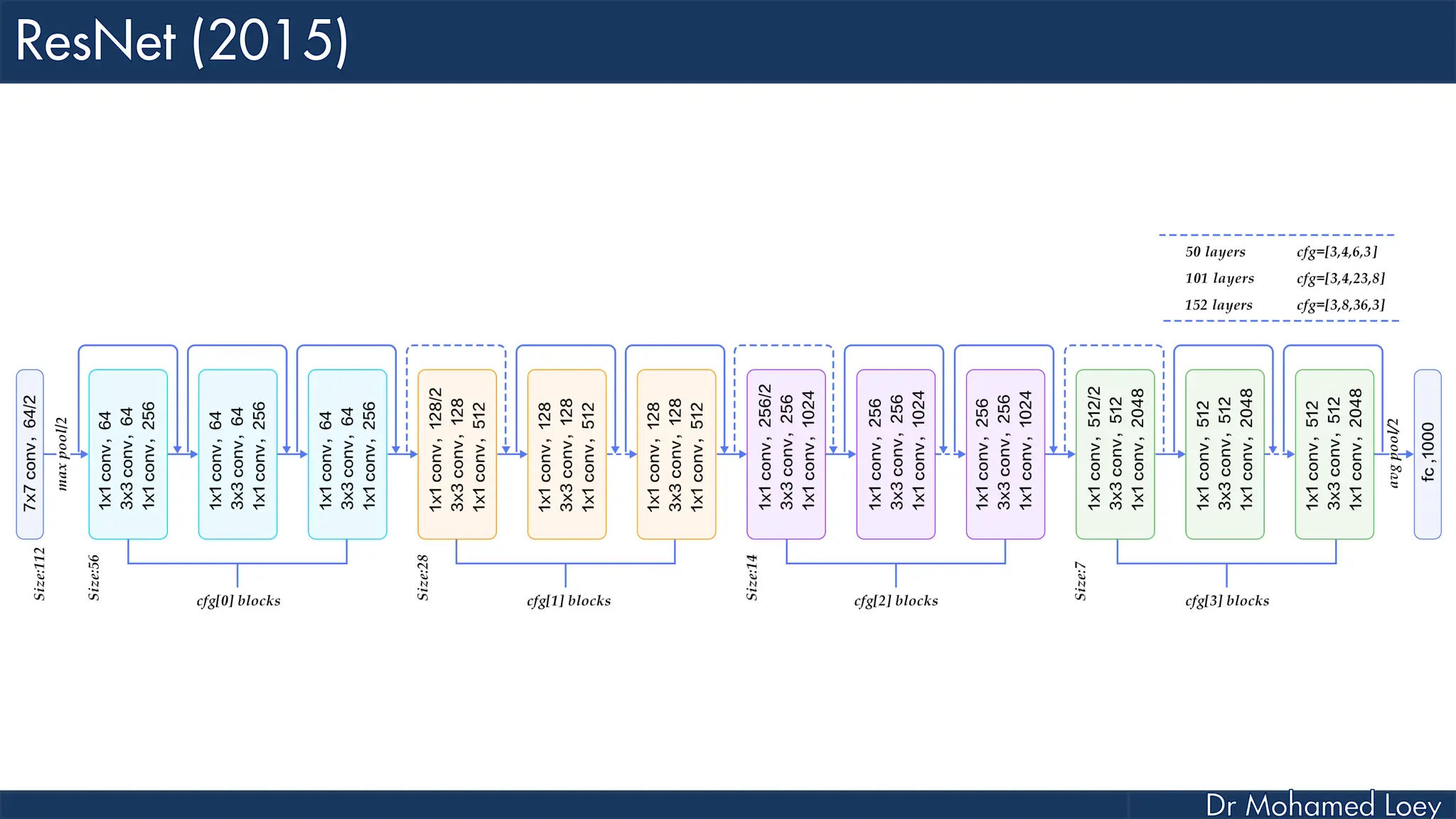
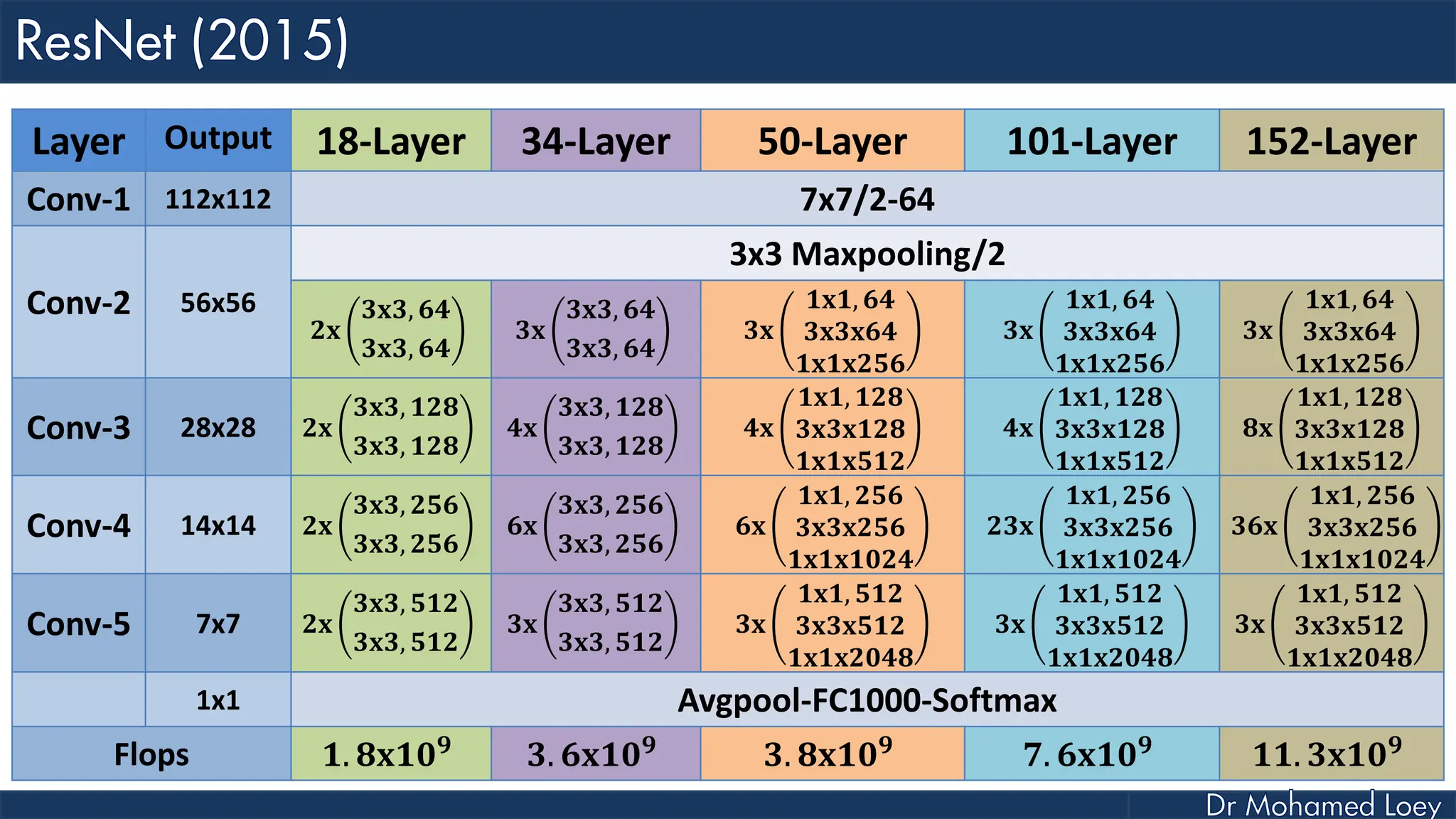
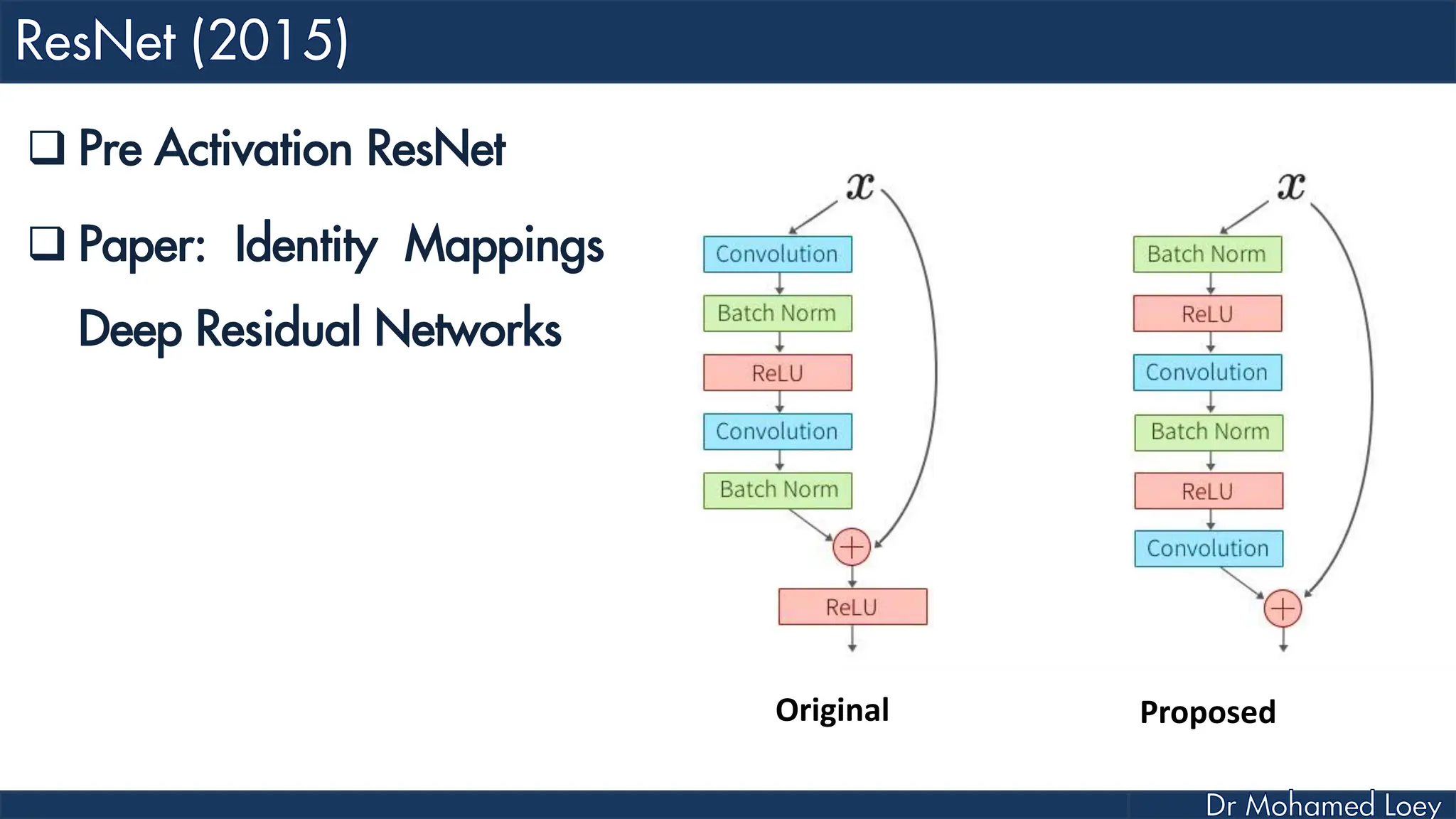
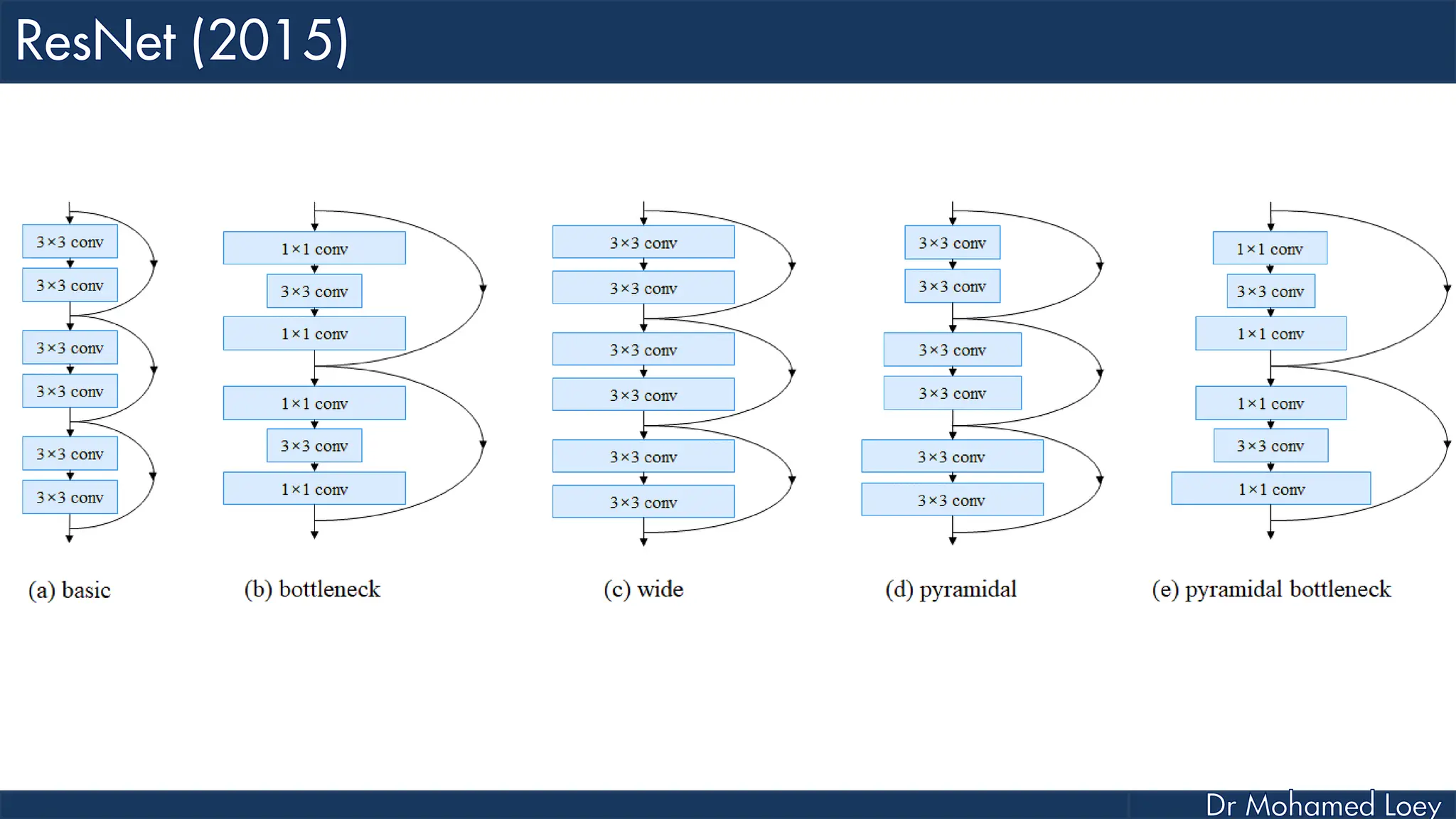
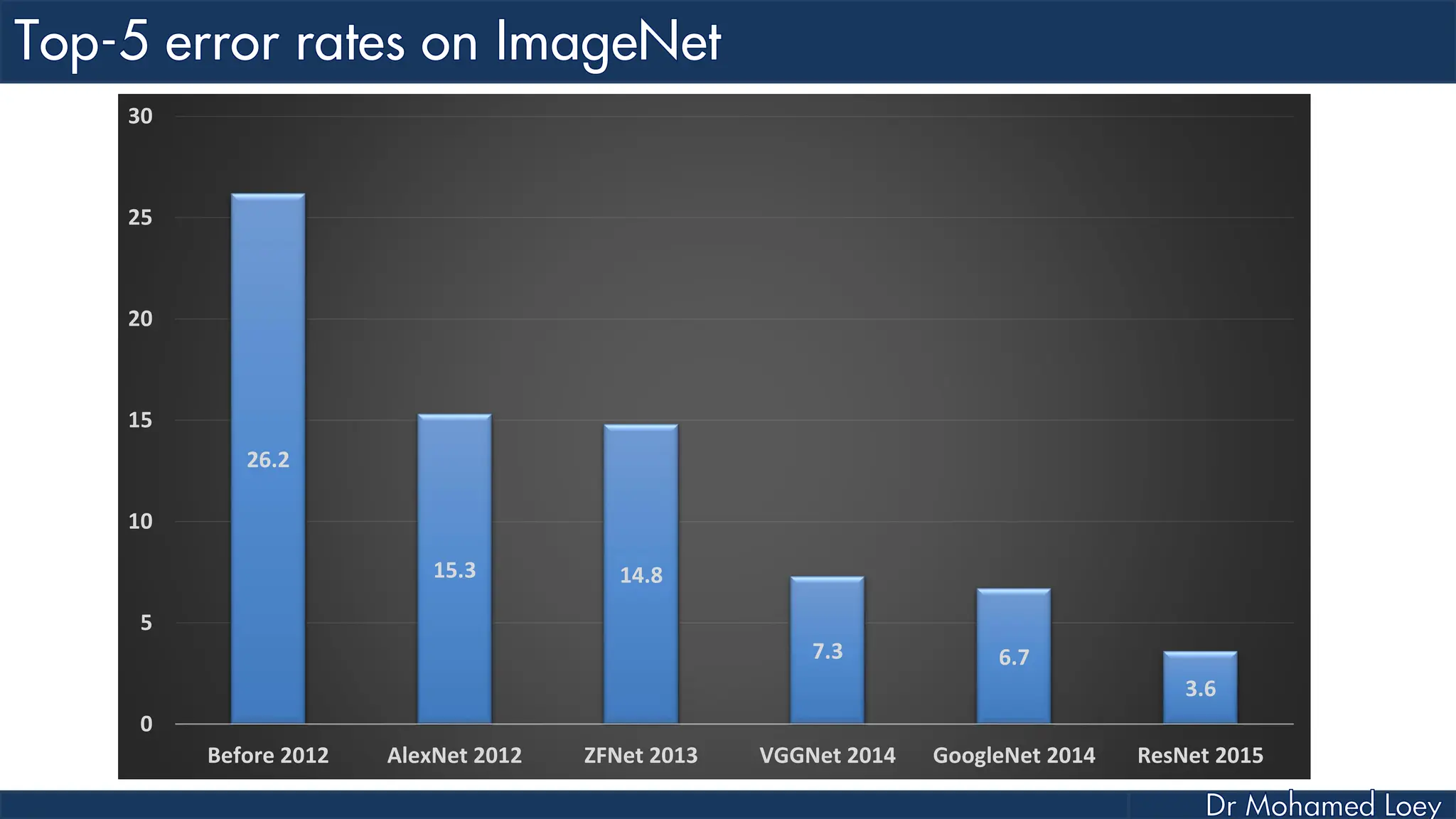
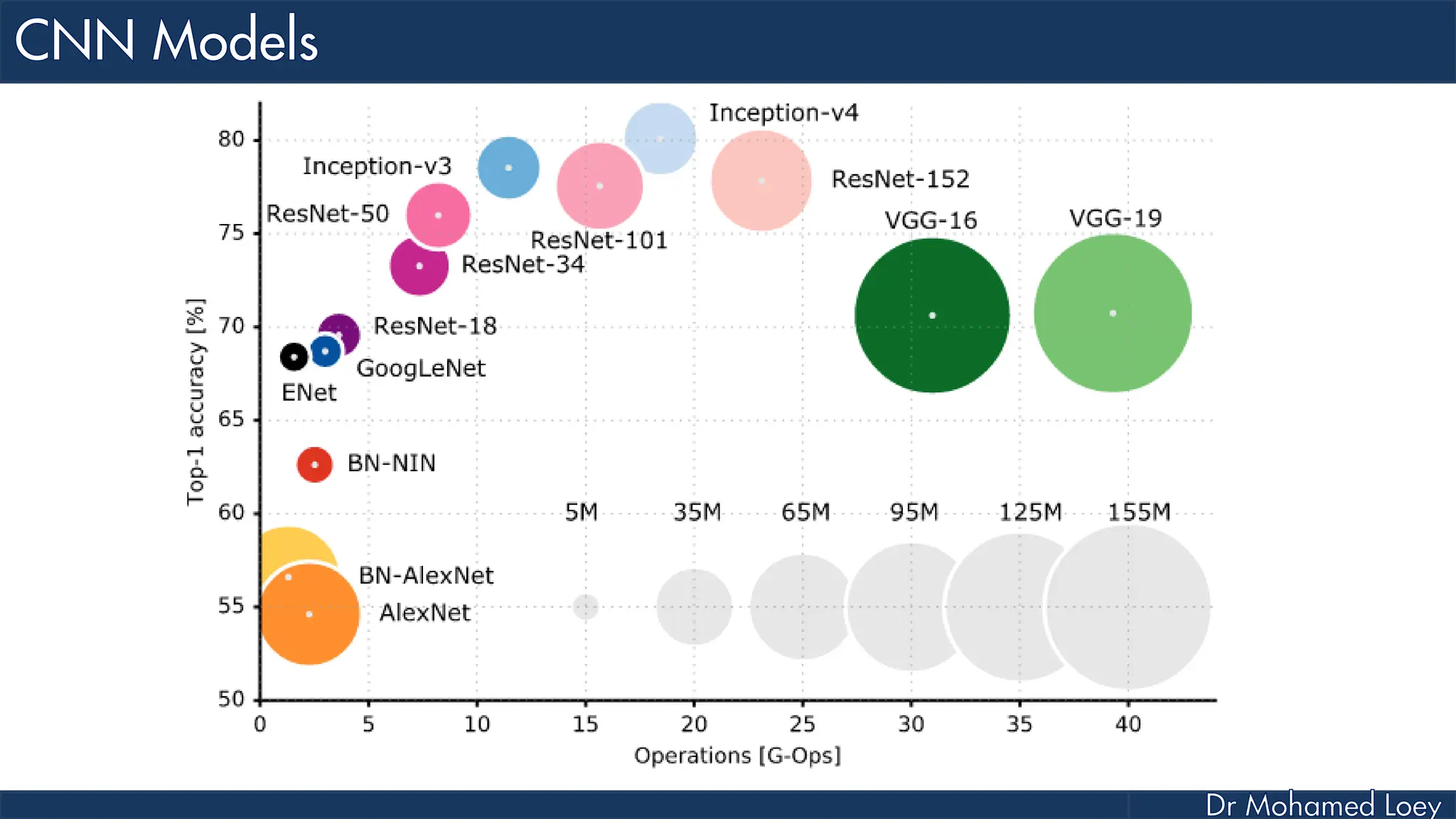
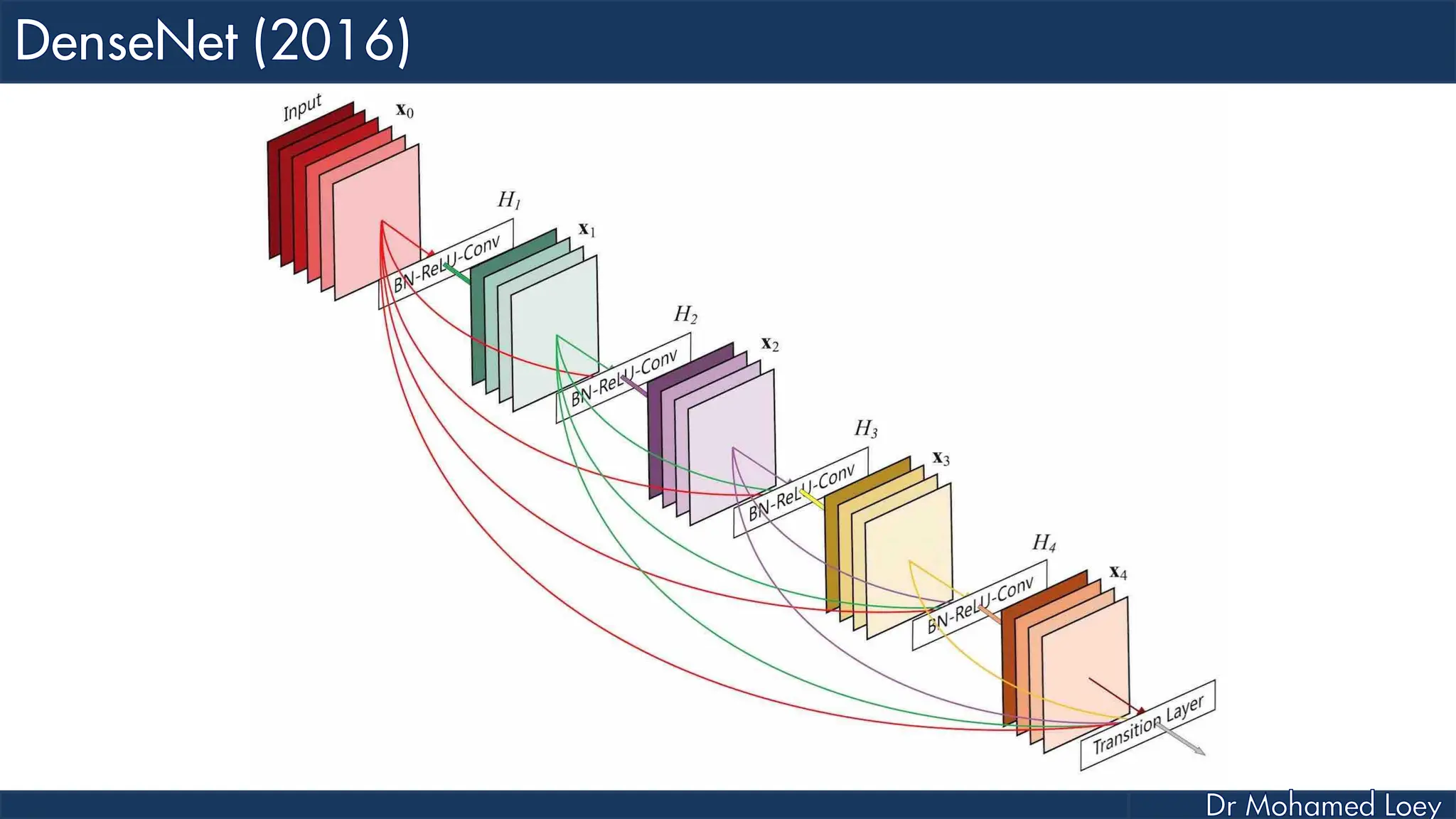
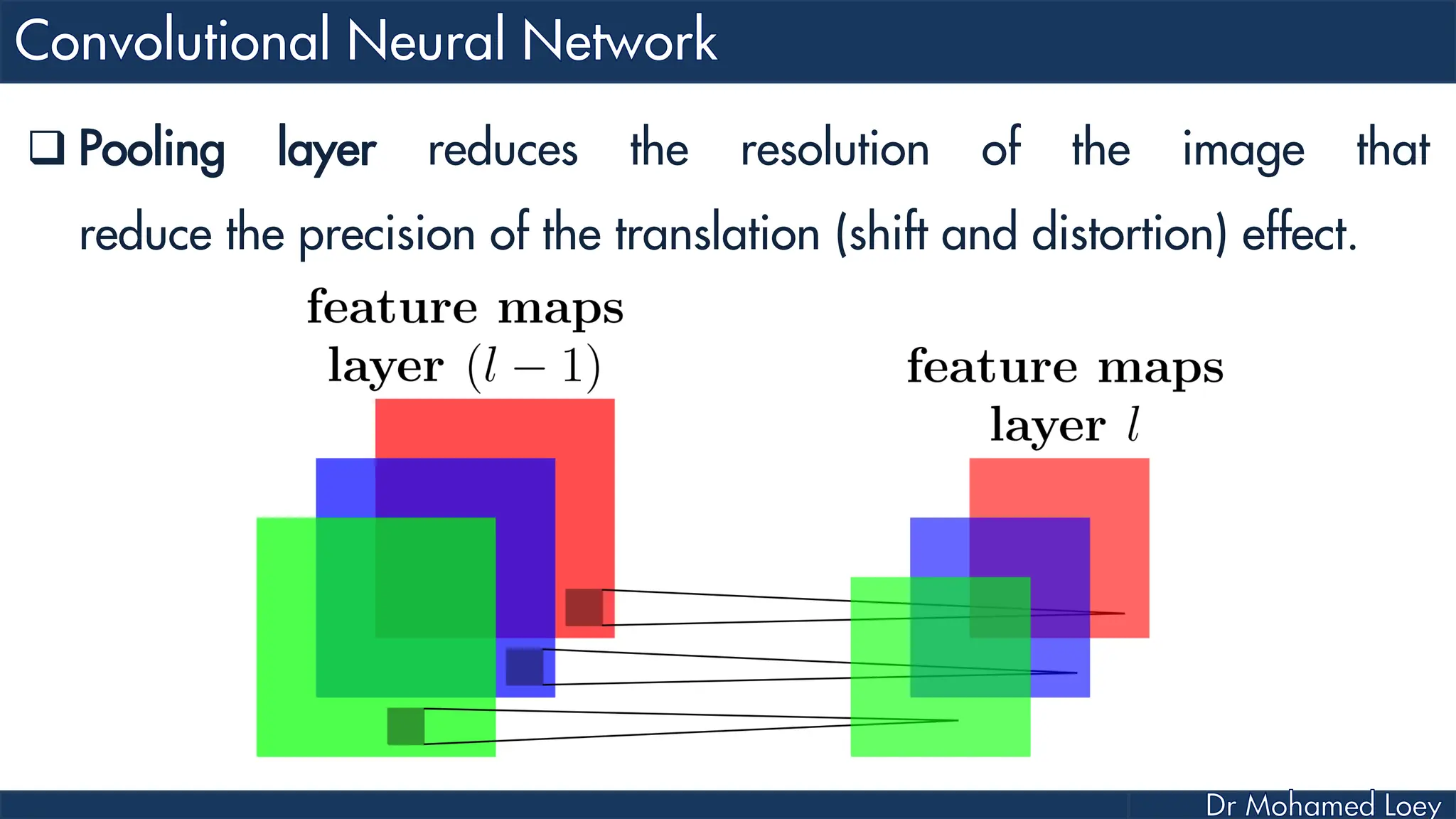
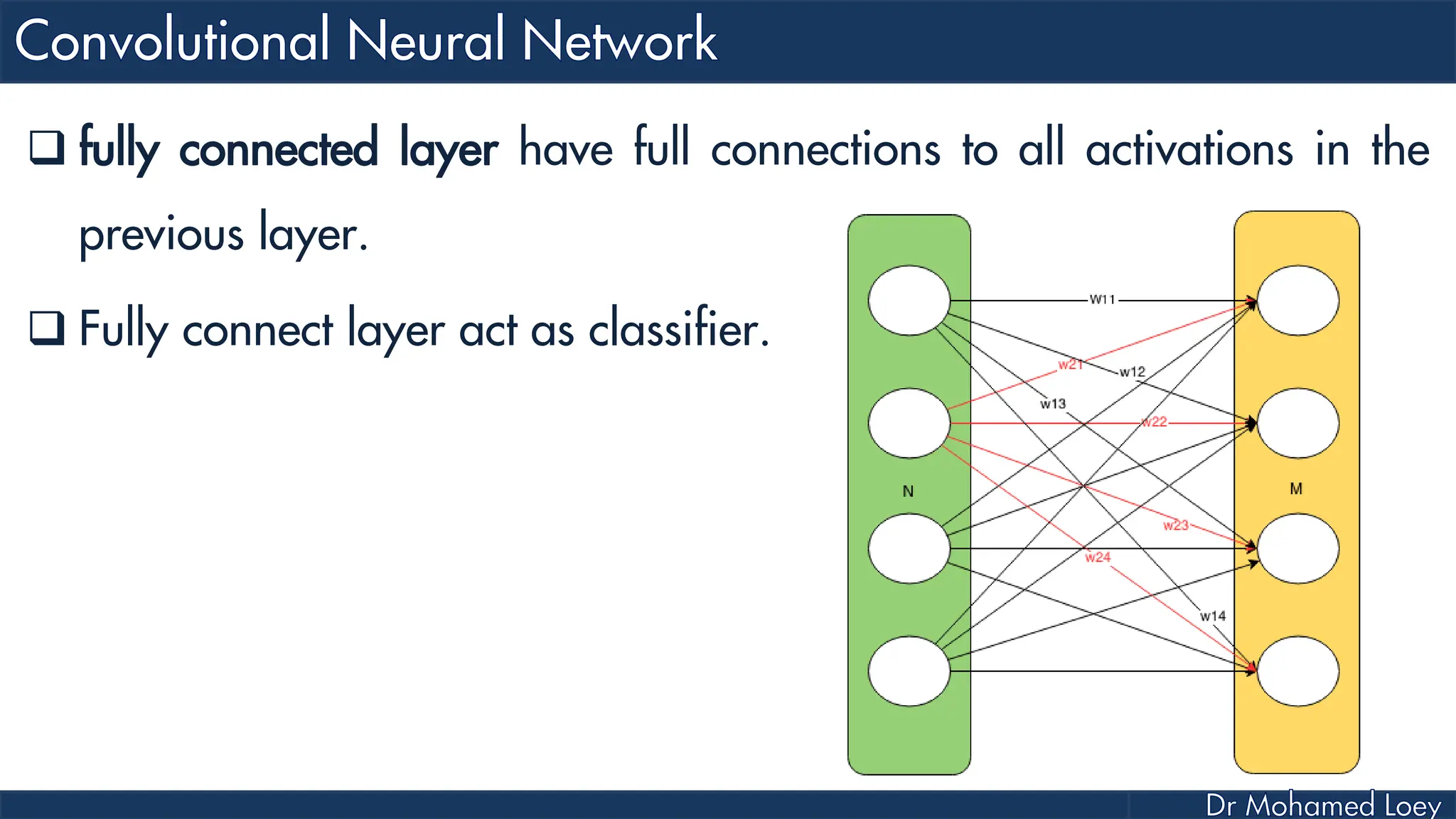
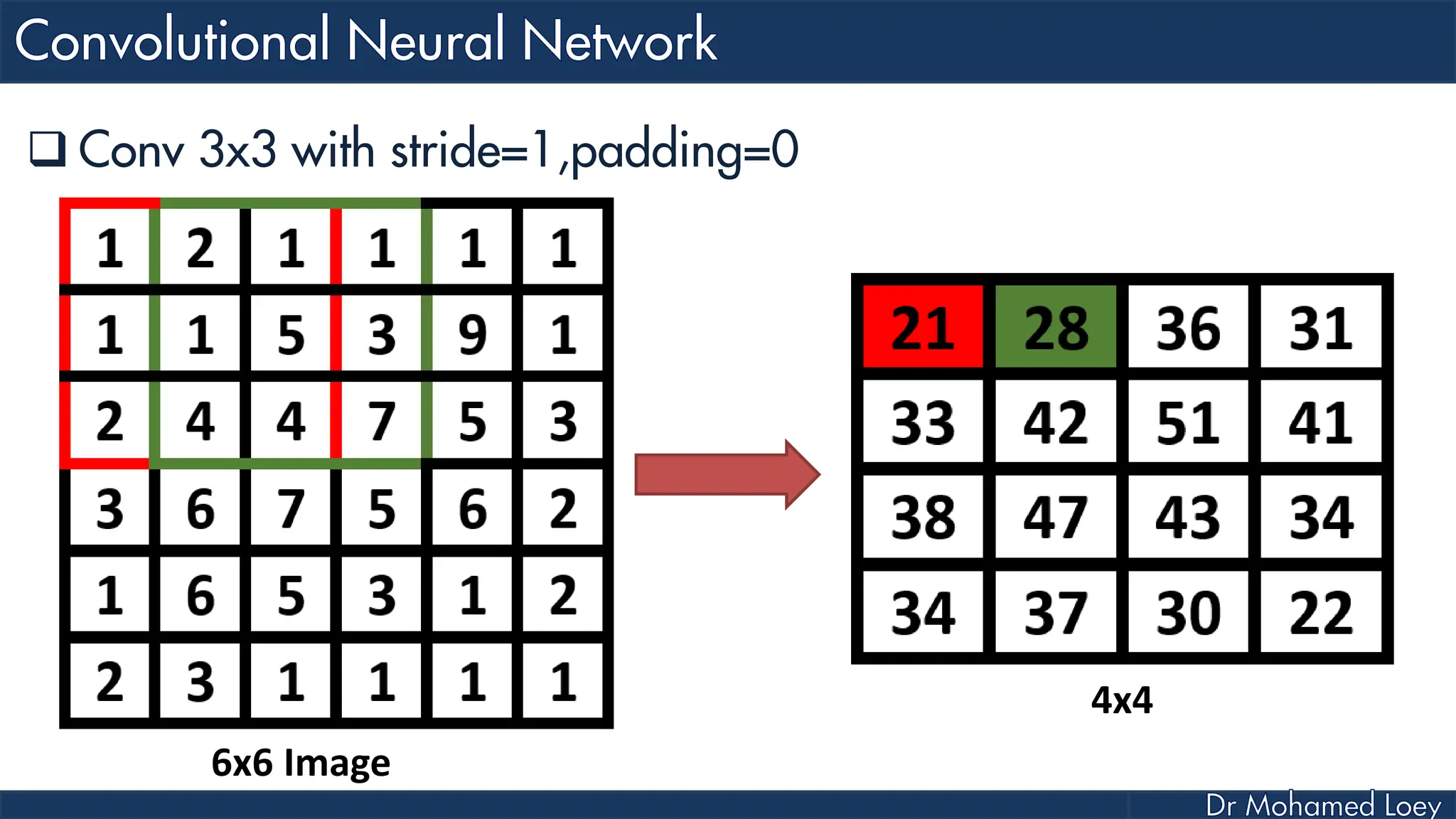
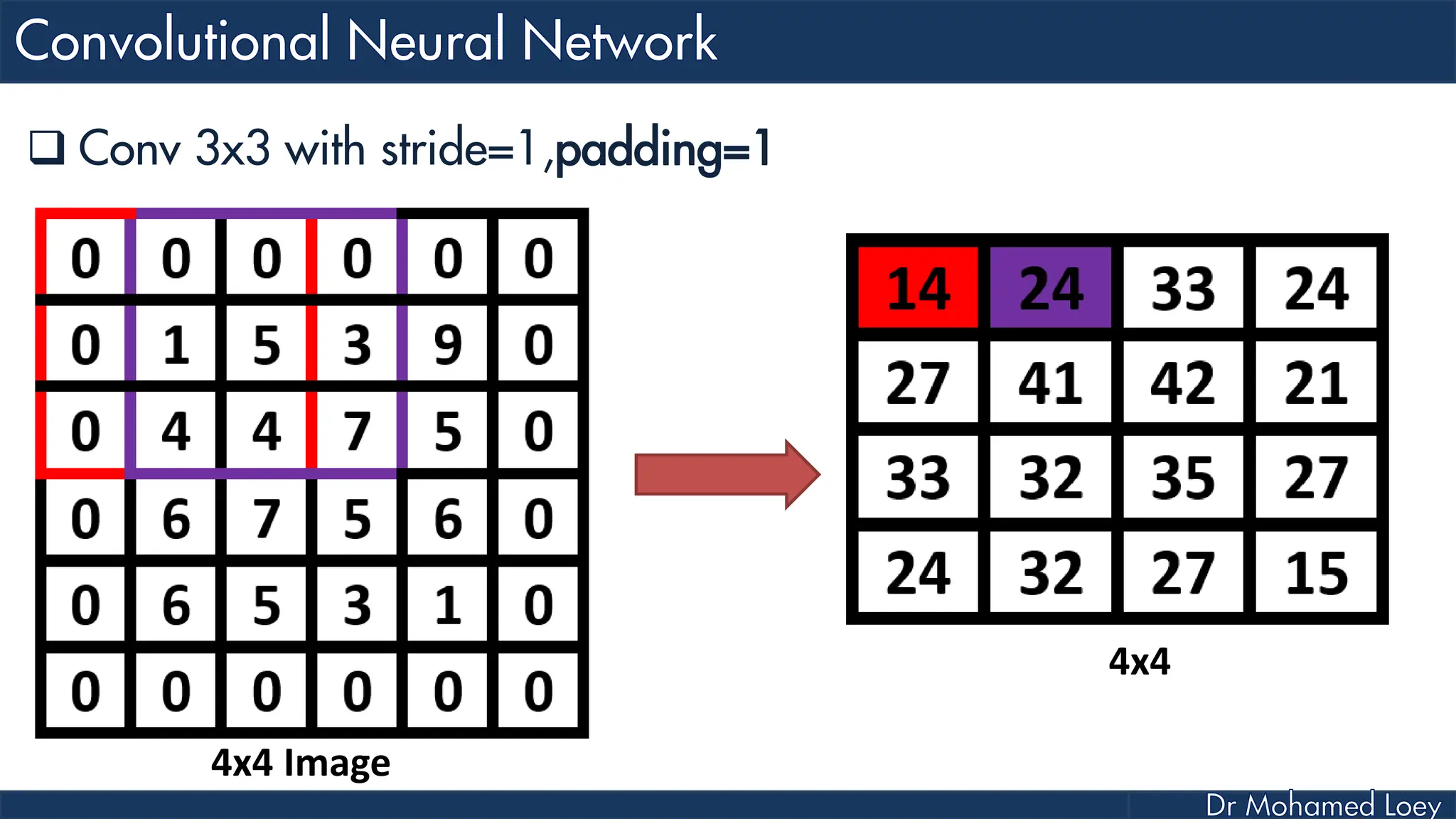
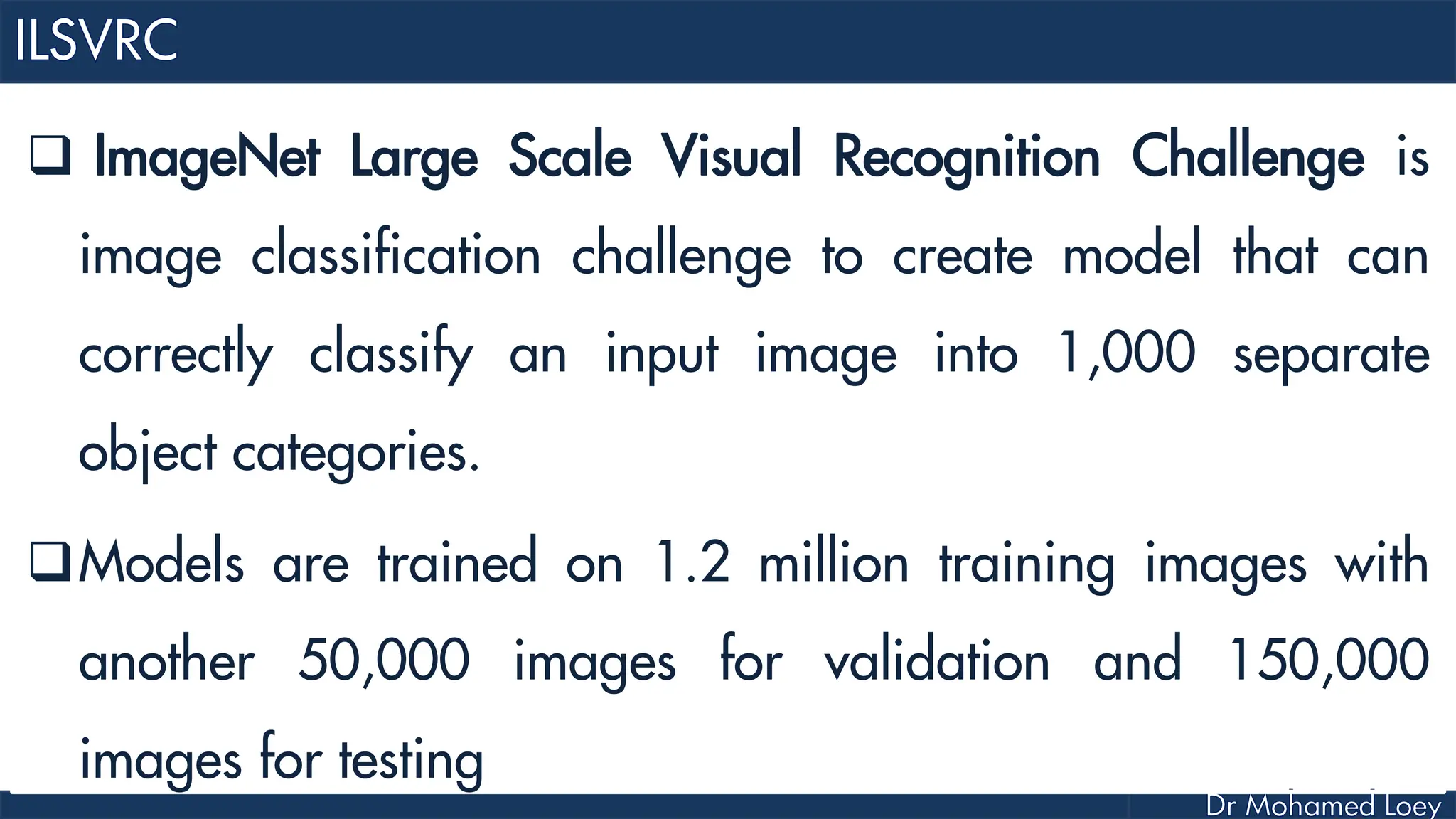
The document outlines the evolution and architecture of various convolutional neural networks (CNNs) developed for the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC) from 2012 to 2015, focusing on models like AlexNet, ZFNet, VGGNet, GoogLeNet, and ResNet. It describes key features such as layer compositions, error rates, and innovations like dropout and batch normalization aimed at improving performance and reducing overfitting. Each network's structure is compared, highlighting advancements in design and training techniques, culminating in the increasing complexity and depth of models over the years.



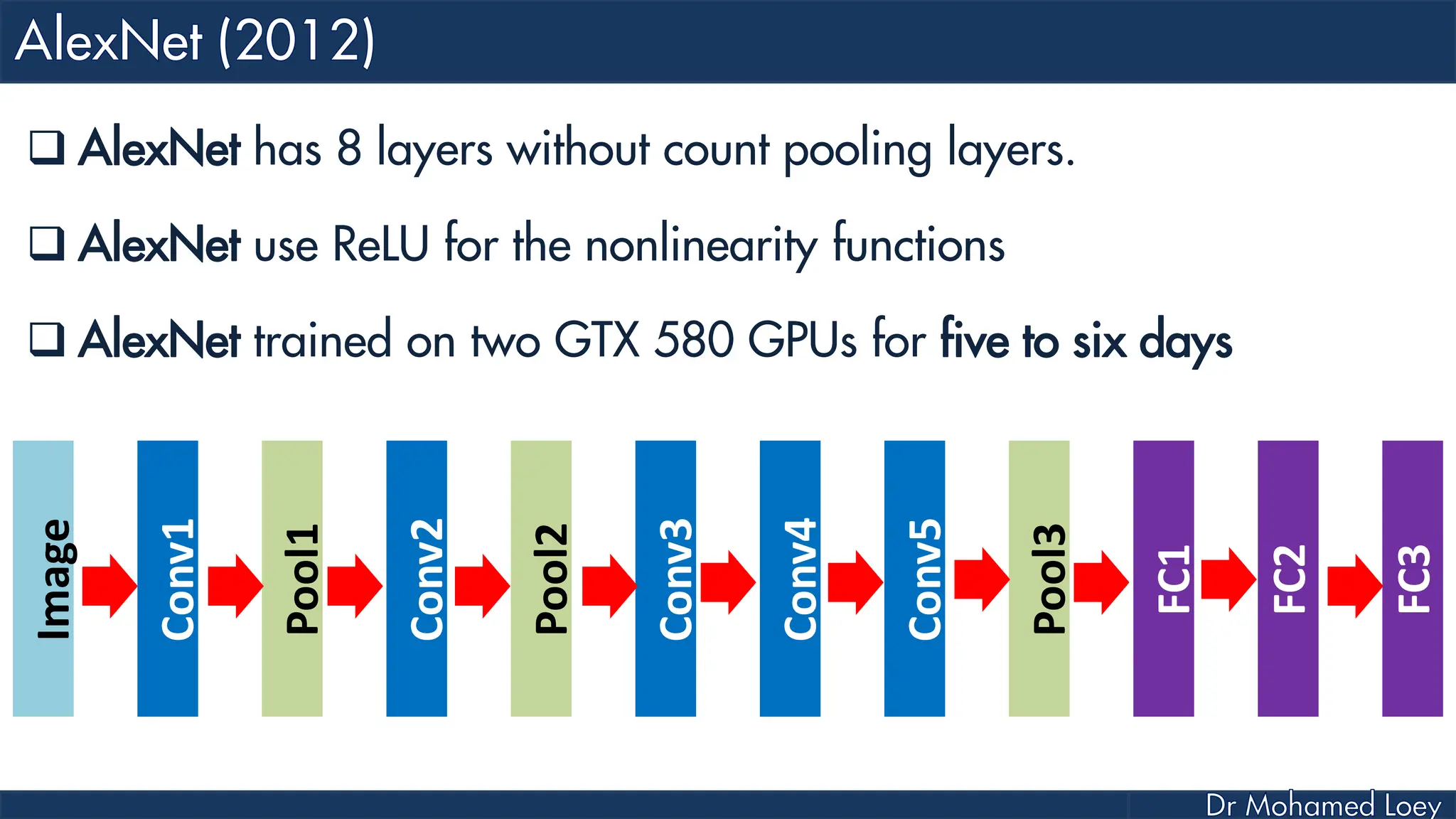
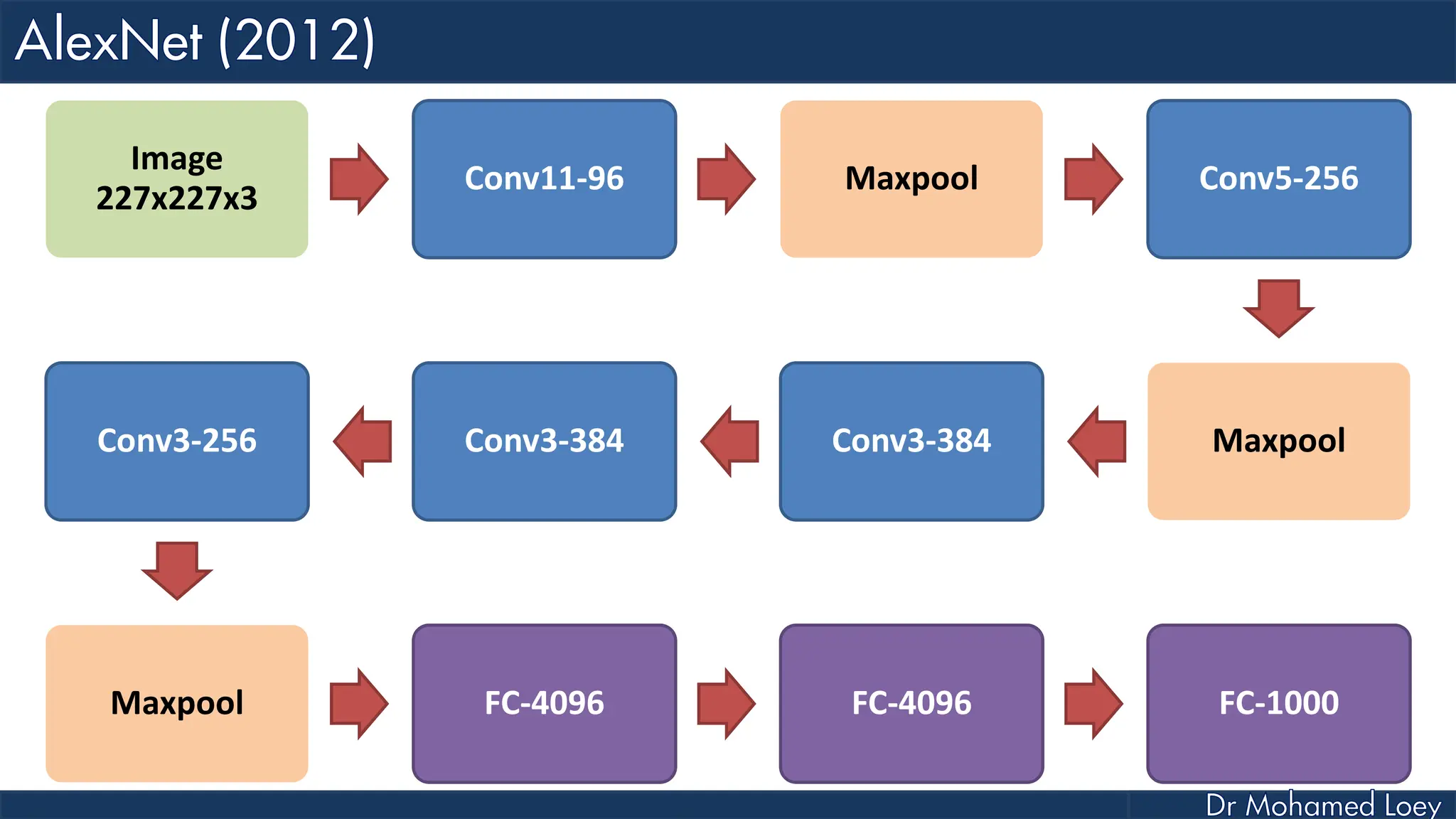
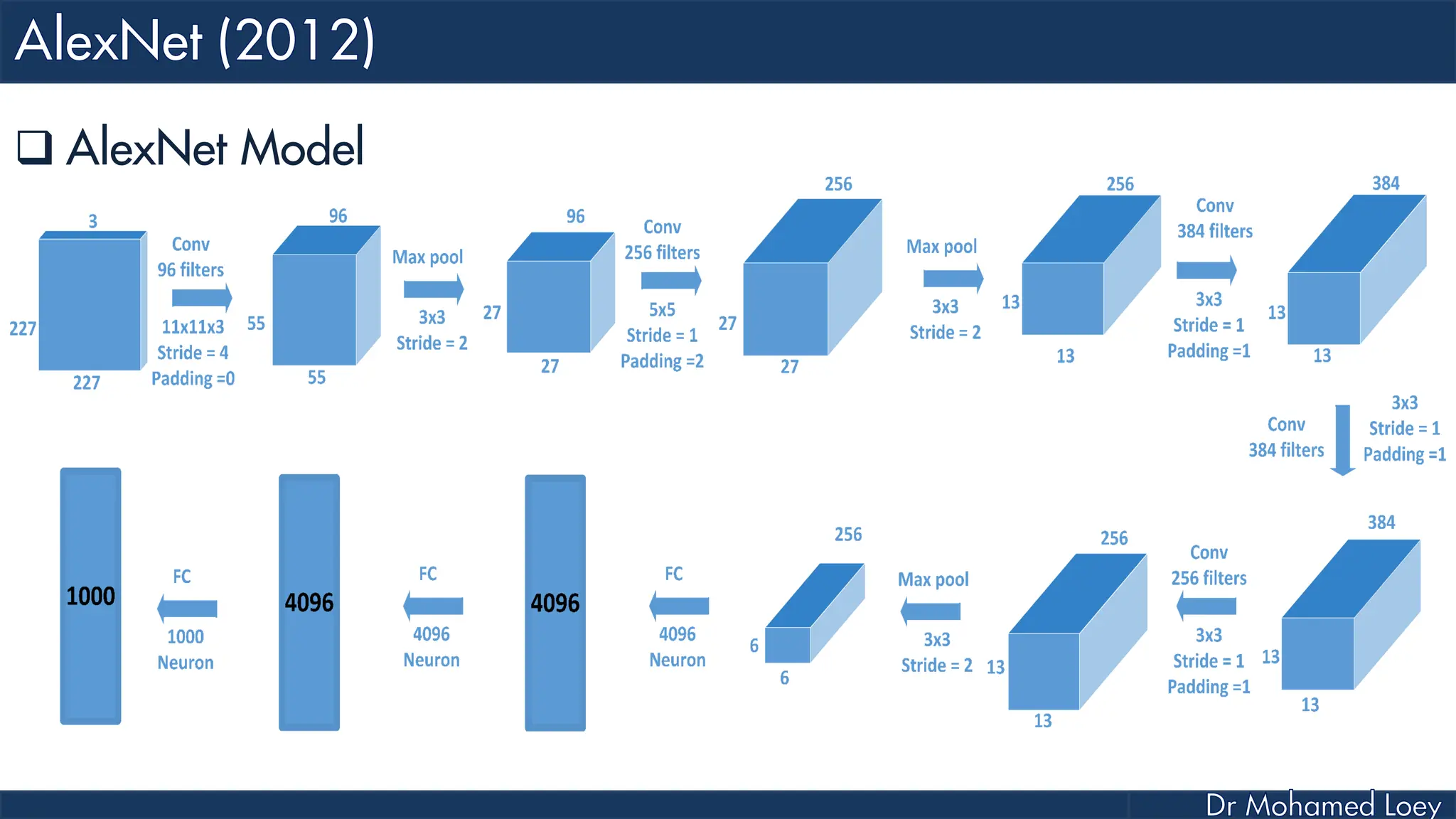
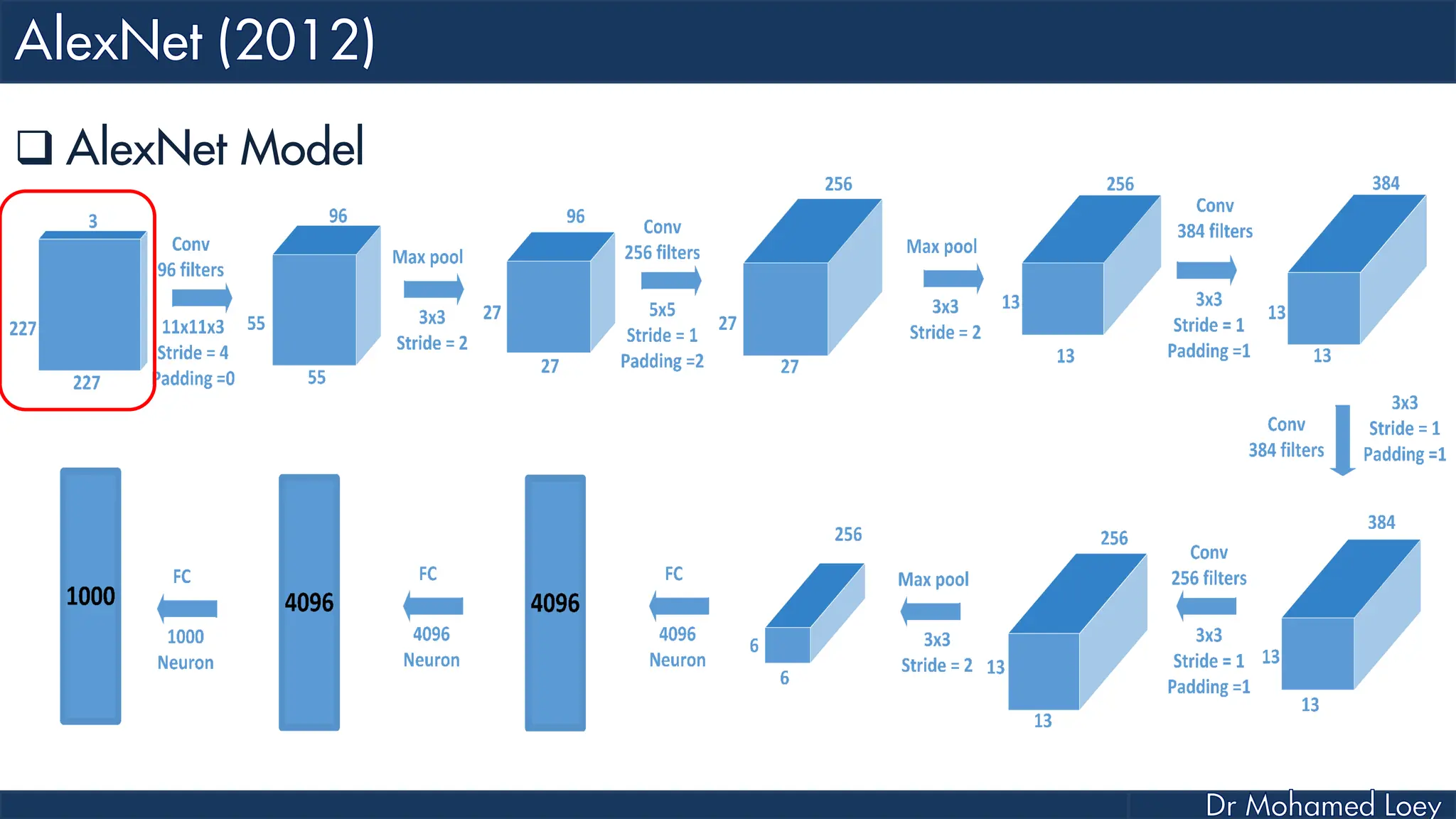
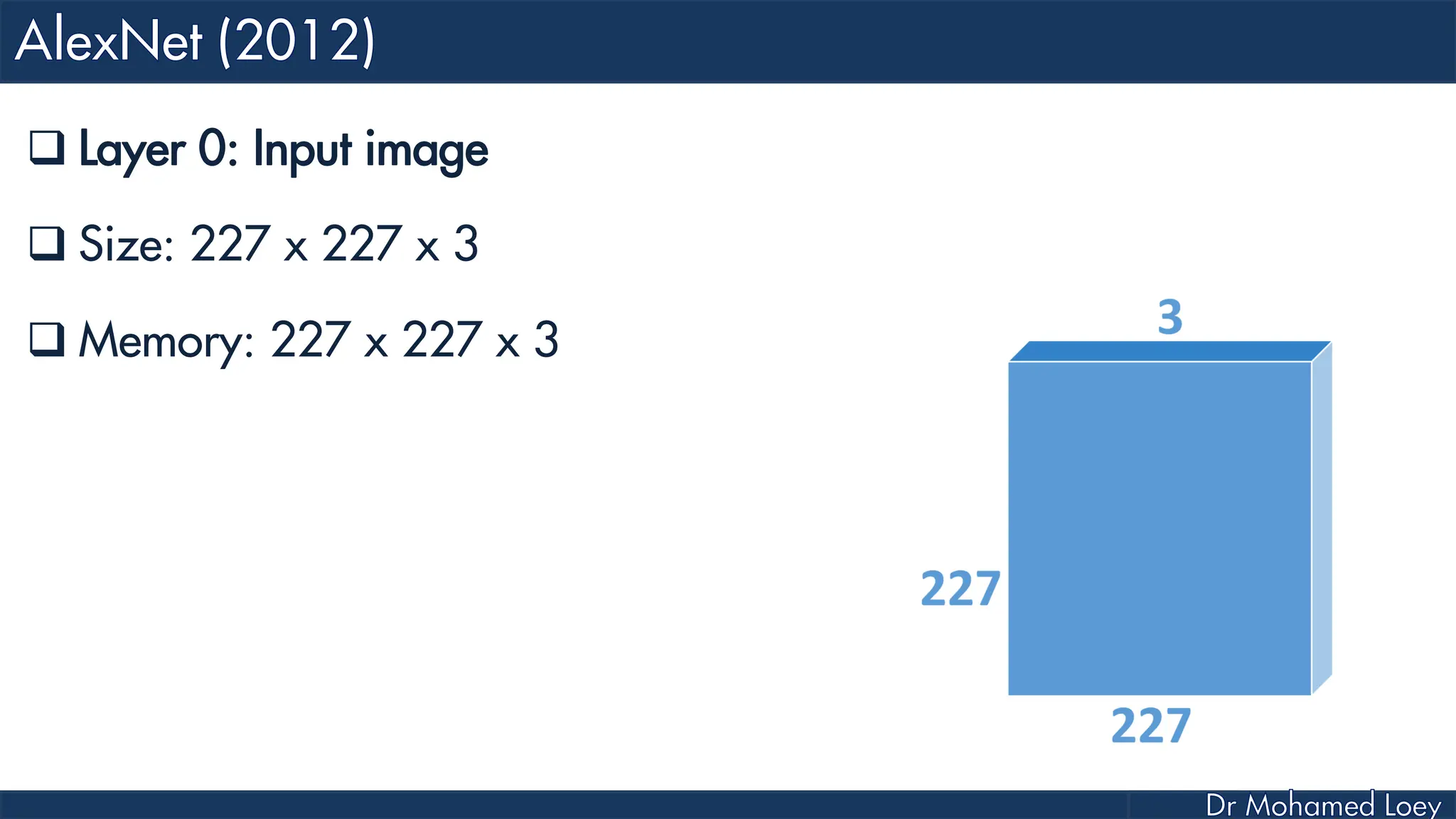
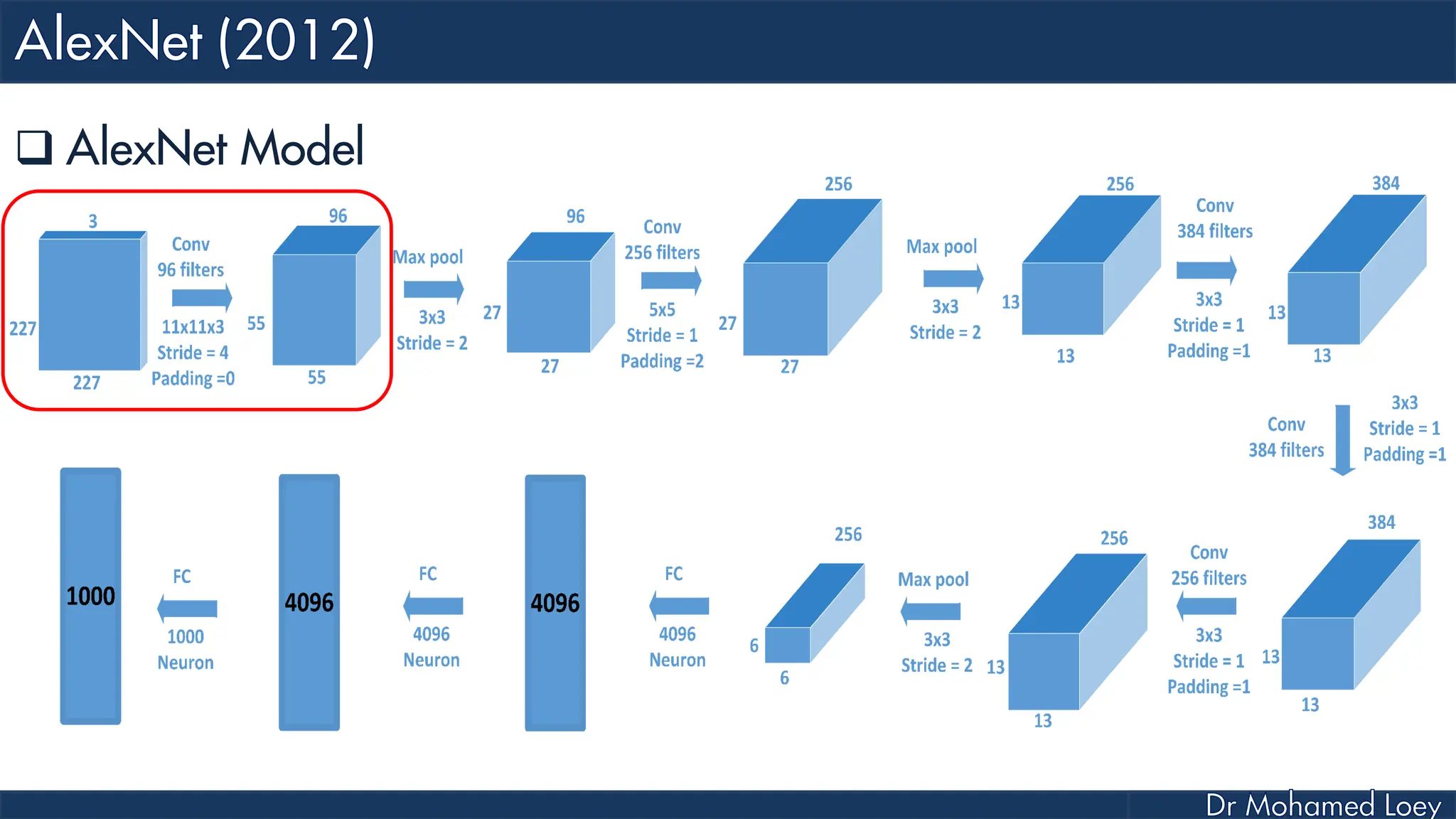
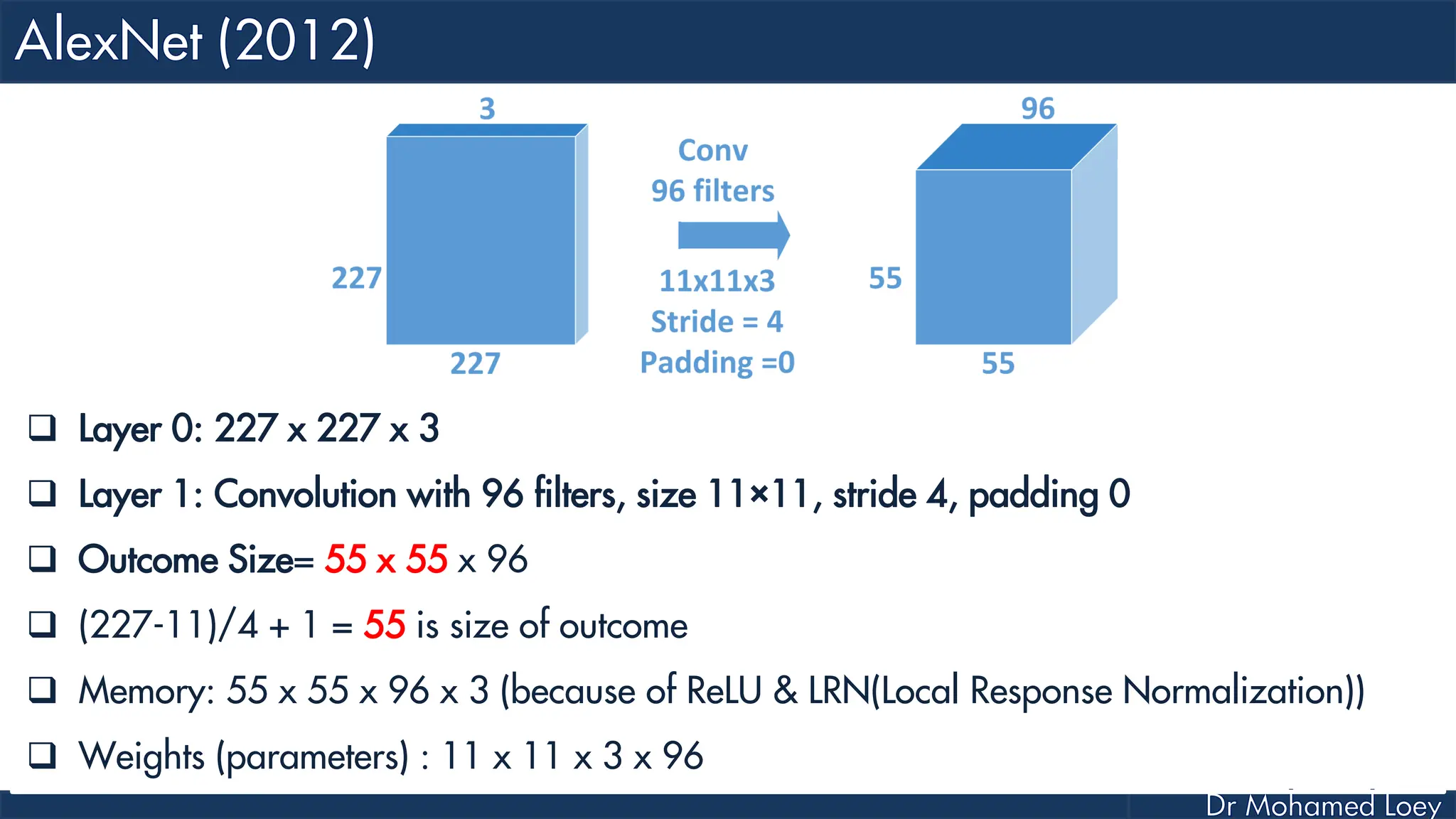
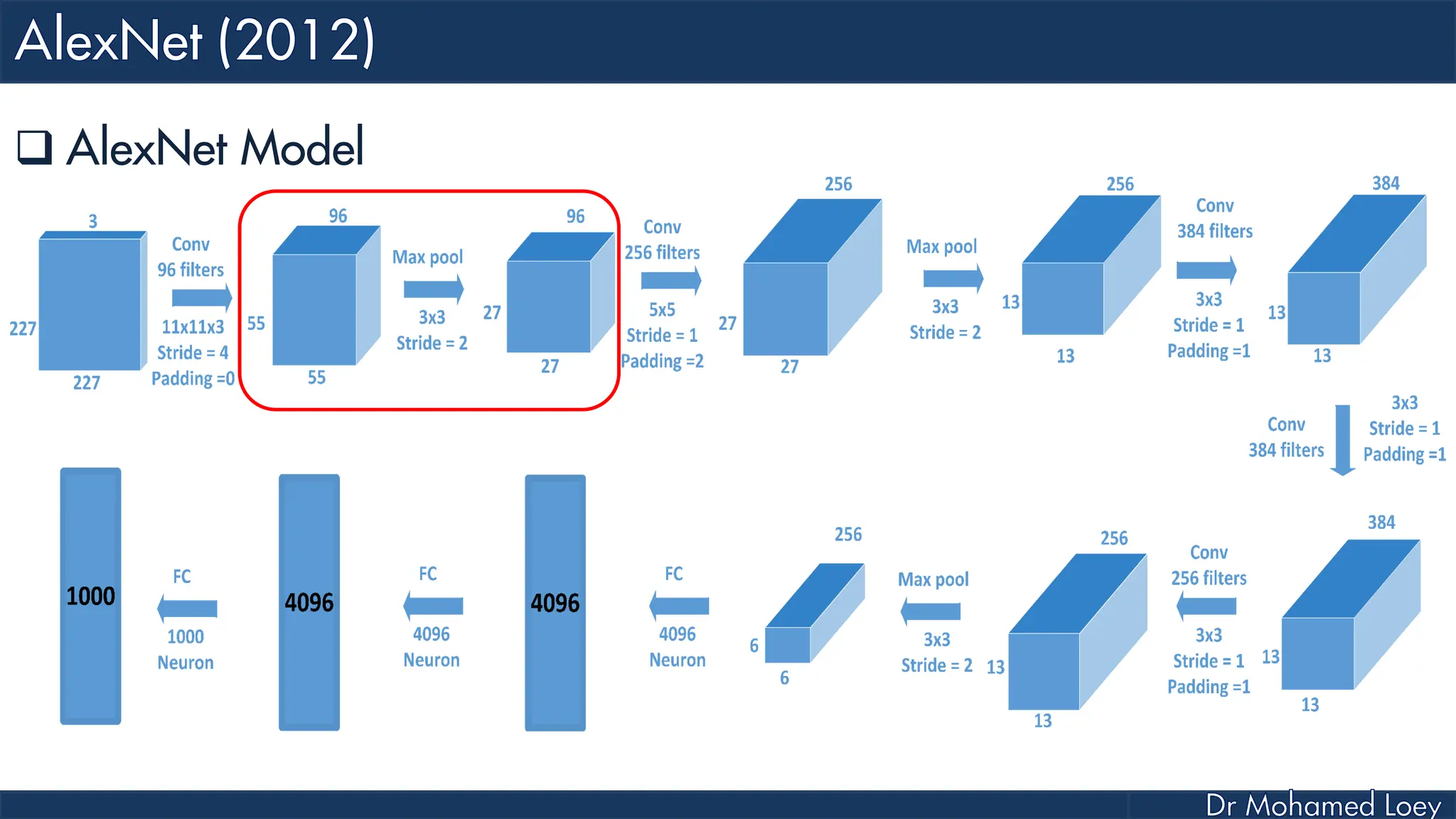
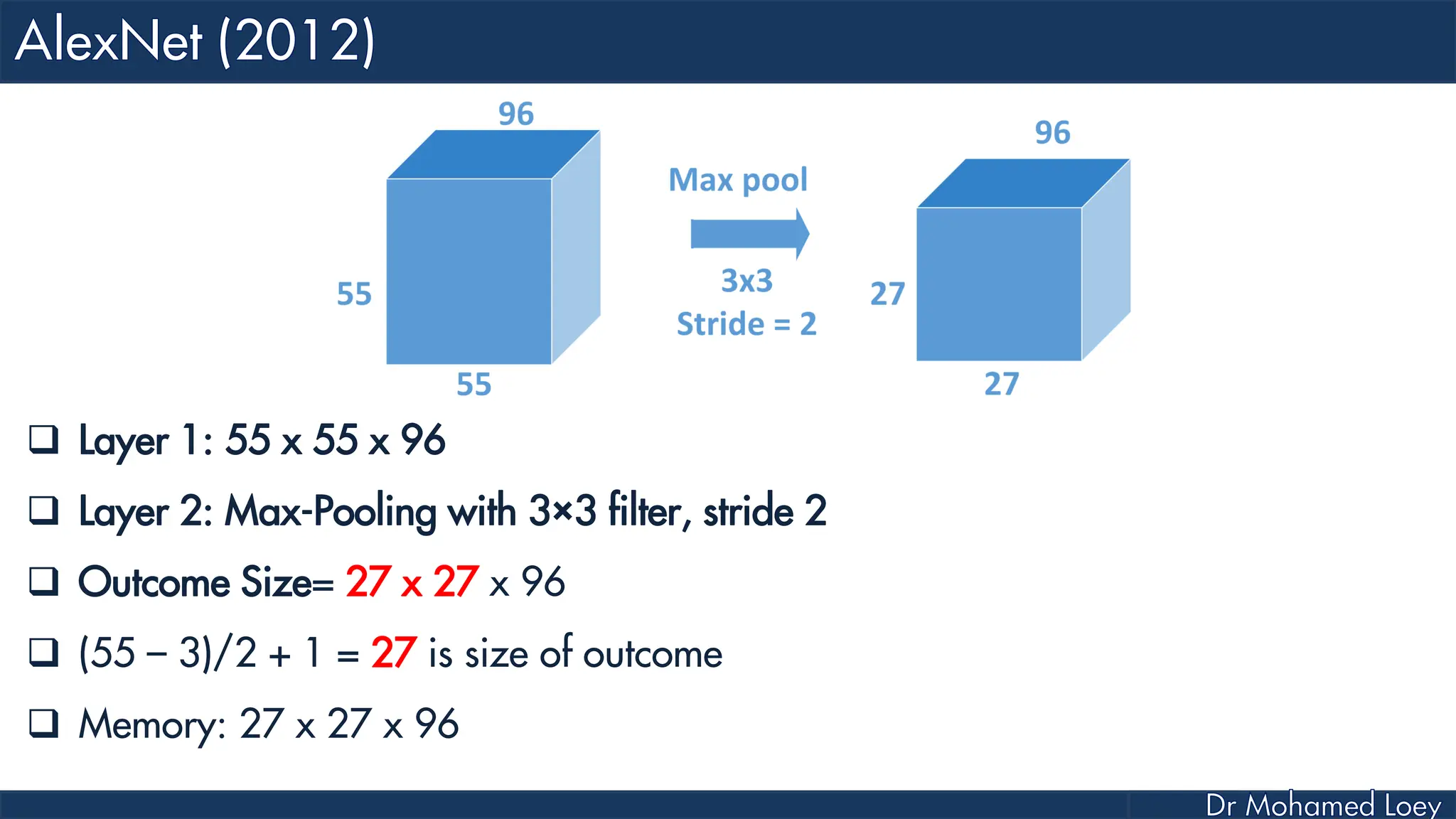
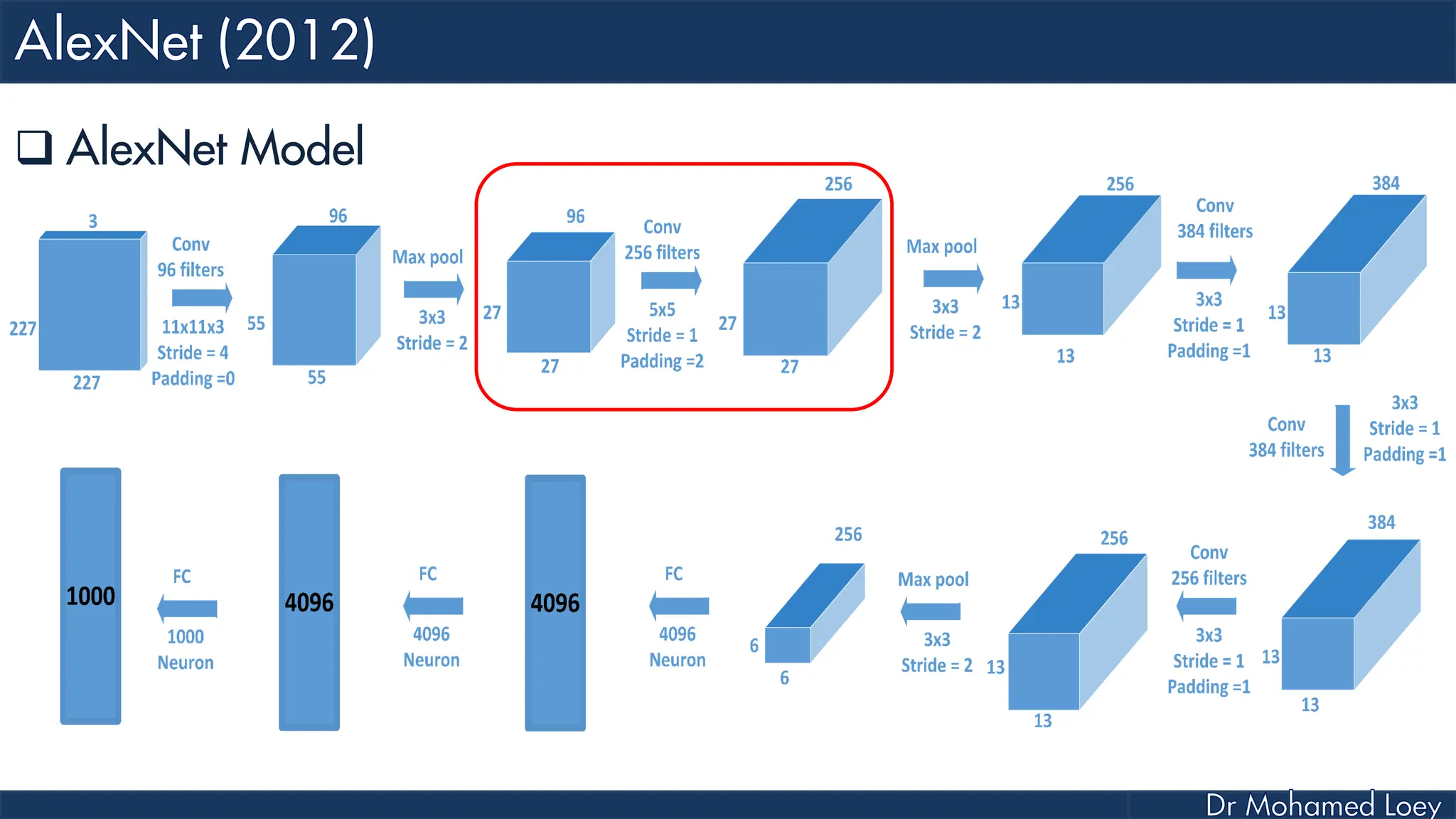
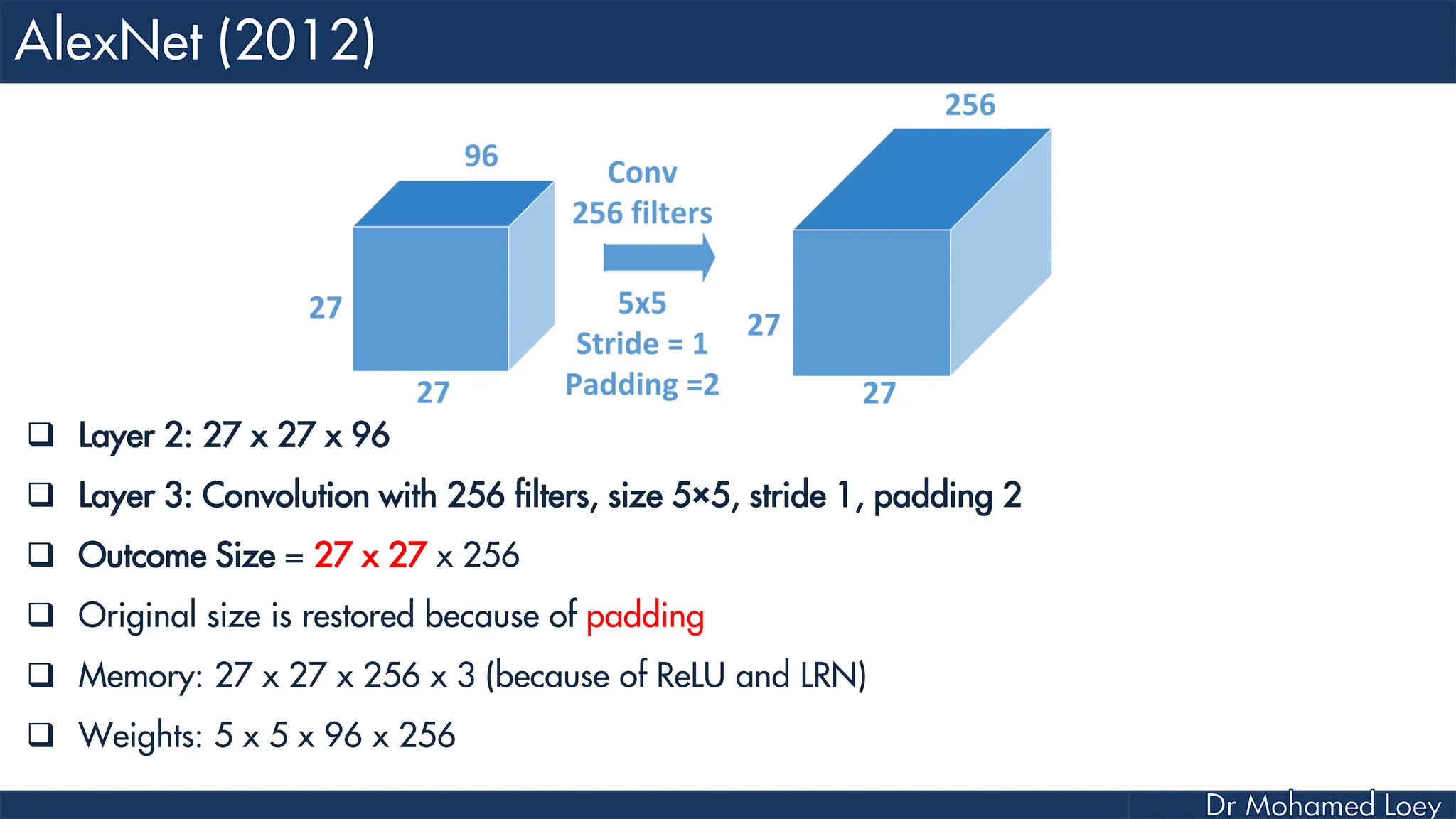
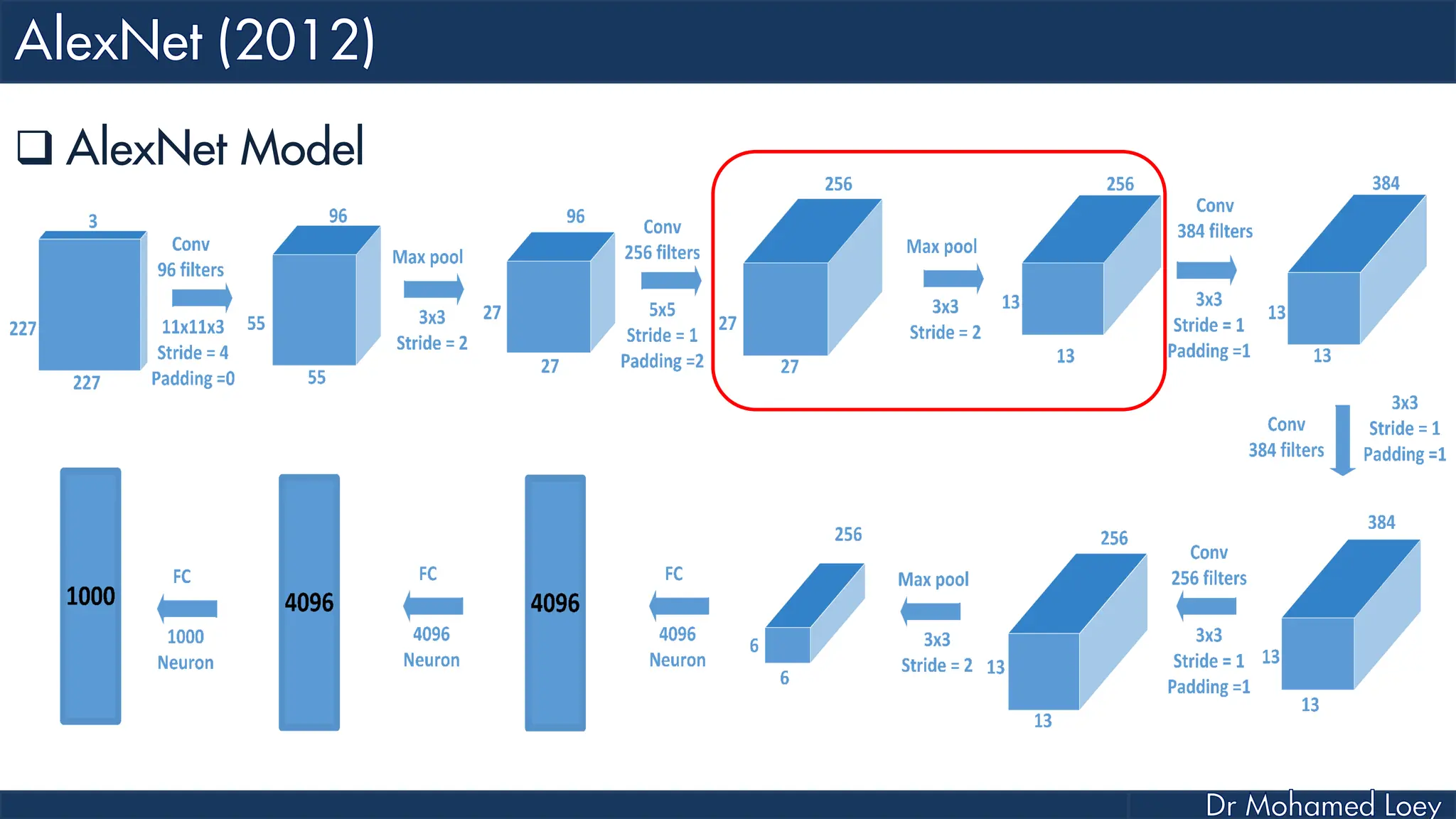
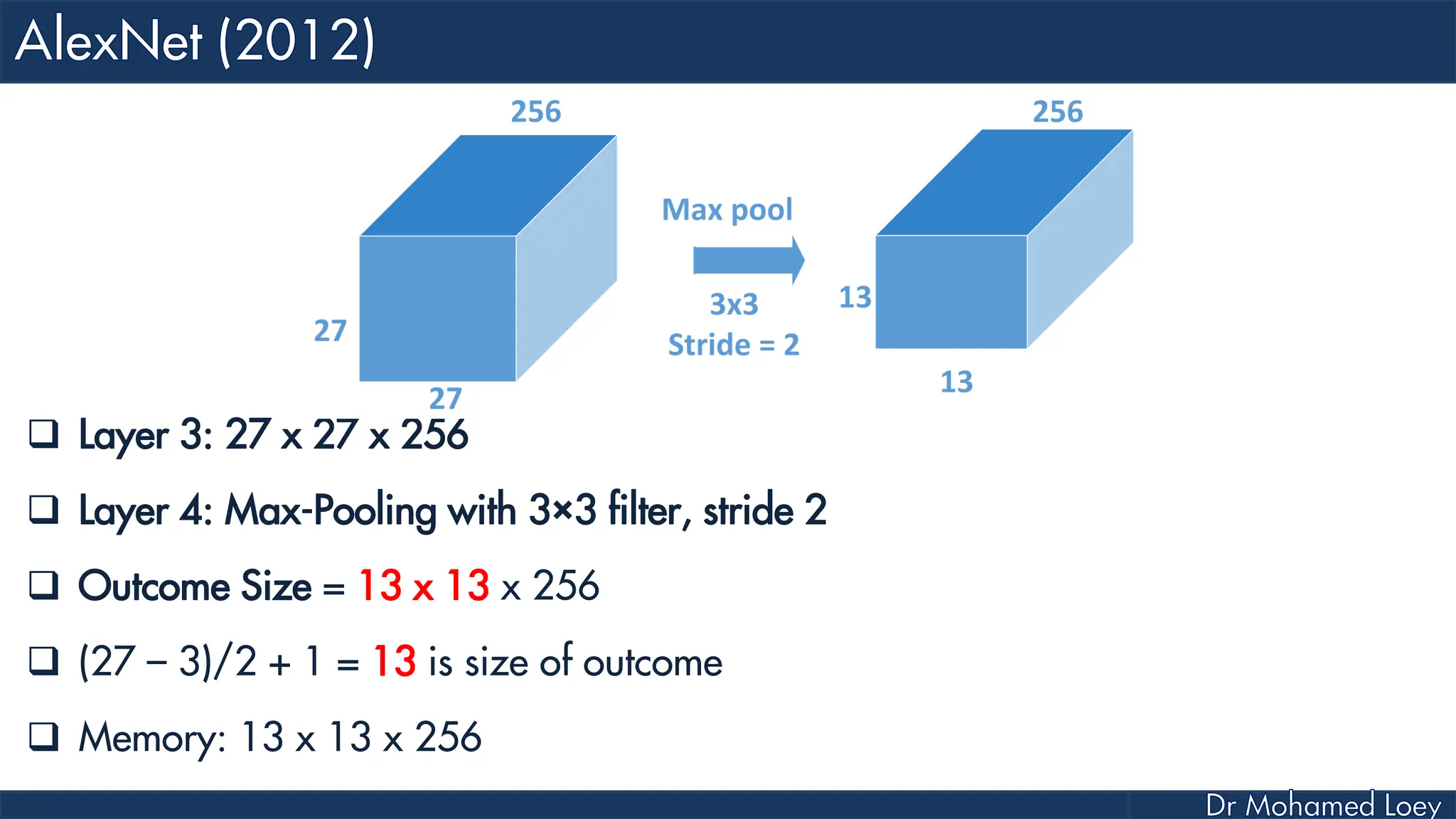
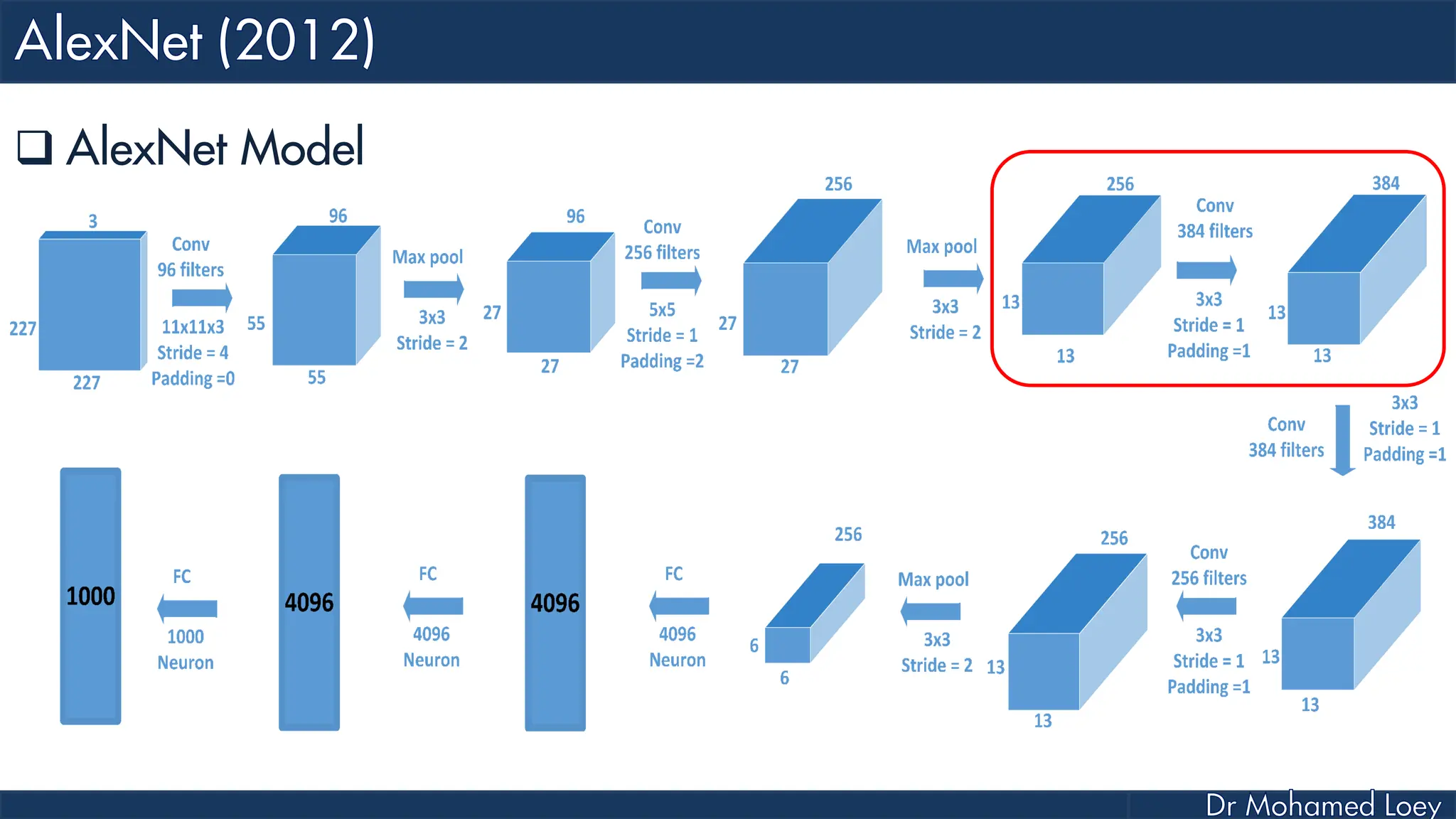
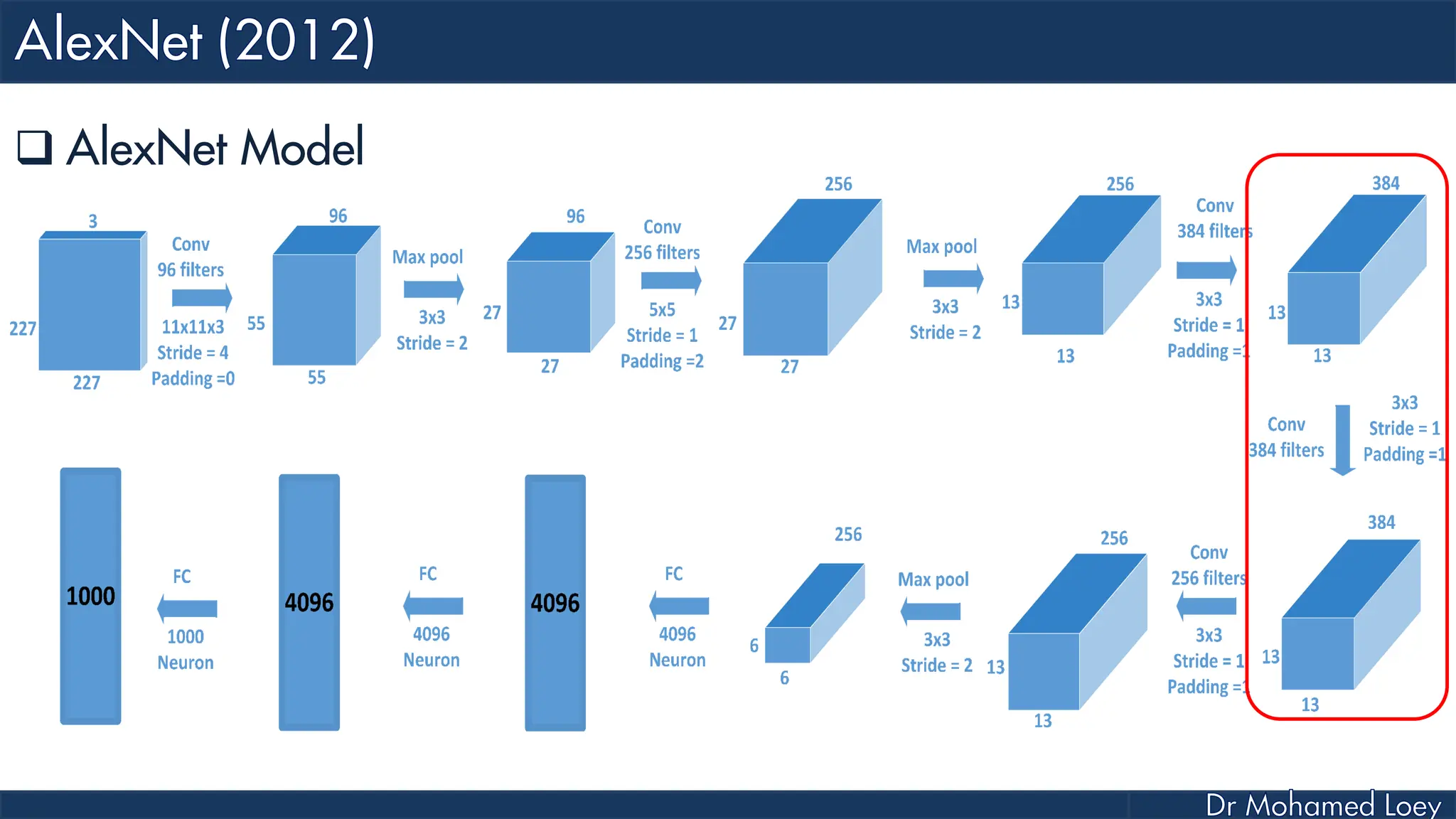

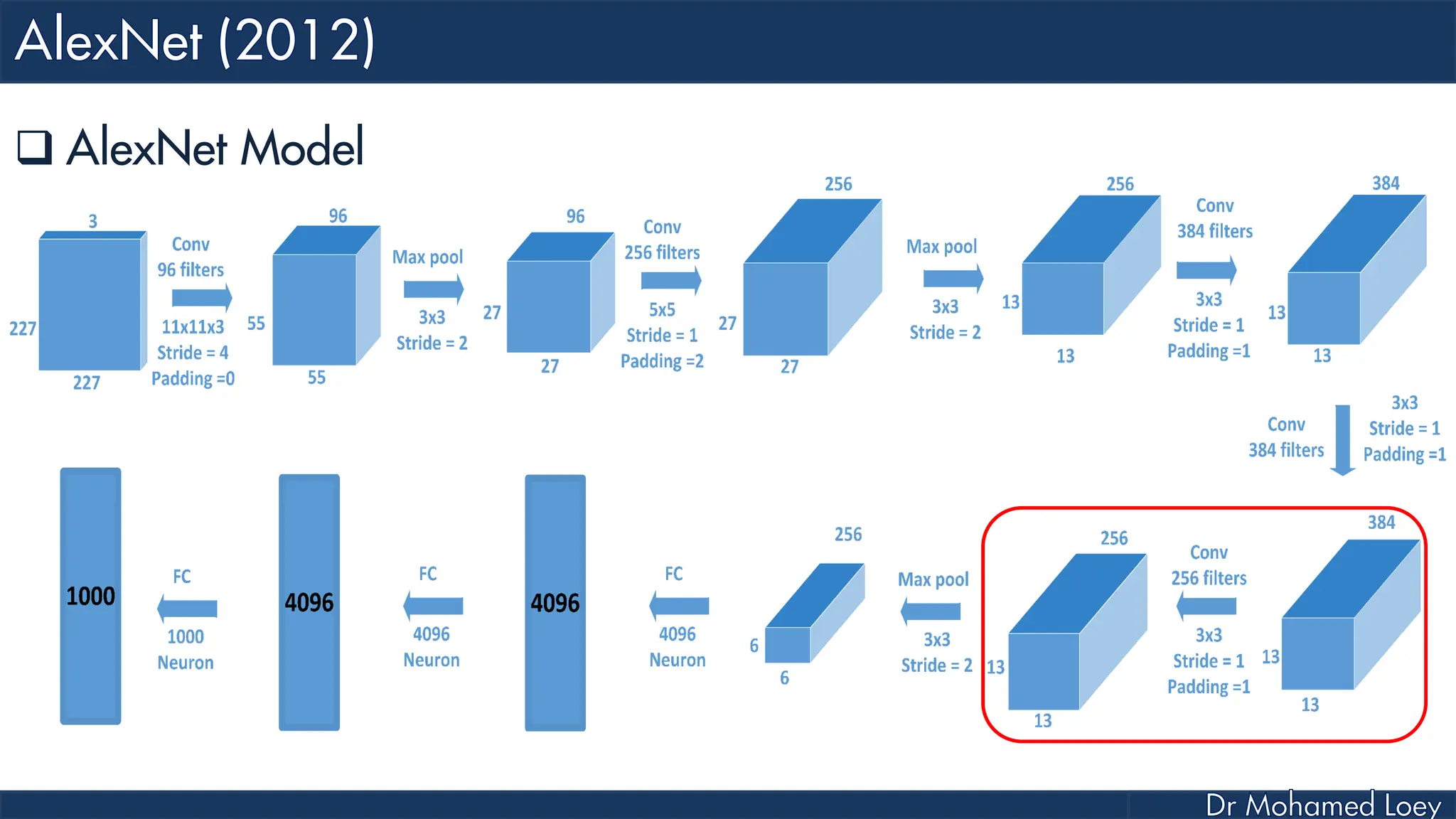
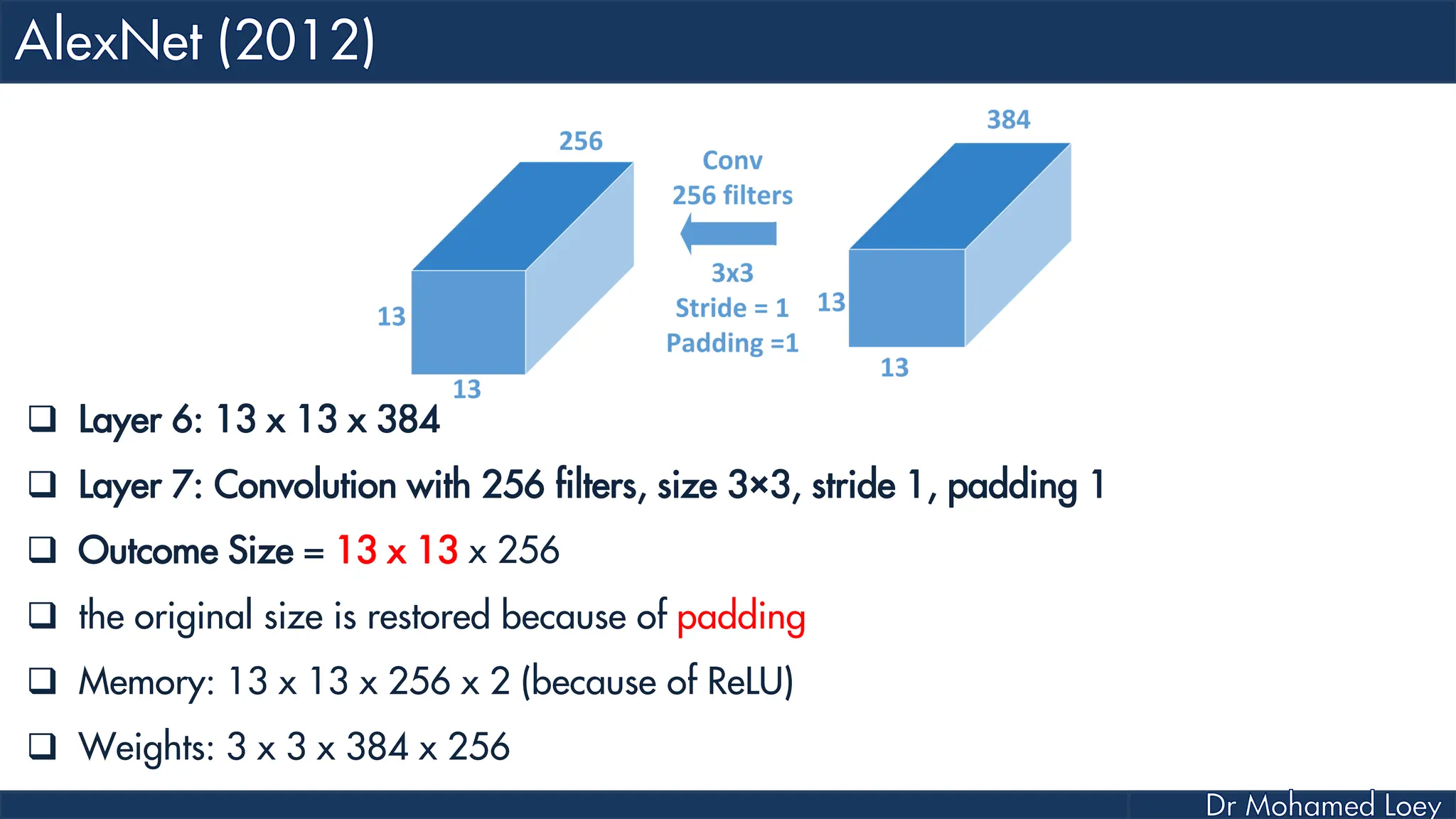
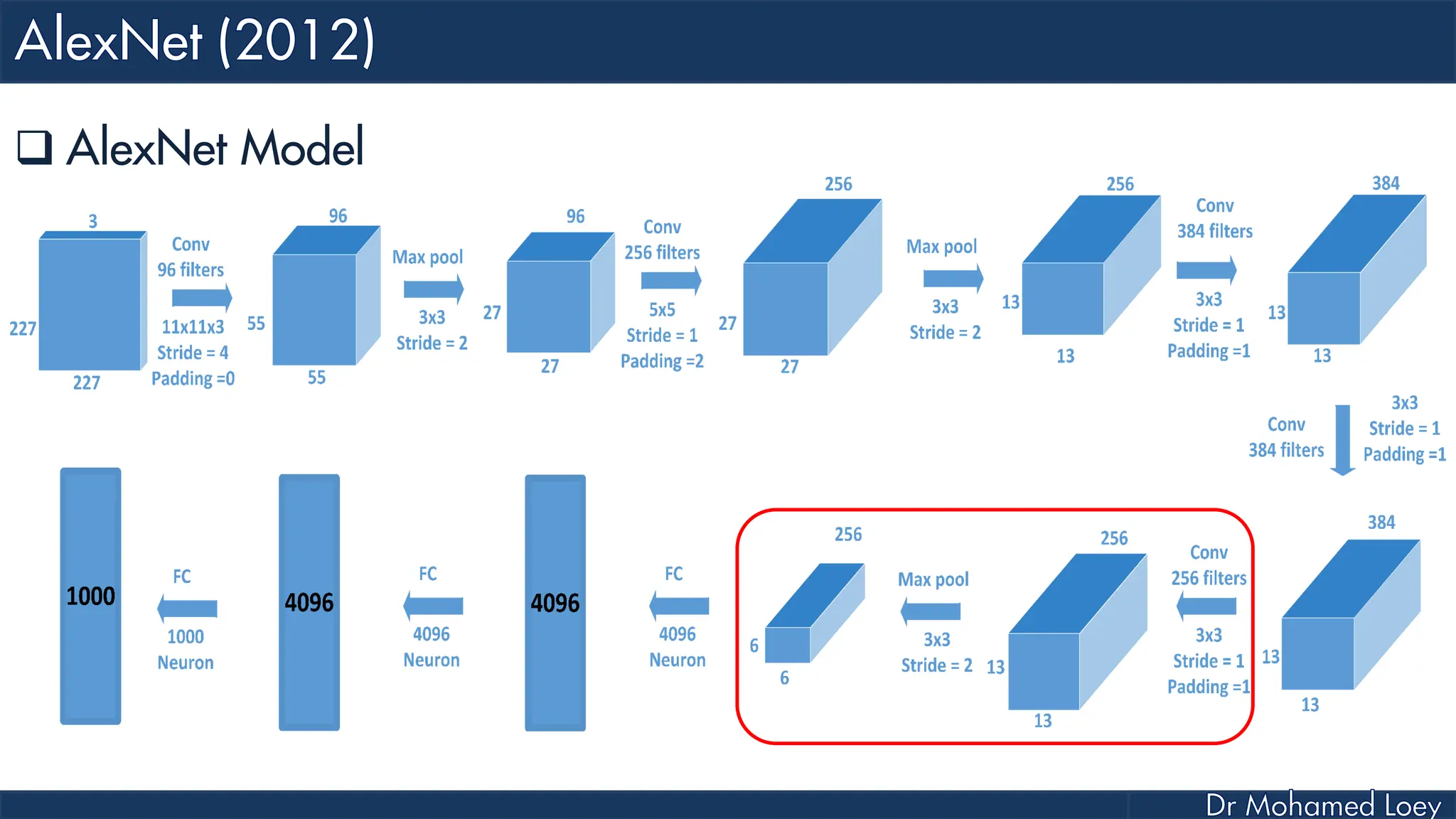
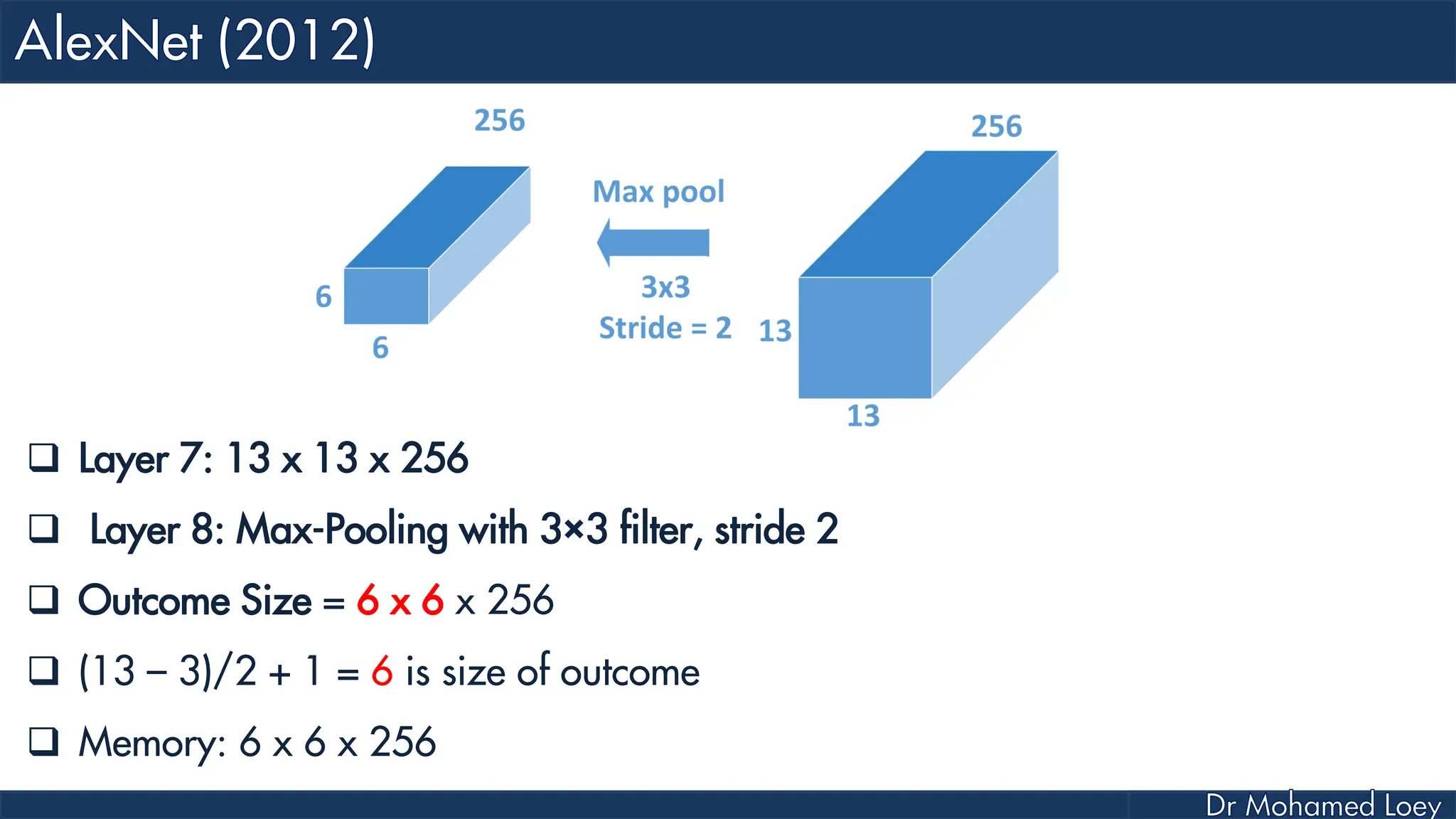
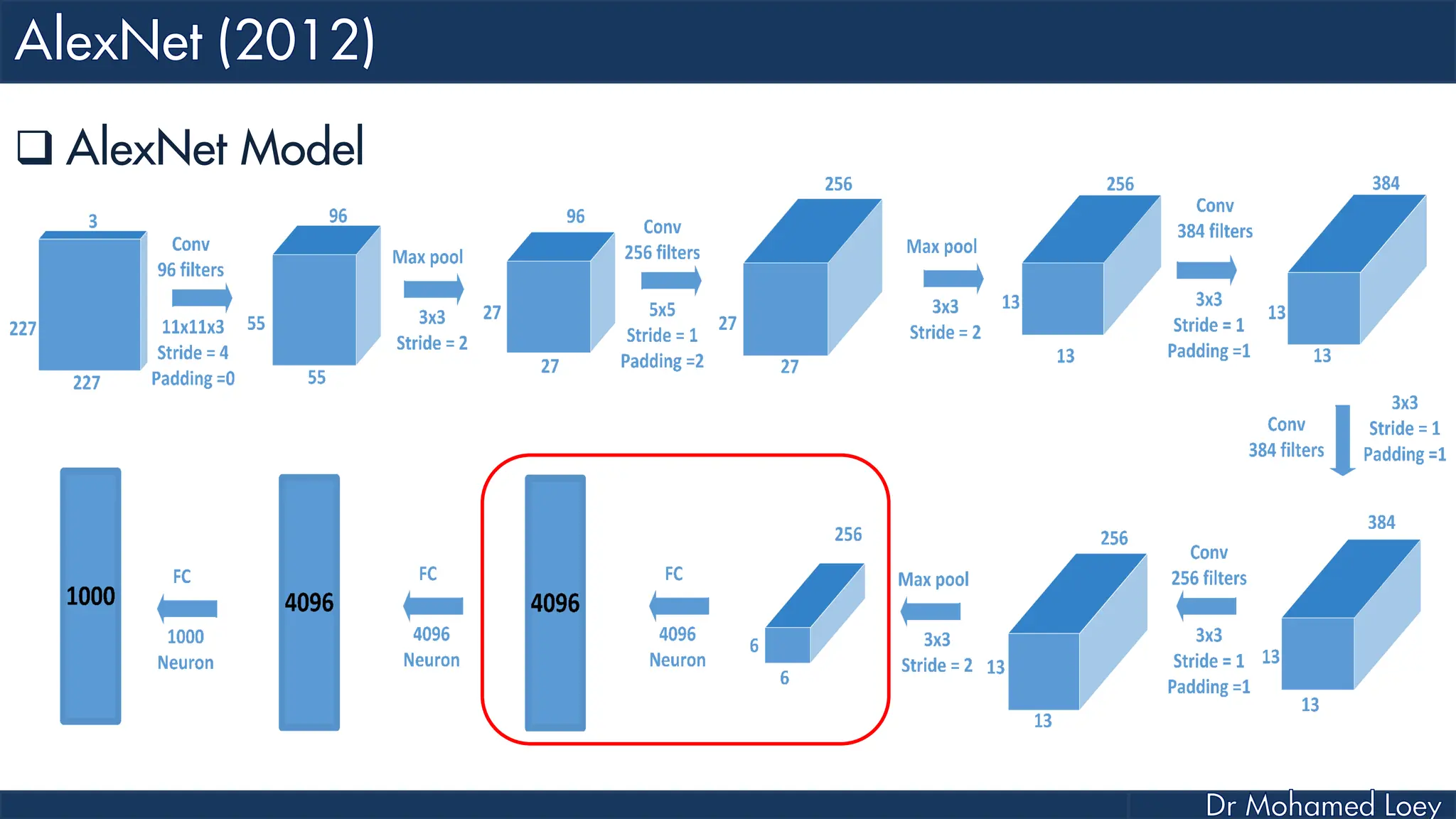
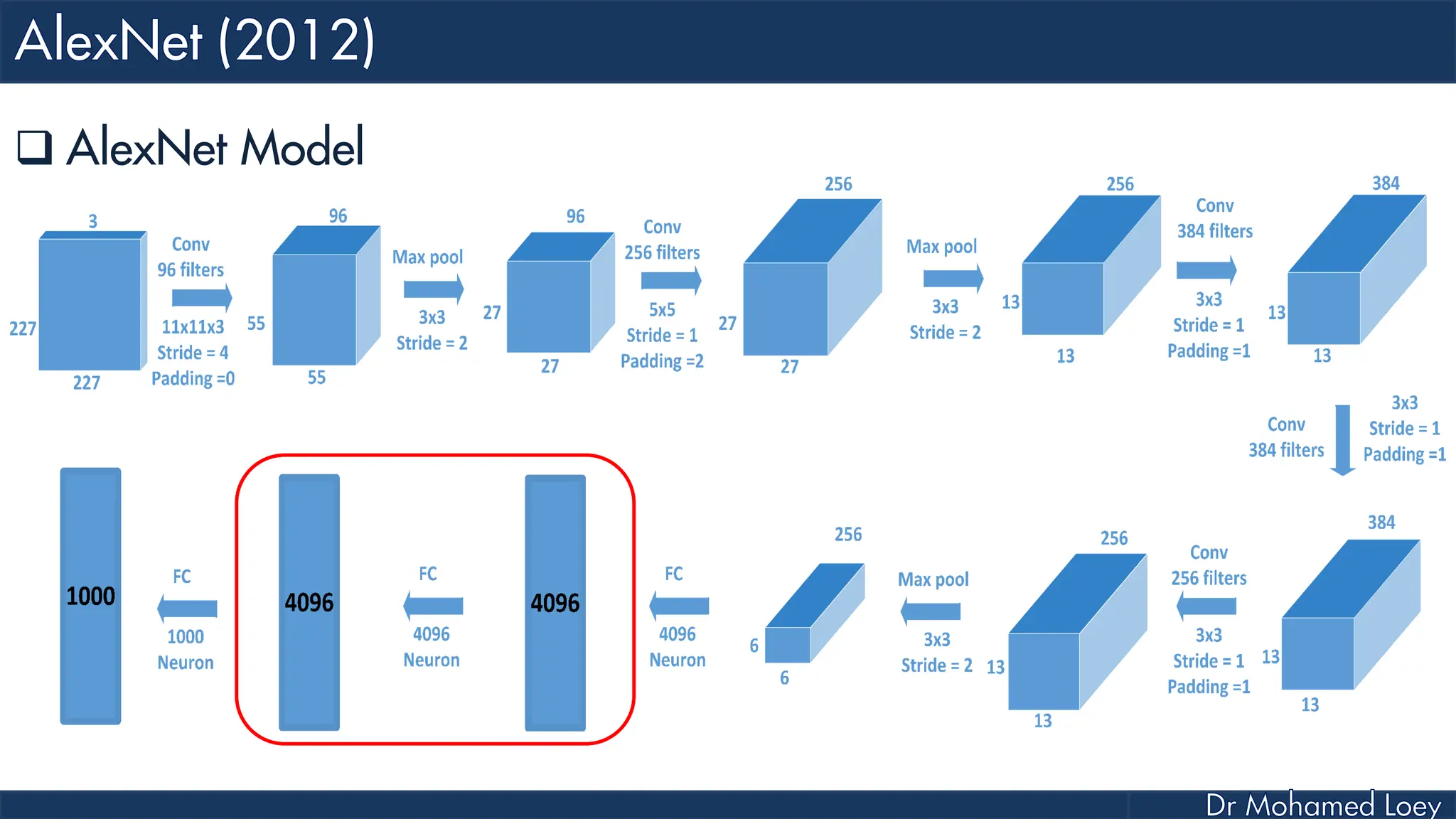
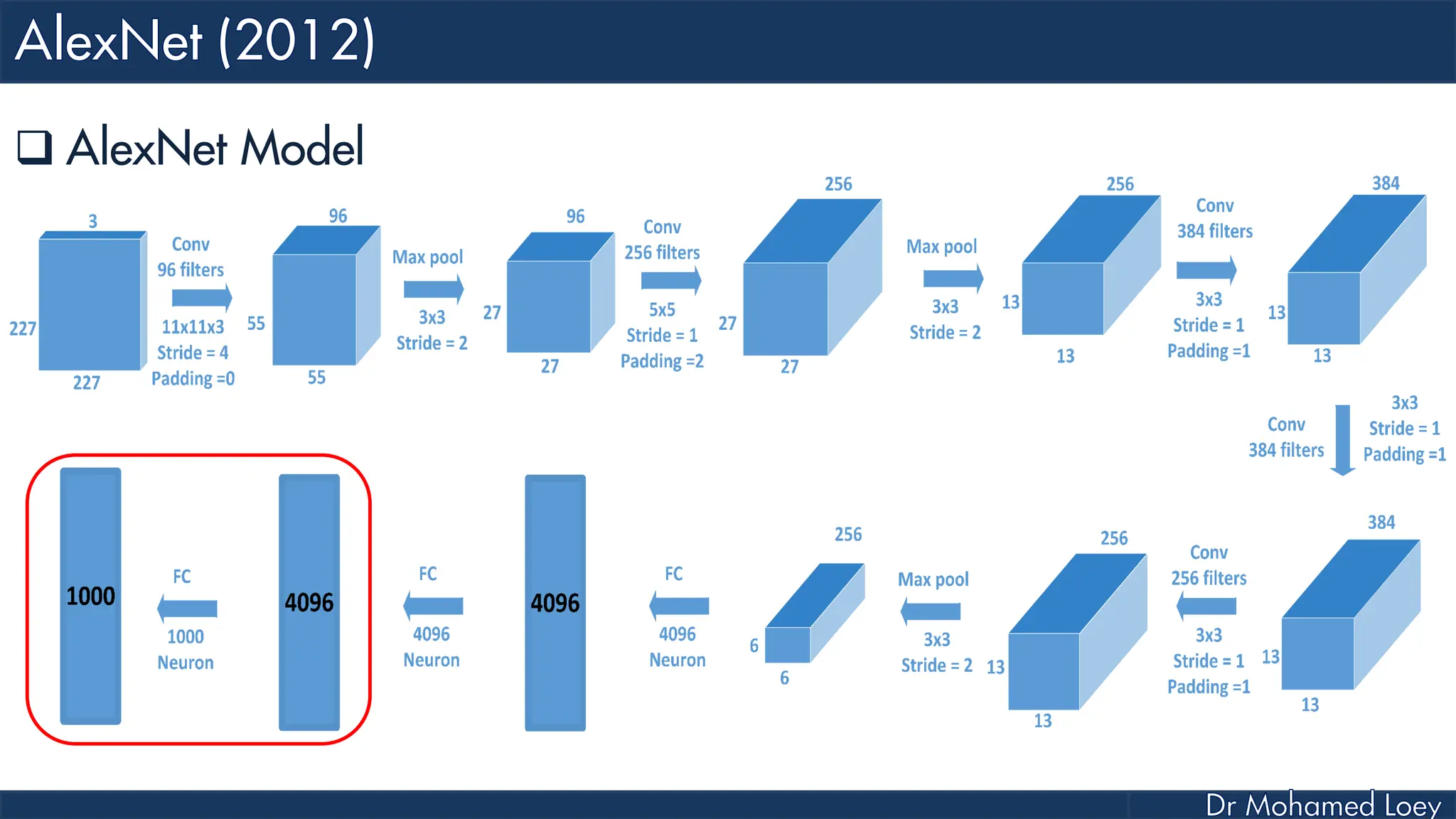

![[227x227x3] INPUT [55x55x96] CONV1 : 96 11x11 filters at stride 4, pad 0 27x27x96] MAX POOL1 : 3x3 filters at stride 2 [27x27x96] NORM1: Normalization layer [27x27x256] CONV2: 256 5x5 filters at stride 1, pad 2 [13x13x256] MAX POOL2: 3x3 filters at stride 2 [13x13x256] NORM2: Normalization layer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancedtopicsincomputerscienence-2-lecture6-240125170823-01d99a6e/75/Lecture-5-Convolutional-Neural-Network-Models-48-2048.jpg)
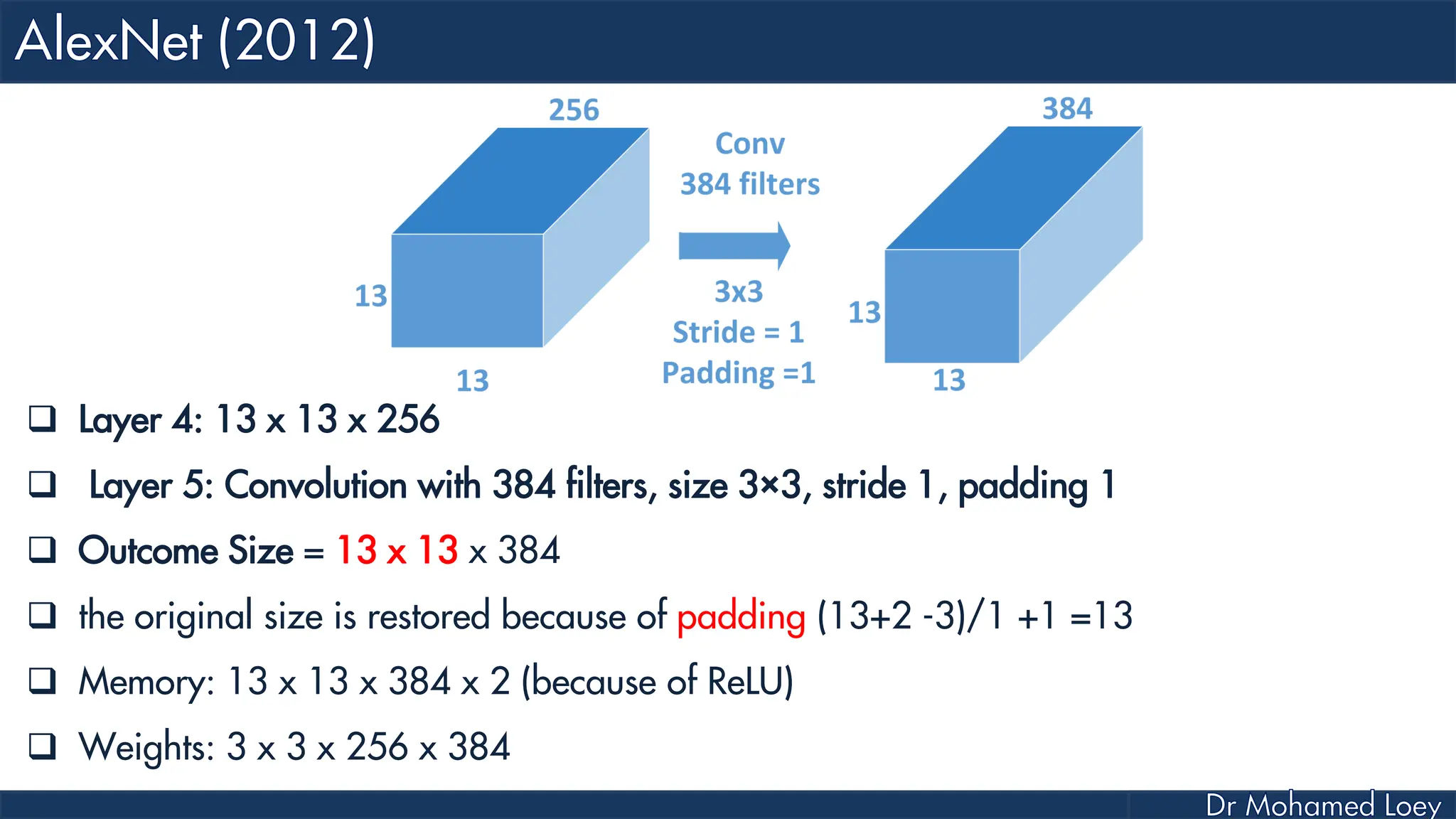
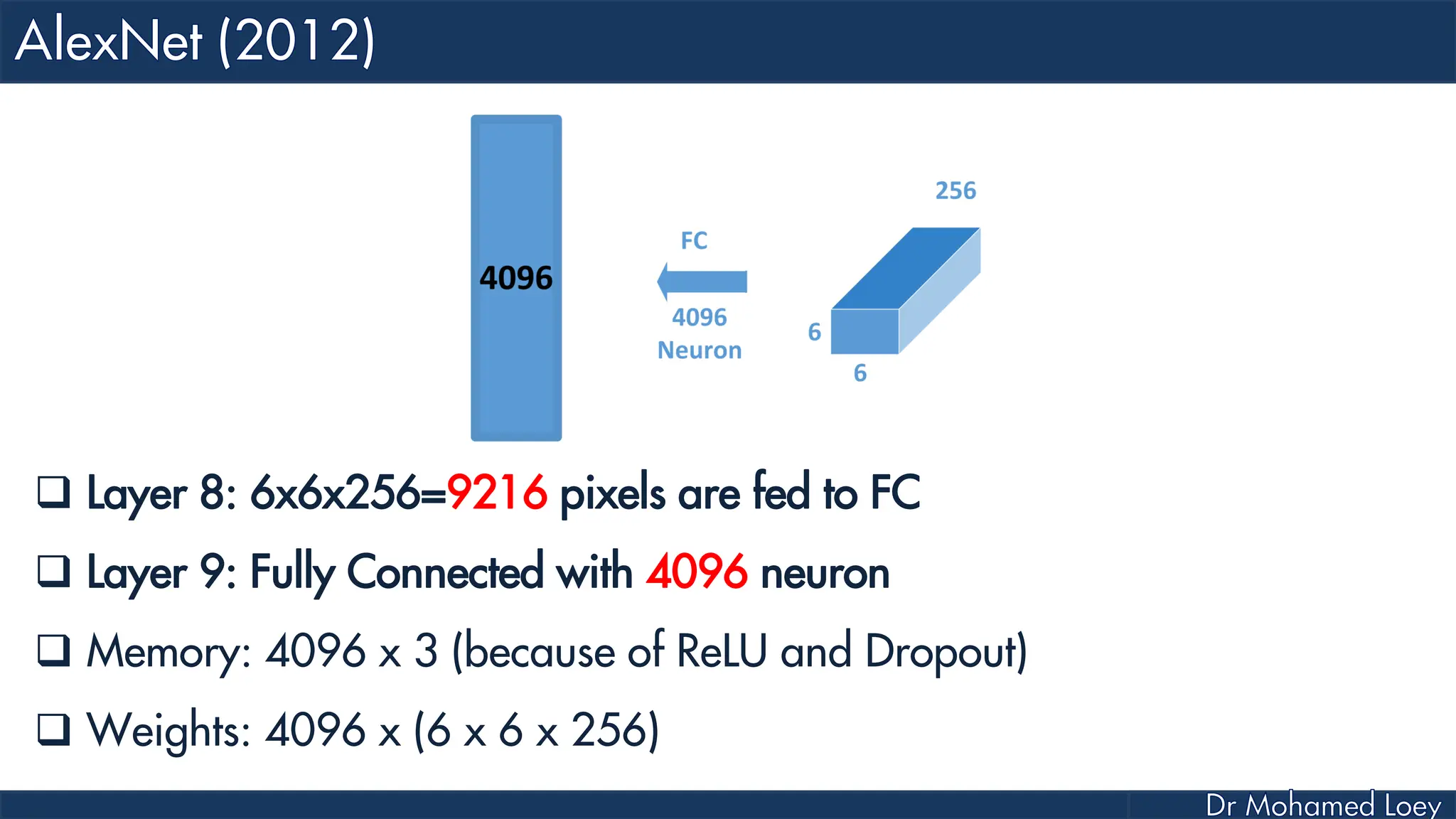
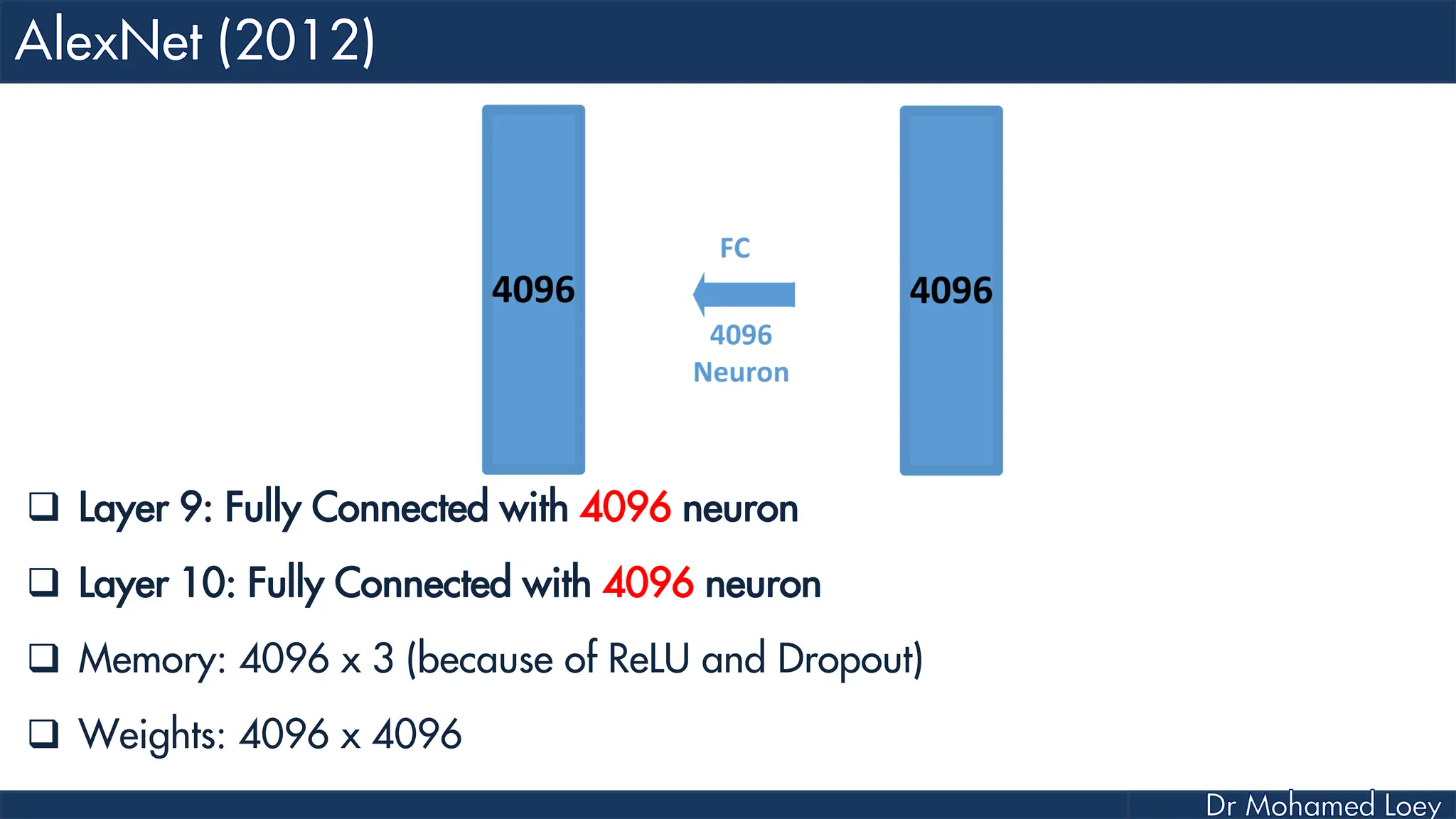
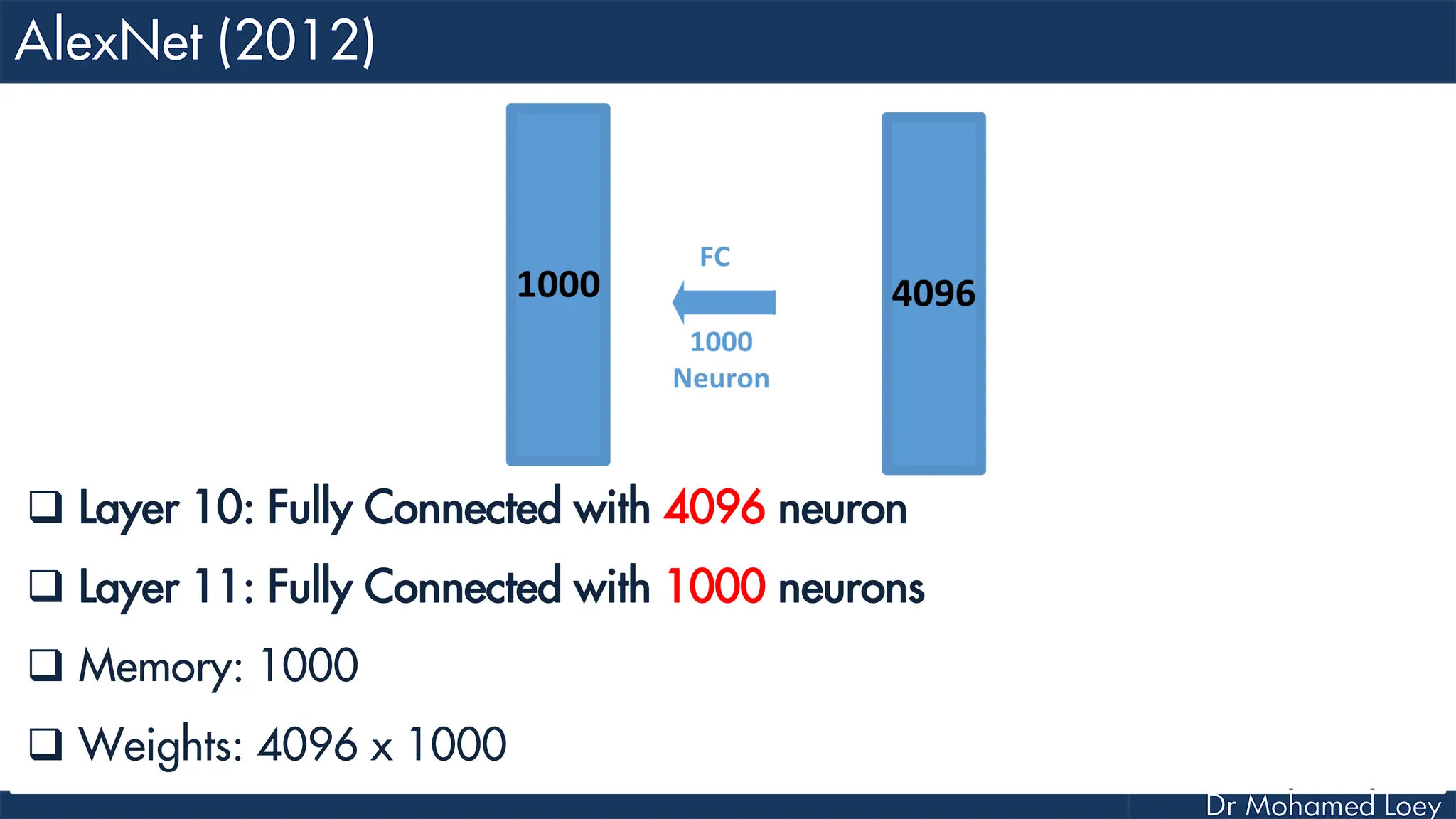
![[13x13x384] CONV3: 384 3x3 filters at stride 1, pad 1 [13x13x384] CONV4: 384 3x3 filters at stride 1, pad 1 [13x13x256] CONV5: 256 3x3 filters at stride 1, pad 1 [6x6x256] MAX POOL3: 3x3 filters at stride 2 [4096] FC6: 4096 neurons [4096] FC7: 4096 neurons [1000] FC8: 1000 neurons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advancedtopicsincomputerscienence-2-lecture6-240125170823-01d99a6e/75/Lecture-5-Convolutional-Neural-Network-Models-49-2048.jpg)