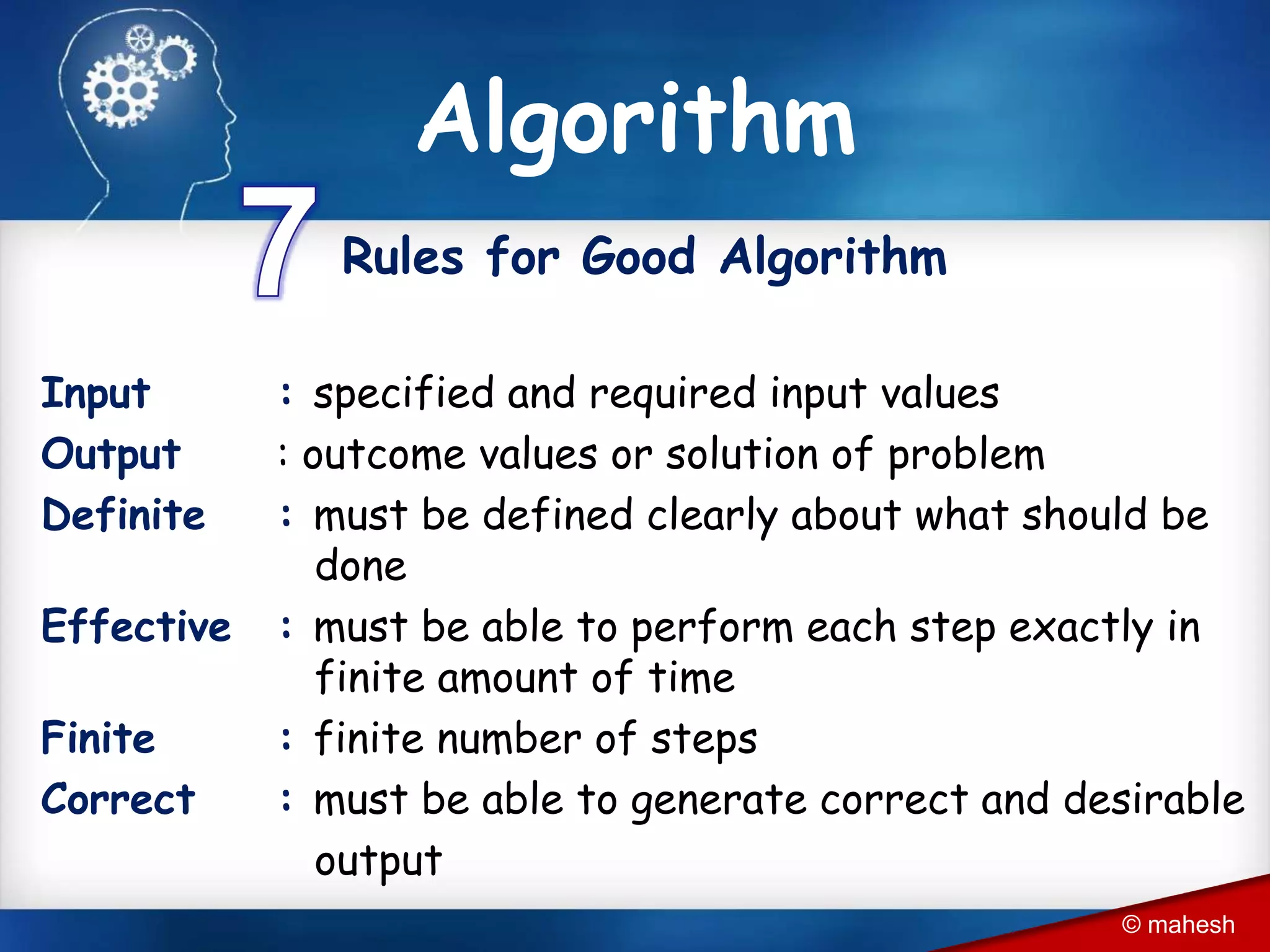
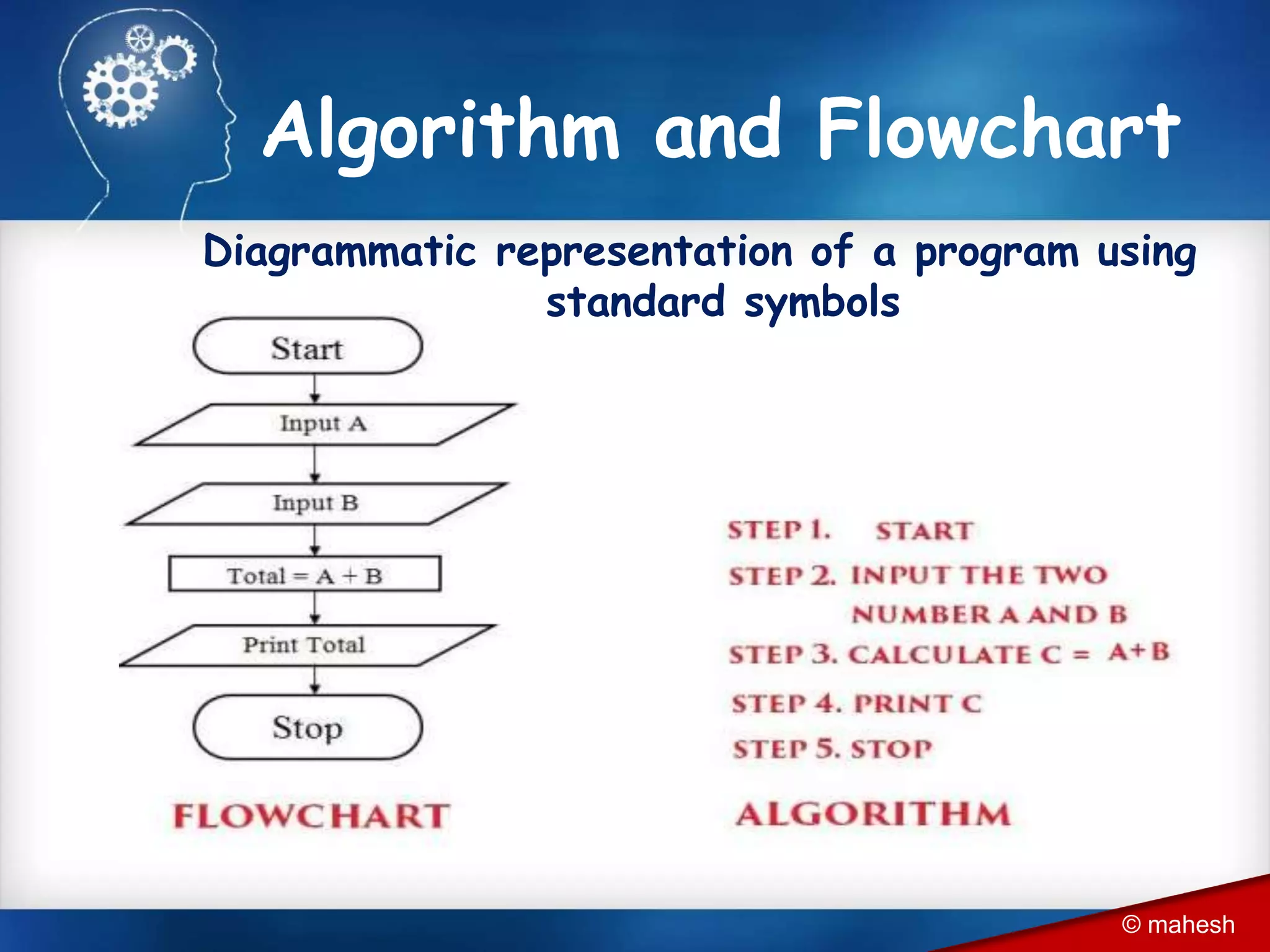
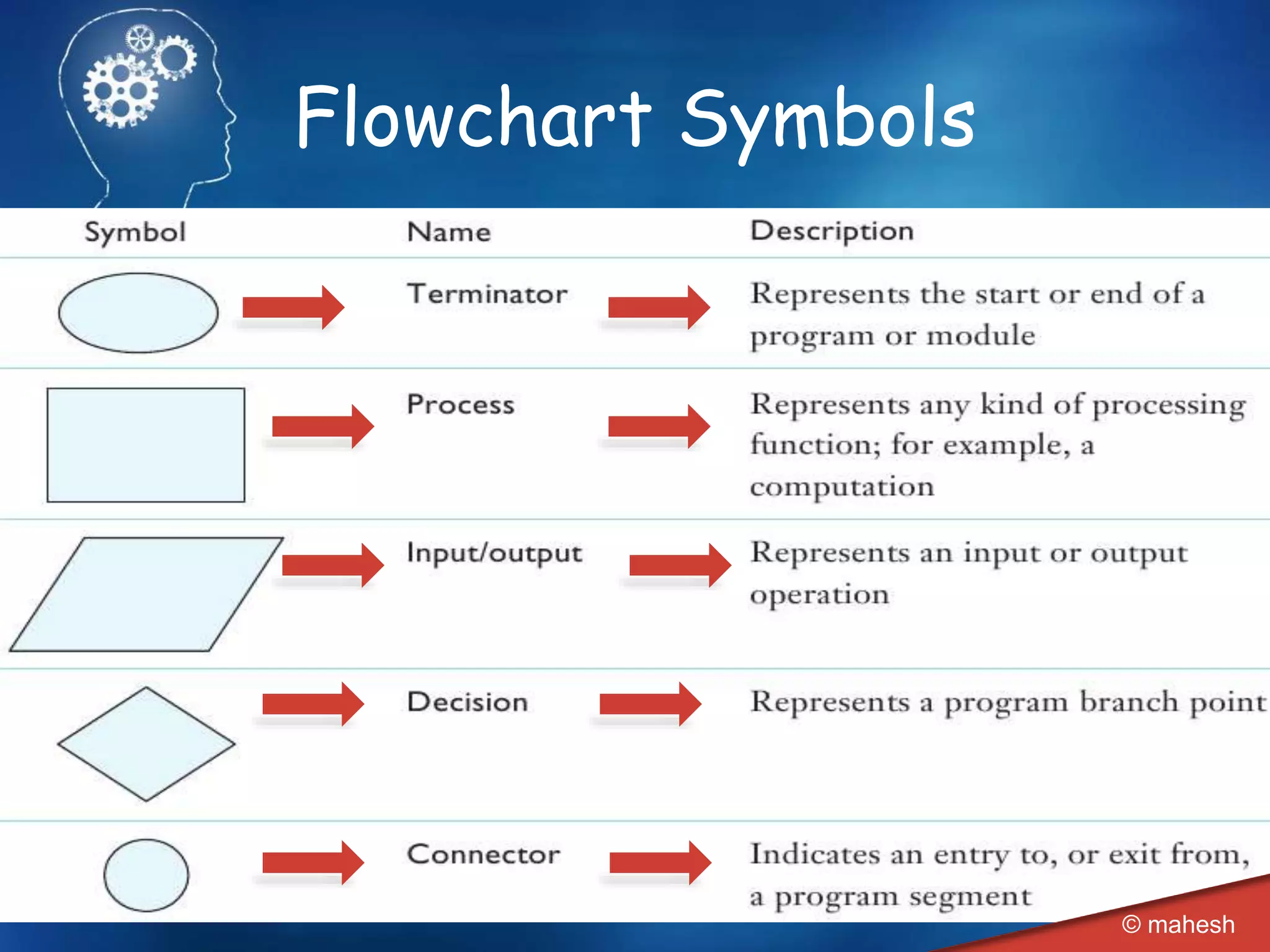
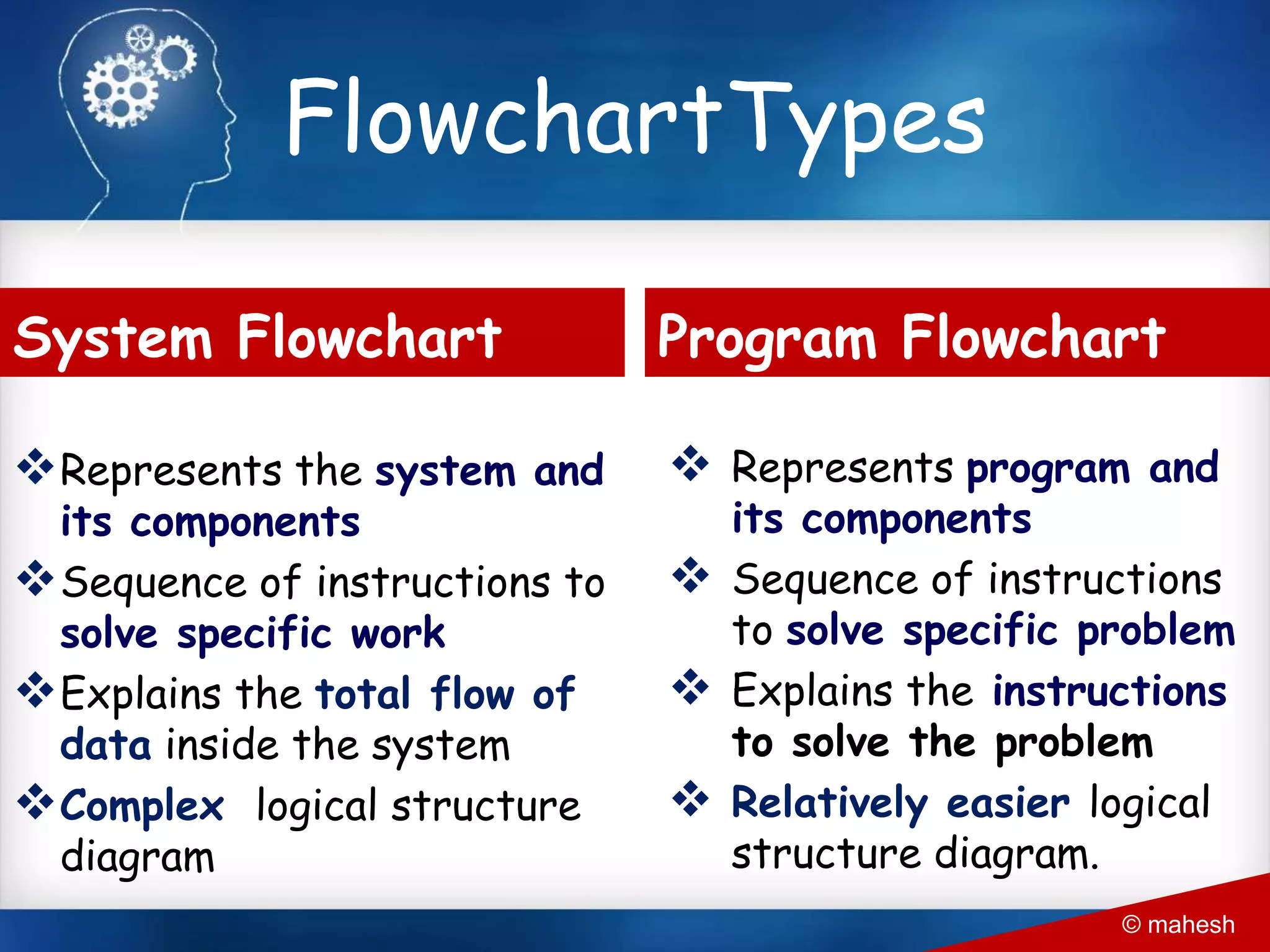
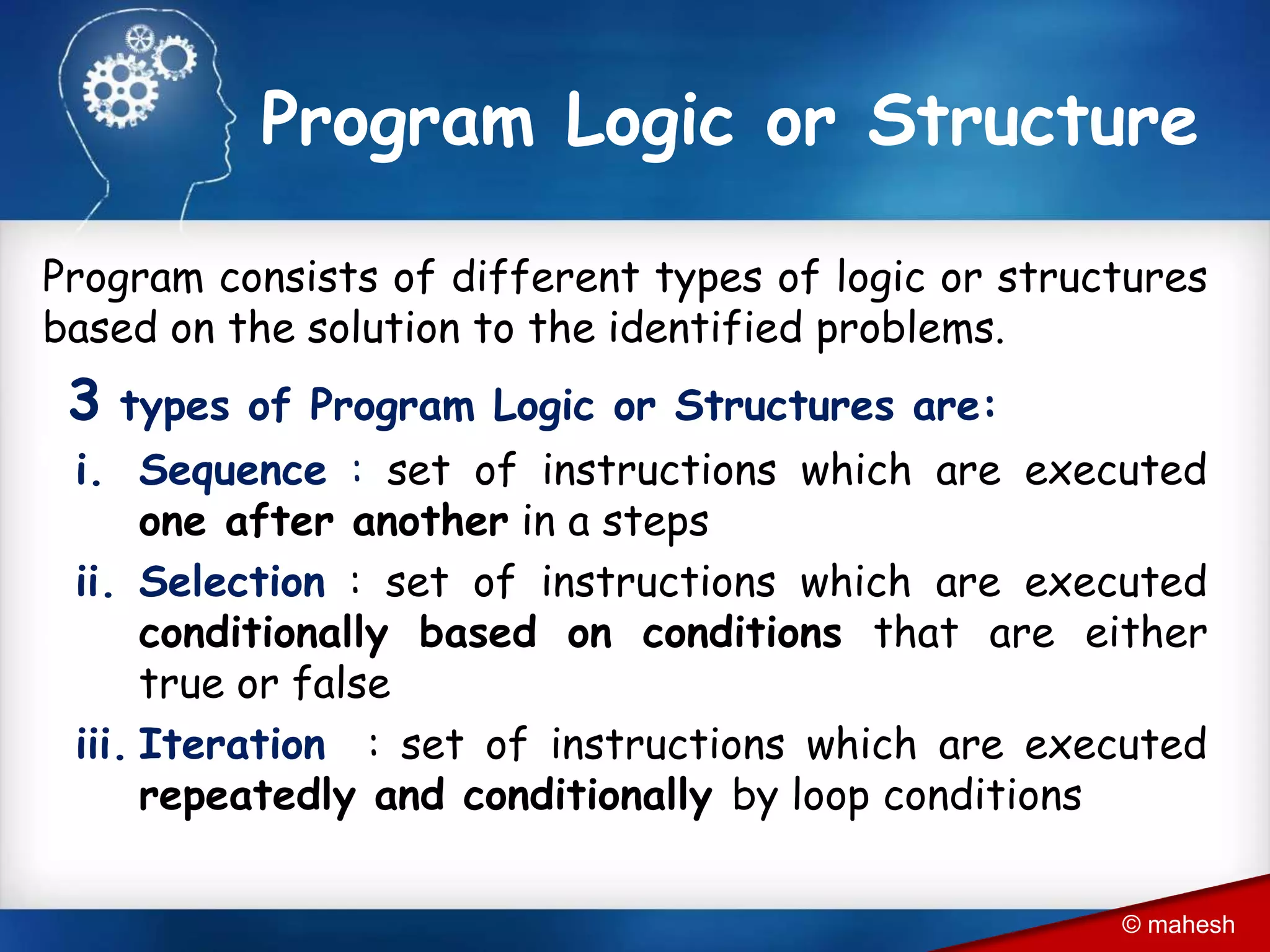
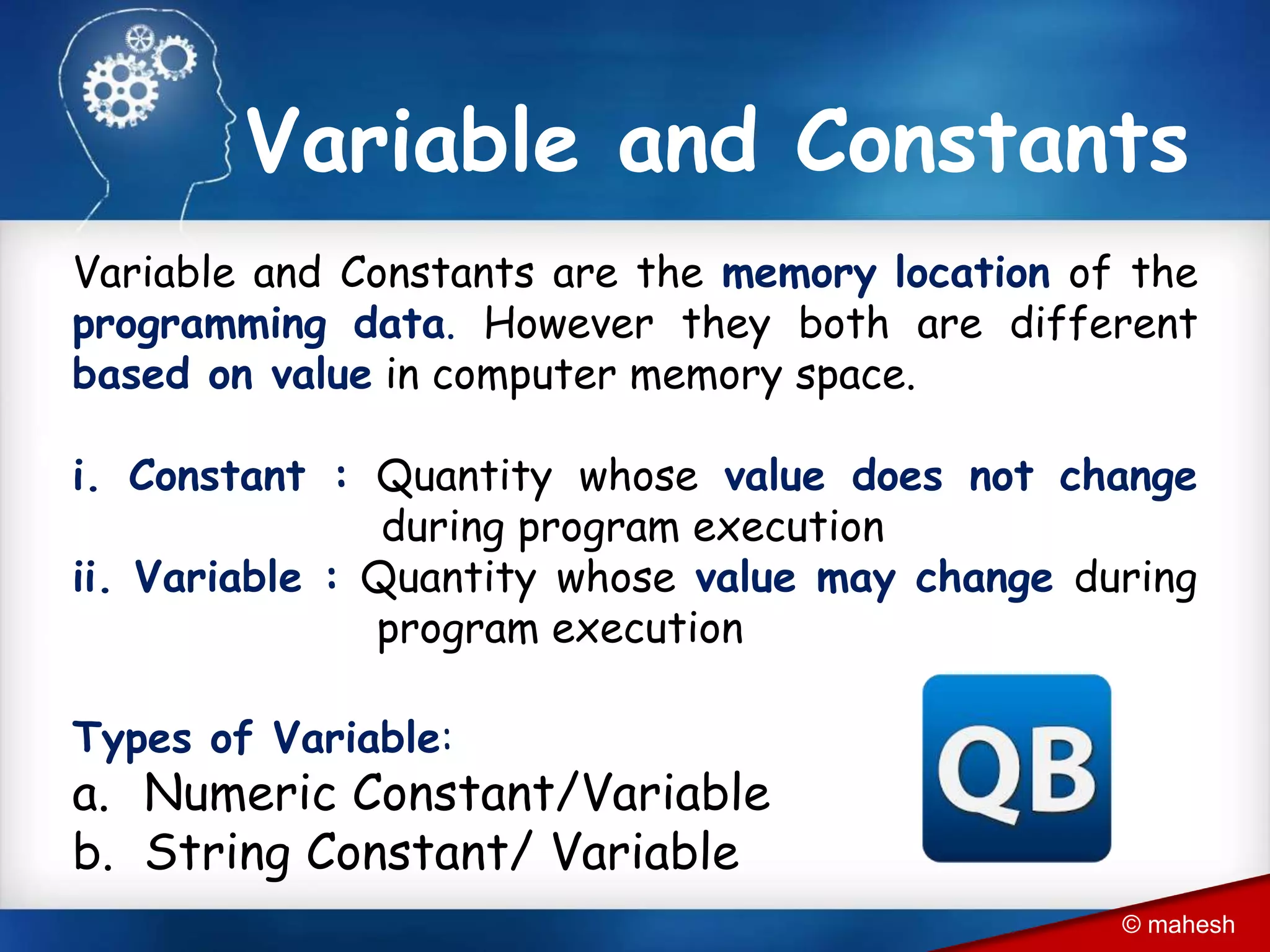
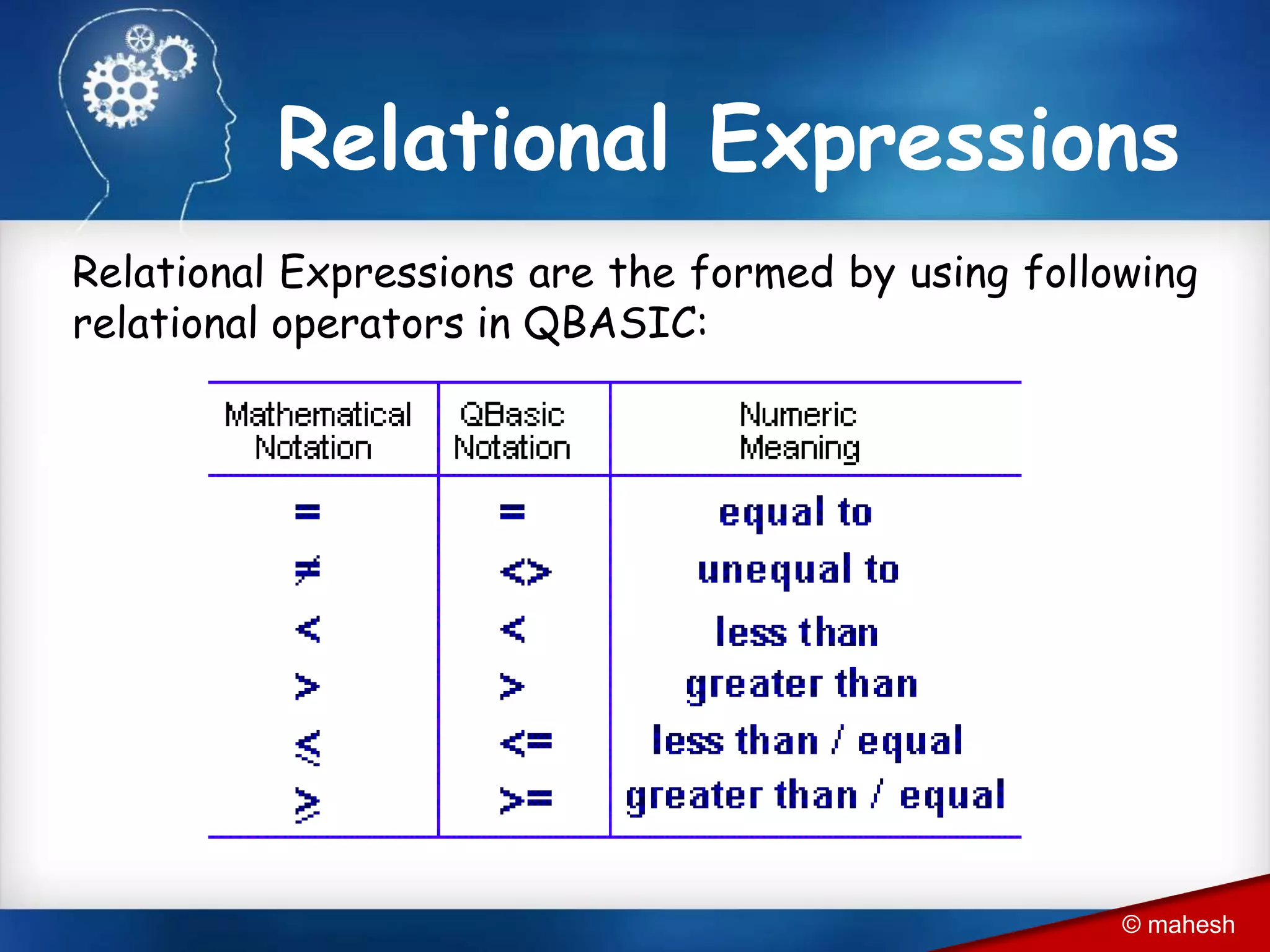
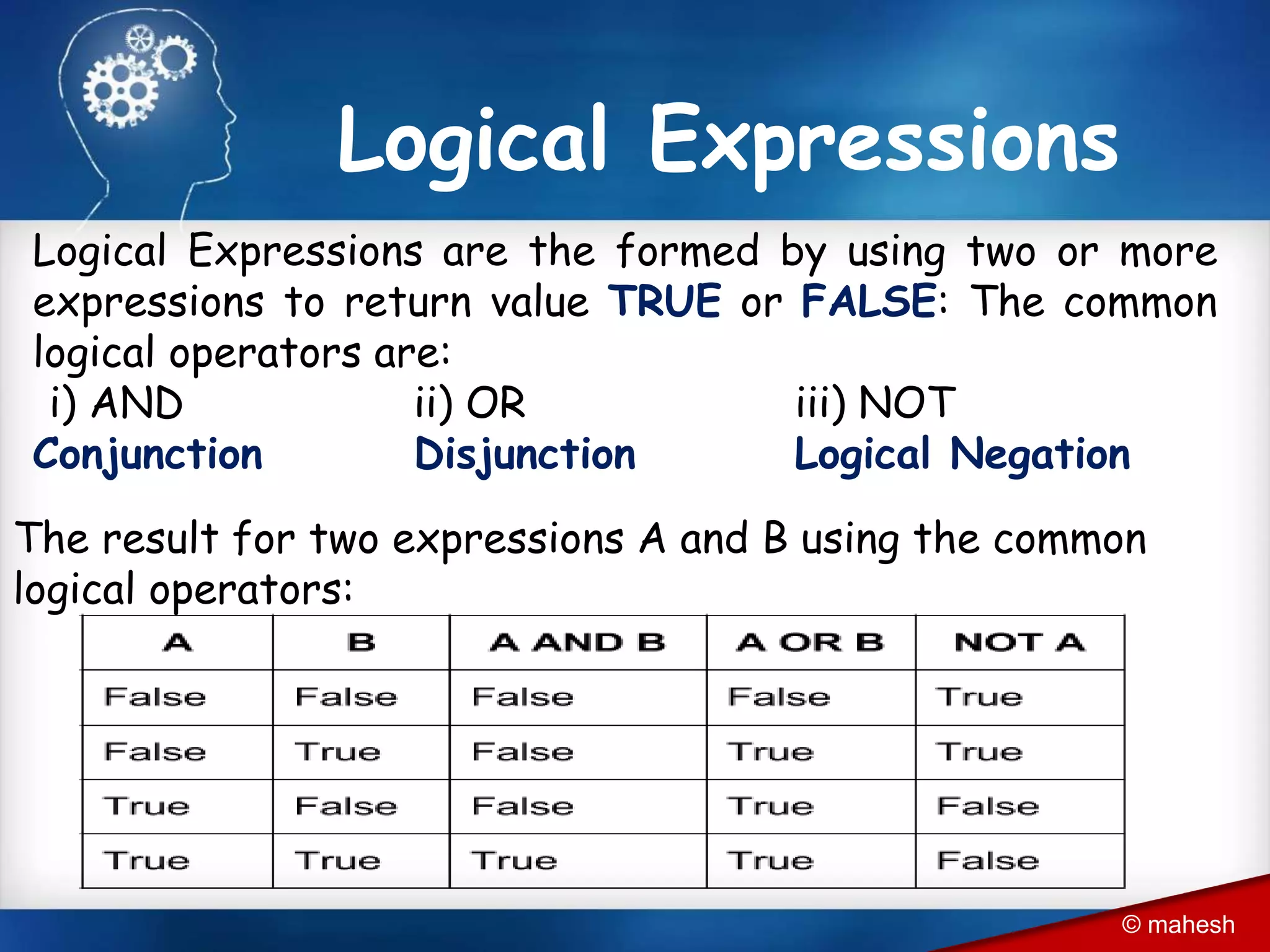
The document is an introduction to QBasic programming, covering fundamental concepts such as algorithms, flowcharts, data structures, and the syntax and functions specific to QBasic. It explains the building blocks of programming, including constants, variables, and expressions, while highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of flowcharts as a programming tool. Additionally, it outlines the structure of QBasic and its components, including character sets, keywords, and library functions.