Download to read offline
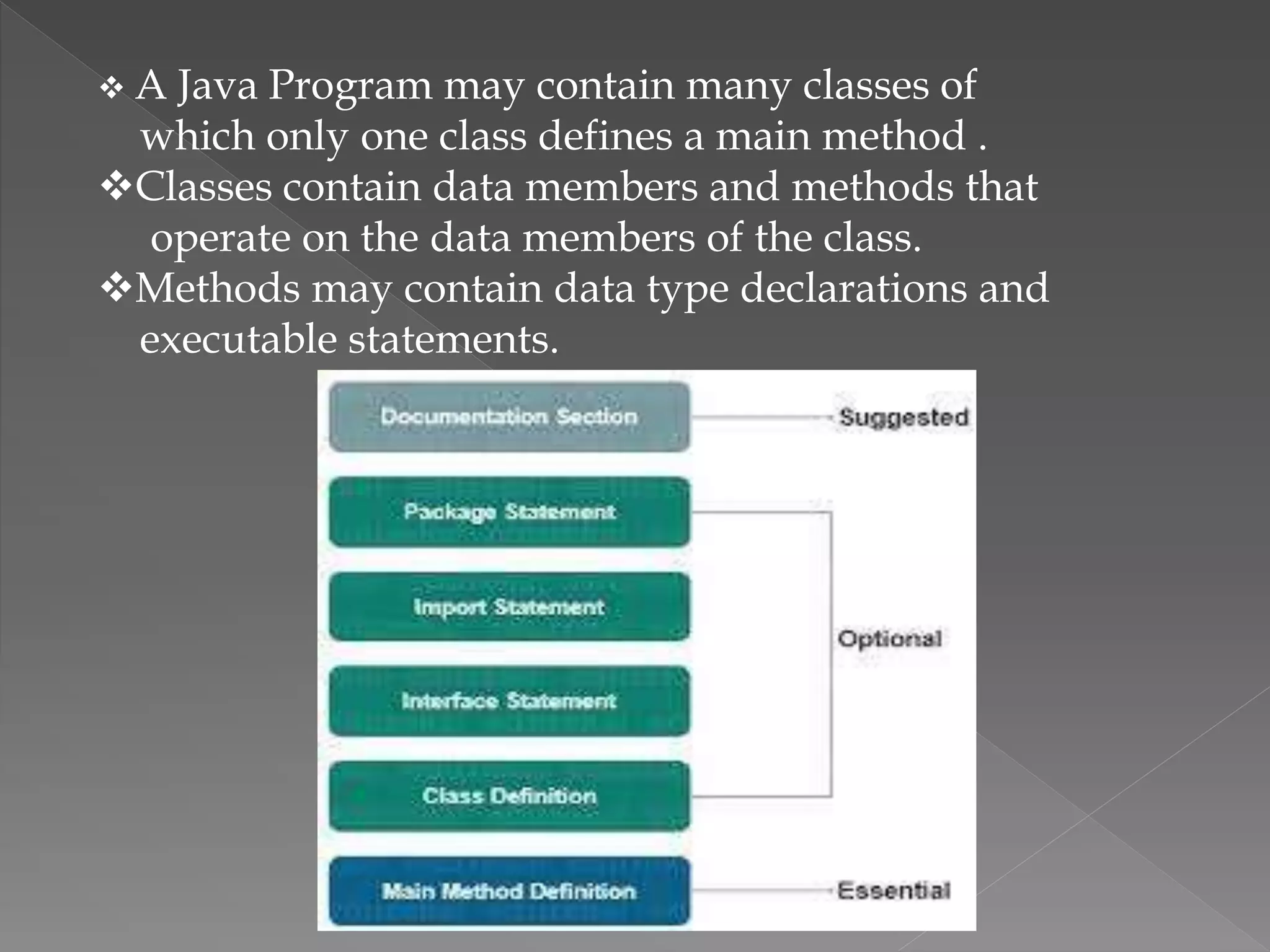



The document discusses the structure of a Java program. A Java program contains classes, with one class containing a main method that acts as the starting point. Classes contain data members and methods that operate on the data. Methods contain declarations and executable statements. The structure also includes sections for documentation, package statements, import statements, interface statements, and class definitions, with the main method class being essential.





Introduction to the Java Program structure, including classes, methods, and essential components like main method, documentation, package, import statements, and interfaces.