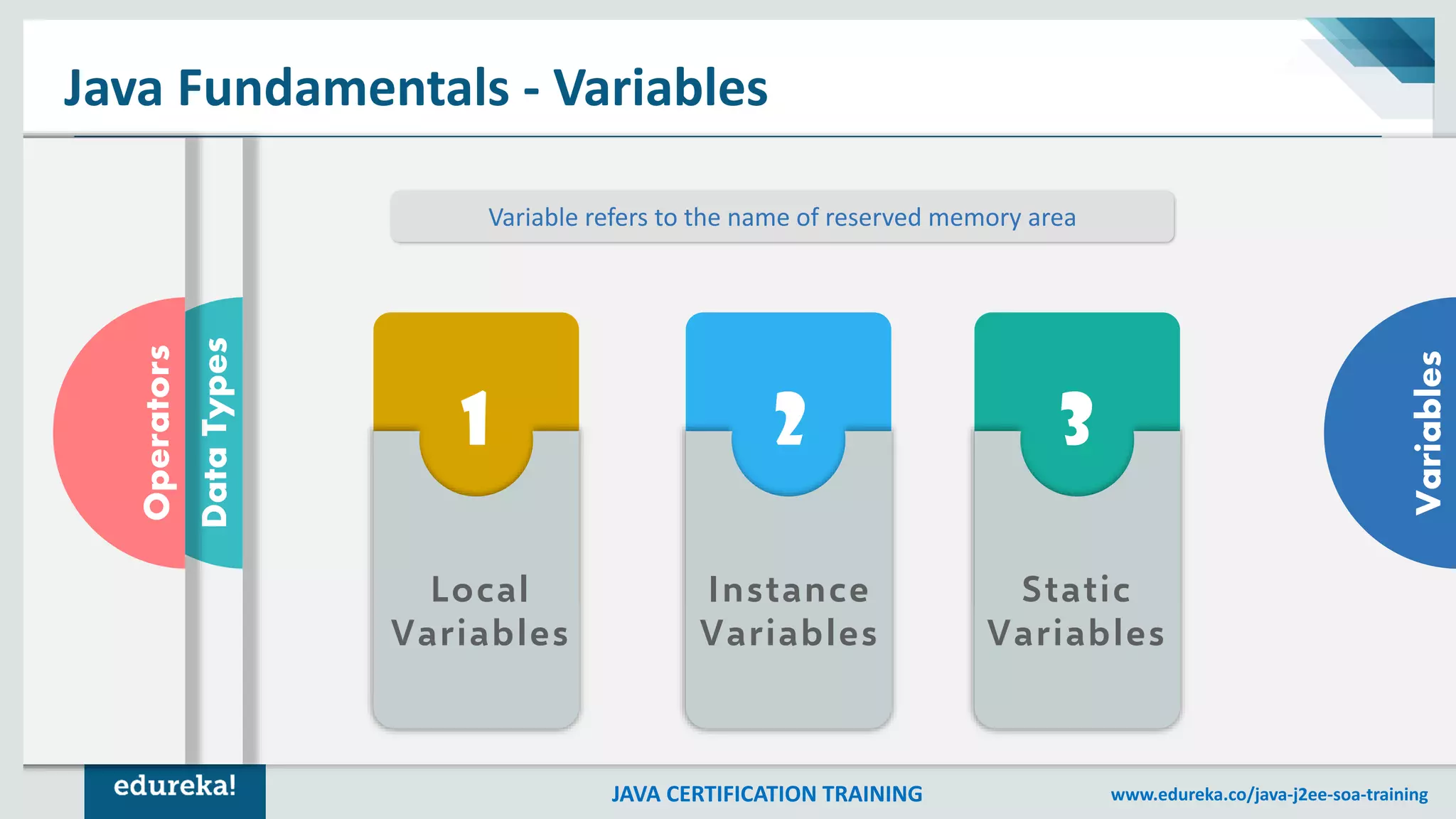
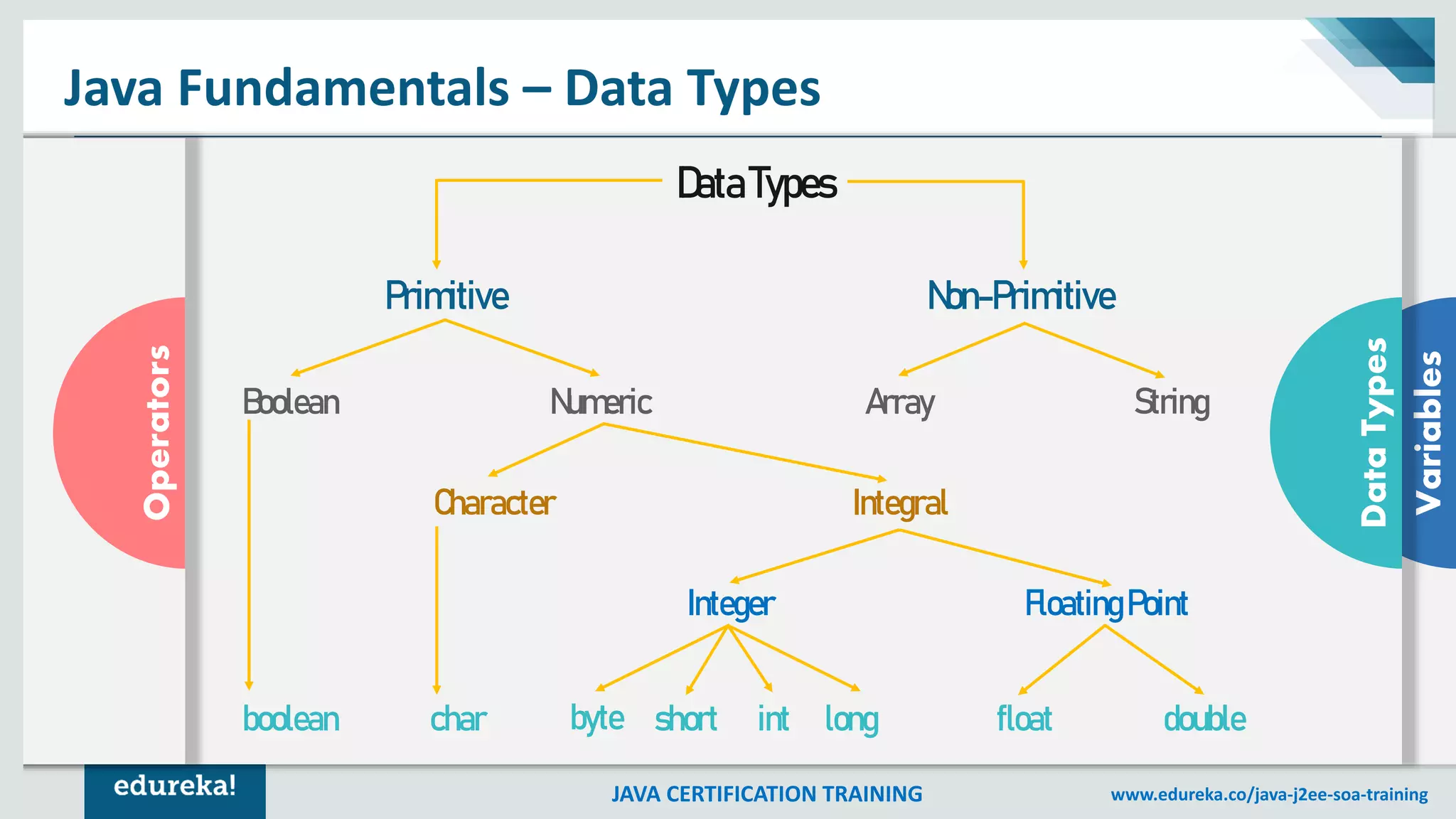
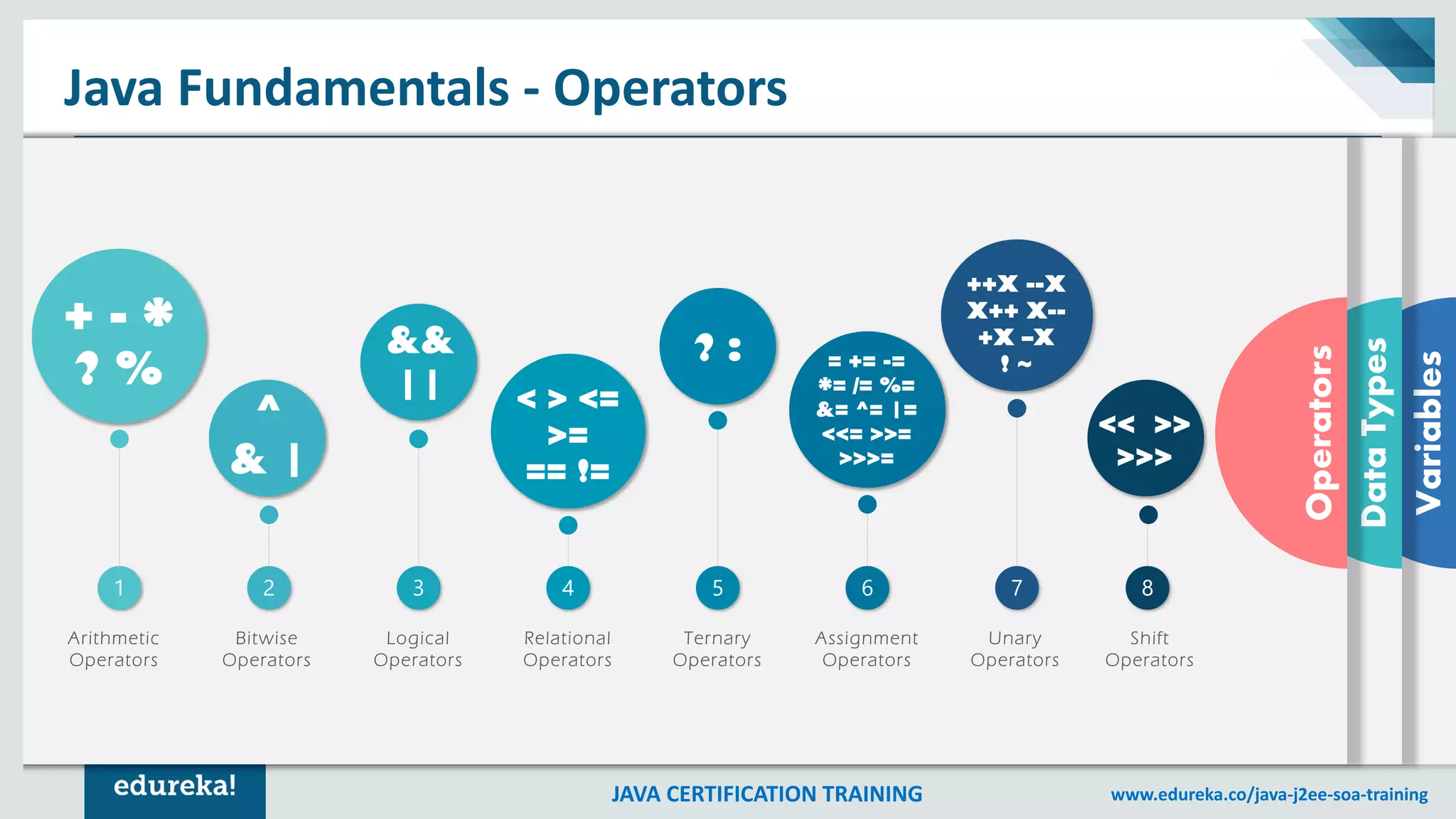
This document outlines a comprehensive Java certification training program, detailing key concepts such as the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and Java Development Kit (JDK). It covers fundamental topics including objects, classes, data types, methods, control structures, loops, and access modifiers, providing syntax examples throughout. The material also explores arrays and various types of statements, offering learners foundational knowledge for programming in Java.


















![JAVA CERTIFICATION TRAINING www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training My First Java Program class Demo{ public static void main(String args[]){ System.out.println("Hello Edureka!!!"); } } public static void main(String args[])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatutorialppt-181105131213/75/Java-Tutorial-For-Beginners-Step-By-Step-Java-Basics-Java-Certification-Training-Edureka-30-2048.jpg)
![JAVA CERTIFICATION TRAINING www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training public static void main String args[] My First Java Program public static void main(String args[])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatutorialppt-181105131213/75/Java-Tutorial-For-Beginners-Step-By-Step-Java-Basics-Java-Certification-Training-Edureka-31-2048.jpg)
![JAVA CERTIFICATION TRAINING www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training public static void main(String args[]) It is a keyword which identifies the class related thing It is used to define the Return Type of the Method It is the name of the method that is searched by JVM as a starting point for an application with a particular signature only It is the parameter to the main Method where the argument name could be anything It is the access modifier of the main method My First Java Program public static void main String args[] NOTE: main() in Java is the most important method as it is the entry point of any java program](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatutorialppt-181105131213/75/Java-Tutorial-For-Beginners-Step-By-Step-Java-Basics-Java-Certification-Training-Edureka-32-2048.jpg)





















![JAVA CERTIFICATION TRAINING www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training Java Arrays – 1 Dimensional 1D 2D Array is an object which contains fixed number of elements of a similar data type under same name arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize]; =myArray new int[5] myArray[0] myArray[1] myArray[2] myArray[3] myArray[4] =myArray[0] 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatutorialppt-181105131213/75/Java-Tutorial-For-Beginners-Step-By-Step-Java-Basics-Java-Certification-Training-Edureka-61-2048.jpg)
![JAVA CERTIFICATION TRAINING www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training 1D 2D Array is an object which contains fixed number of elements of a similar data type under same name arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize]; =myArray new int[5] myArray[0] myArray[1] myArray[2] myArray[3] myArray[4] =myArray[2] 10 30 =myArray[3] 40 =myArray[4] 50 =myArray[1] 20 Java Arrays – 1 Dimensional](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatutorialppt-181105131213/75/Java-Tutorial-For-Beginners-Step-By-Step-Java-Basics-Java-Certification-Training-Edureka-62-2048.jpg)
![JAVA CERTIFICATION TRAINING www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training 1D 2D Array is an object which contains fixed number of elements of a similar data type under same name arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize]; =myArray new int[5] myArray[0] myArray[1] myArray[2] myArray[3] myArray[4] 10 30 40 5020 Java Arrays – 1 Dimensional](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatutorialppt-181105131213/75/Java-Tutorial-For-Beginners-Step-By-Step-Java-Basics-Java-Certification-Training-Edureka-63-2048.jpg)
![JAVA CERTIFICATION TRAINING www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training 1D 2D Java Arrays – 2 Dimensional Like a 1D array, a 2D array is also a collection of data cells, all of the same type, which can be given a single name datatype[][] arrayRefVar = new dataType[row][col]; =int[][] myArray new int[2][2] myArray[0][0] myArray[0][1] myArray[1][0] myArray[1][1] =myArray[0][0] 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatutorialppt-181105131213/75/Java-Tutorial-For-Beginners-Step-By-Step-Java-Basics-Java-Certification-Training-Edureka-64-2048.jpg)
![JAVA CERTIFICATION TRAINING www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training 1D 2D Java Arrays – 2 Dimensional Like a 1D array, a 2D array is also a collection of data cells, all of the same type, which can be given a single name datatype[][] arrayRefVar = new dataType[row][col]; =int[][] myArray new int[2][2] myArray[0][0] myArray[0][1] myArray[1][0] myArray[1][1] =myArray[0][1] 200 100 =myArray[1][0] 300 =myArray[1][1] 400](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatutorialppt-181105131213/75/Java-Tutorial-For-Beginners-Step-By-Step-Java-Basics-Java-Certification-Training-Edureka-65-2048.jpg)
![JAVA CERTIFICATION TRAINING www.edureka.co/java-j2ee-soa-training 1D 2D Java Arrays – 2 Dimensional Like a 1D array, a 2D array is also a collection of data cells, all of the same type, which can be given a single name datatype[][] arrayRefVar = new dataType[row][col]; =int[][] myArray new int[2][2] myArray[0][0] myArray[0][1] myArray[1][0] myArray[1][1] 200100 300 400](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javatutorialppt-181105131213/75/Java-Tutorial-For-Beginners-Step-By-Step-Java-Basics-Java-Certification-Training-Edureka-66-2048.jpg)
