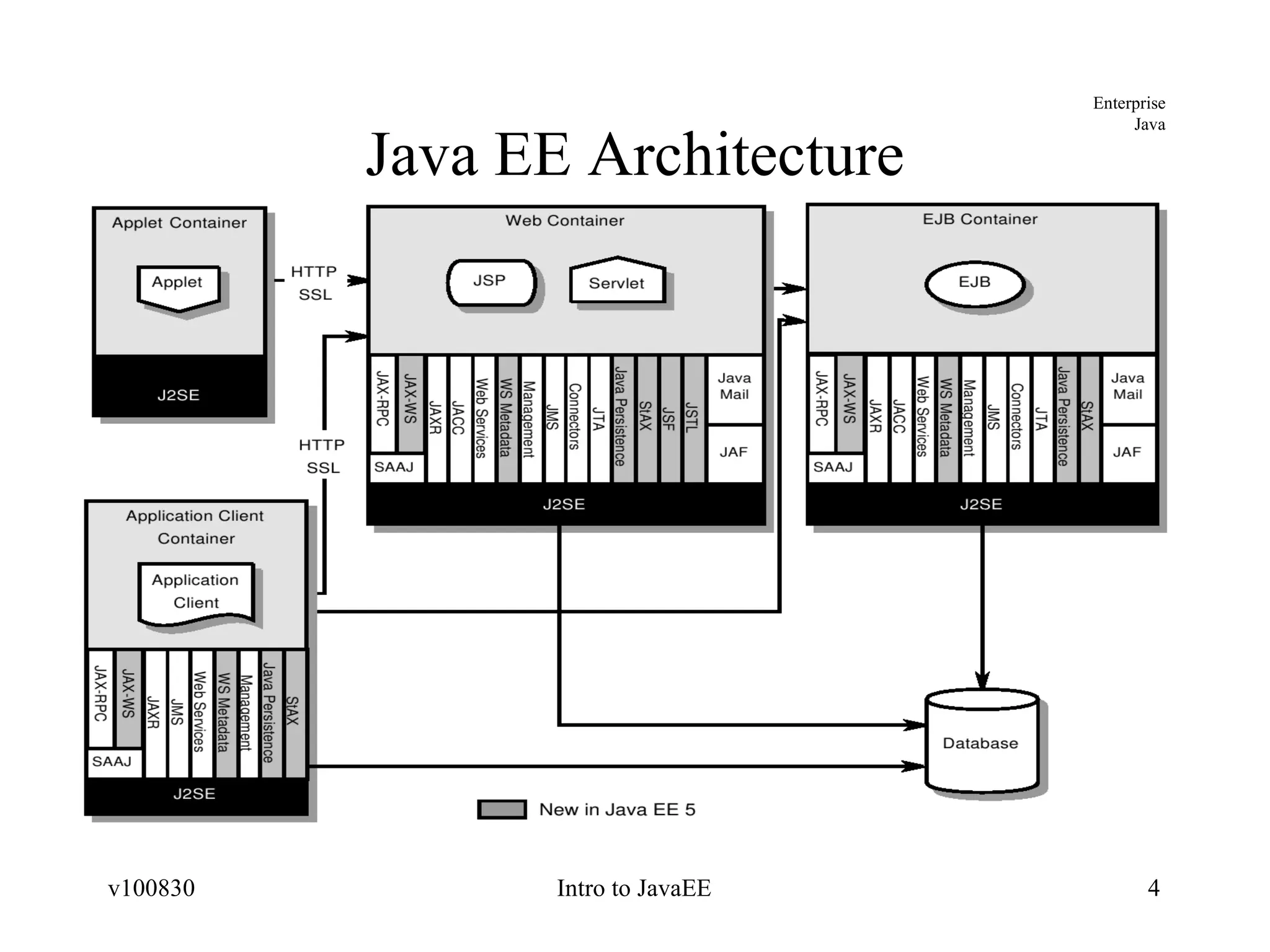
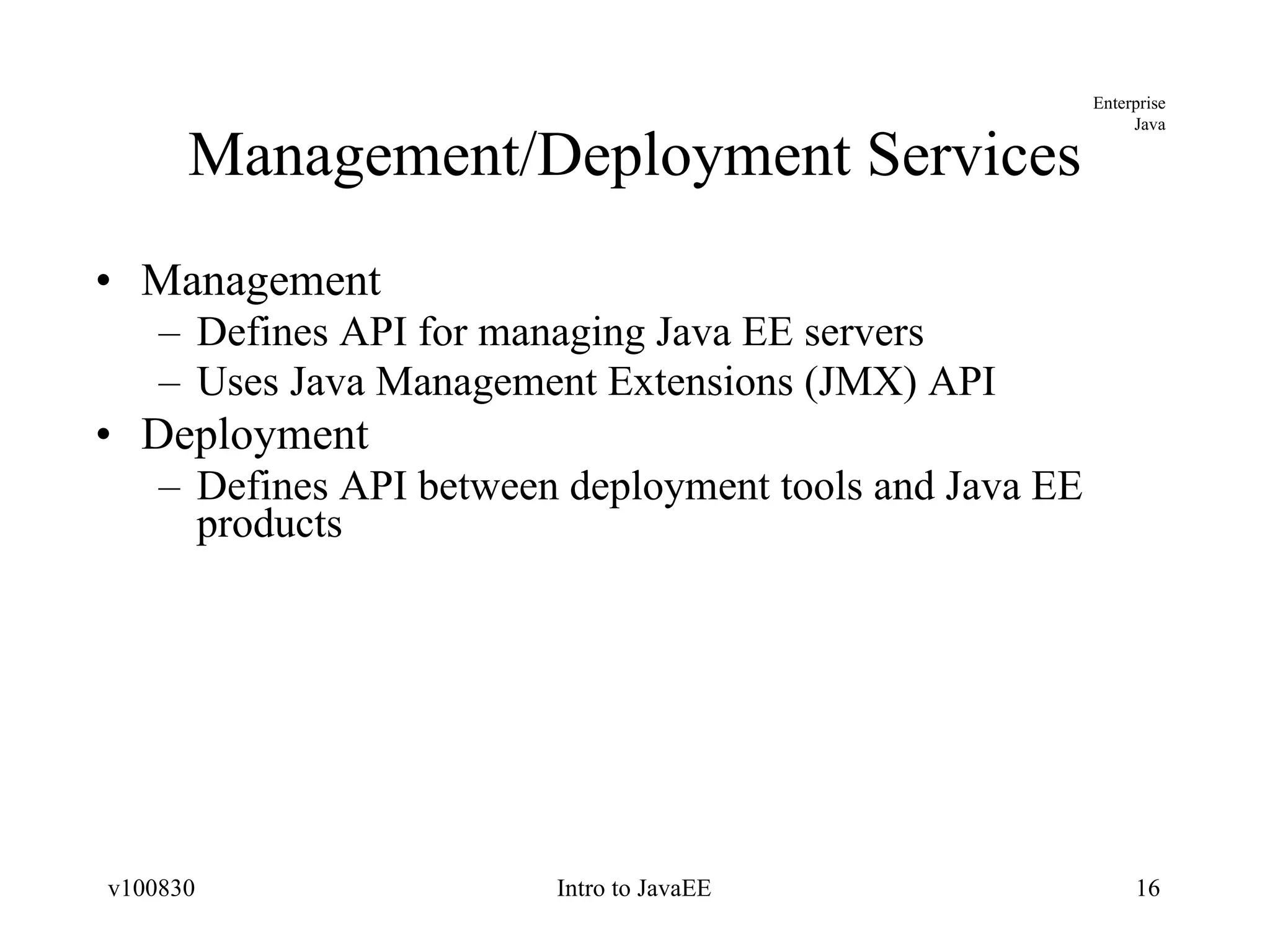
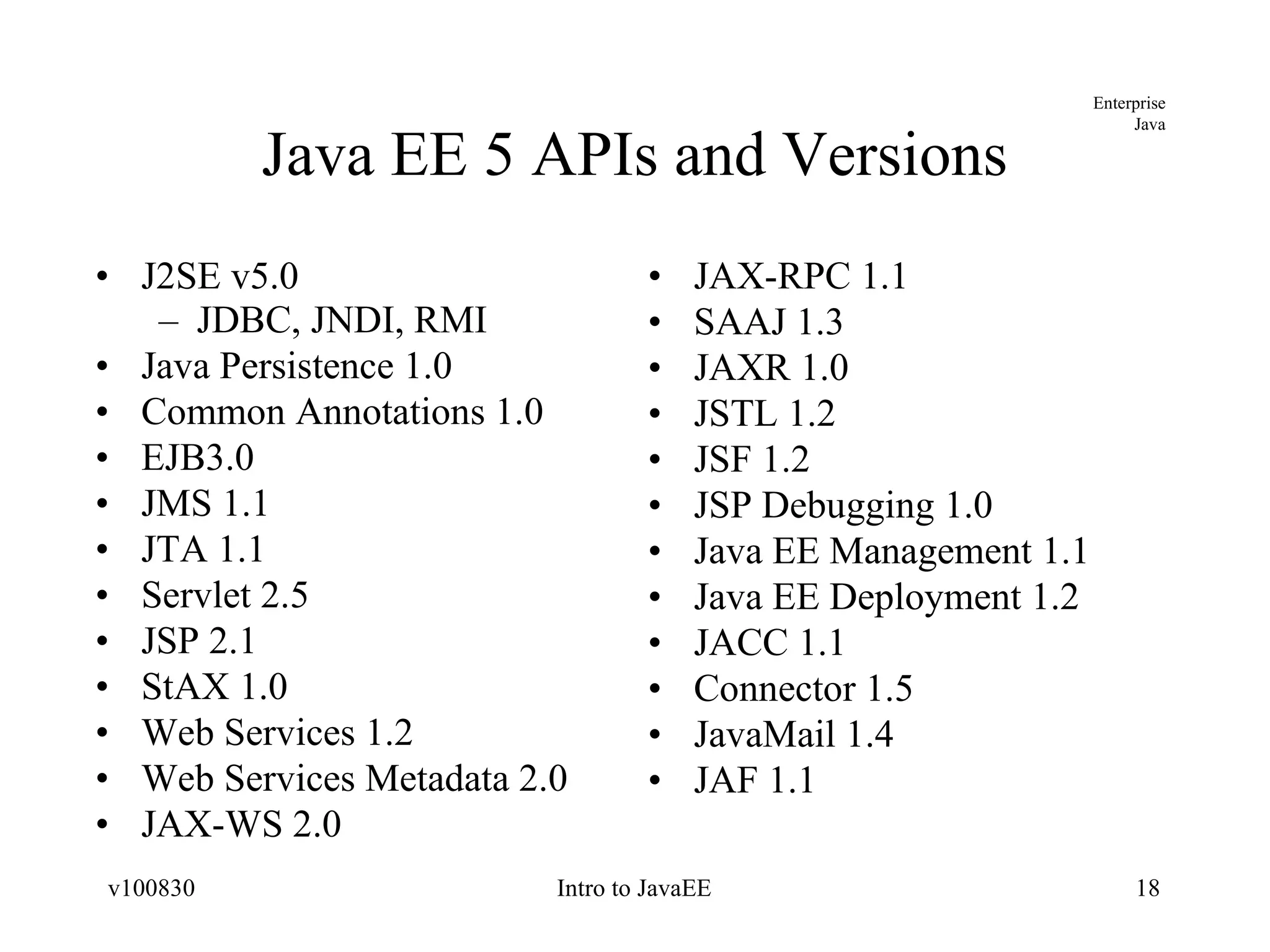
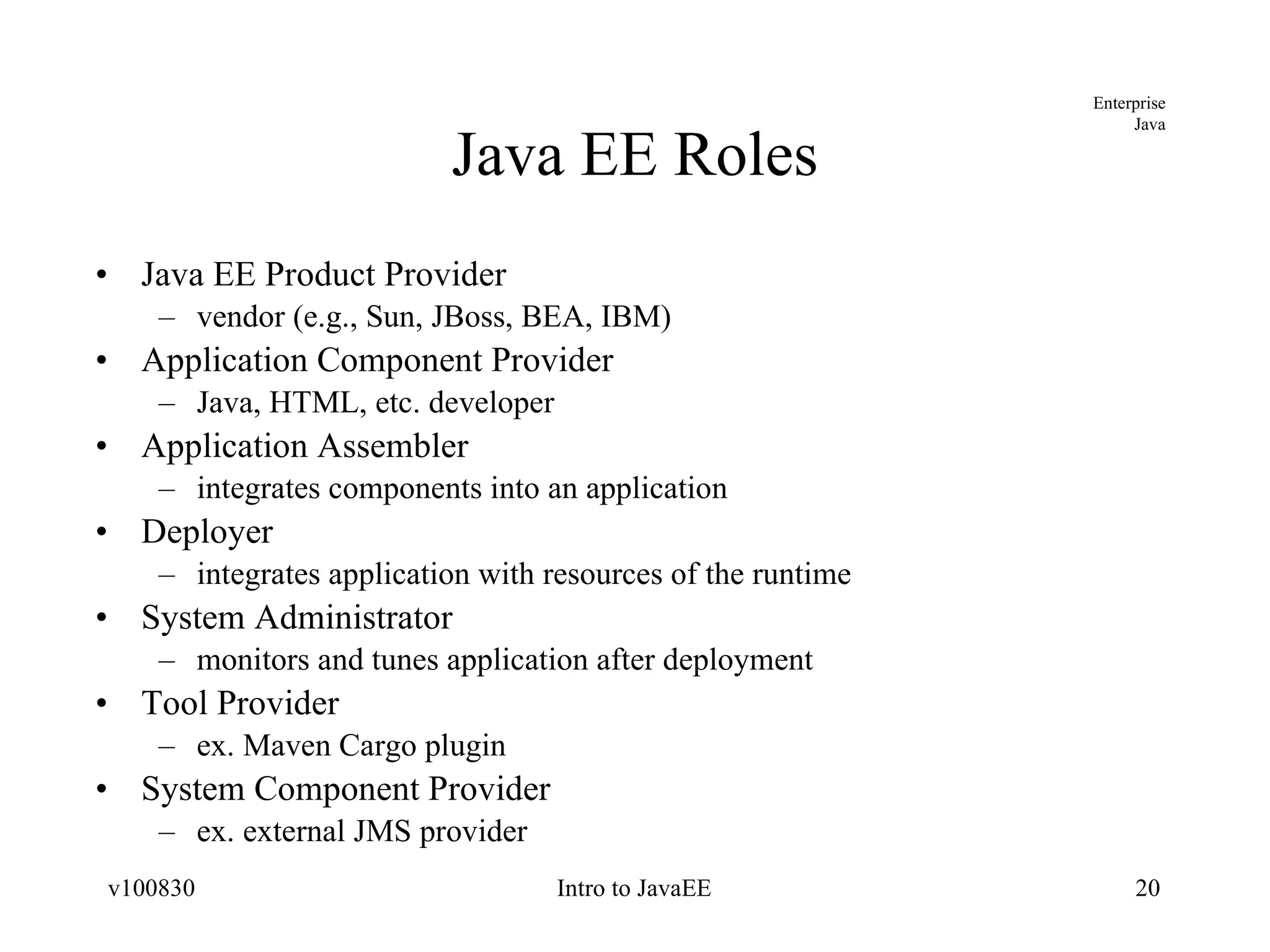
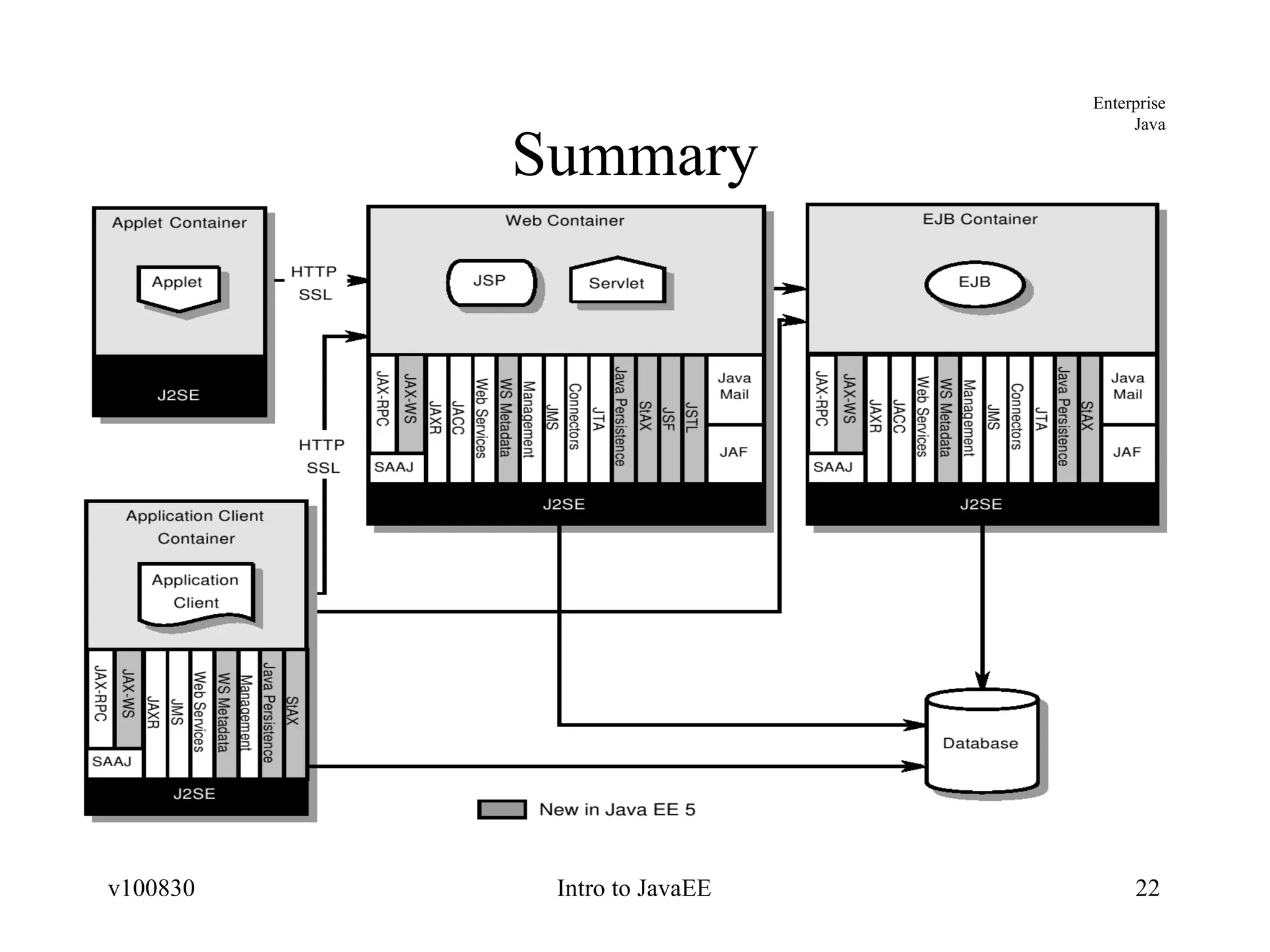
The document provides an overview of the Java EE platform, including its goals, architecture, components, services, and APIs. It describes the different levels of the Java technology stack including Java SE, Java ME, and Java EE. It explains the purpose of containers, application components, and resource adapters in the Java EE architecture. It also summarizes the standard services, such as communication, transaction, persistence, security, and management services that are provided in Java EE.