Downloaded 132 times
![CPU Architecture - Advanced Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University Some of slides are referred to: [1] 3.3 Computer Architectures, slideshare.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-151023062119-lva1-app6892/75/CPU-Architecture-Advanced-1-2048.jpg)



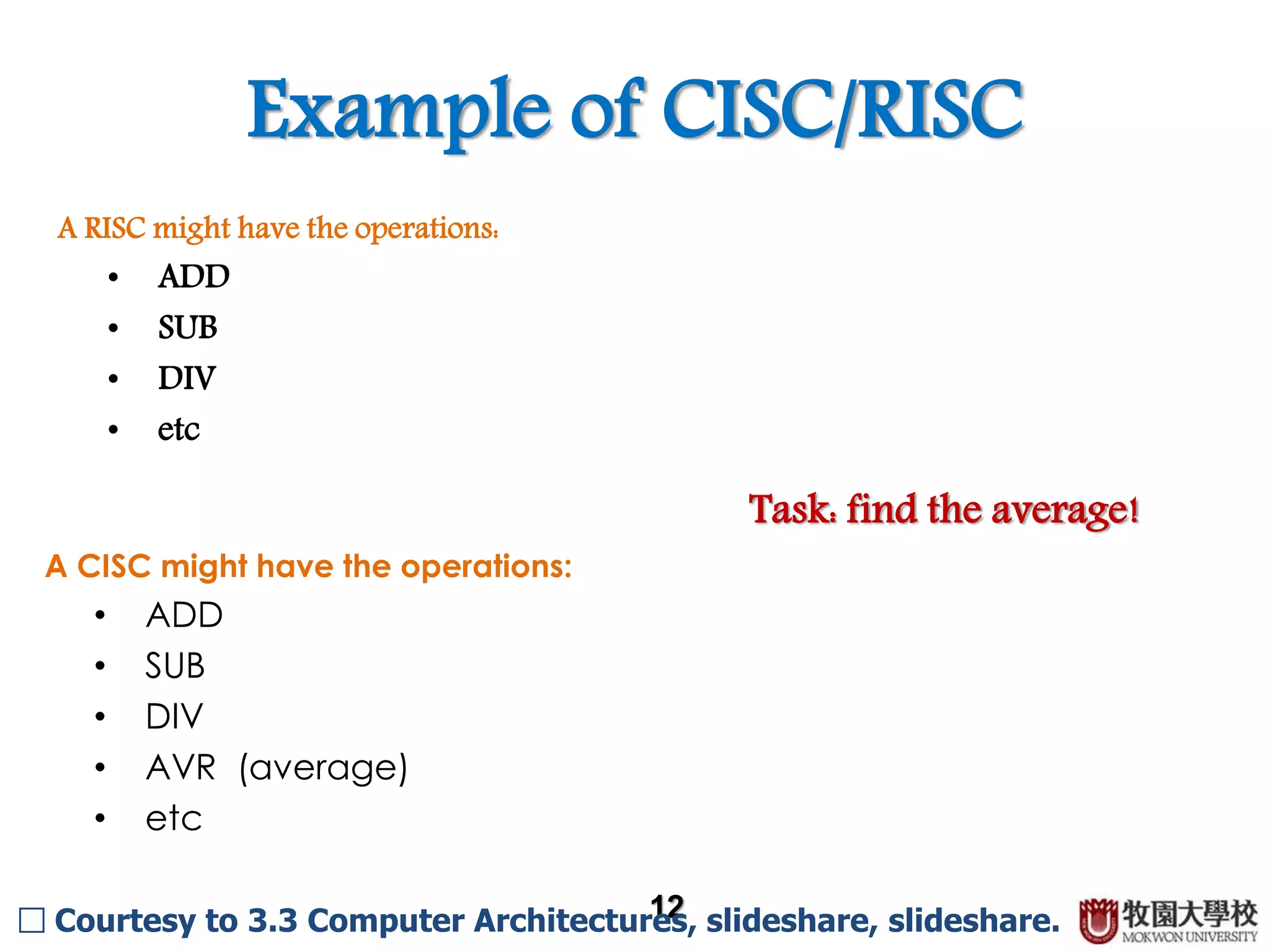

The document discusses advanced CPU architecture. It describes the von Neumann architecture which uses a single processor for program control and follows a fetch-decode-execute-store cycle to process instructions one at a time in a linear sequence from memory. It also describes the differences between CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) and RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer), with CISC having more complex instructions that can perform tasks in one cycle while RISC uses simpler instructions that may require multiple cycles to complete complex tasks. An example is provided to illustrate how a RISC would take more cycles than a CISC to compute an average.
![CPU Architecture - Advanced Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University Some of slides are referred to: [1] 3.3 Computer Architectures, slideshare.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-151023062119-lva1-app6892/75/CPU-Architecture-Advanced-1-2048.jpg)











Overview of CPU architecture, presented by Yong Heui Cho at Mokwon University.
Outline of basic computer design elements including sequential logic circuits and advanced CPU architecture.
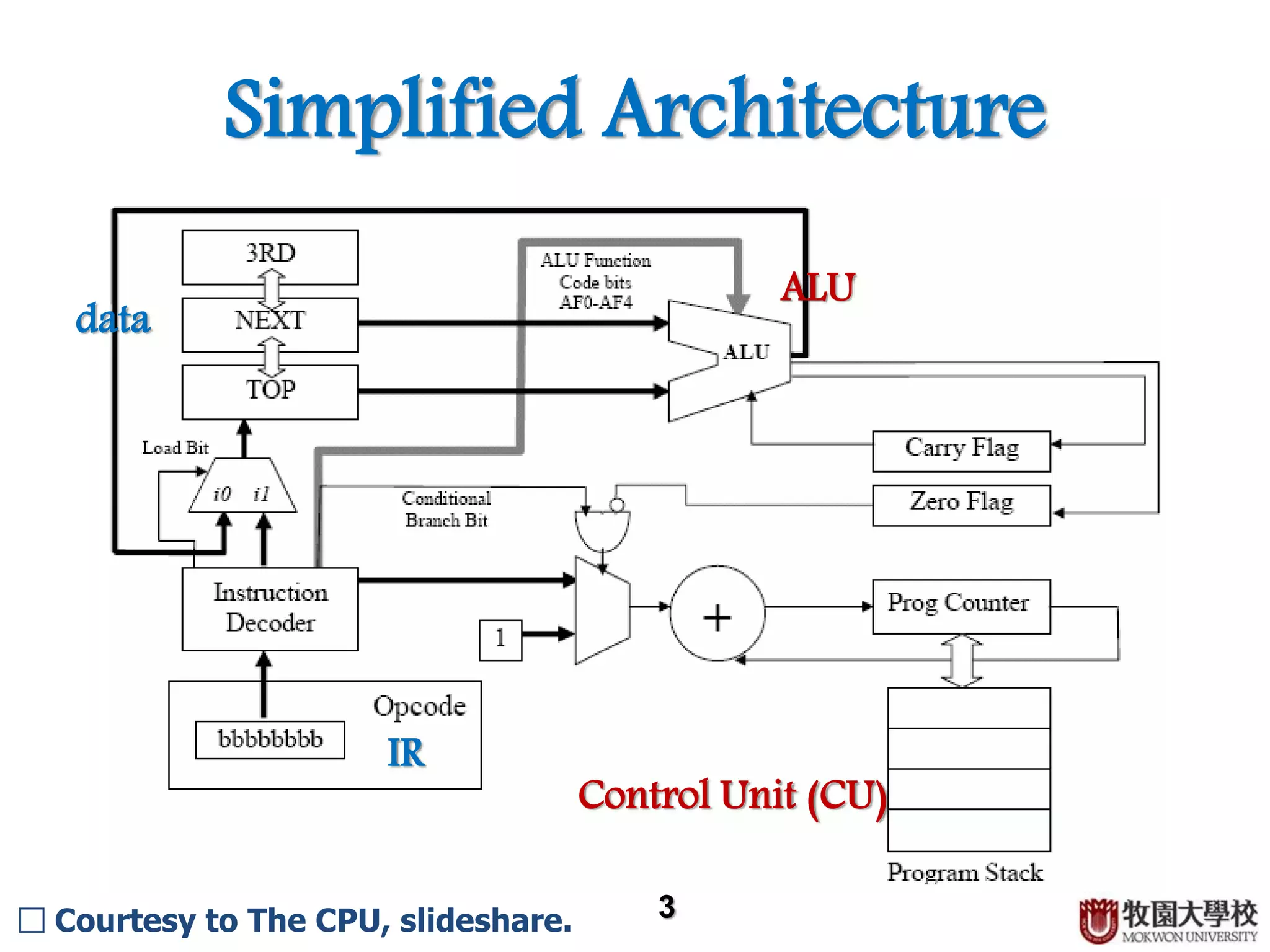
Introduction to simplified architecture with key components: IR, data, Control Unit, and ALU.
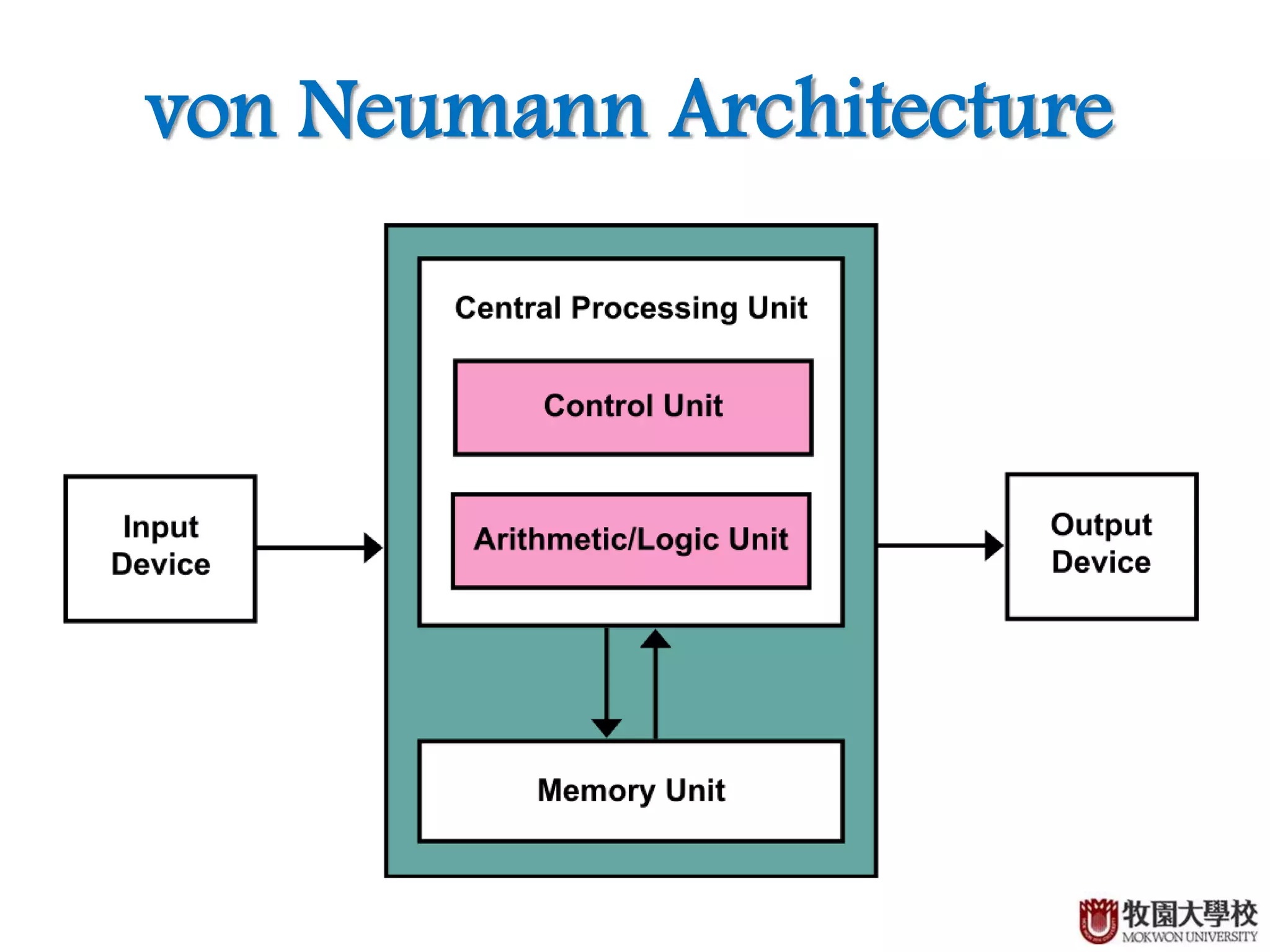
Explanation of von Neumann architecture and its principles.
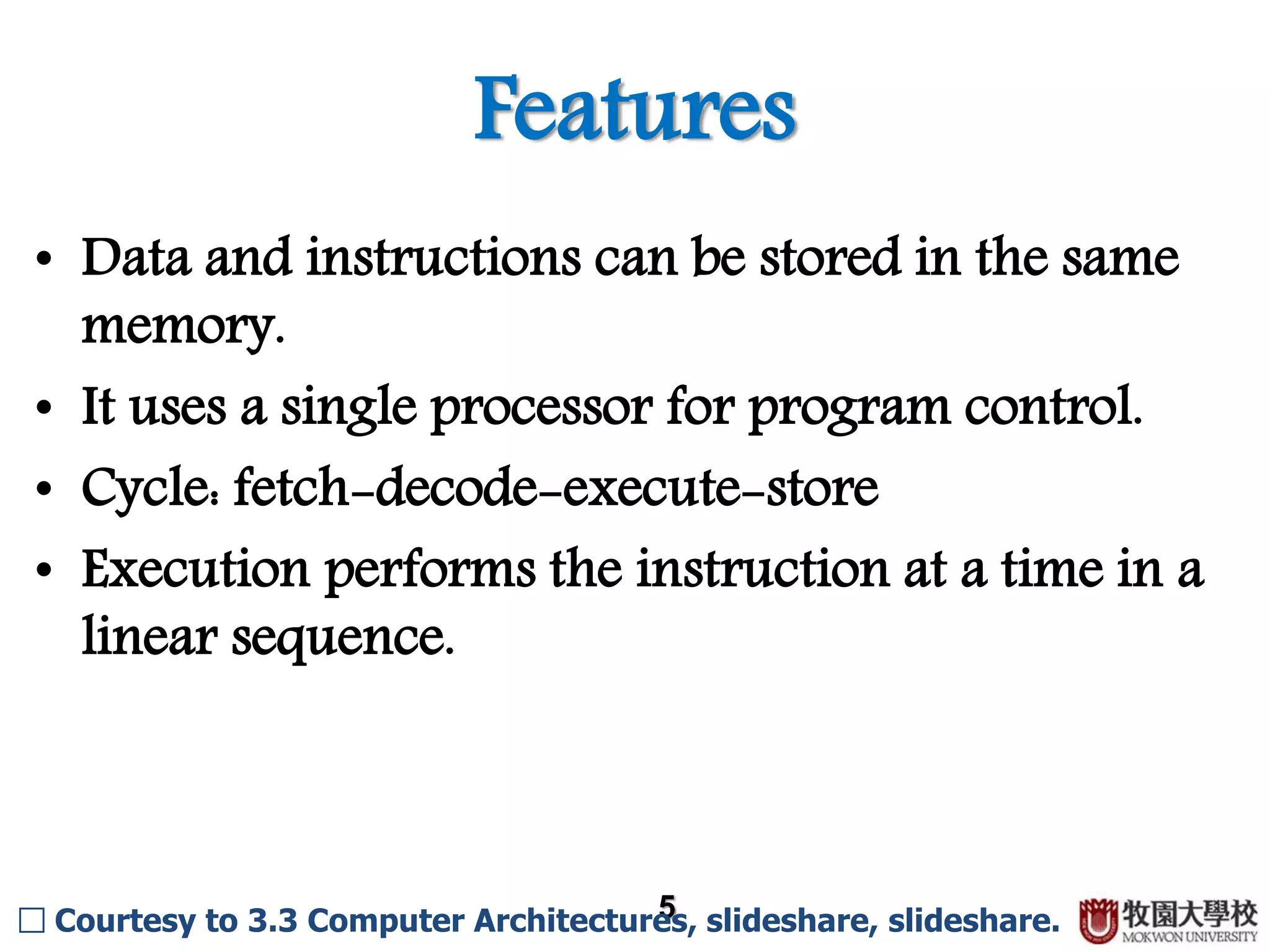
Details about data and instructions stored in the same memory, single processor use, and linear execution cycle.
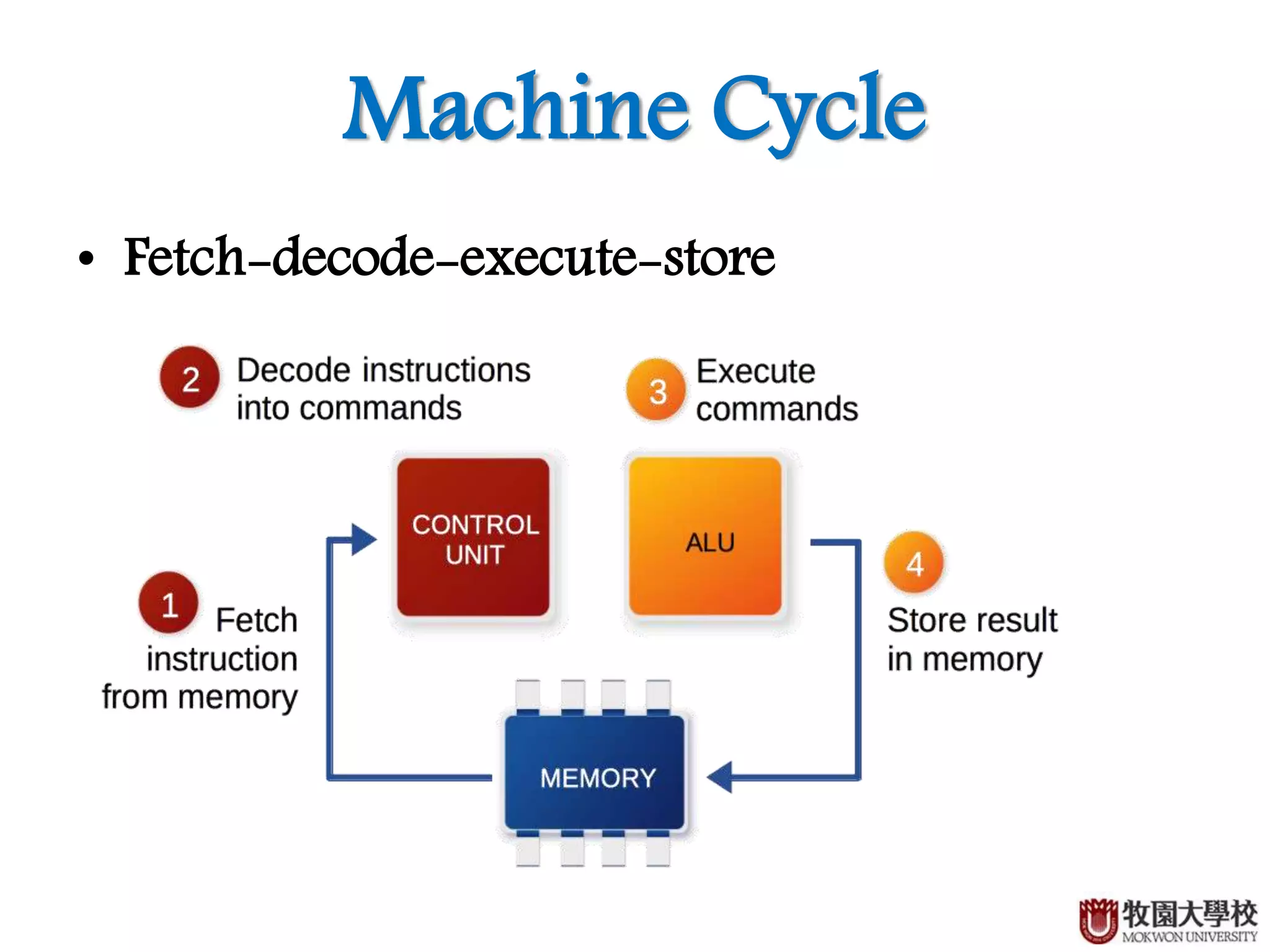
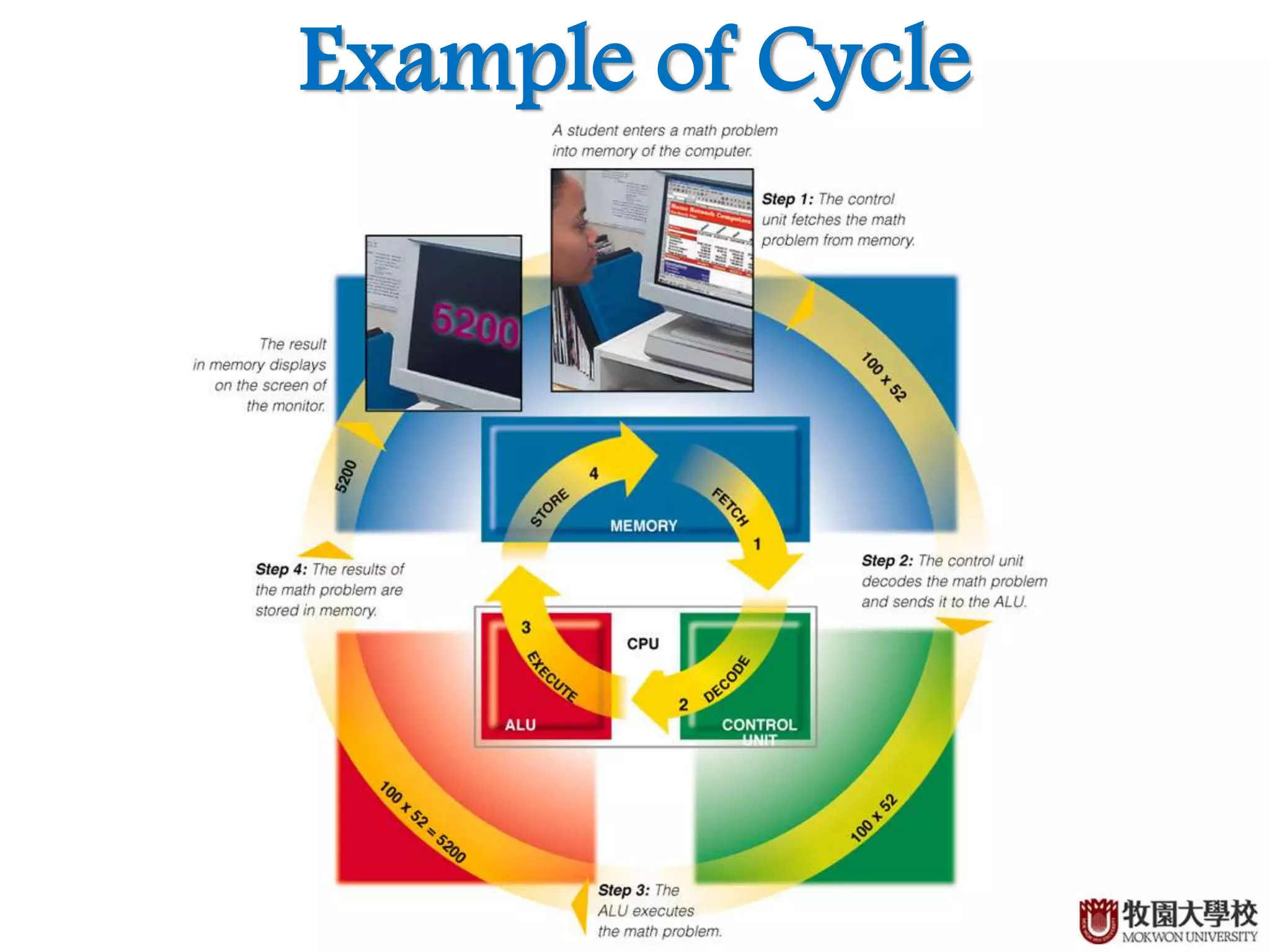
Definition and breakdown of the fetch-decode-execute-store machine cycle.
Provided example illustrating the machine cycle process.
Description of Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC) with emphasis on its complex instructions and benefits.
Applications of CISC in PCs, servers, and mobile devices.
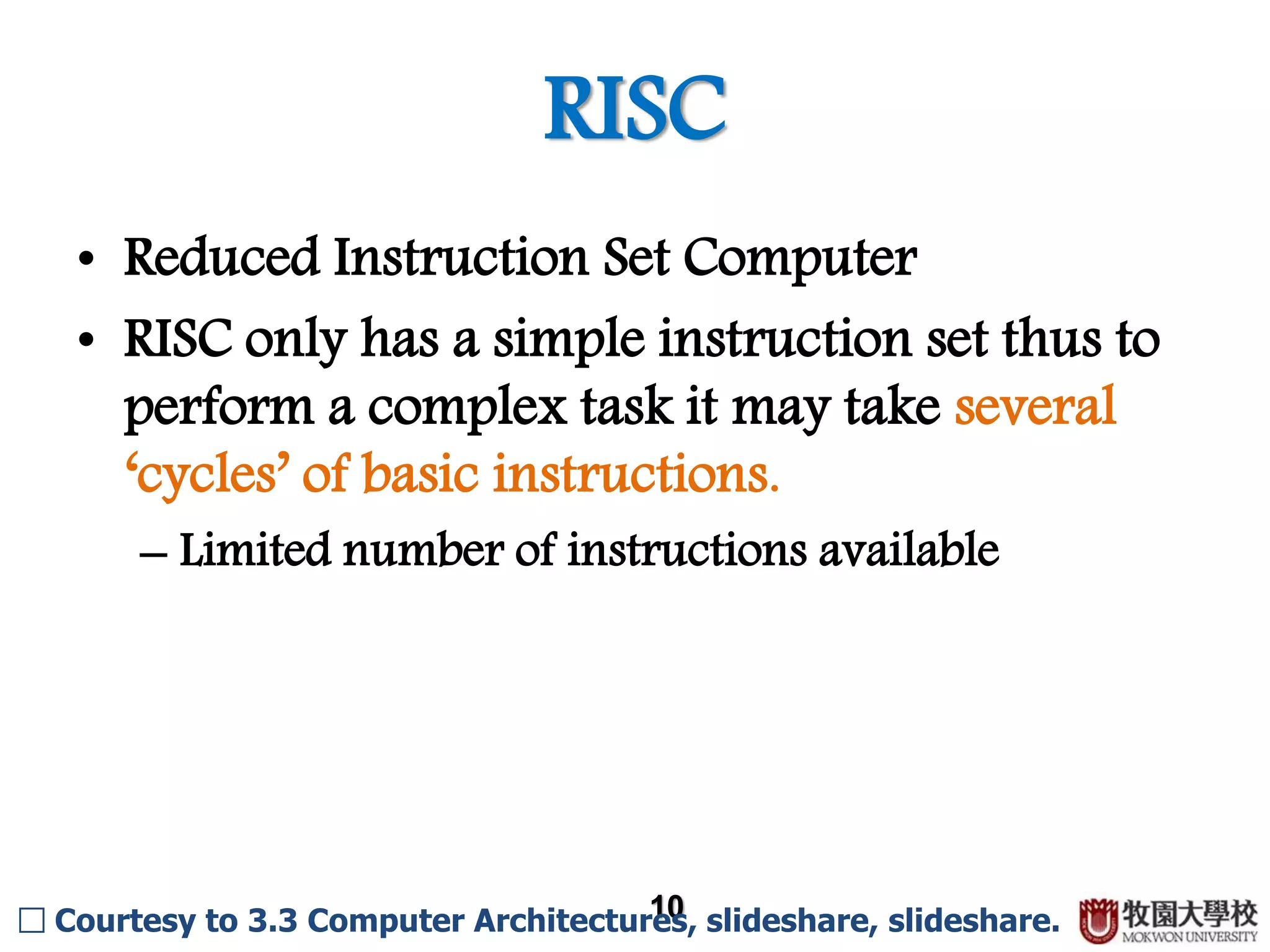
Description of Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) and its limited instruction set capabilities.
Applications of RISC technology in mobile devices, PCs, and servers.
Comparison of CISC and RISC instruction sets, showing differences in operations for similar tasks.