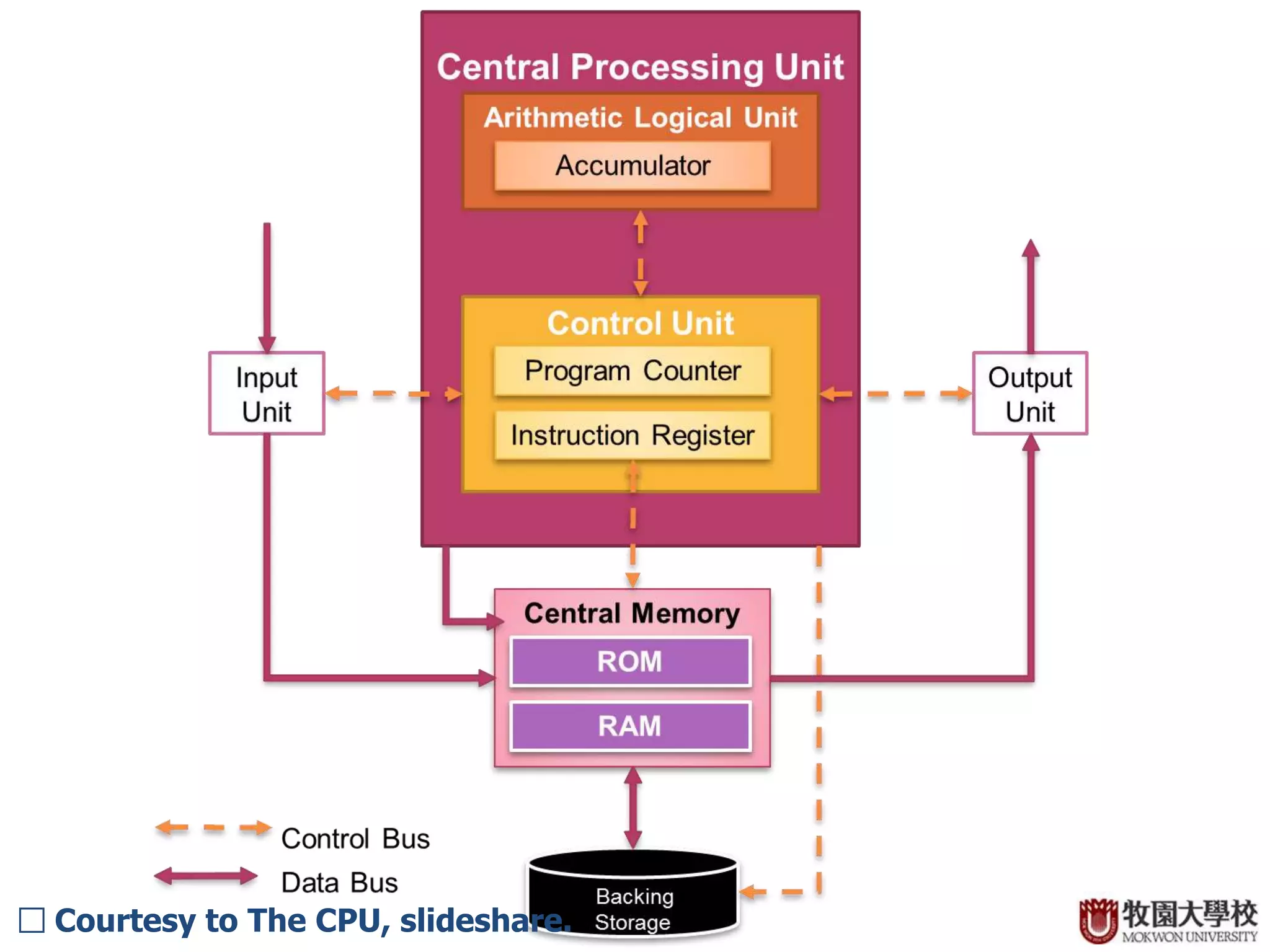
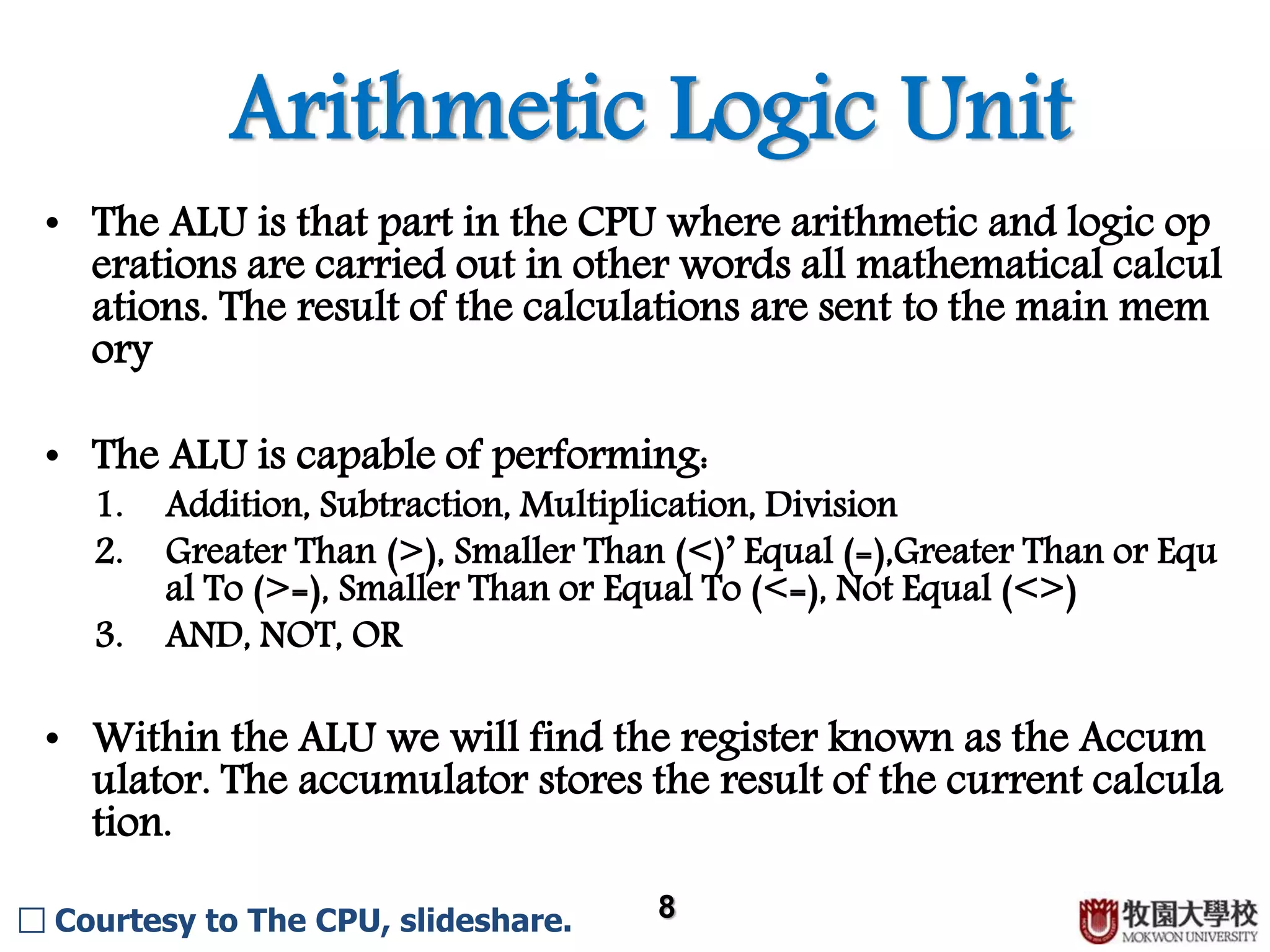
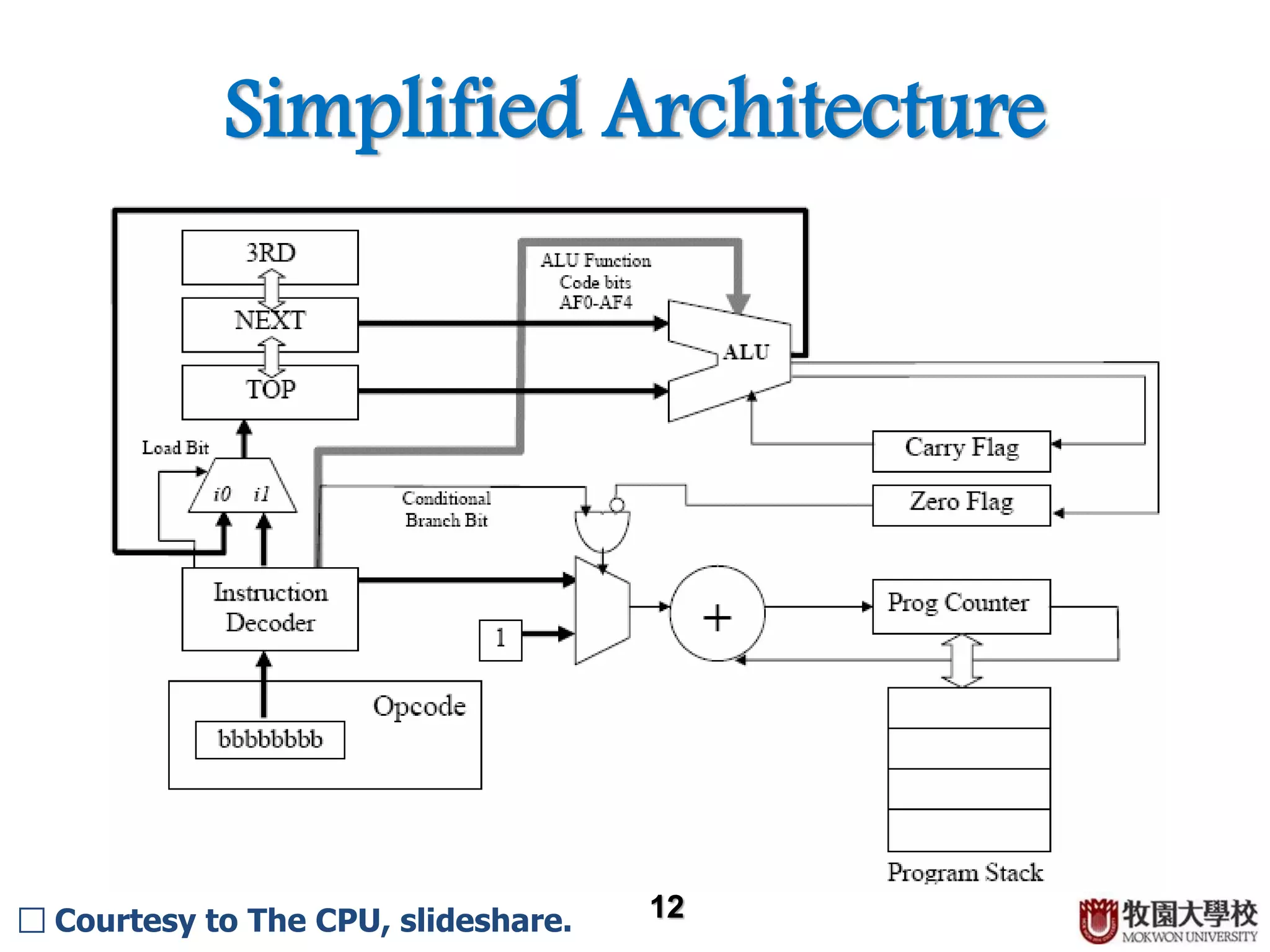
The CPU contains several key components that work together to process instructions. The control unit decodes instructions and controls the order of operations. It contains an instruction register that stores the current instruction and a program counter that tracks the computer's position in its instruction set. The arithmetic logic unit performs arithmetic and logical operations and contains an accumulator to store results. Other components include registers for temporary storage, buses for transmitting data, and caches for faster access to frequently used instructions and data.
![CPU Architecture - Basic Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University Some of slides are referred to: [1] The CPU, slideshare.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-151016025242-lva1-app6891/75/CPU-Architecture-Basic-1-2048.jpg)