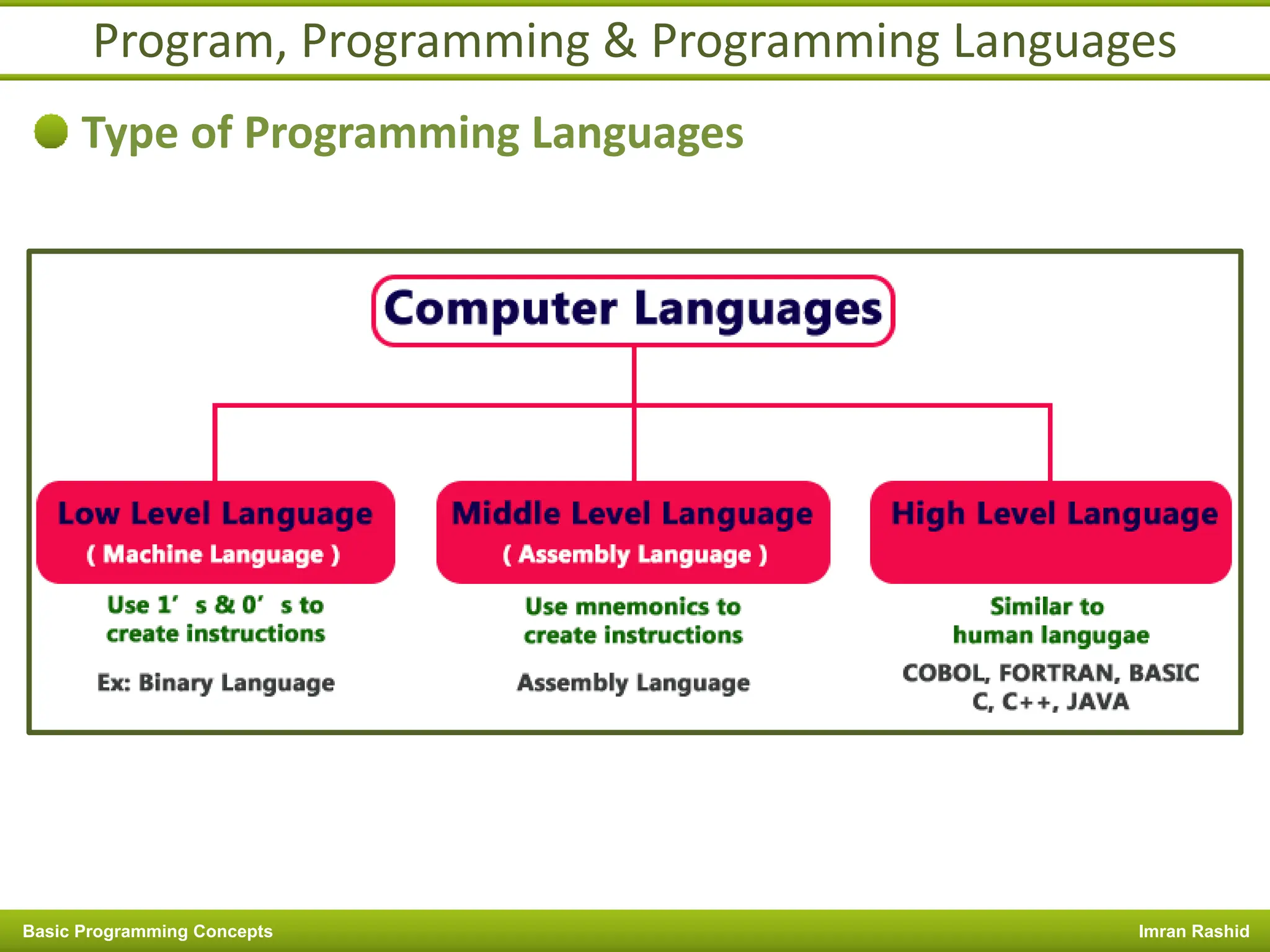
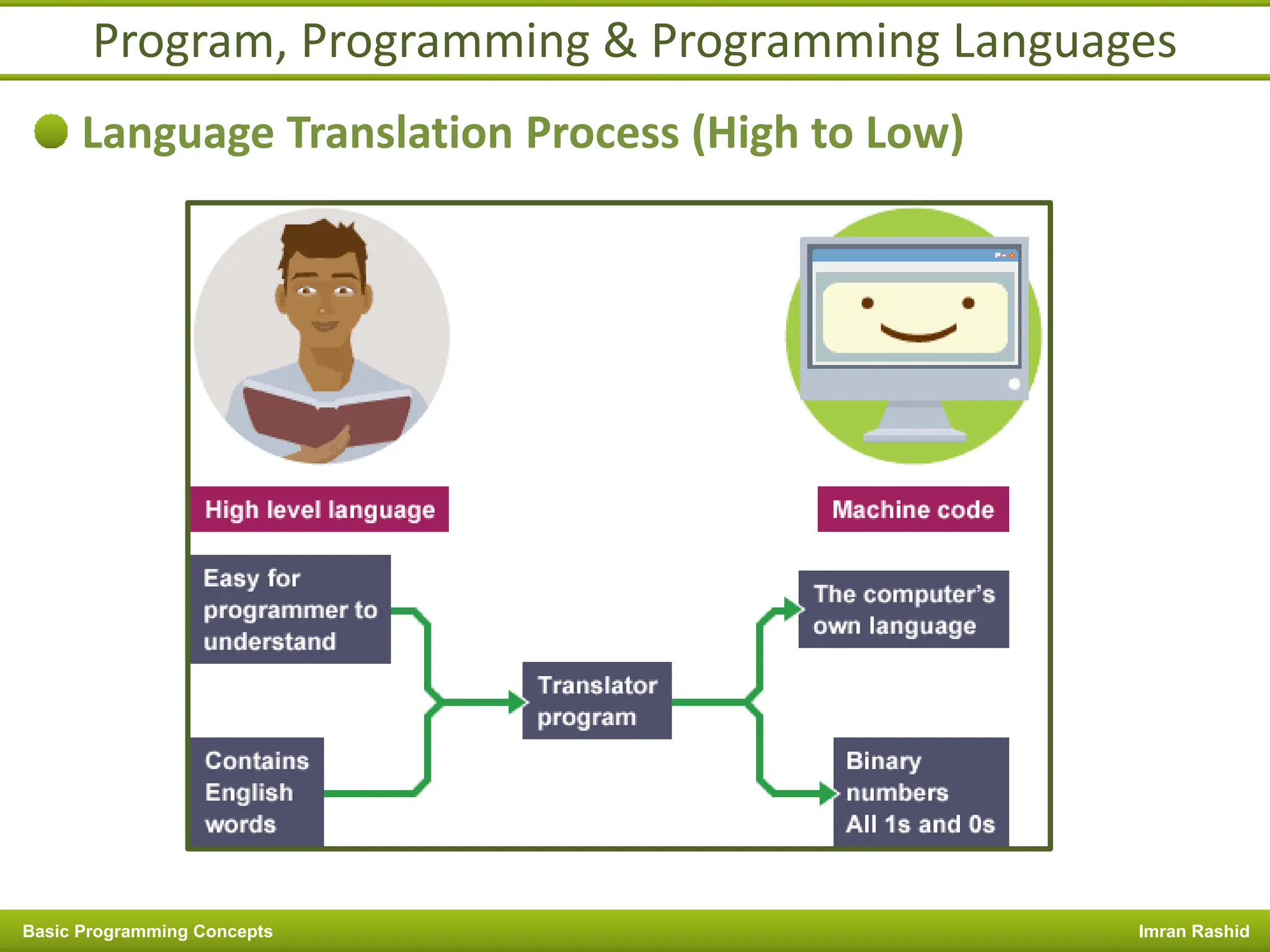
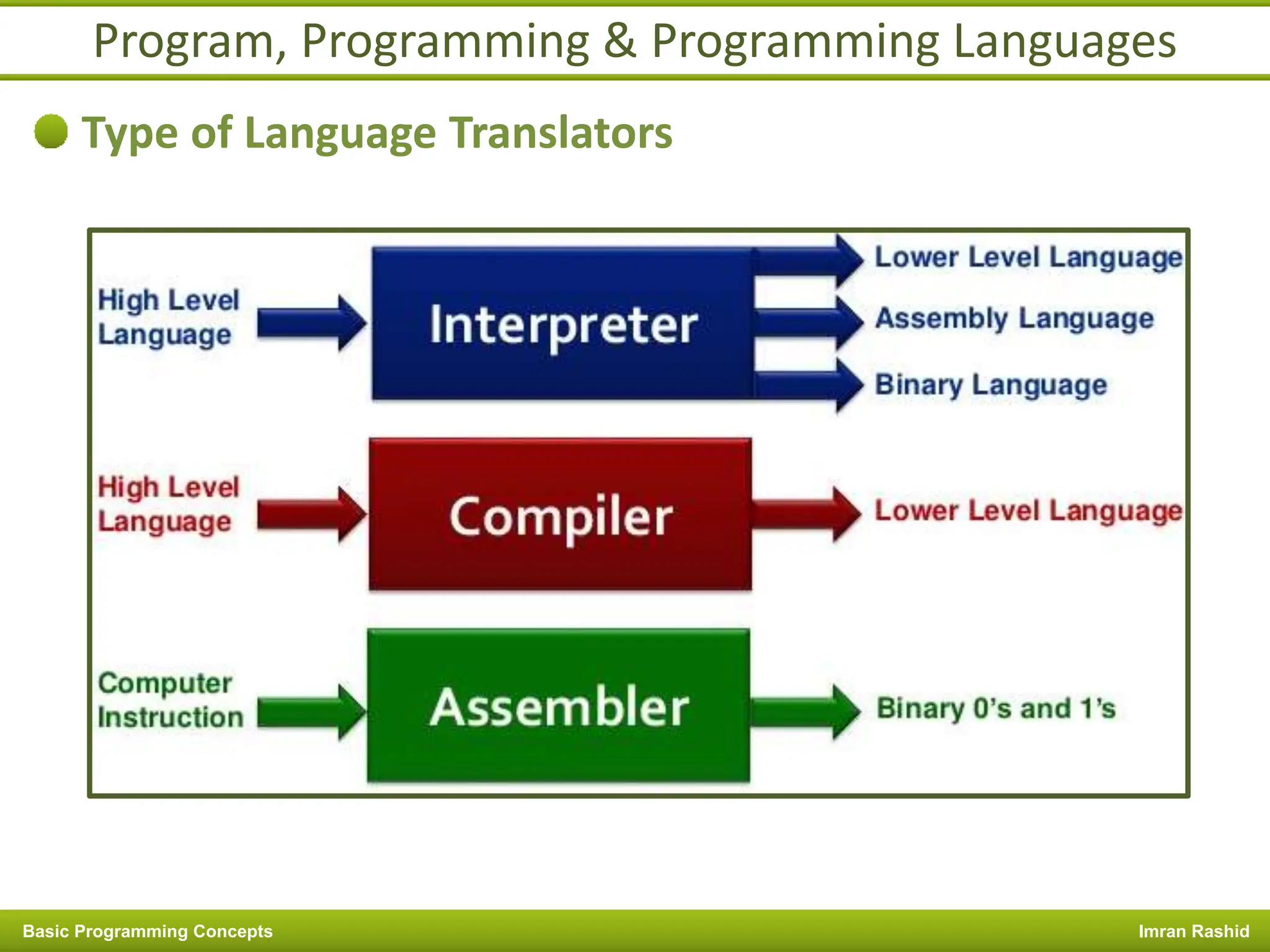
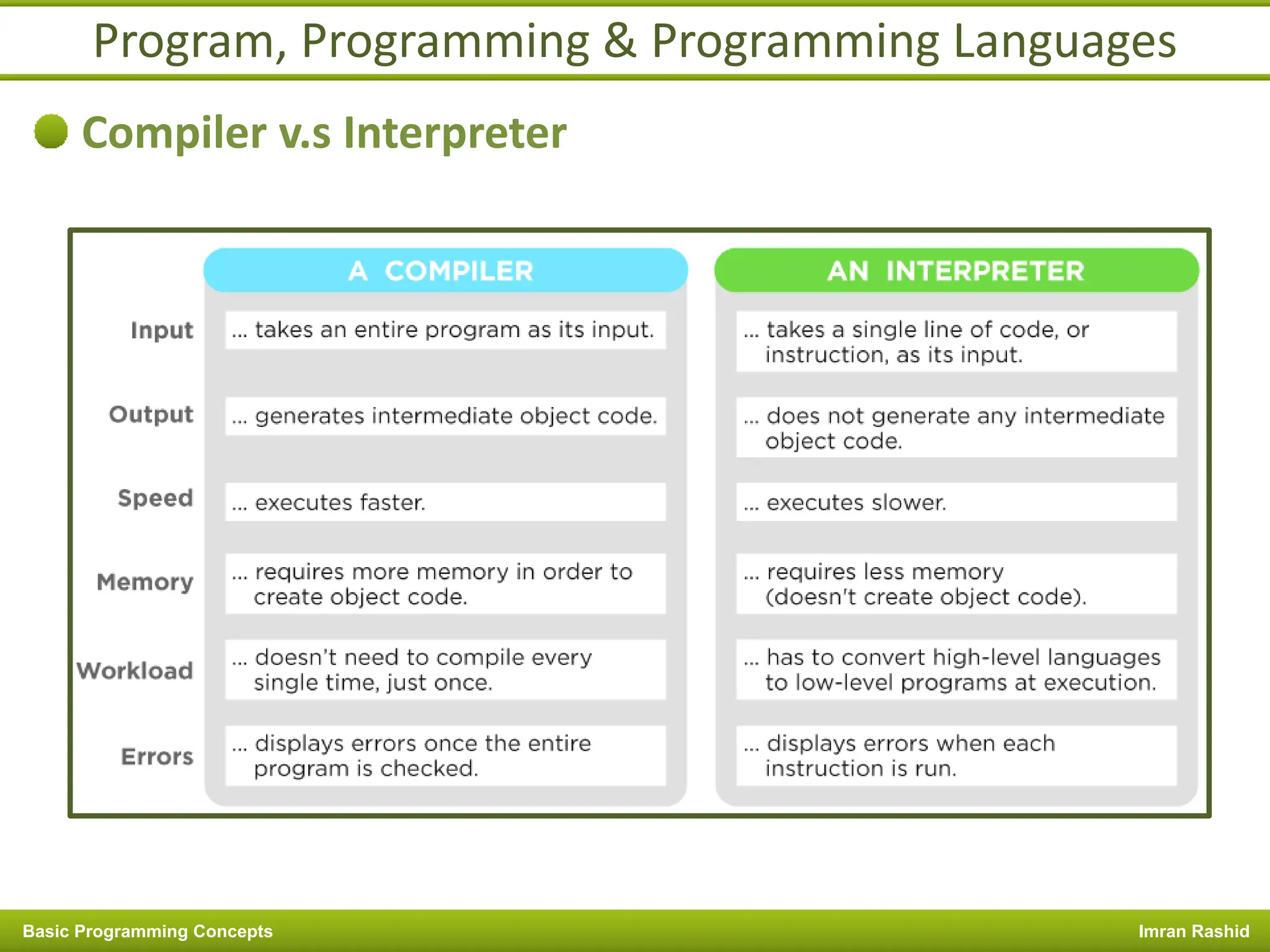
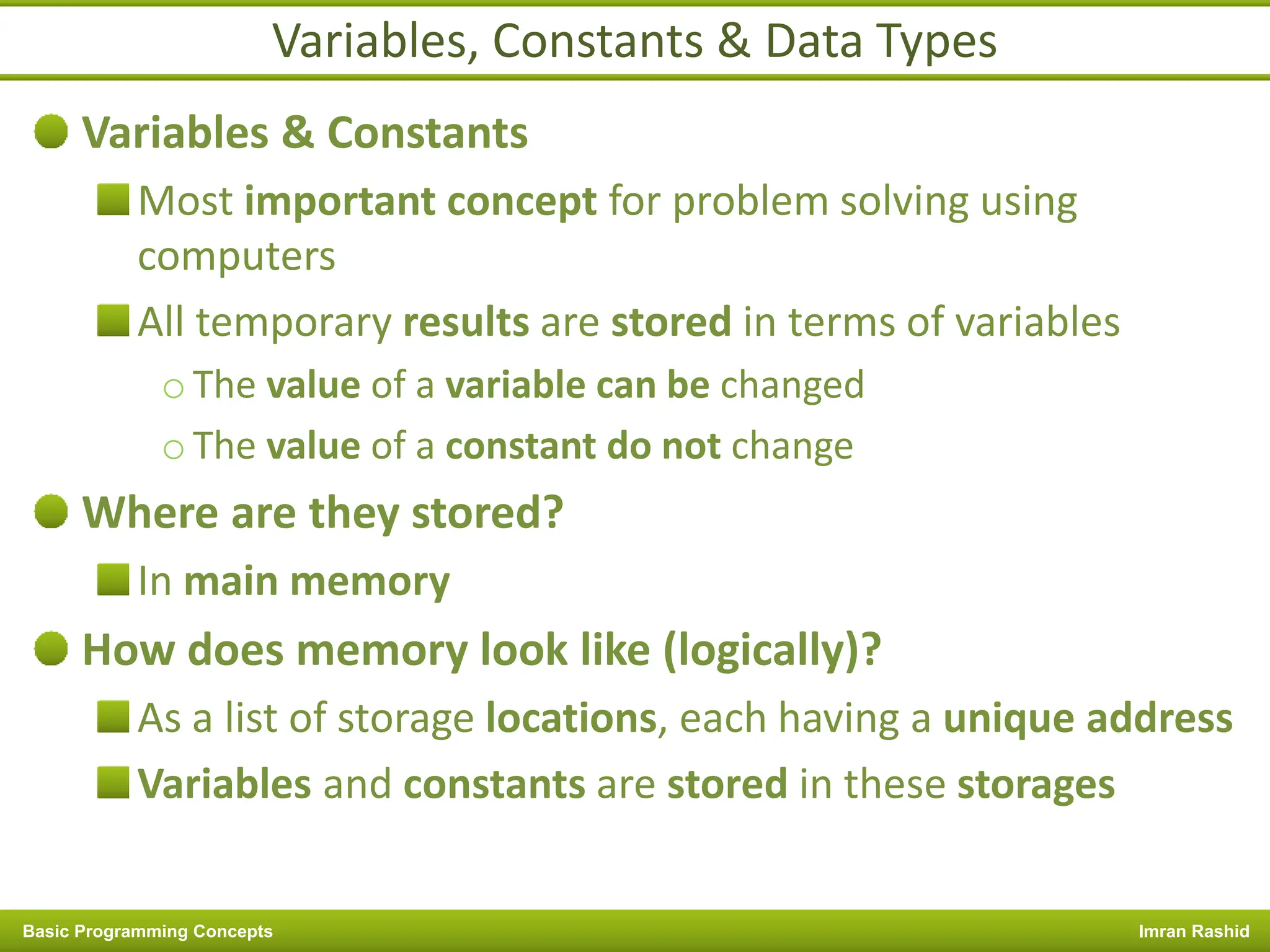
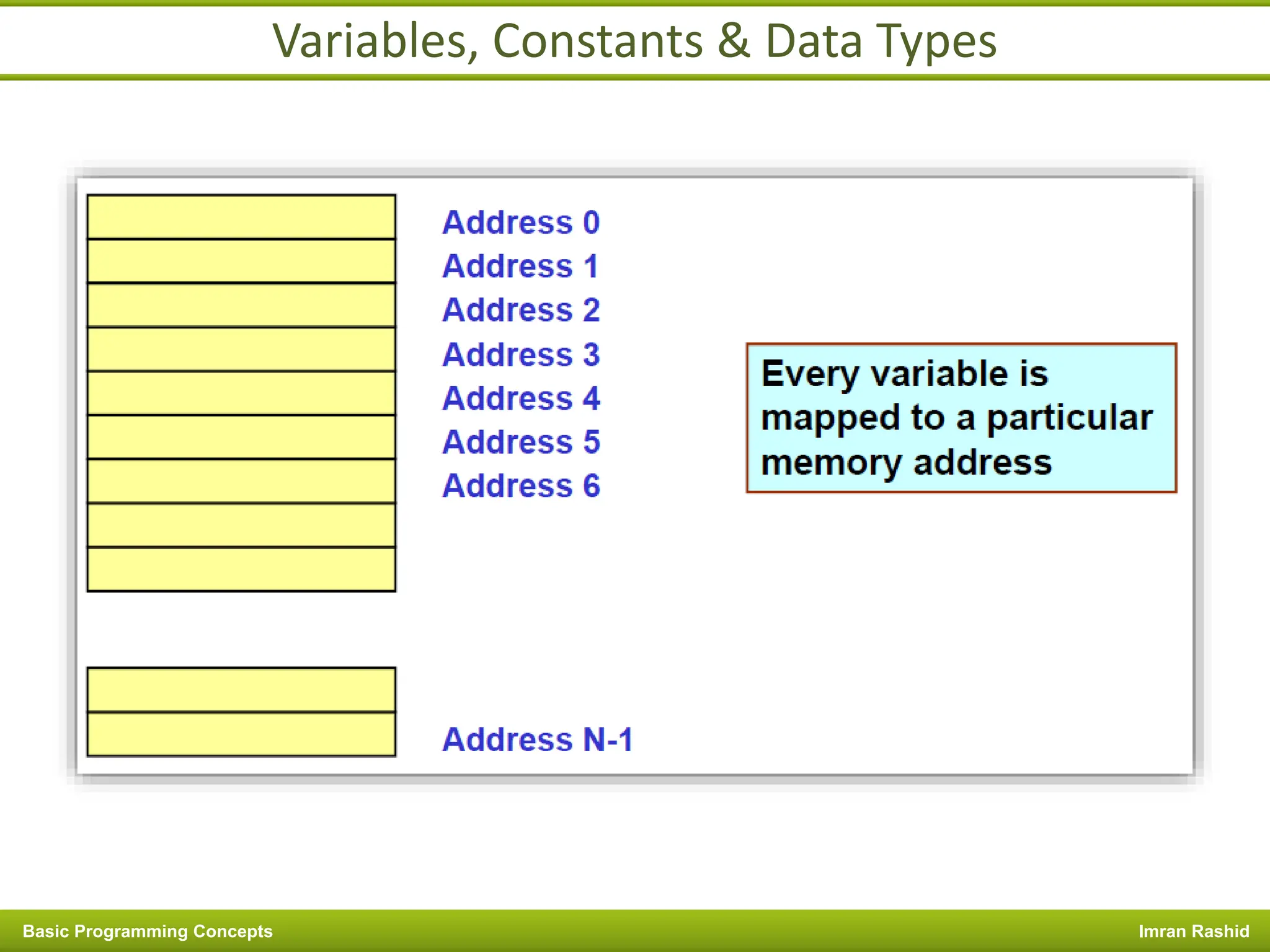
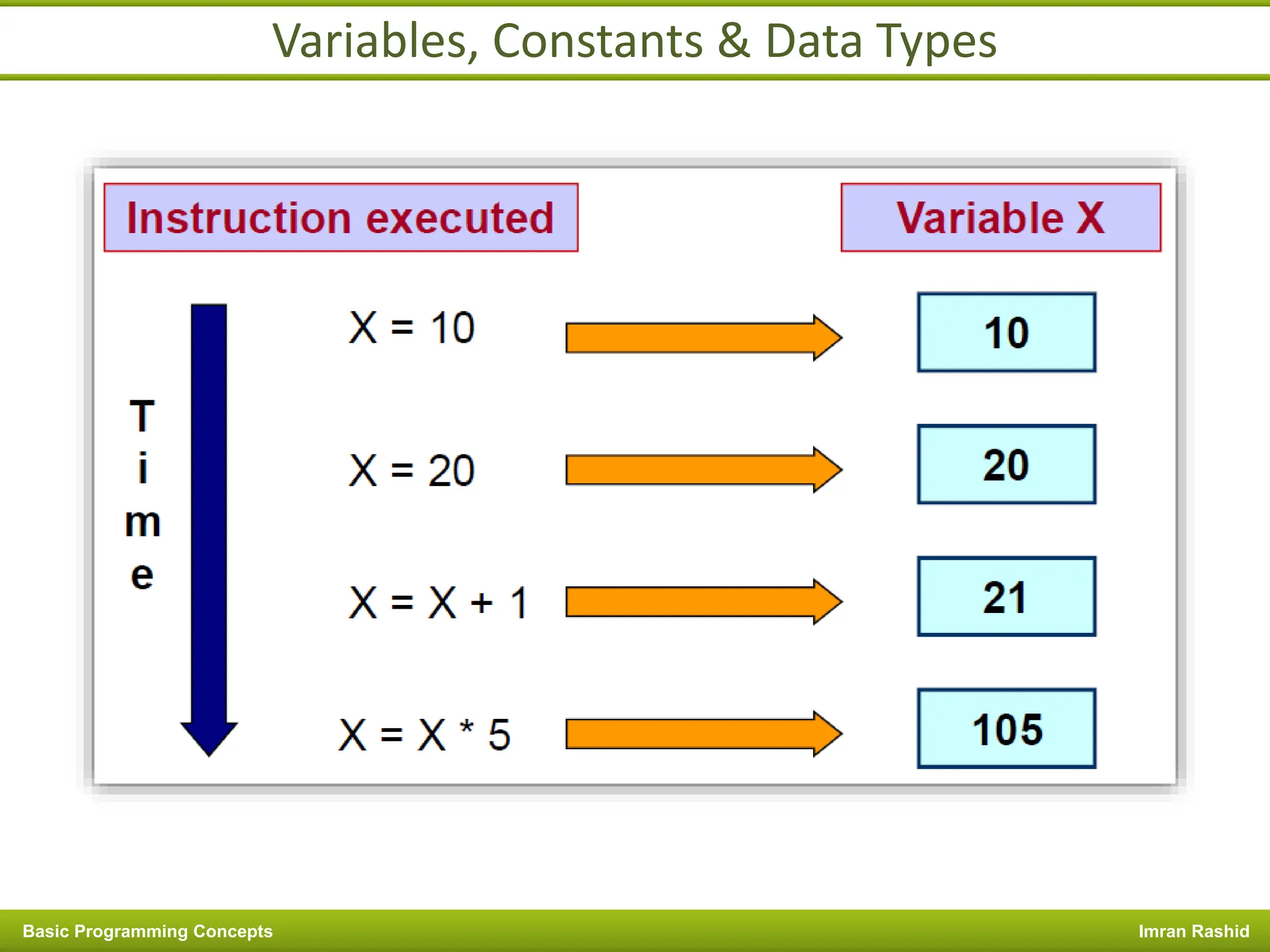
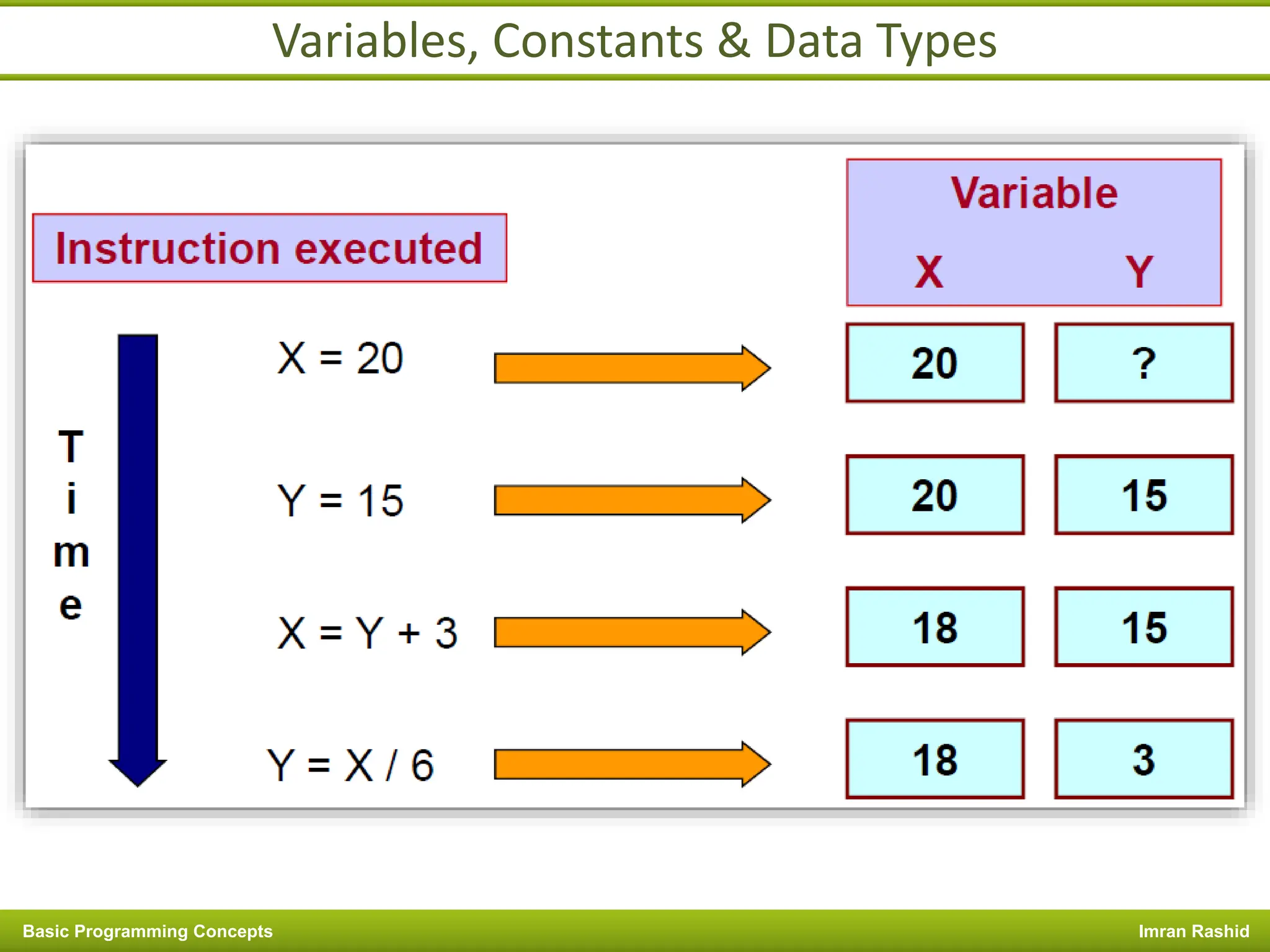
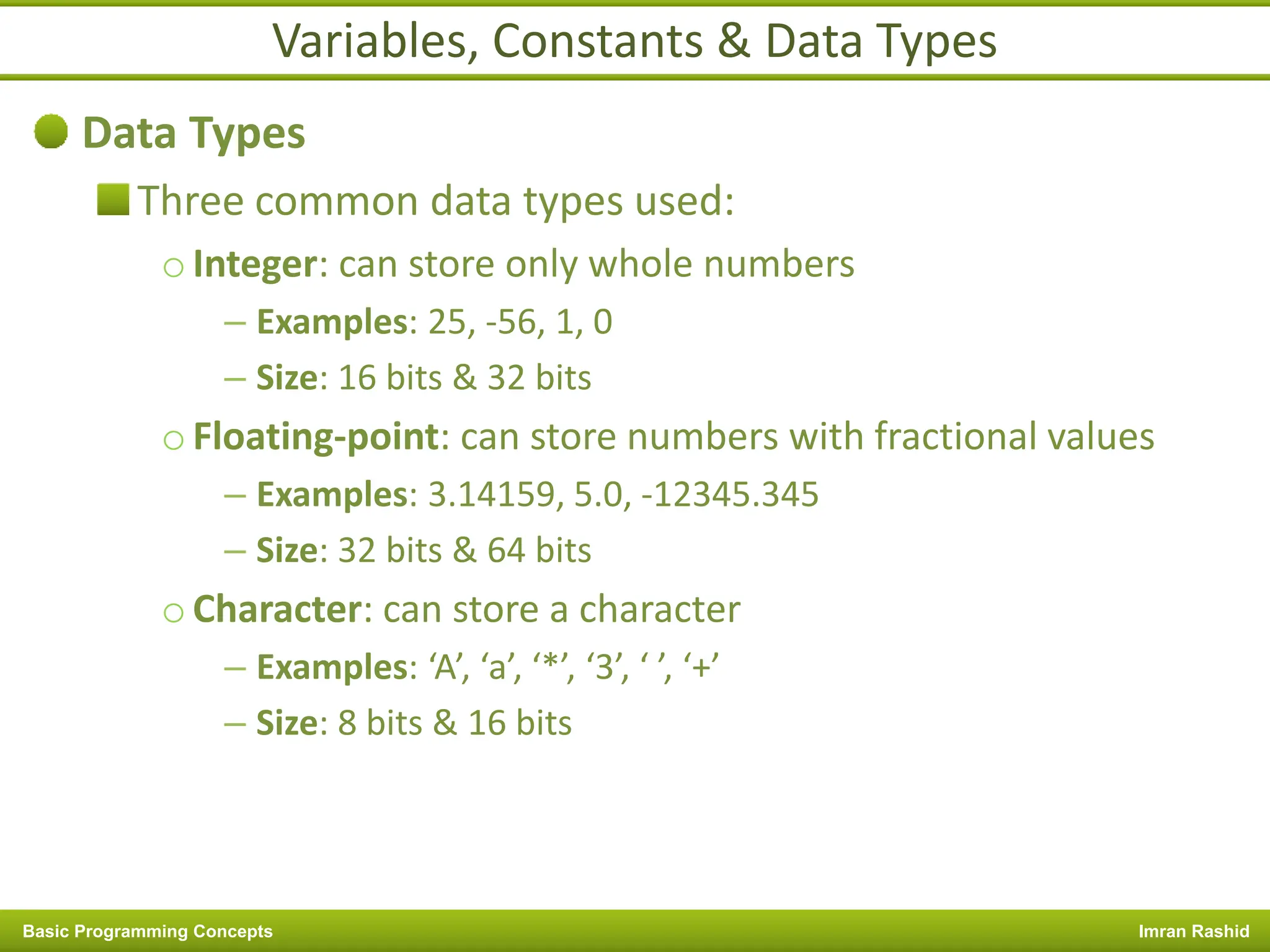
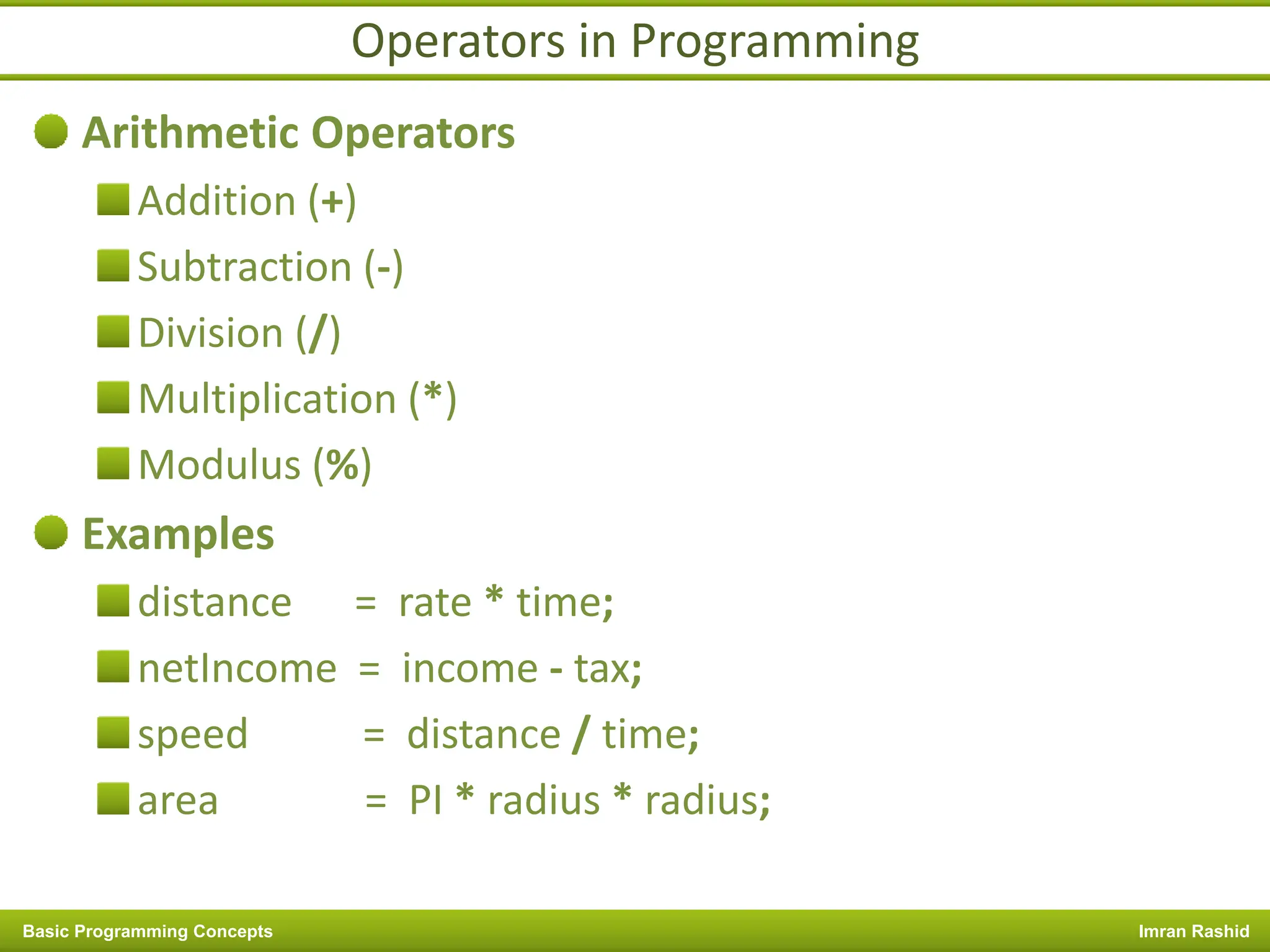
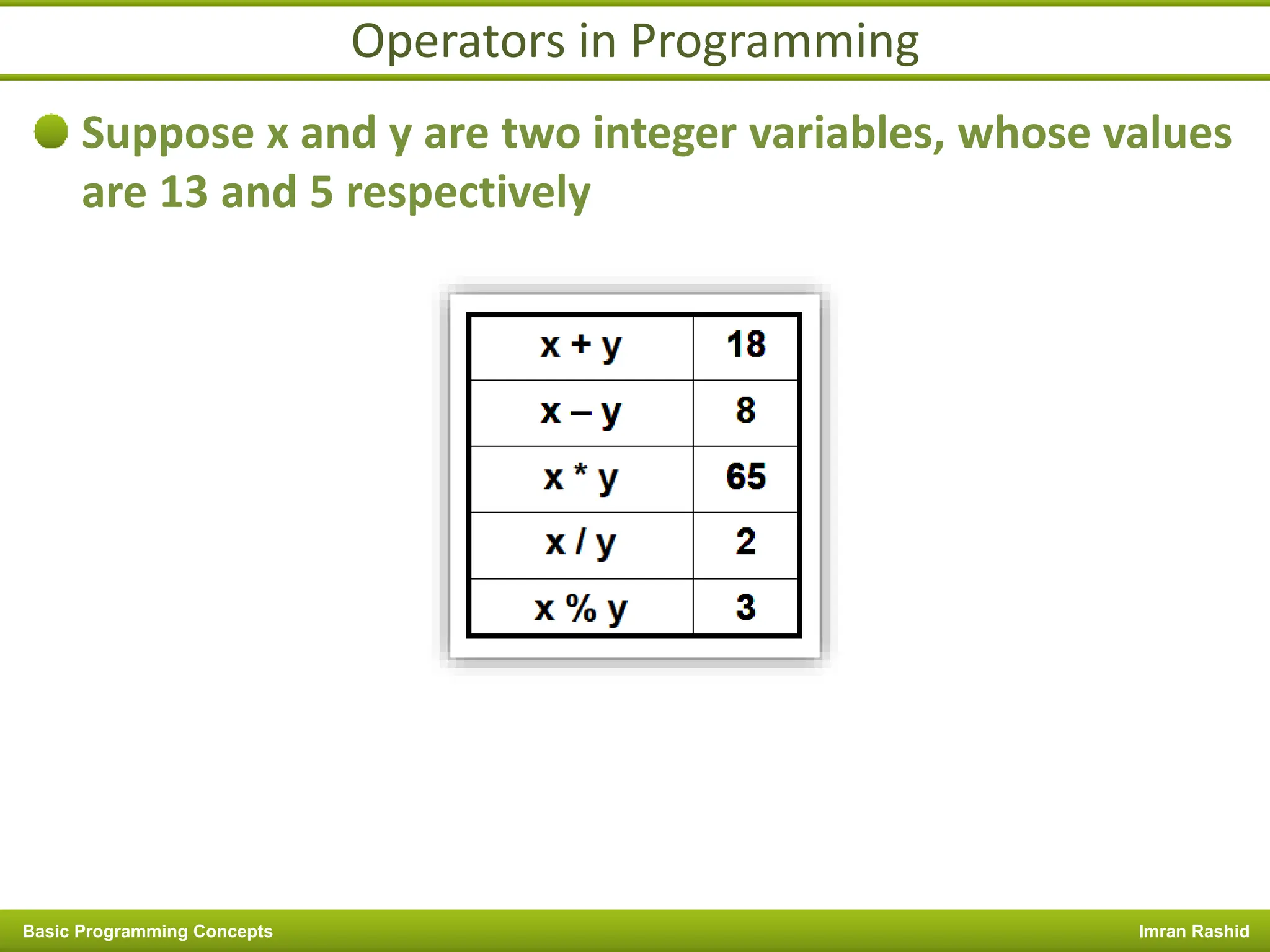
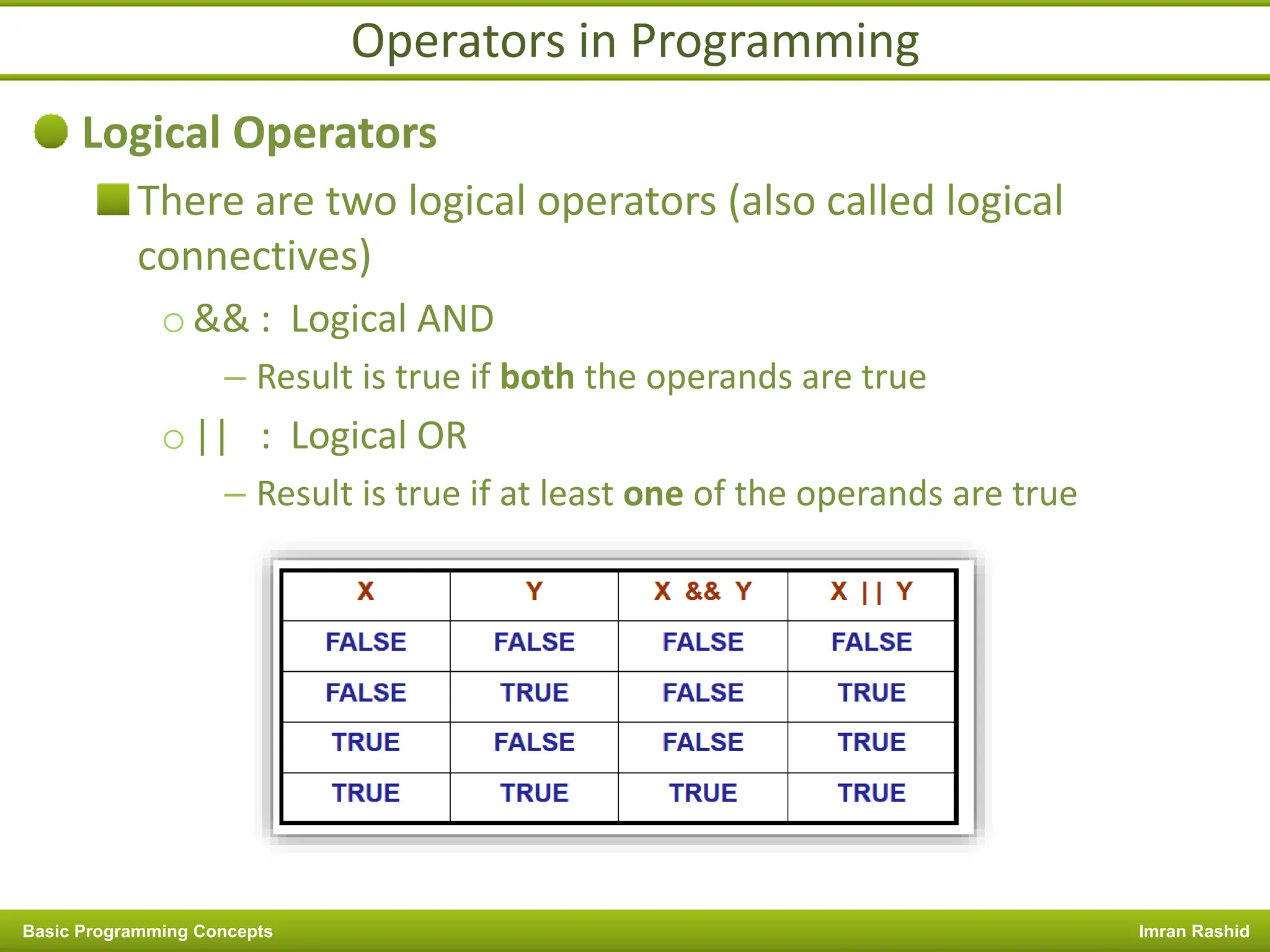
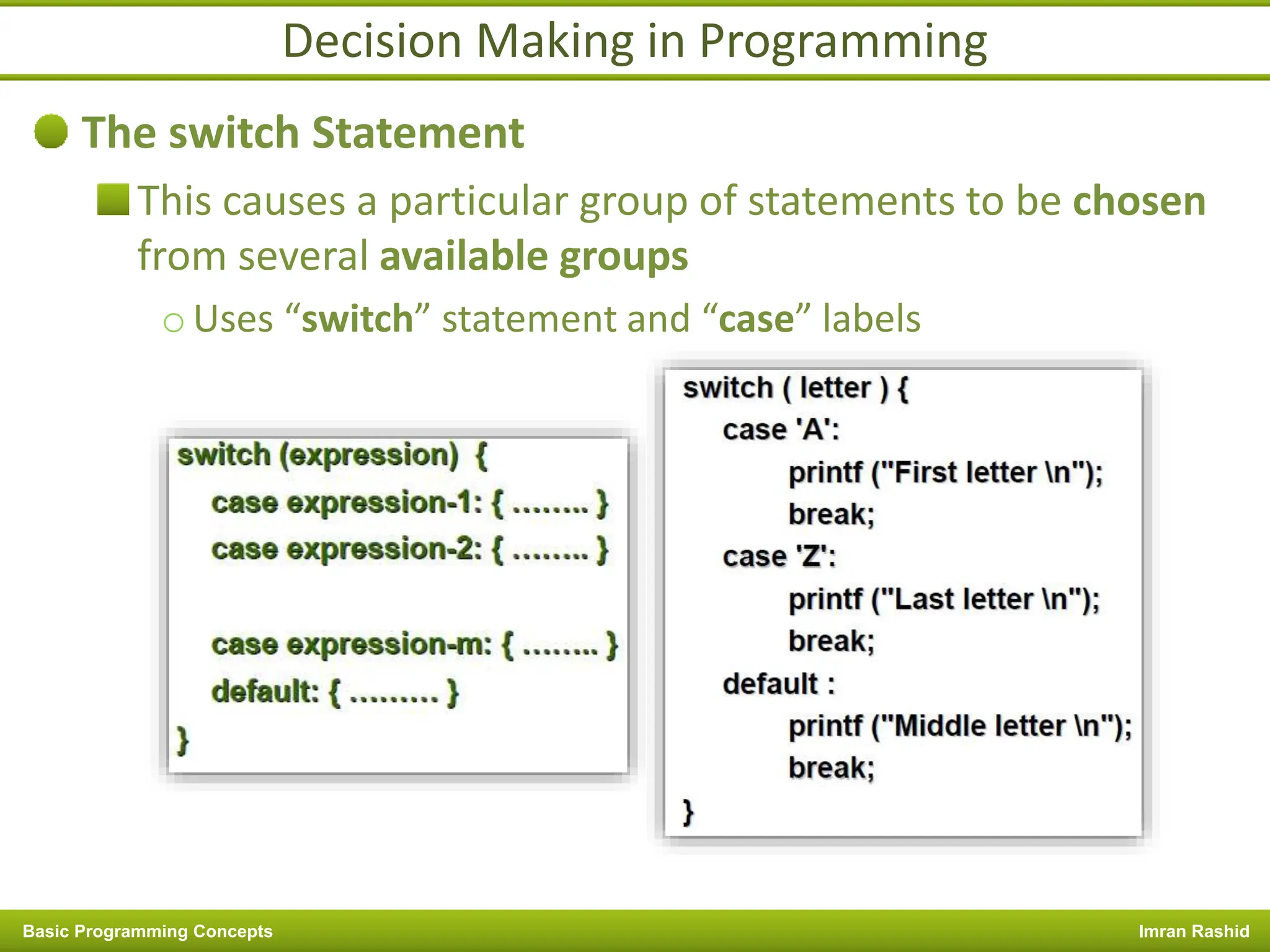
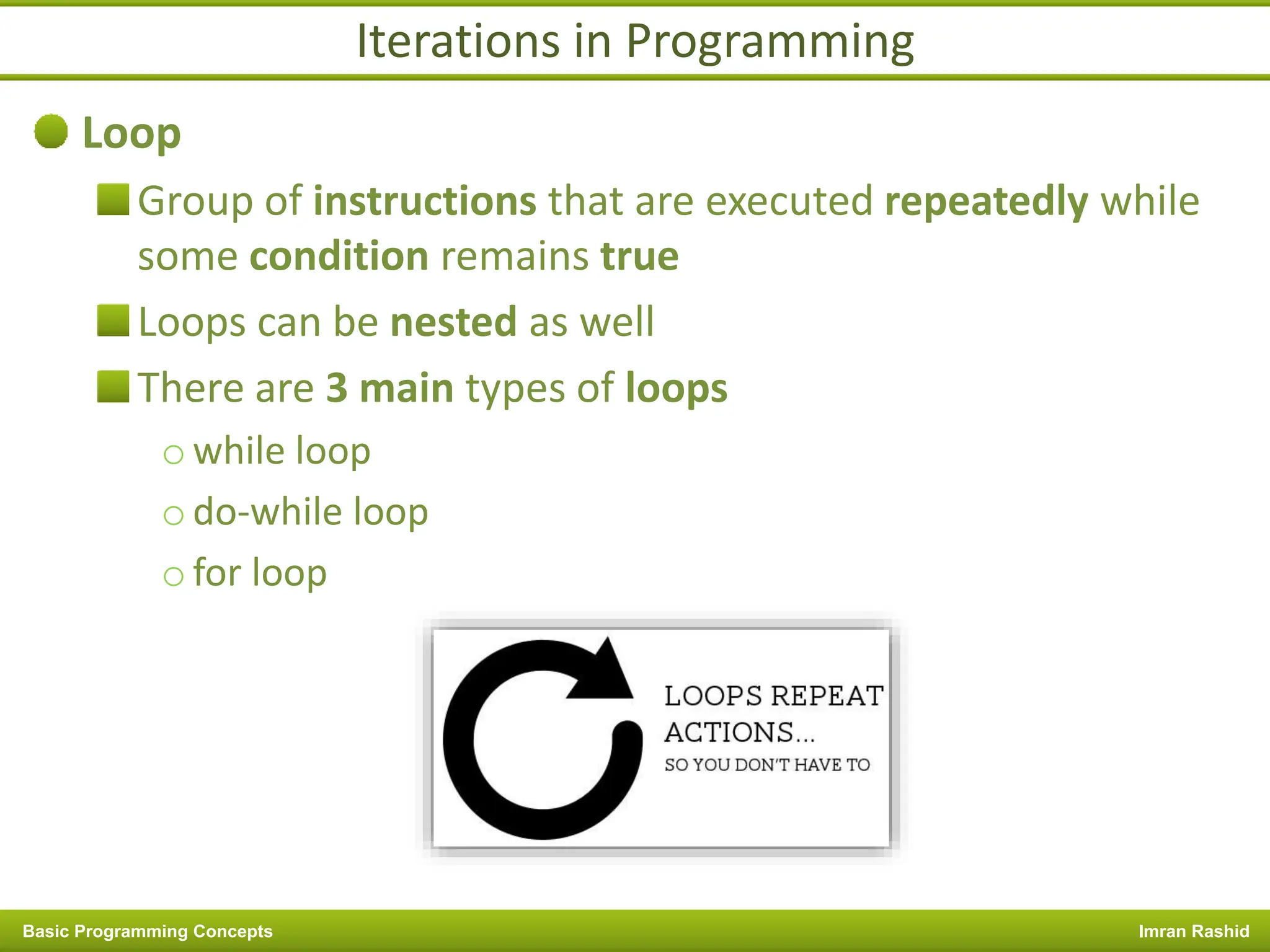
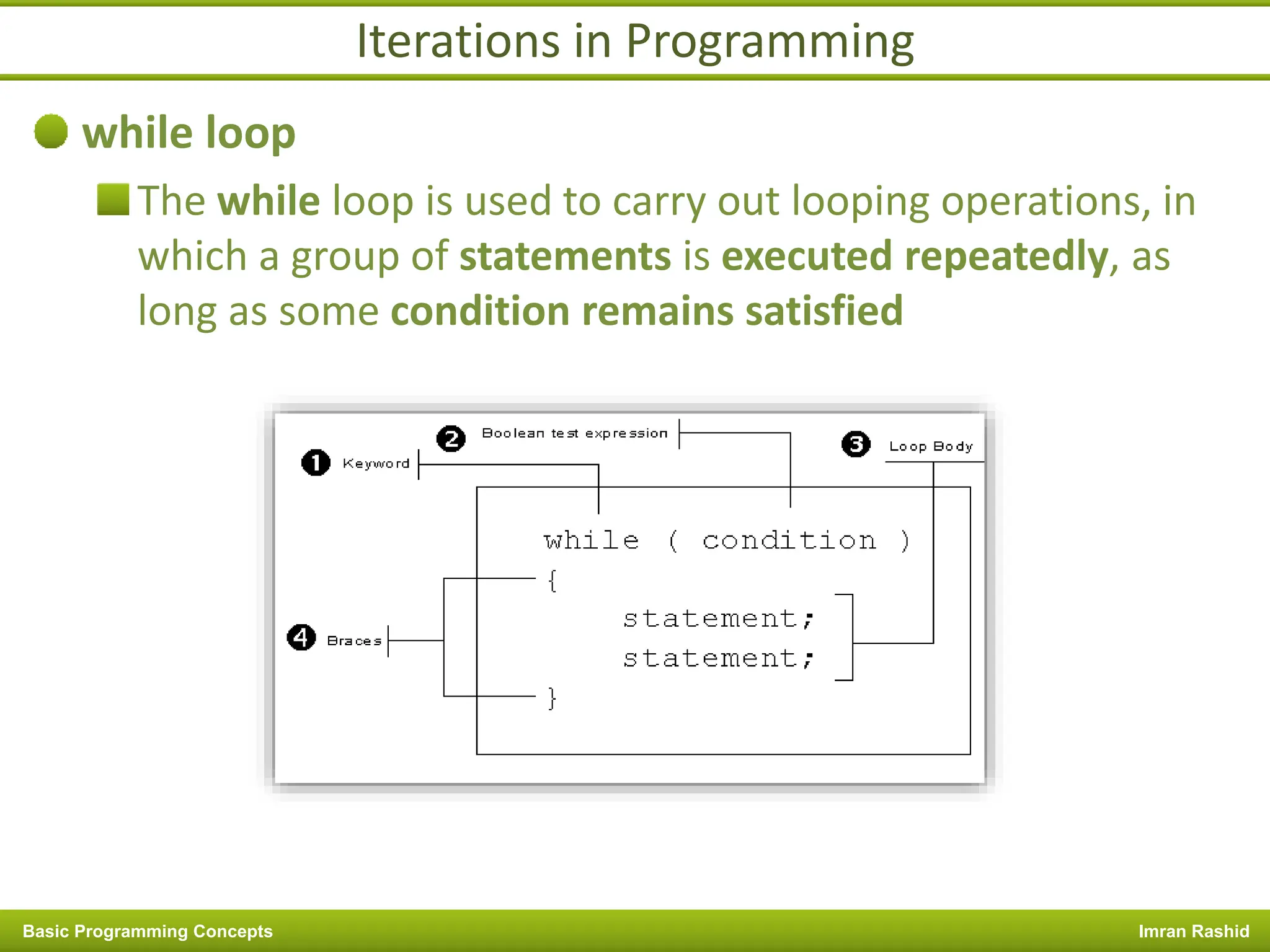
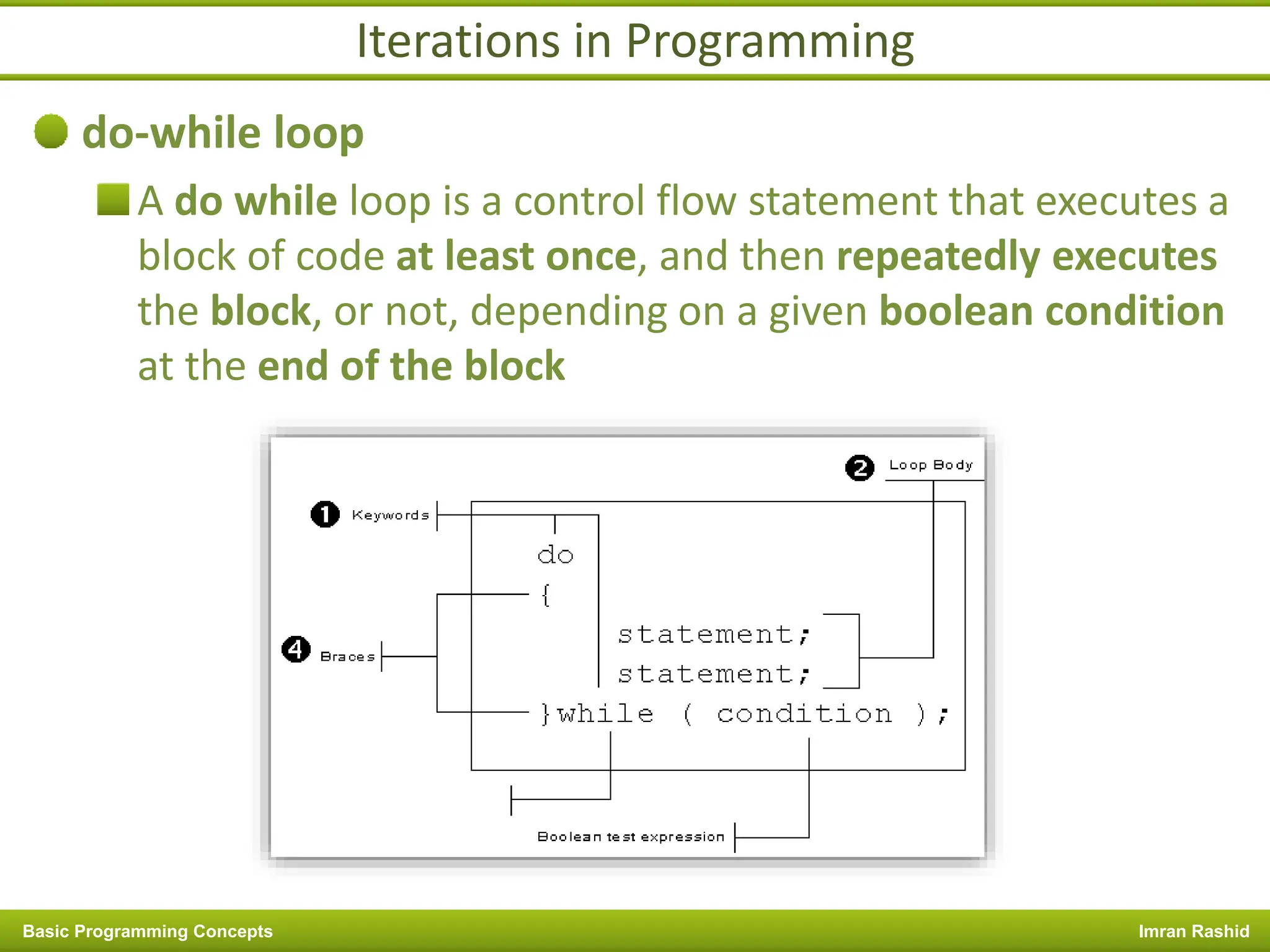
This document provides an overview of basic programming concepts including programs, programming languages, variables, data types, operators, and control structures. It discusses: - What a program and programming are and how programming languages are used to communicate with machines. Common language types include high-level languages, low-level languages, and translators. - The basics of variables, constants, and data types. Variables and constants store values in memory locations and have types like integer, floating-point, and character. - Common operators for arithmetic, comparison, and logic and how they are used. Operator precedence is also covered. - Control structures for decision making and iteration. Structures like if, if-else,











![Basic Programming Concepts Imran Rashid LAB Total Marks: [2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 10] Q: In GIMS there are 500 students, 12 class rooms, 2 labs, 4 departments, 20 admin staff, 32 teachers, 6 degree programs (e.g. BSCS/BSIT), & 3 busses. 1. Store this information in proper data types, variable/constant names & values (use proper naming conventions)? 2. Every teacher starts his/her lecture at certain time & it has an end time (which programming construct is applied in this scenario & how)? 3. A teacher can arrange extra/makeup classes only of the room & class is free (which programming construct is applied in this scenario & how)? 4. Bus 1, 2 & 3 has fixed root (e.g. bus 1 move students from Kharian to Gujrat) (which programming construct is applied in this scenario & how)? 5. A teacher might be a permanent one or visiting (which programming construct is applied in this scenario & how)?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofprogramming-240123124259-14fabda4/75/Basic-of-Programming-Introduction-to-Programming-33-2048.jpg)
![Basic Programming Concepts Imran Rashid ASSIGNMENT Submission Date 22/10/2018 & in written form [10] Q1 (a): Do some R&D on the internet and write down the syntaxes of the following things: 1. How to declare a variable 2. How to declare a constant 3. How to make a decision with if-else-if & switch 4. How to make an unknown and known iteration (for & while/do-while) Q1 (b): Do the above mention activities in the following languages: 1. C++ 2. PHP 3. JavaScript 4. C#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofprogramming-240123124259-14fabda4/75/Basic-of-Programming-Introduction-to-Programming-34-2048.jpg)
