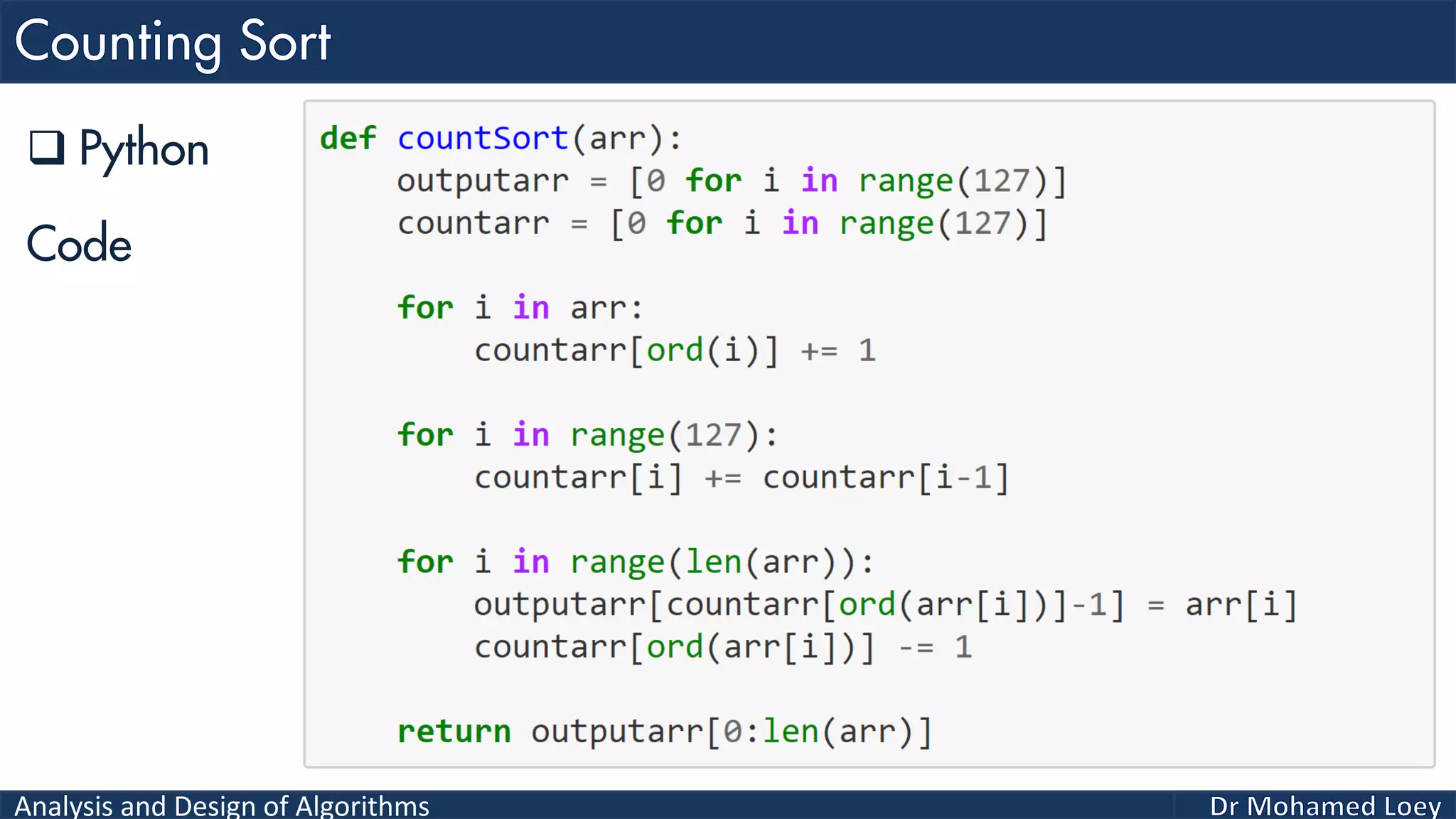
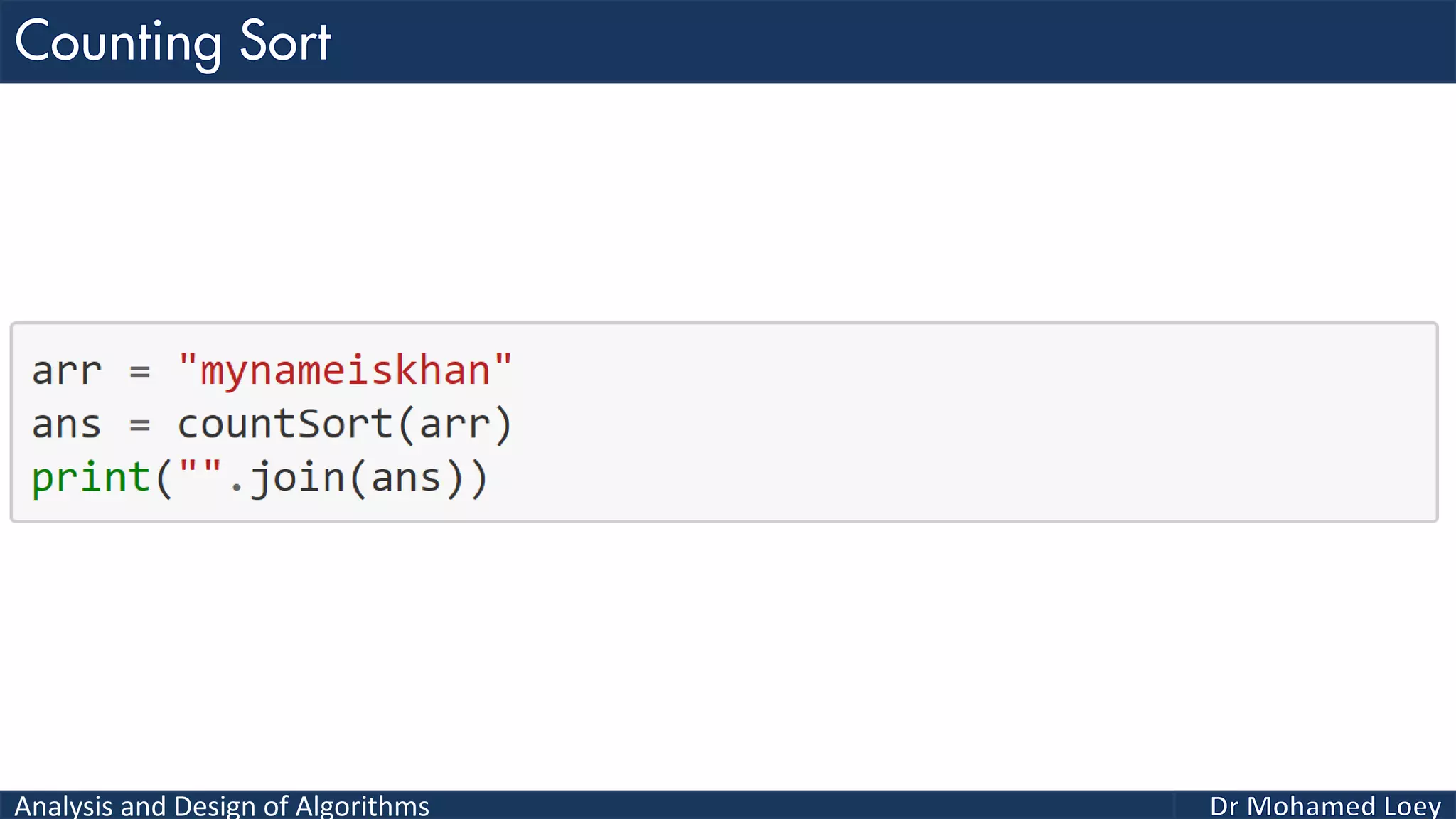
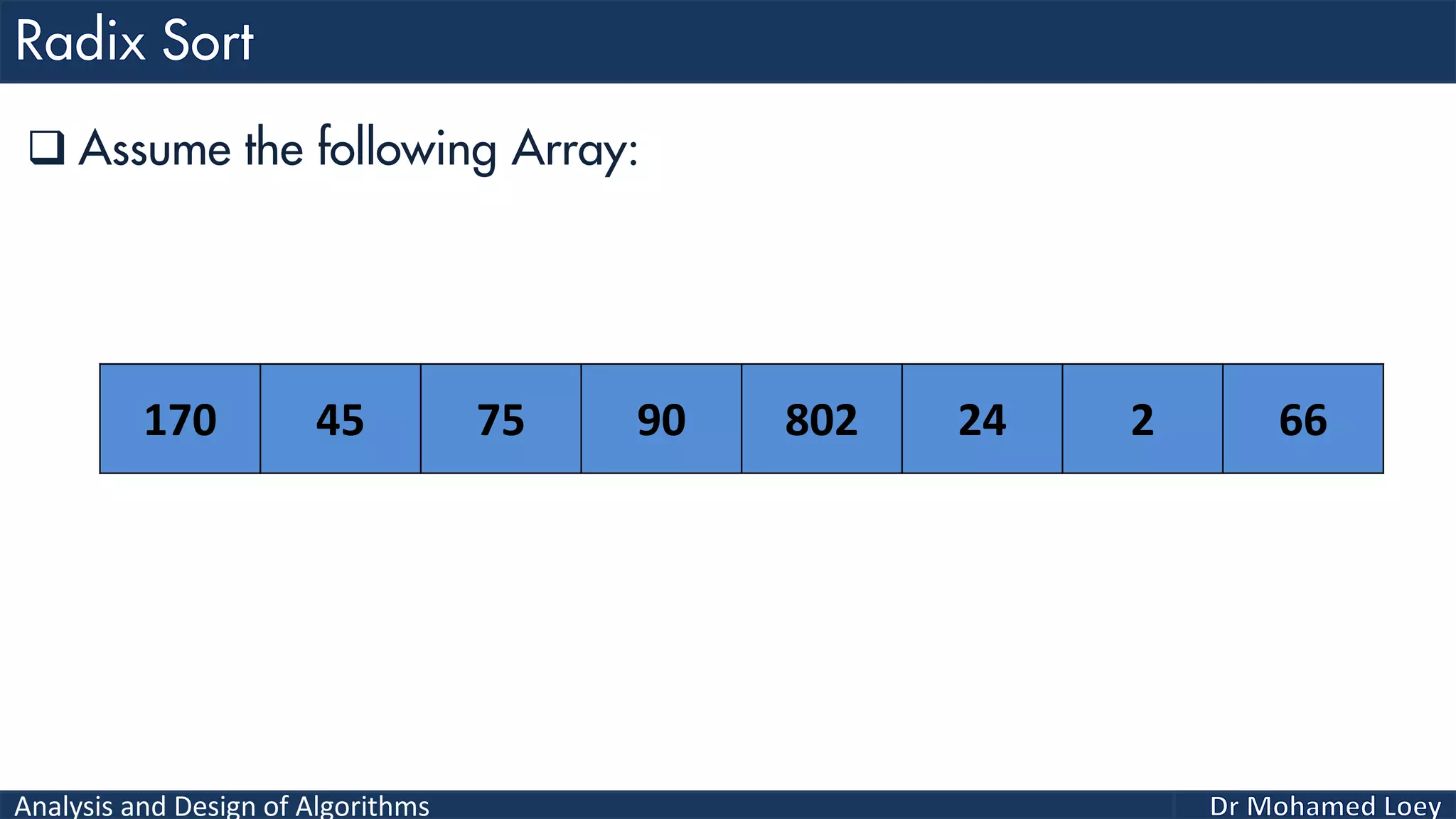
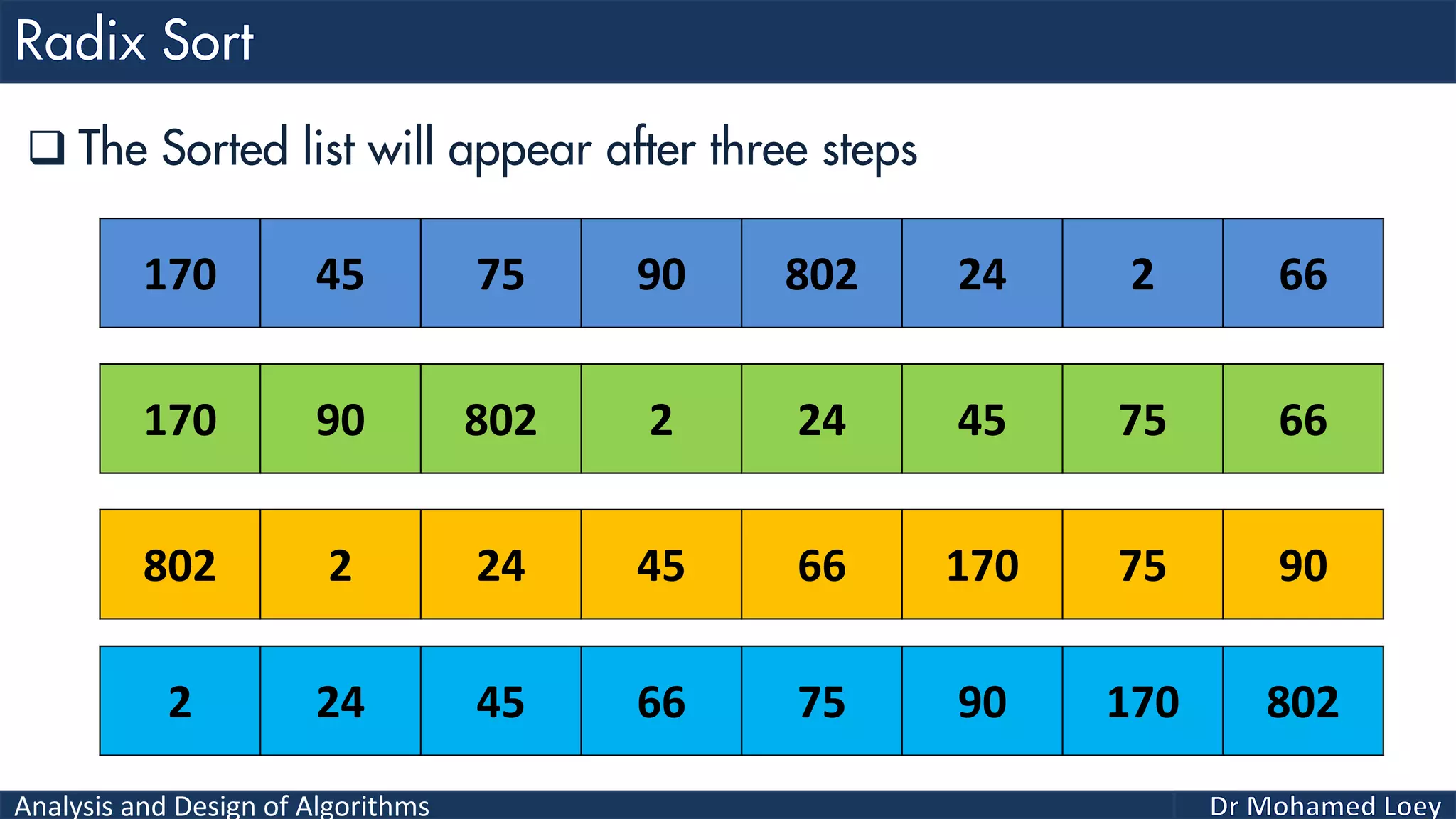
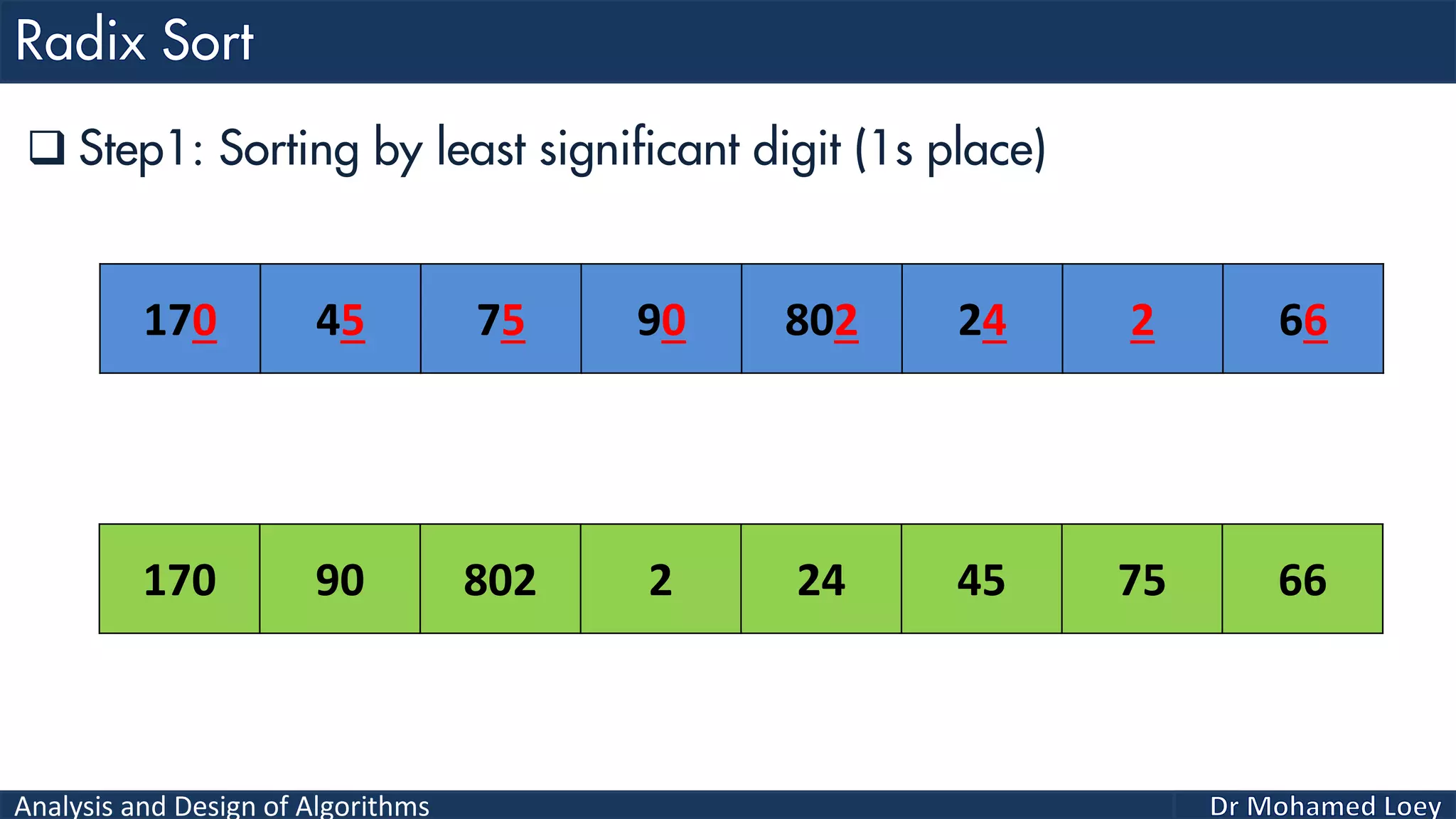
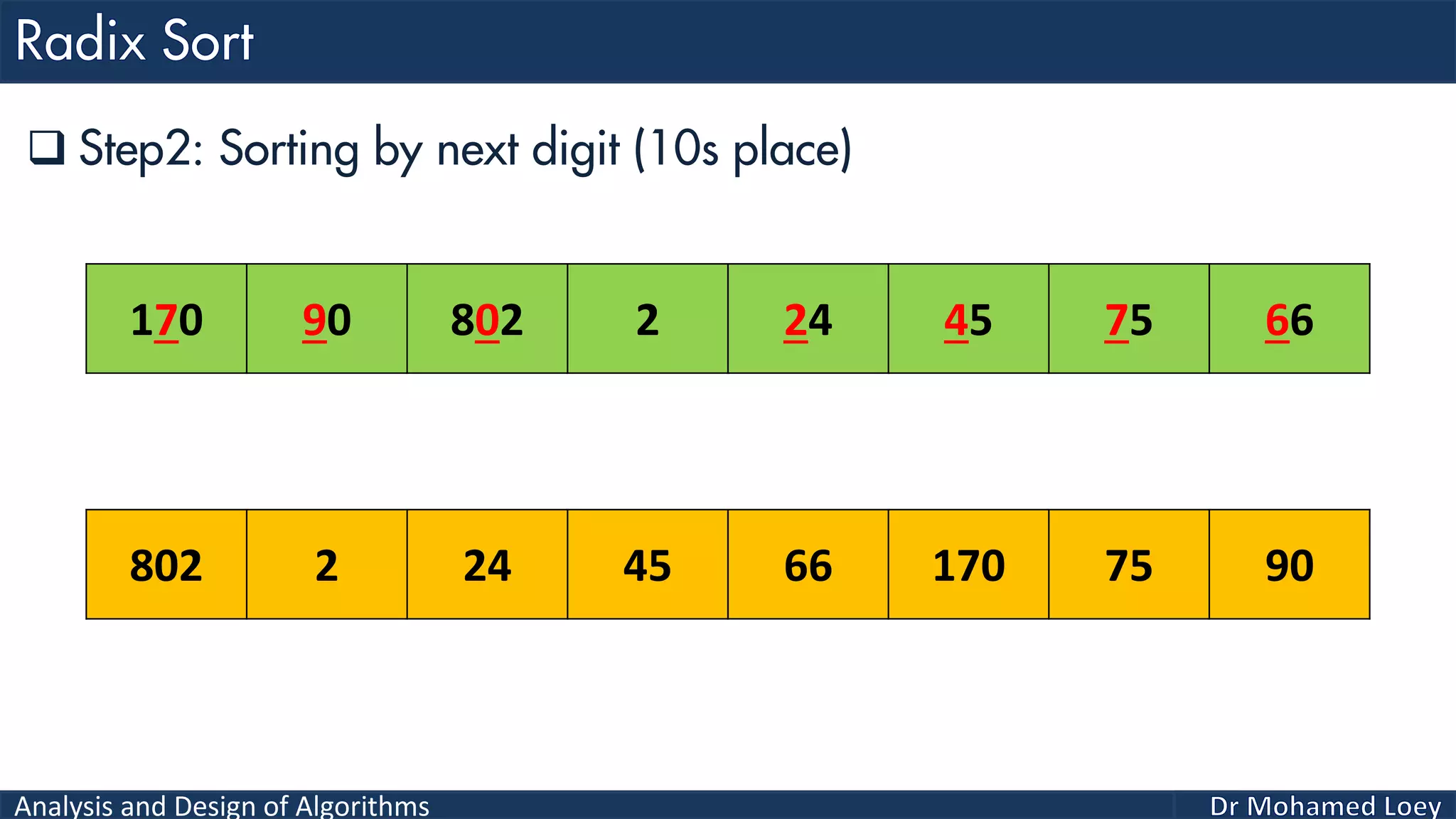
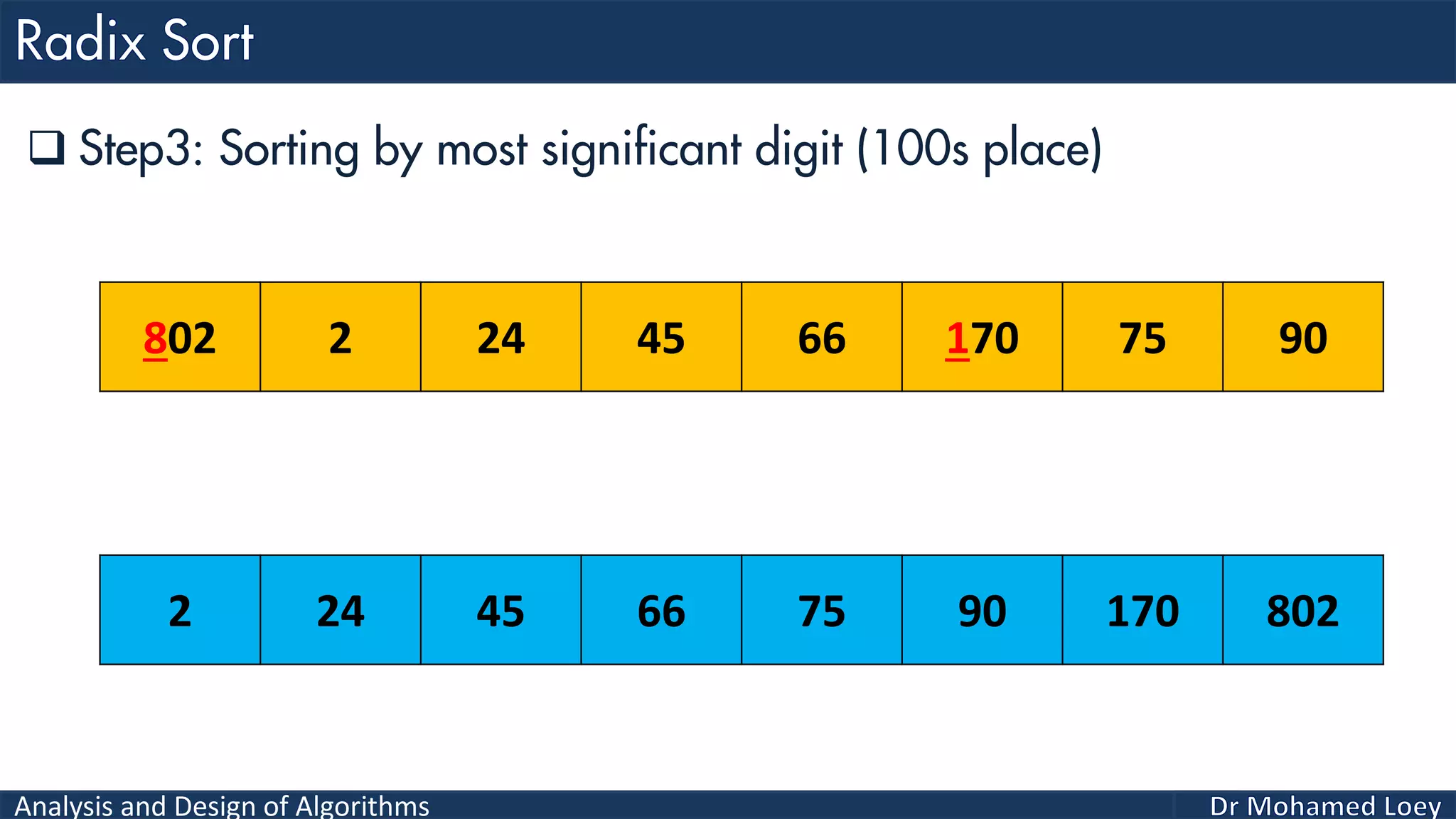
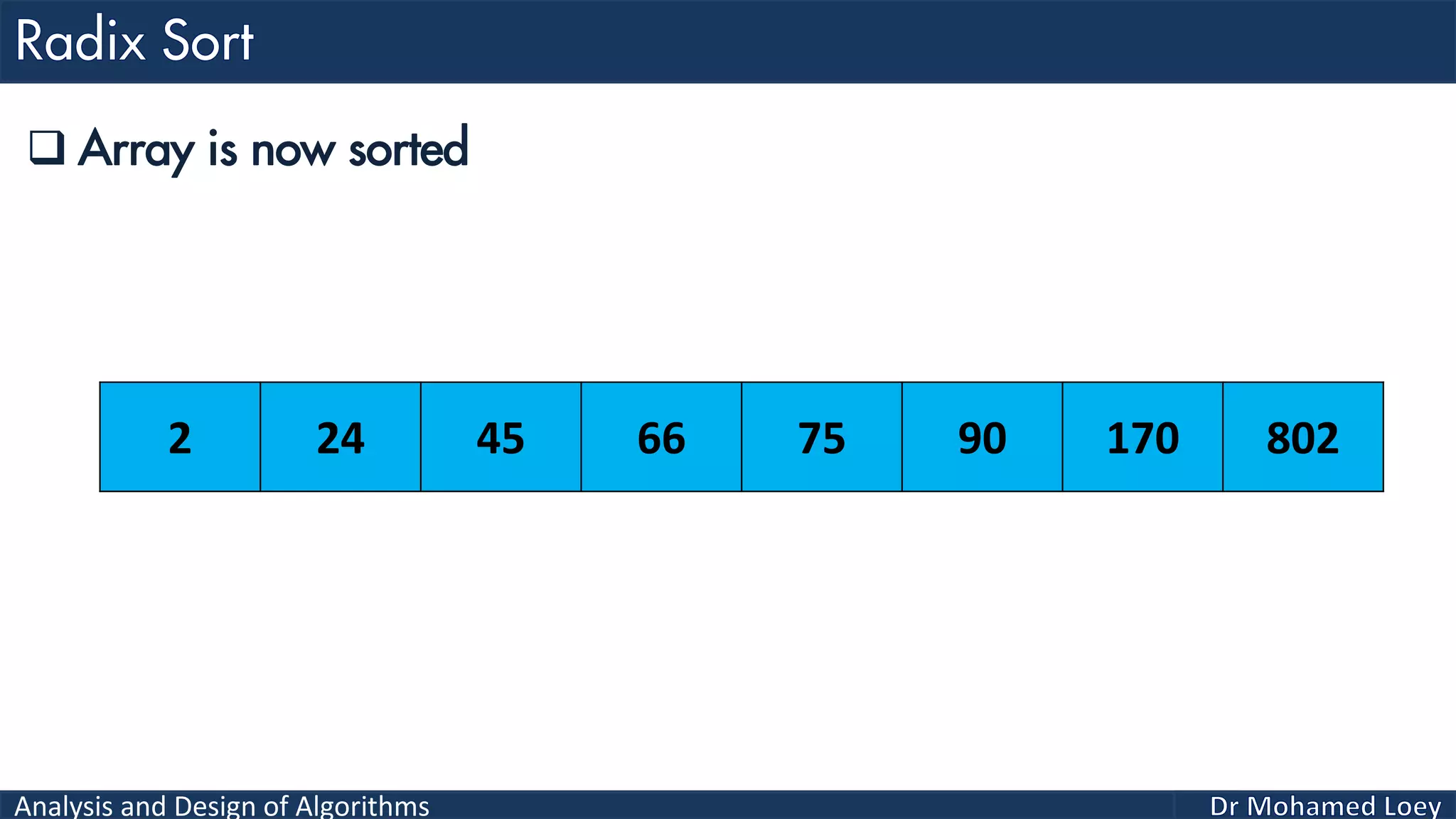
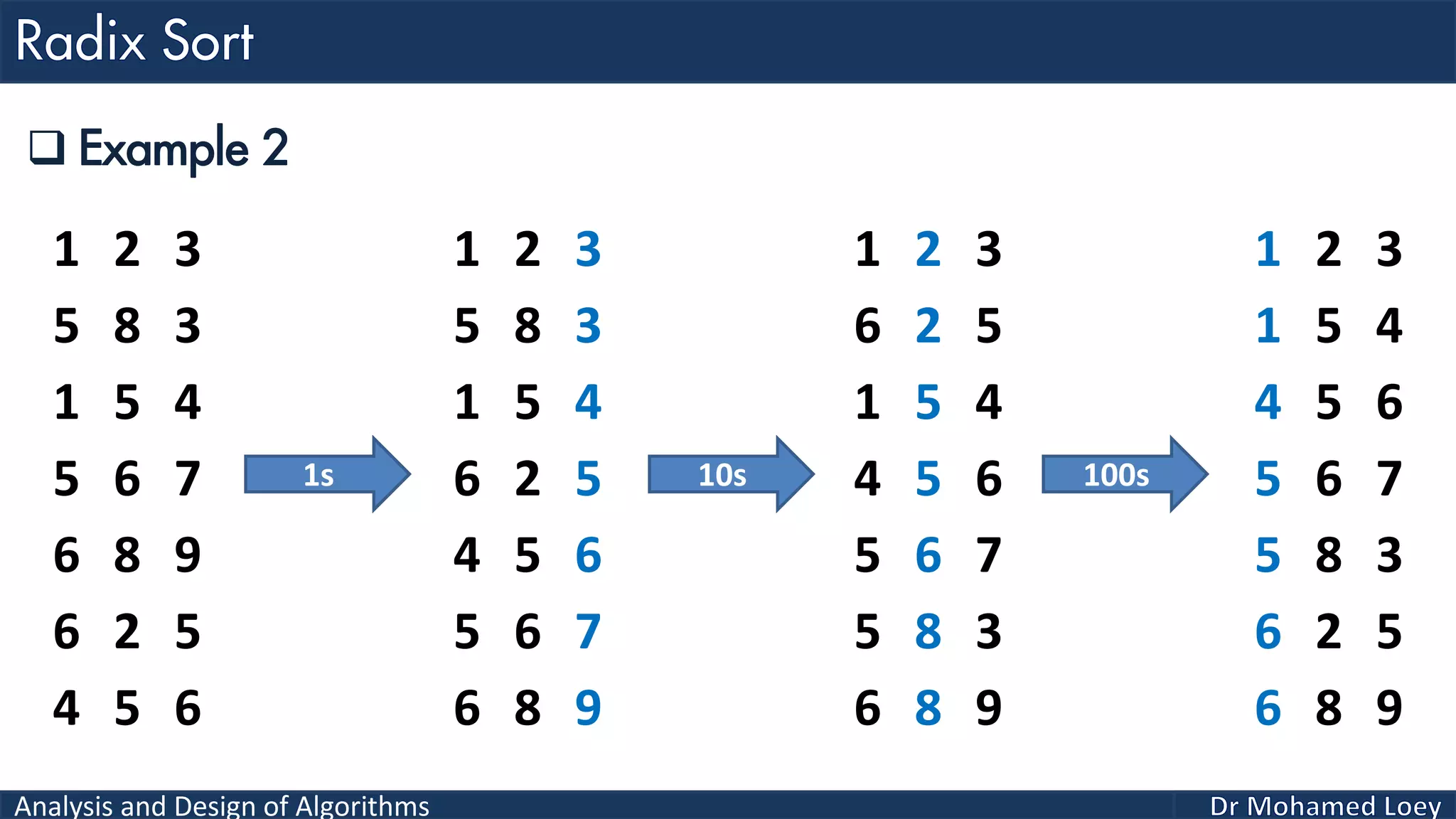
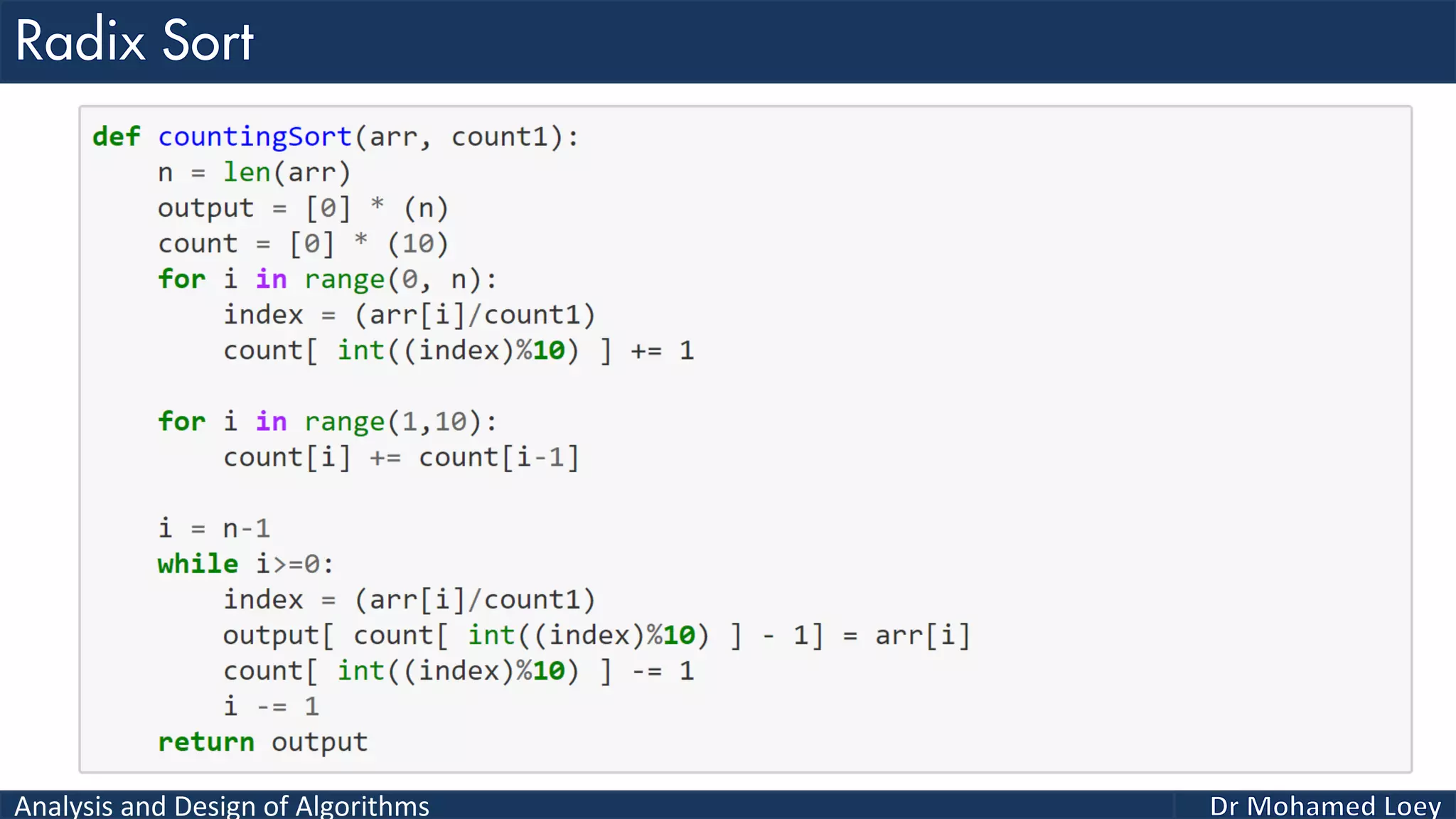
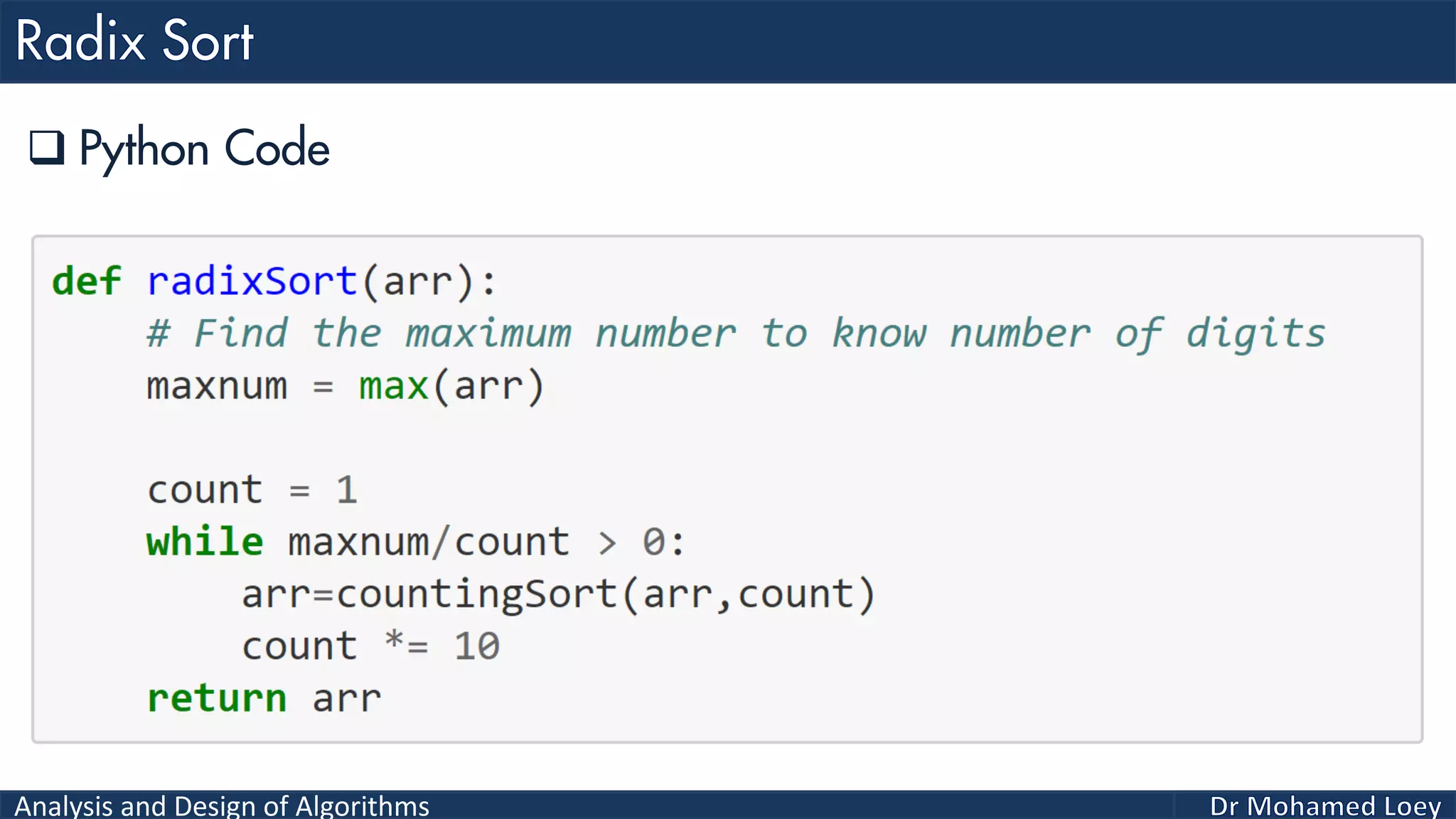
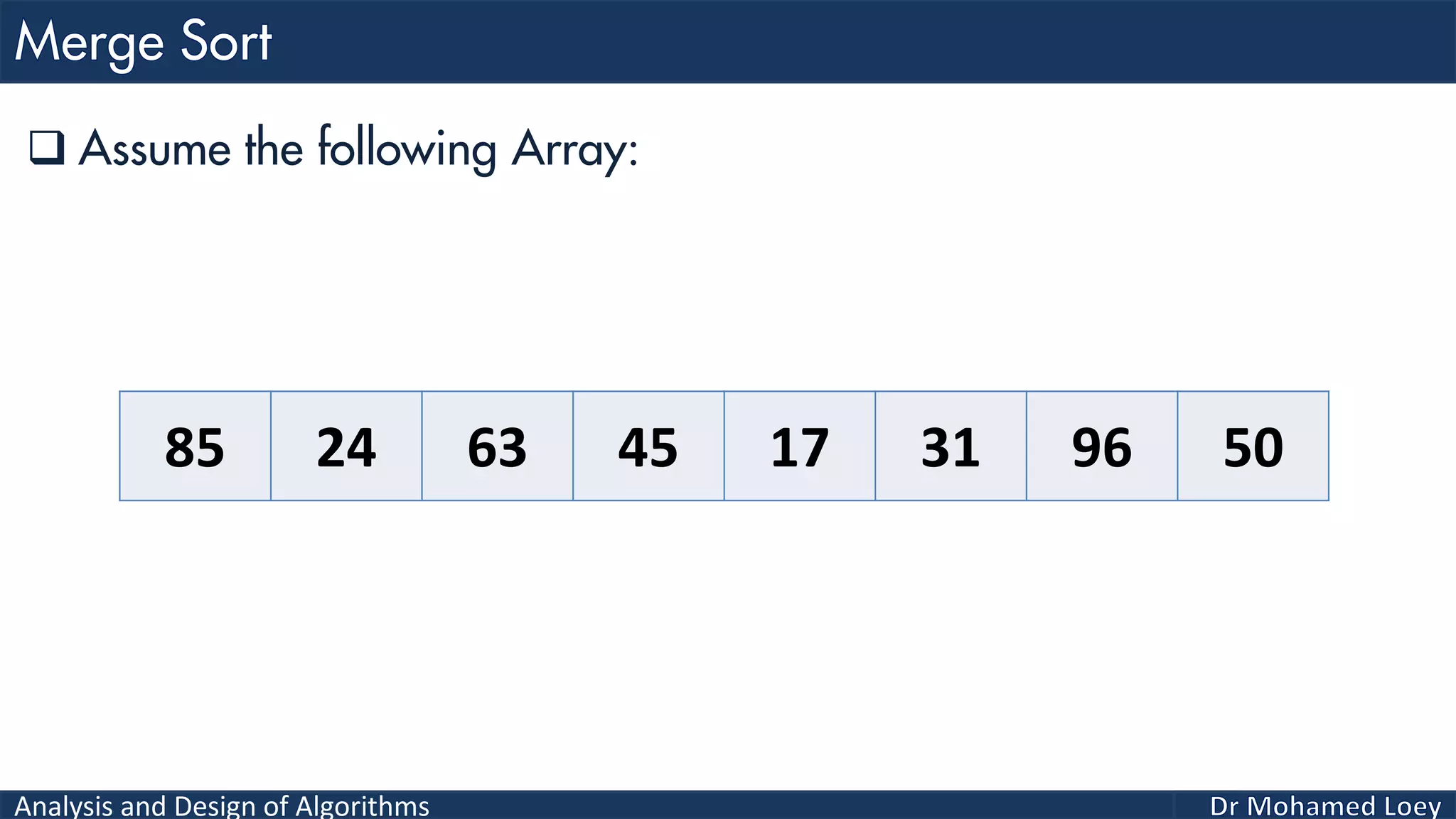
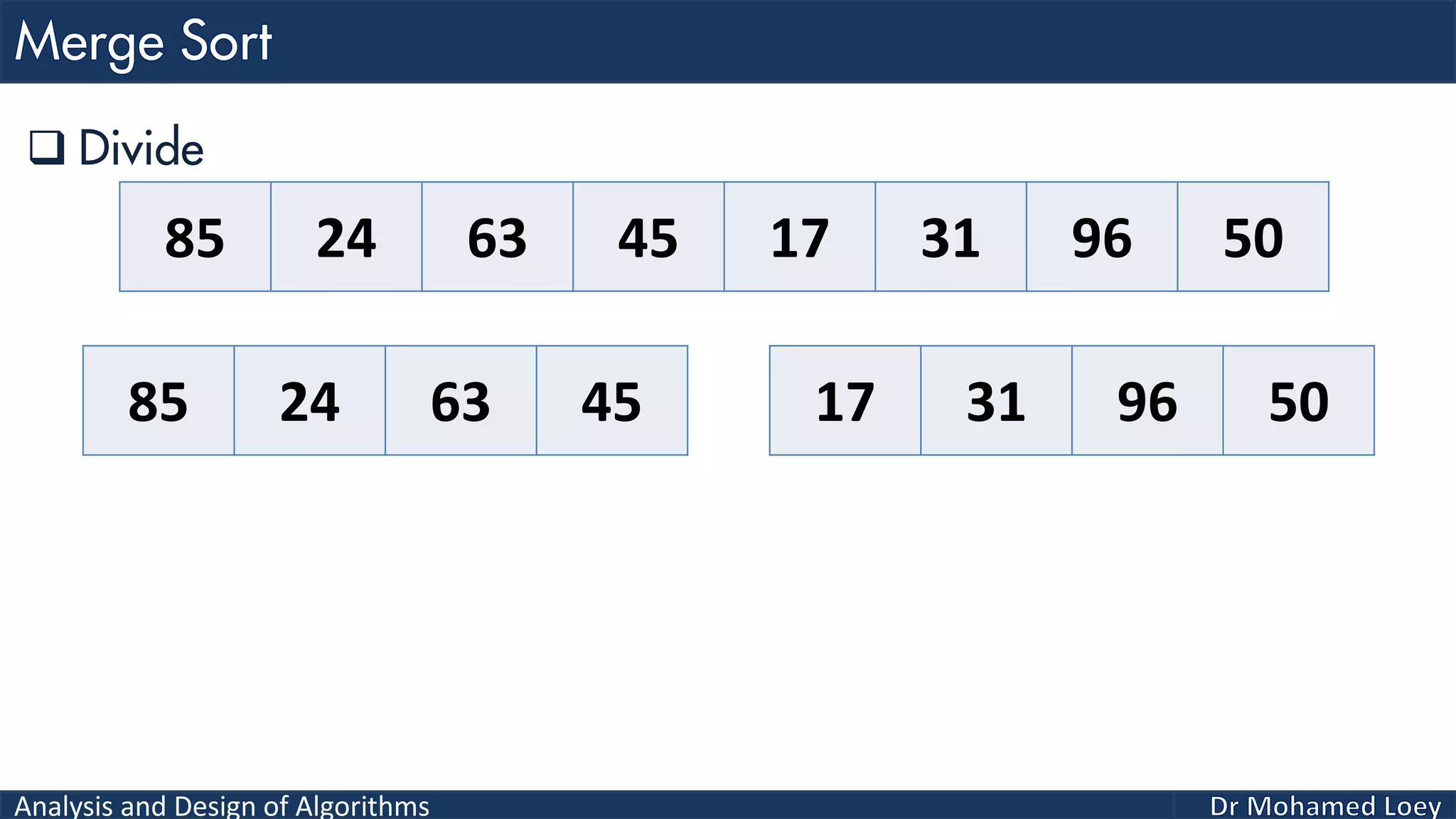
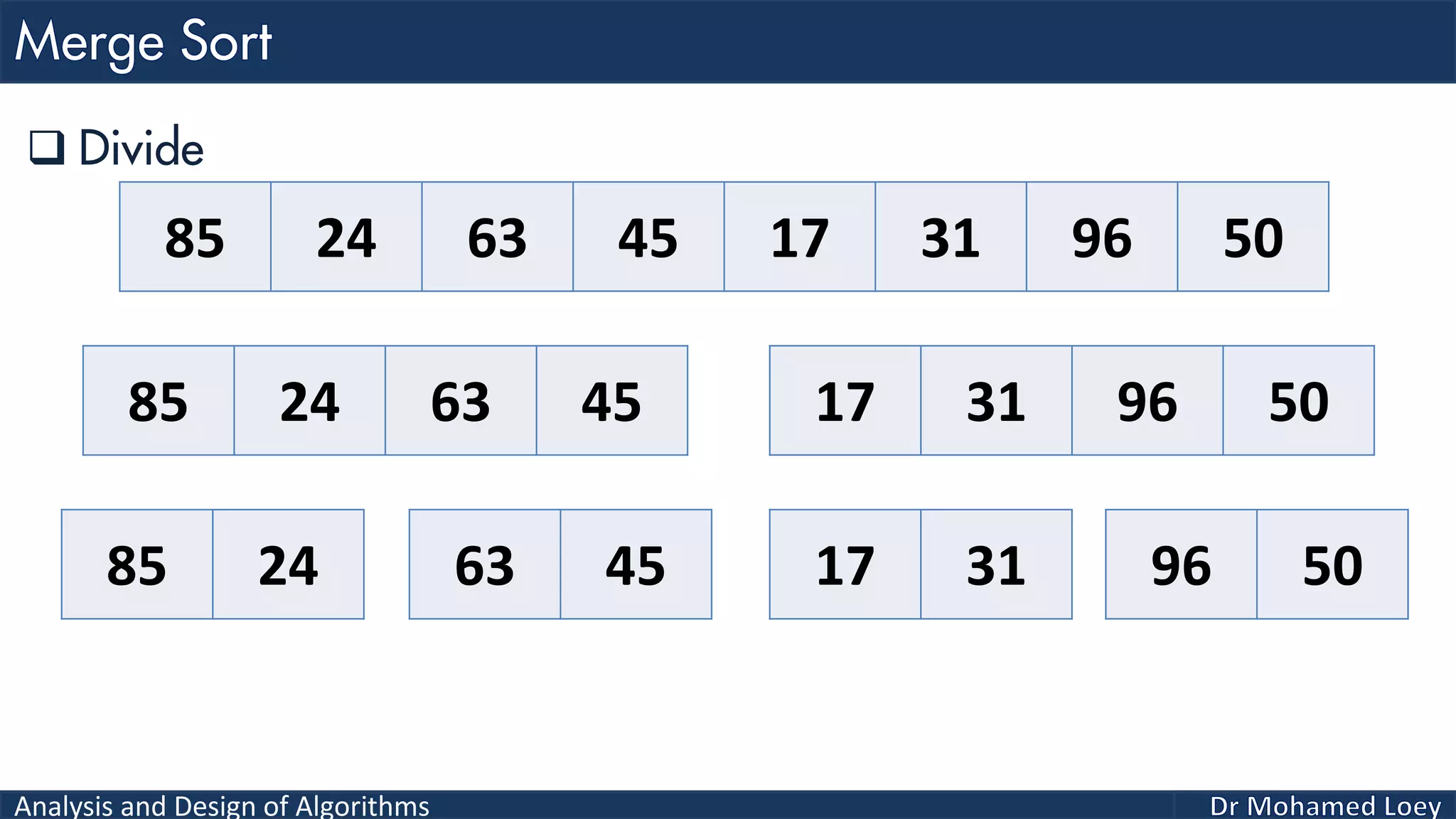
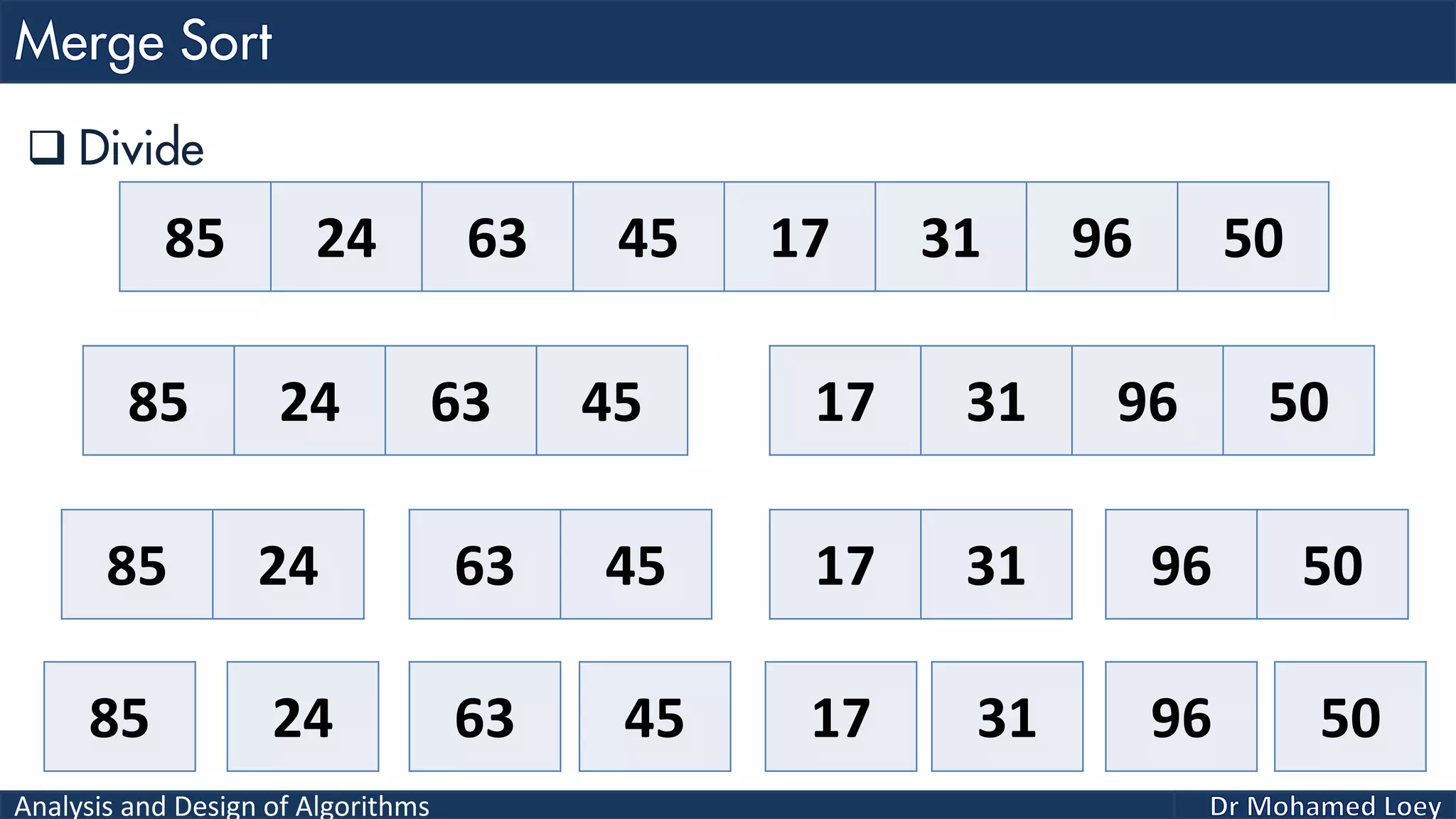
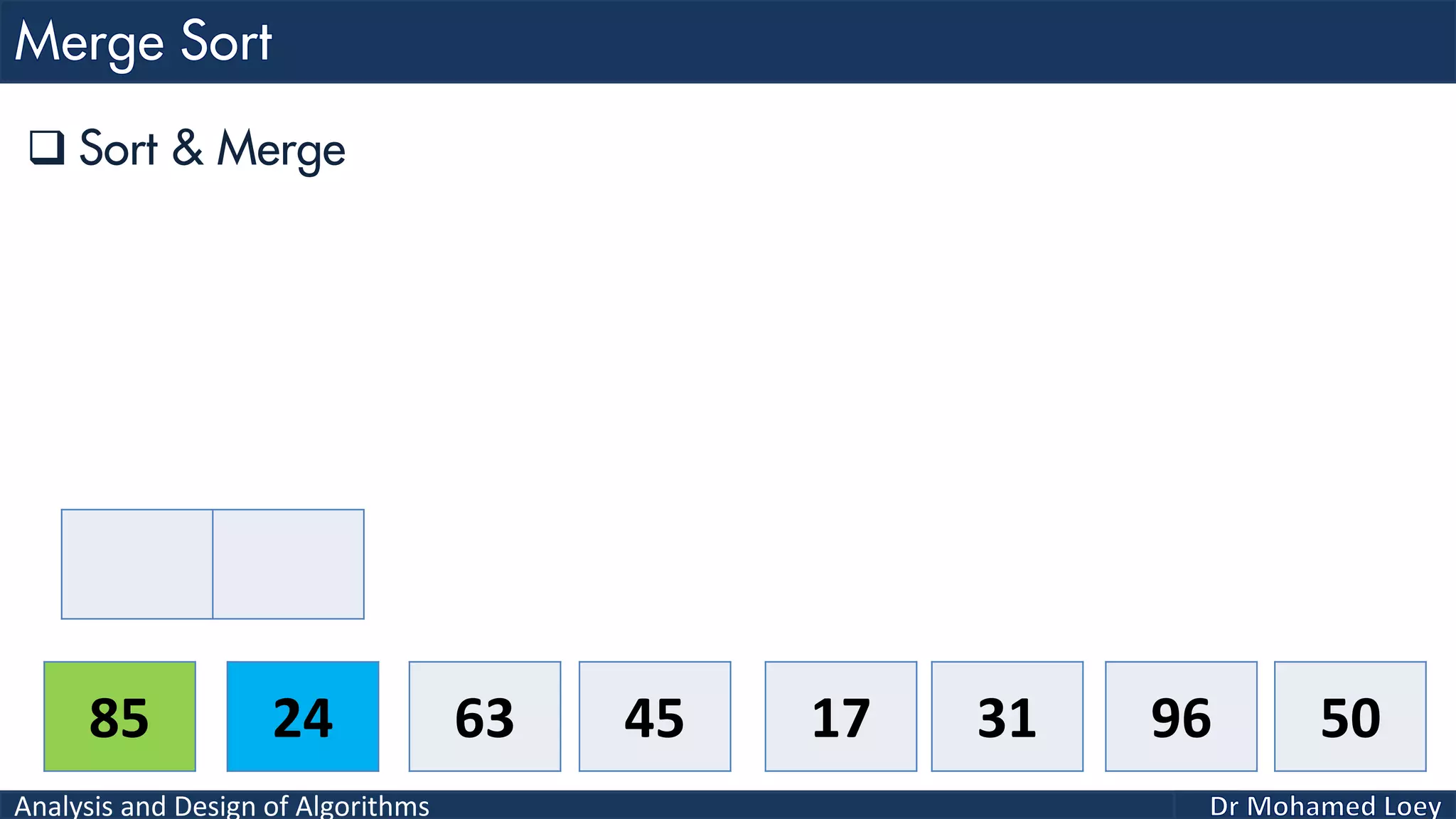
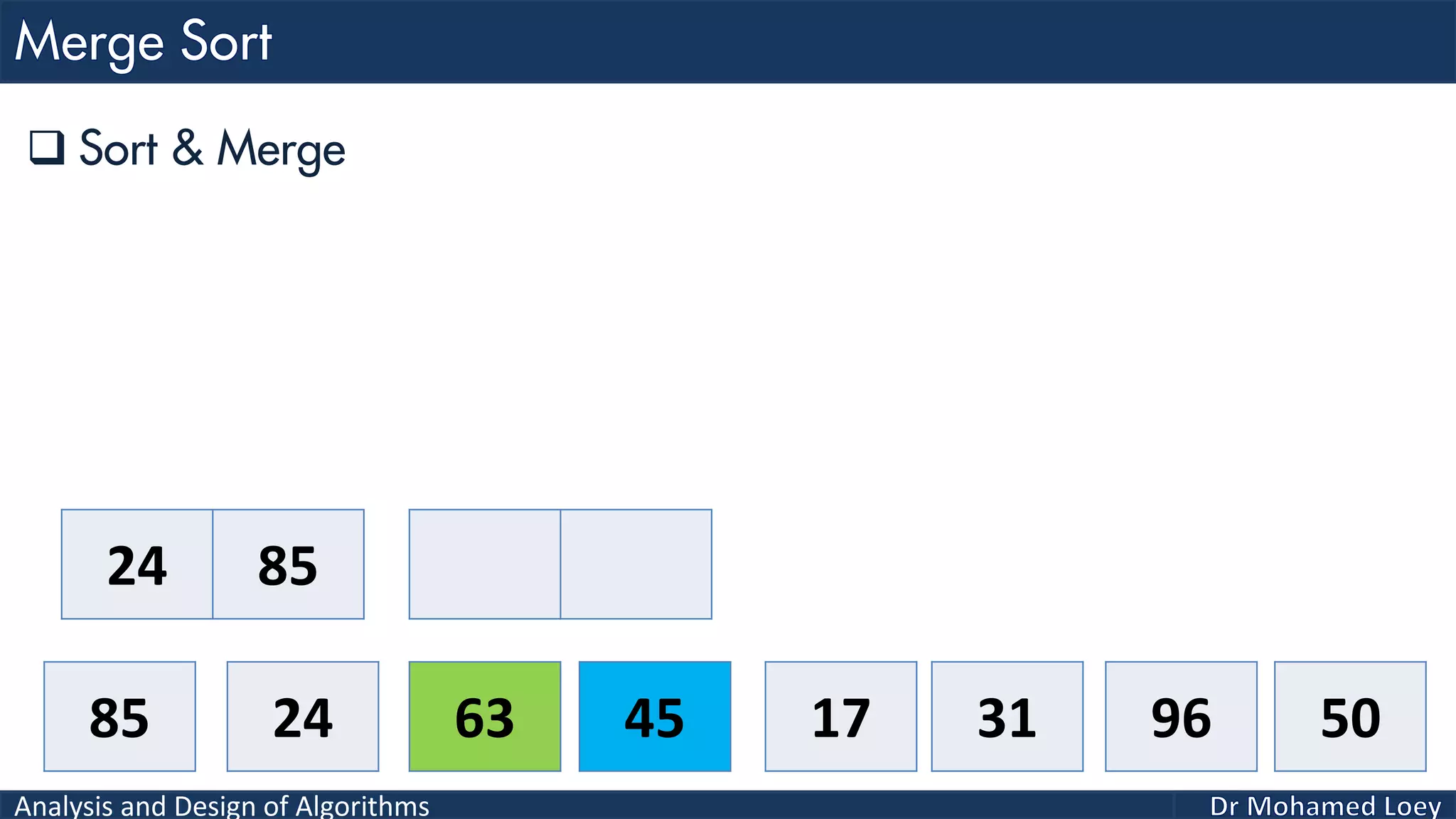
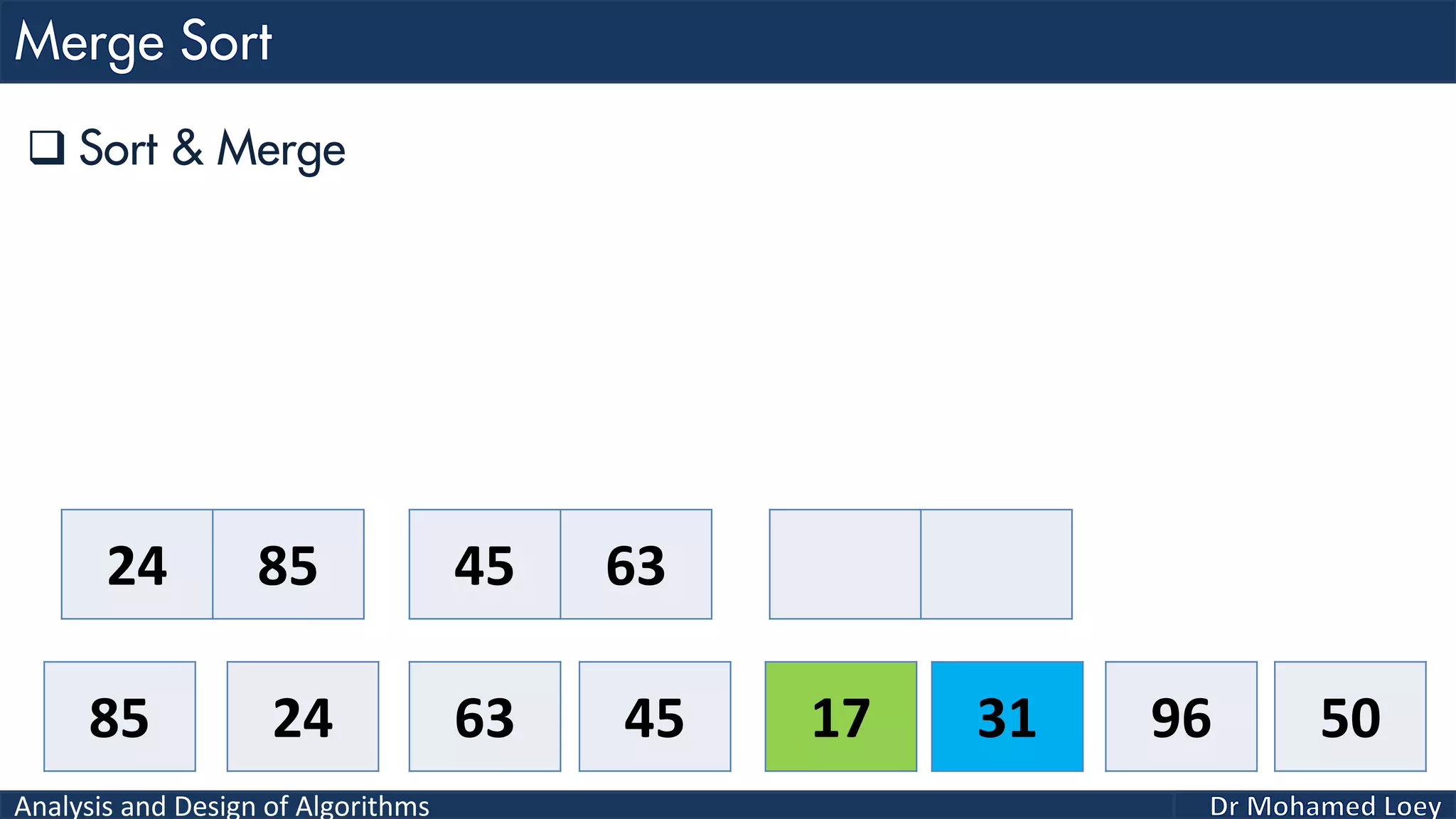
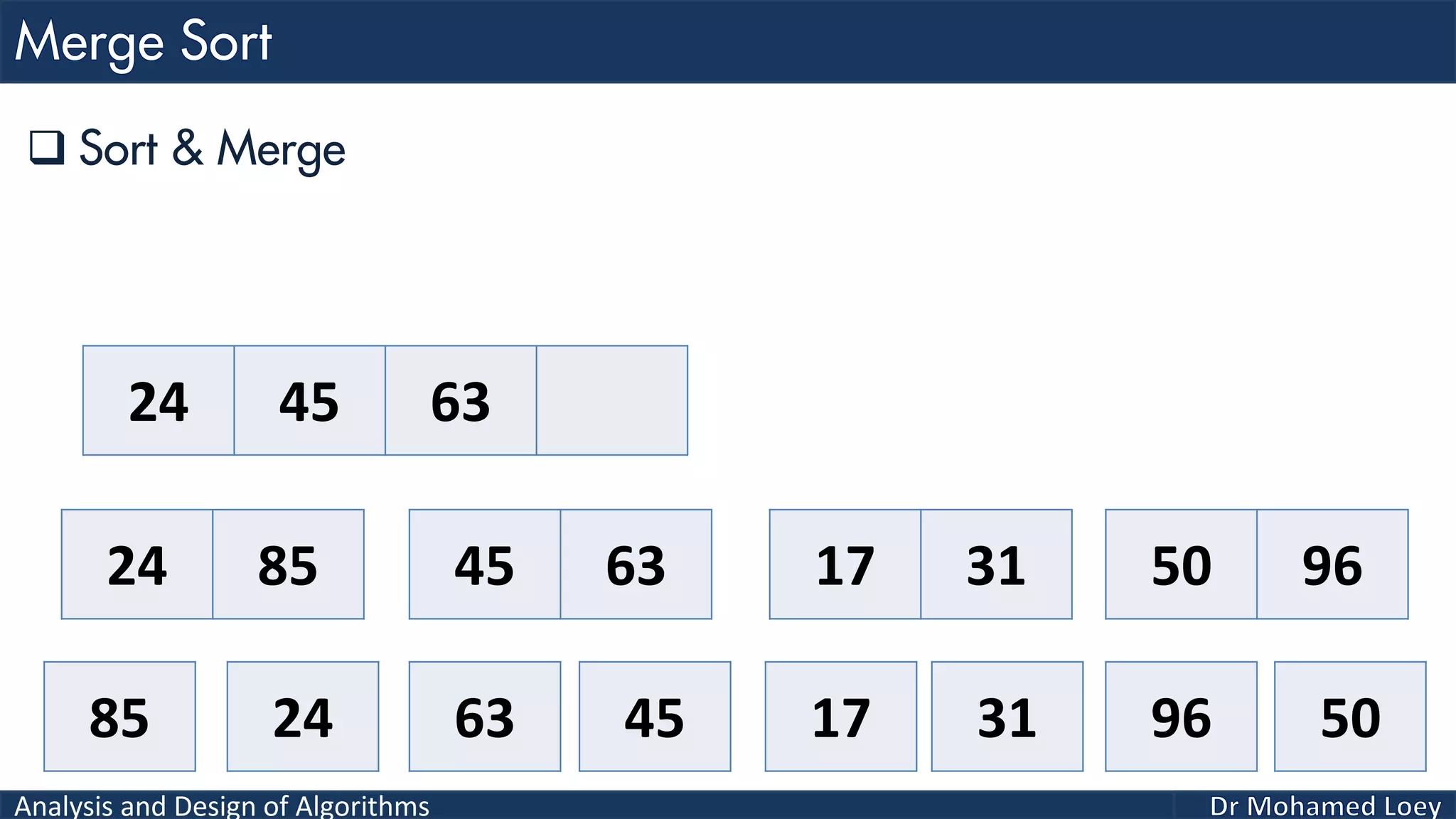
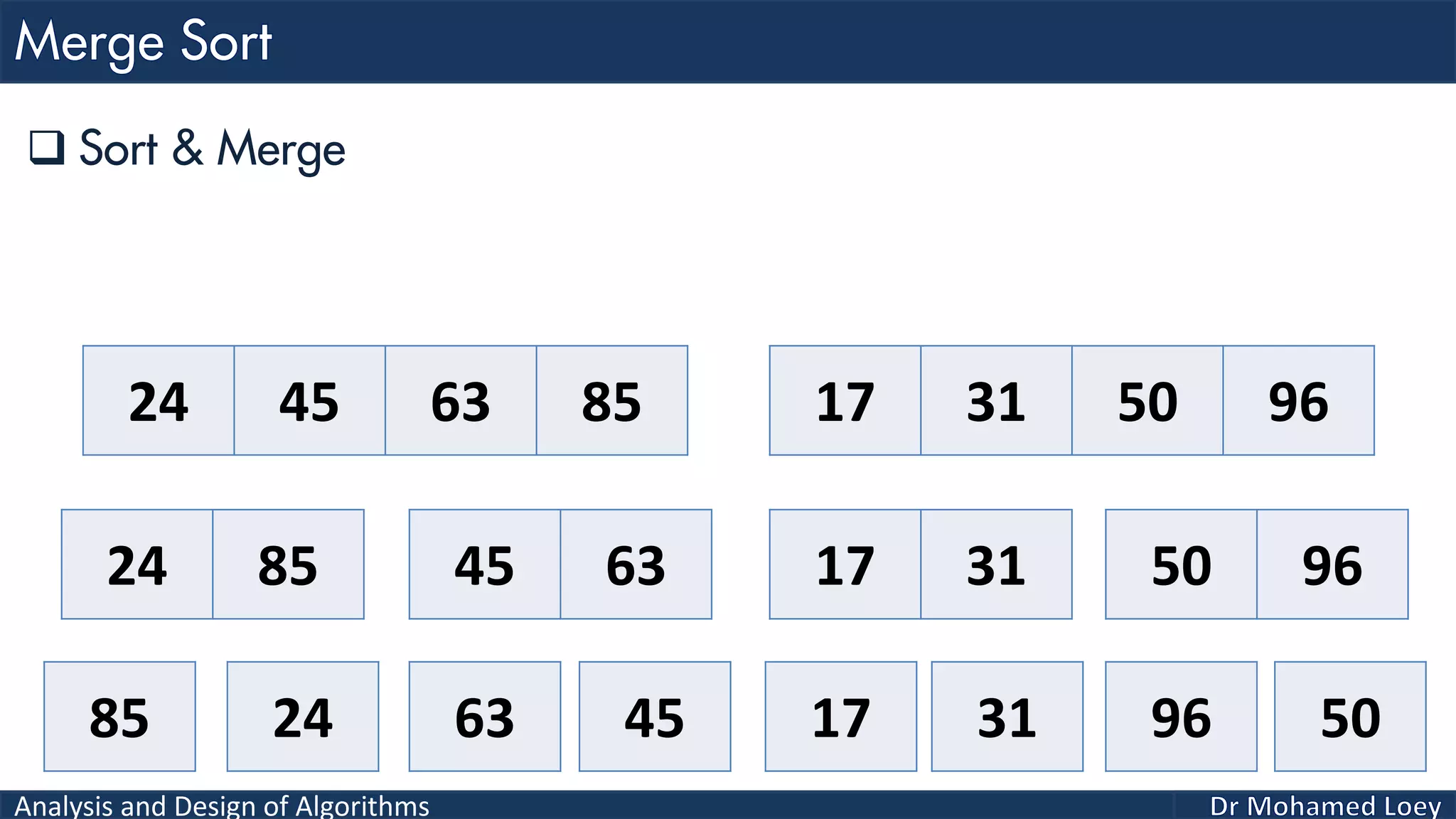
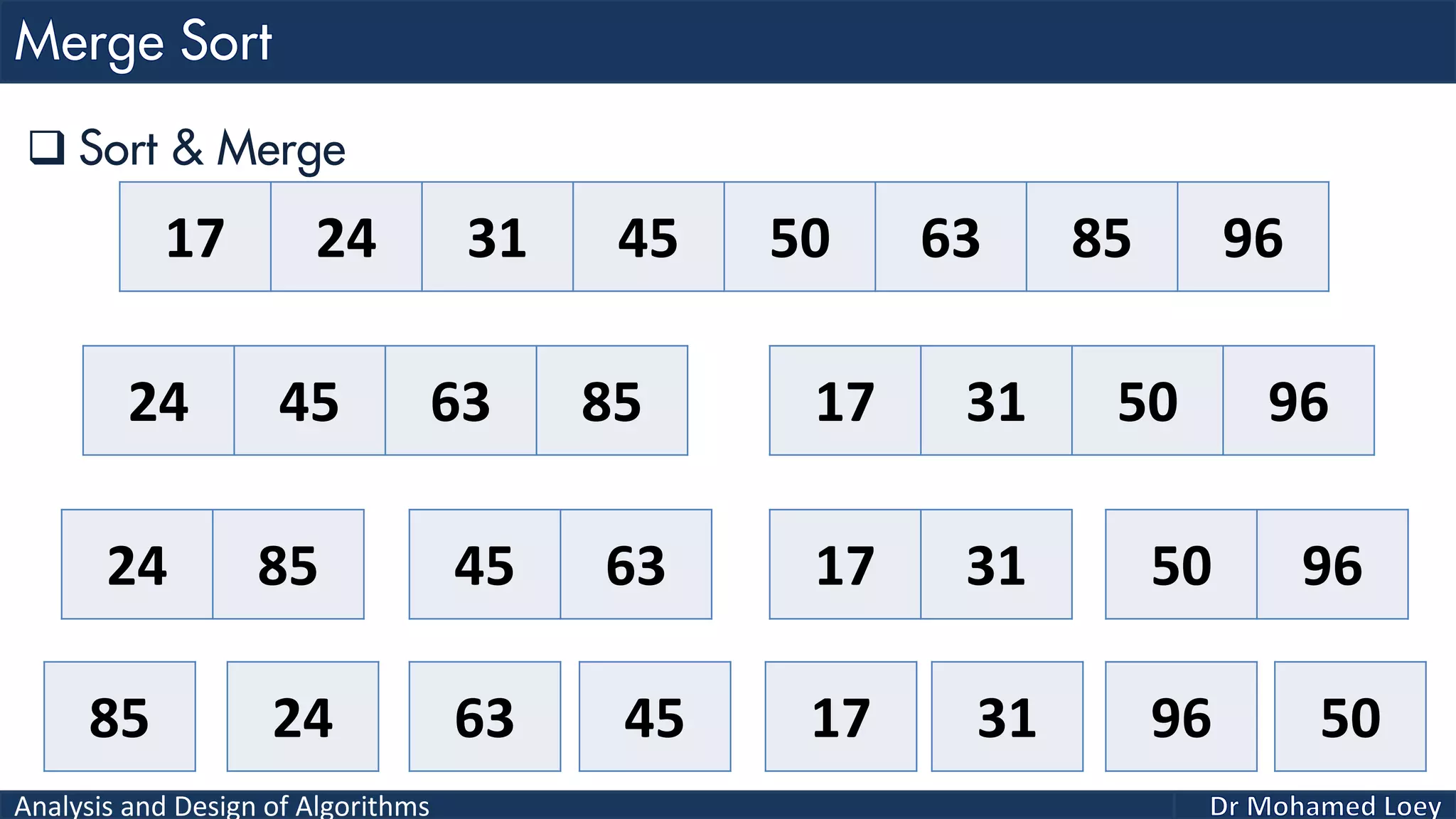
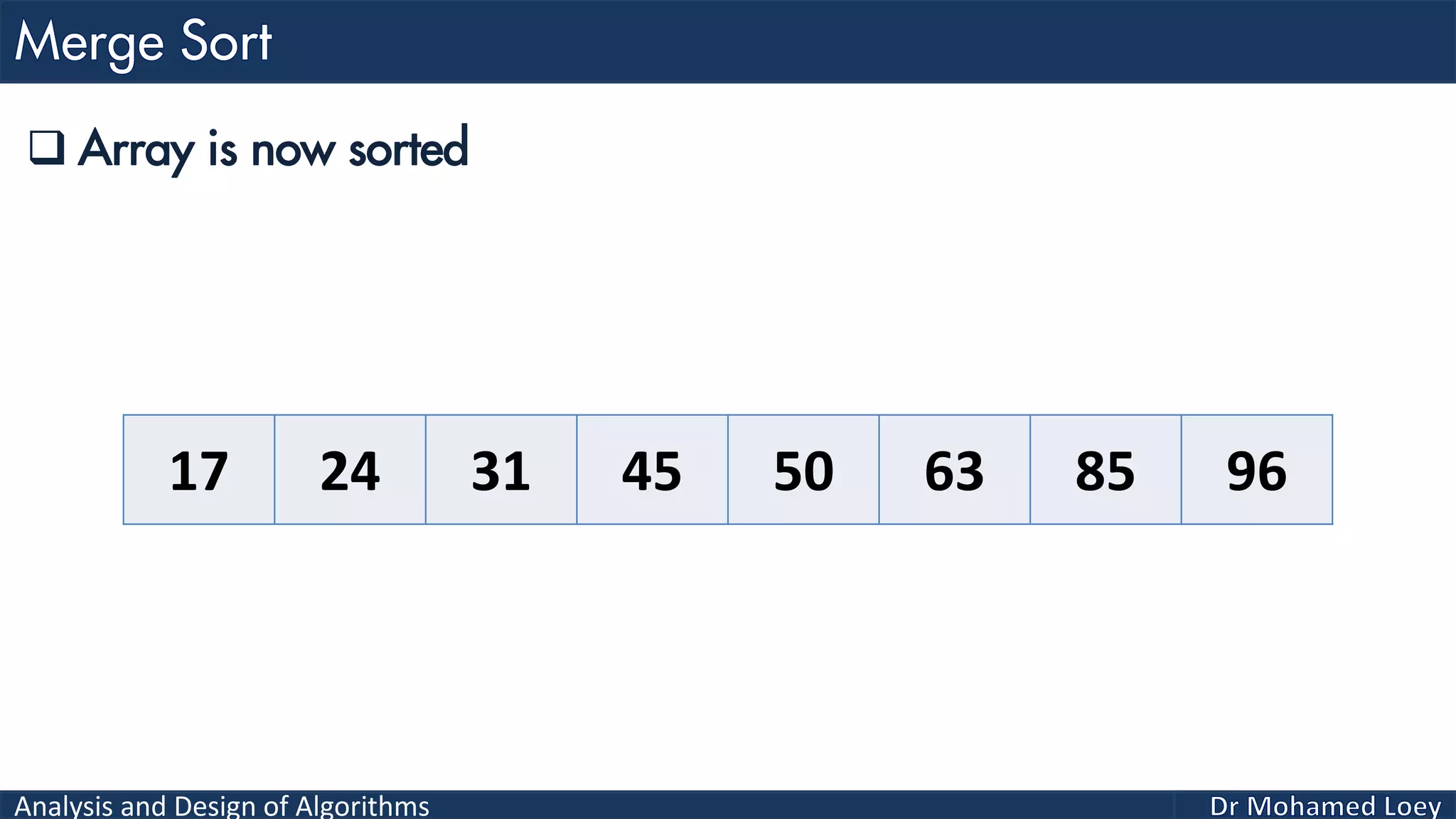
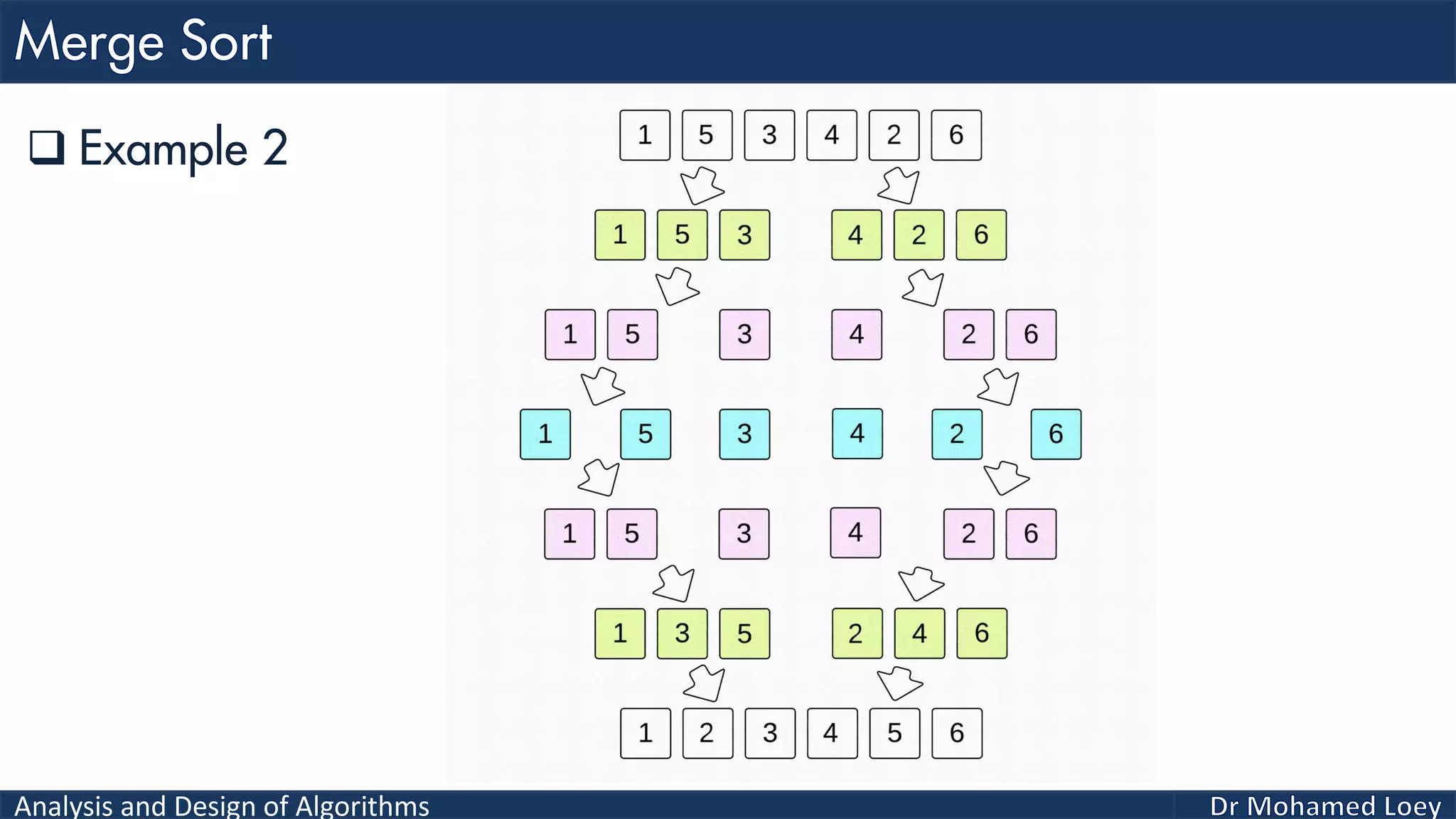
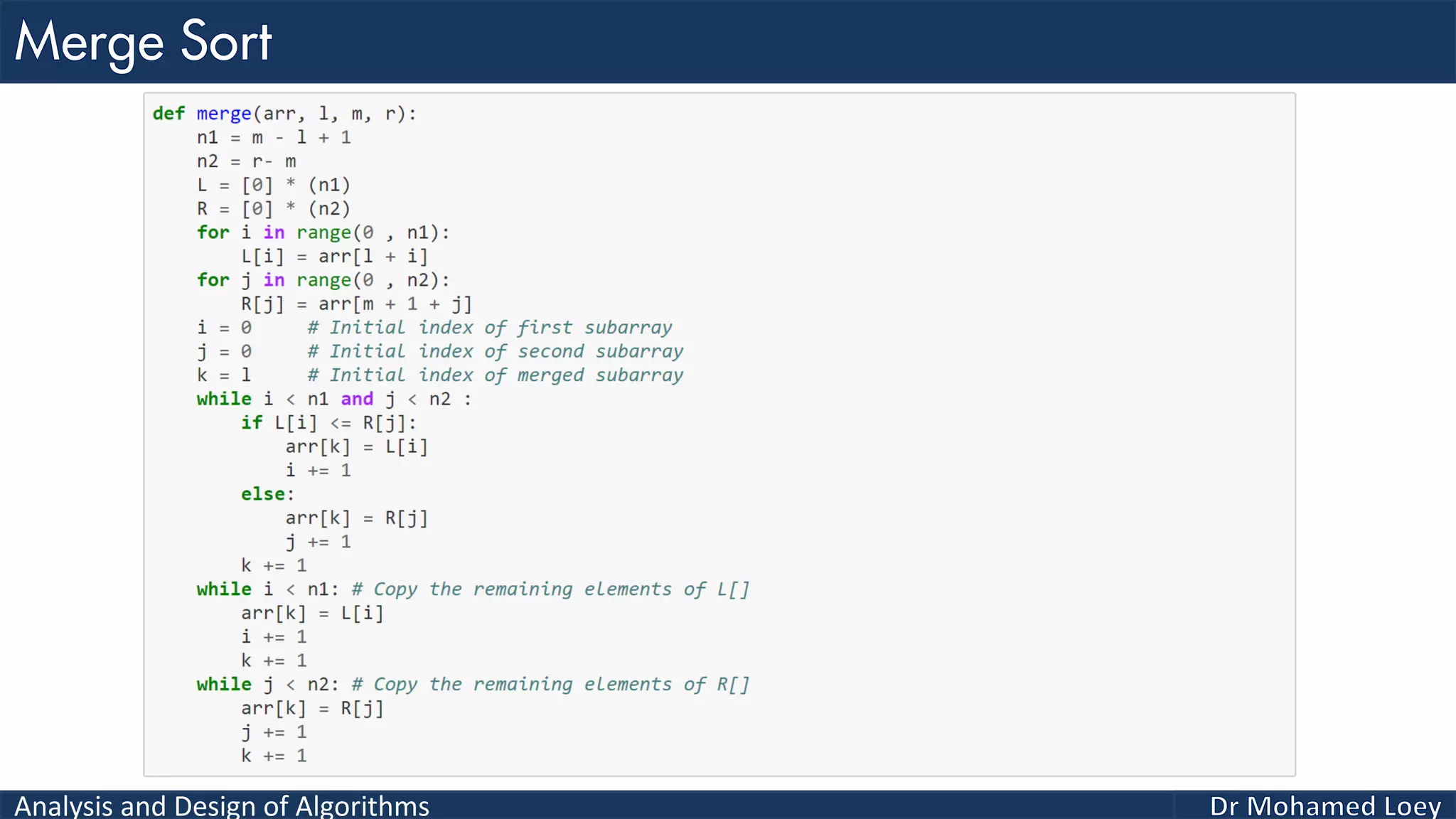
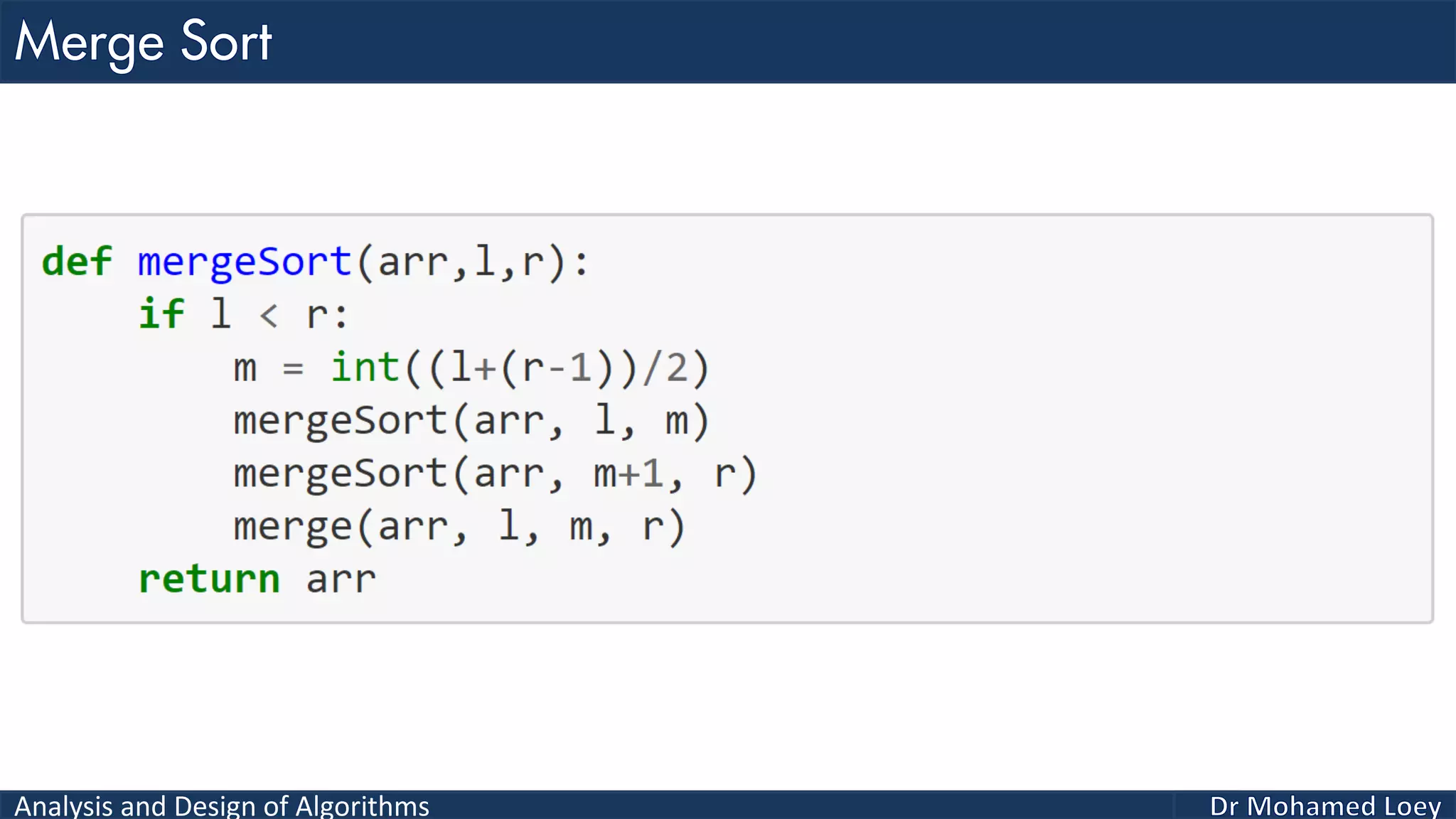
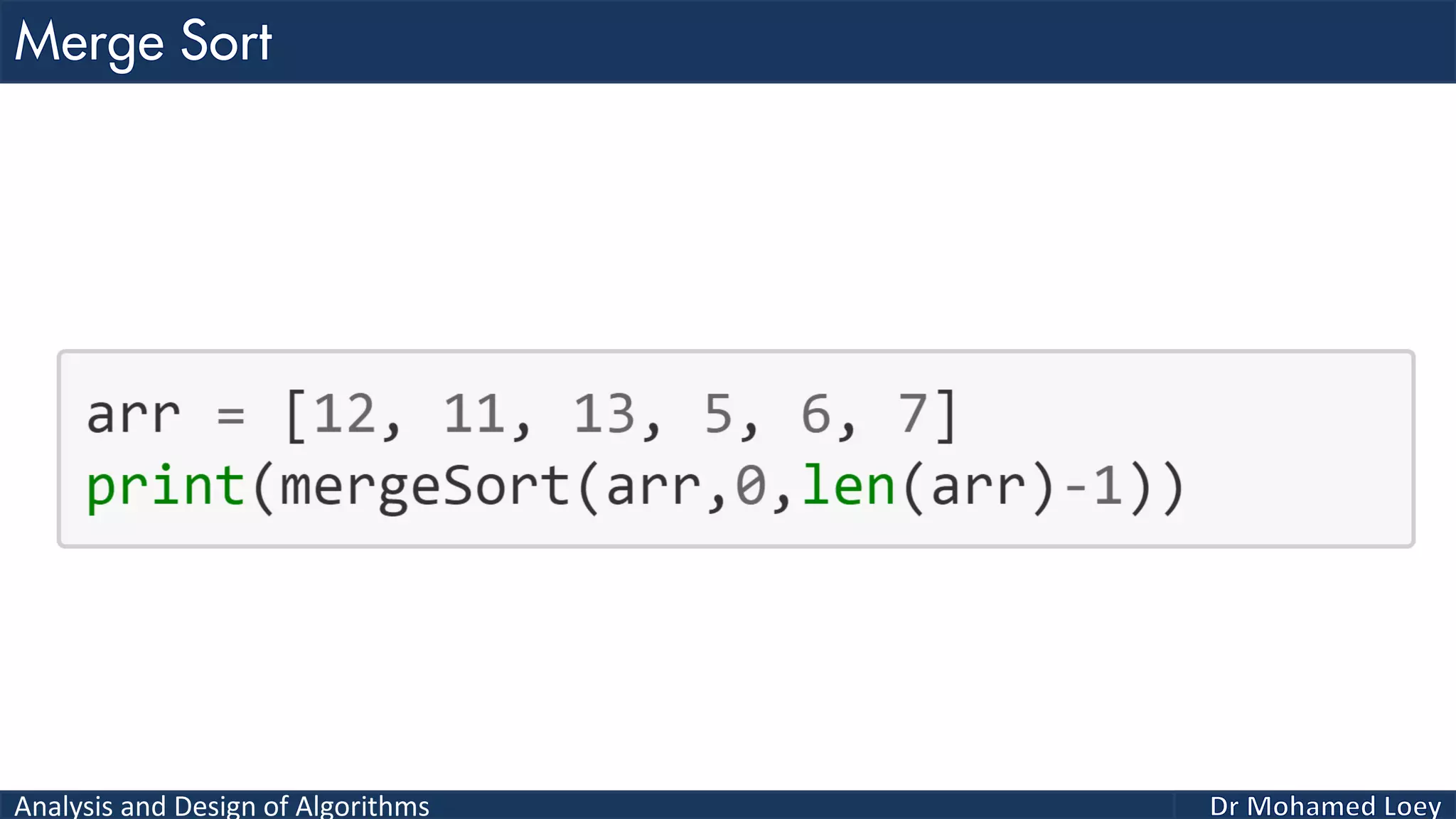
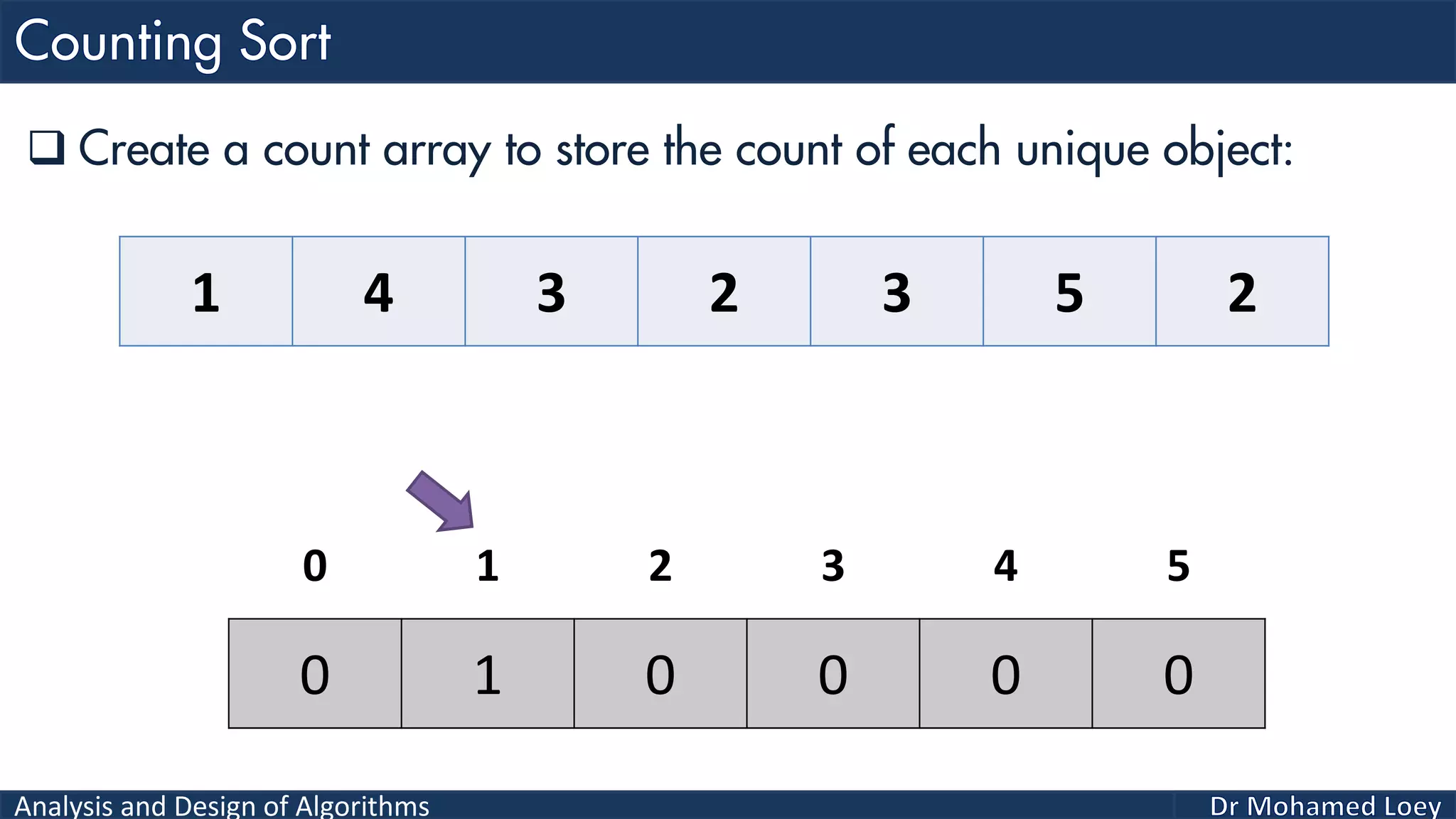
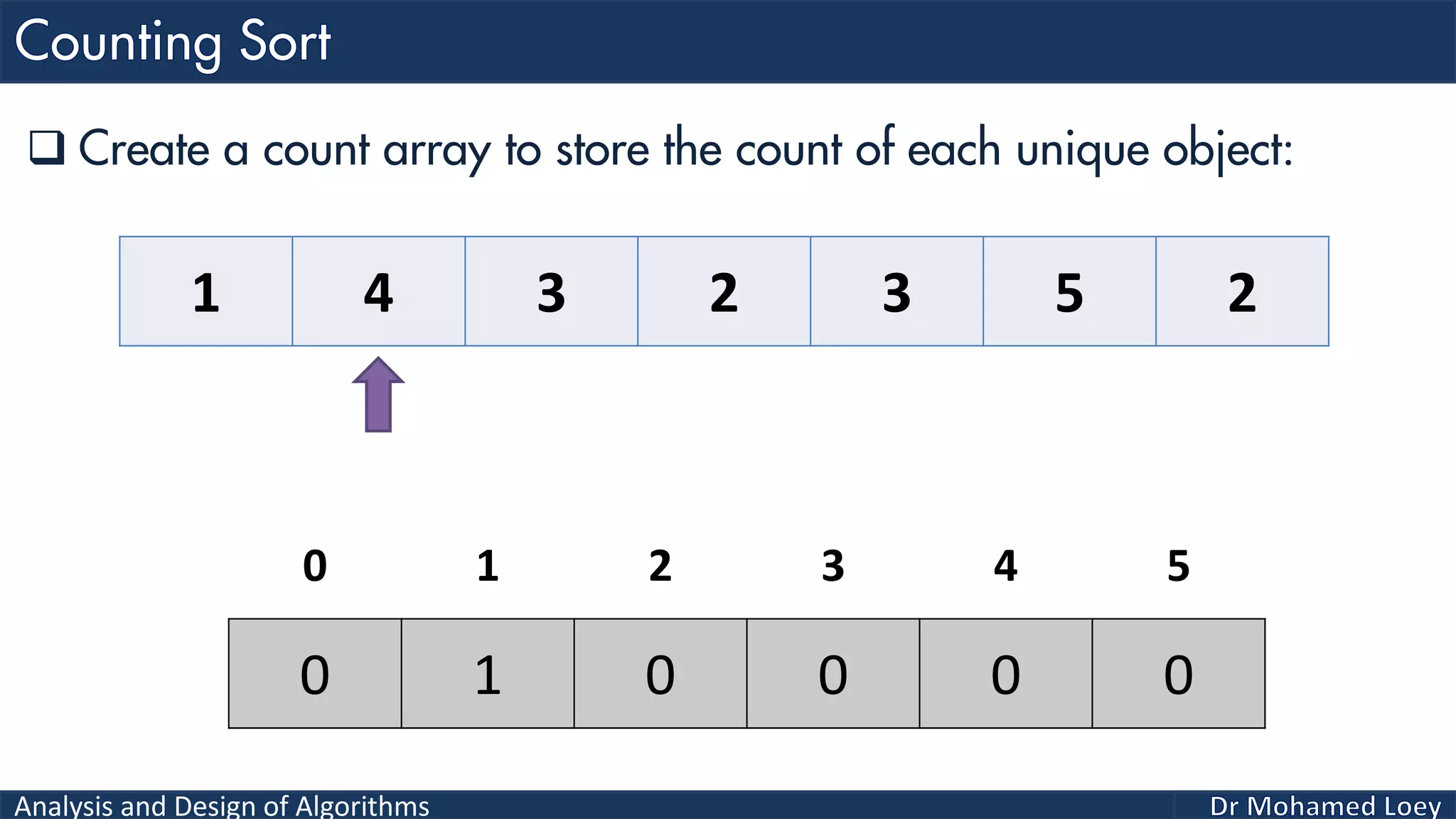
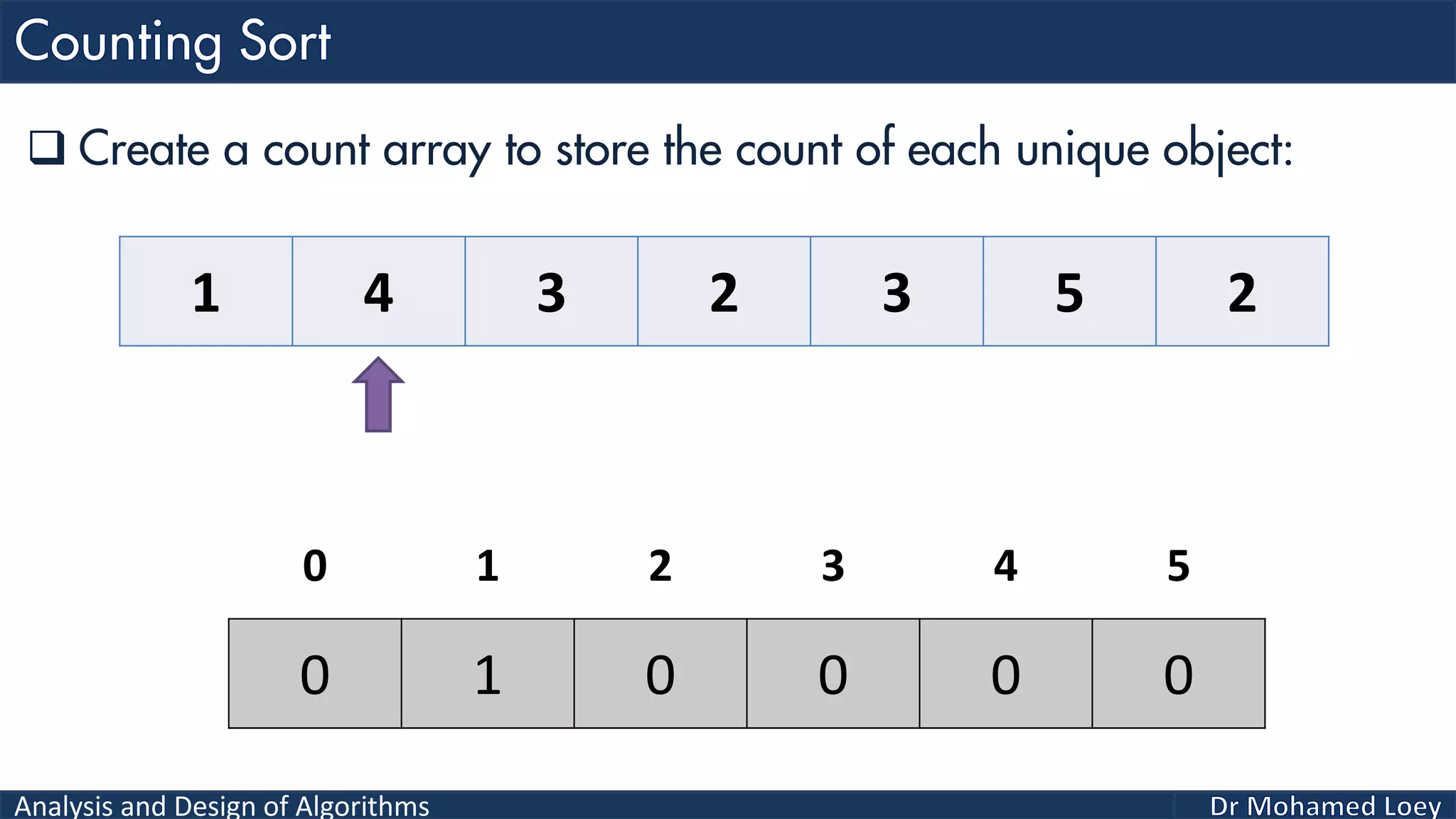
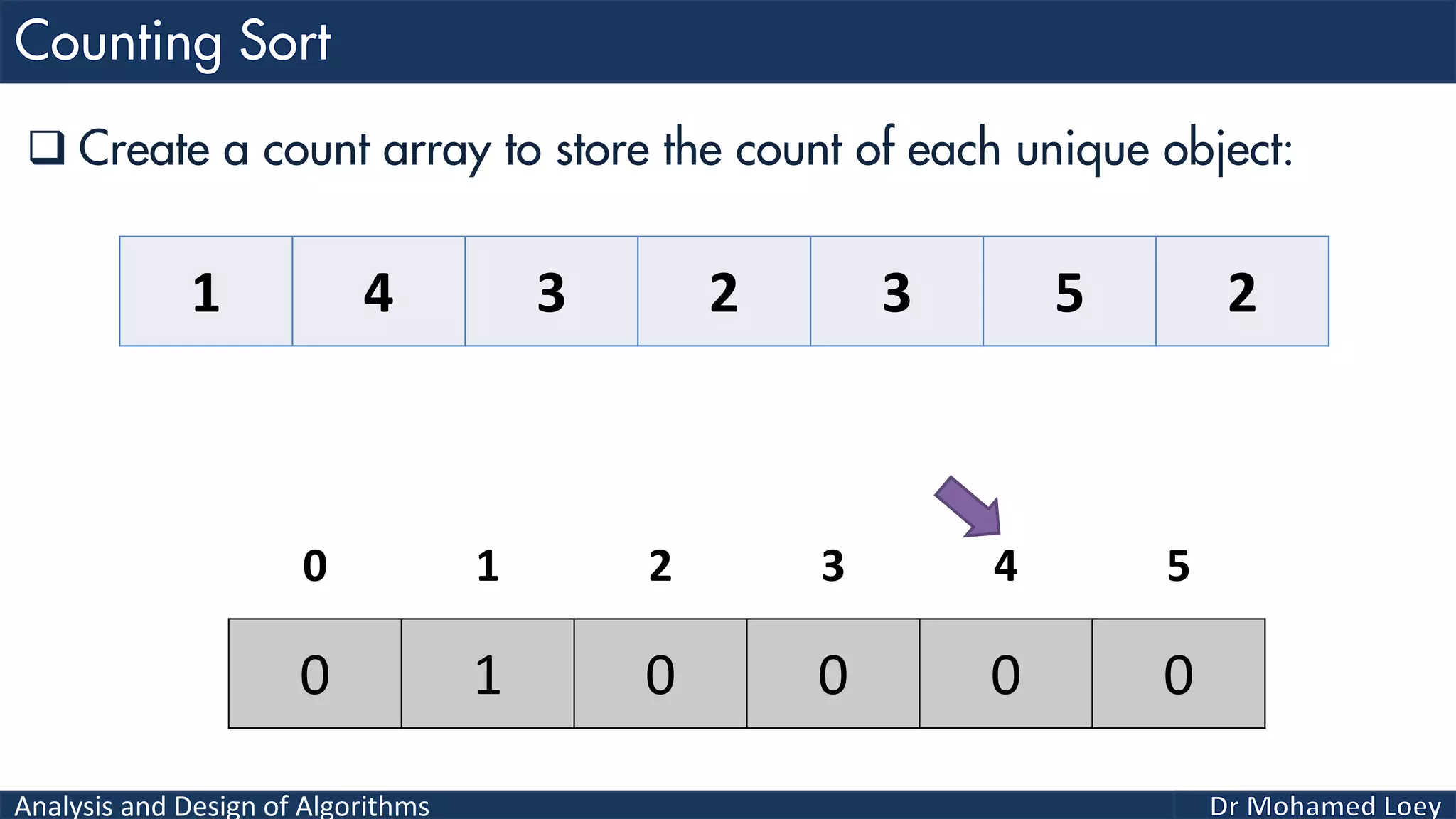
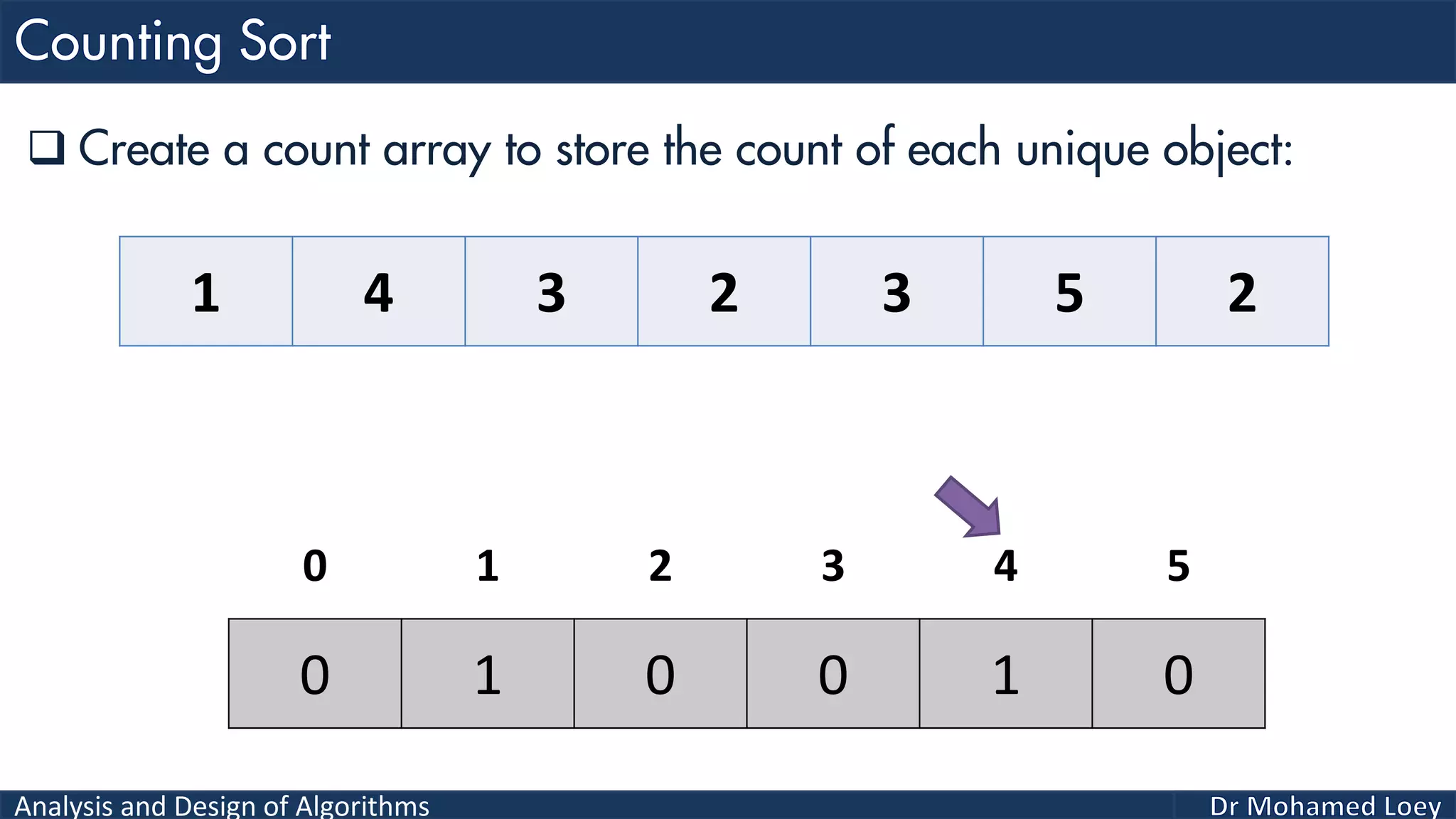
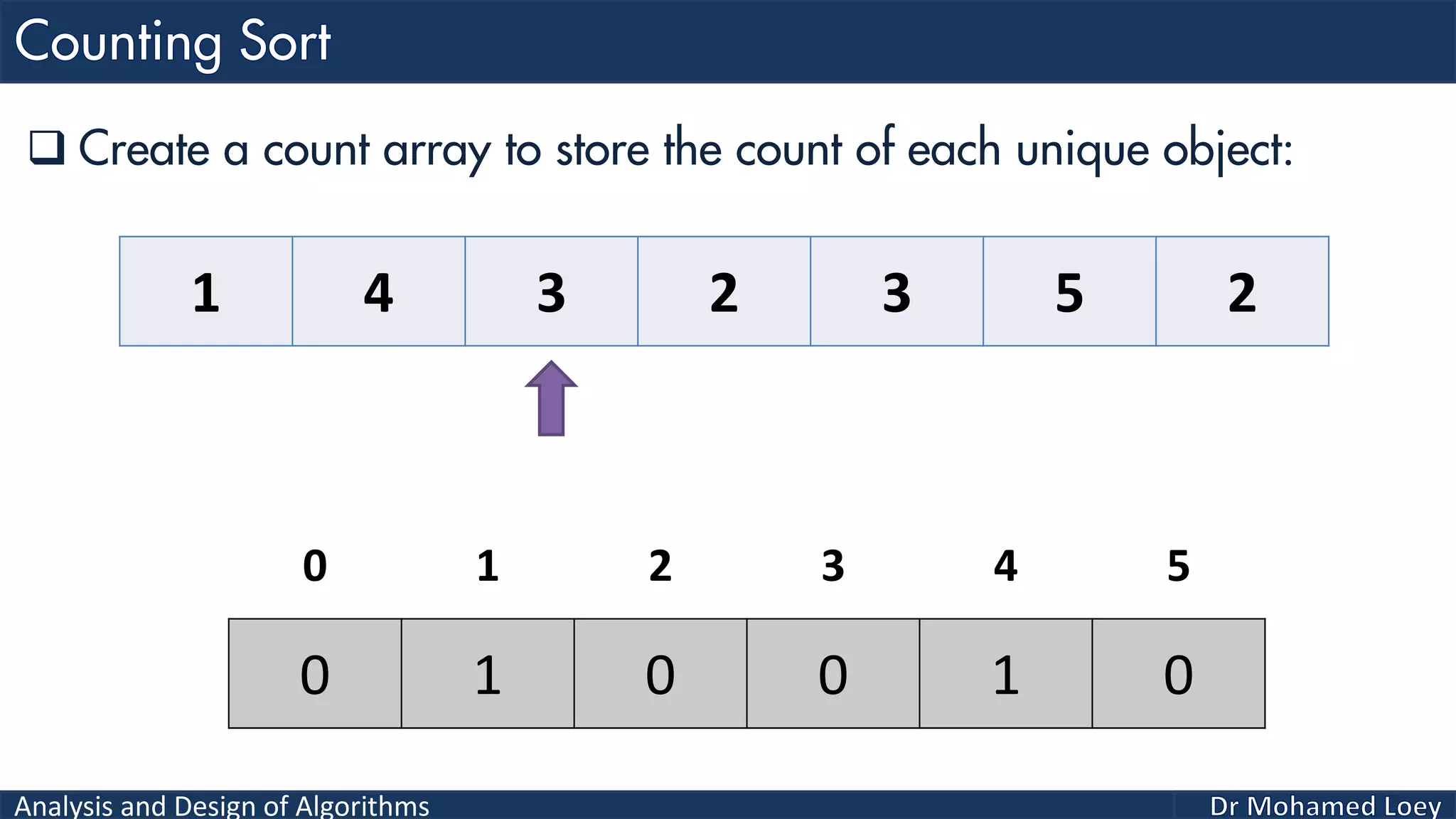
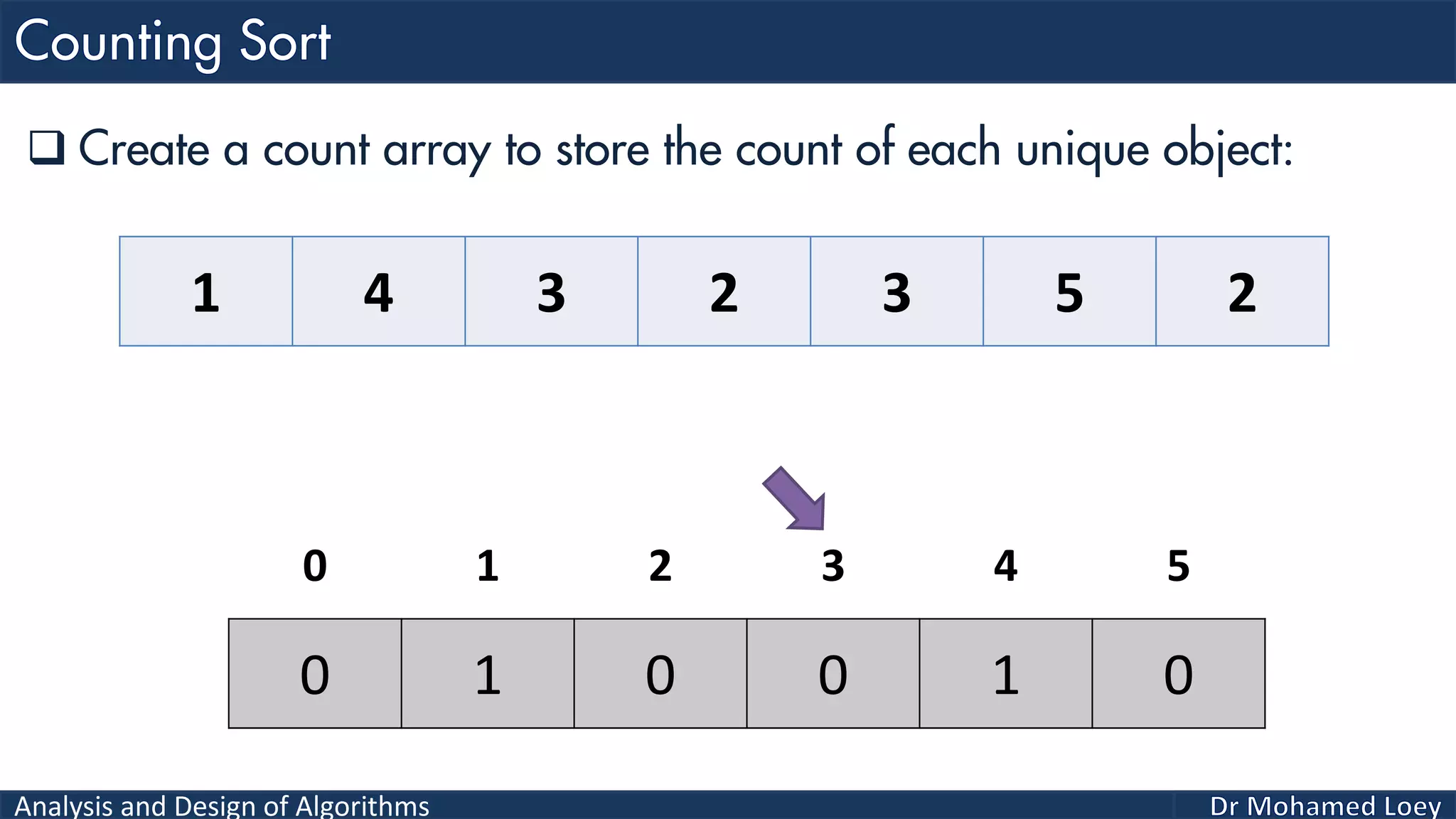
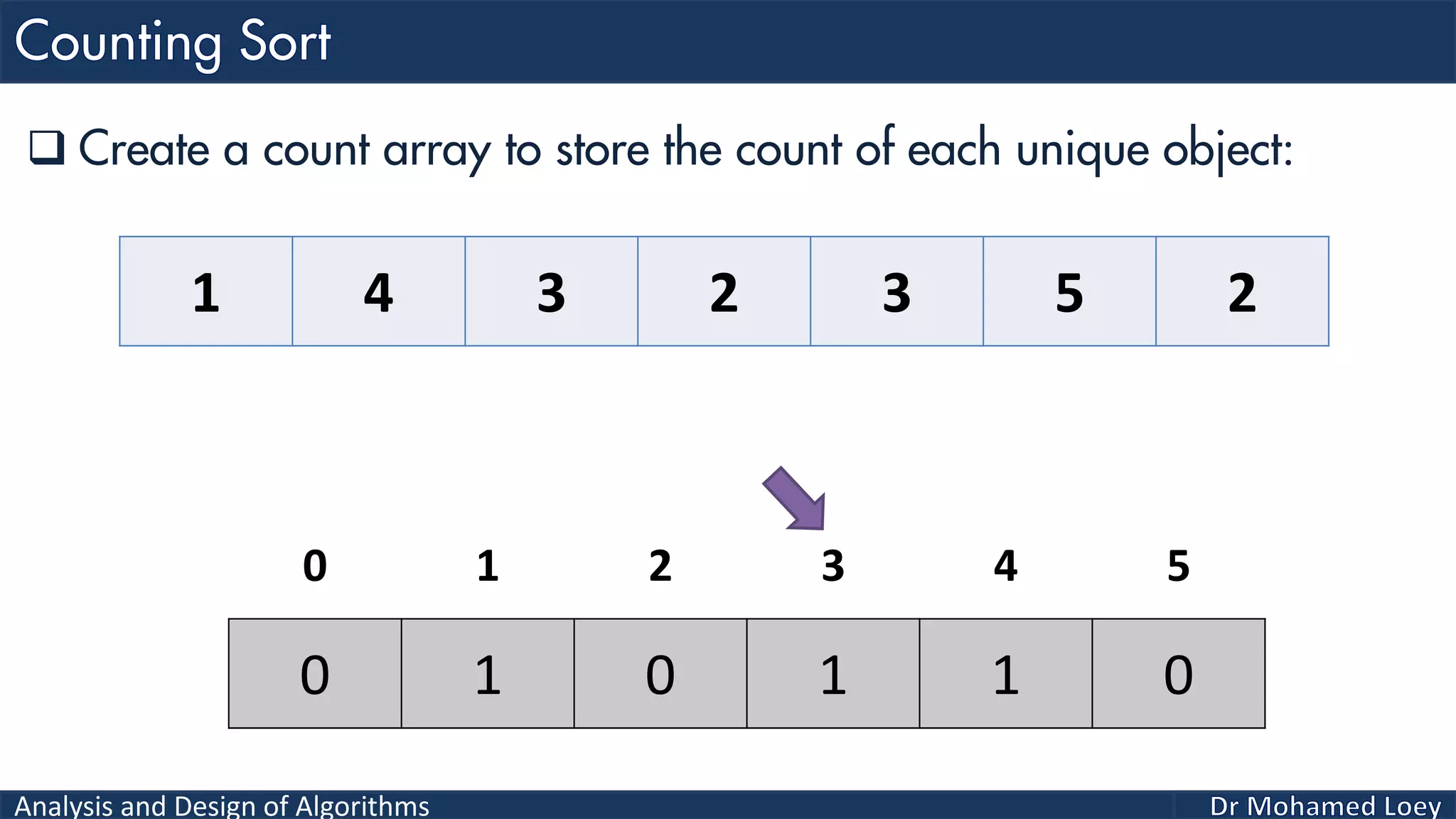
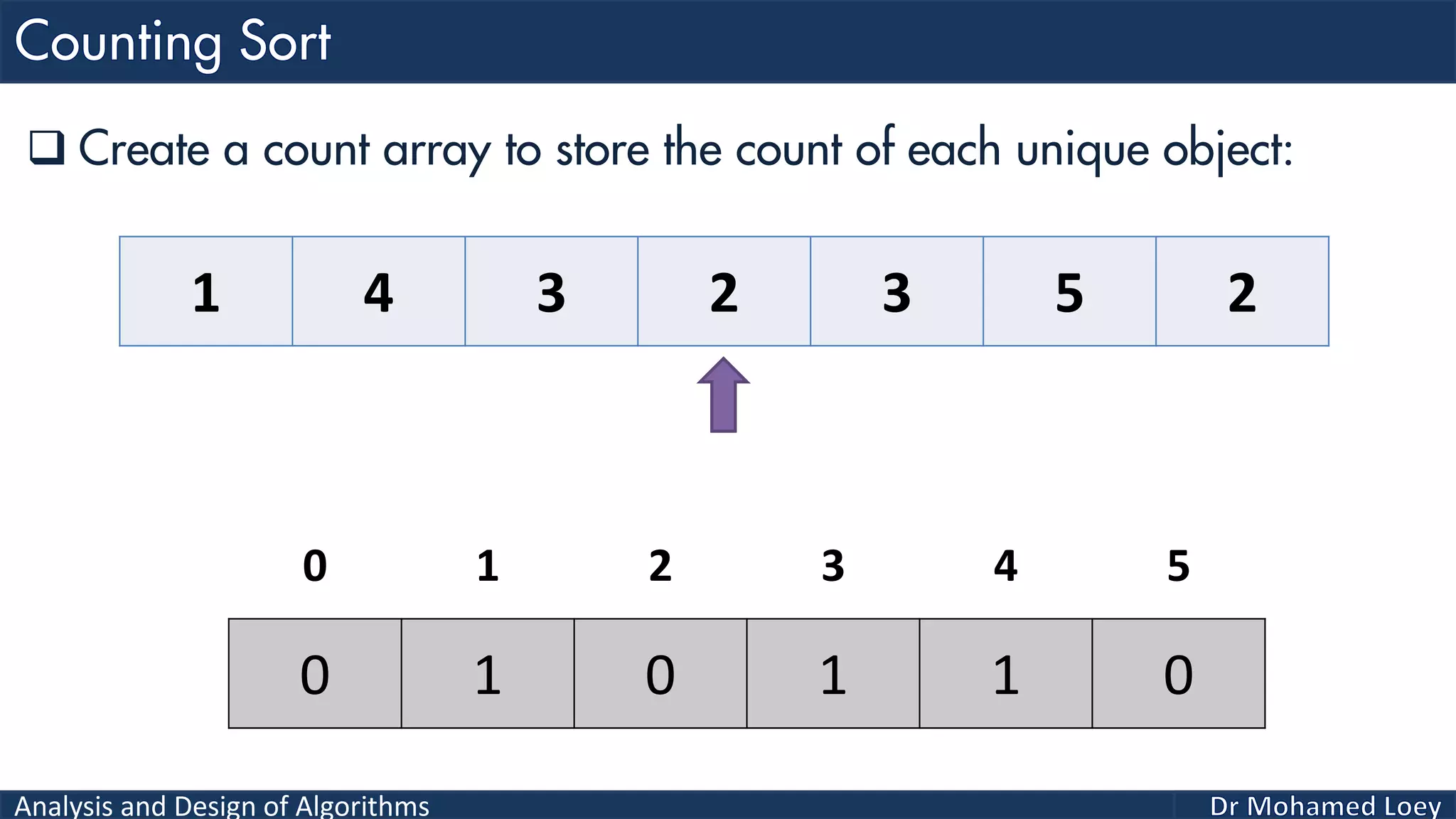
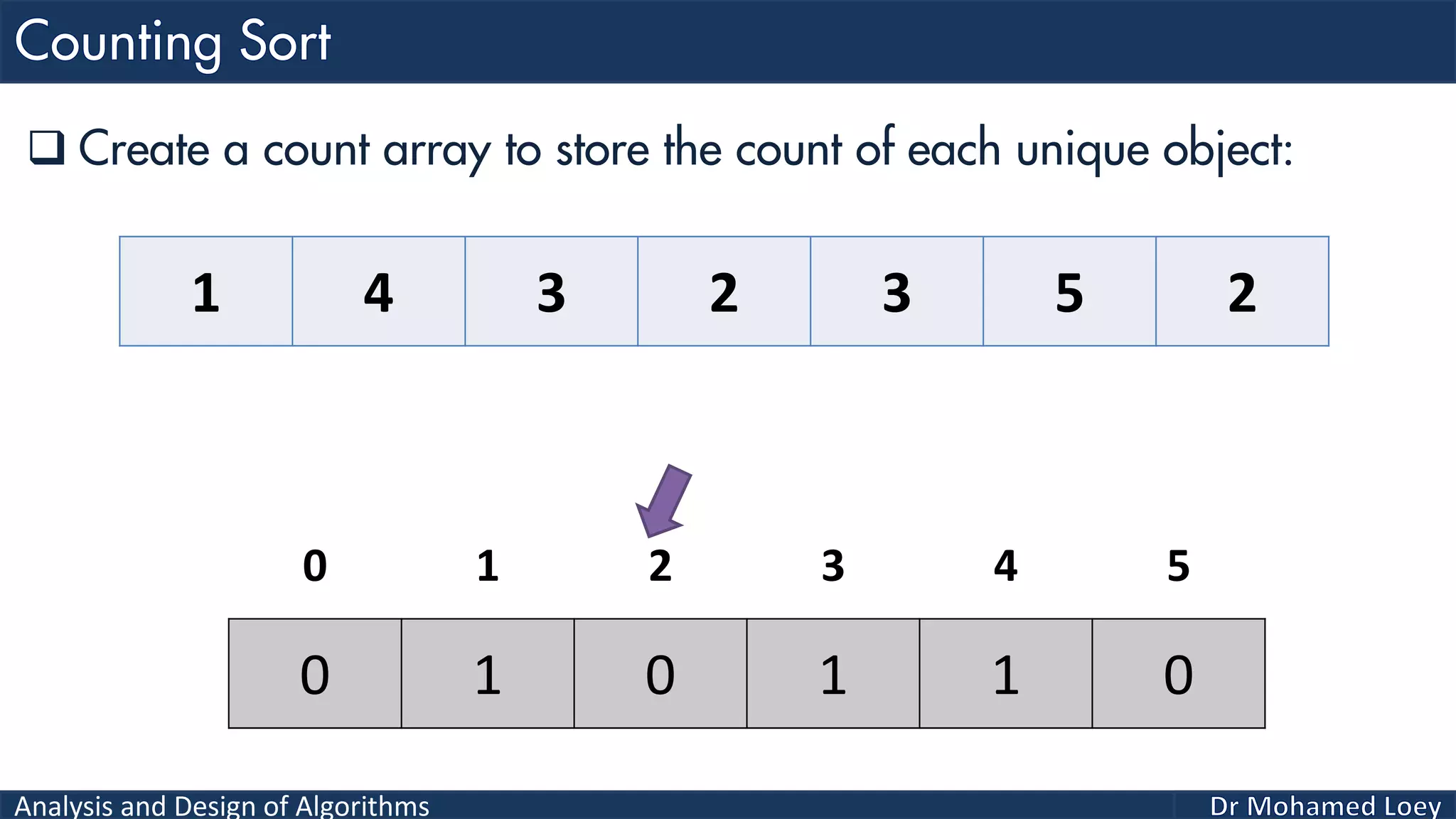
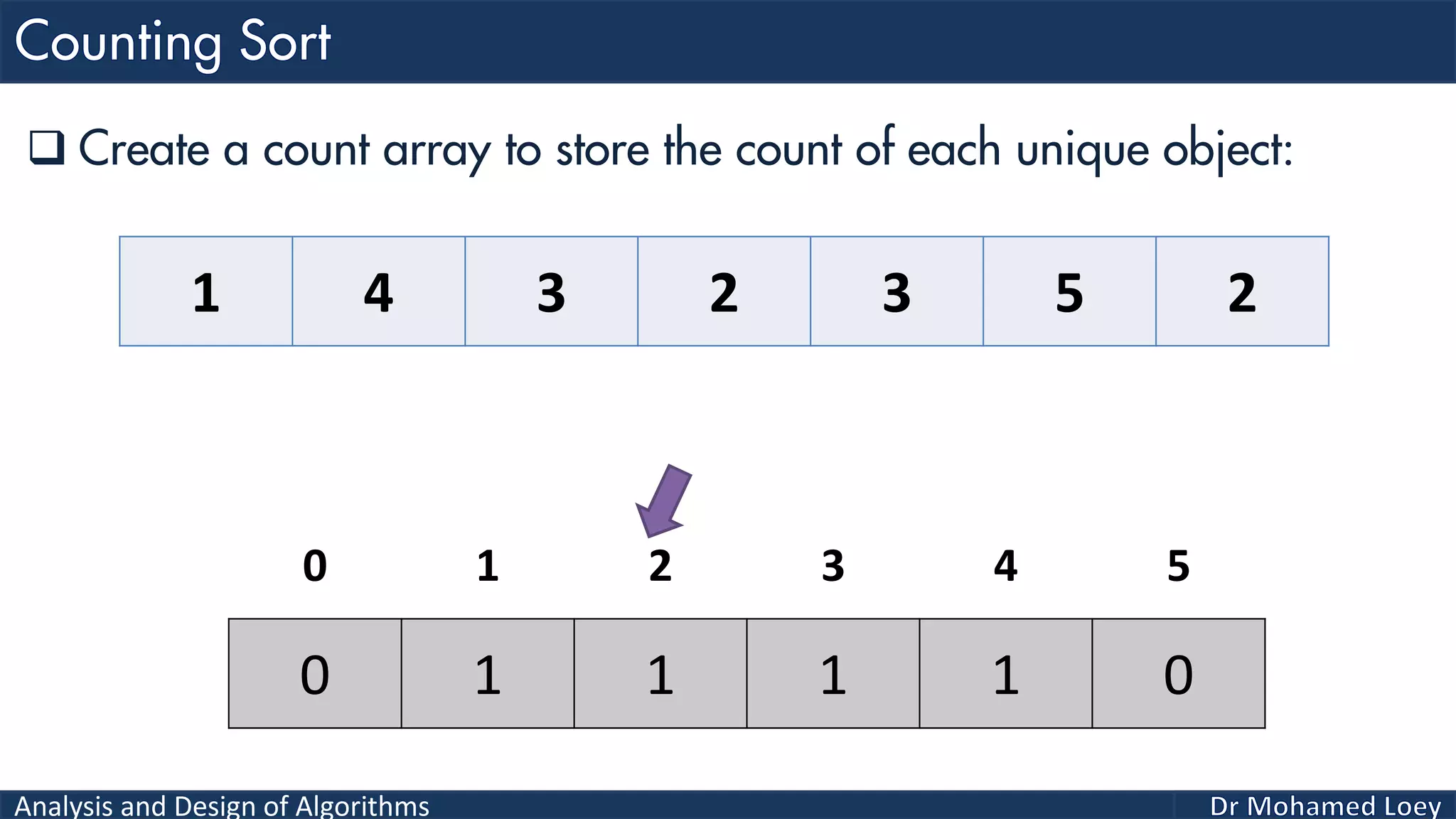
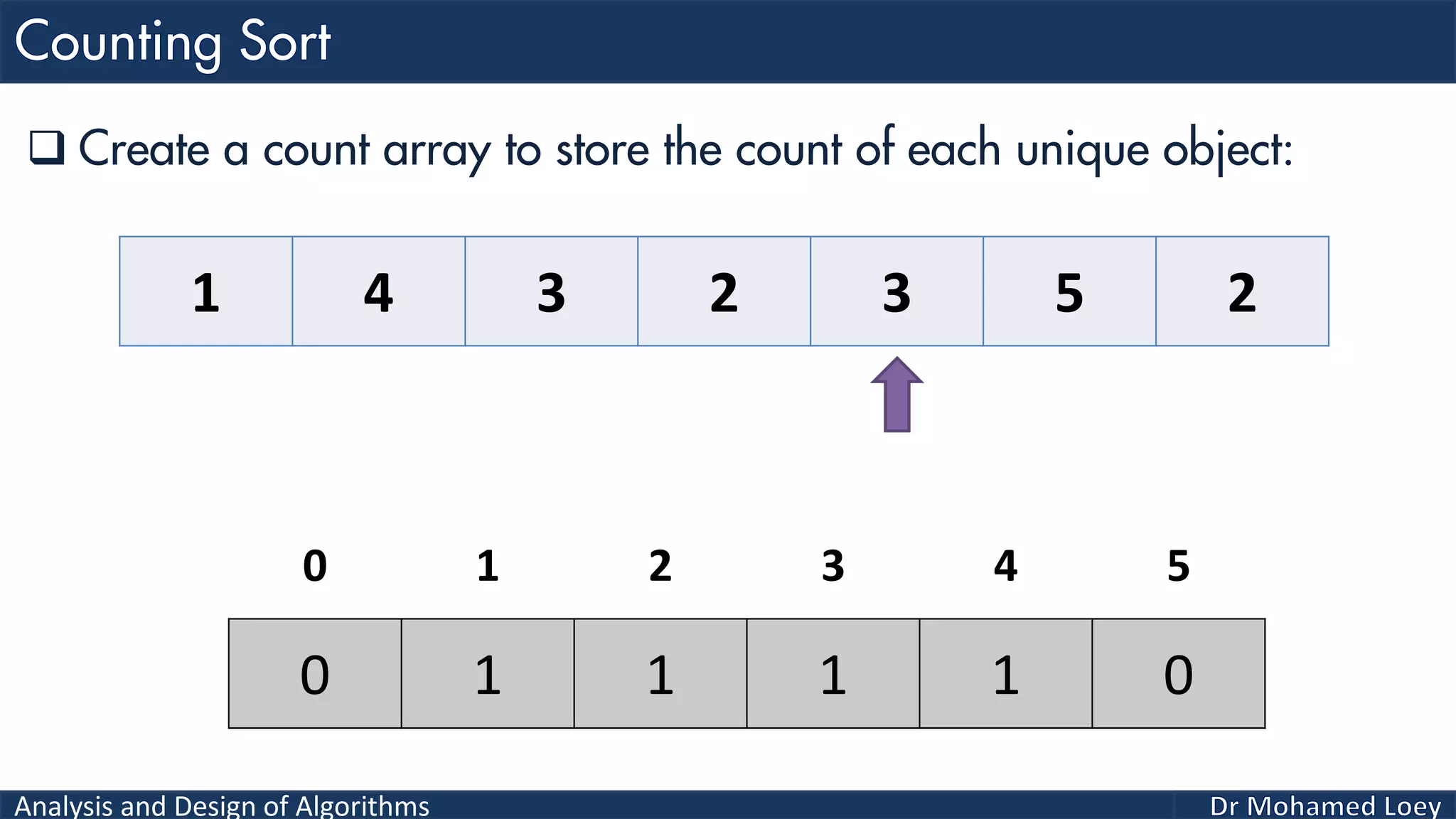
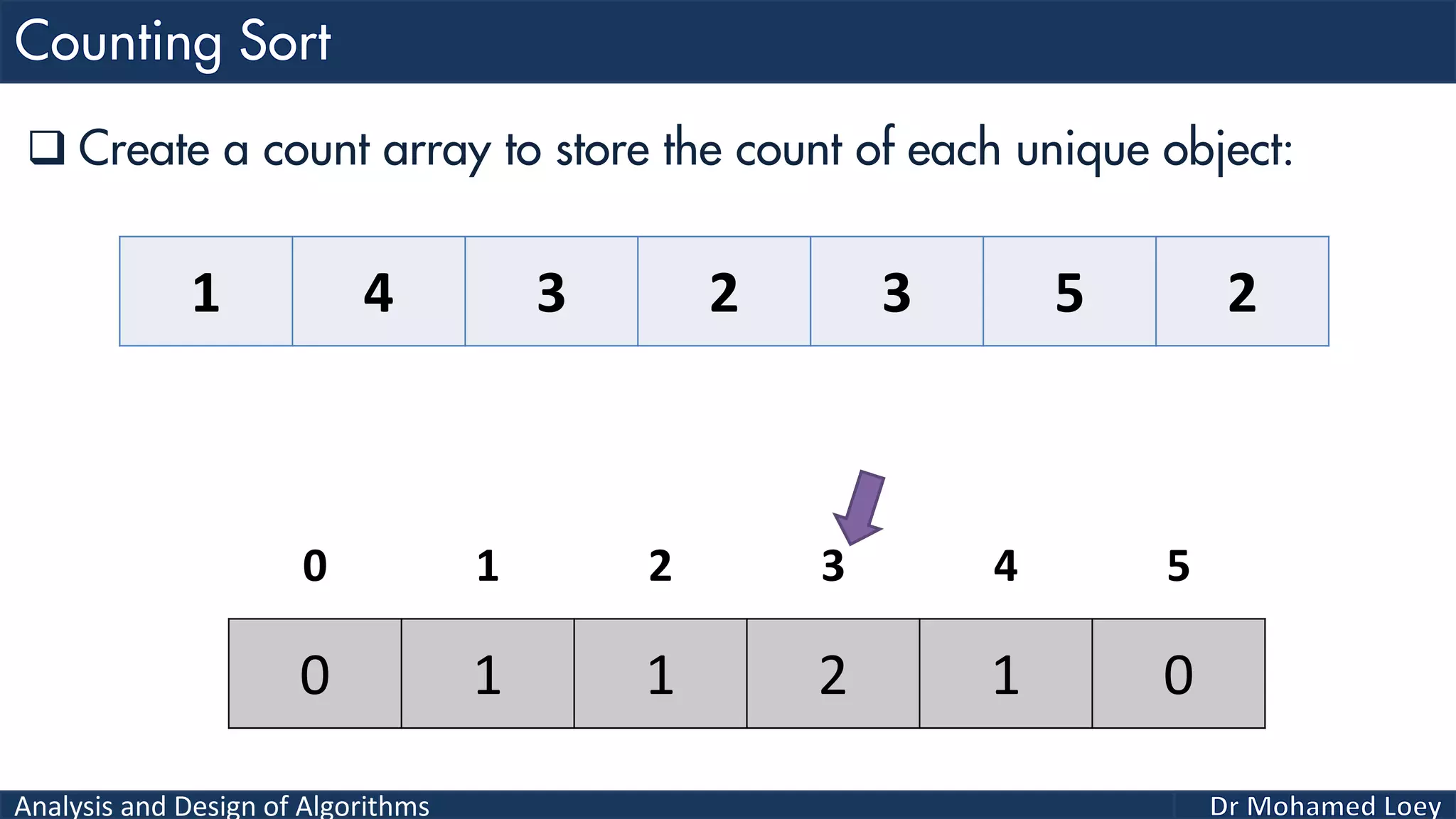
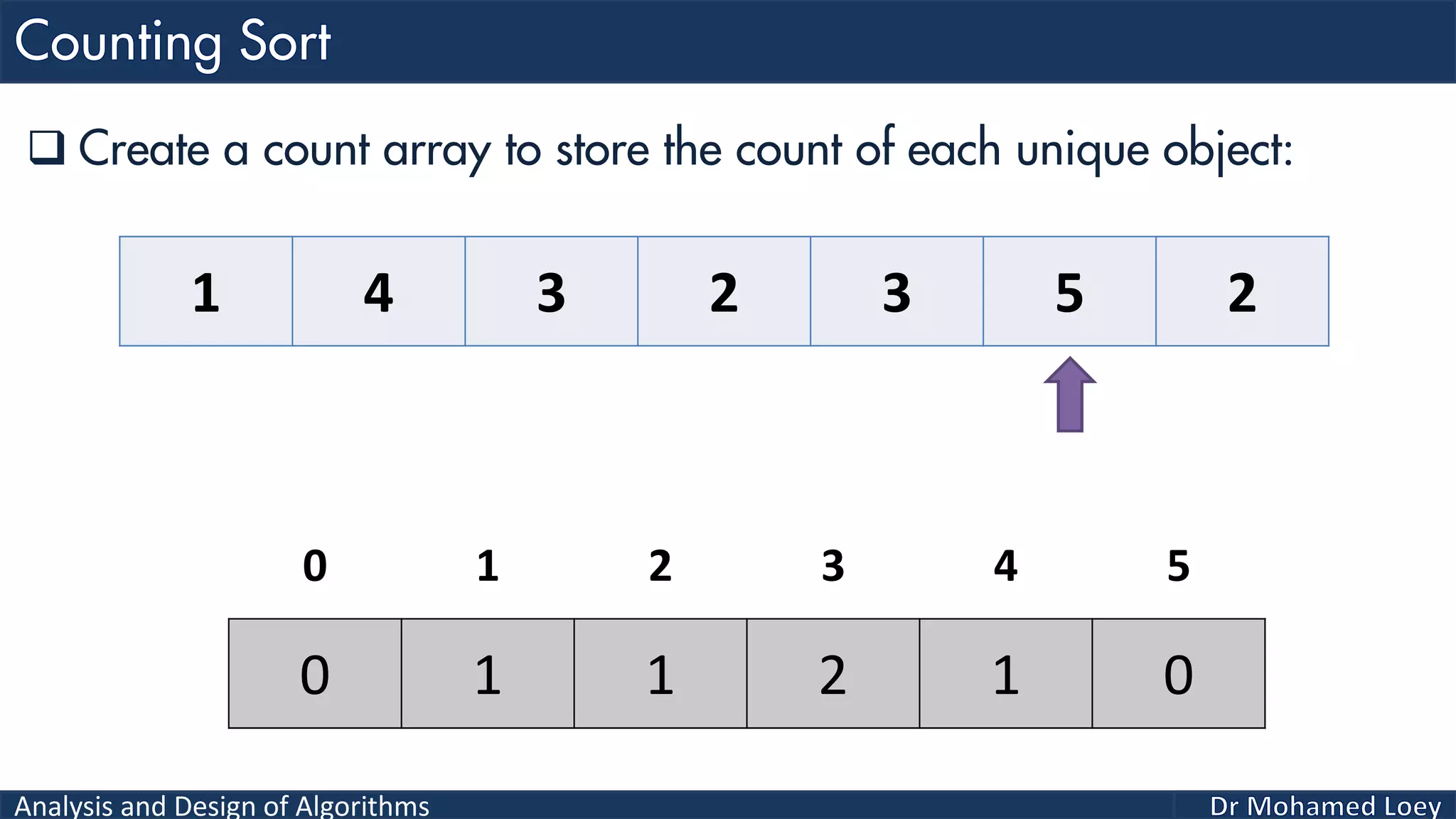
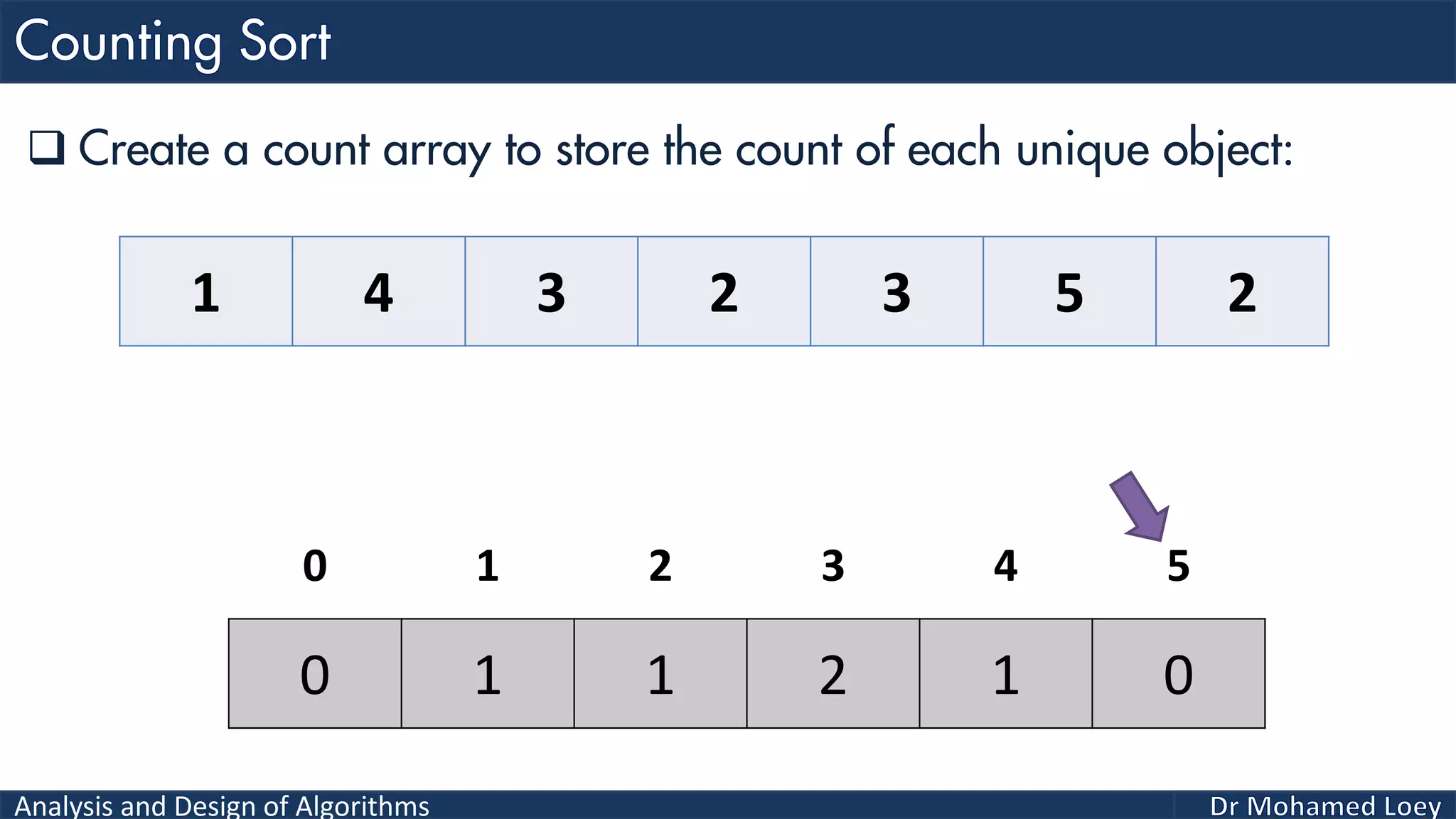
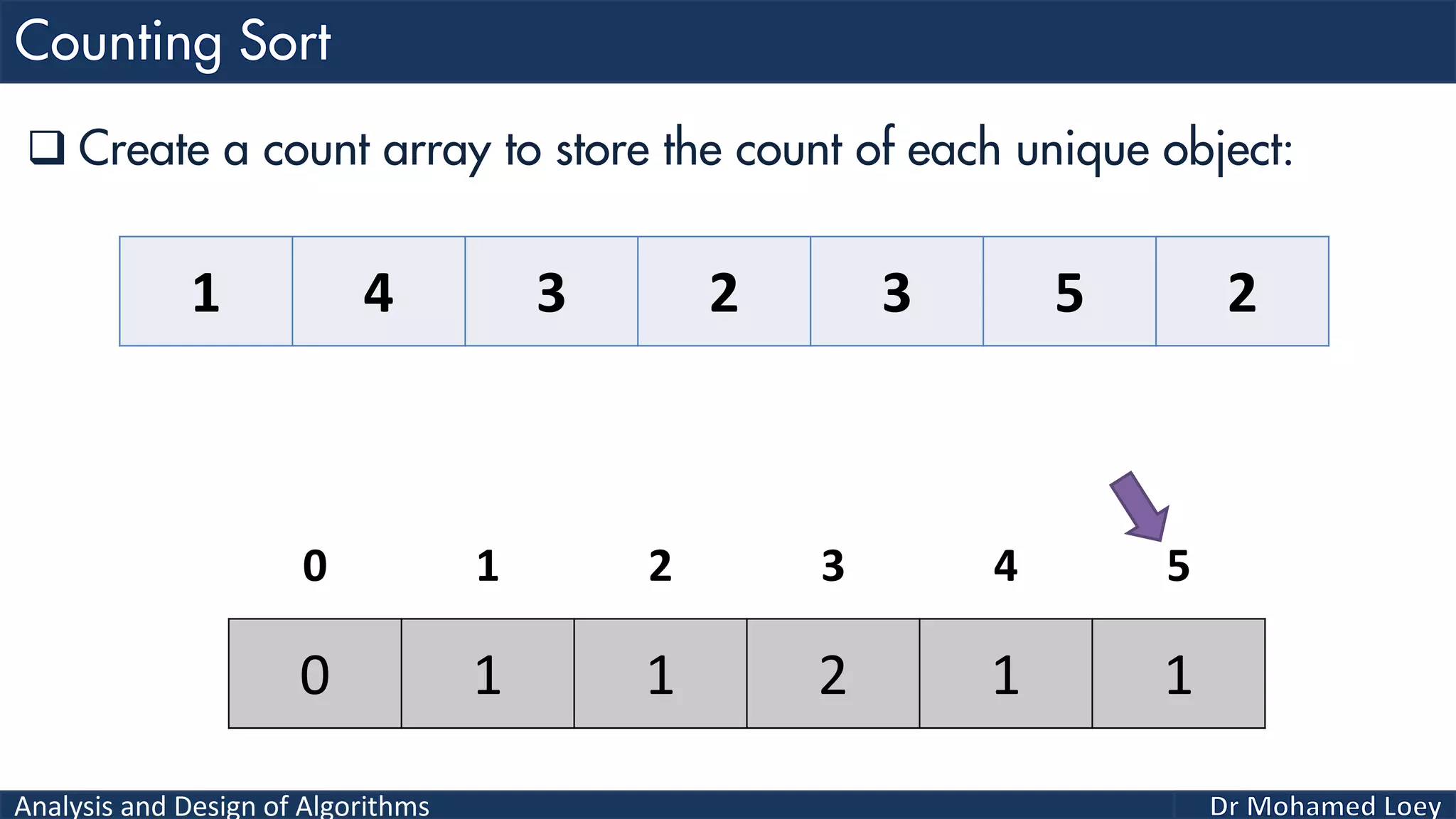
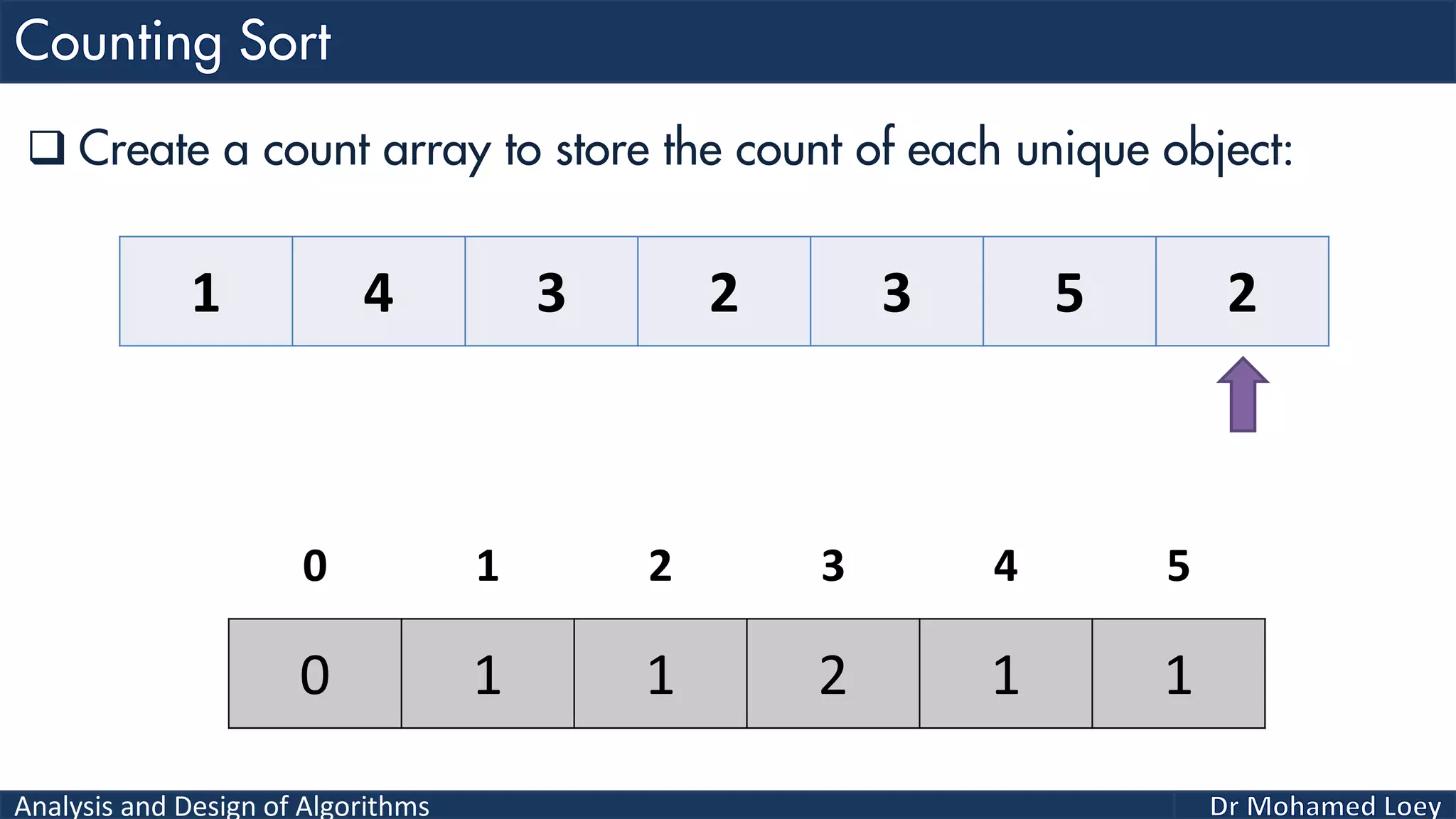
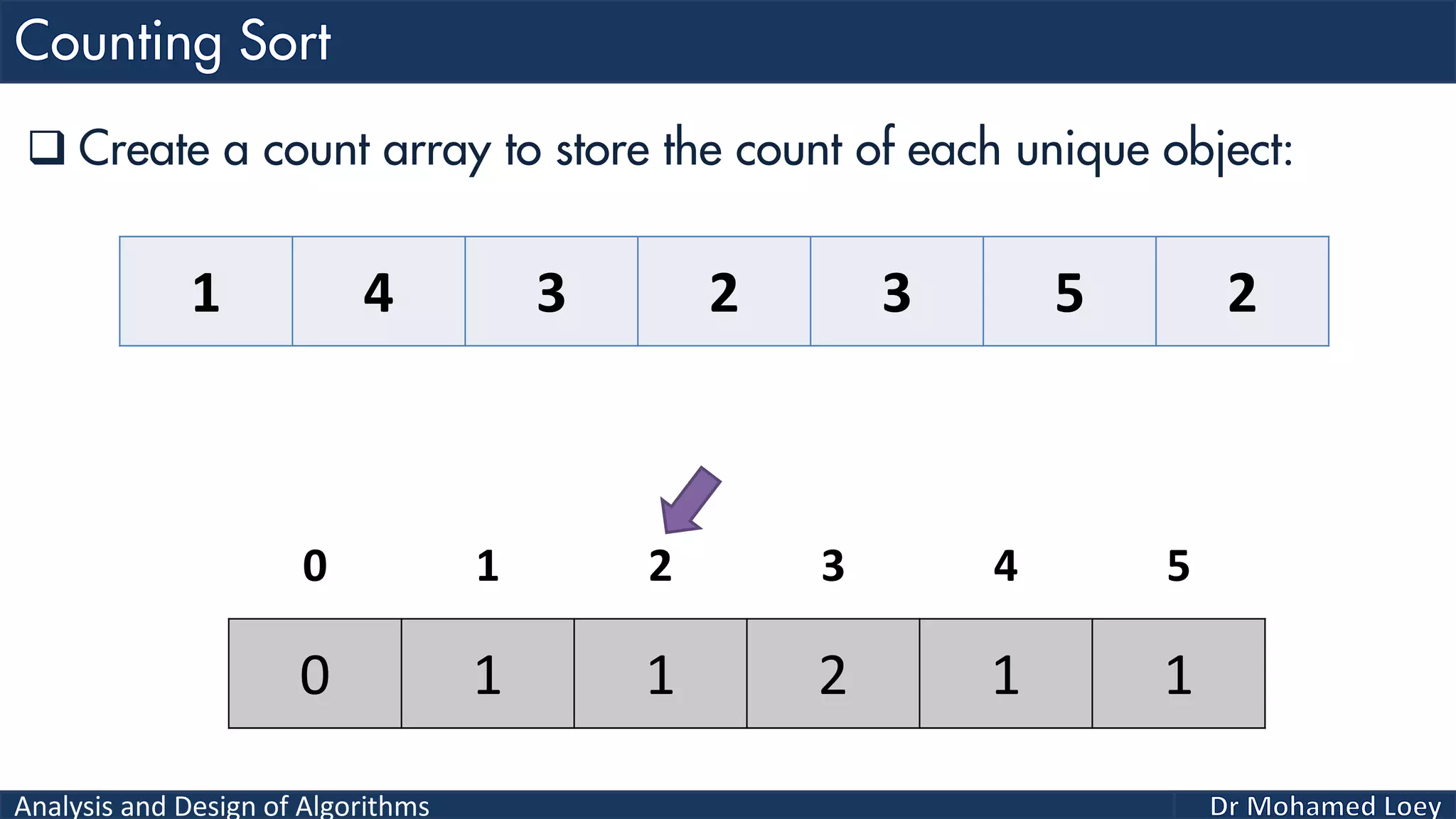
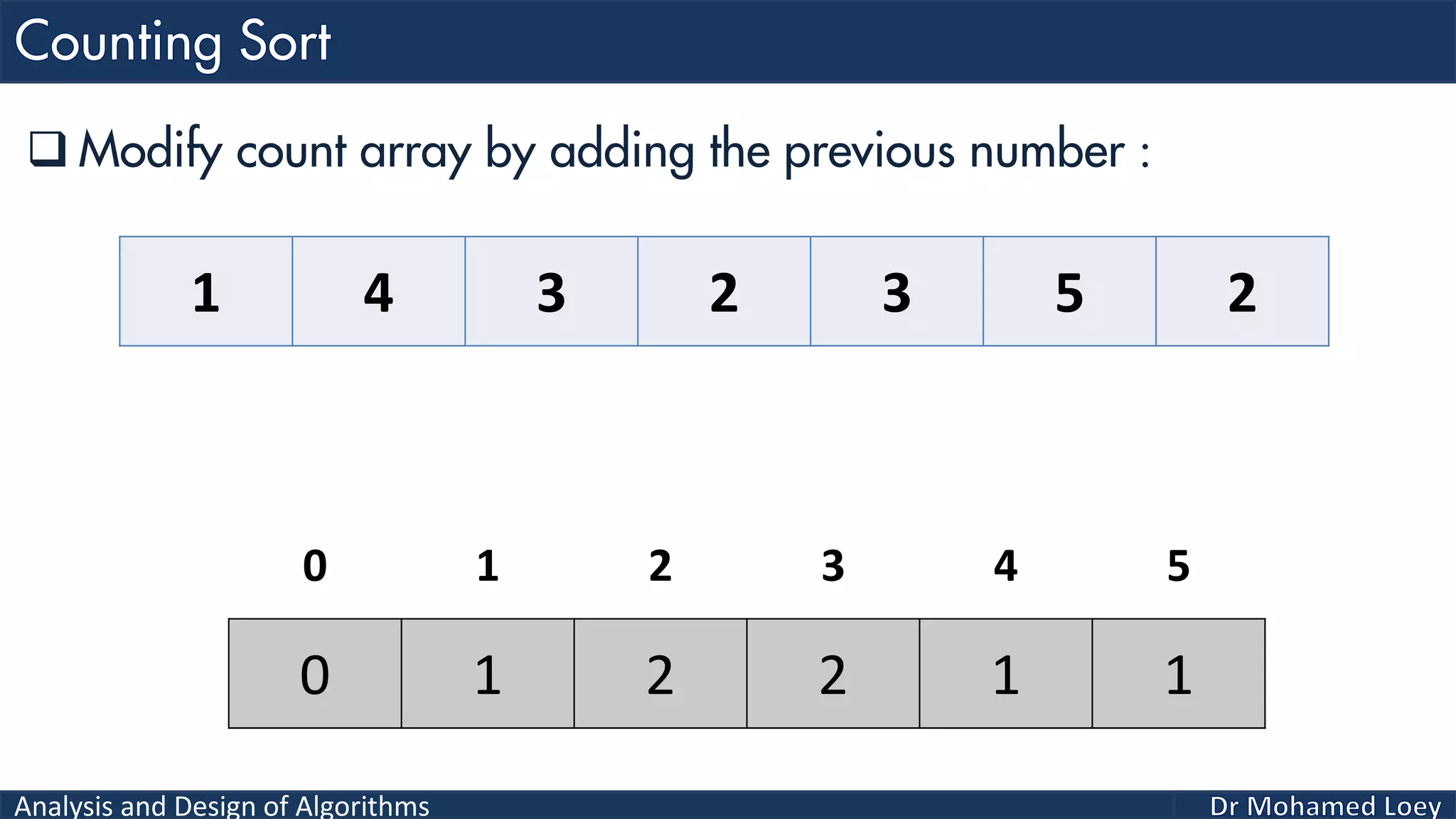
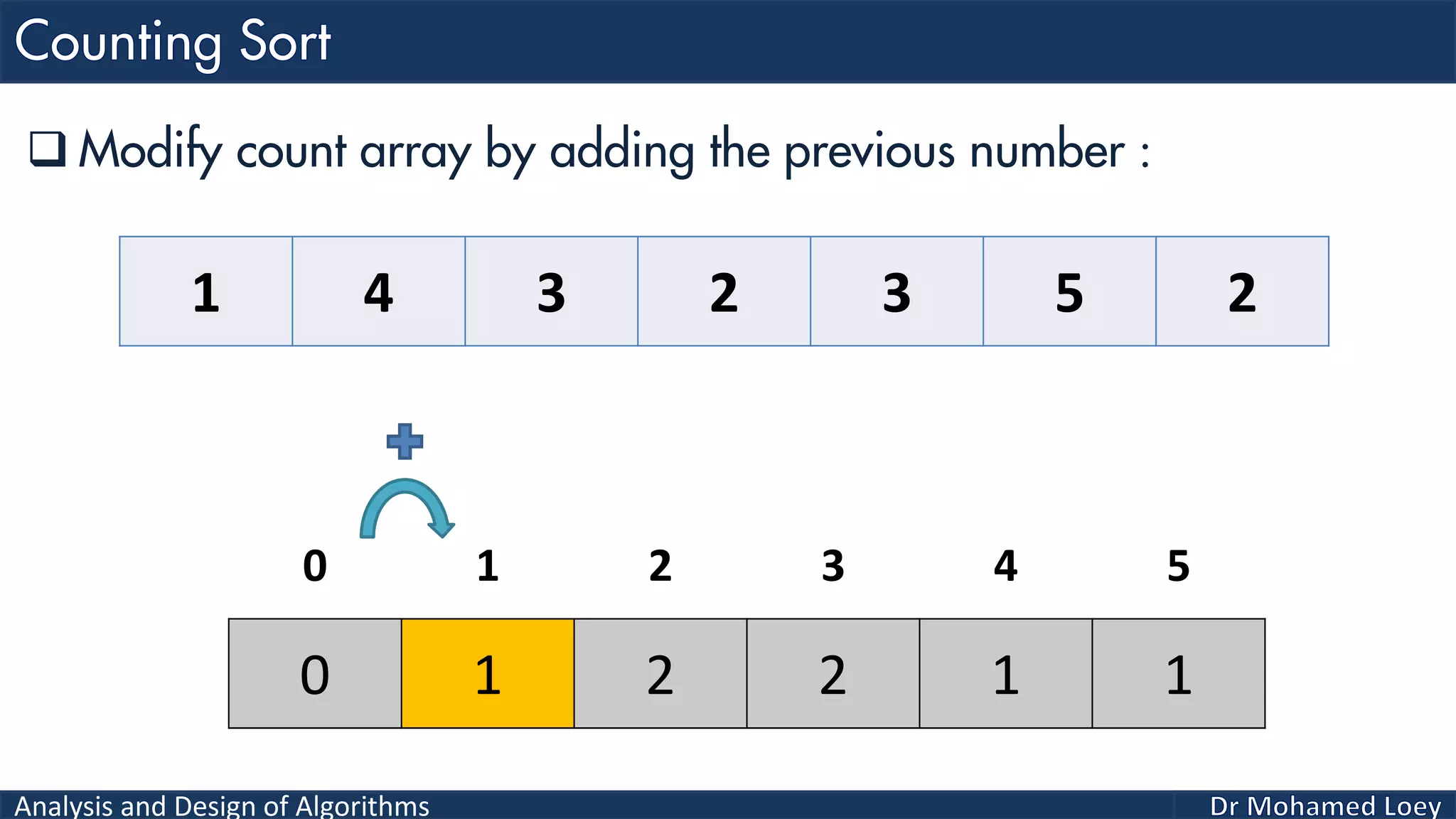
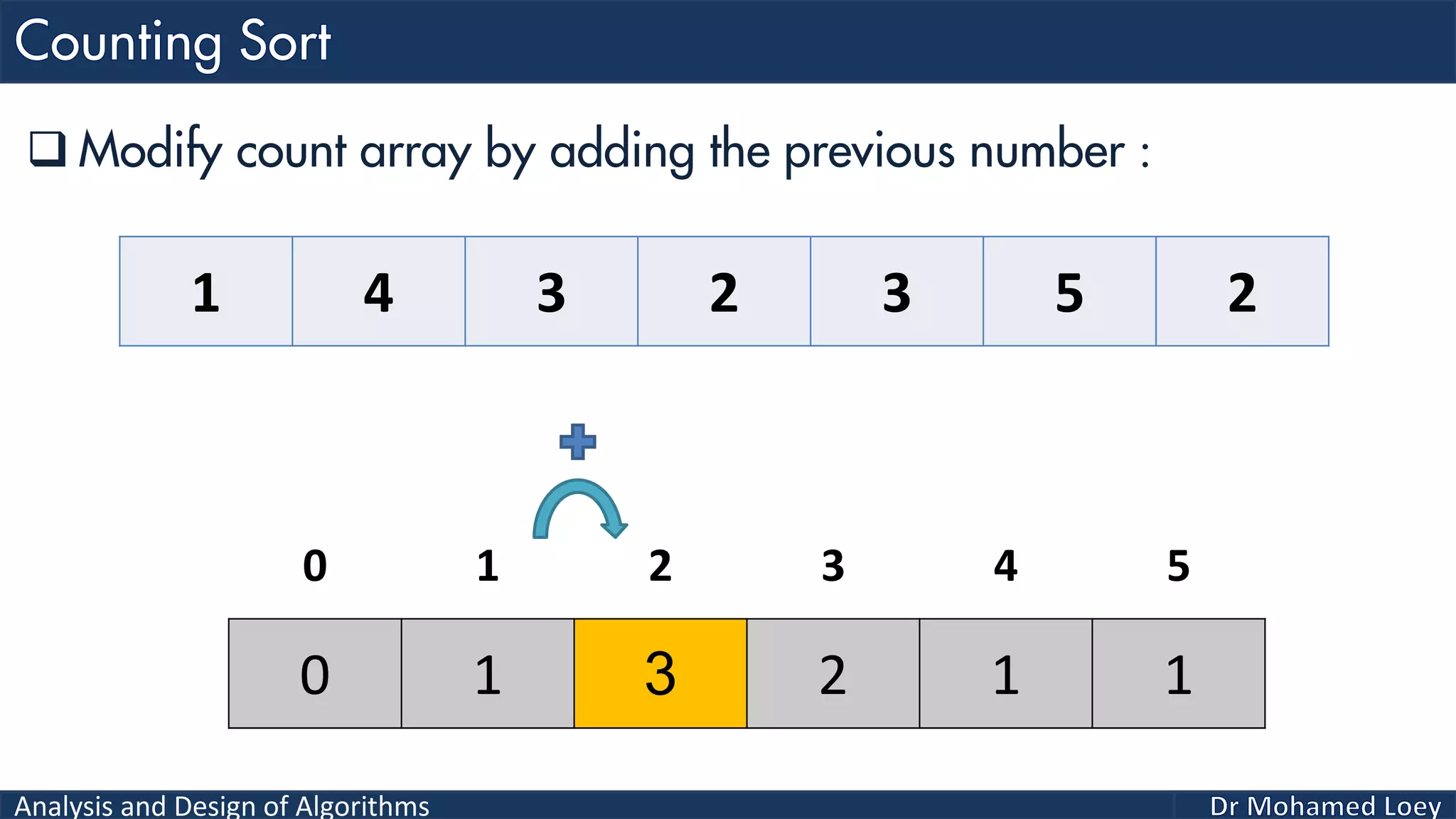
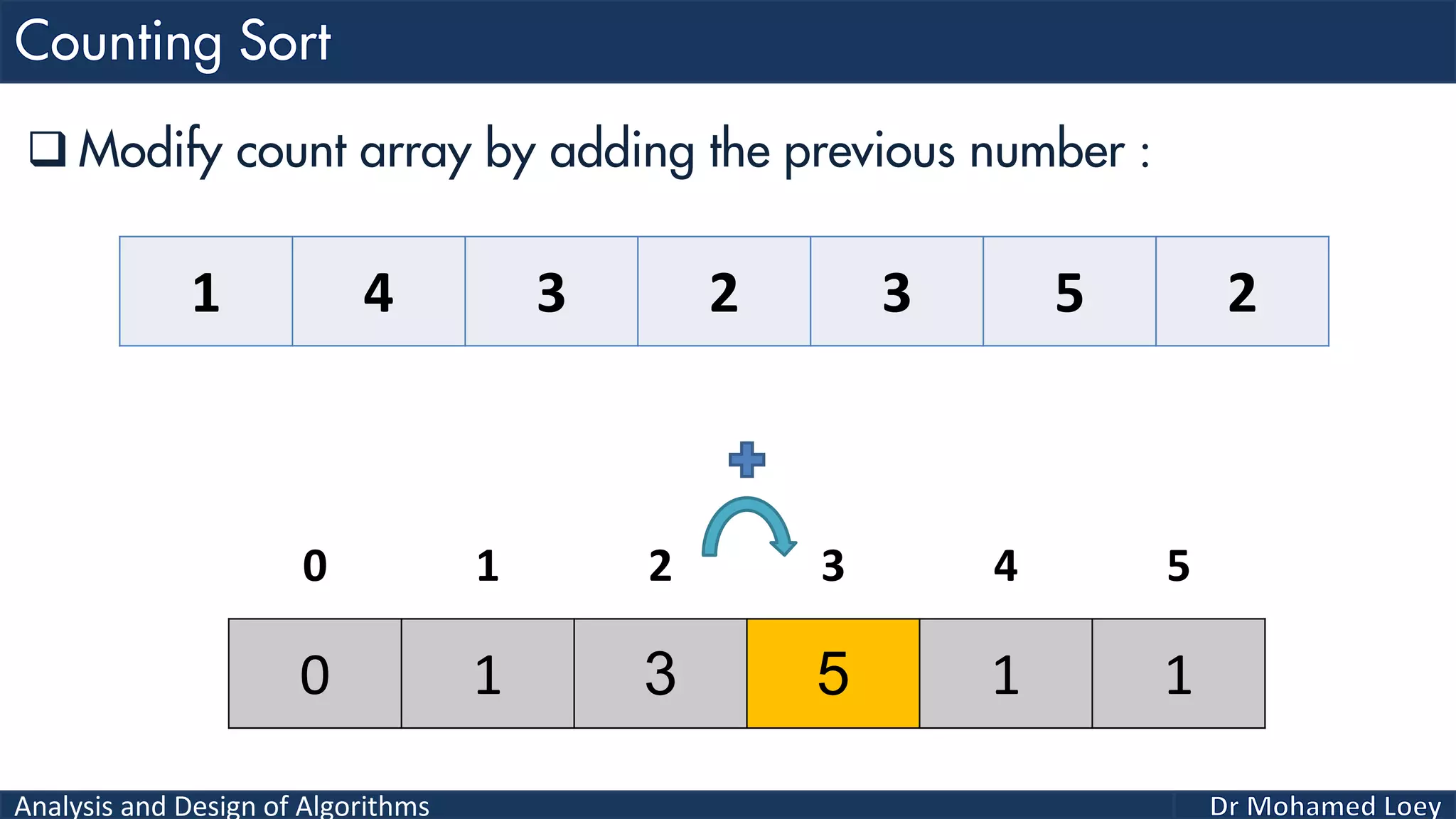
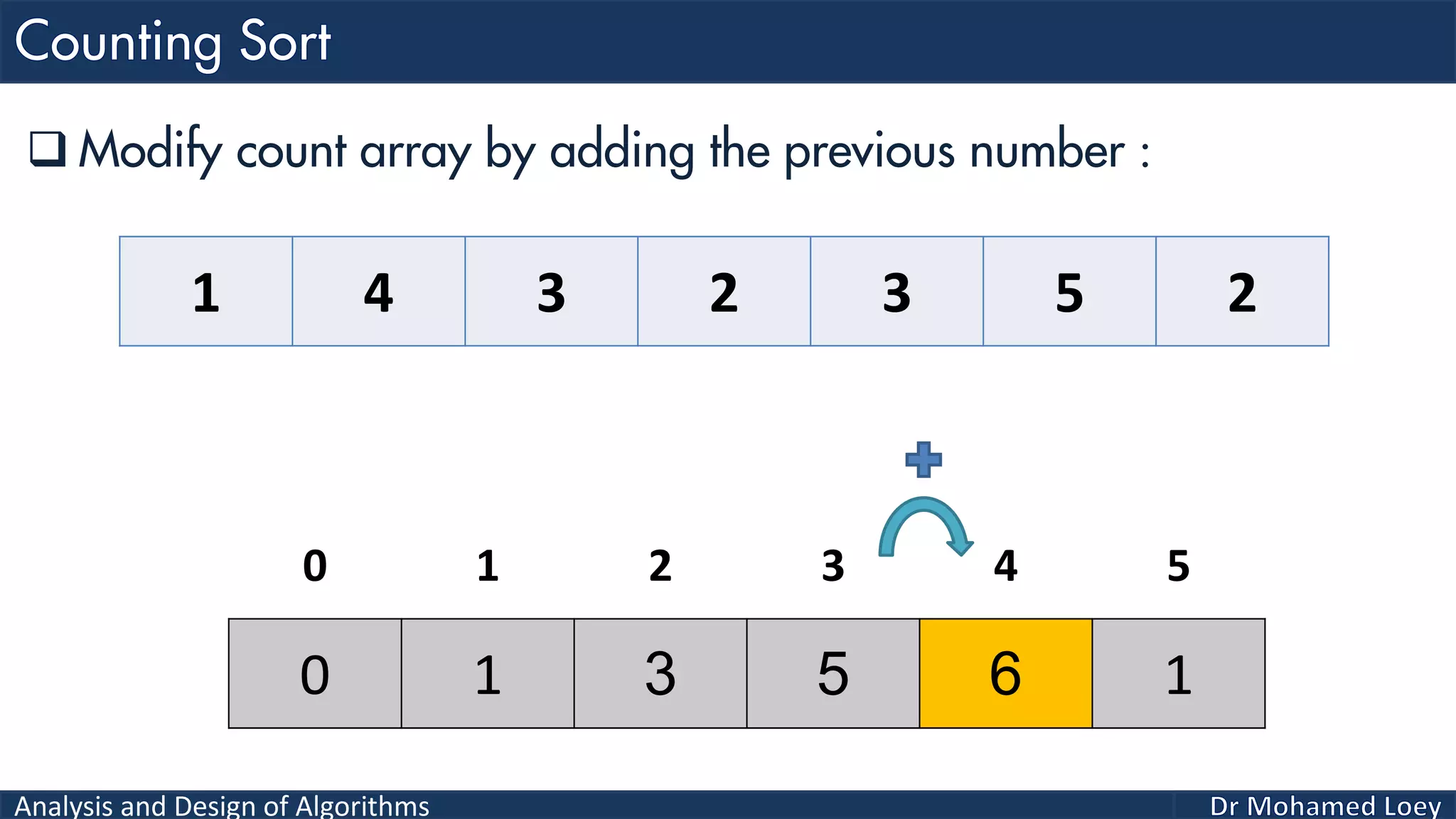
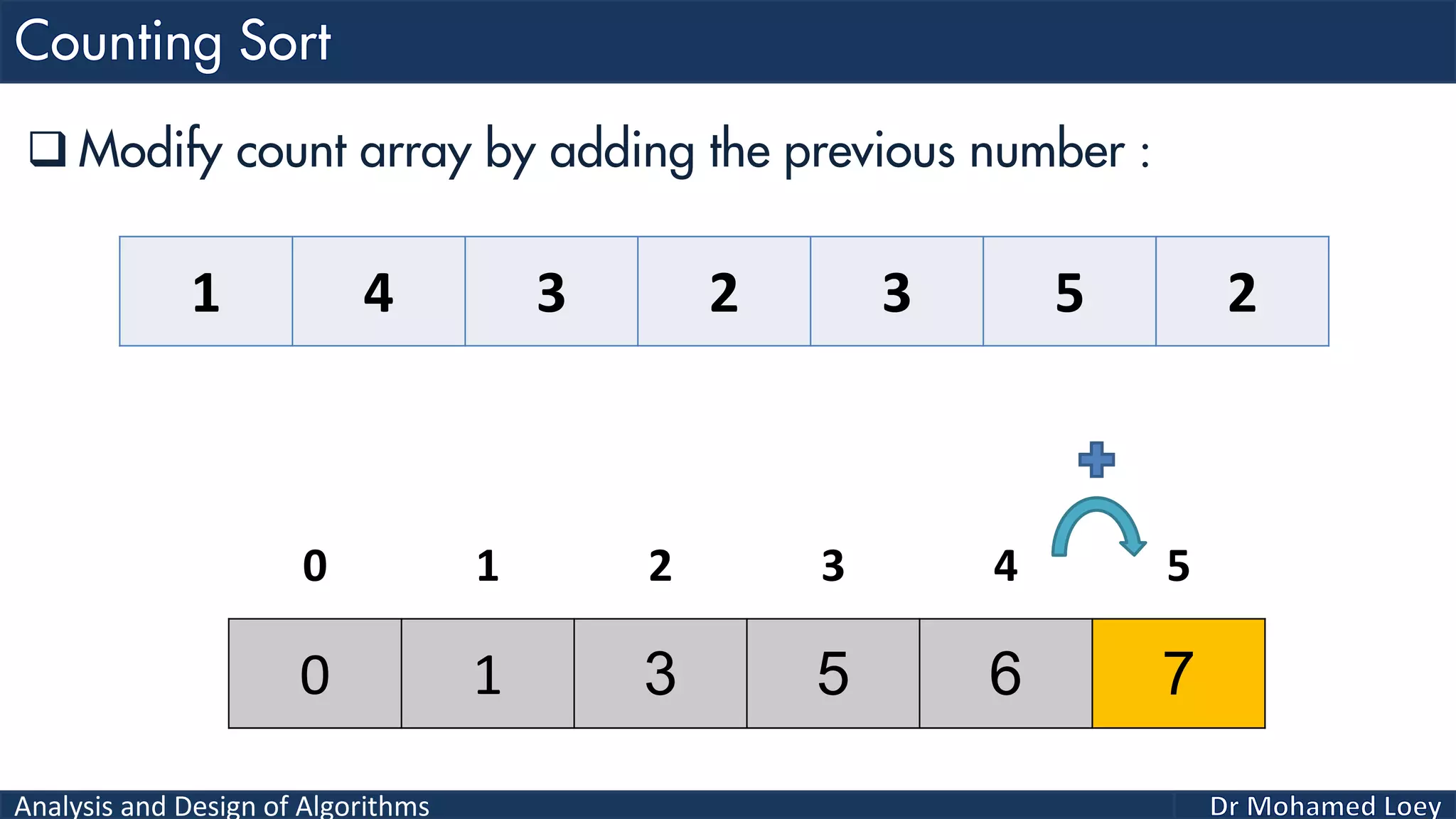
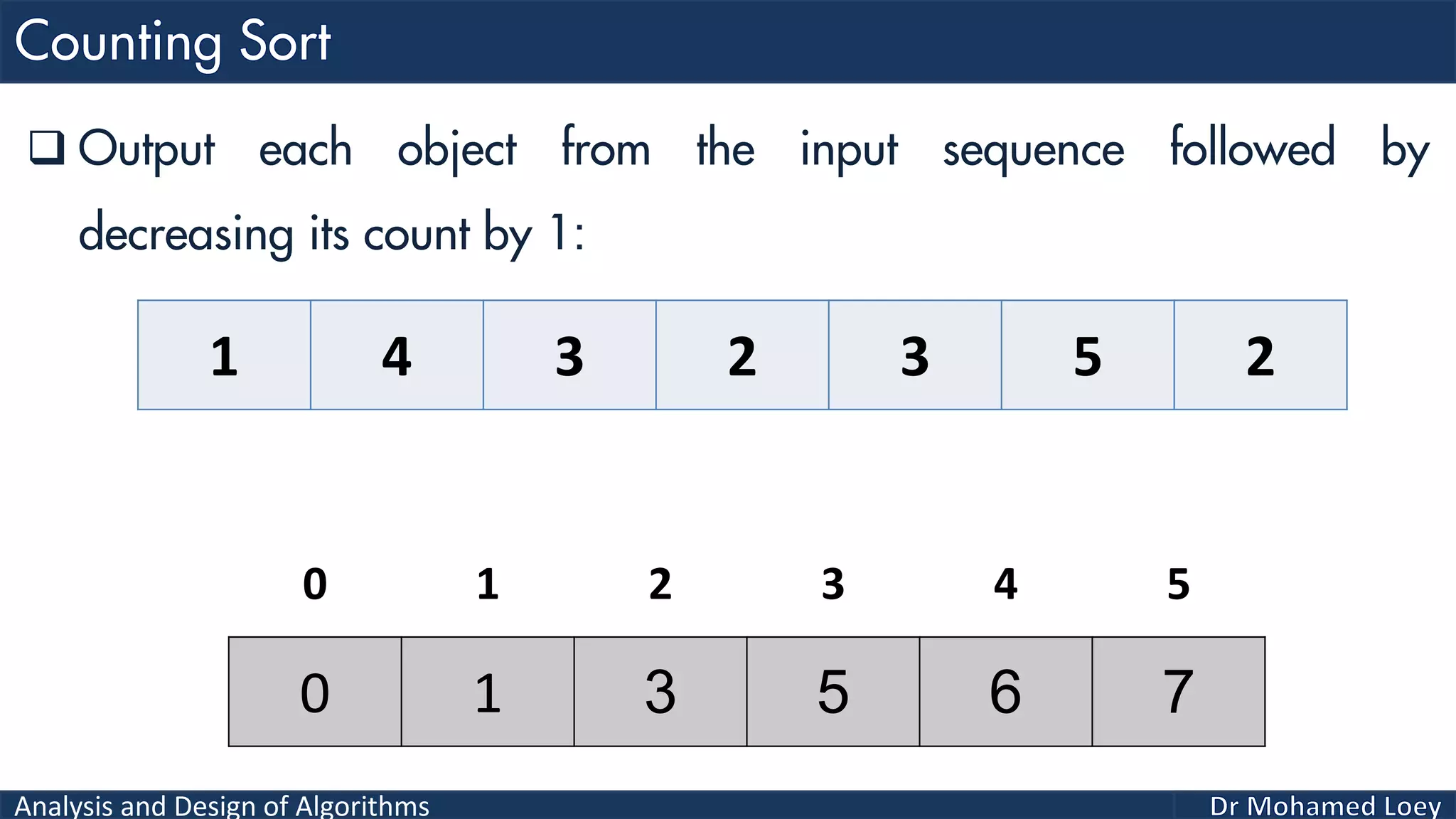
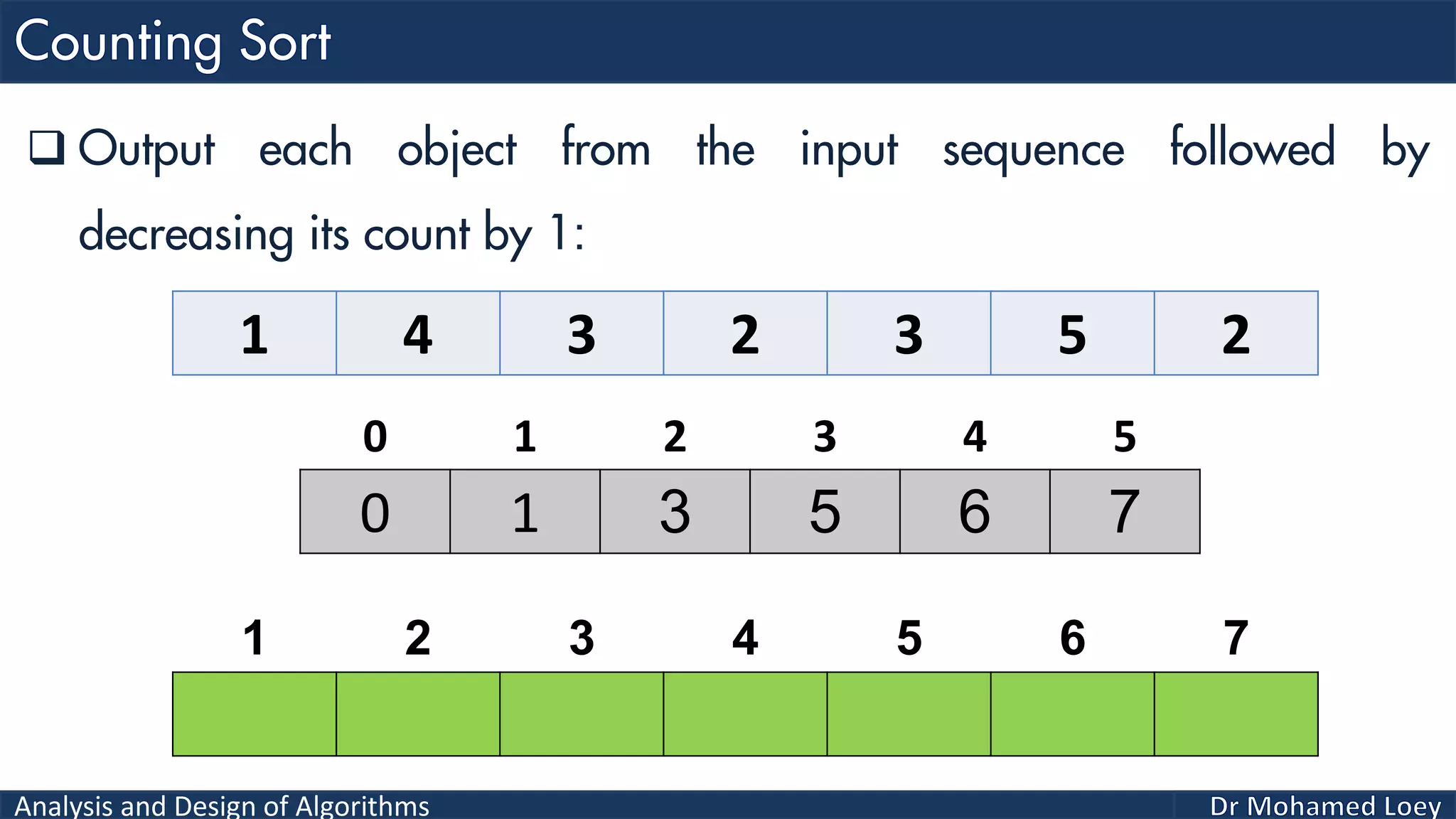
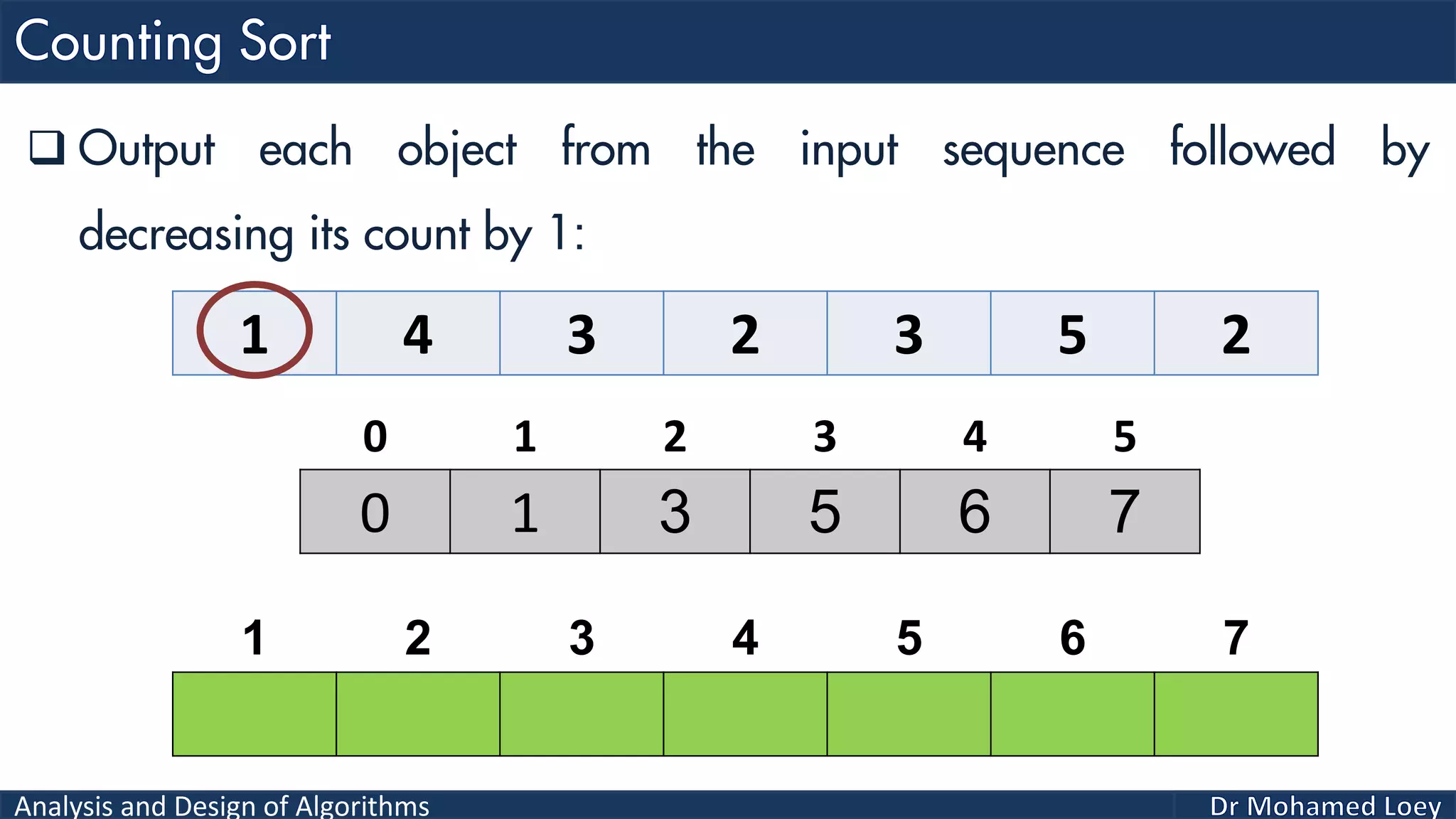
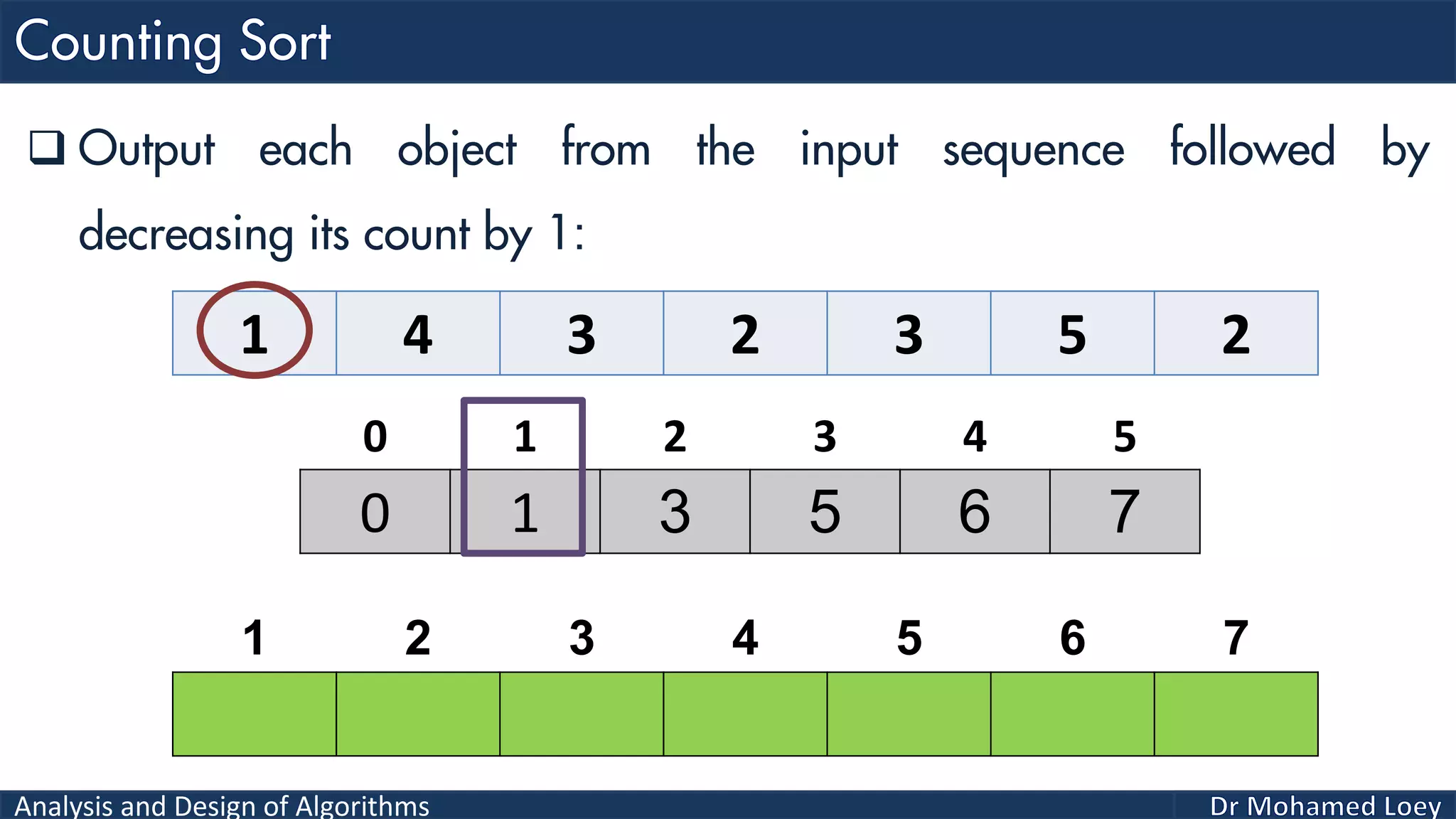
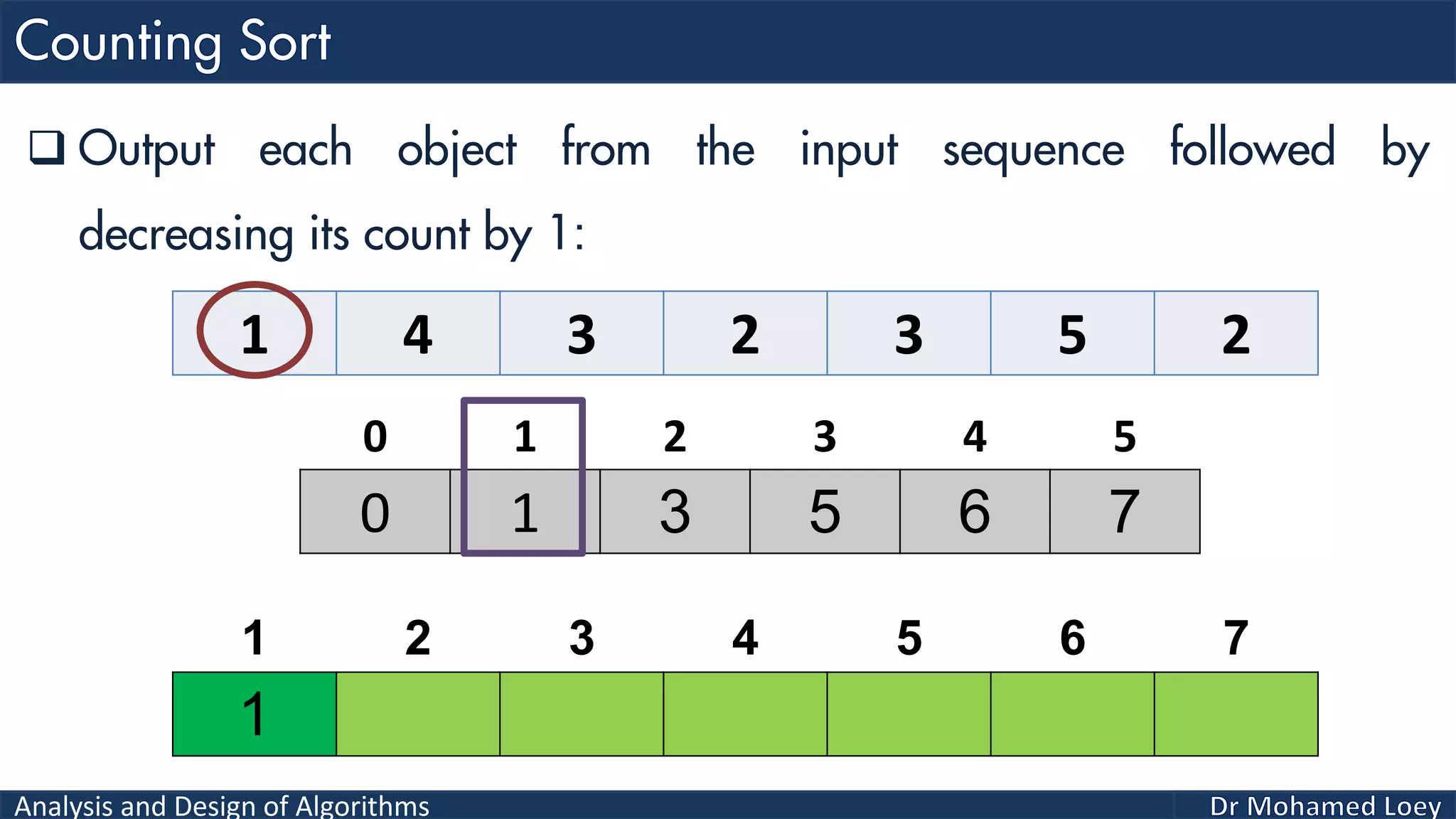
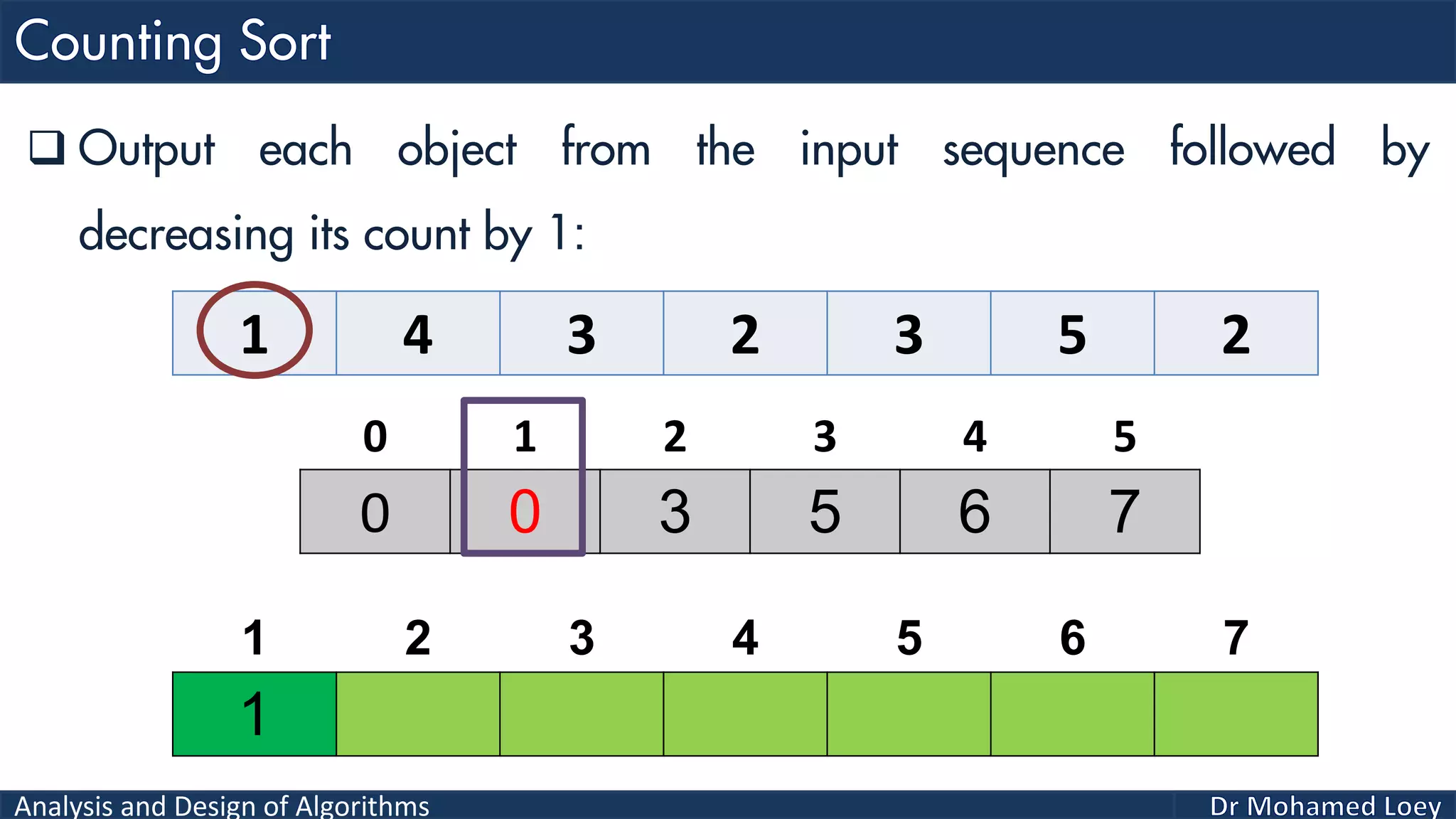
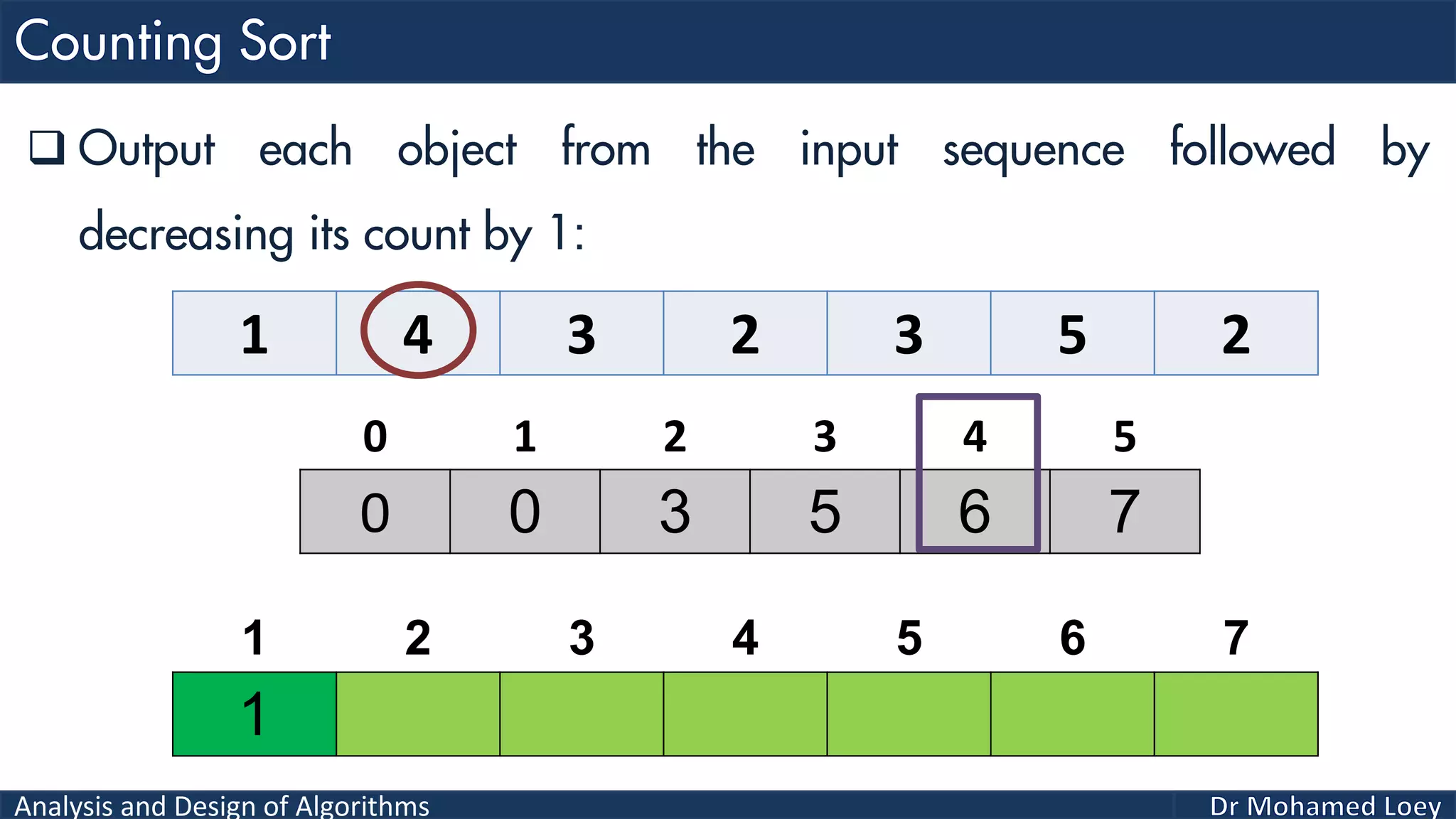
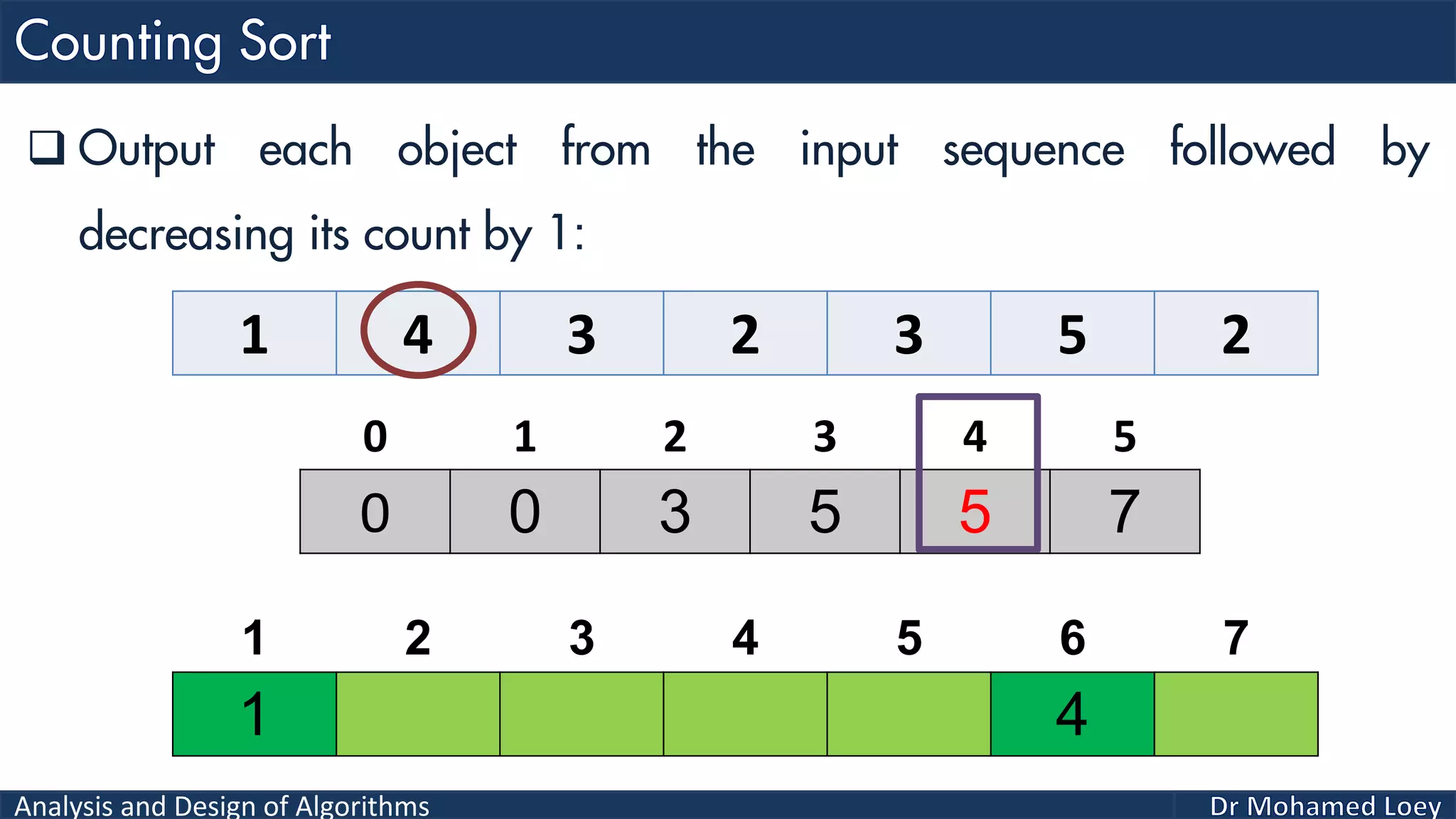
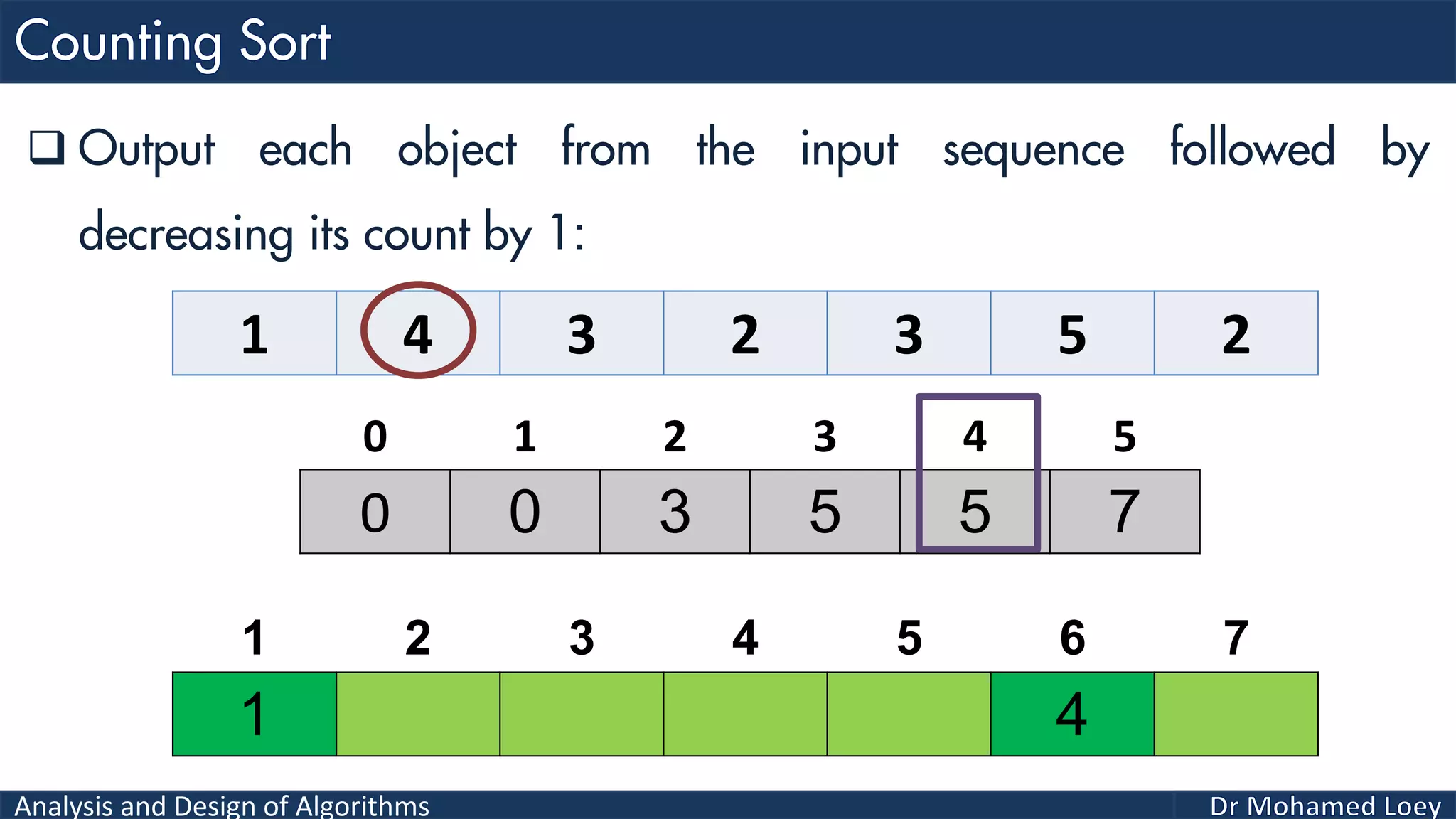
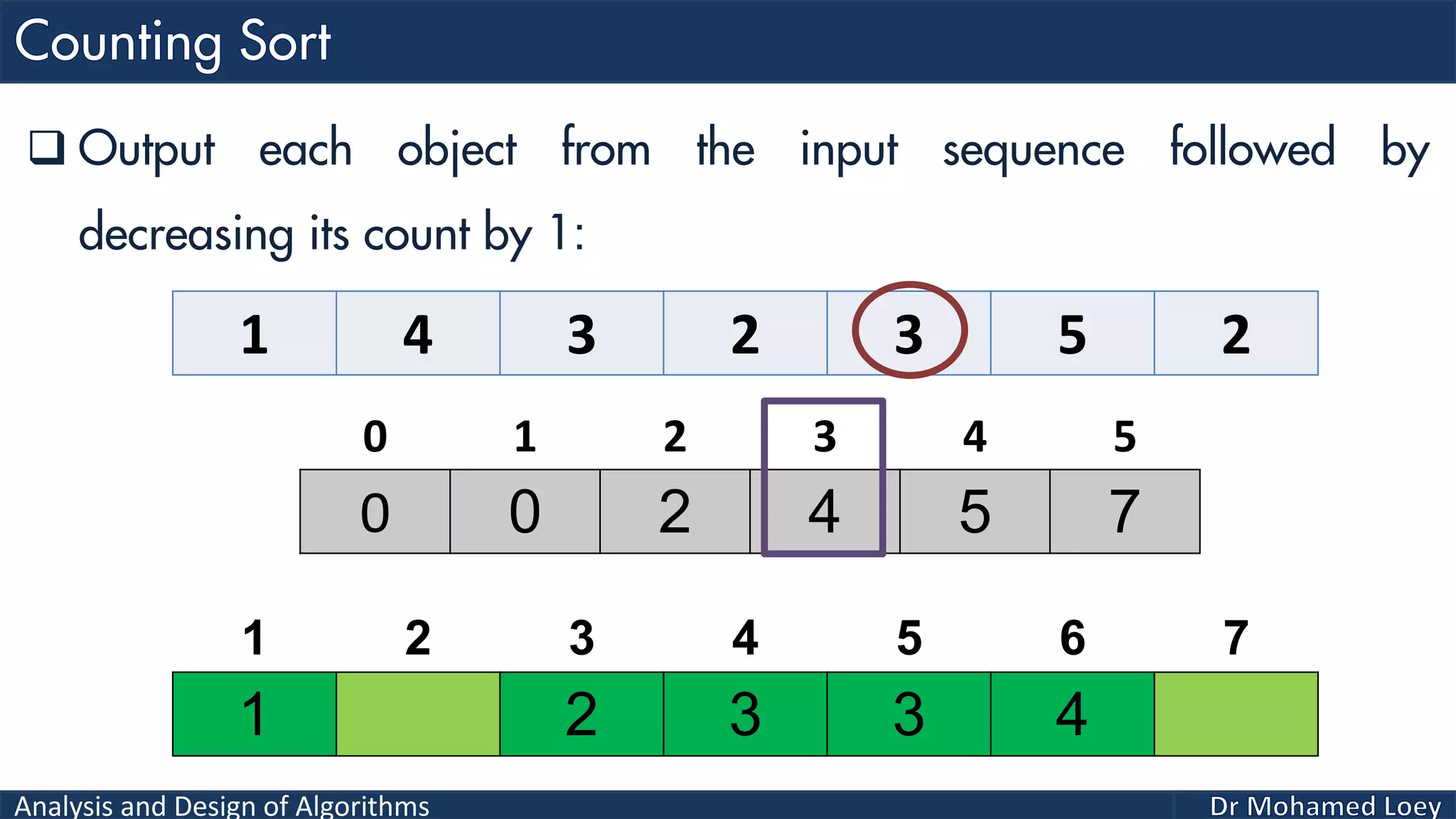
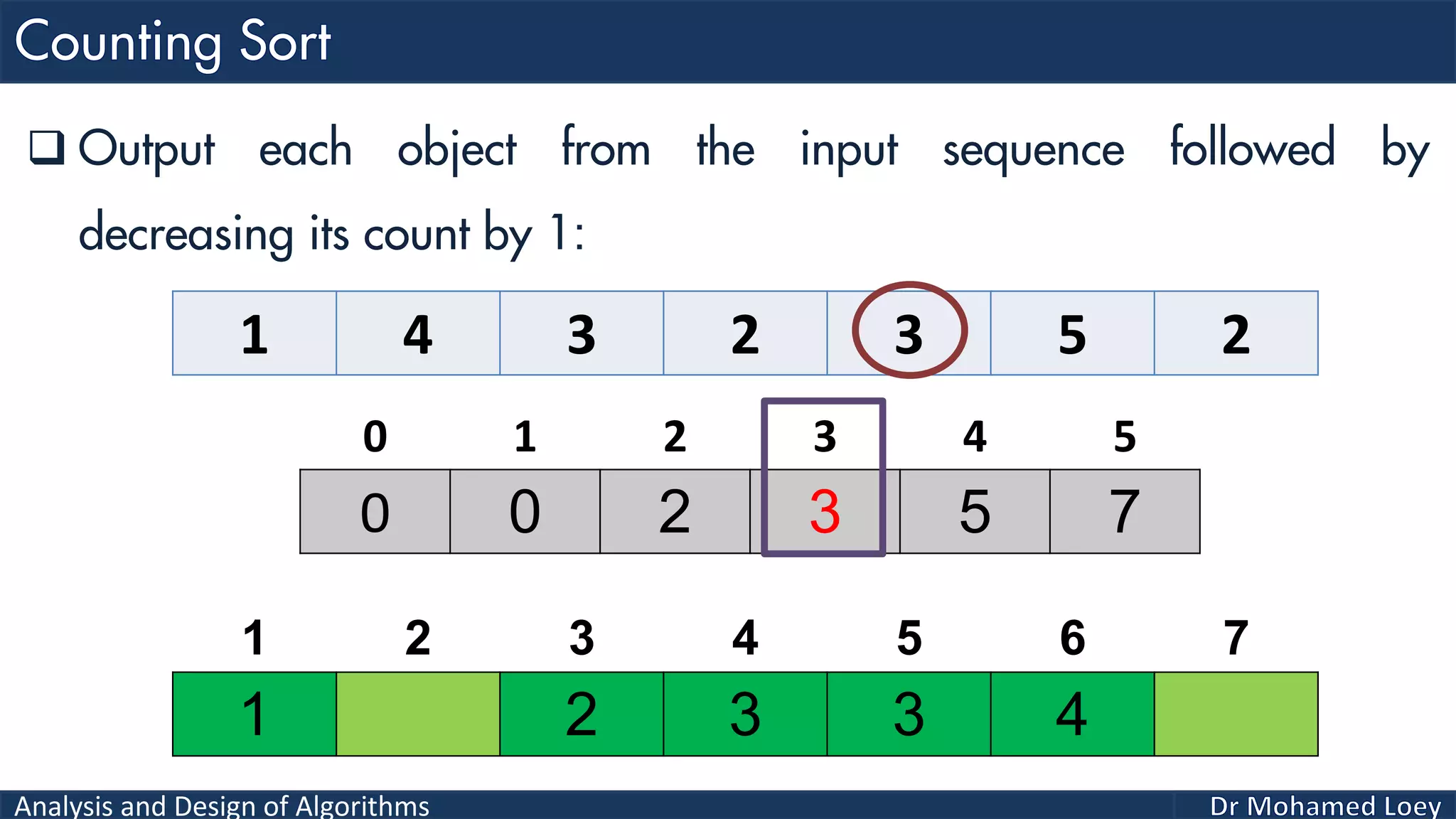
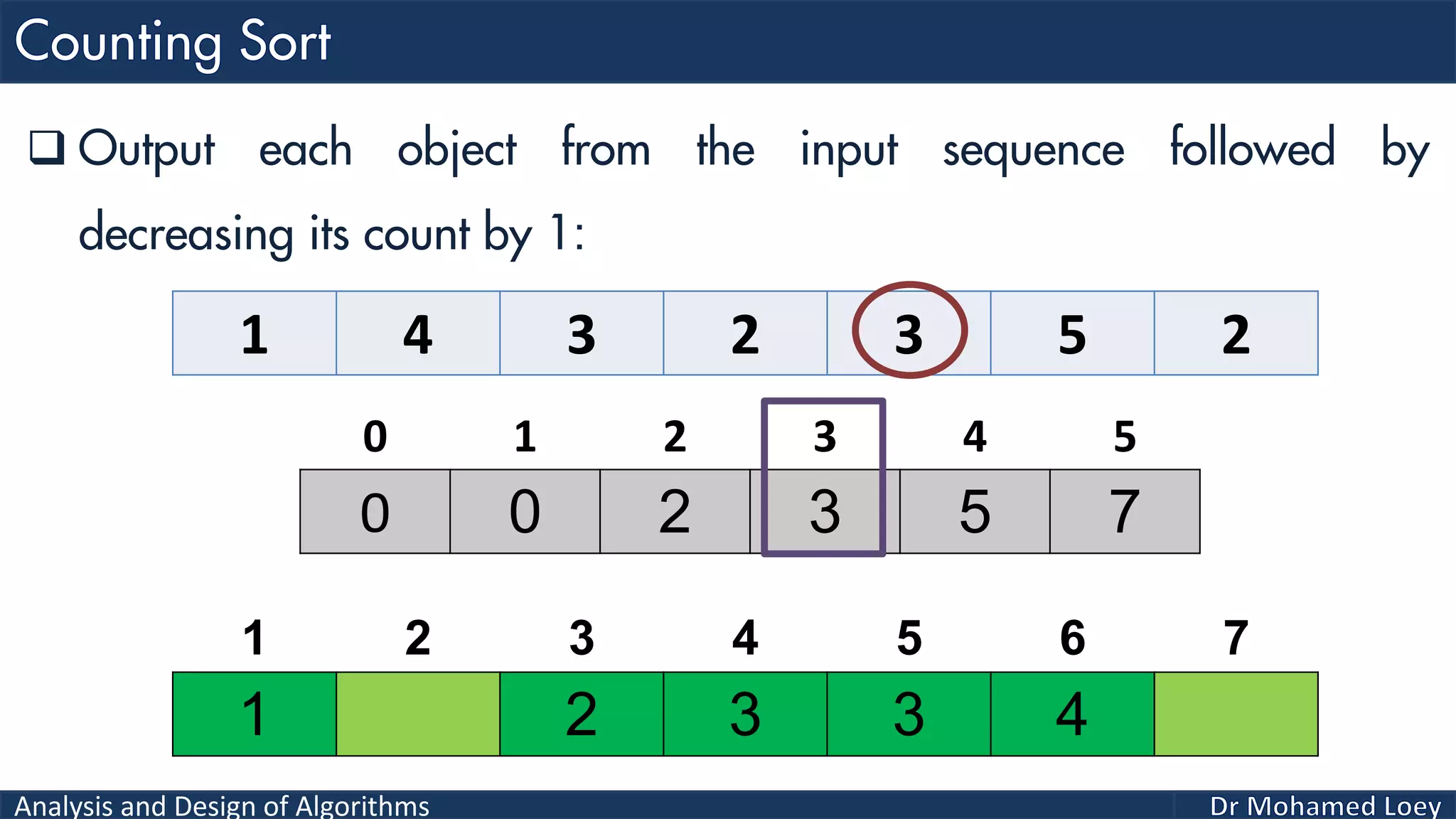
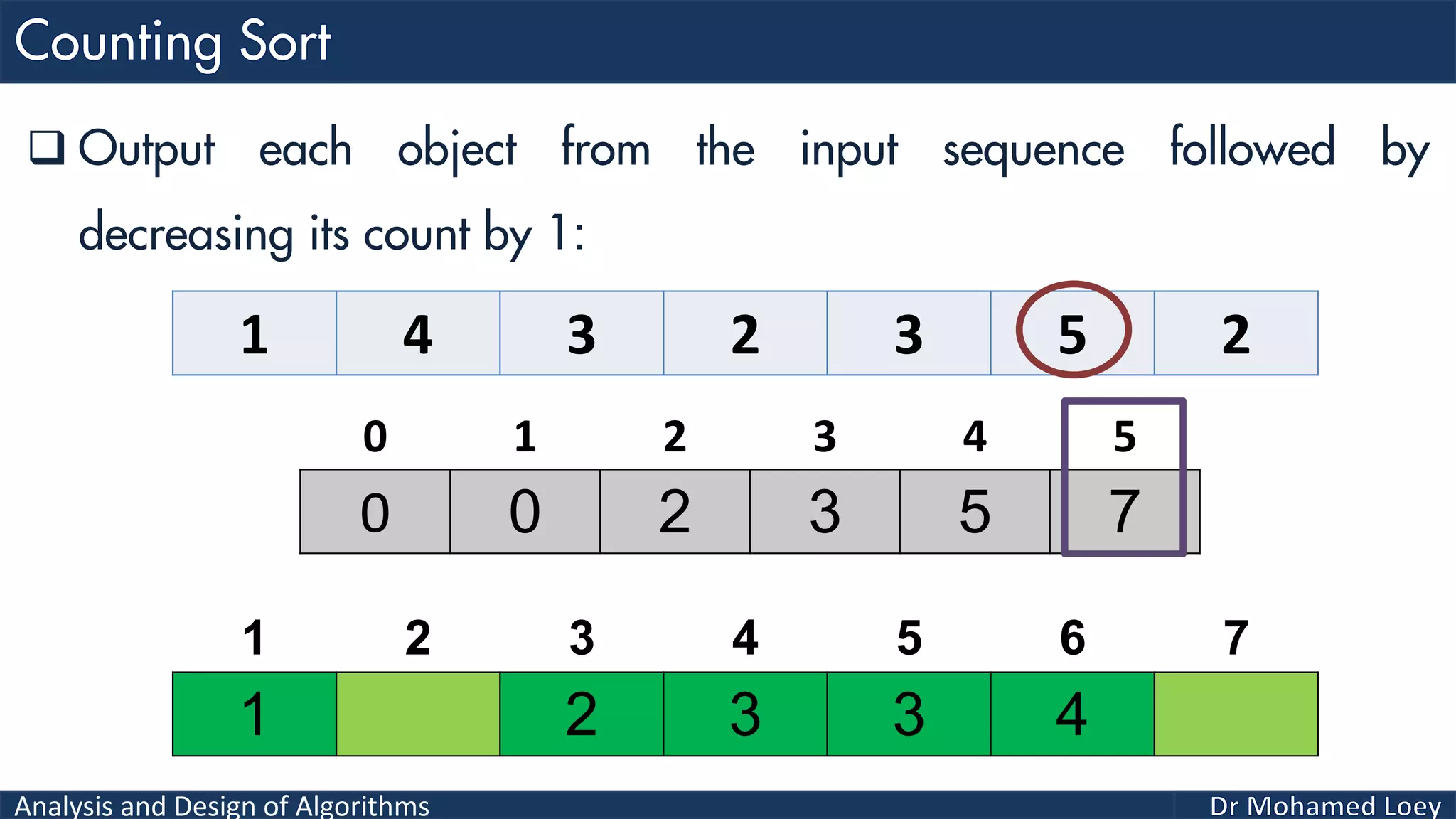
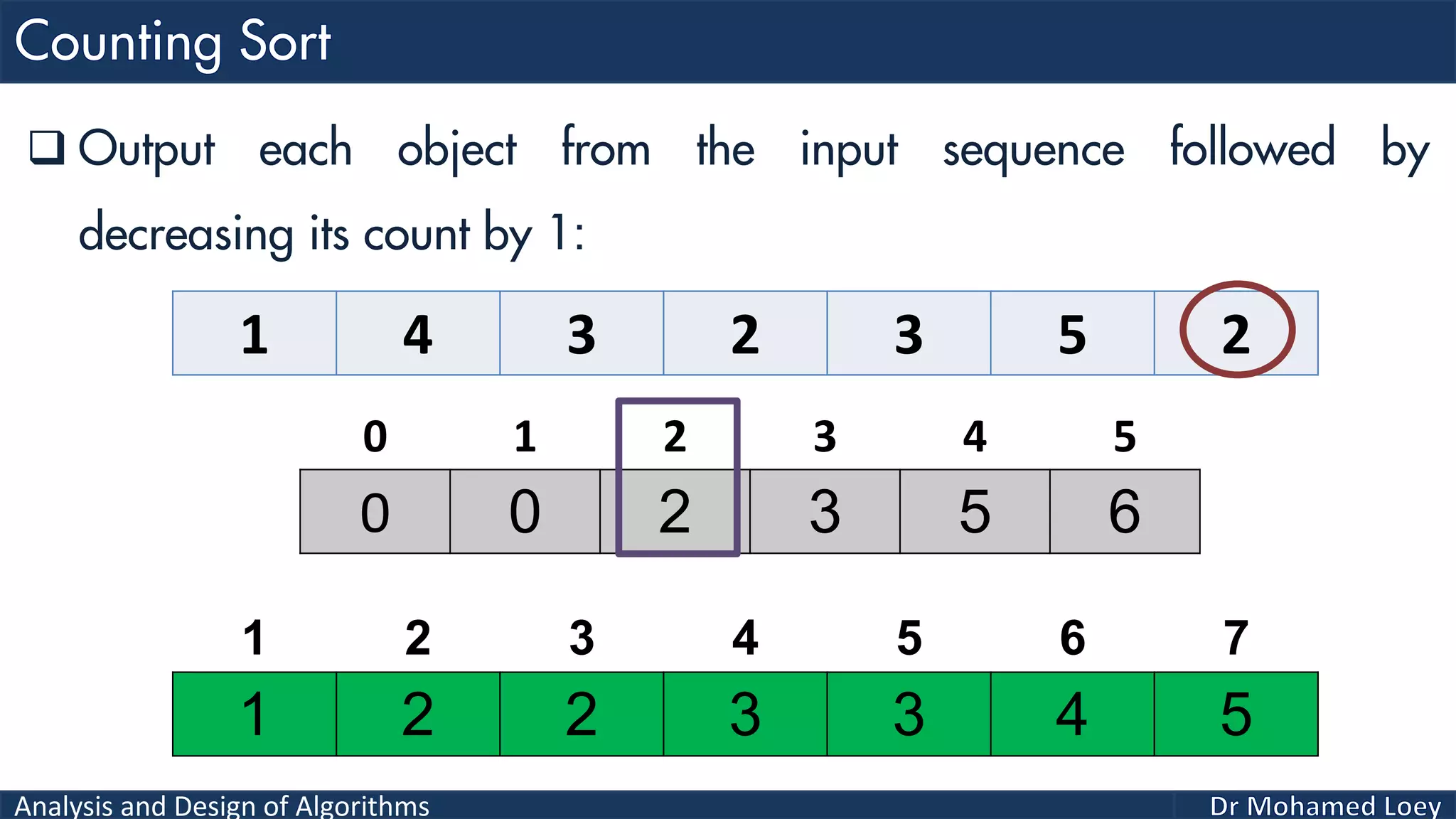
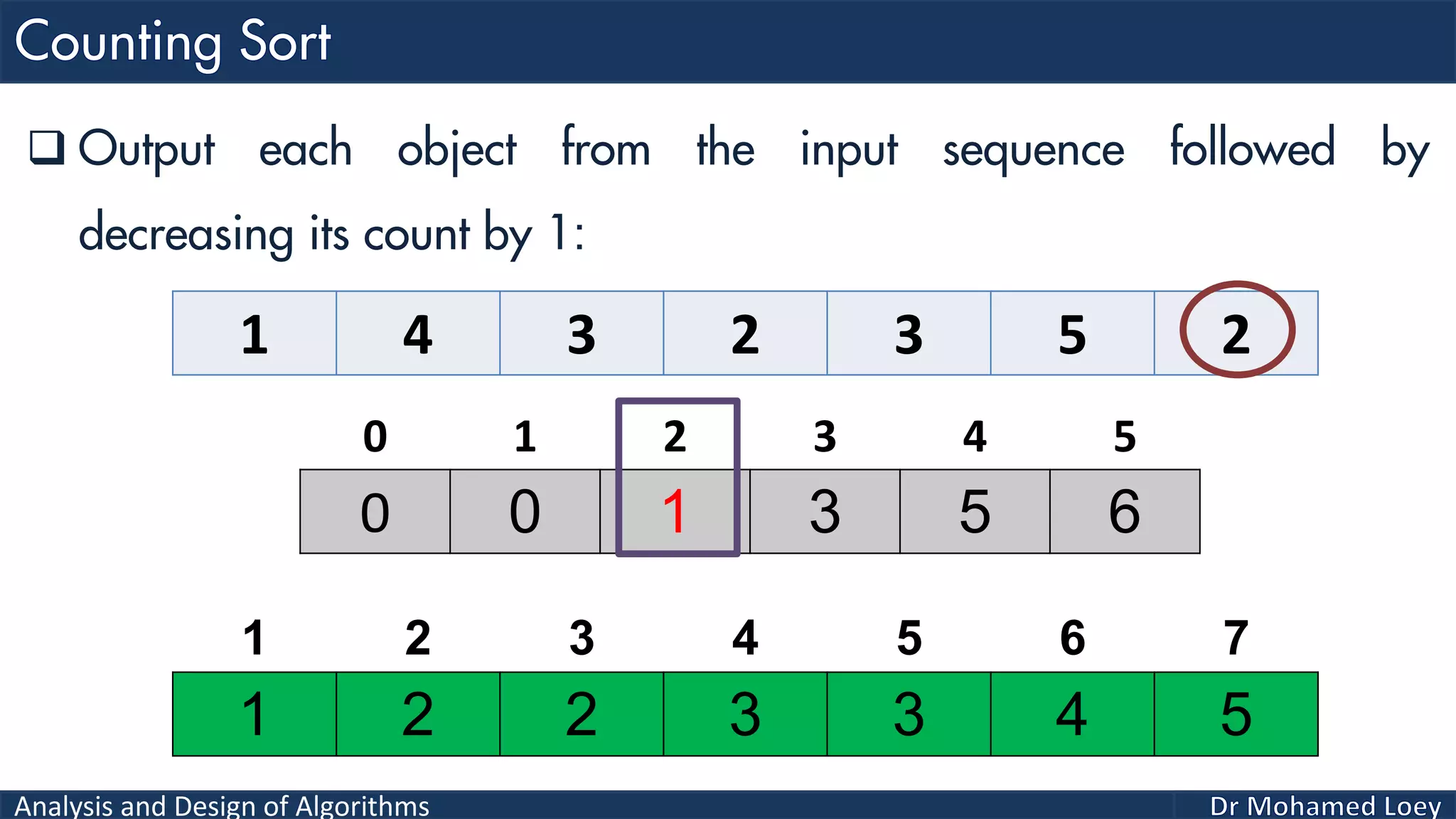
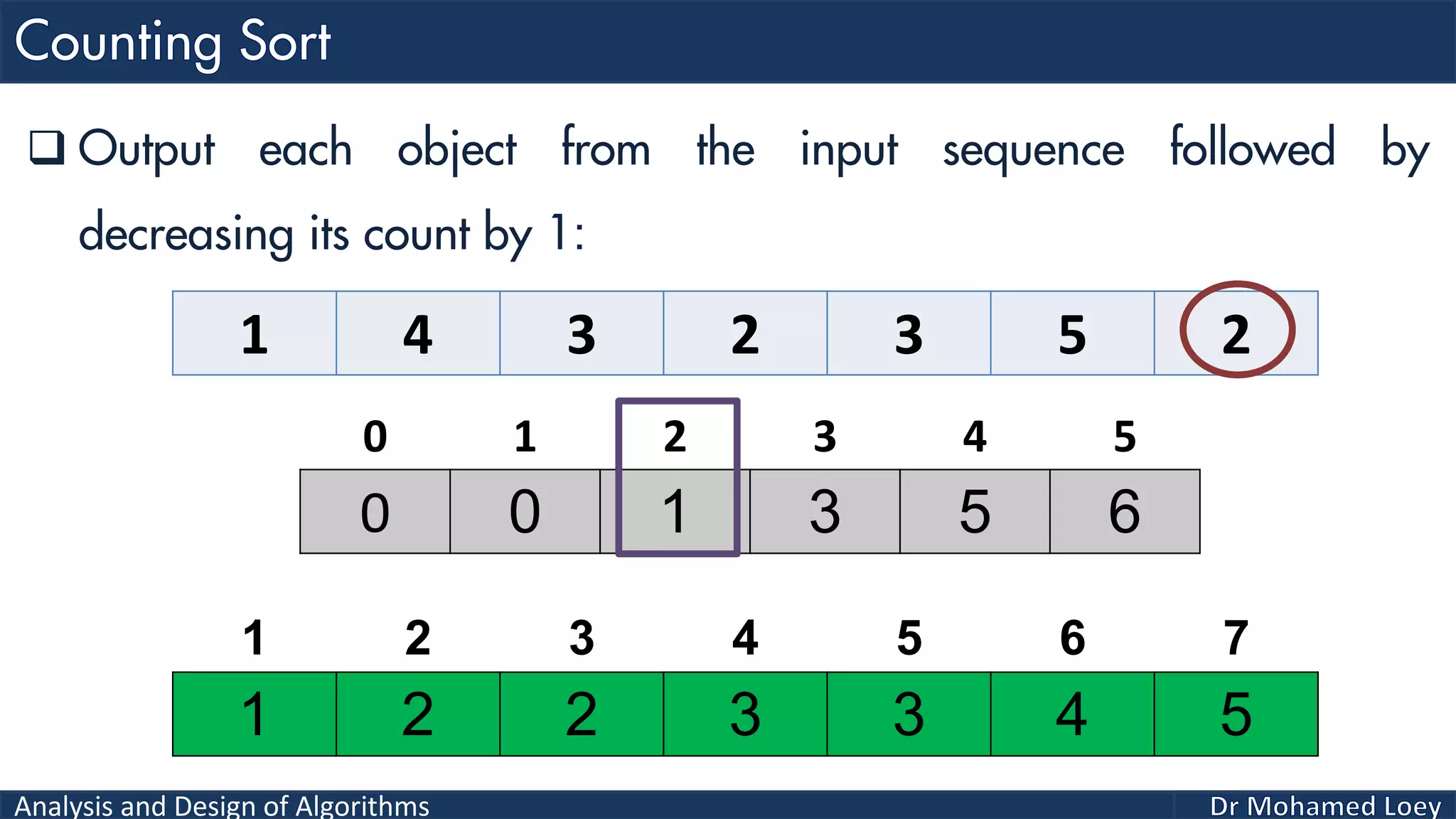
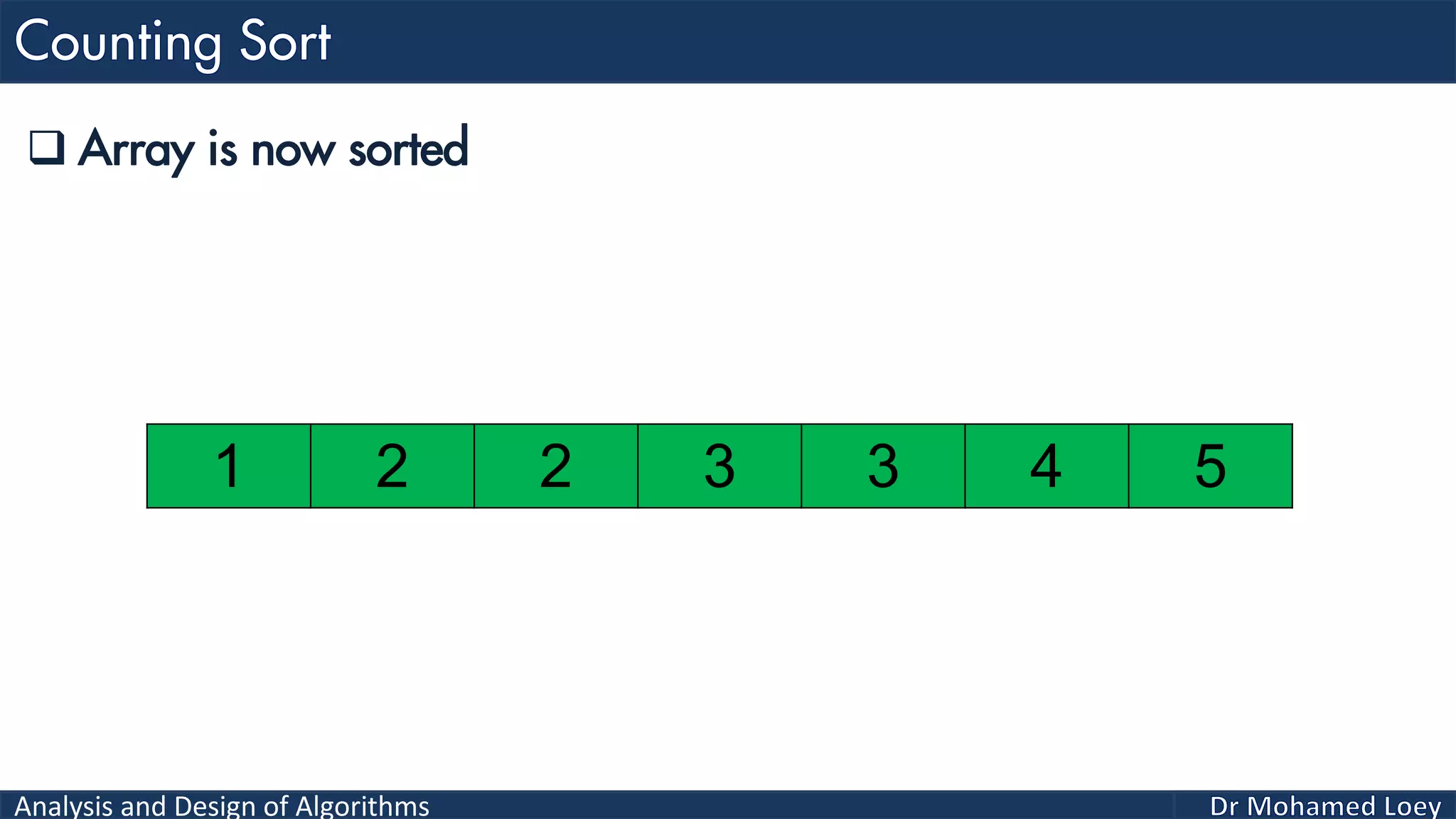
The document discusses sorting algorithms, focusing primarily on counting sort, which is a non-comparison based sorting technique that counts the occurrences of each unique key within a defined range. It outlines the steps for implementing counting sort, including creating a count array, modifying it, and producing the output array based on this count. An illustrative example is provided to demonstrate the counting sort process and its implementation details.









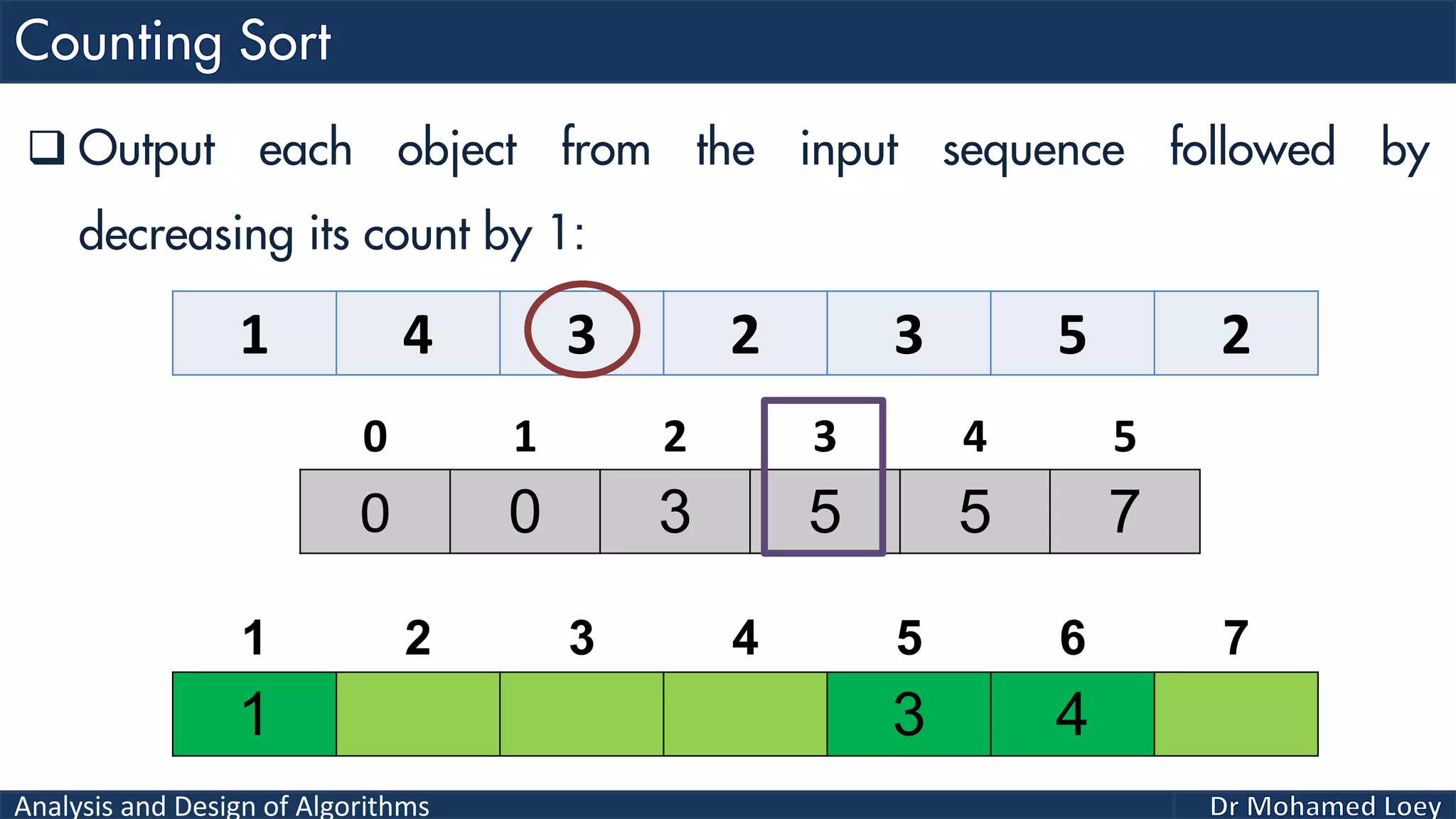
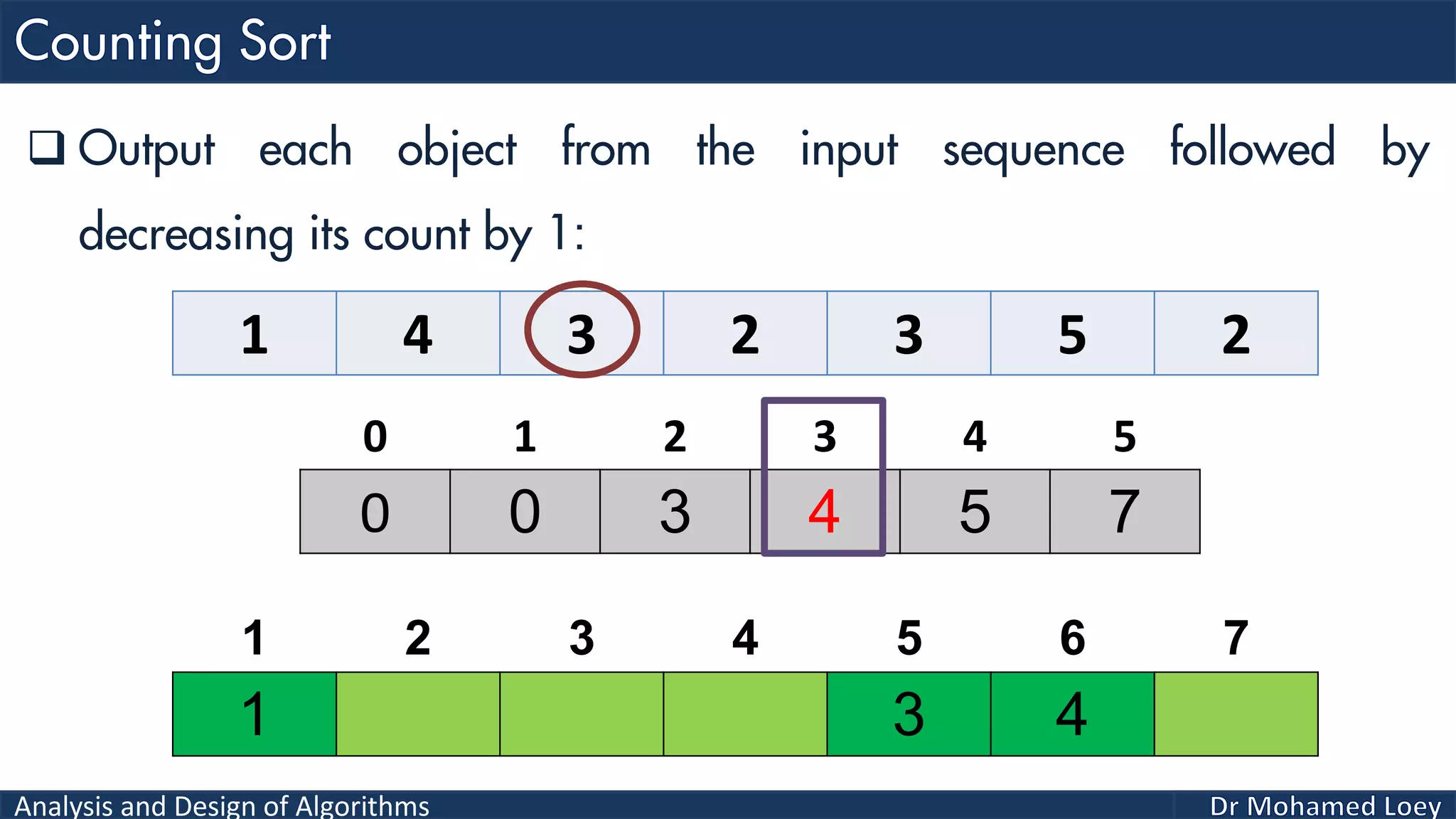
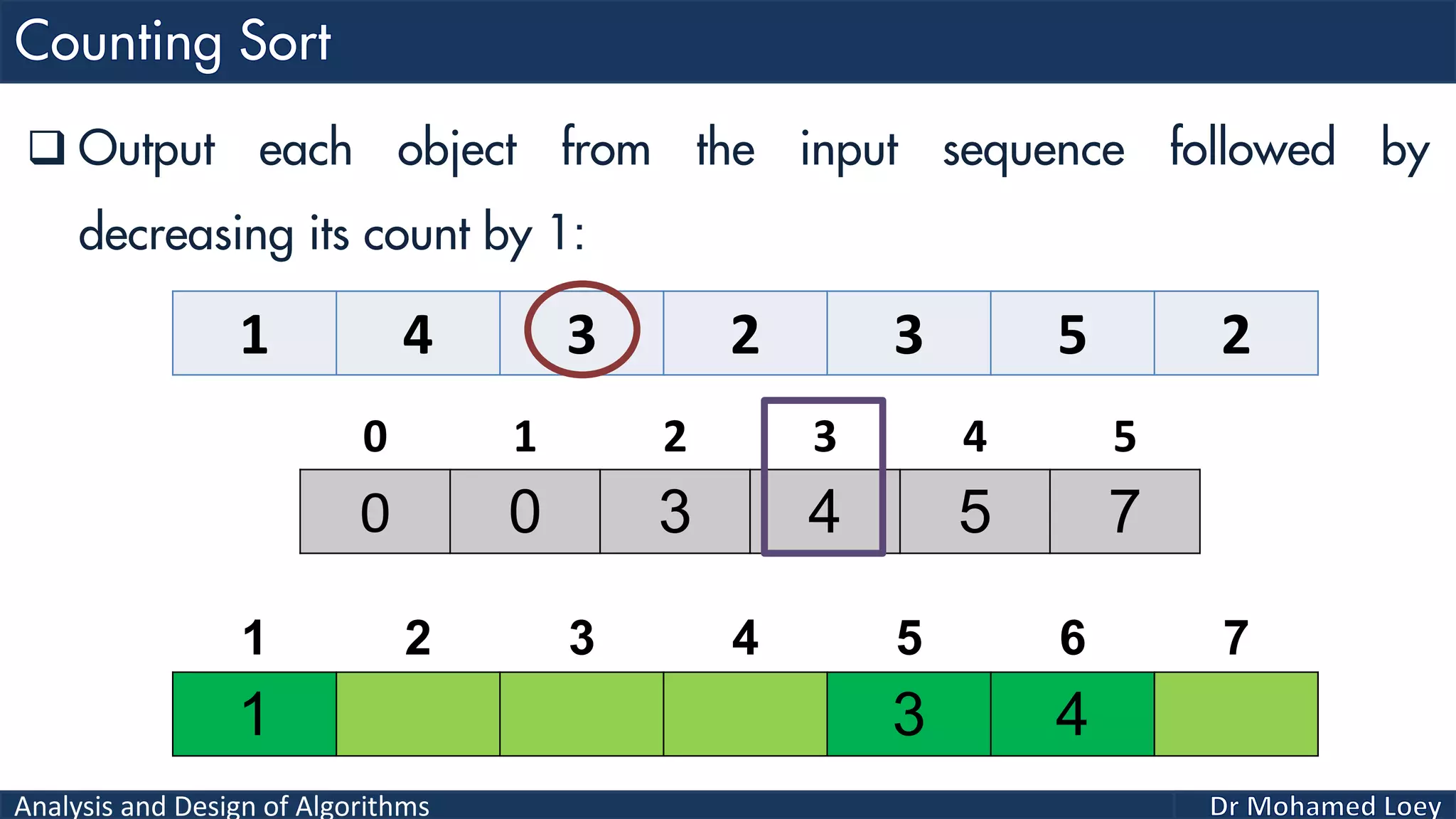
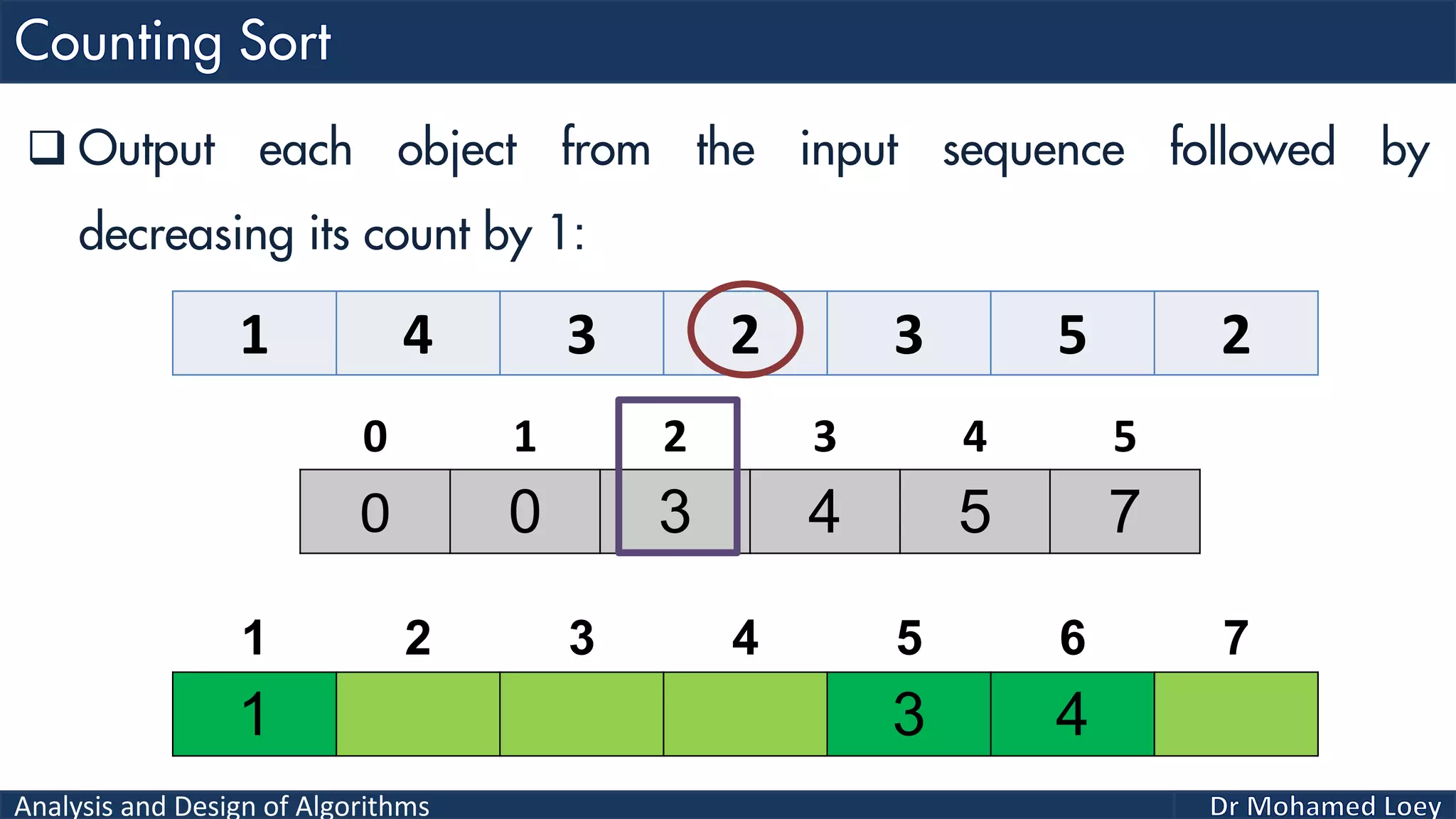
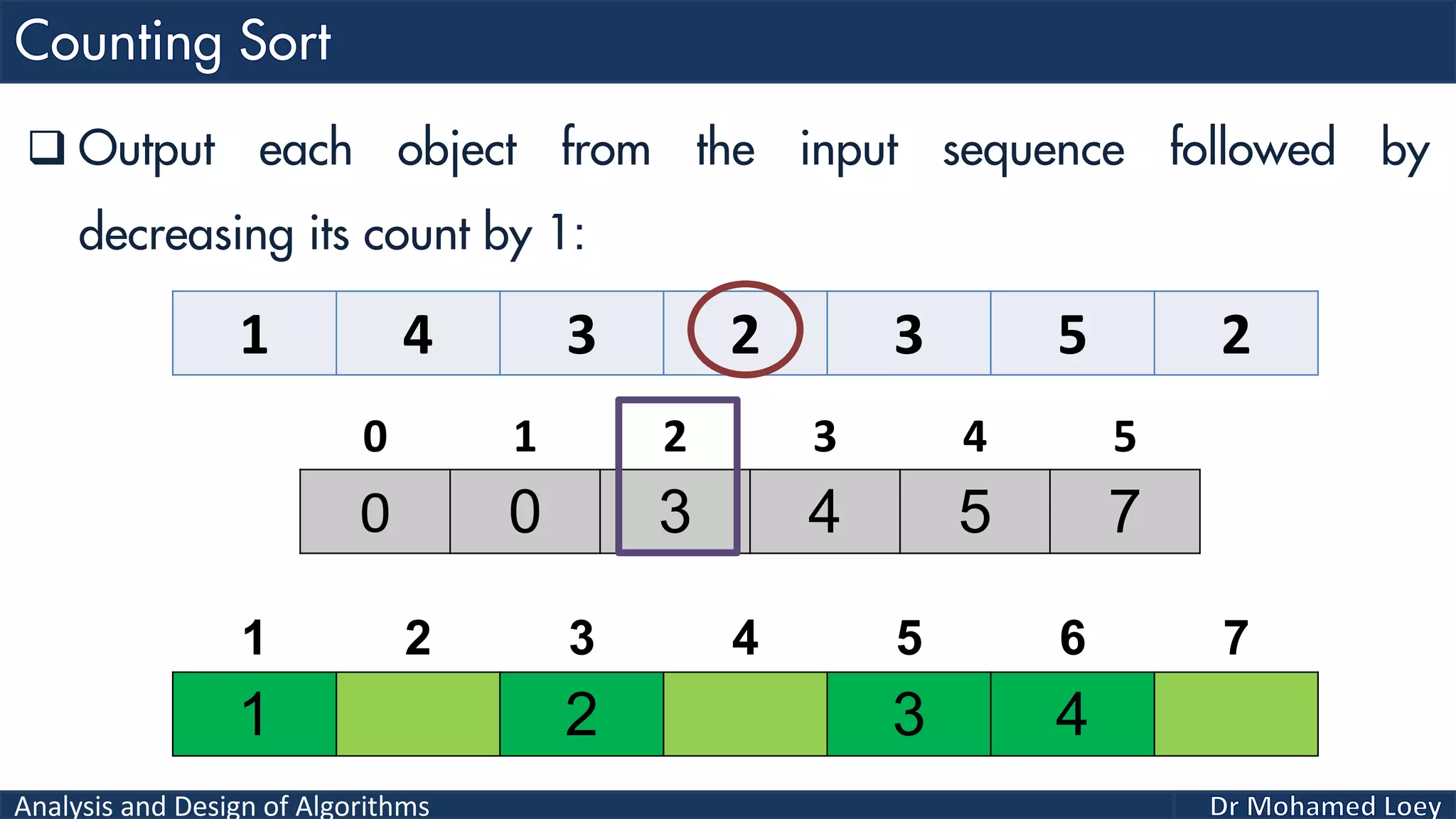
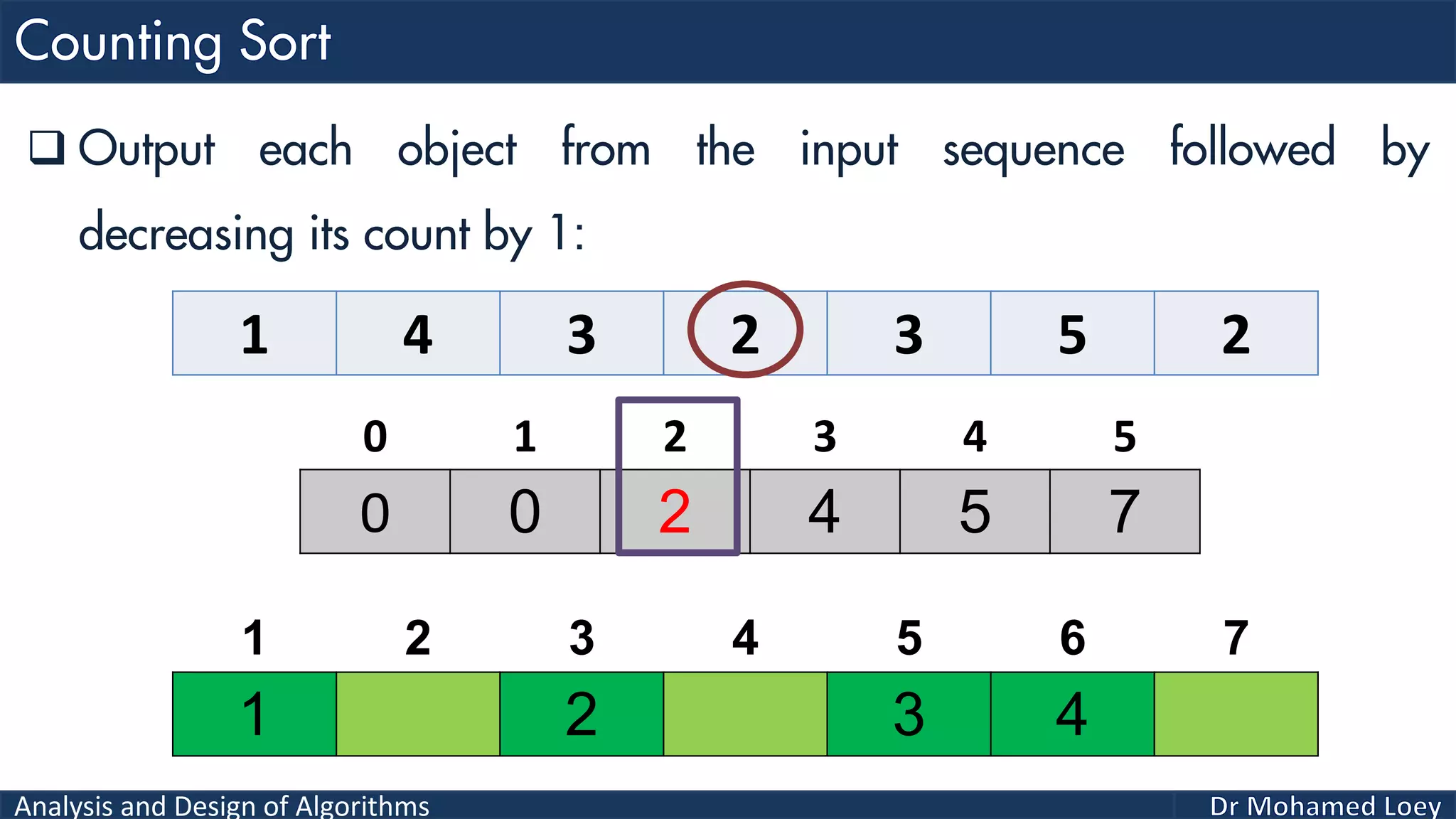
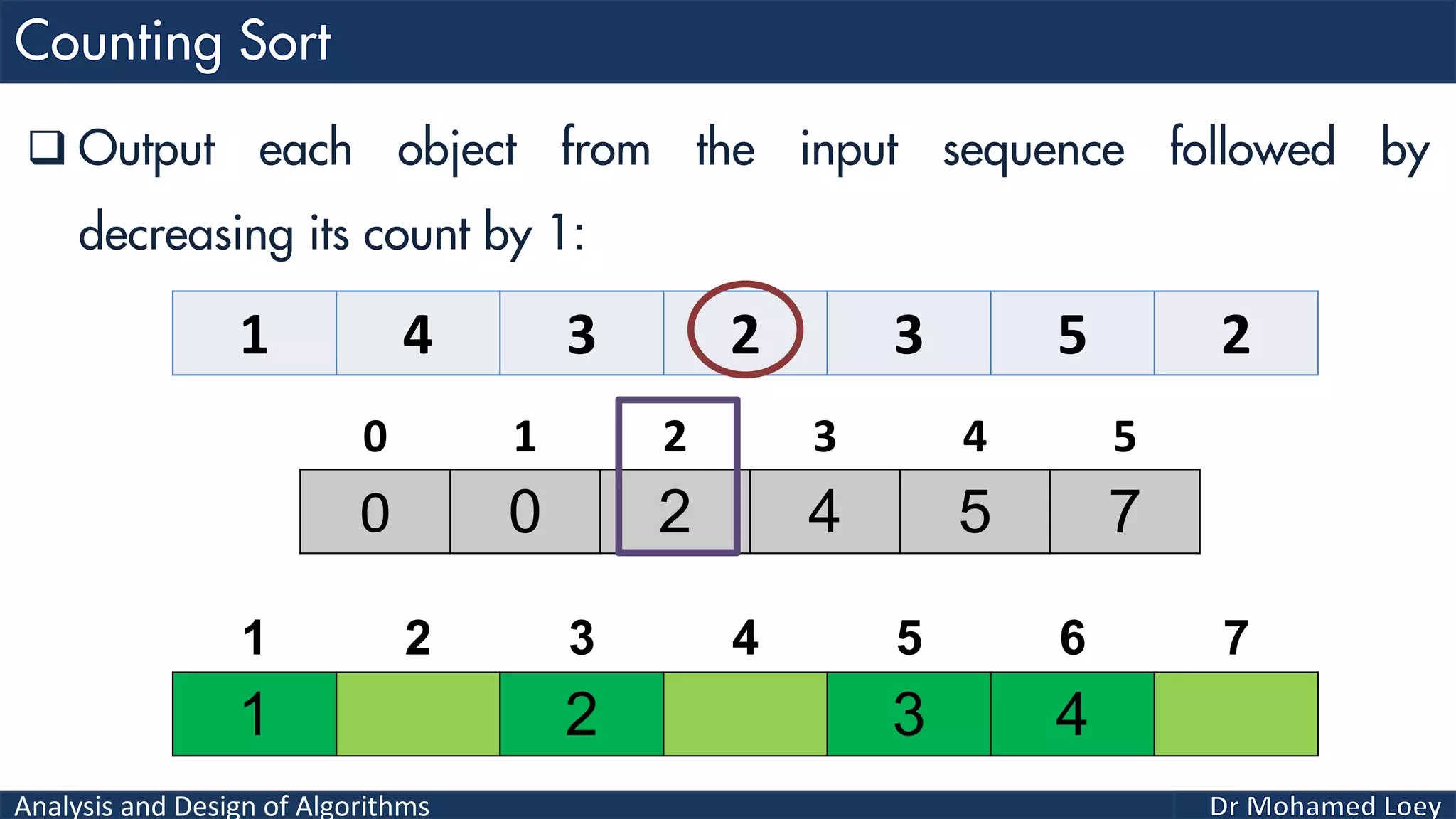
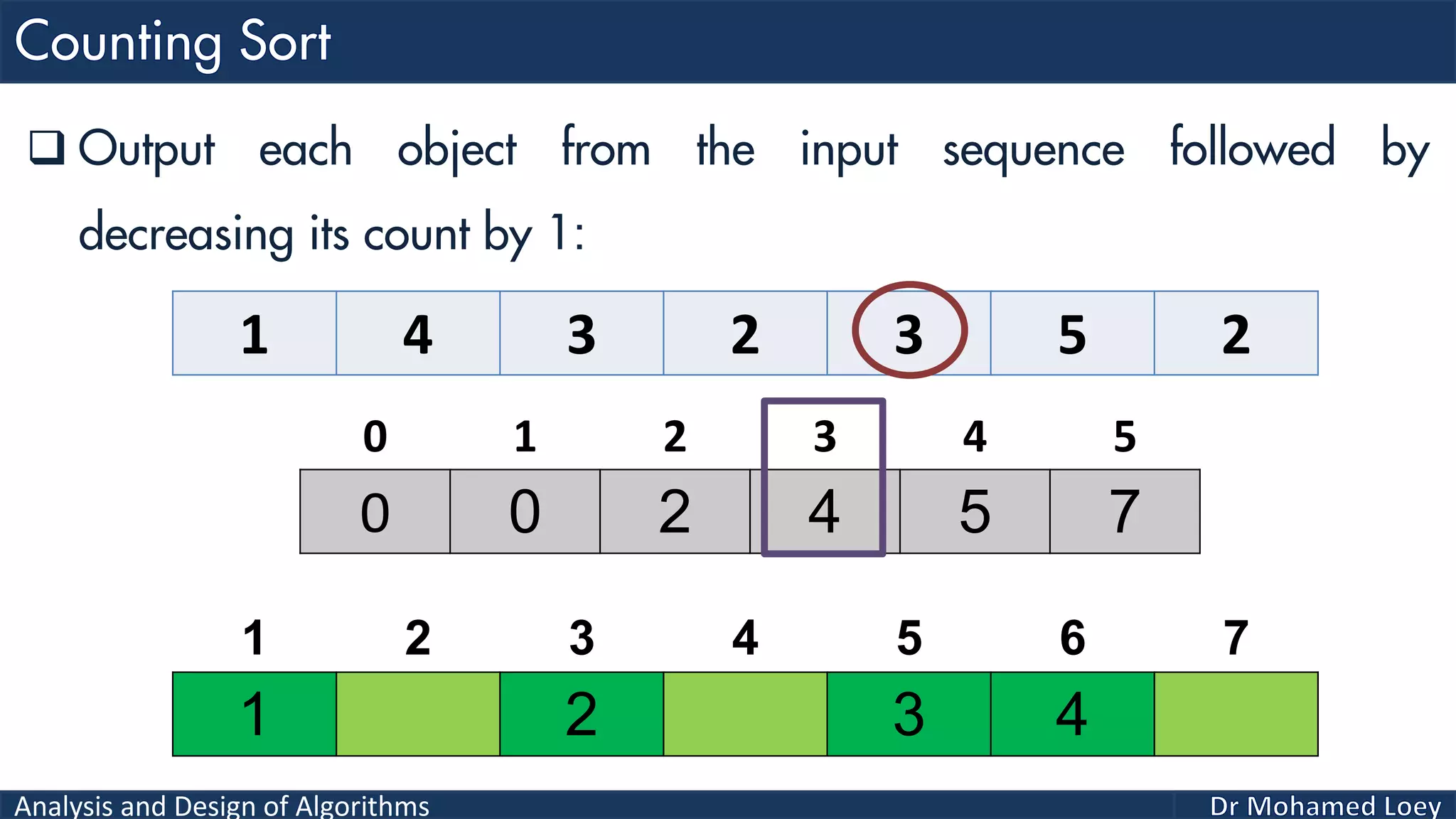
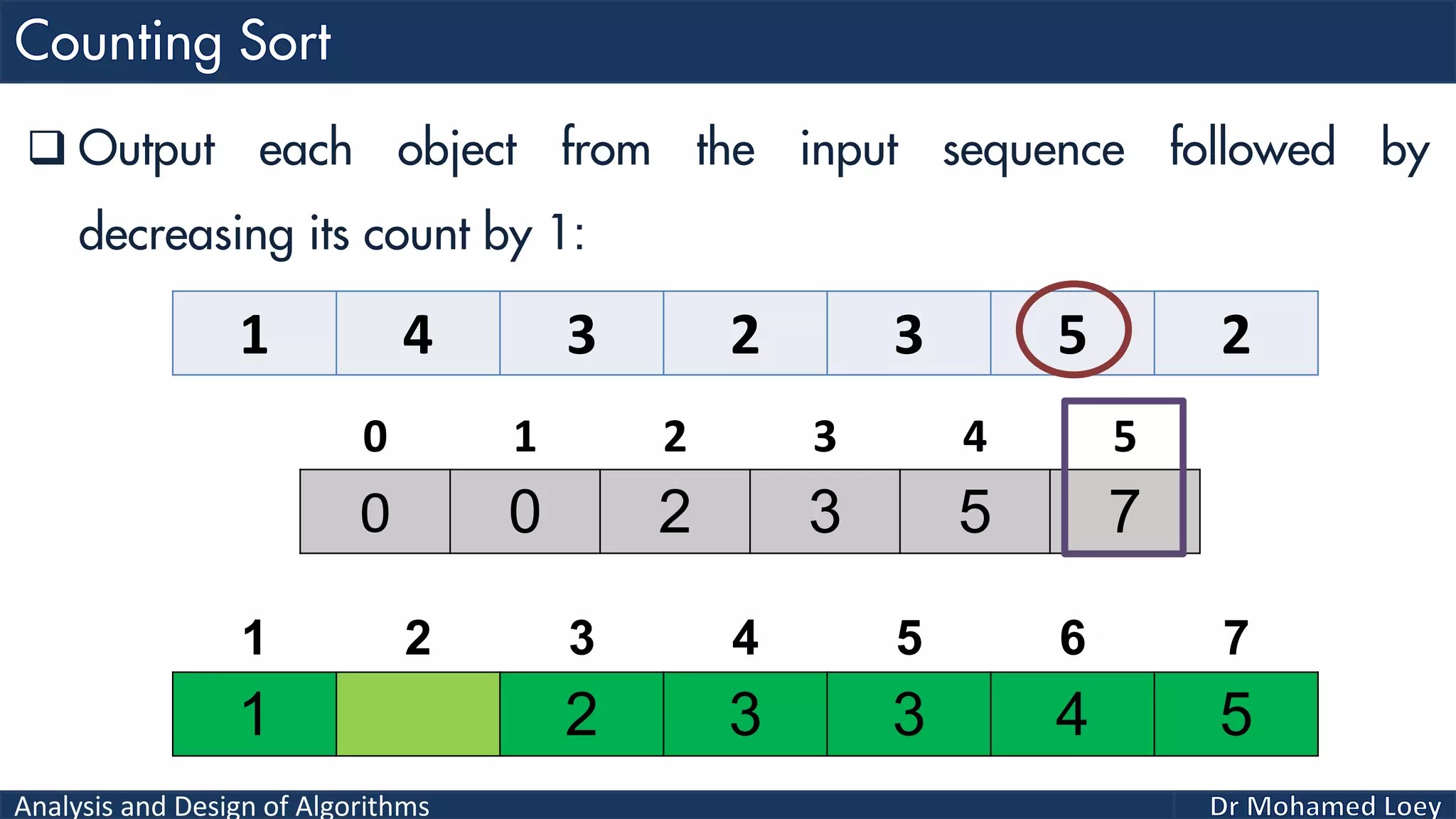
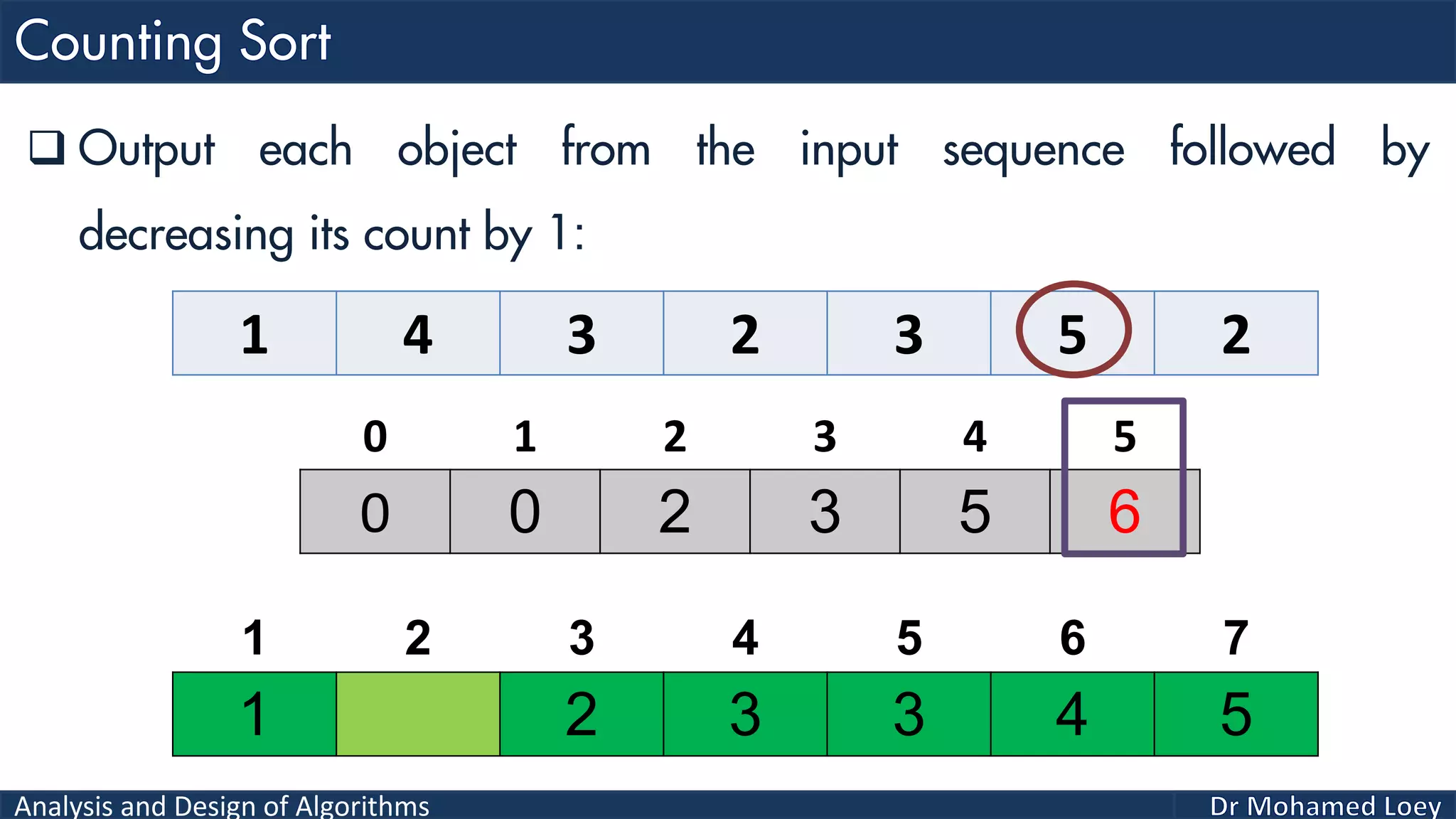
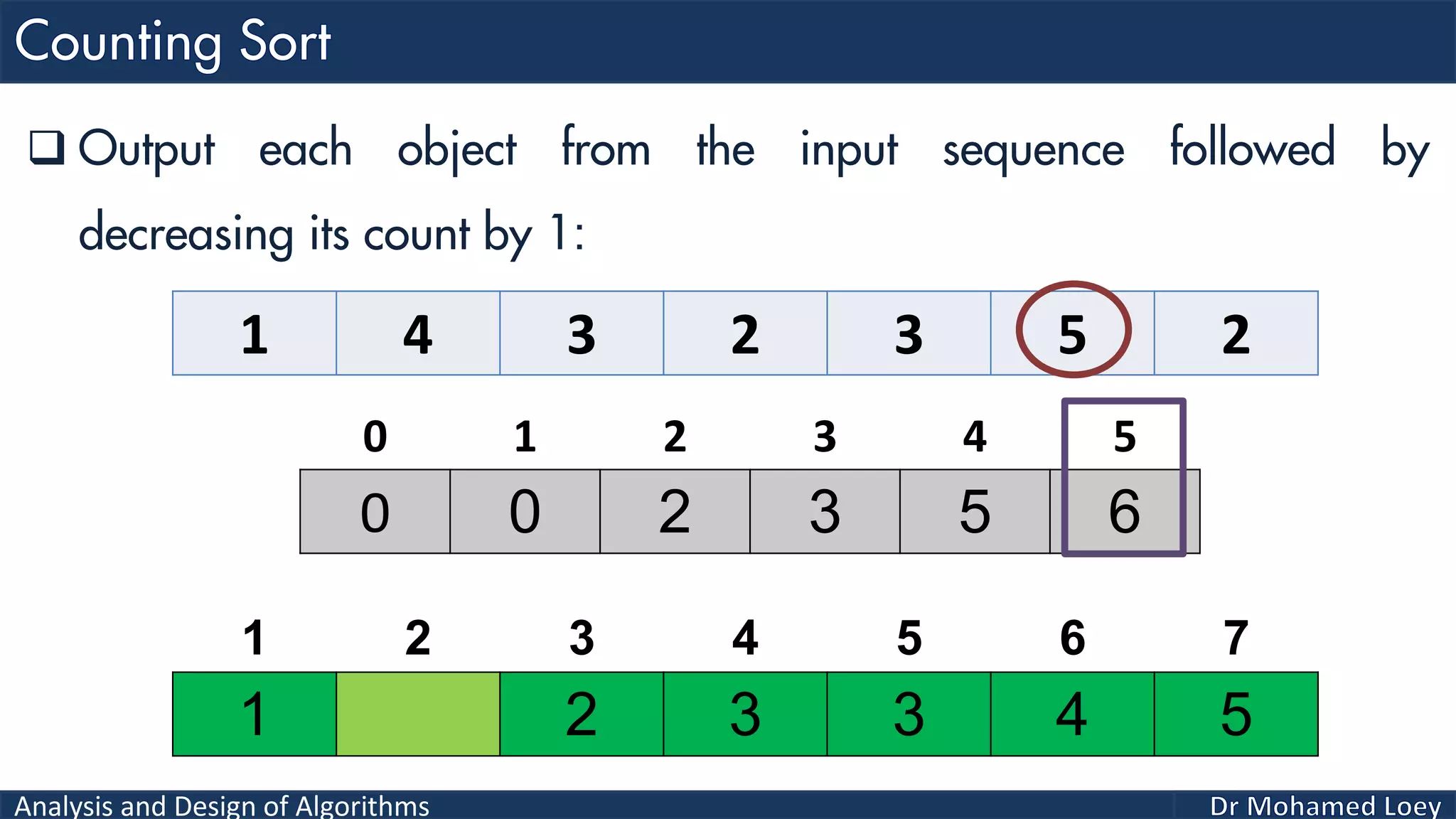
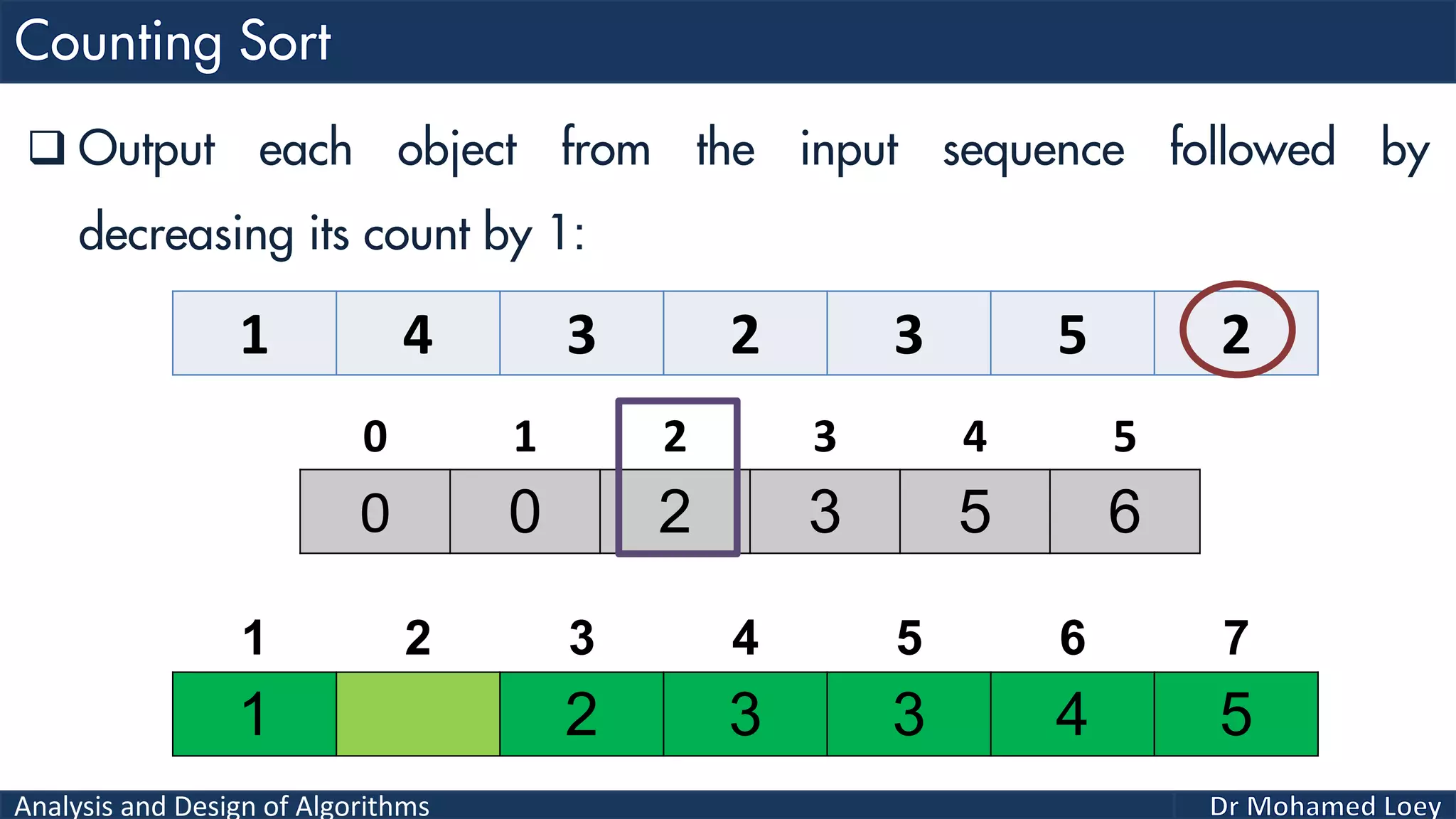
![Analysis and Design of Algorithms 2 4 1 1 3 Example 2: 0 1 2 3 4 0 2 1 1 1 0 2 3 4 5 2 Count Range=[0-4] Add 1 2 3 4 5 Output 0 1 2 3 4 0 2 2 4 5Reduce 0 1 2 3 4 2 4 1 2 3 4 5 Output 0 2 2 4 4Reduce 0 1 2 3 4 1 2 4 1 2 3 4 5 Output 0 1 2 4 4Reduce 0 1 2 3 4 1 1 2 4 1 2 3 4 5 Output 0 0 2 4 4Reduce 0 1 2 3 4 1 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 Output 1 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 Sorted](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithms-lecture5-171025144935/75/Algorithms-Lecture-5-Sorting-Algorithms-II-66-2048.jpg)