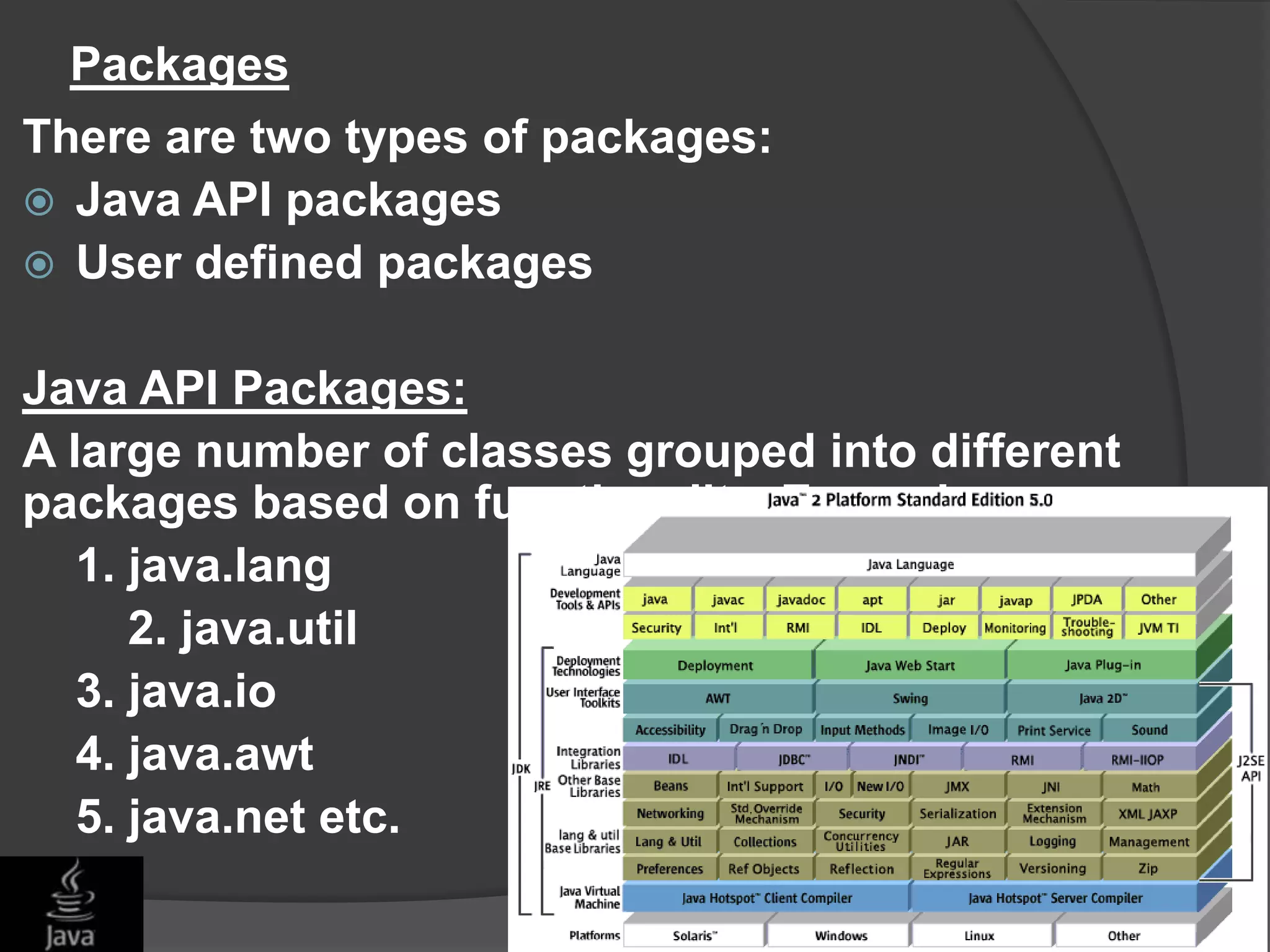
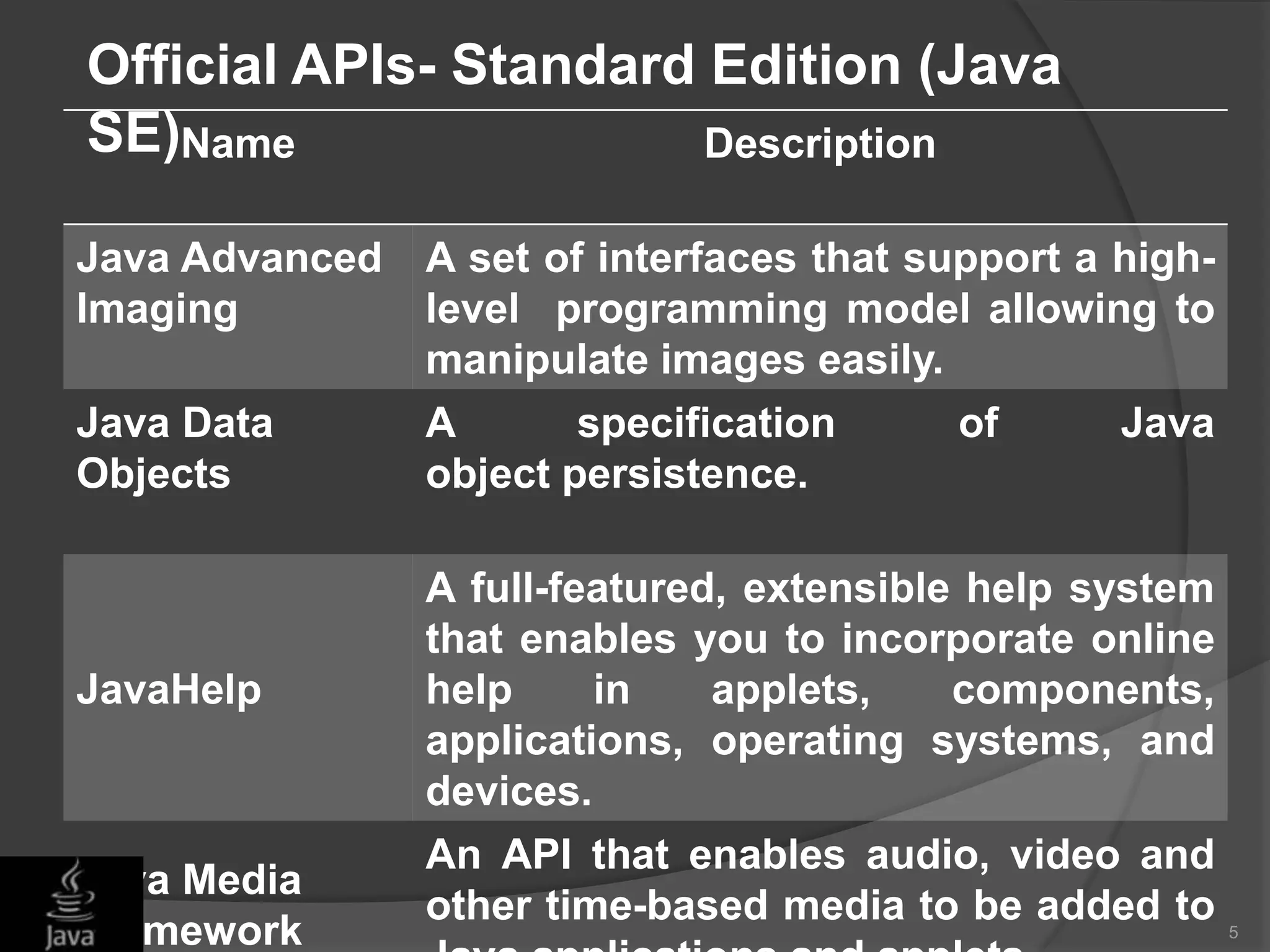
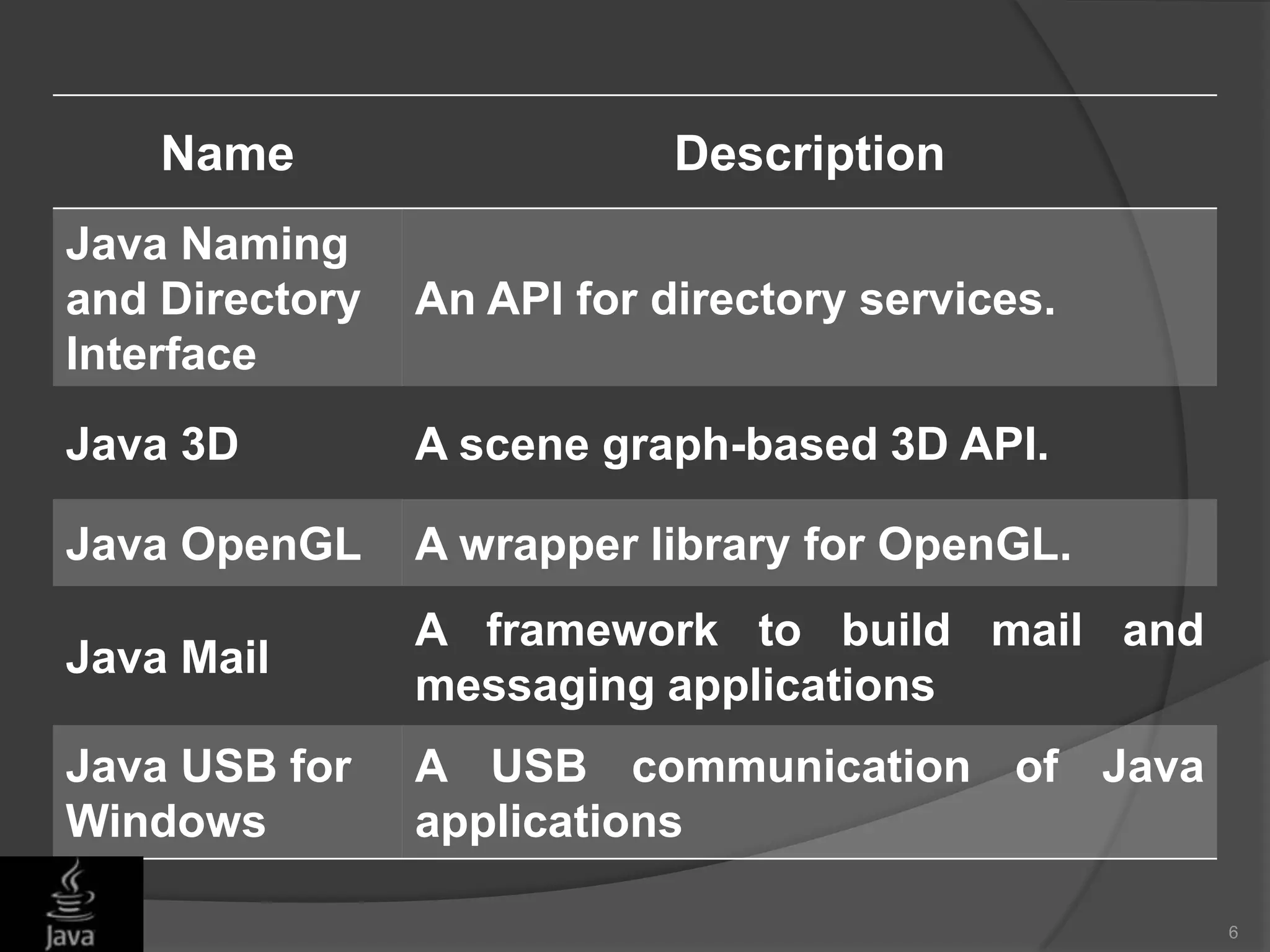
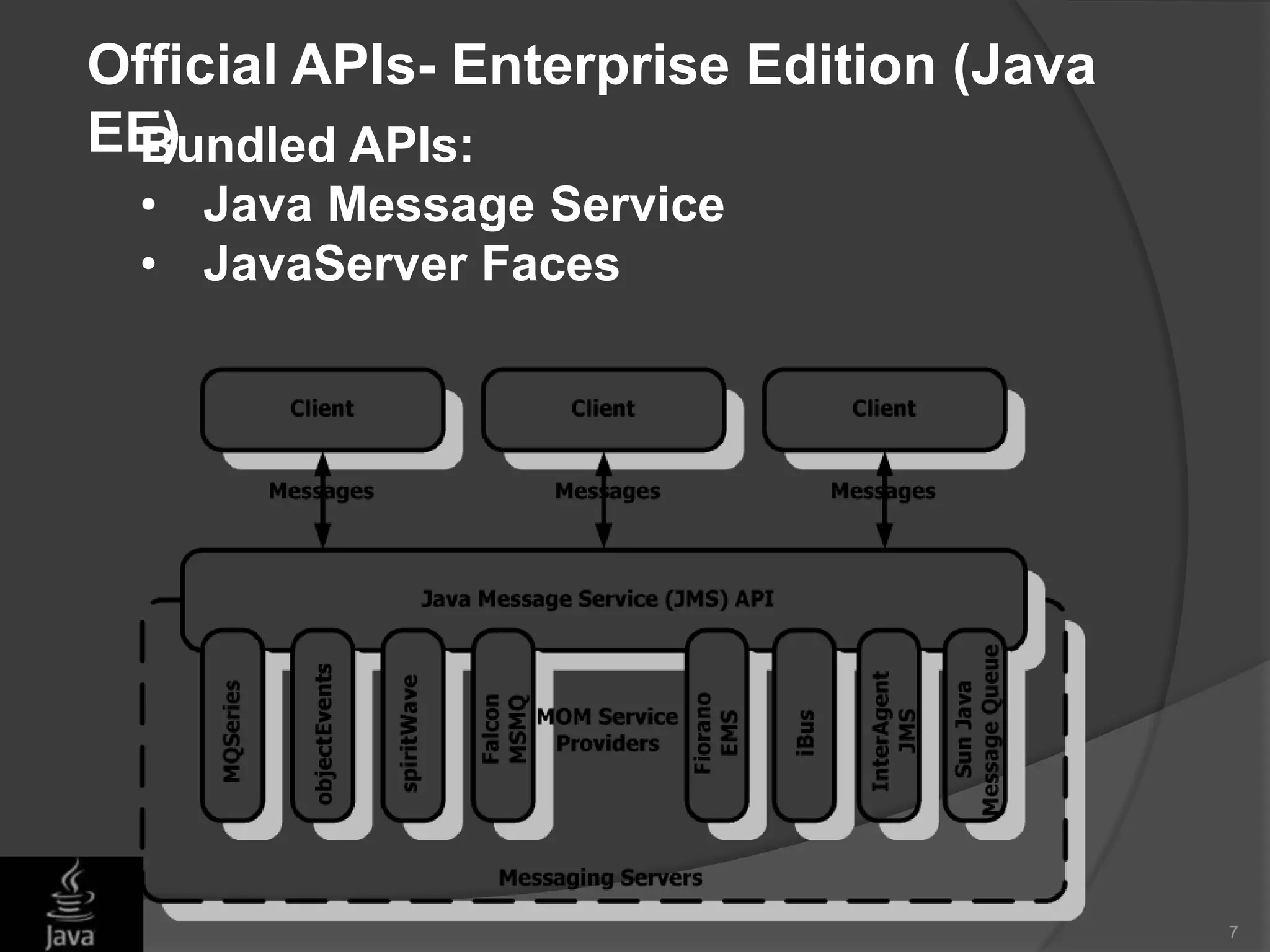
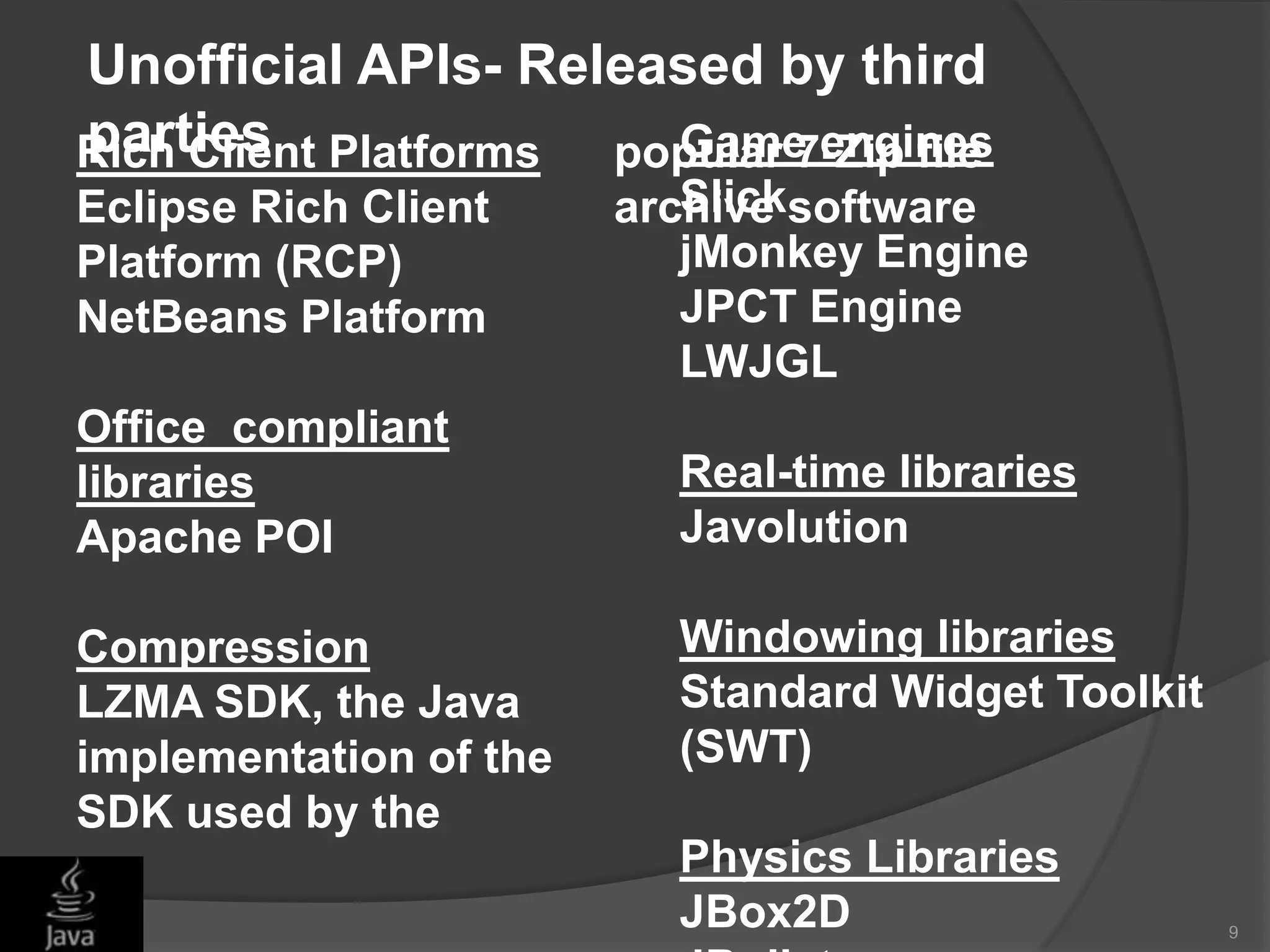
This document discusses Java application programming interfaces (APIs). It begins by explaining that there are three types of Java APIs: 1) the core Java API contained in the JDK, 2) optional APIs that can be downloaded separately, and 3) unofficial APIs developed by third parties. It then provides examples of popular Java APIs, grouping them into categories like the official APIs for Java SE, EE, and ME platforms, as well as unofficial APIs released by third parties. The document serves to outline the different types and categories of Java APIs and provide illustrative examples.