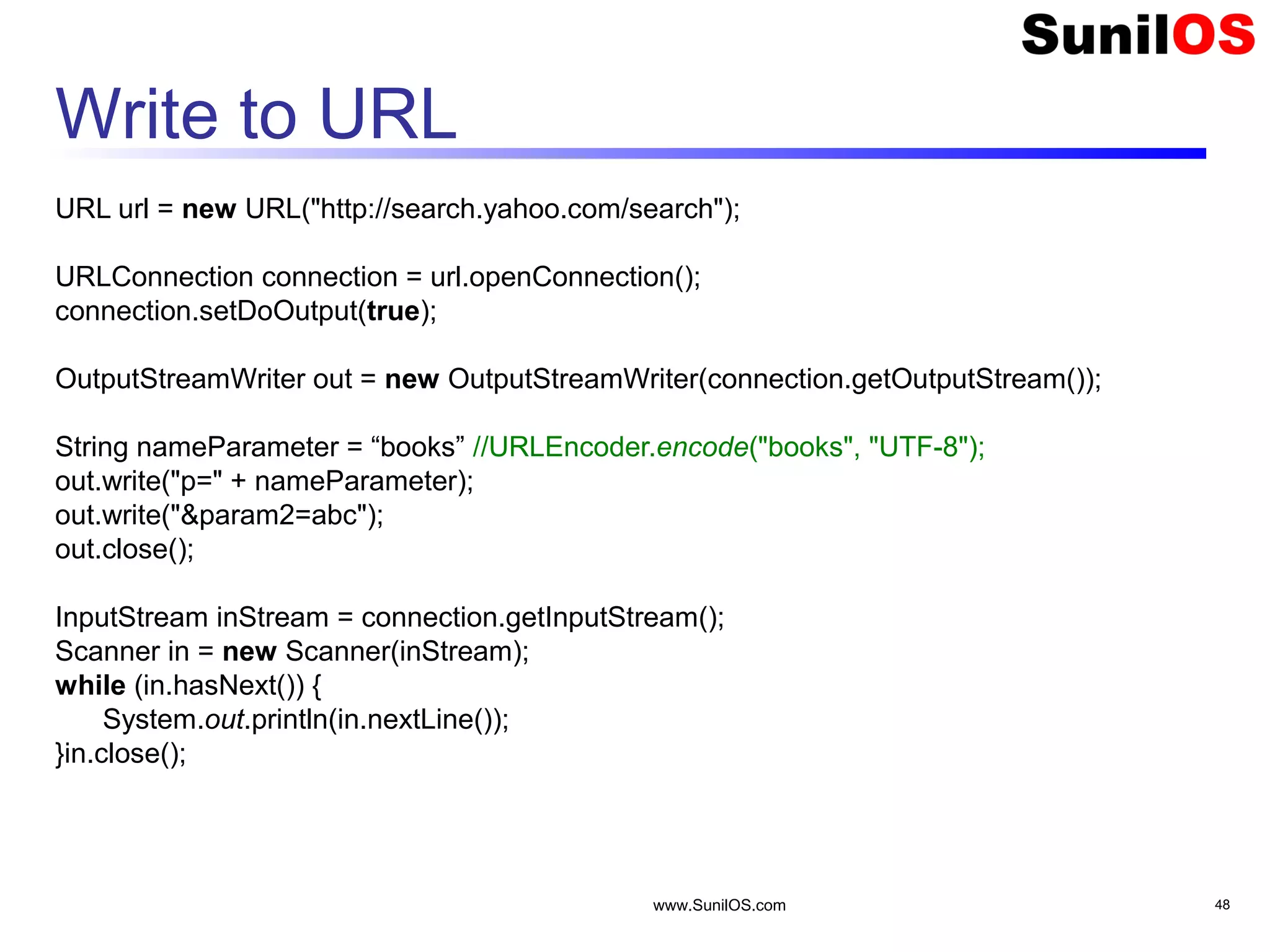
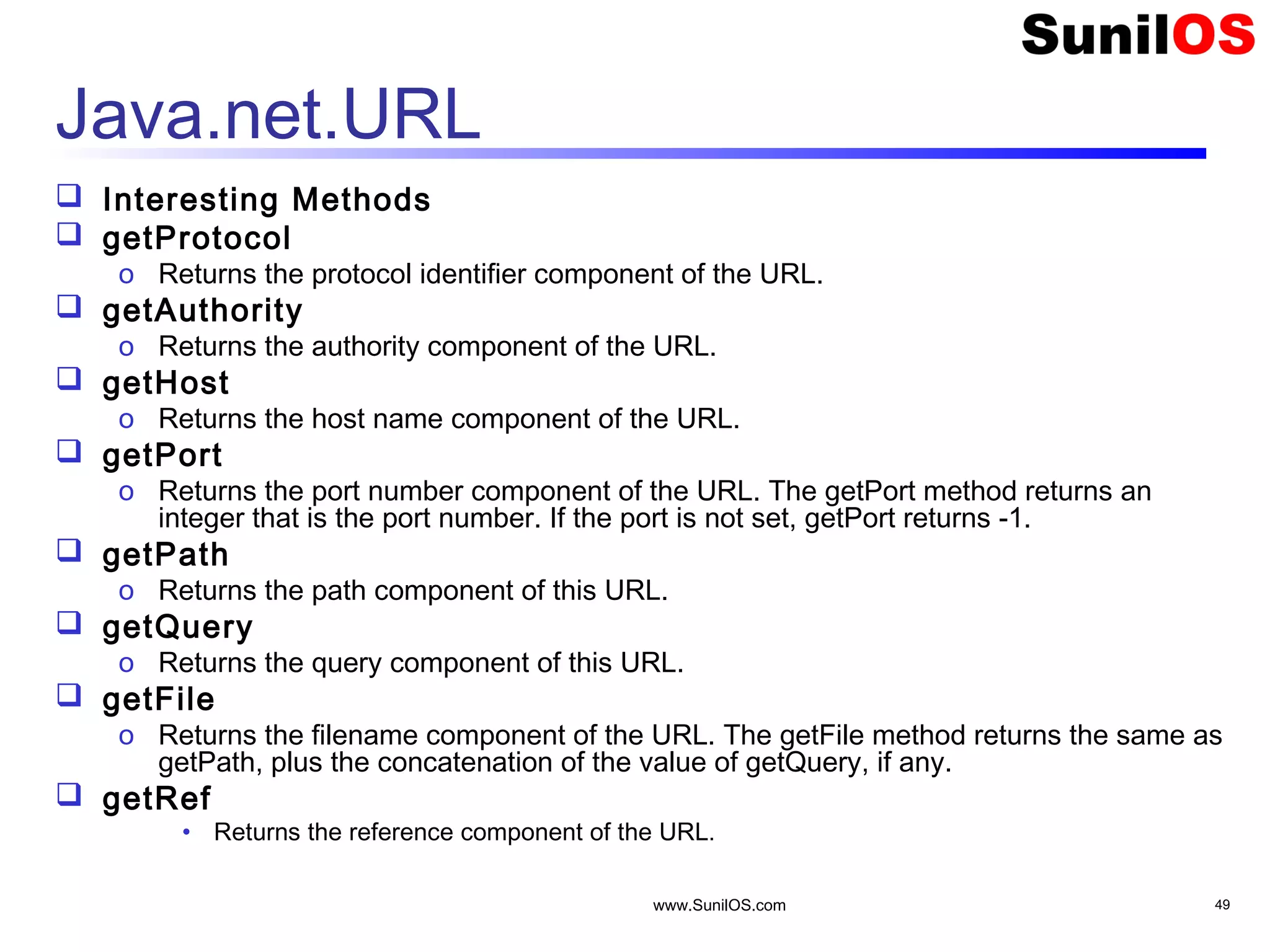
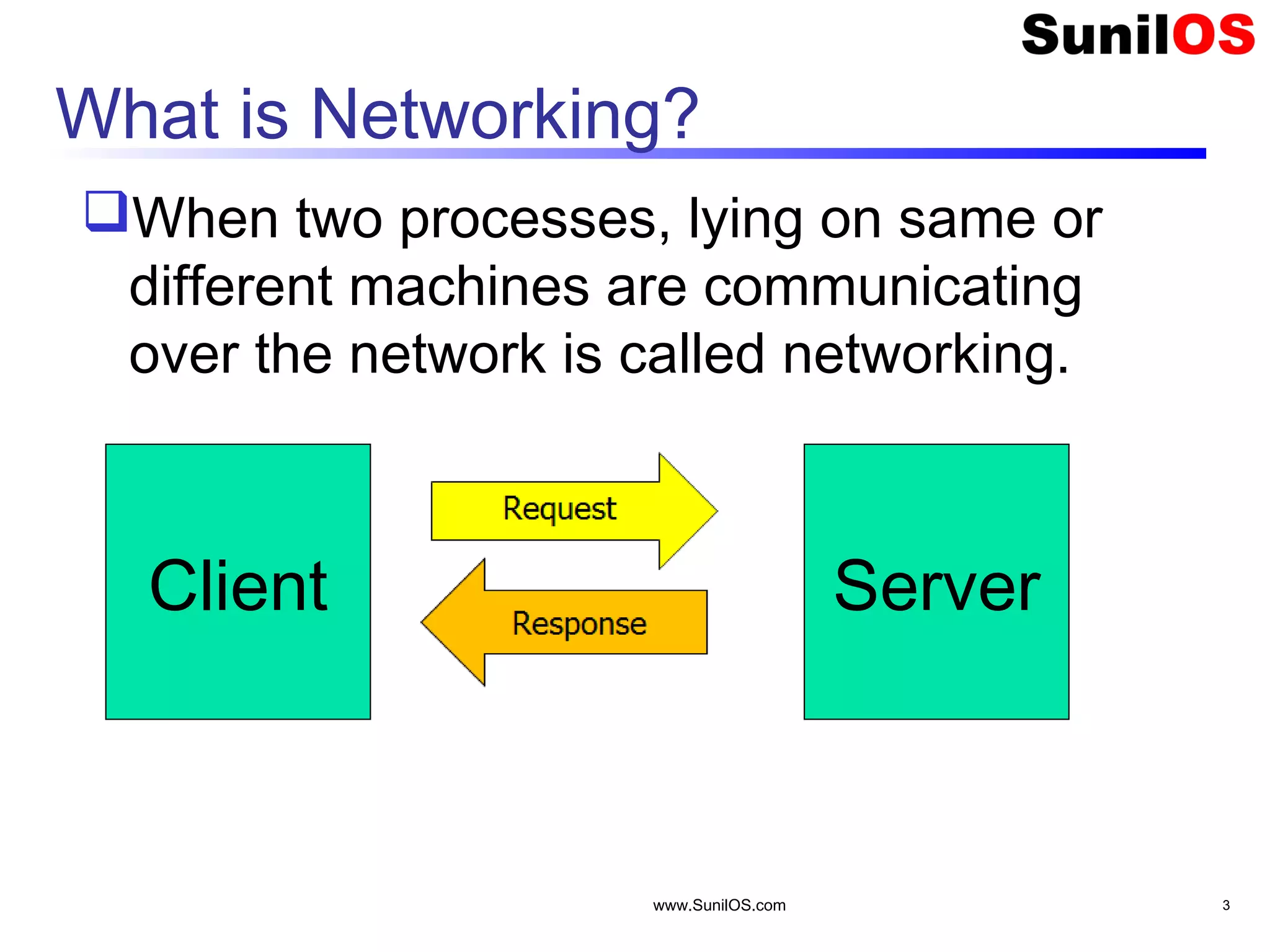
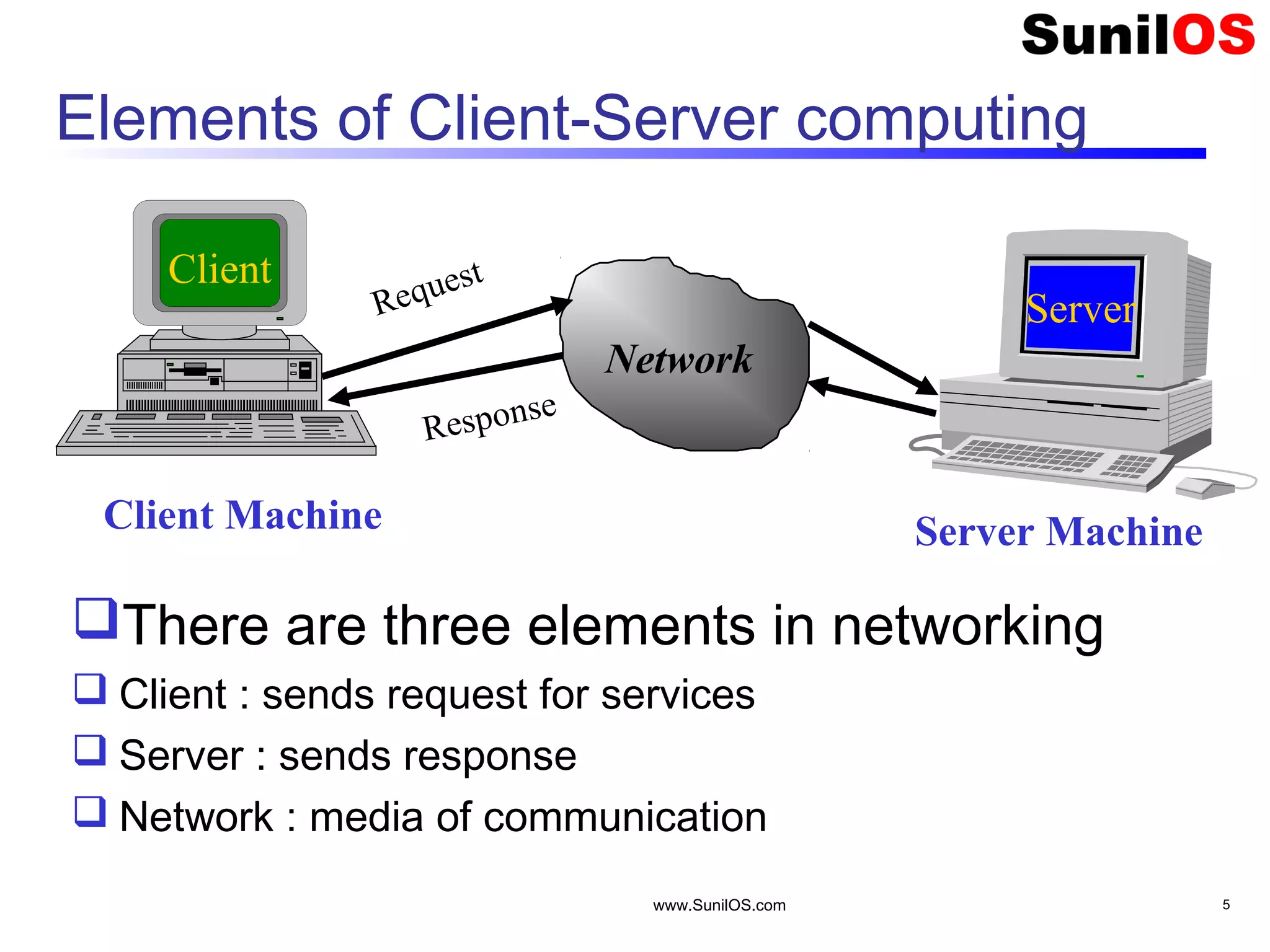
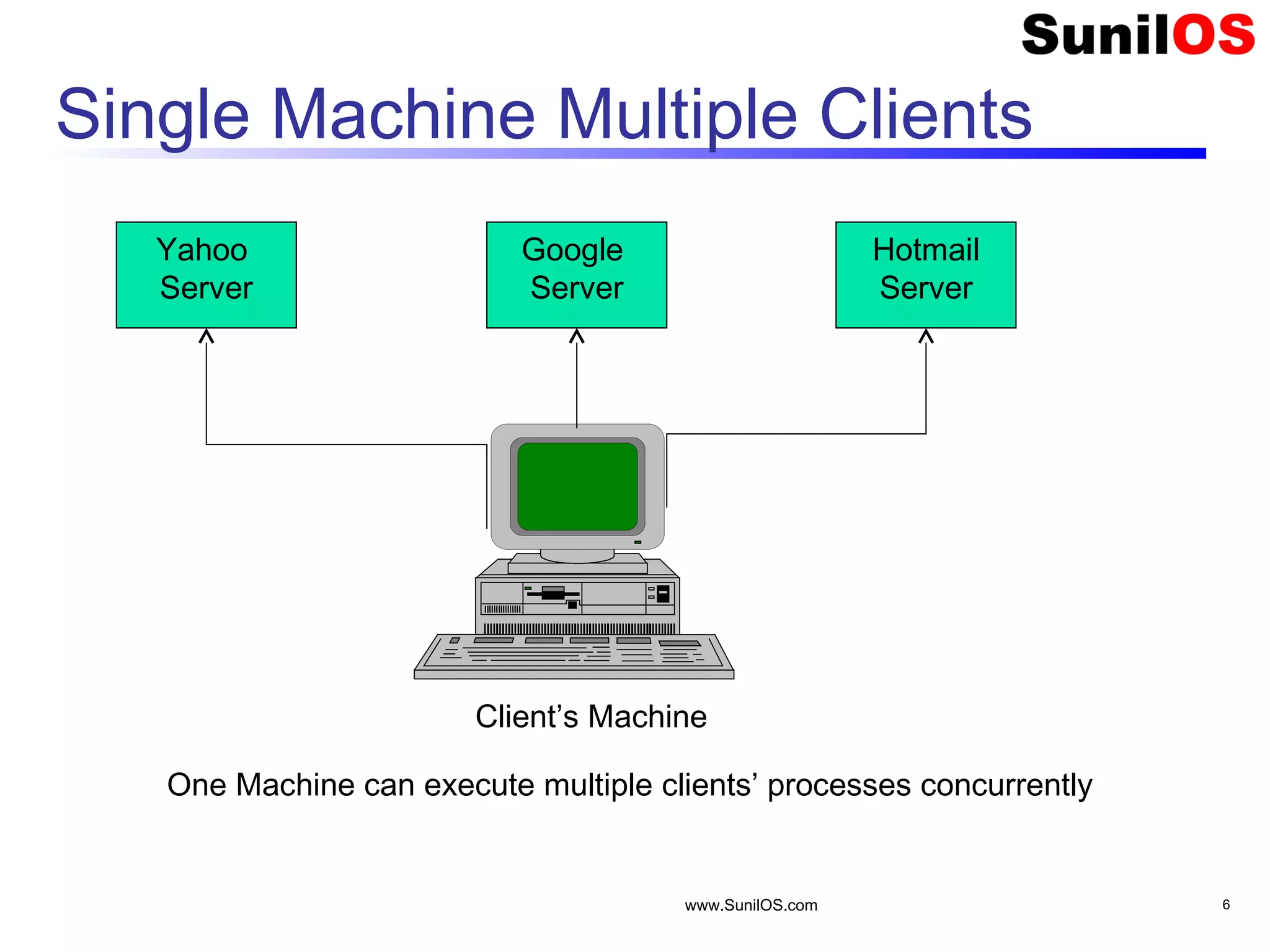
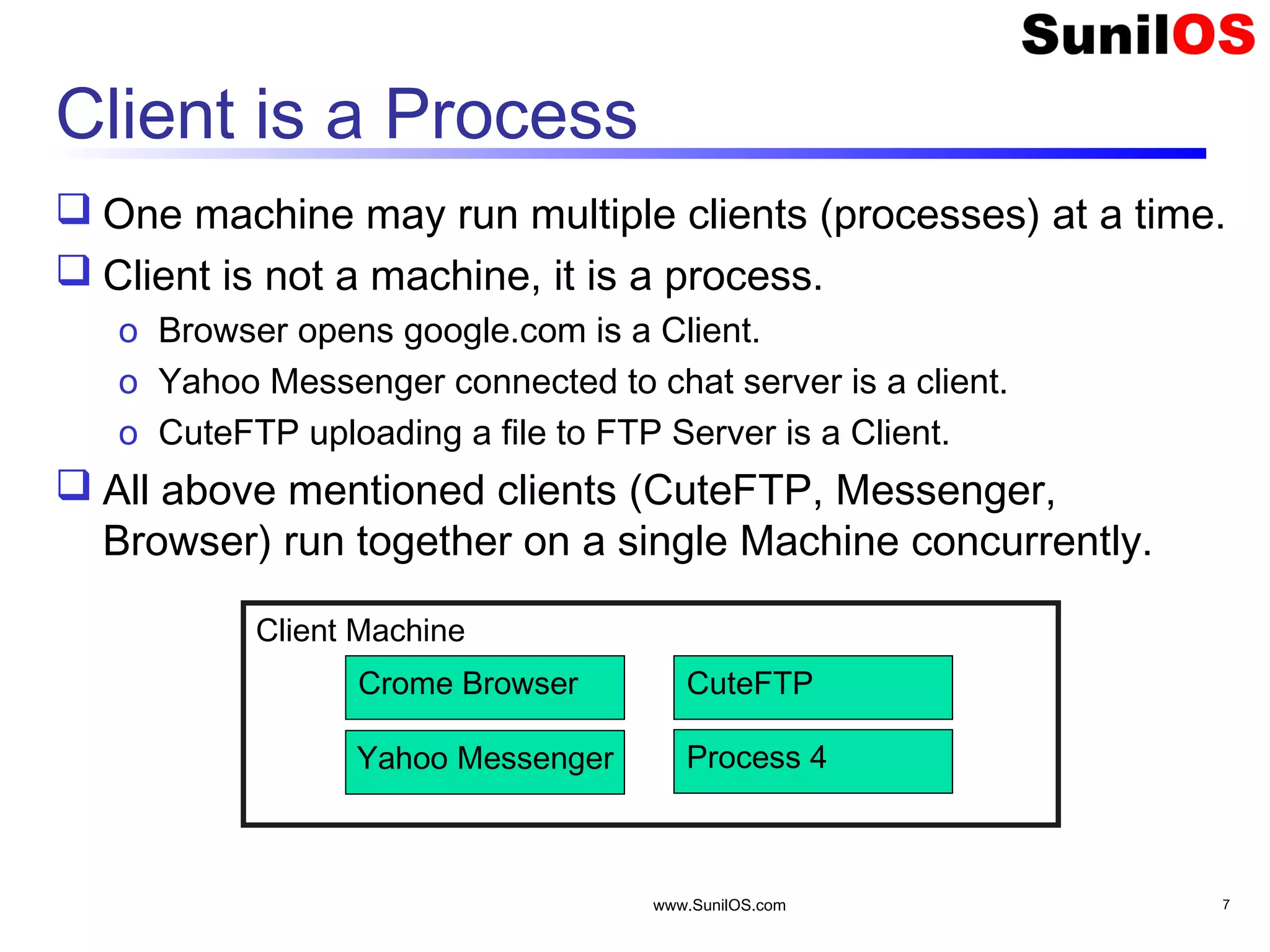
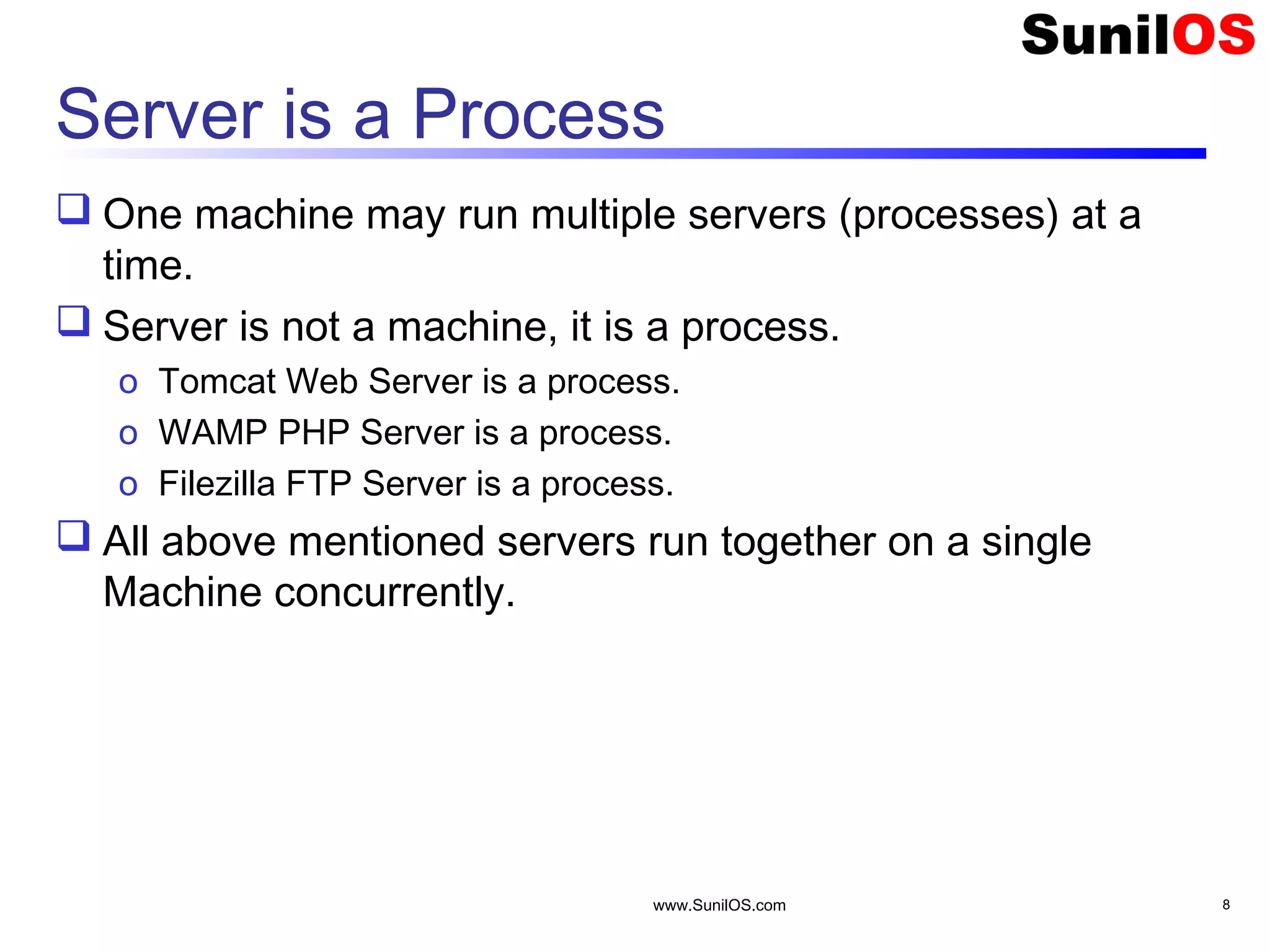
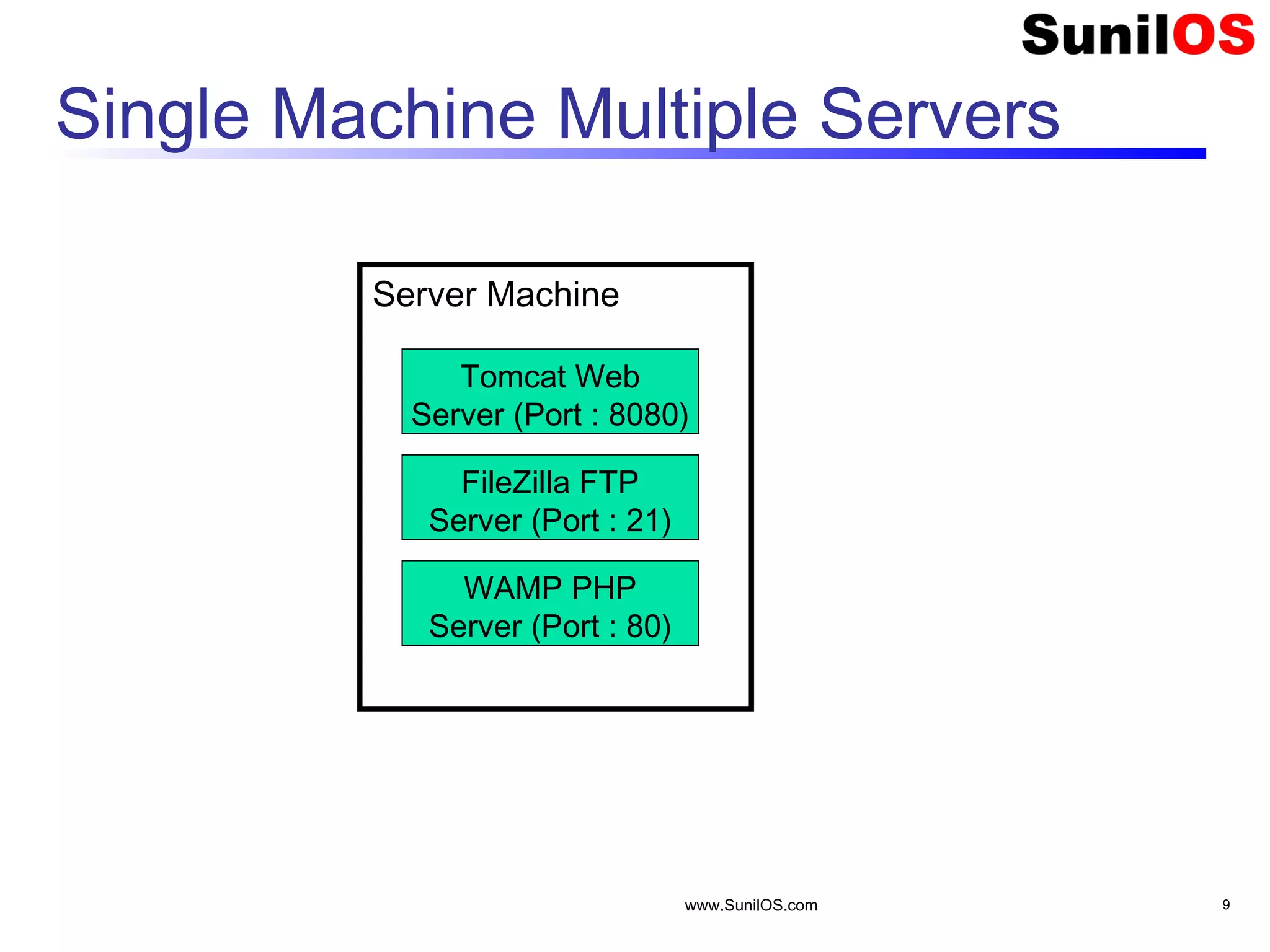
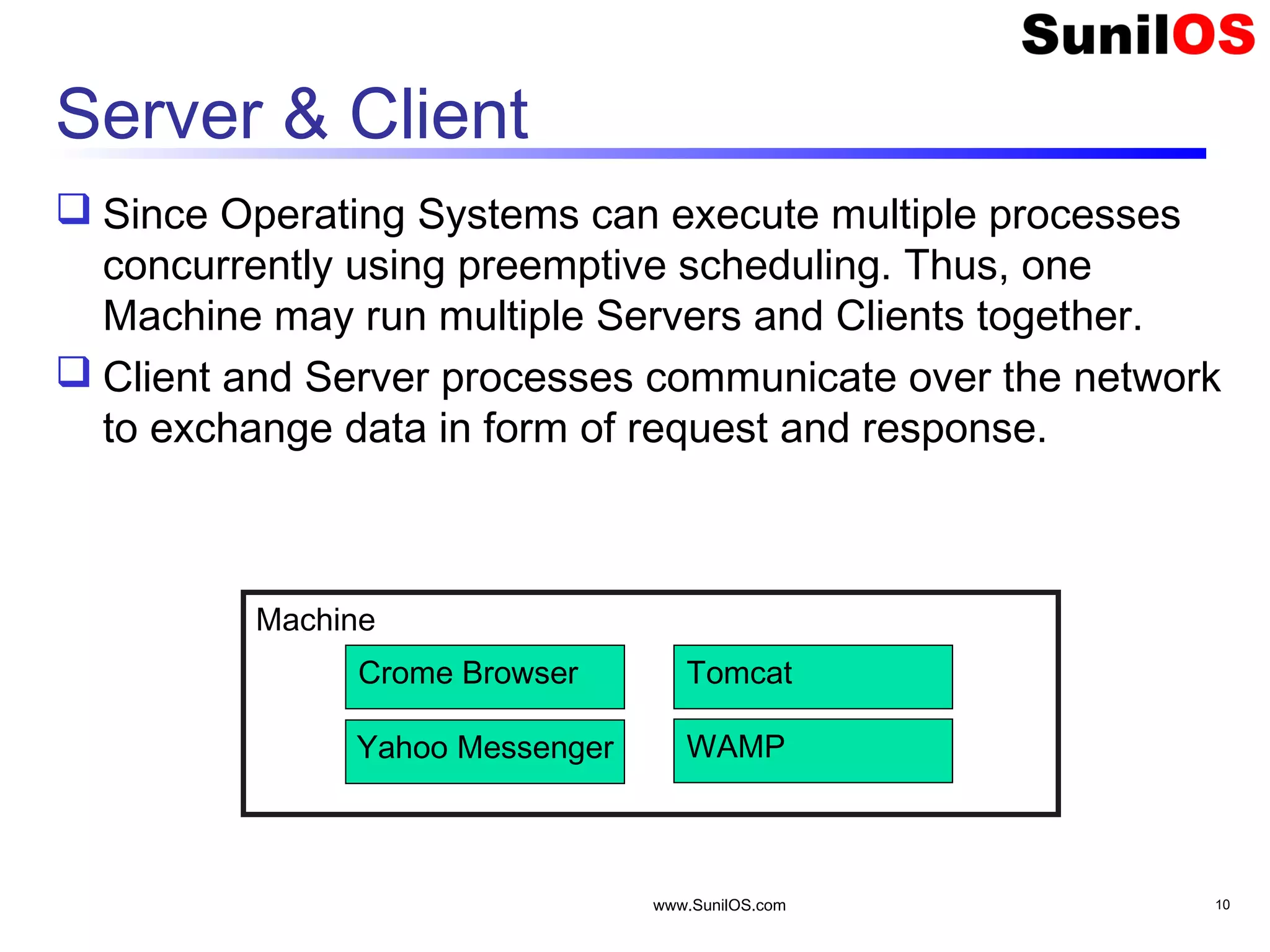
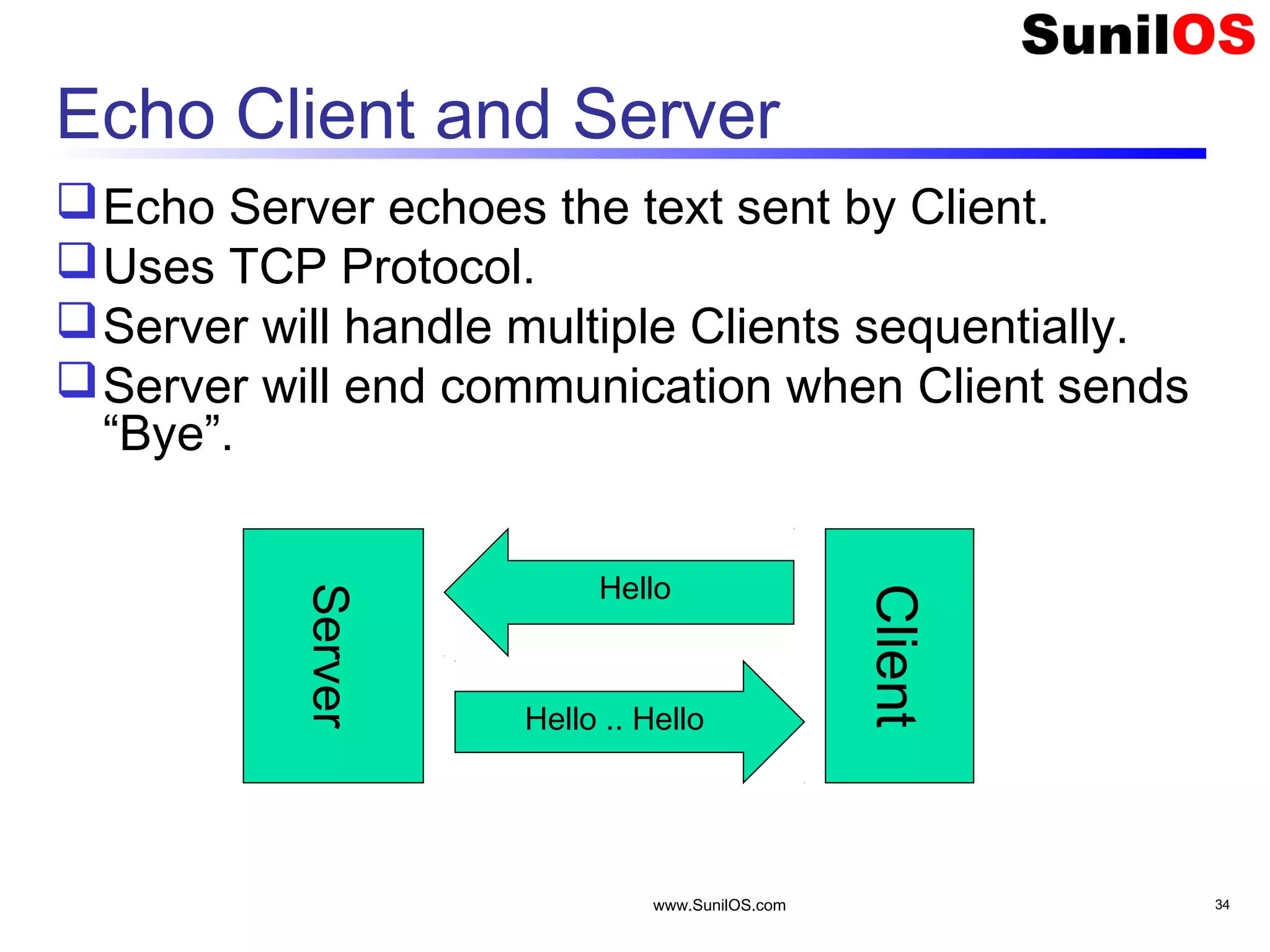
This document provides an overview of client-server networking concepts in Java. It discusses elements like network basics, ports and sockets. It explains how to implement both TCP and UDP clients and servers in Java using socket classes. Sample code is provided for an echo client-server application using TCP and a quote client-server application using UDP. Exception handling for sockets is also demonstrated.









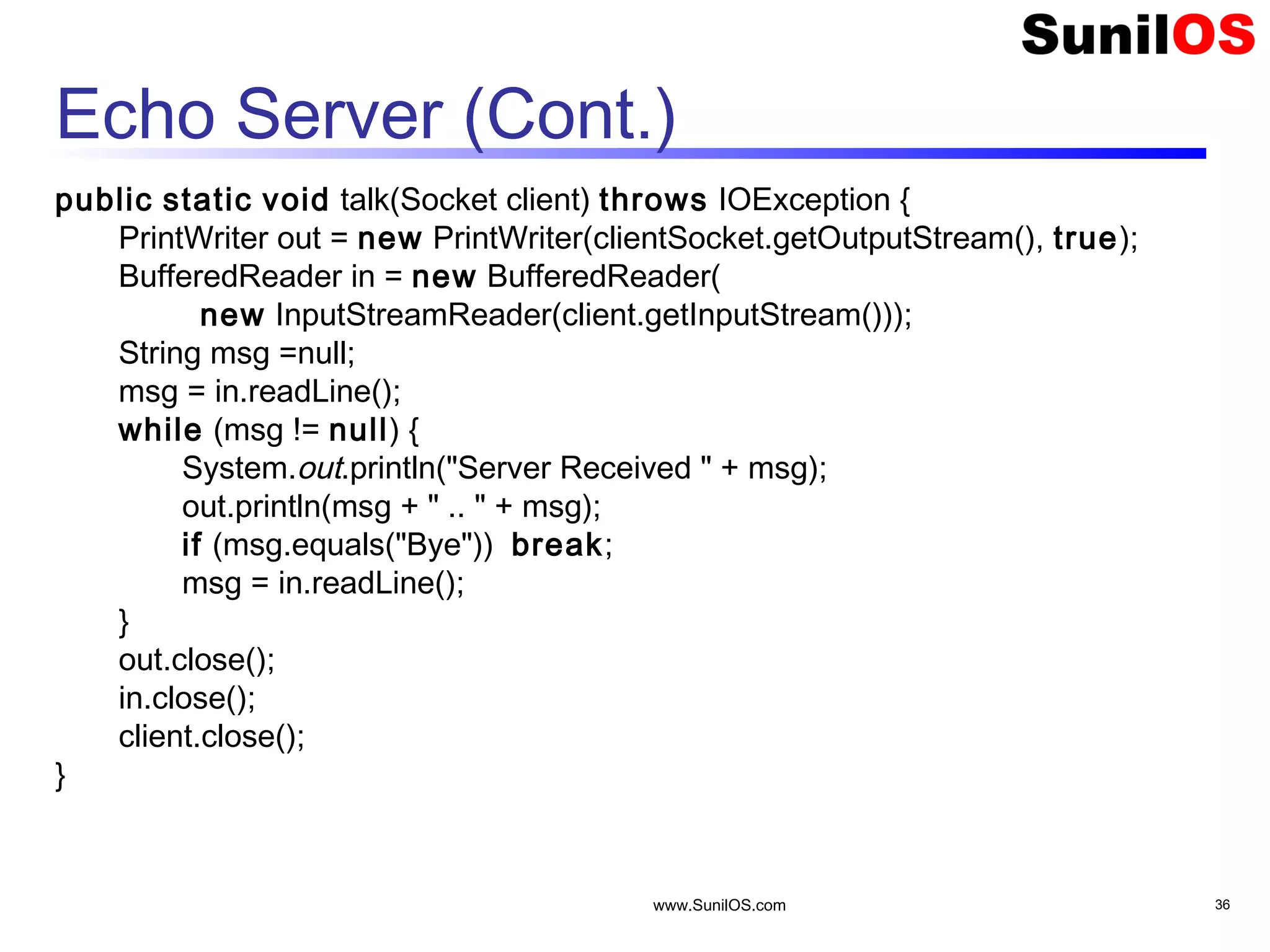
![www.SunilOS.com 35 Echo Server public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket ss= new ServerSocket(4444); System.out.println("Echo Server Started"); Socket client= null; boolean flag = true; while (flag) { client = ss.accept(); //Accept Client talk(client); //Talk to the client } System.out.println("Echo Server Stopped"); ss.close(); //Close server }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkingv2-151109154842-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Networking-35-2048.jpg)
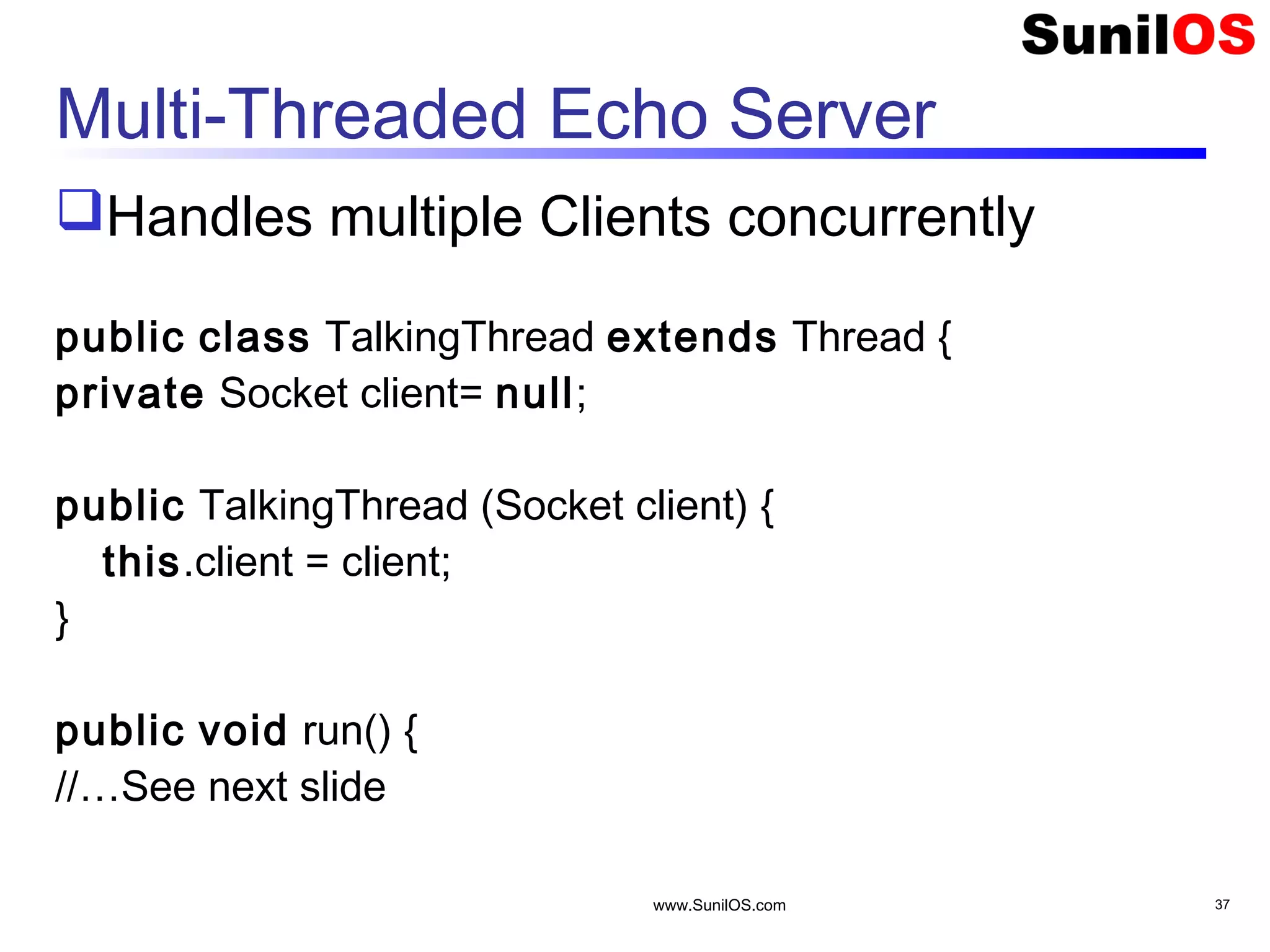
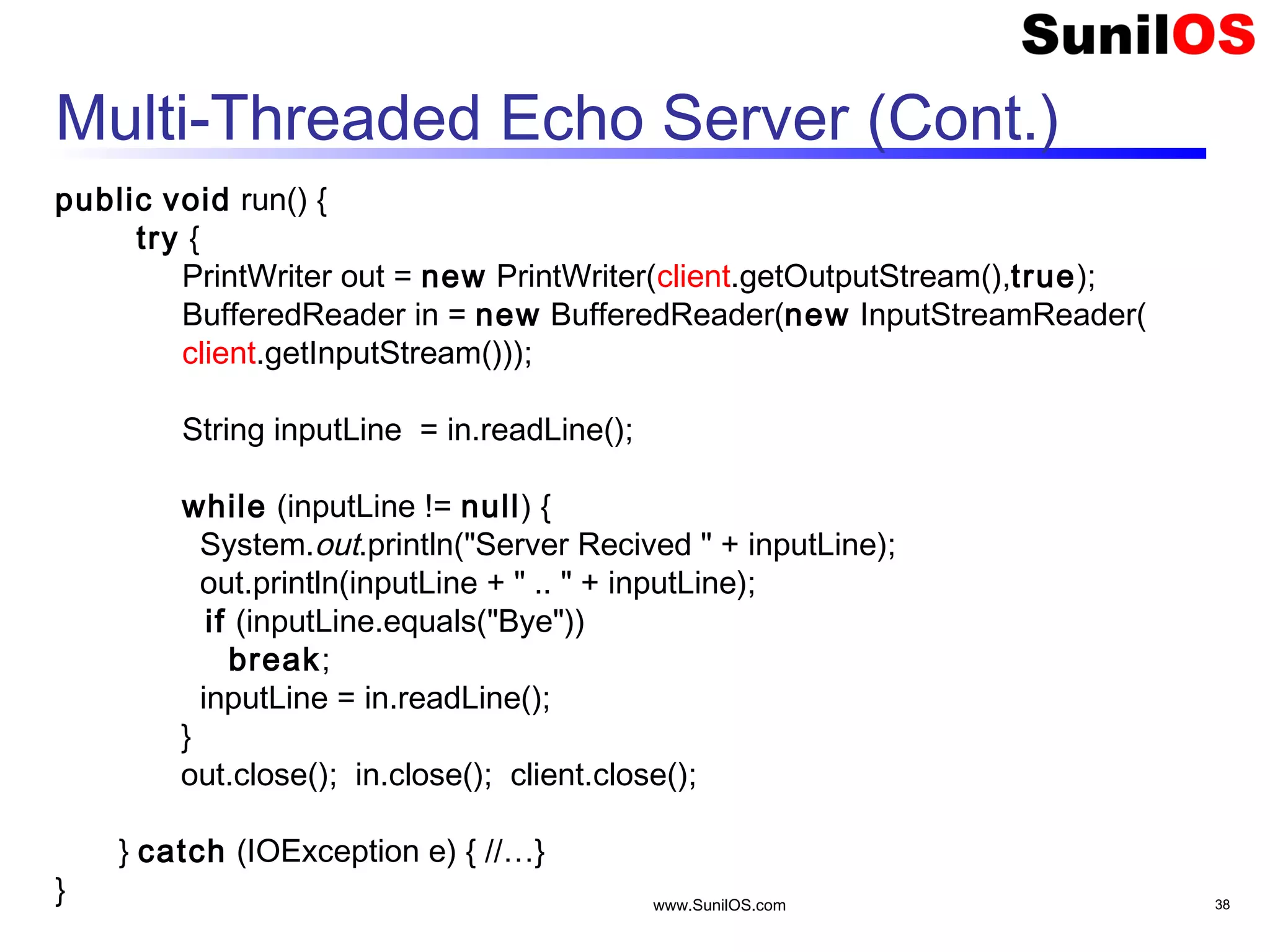
![www.SunilOS.com 39 Multi-Threaded Echo Server (Cont.) Starts Multithreaded Server public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(4444); Socket clientSocket = null; boolean flag = true; while (flag) { client = server.accept(); TalkingThread t = new TalkingThread(client); t.start(); } System.out.println("Echo Server Stopped”); server.close(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkingv2-151109154842-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Networking-39-2048.jpg)
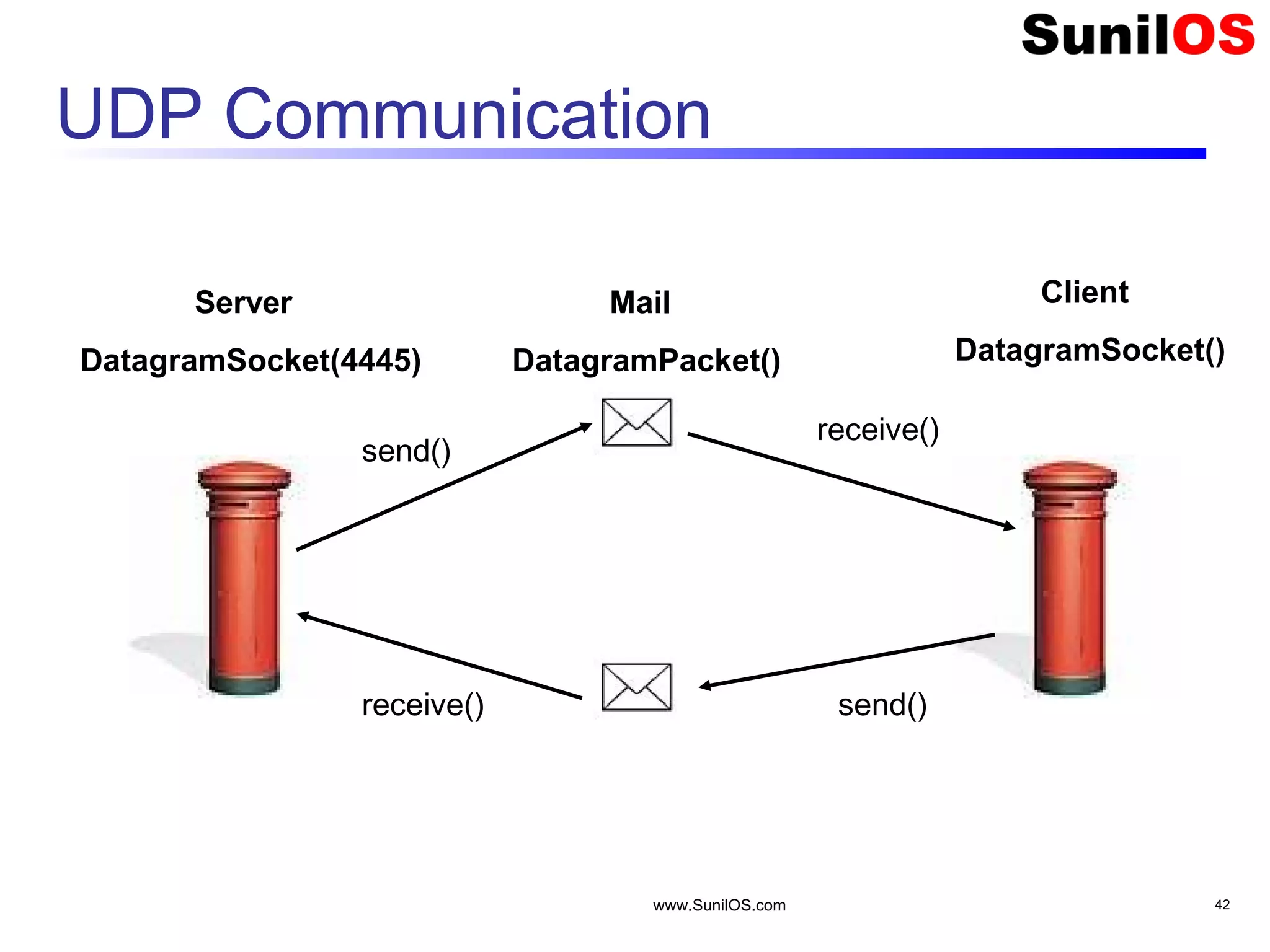
![www.SunilOS.com 44 Quote Server String[] quotes = { "Bura mat Dekho", "Bura Mat kaho", "Bura mat suno" }; DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(4445); byte[] buf = new byte[256]; DatagramPacket emptyPkt = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); while (true) { //Infinite loop socket.receive(emptyPkt); InetAddress address = emptyPkt.getAddress(); int port = emptyPkt.getPort(); int ind = Math.random()*2; //get random index String q= quotes[ind]; // Today’s quote"; byte[] quoteBuf = q.getBytes(); DatagramPacket quotePkt = new DatagramPacket(quoteBuf, quoteBuf.length, address, port); socket.send( quotePkt ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkingv2-151109154842-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Networking-44-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 45 Quote Client Sends empty packet and receives Quote of the Moment. DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(); // send request byte[] buf = new byte[256]; InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("localhost"); DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, address,4445); socket.send(packet); // get response packet = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length); socket.receive(packet); // display response String received = new String(packet.getData()); System.out.println("Quote of the Moment: " + received); socket.close();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkingv2-151109154842-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Networking-45-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 46 Read From URL Reads text from URL public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { InputStream inStream = null; URL u = null; try { u = new URL("http://www.yahoo.com"); inStream = u.openStream(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Error in URL"); System.exit(0); } Scanner in = new Scanner(inStream); while (in.hasNext()) { System.out.println(in.nextLine()); } in.close(); } import java.util.Scanner; import java.net.URL; import java.io.*;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkingv2-151109154842-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Networking-46-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 47 Read from URL (Cont.) public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { URL yahoo = new URL("http://www.yahoo.com/"); URLConnection yahooConnection = yahoo.openConnection(); yahooConnection.connect(); InputStream inStream = yahooConnection.getInputStream(); Scanner in = new Scanner(inStream); while (in.hasNext()) { System.out.println(in.nextLine()); } inStream.close(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networkingv2-151109154842-lva1-app6892/75/Java-Networking-47-2048.jpg)