This document provides an introduction and overview of key PHP concepts including variables, constants, strings, loops, conditional statements, functions, include/require, and variable scope. It includes code examples for while, do-while, for, and foreach loops. Conditional statements covered include if, elseif, else, switch, ternary operator. The document also discusses functions, passing by value vs reference, variable-length parameters, and returning values. It covers including/requiring files and variable scope rules. Finally, it provides exercises to reinforce the concepts.






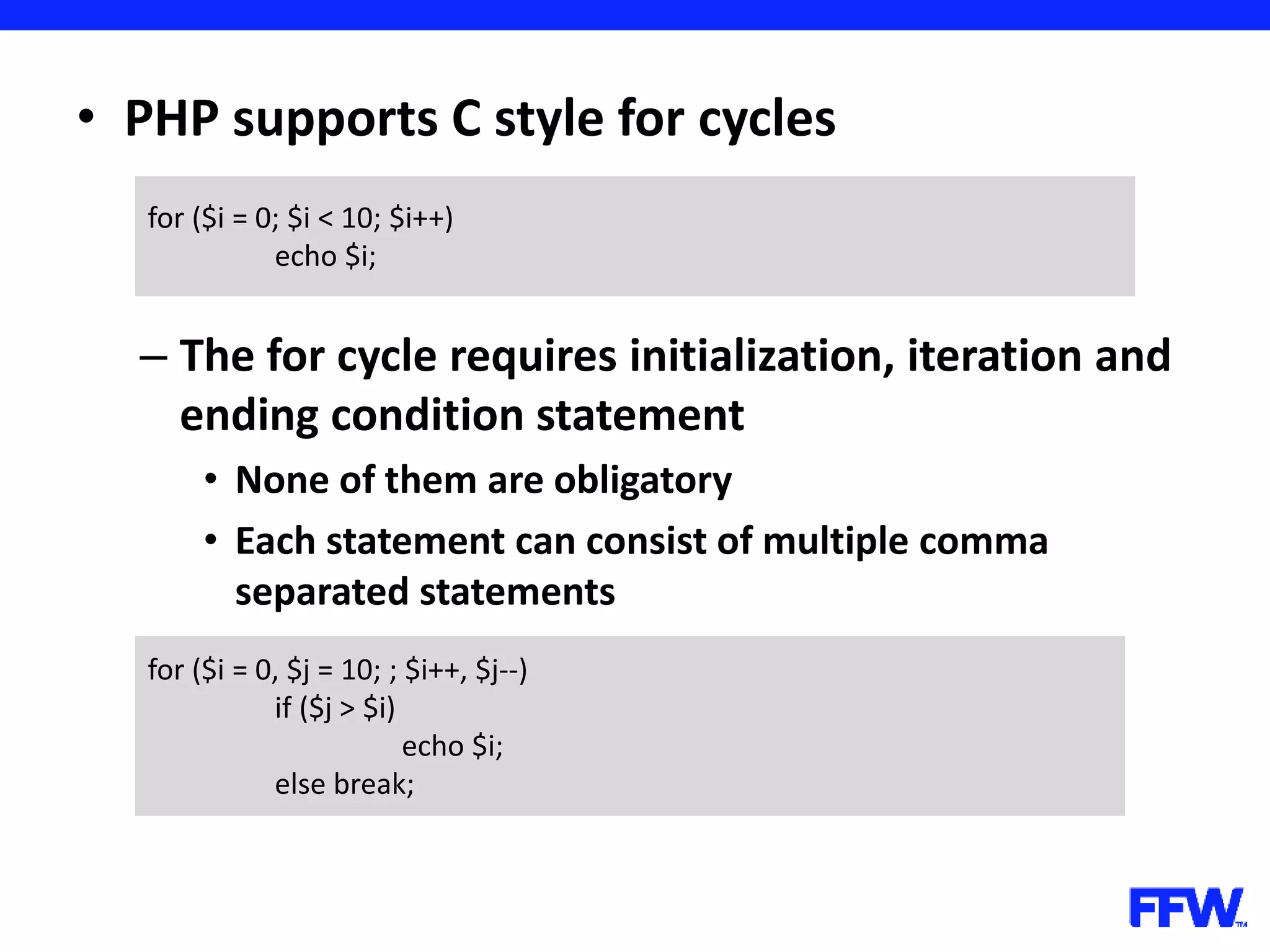




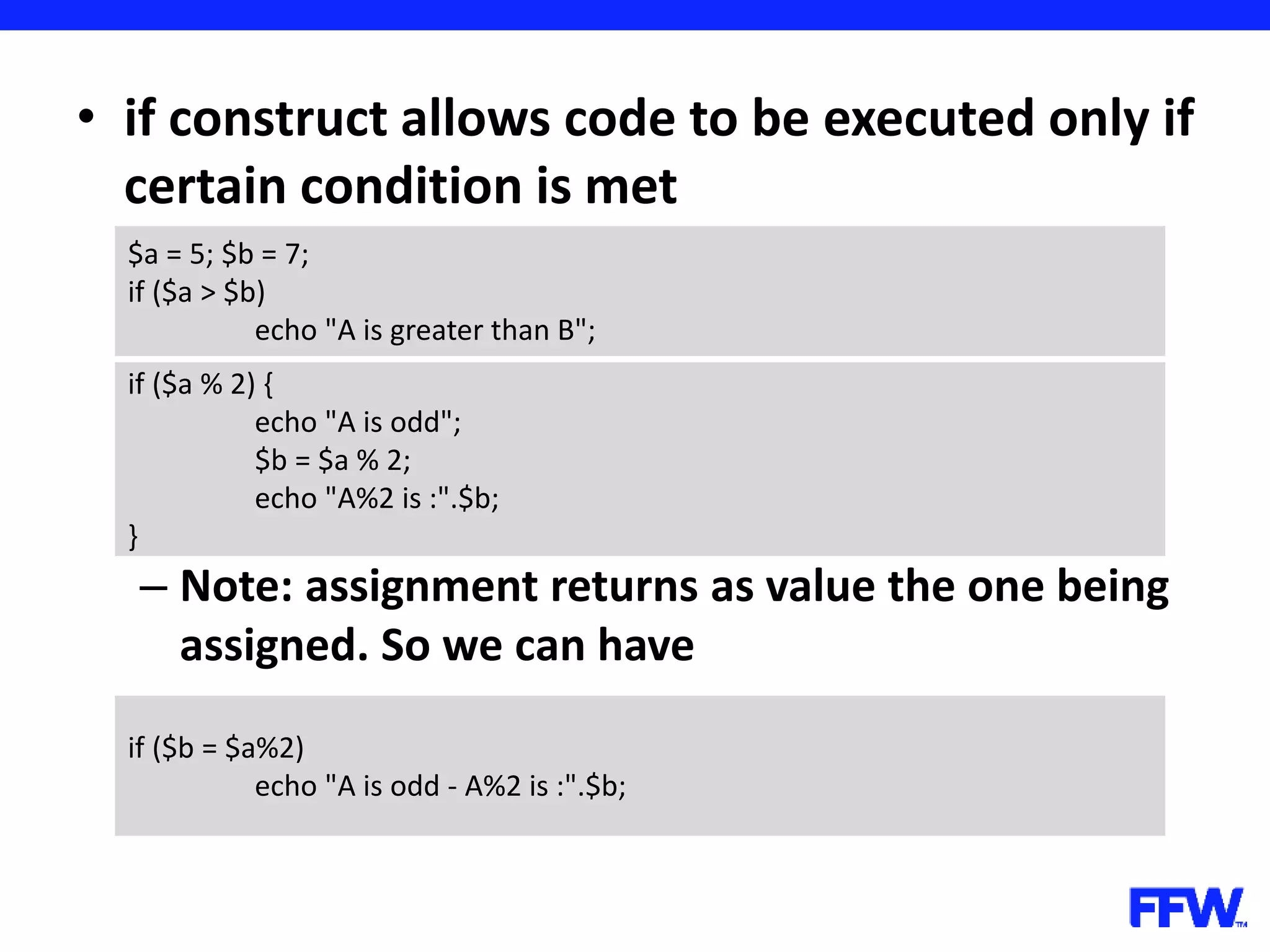


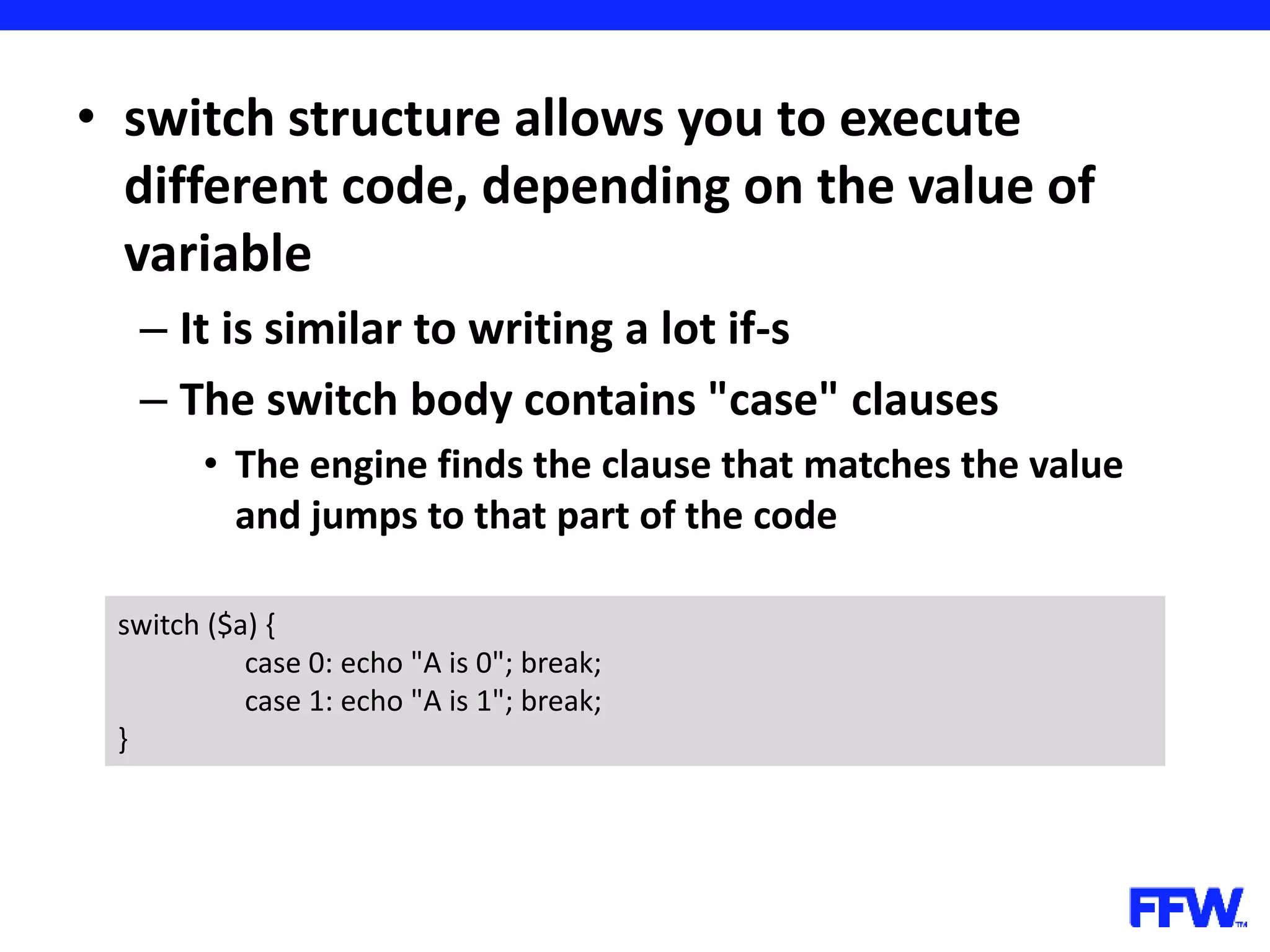





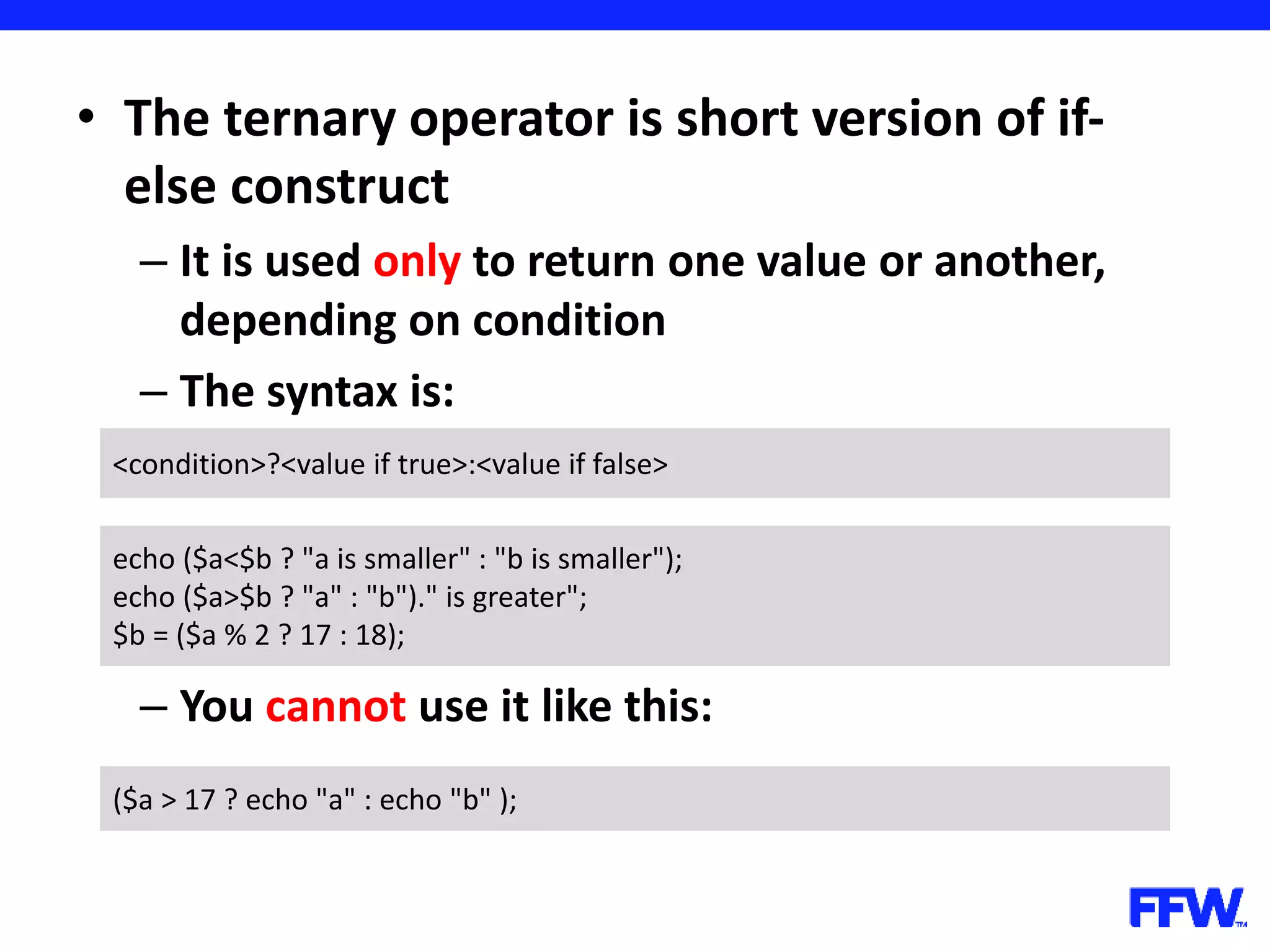



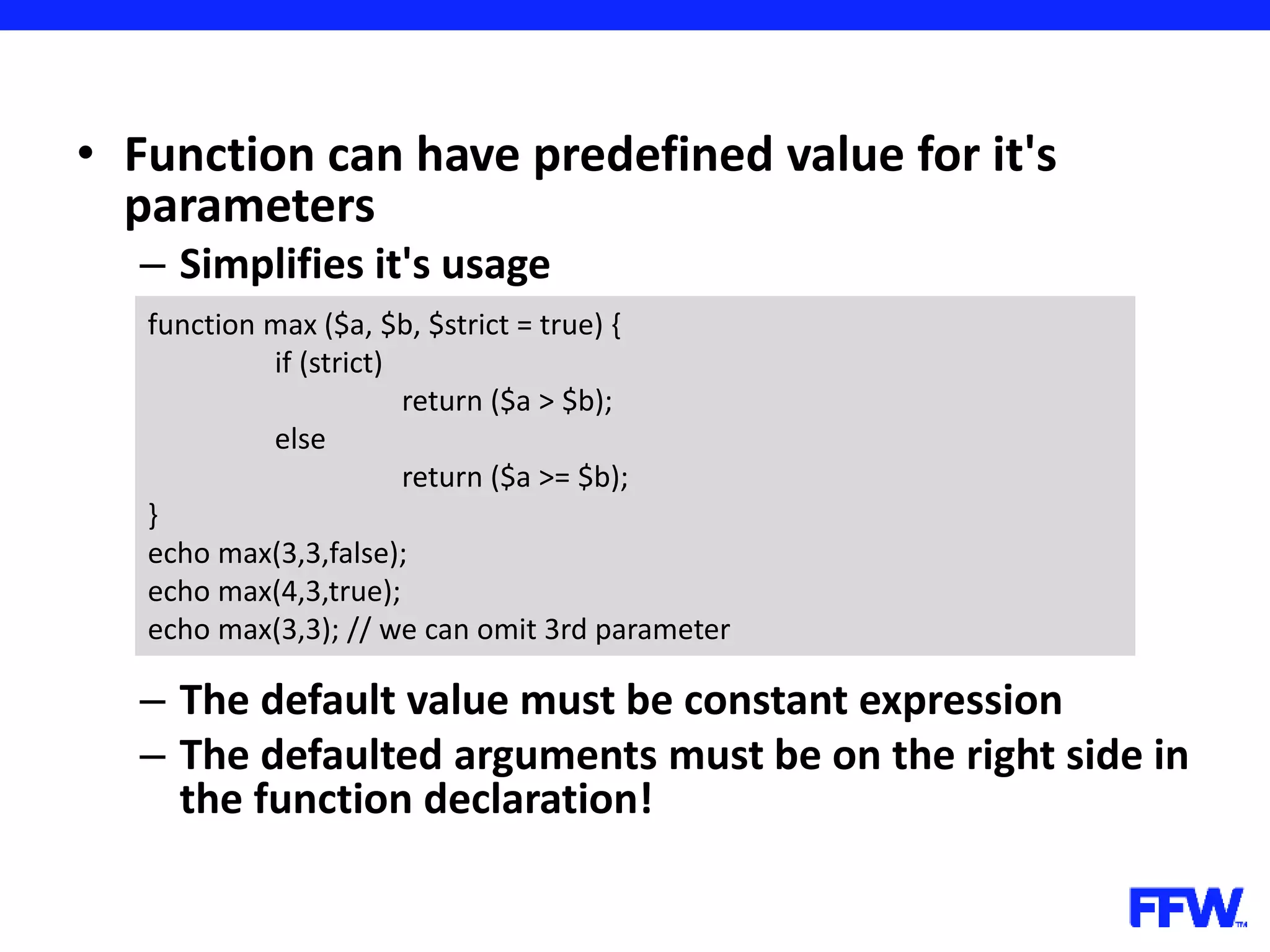




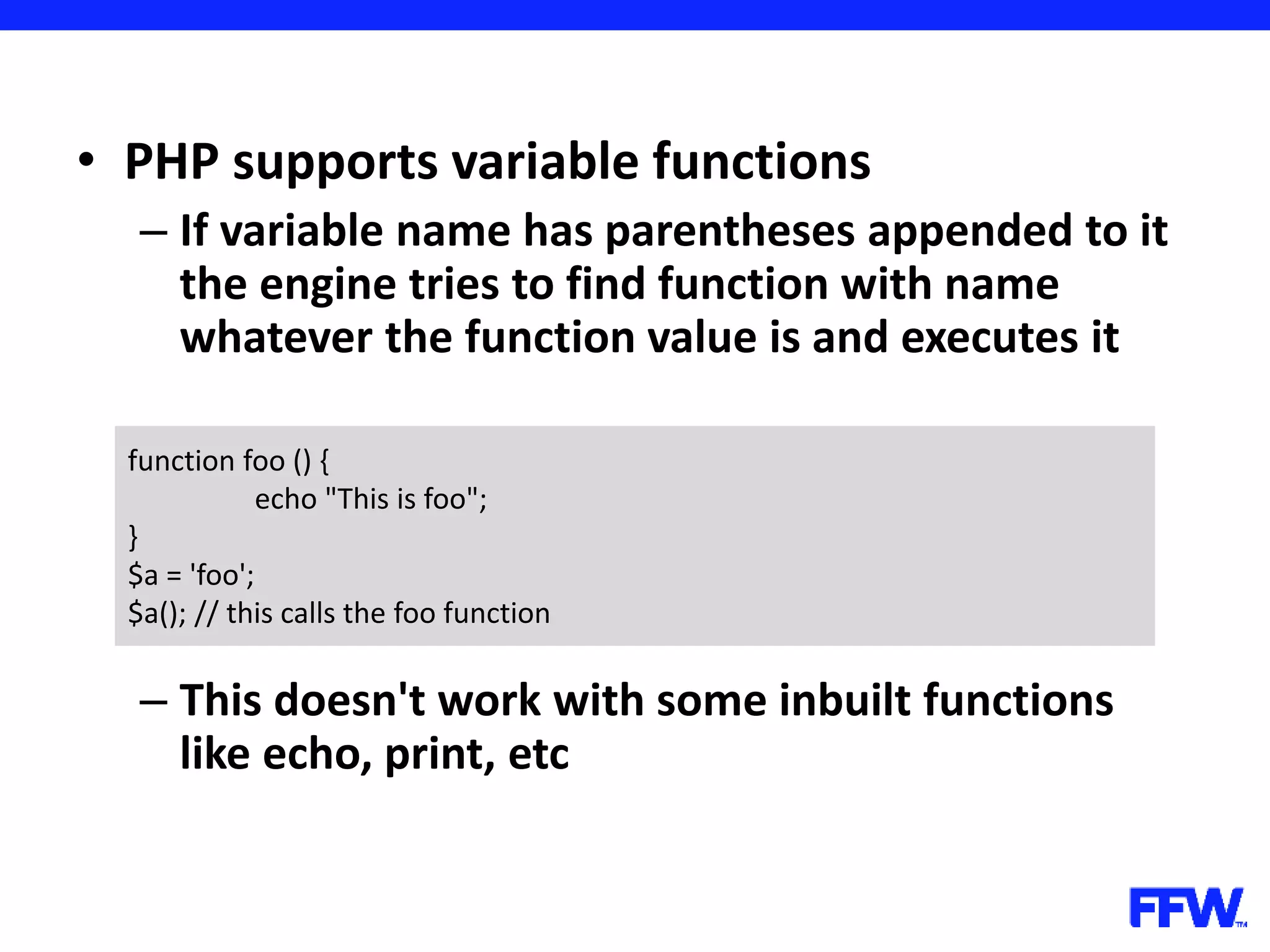






![• Variables, declared in loops are accessible after loop is over – In the example you have to declare the array before the loop for ($i = 0; $i < 5; $i++) { $arr[] = $i; } print_r ($arr); // outputs 5; $arr = array(); for ($i = 0; $i < 5; $i++) { $arr[] = $i; } print_r ($arr); // works too](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductioninphppart2-160727150152/75/Introduction-in-php-part-2-37-2048.jpg)





