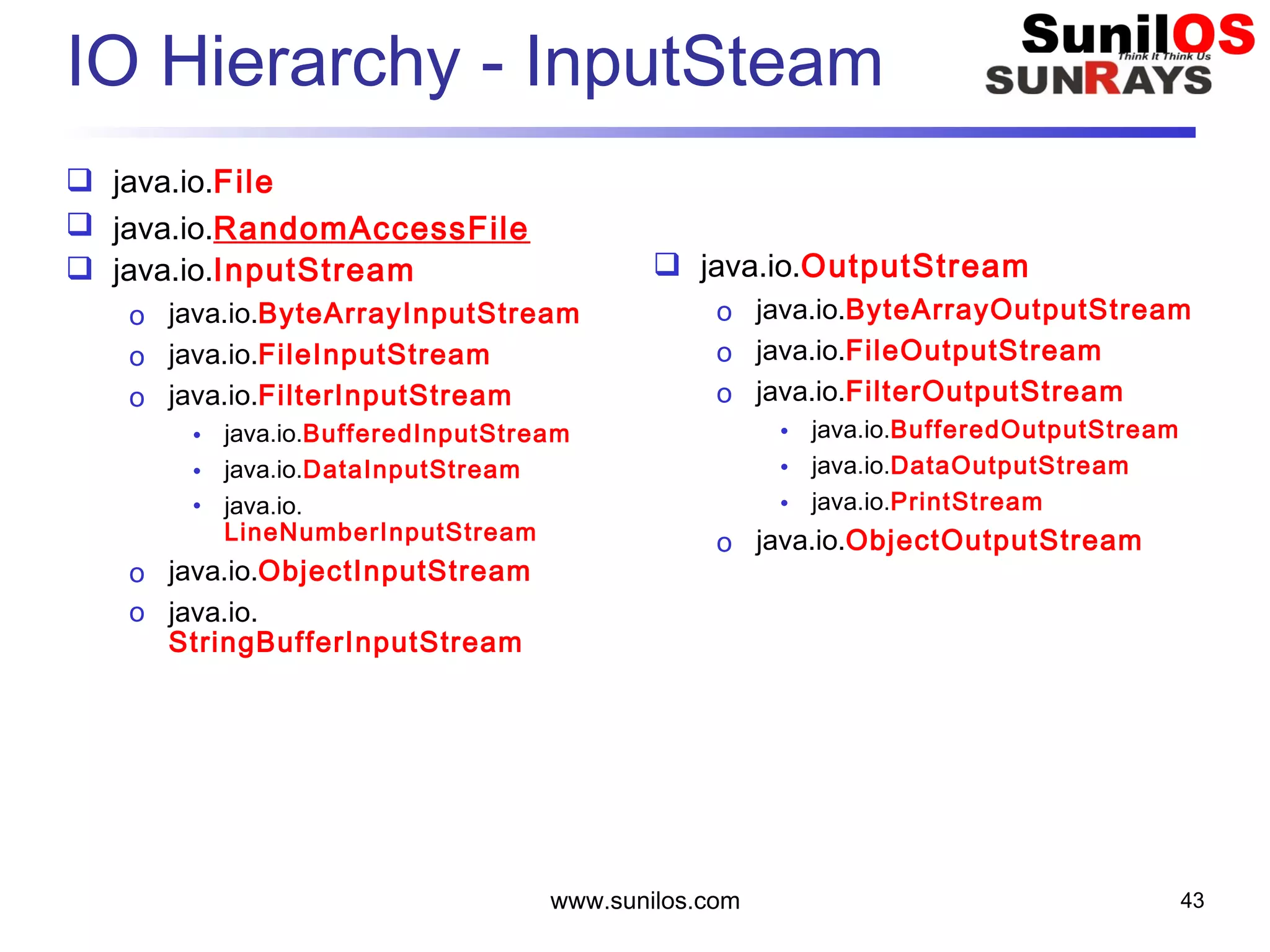
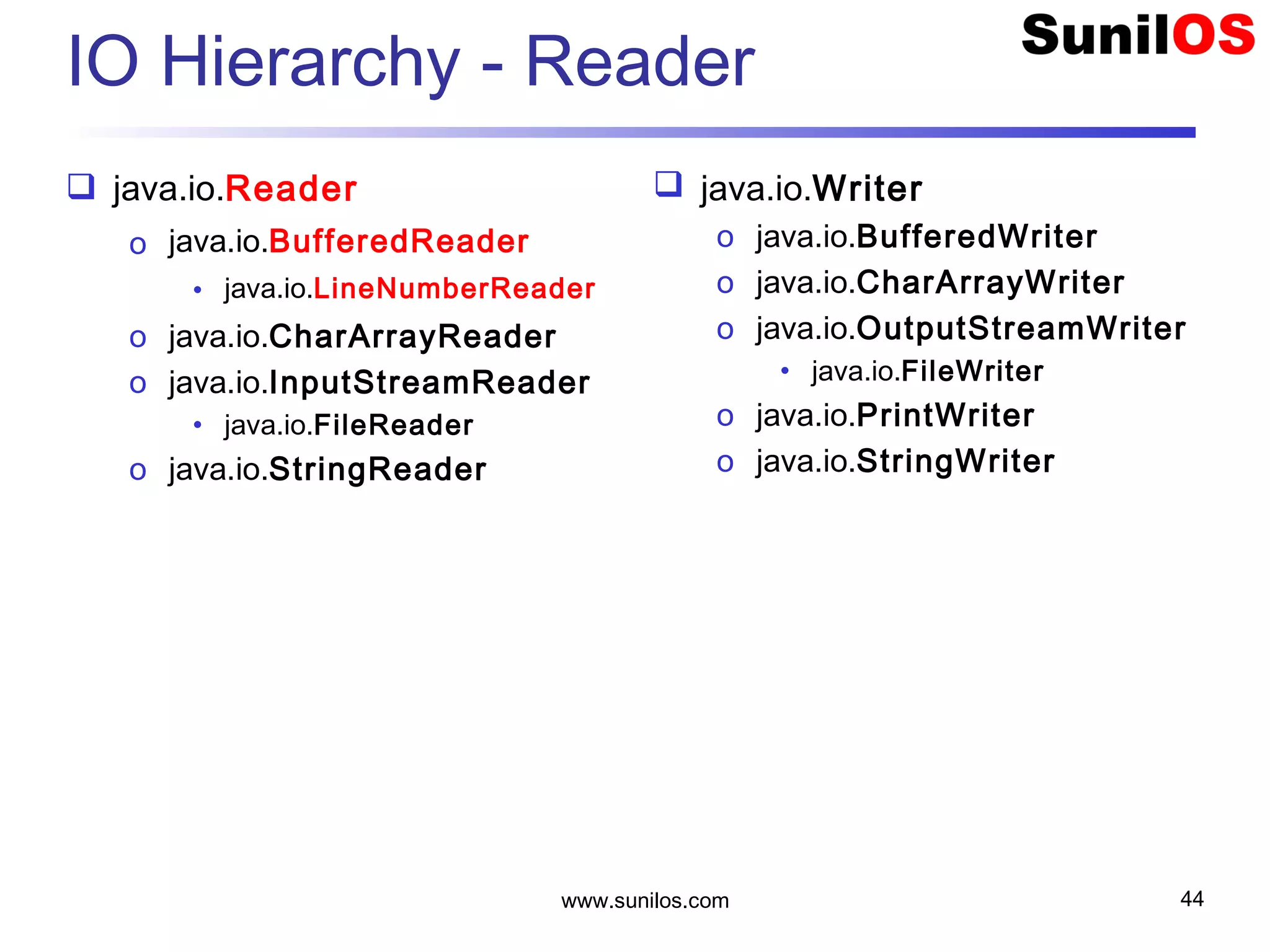
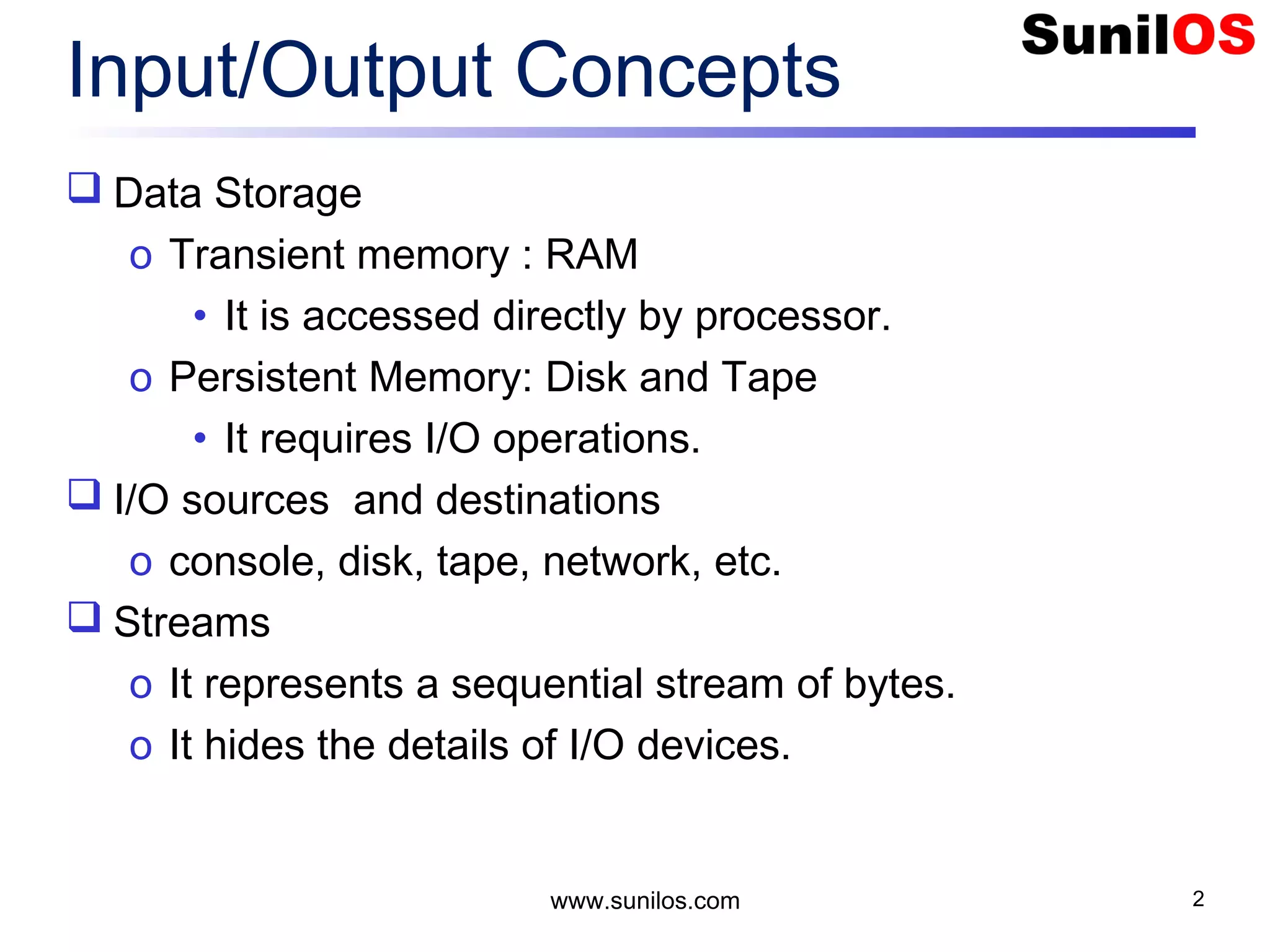
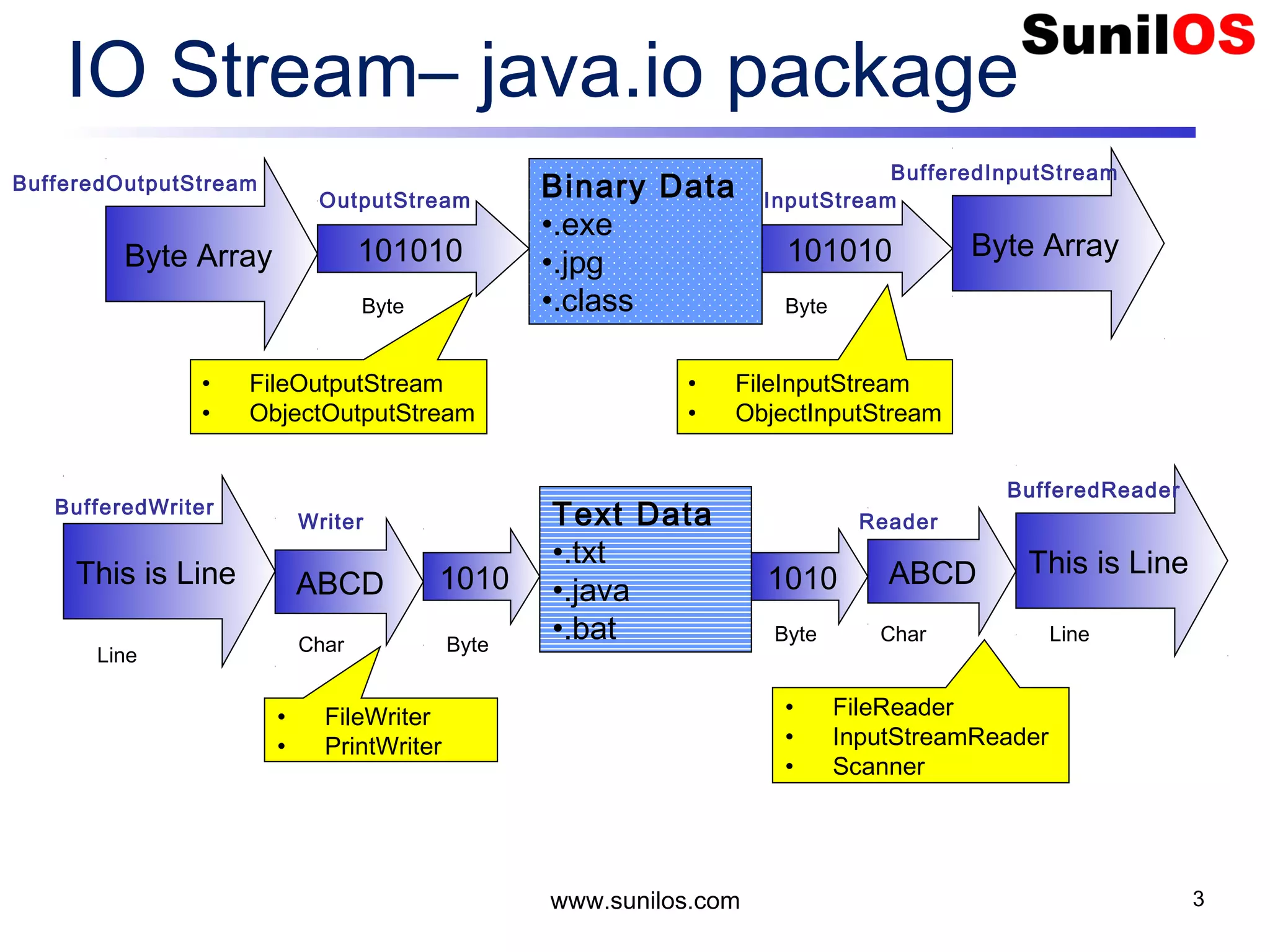
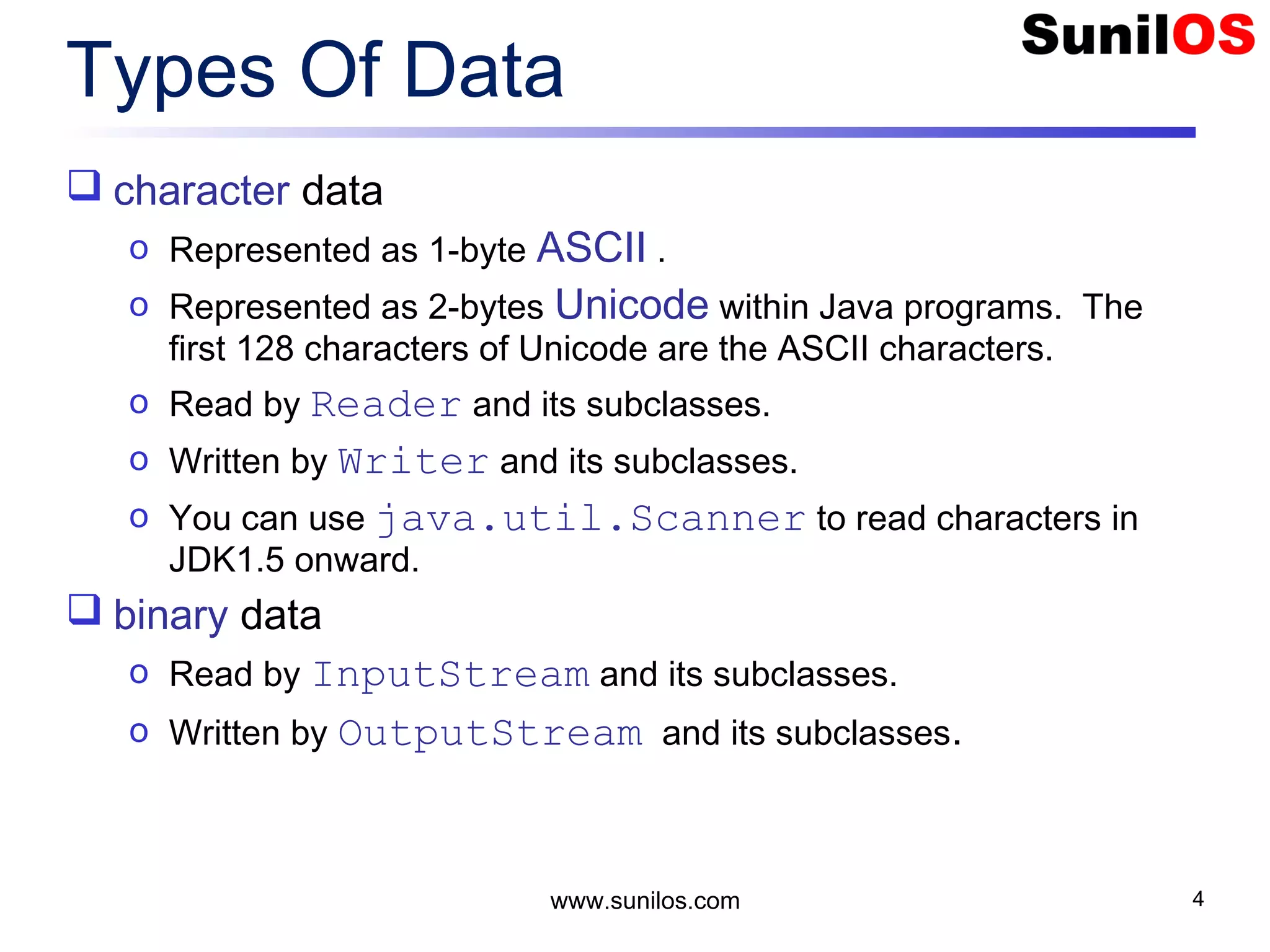
The document discusses input/output streams in Java. It covers: - Different types of data storage including transient RAM and persistent storage like disks. - I/O sources and destinations like consoles, disks, networks etc. and how streams represent sequential bytes to abstract I/O details. - Common Java I/O stream classes like FileReader, FileWriter, InputStream and OutputStream for reading/writing text and binary data from files. - Using File class to represent files and directories with methods to check attributes, read content and manipulate files.
![www.sunilos.com 5 Attrib.java : c:>java Attrib <fileName> import java.io.File; java.util.Date; public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("c:/temp/a.txt”"); // File f = new File("c:/temp” , “a.txt"); if(f.exists()){ System.out.println(“Name” + f.getName()); System.out.println("Absolute path: " + f.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println(" Is writable “ + f.canWrite()); System.out.println(" Is readable“ + f.canRead()); System.out.println(" Is File“ + f.isFile()); System.out.println(" Is Directory“ + f.isDirectory()); System.out.println("Last Modified at " + new Date(f.lastModified())); System.out.println(“Length " + f.length() + " bytes long."); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-5-2048.jpg)
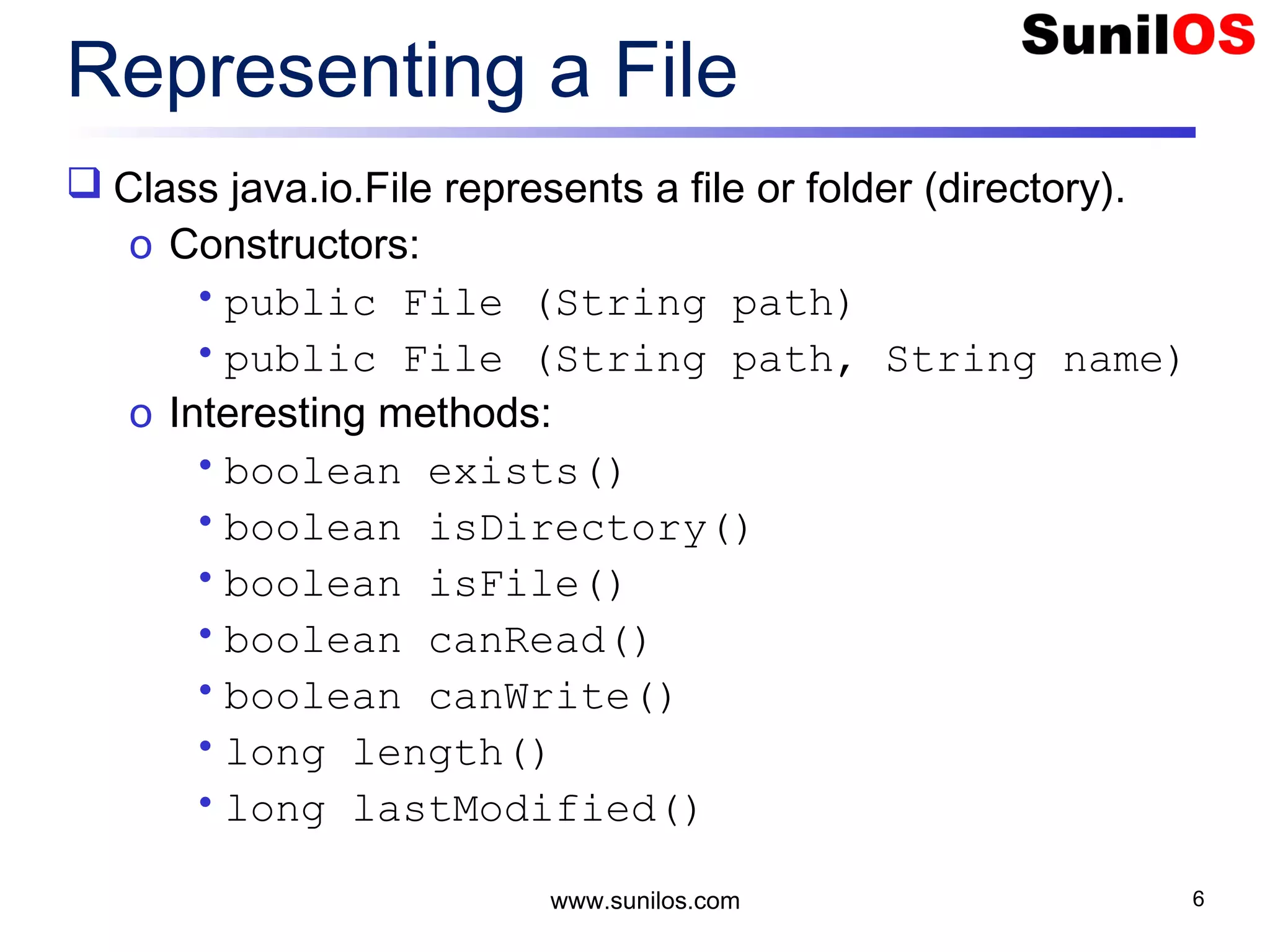
![www.sunilos.com 7 Representing a File (Cont.) More interesting methods: o boolean delete() o boolean renameTo(File dest) o boolean mkdir() o String[] list() o File[] listFiles() o String getName()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-7-2048.jpg)
![www.sunilos.com 8 Display file and subdirectories This program displays files and subdirectories of a directory. public static void main(String[] args) { File directory = new File("C:/temp"); //File directory = new File(args[0]); String[] list = directory.list(); for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + list[i]); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-8-2048.jpg)
![www.sunilos.com 9 Display only files from a folder public static void main(String[] args) { File directory = new File("C:/temp"); //File directory = new File(args[0]); String[] list = directory.list(); for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { File f = new File(“c:/temp”,list[i]); if(f.isFile()){ System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + list[i]); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-9-2048.jpg)
![www.sunilos.com 10 Display only files from a folder public static void main(String[] args) { File directory = new File("C:/temp"); File[] list = directory.listFiles(); for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { if (list[i].isFile()) { System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + list[i].getName()); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-10-2048.jpg)
![www.sunilos.com 11 FileReader- Read char from a file public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ FileReader reader = new FileReader(“c:/test.txt”); int ch = reader.read(); char chr; while(ch != -1){ chr = (char)ch; System.out.print( chr); ch = reader.read(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-11-2048.jpg)
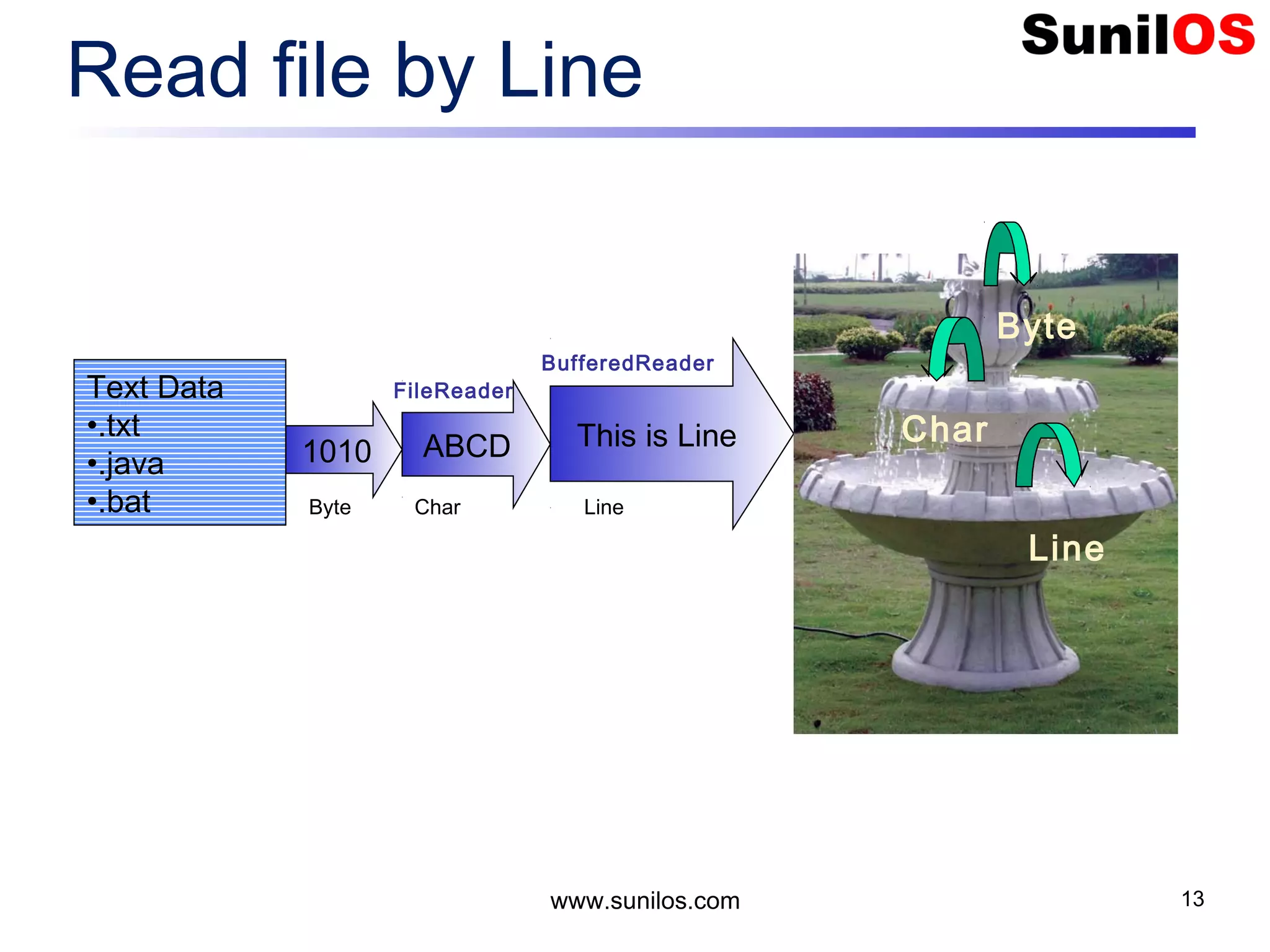
![www.sunilos.com 12 Read a file line by line public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { FileReader reader = new FileReader("c:/test.txt"); BufferedReader br= new BufferedReader(reader); String line = br.readLine(); while (line != null) { System.out.println(line); line = br.readLine(); } reader.close(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-12-2048.jpg)
![www.sunilos.com 14 Write to a File public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("c:/newtest.txt"); PrintWriter pw= new PrintWriter(writer); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { pw.println(i + " : Line"); } pw.close(); writer.close(); System.out.println(“File is successfully written, Pl check c:/newtest.txt "); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-14-2048.jpg)
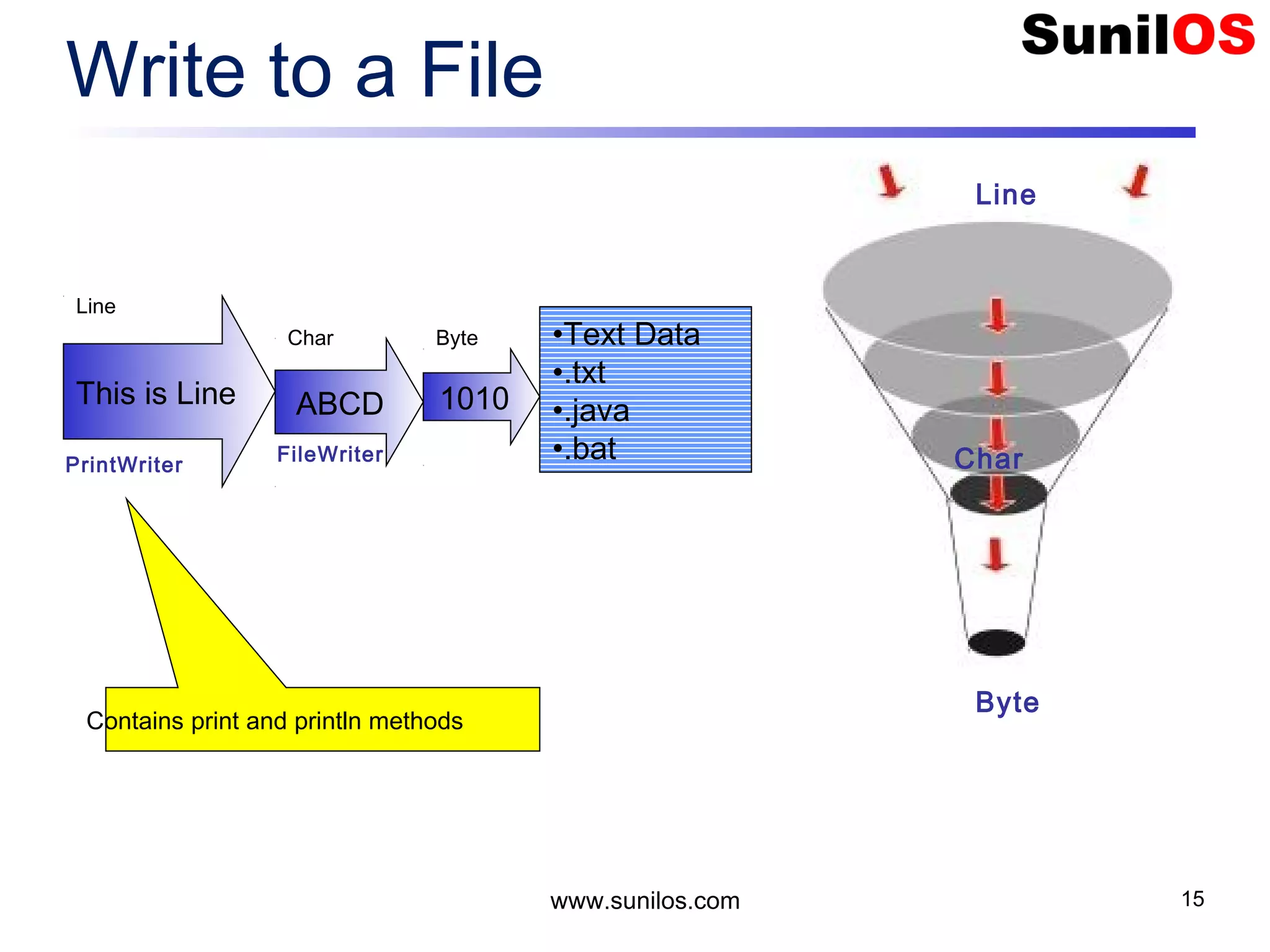
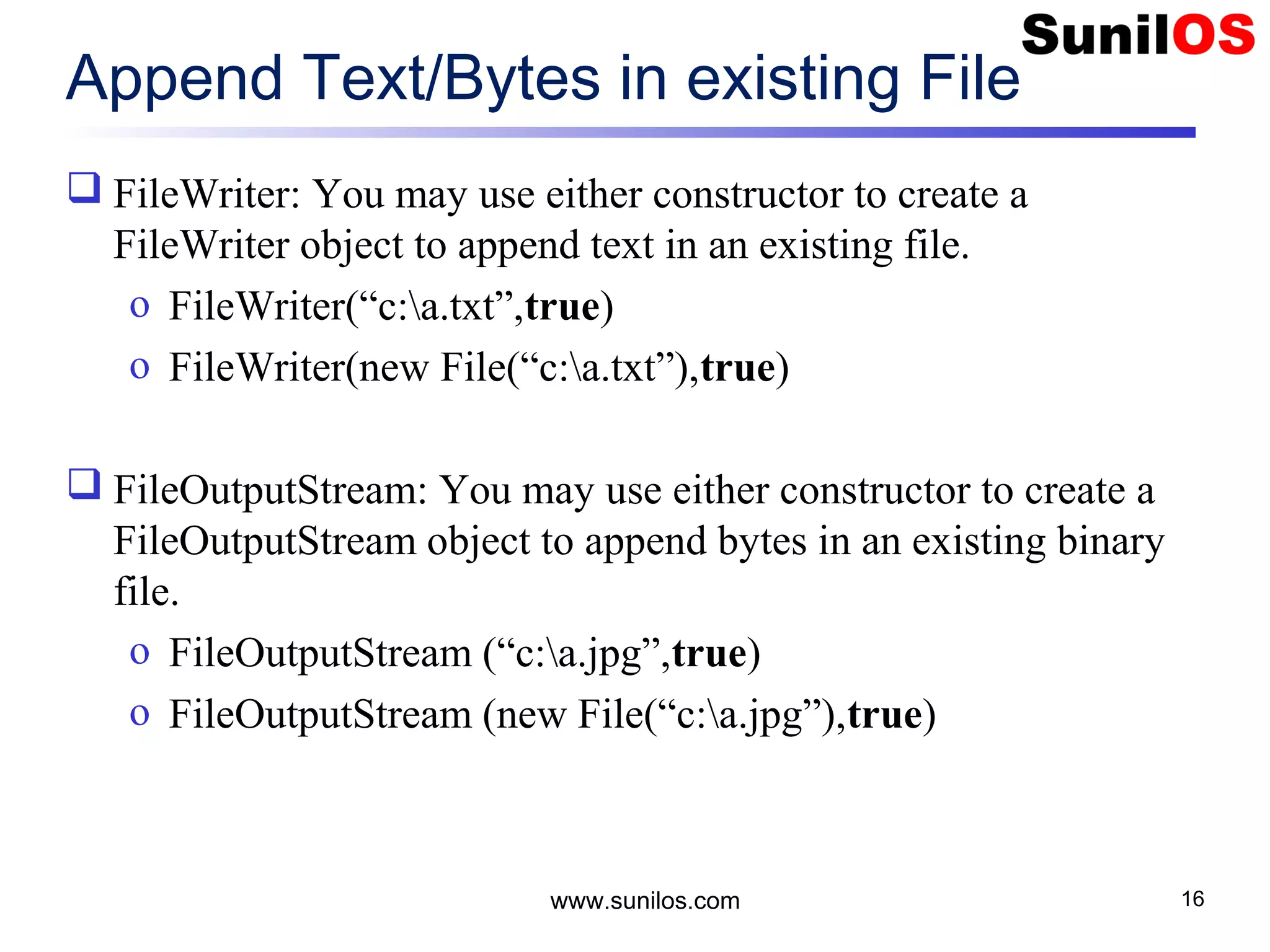

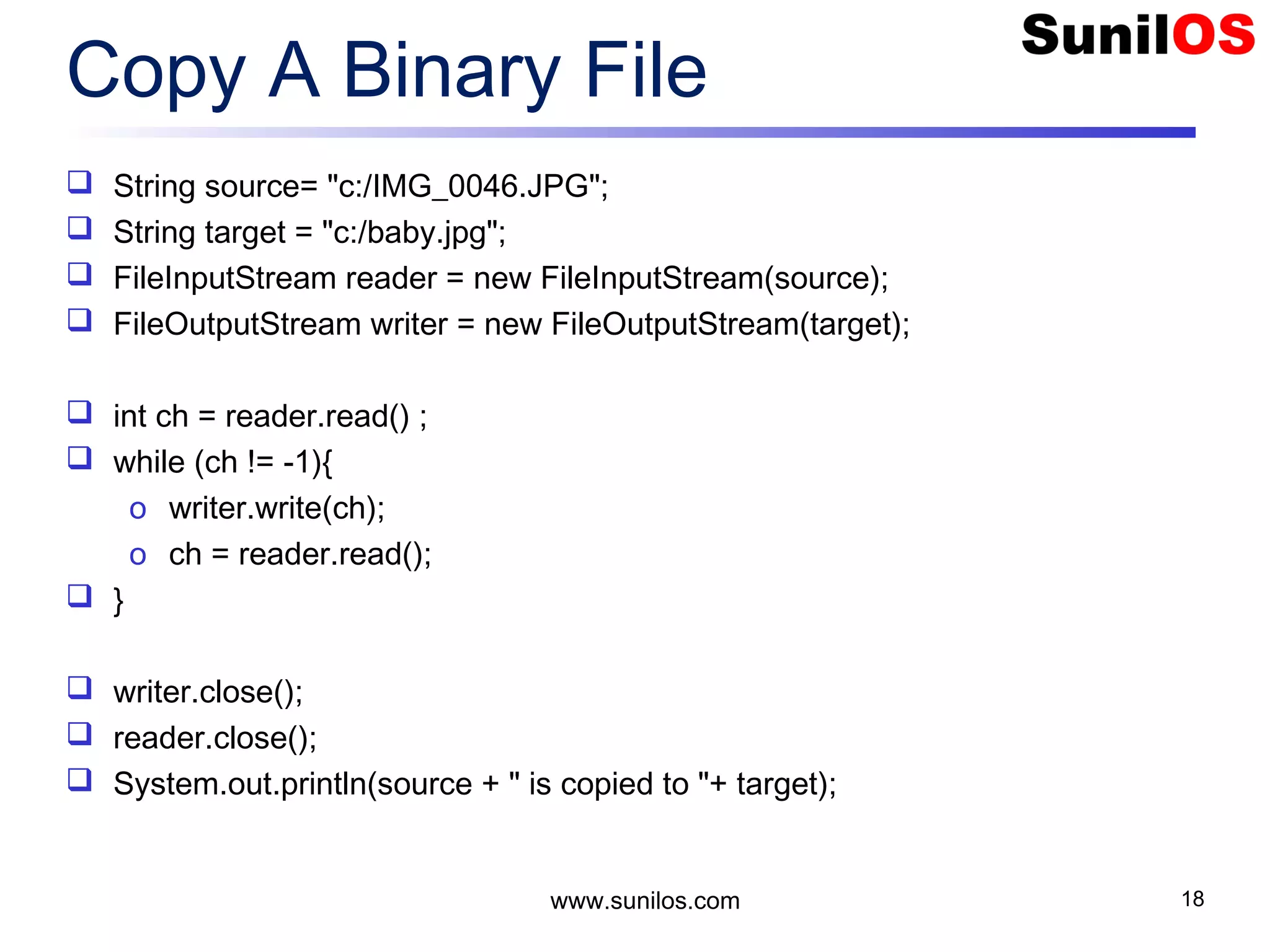
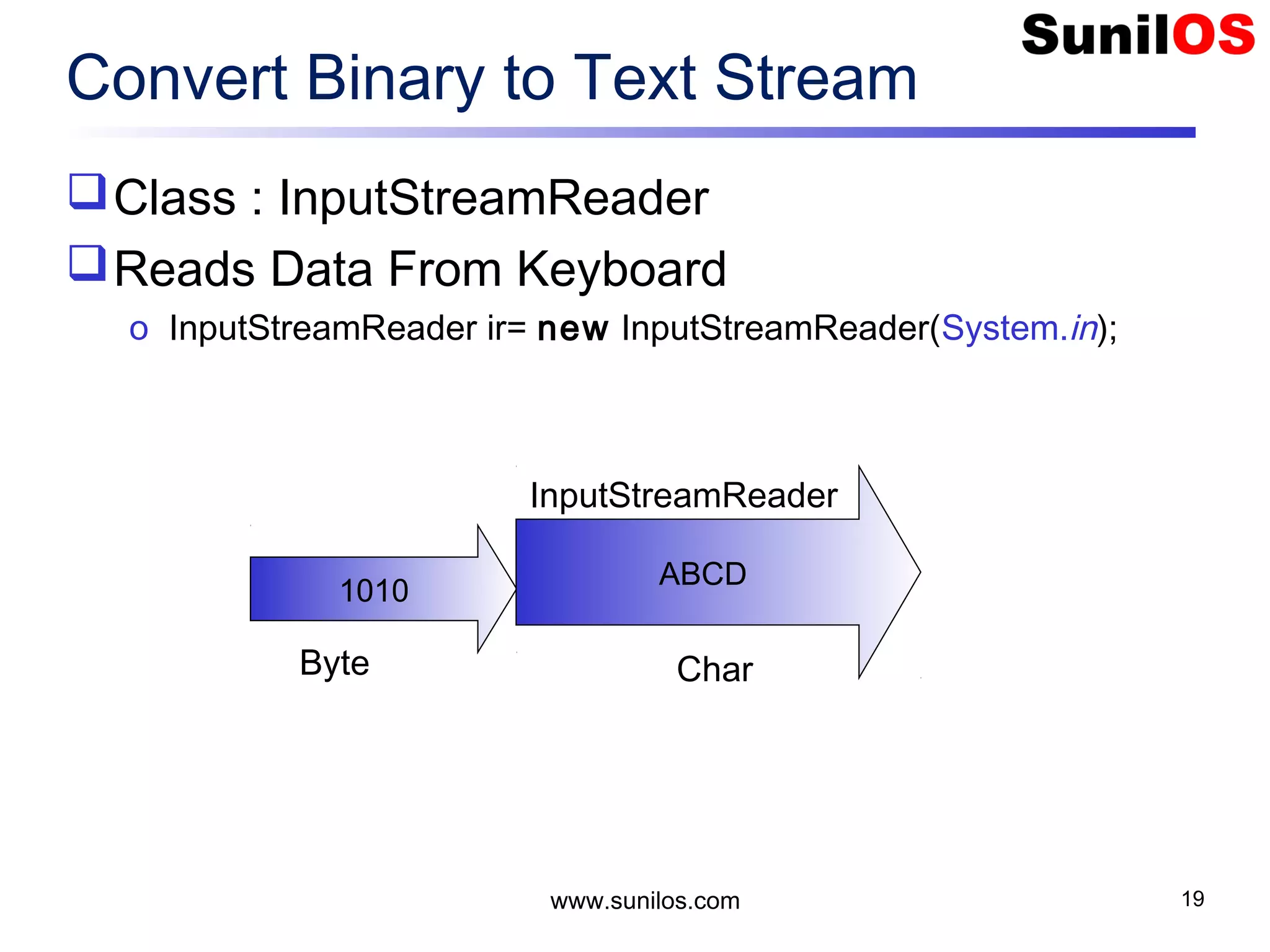

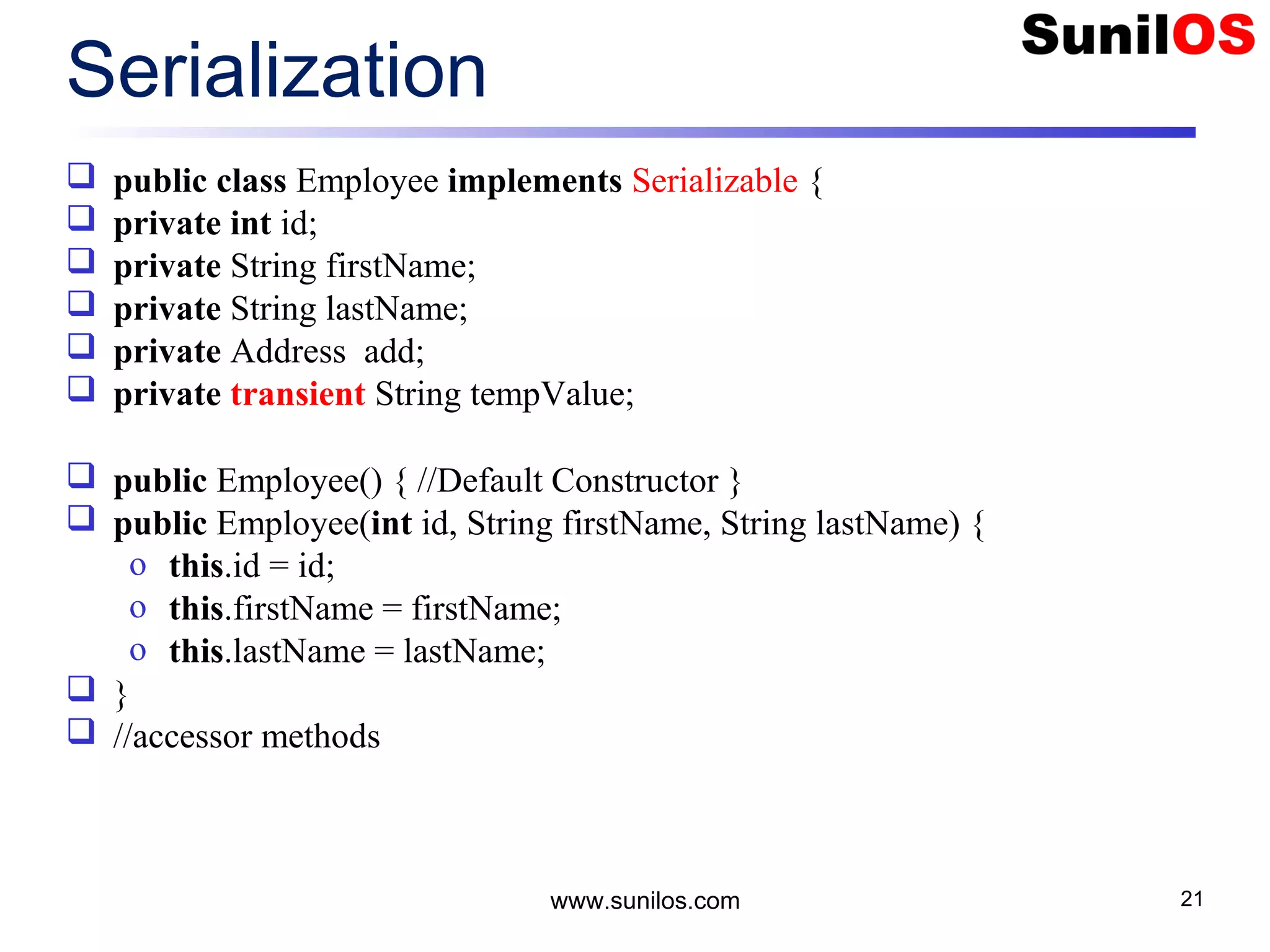
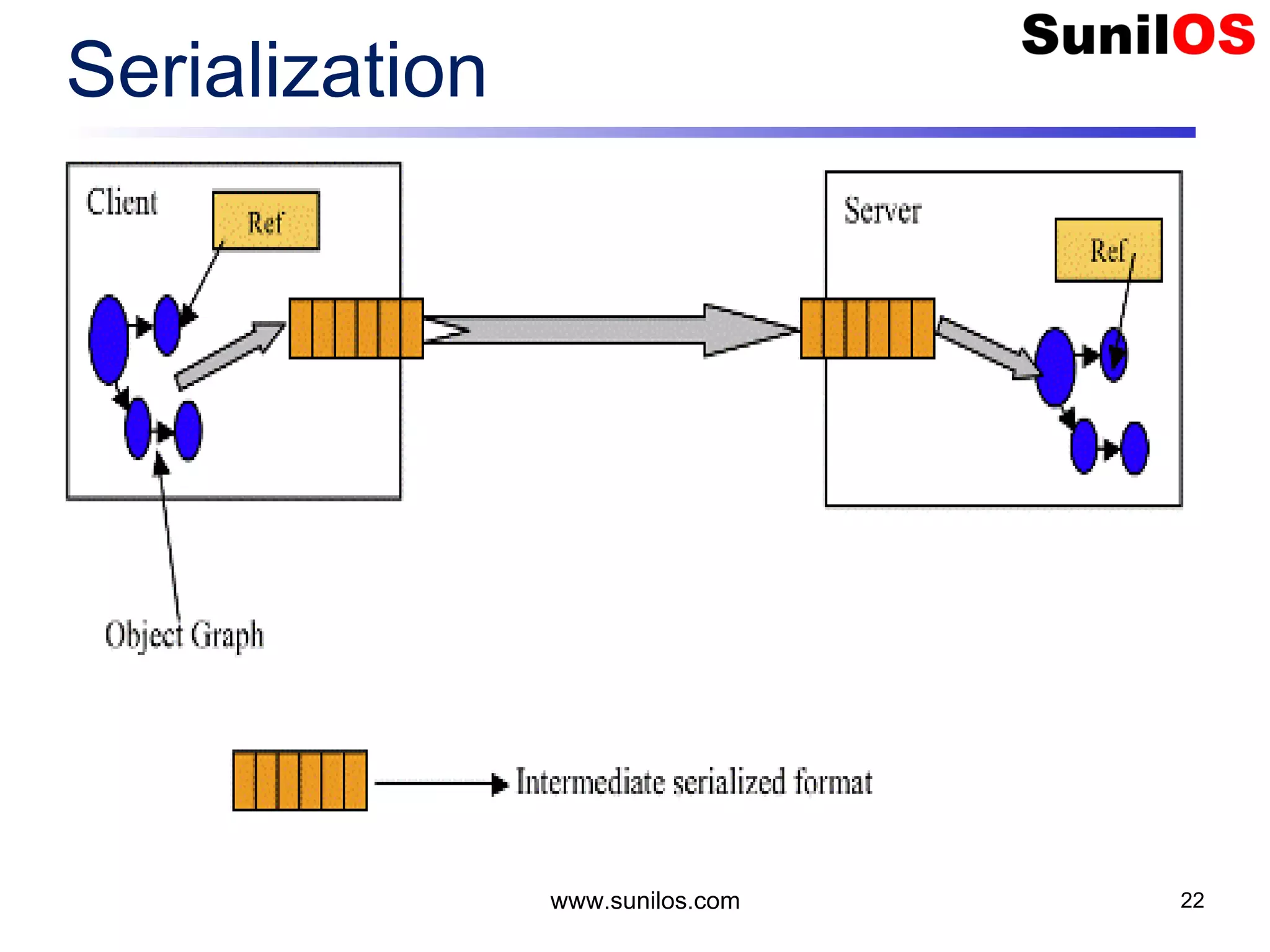

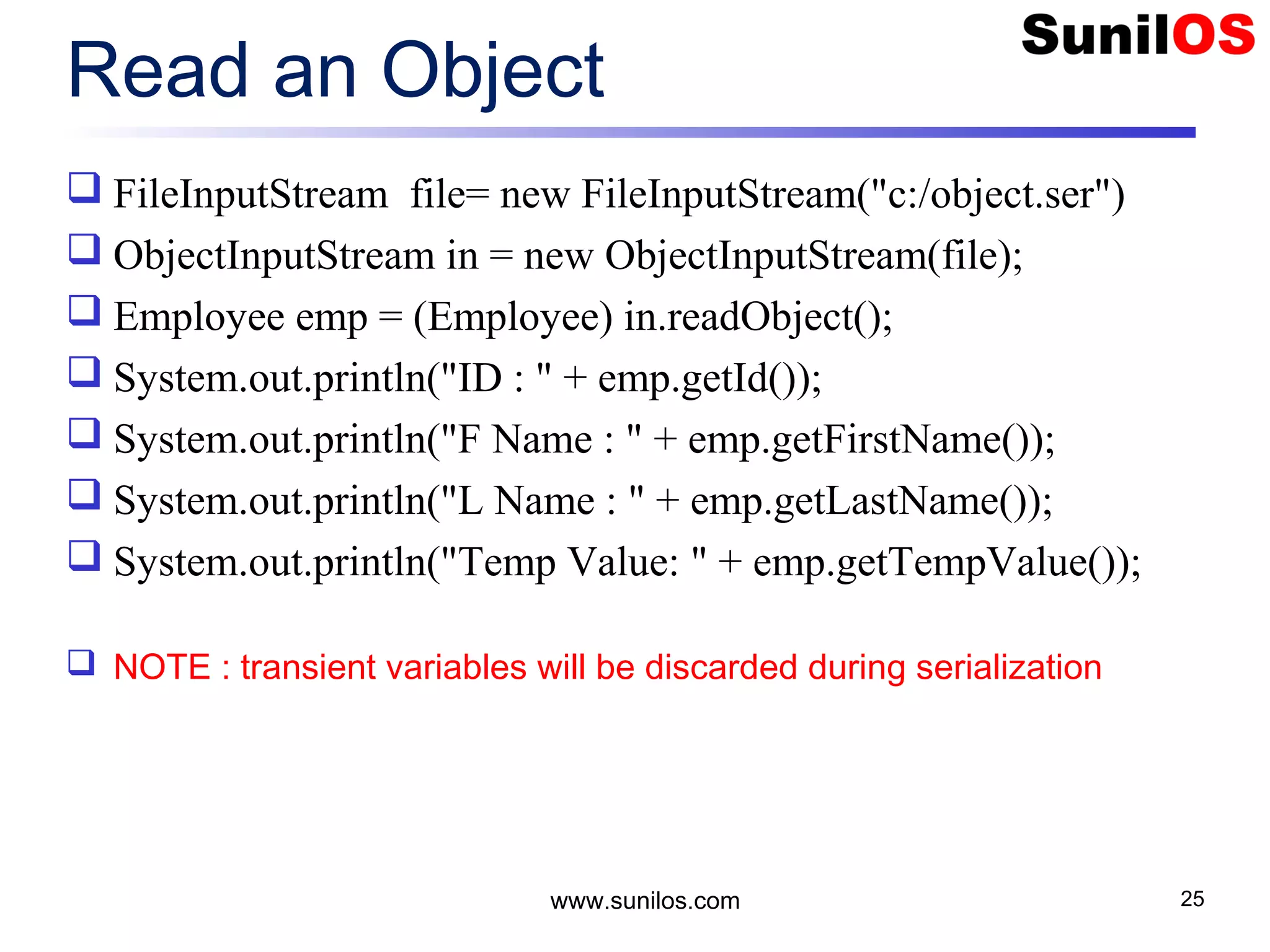
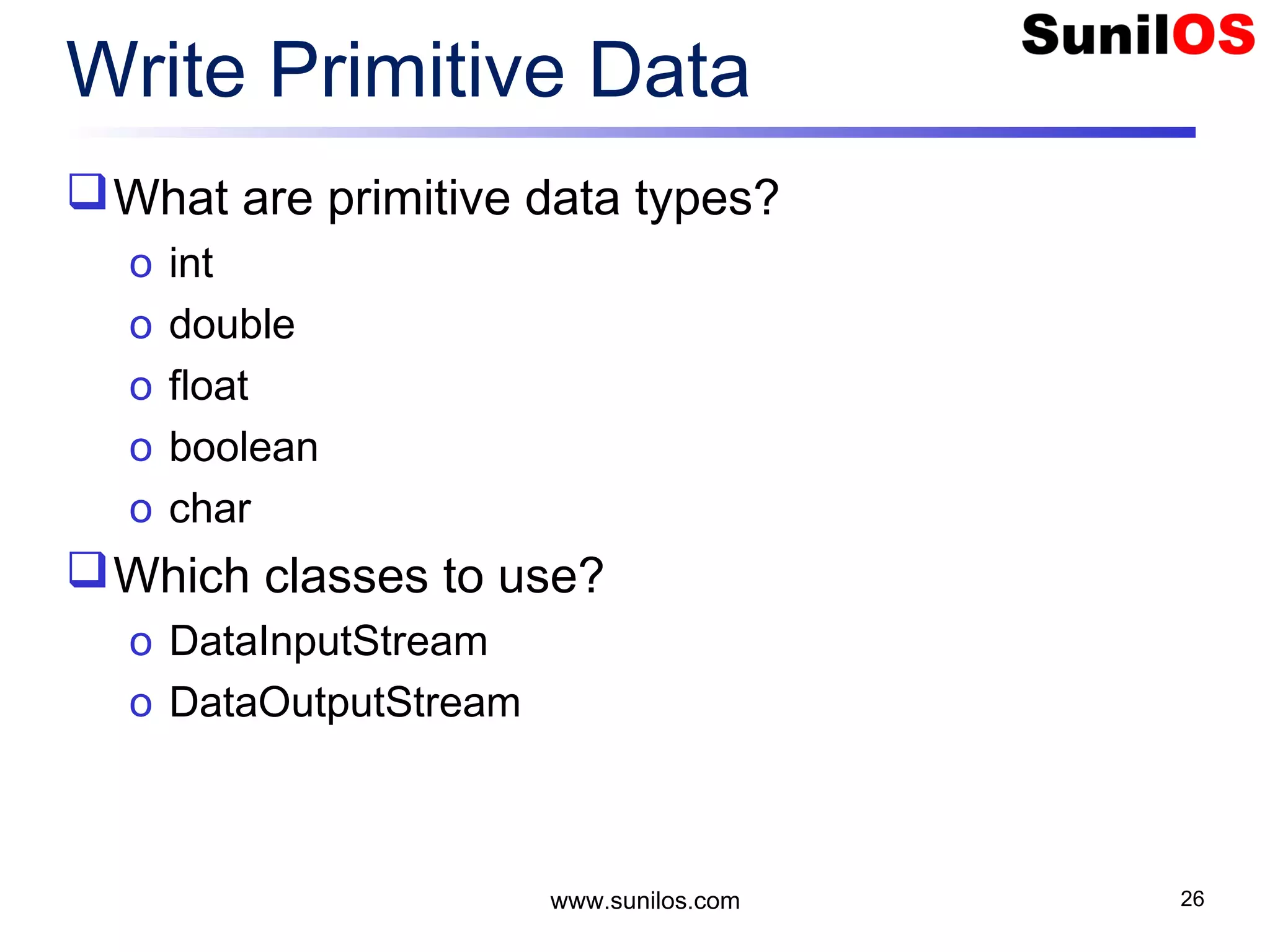
![Write Primitive Data public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { o FileOutputStream file = new FileOutputStream("c:/primitivedata.dat"); o DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(file); o out.writeInt(1); o out.writeBoolean(true); o out.writeChar('A'); o out.writeDouble(1.2); o out.close(); o file.close() o System.out.println("Primitive Data successfully written"); } www.sunilos.com 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-27-2048.jpg)
![Read Primitive Data public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { o FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream("c:/primitivedata.dat"); o DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(file); o System.out.println(in.readInt()); o System.out.println(in.readBoolean()); o System.out.println(in.readChar()); o System.out.println(in.readDouble()); o in.close(); } www.sunilos.com 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-28-2048.jpg)
![www.sunilos.com 29 Primitive File - Write public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { long dataPosition = 0; // to be determined later RandomAccessFile in = new RandomAccessFile("datafile.dat", "rw"); // Write to the file. in.writeLong(0); // placeholder in.writeChars("blahblahblah"); dataPosition = in.getFilePointer(); in.writeInt(123); in.writeBytes(“Blahblahblah"); // Rewrite the first byte to reflect updated data position. in.seek(0); in.writeLong(dataPosition); in.close(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-29-2048.jpg)
![www.sunilos.com 30 Primitive File - Read public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { long dataPosition = 0; int data = 0; RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("datafile", "r"); // Get the position of the data to read. dataPosition = raf.readLong(); System.out.println("dataPosition : " + dataPosition); // Go to that position. raf.seek(dataPosition); // Read the data. data = raf.readInt(); raf.close(); System.out.println("The data is: " + data); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-30-2048.jpg)
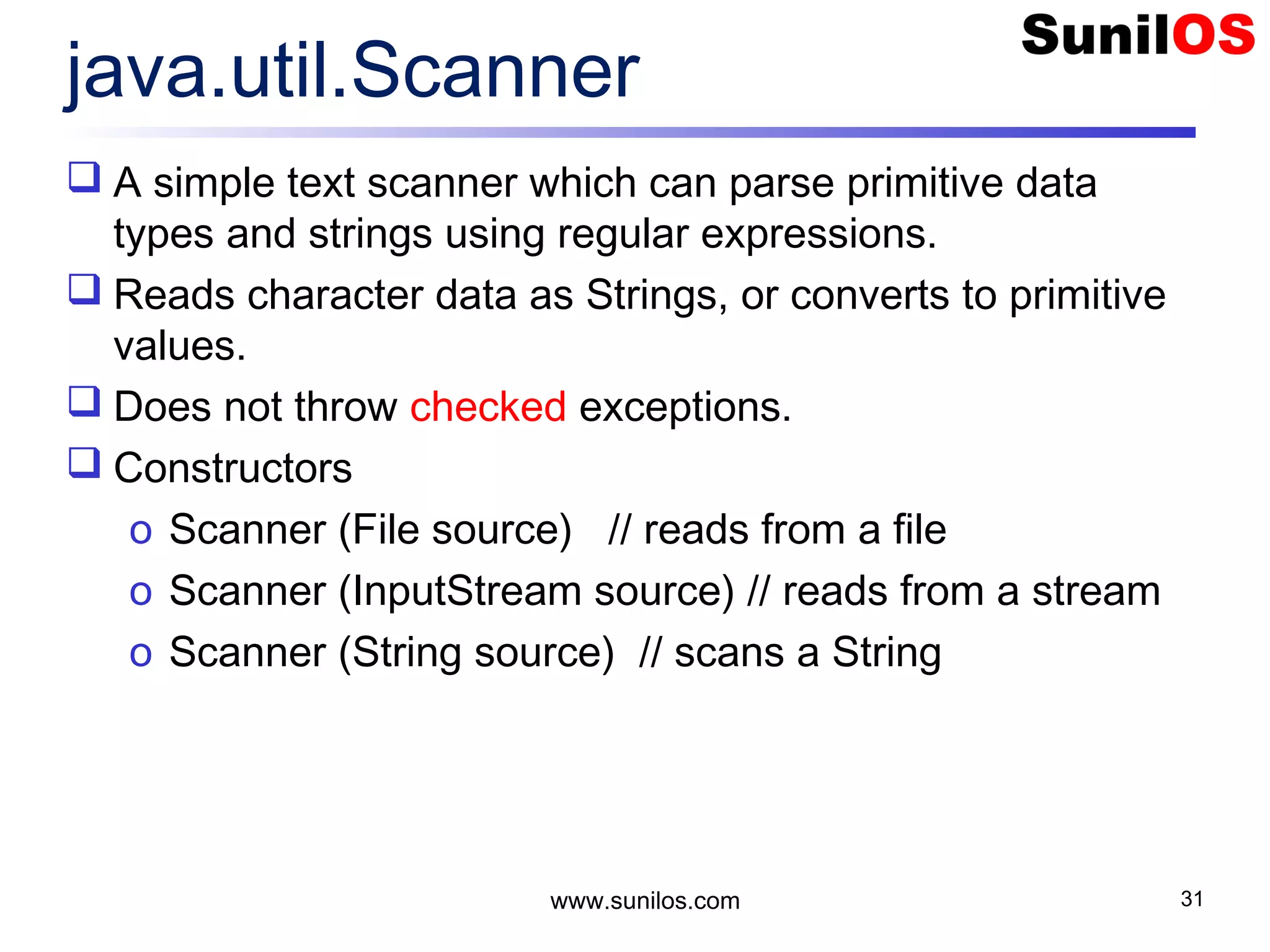
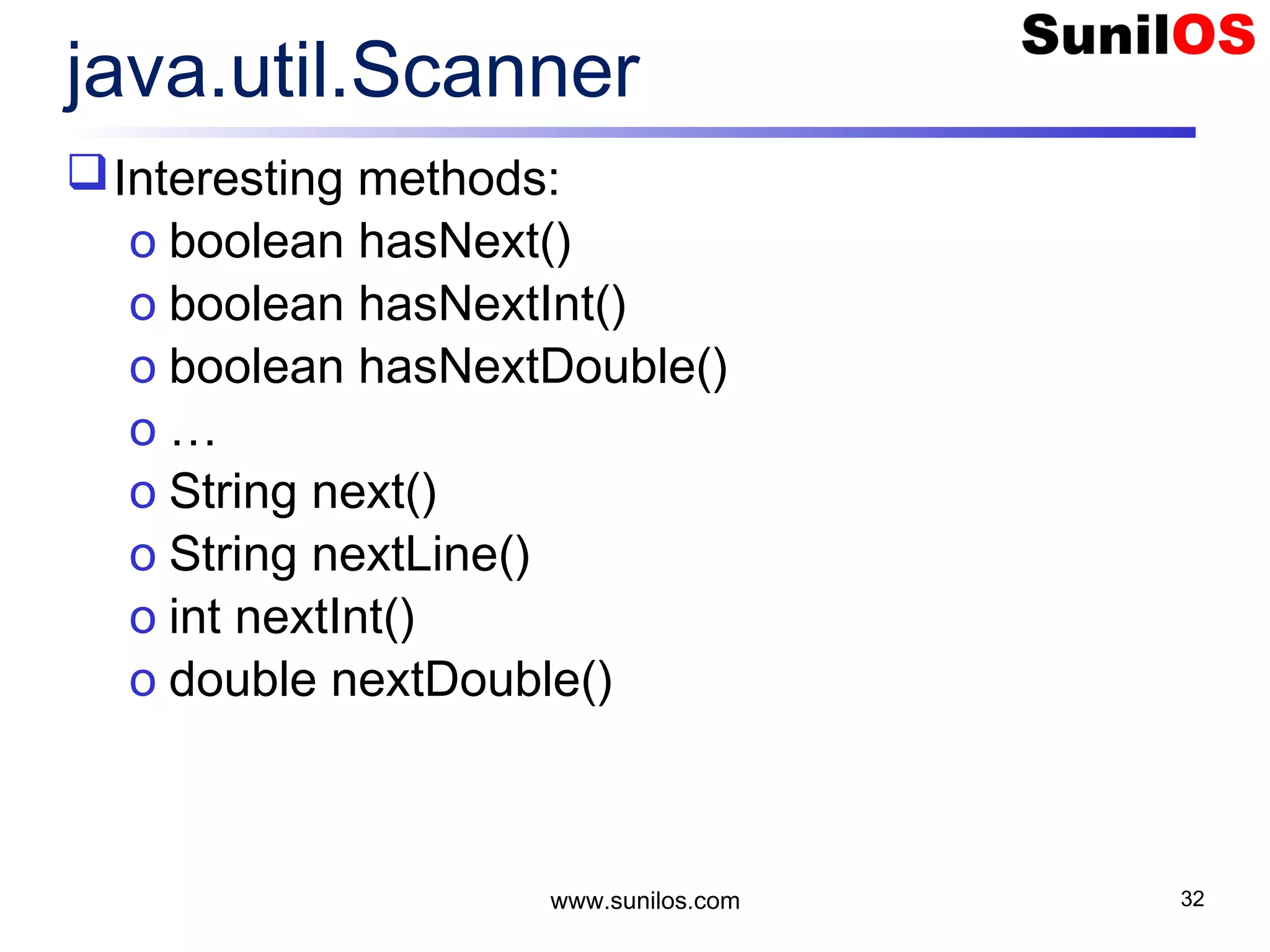
![www.sunilos.com 33 Read File By Scanner public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ FileReader reader = new FileReader("c:/newtest.txt"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(reader); while(sc.hasNext()){ System.out.println(sc.nextLine()); } reader.close(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-33-2048.jpg)
![Token A String Breaks string into tokens. public static void main(String[] args) { o String str = “This is Java, Java is Object Oriented Language, Java is guarantee for job"; o StringTokenizer stn = new StringTokenizer(str, ","); o String token = null; o while (stn.hasMoreElements()) { o token = stn.nextToken(); o System.out.println(“Token is : " + token); o } } www.sunilos.com 34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-34-2048.jpg)
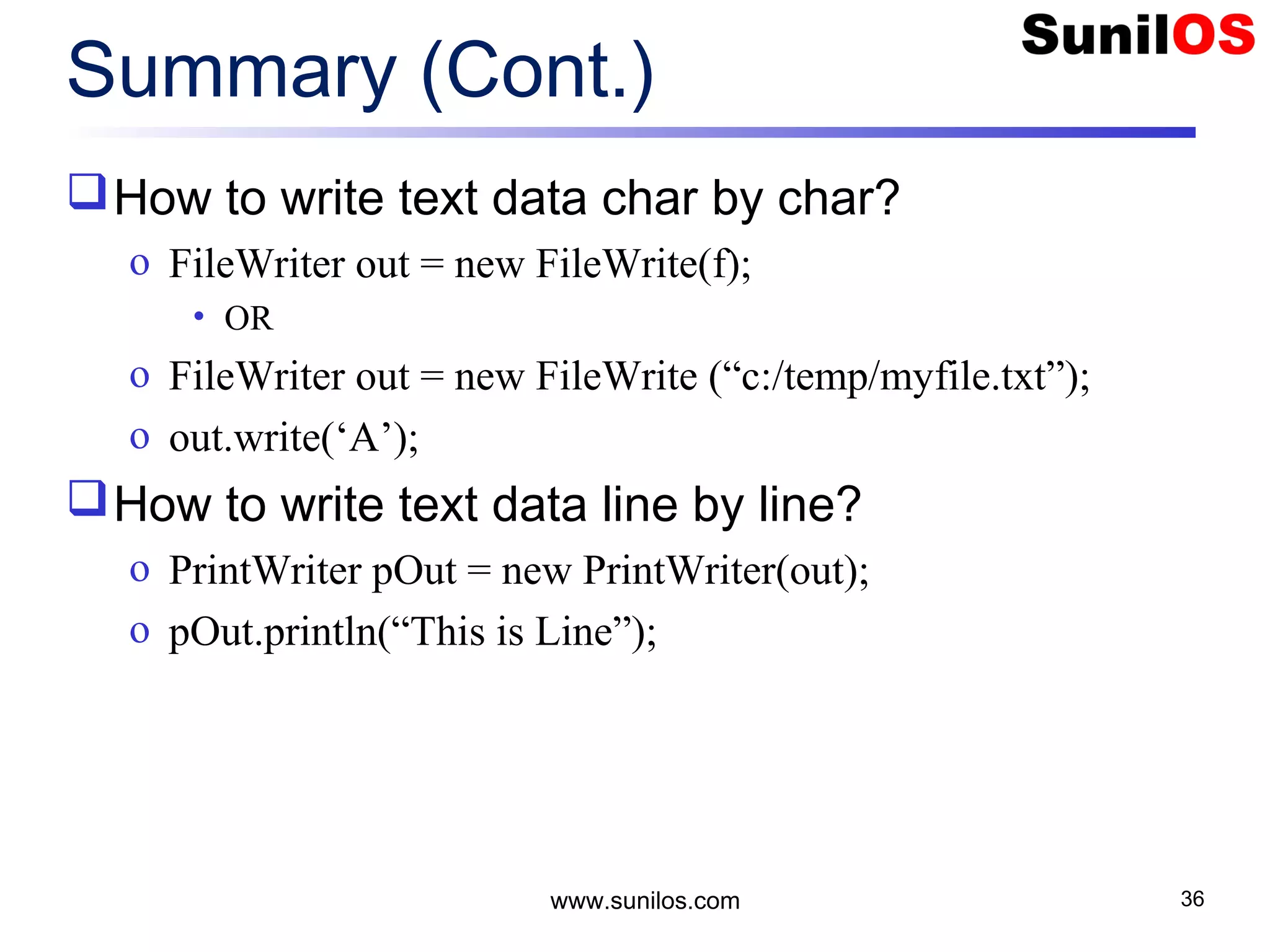
![www.sunilos.com 38 Summary (Cont.) How to write binary data byte by byte? o FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(f); • OR o FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream (“c:/temp/myfile.txt”); o out.write(1); How to write binary data as byte array? o BufferedOutputStream bOut = new BufferedOutputStream (out); o bOut.write(byte[]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-38-2048.jpg)
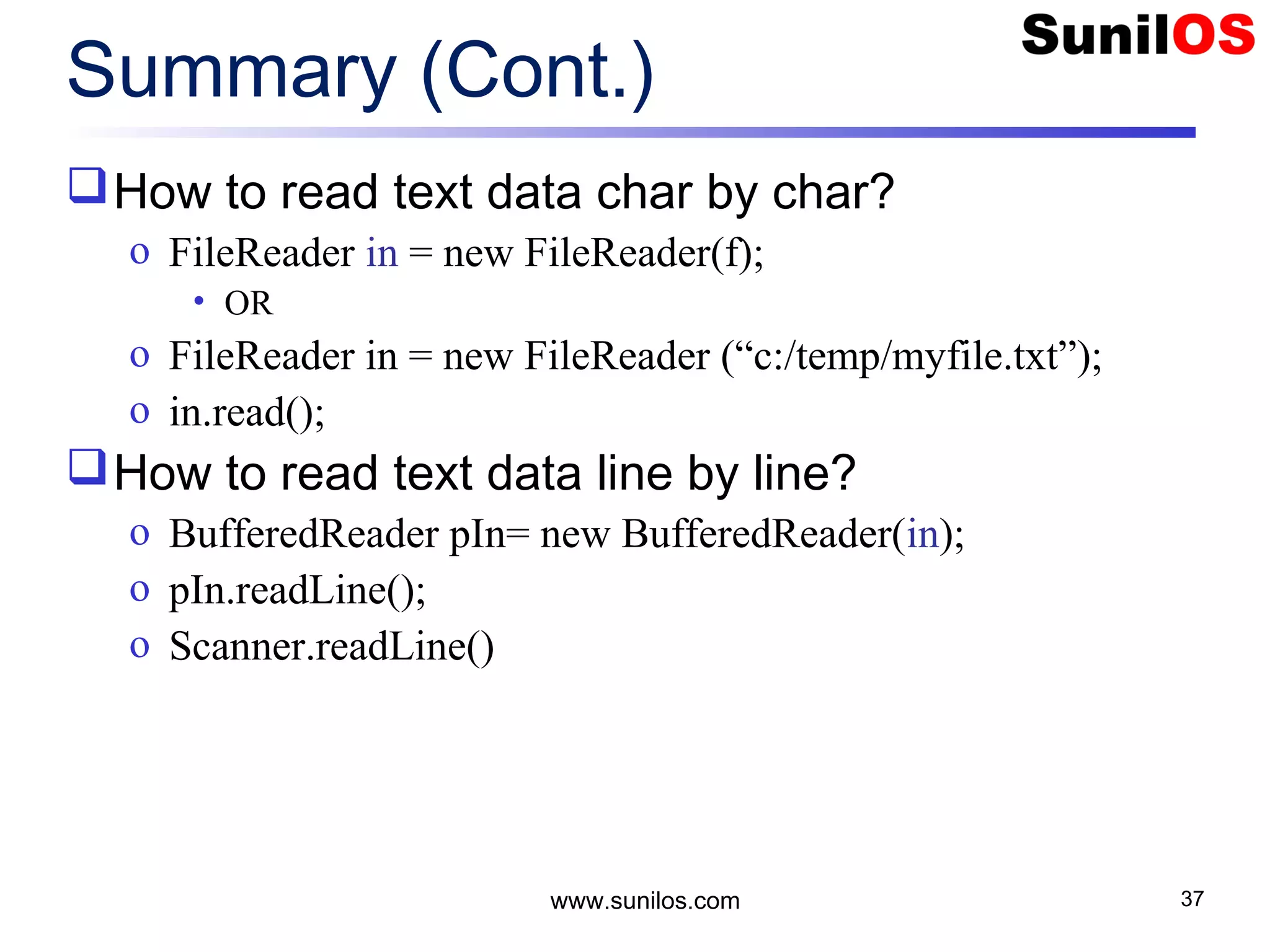
![www.sunilos.com 39 Summary (Cont.) How to read binary data byte by byte? o FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(f); • OR o FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream (“c:/temp/myfile.txt”); o in.read(); How to read binary data as byte array? o BufferedInputStream bIn = new BufferedInputStream (in); o byte[] buffer = new byte[256]; o bIn.read(buffer);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iostreamsv2-151225120725/75/Java-Input-Output-and-File-Handling-39-2048.jpg)