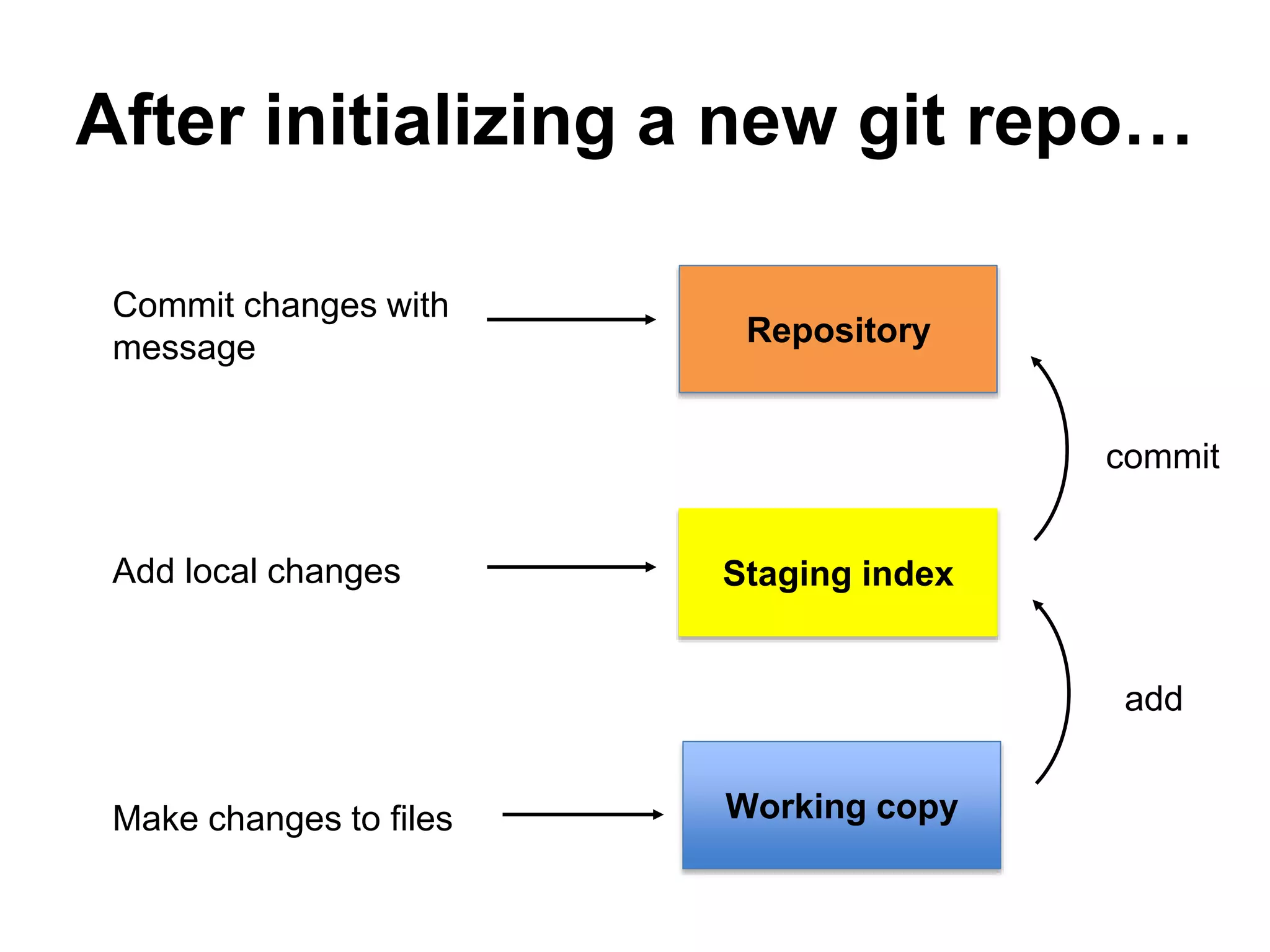
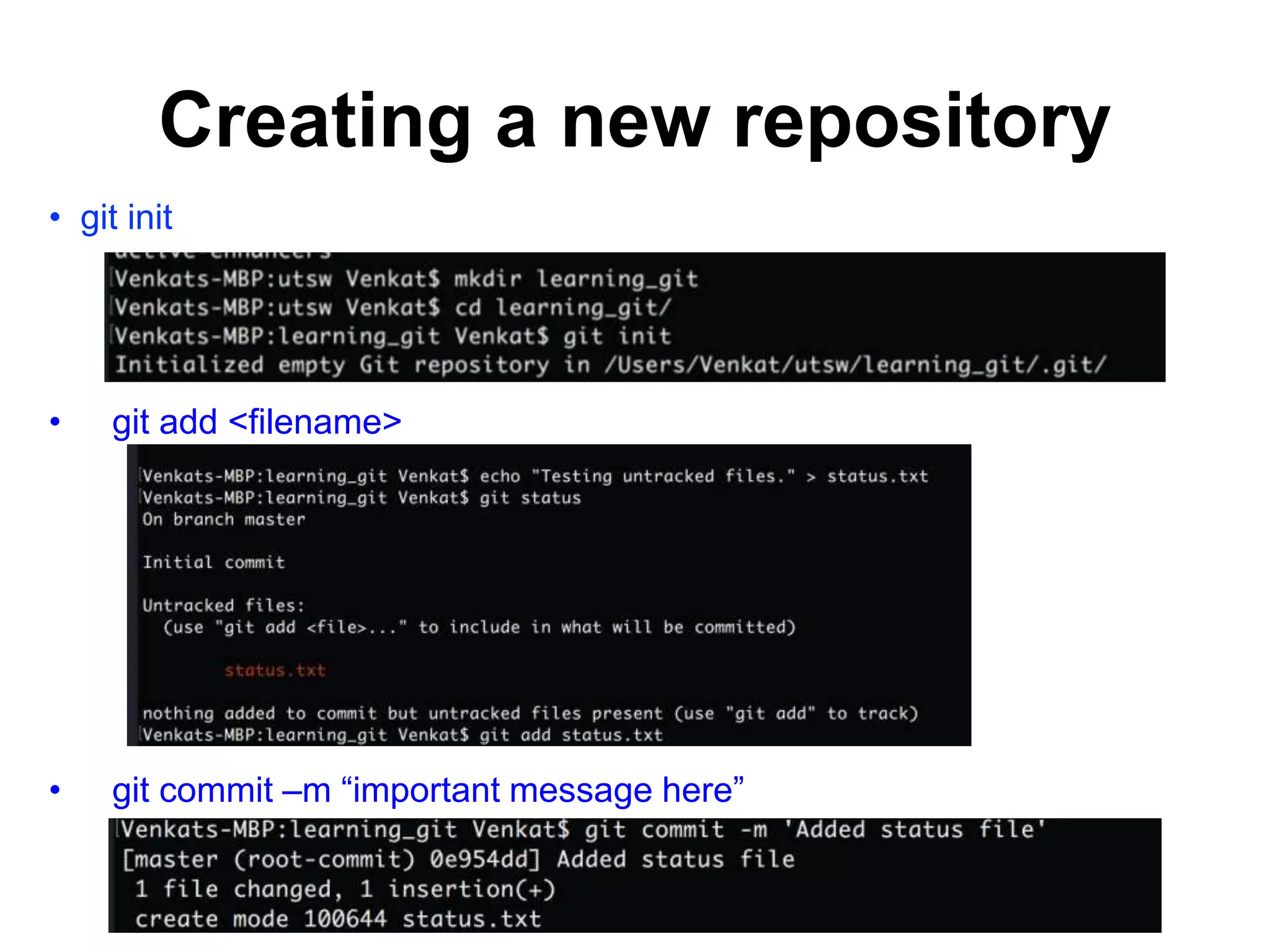
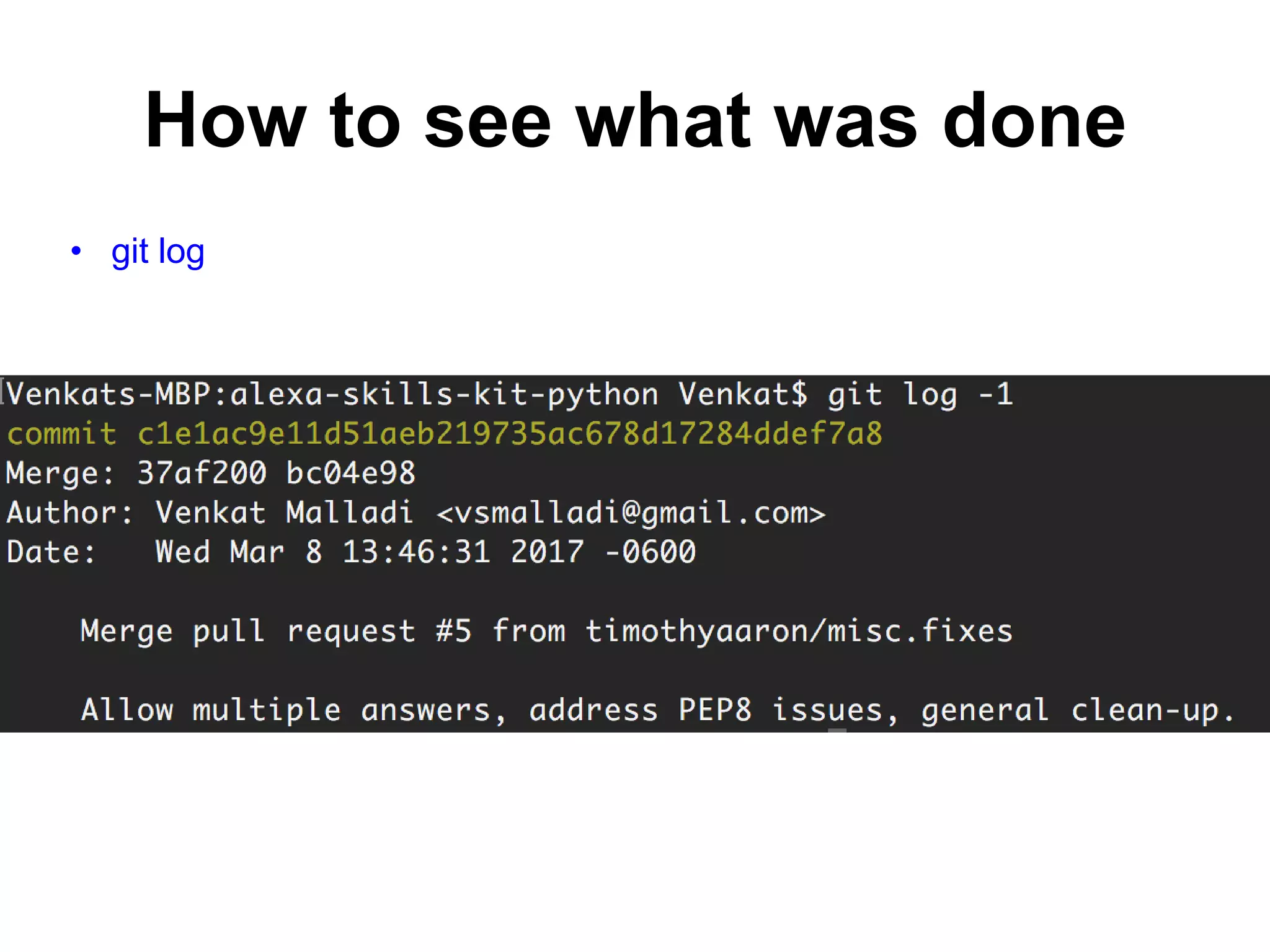
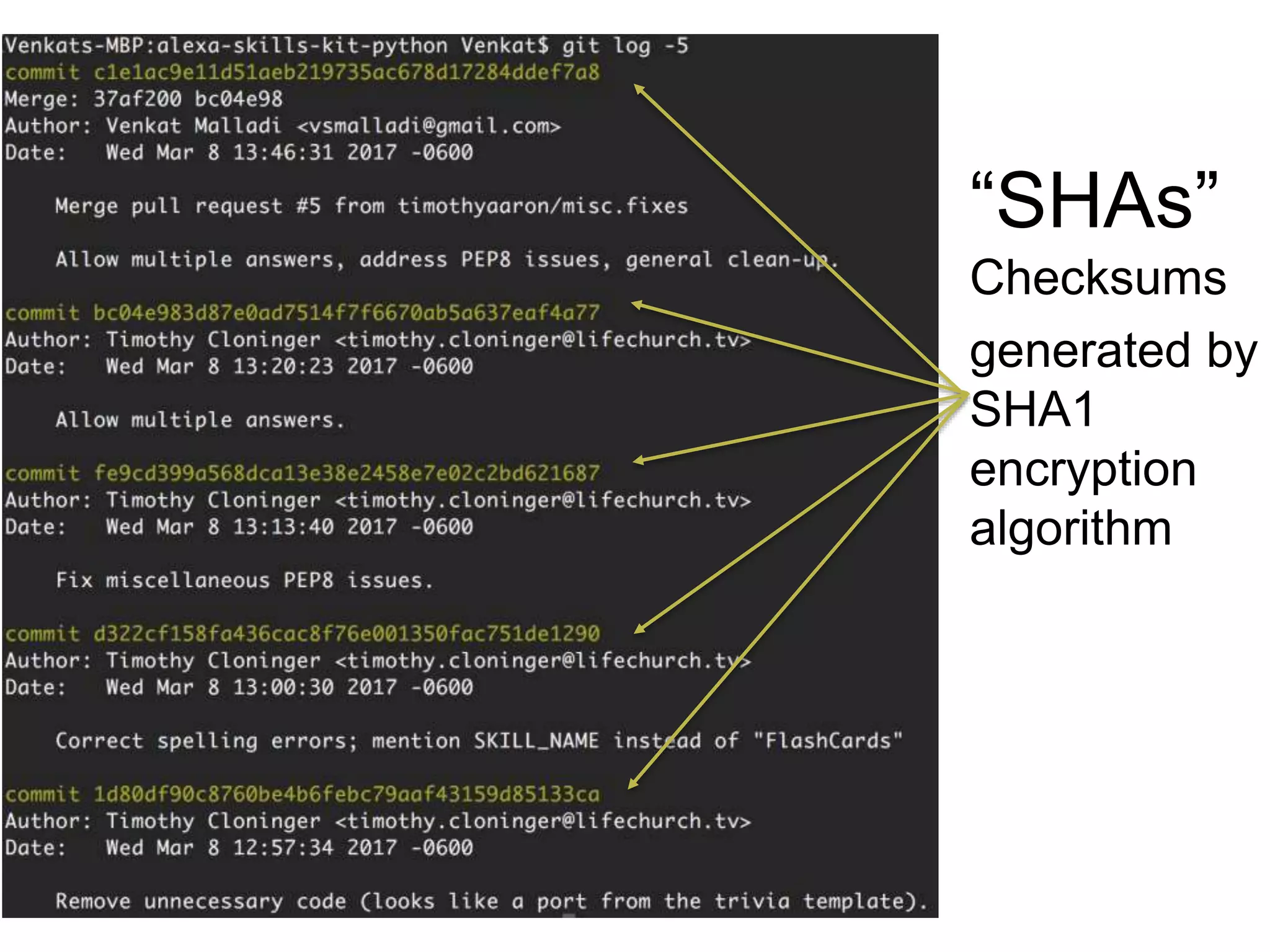
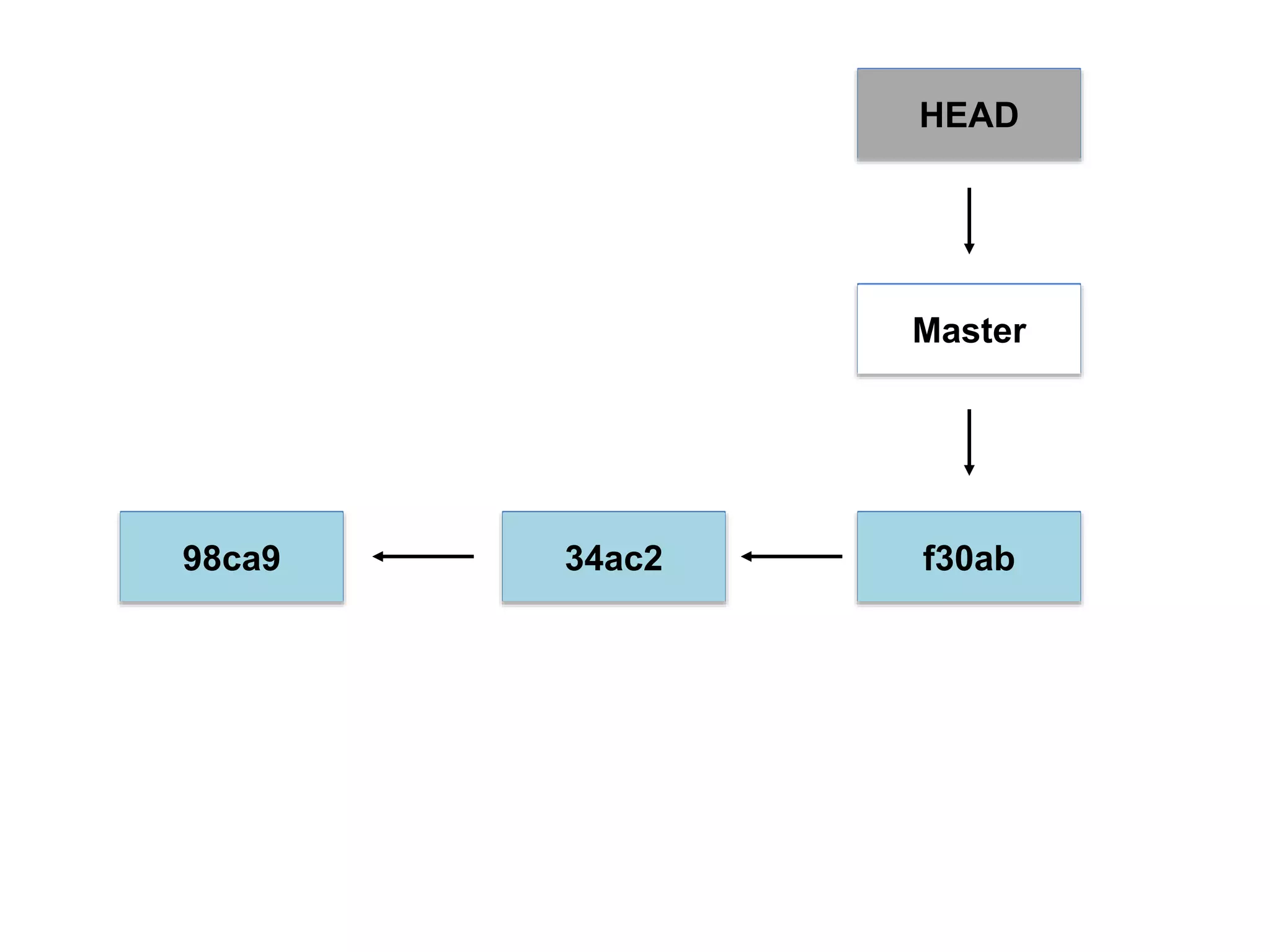
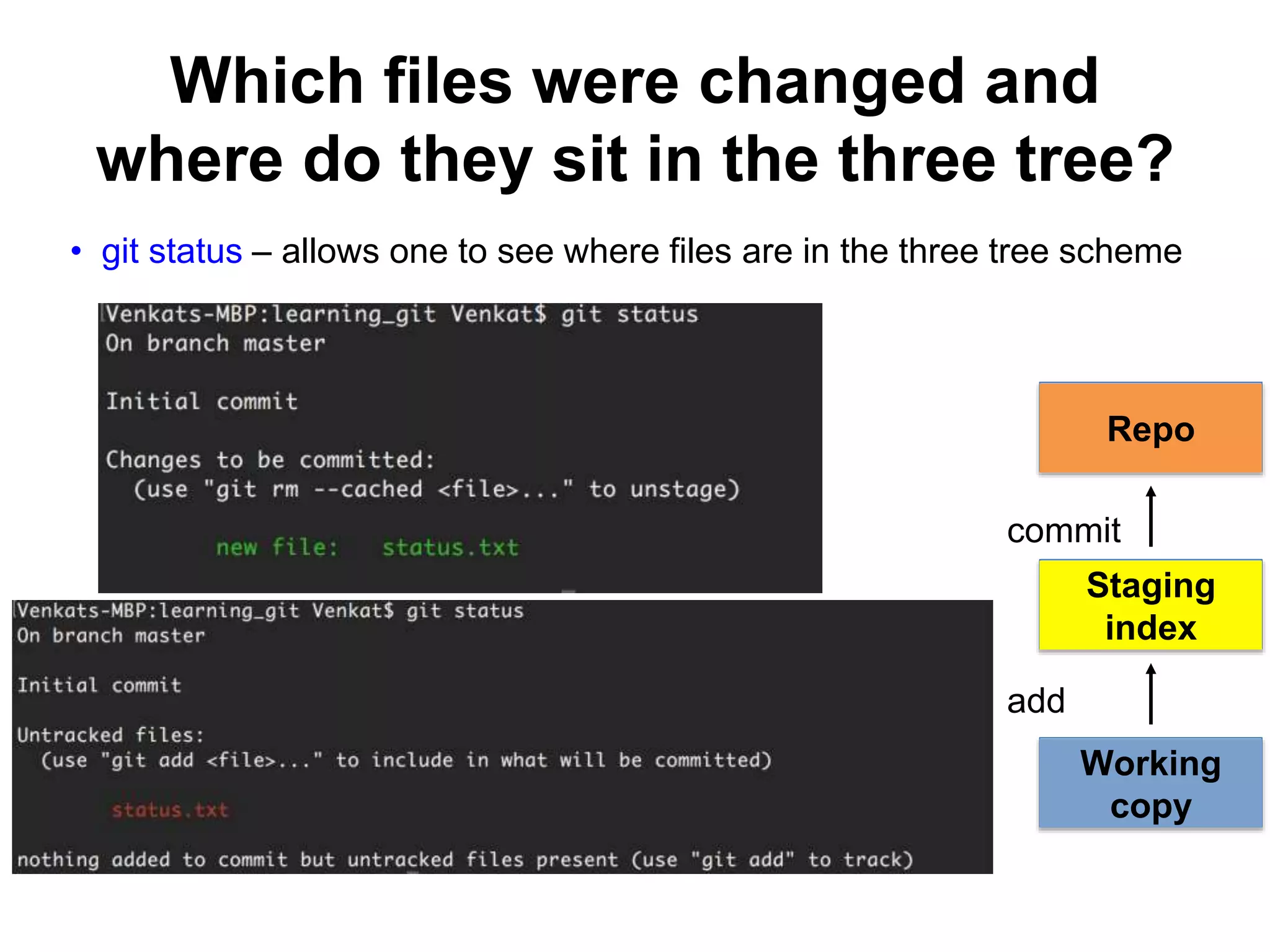
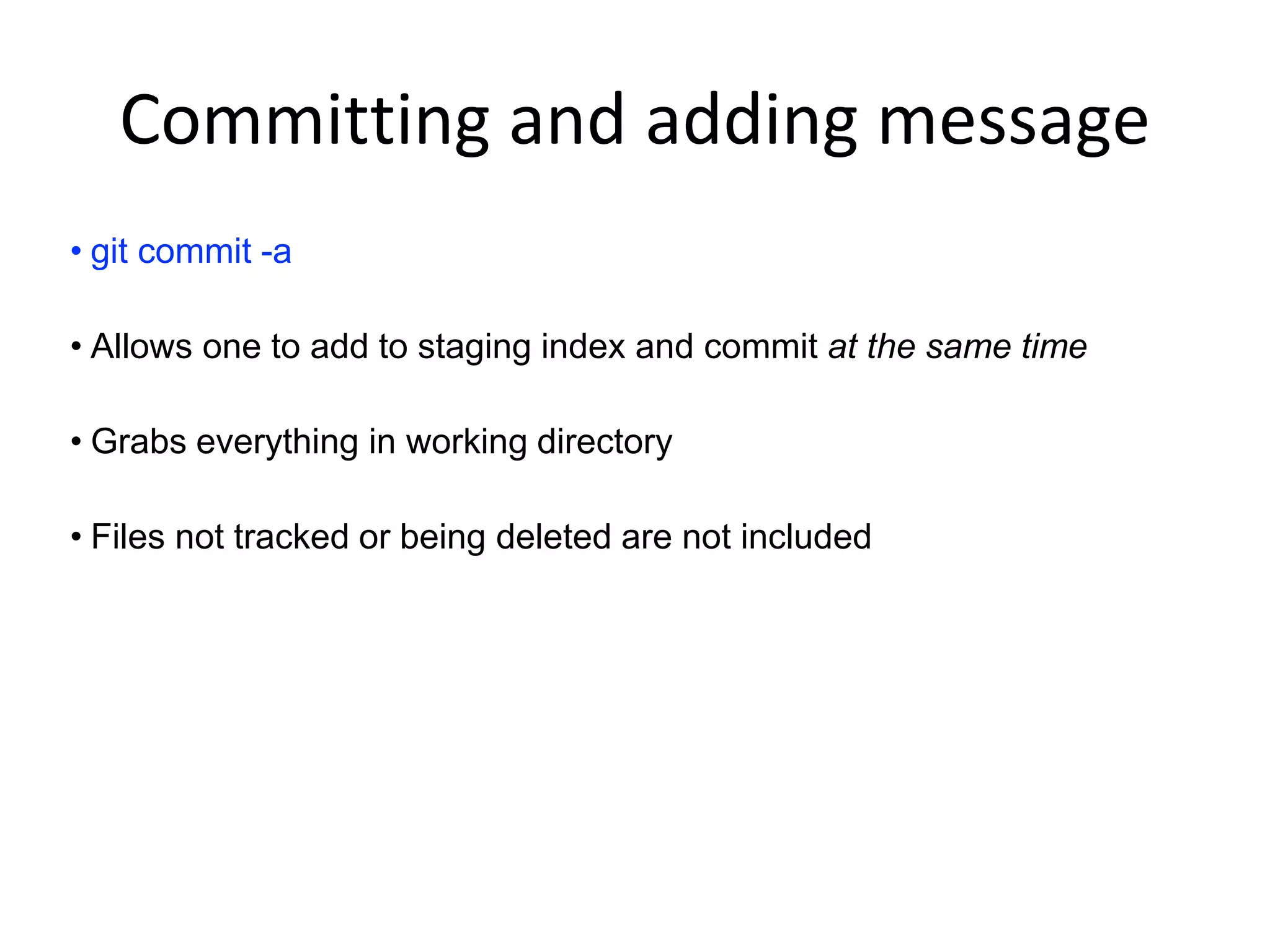
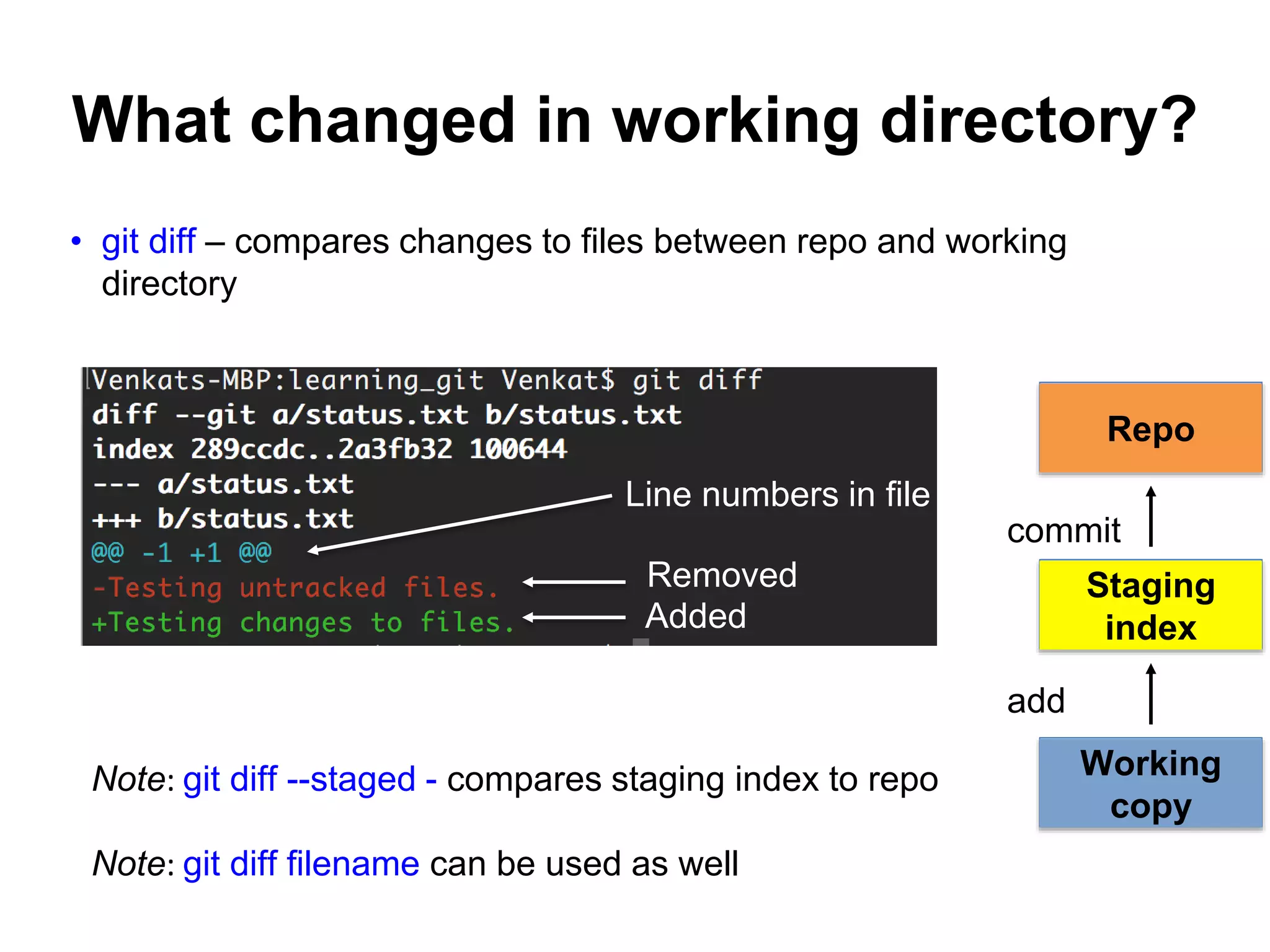
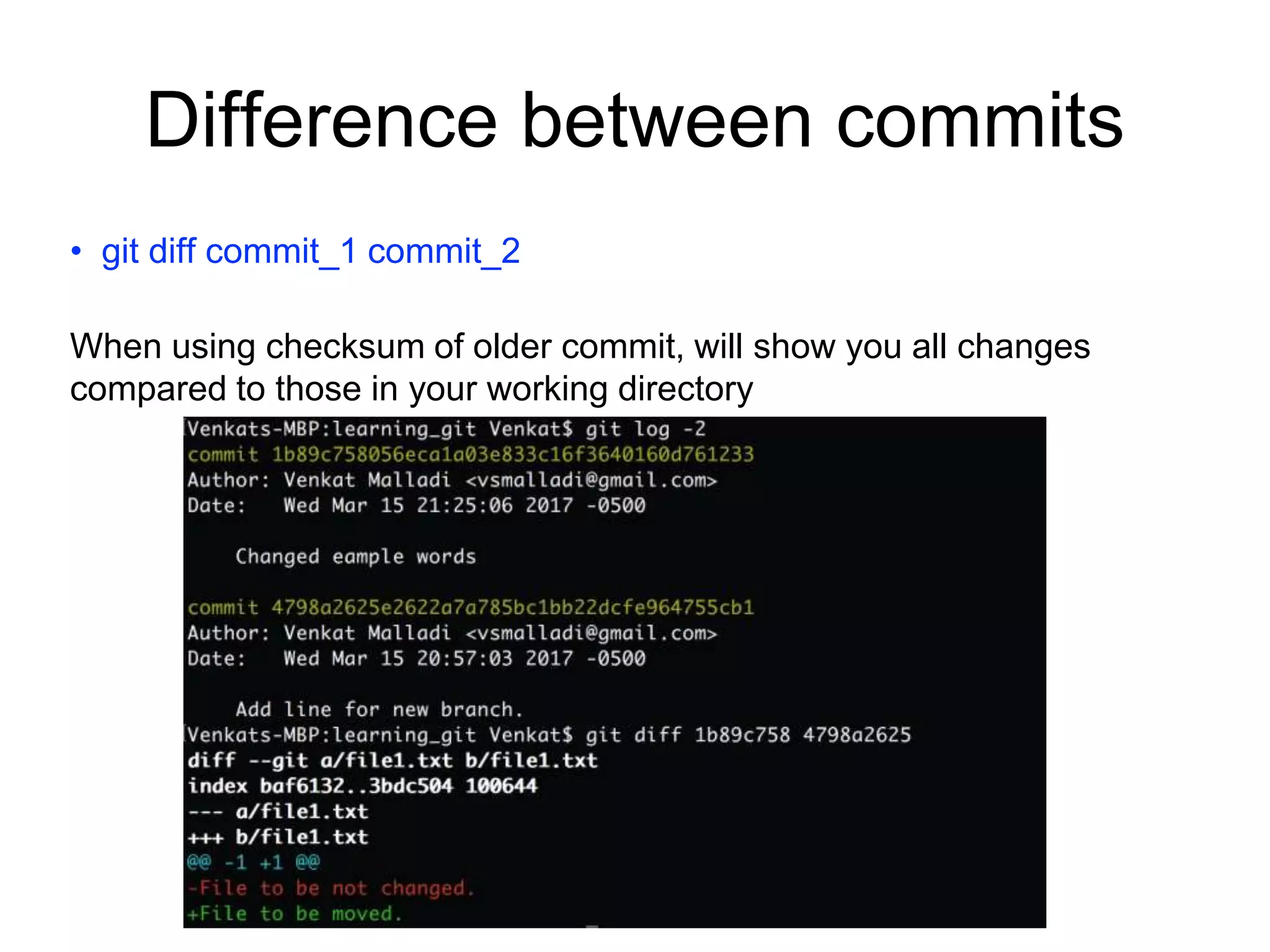
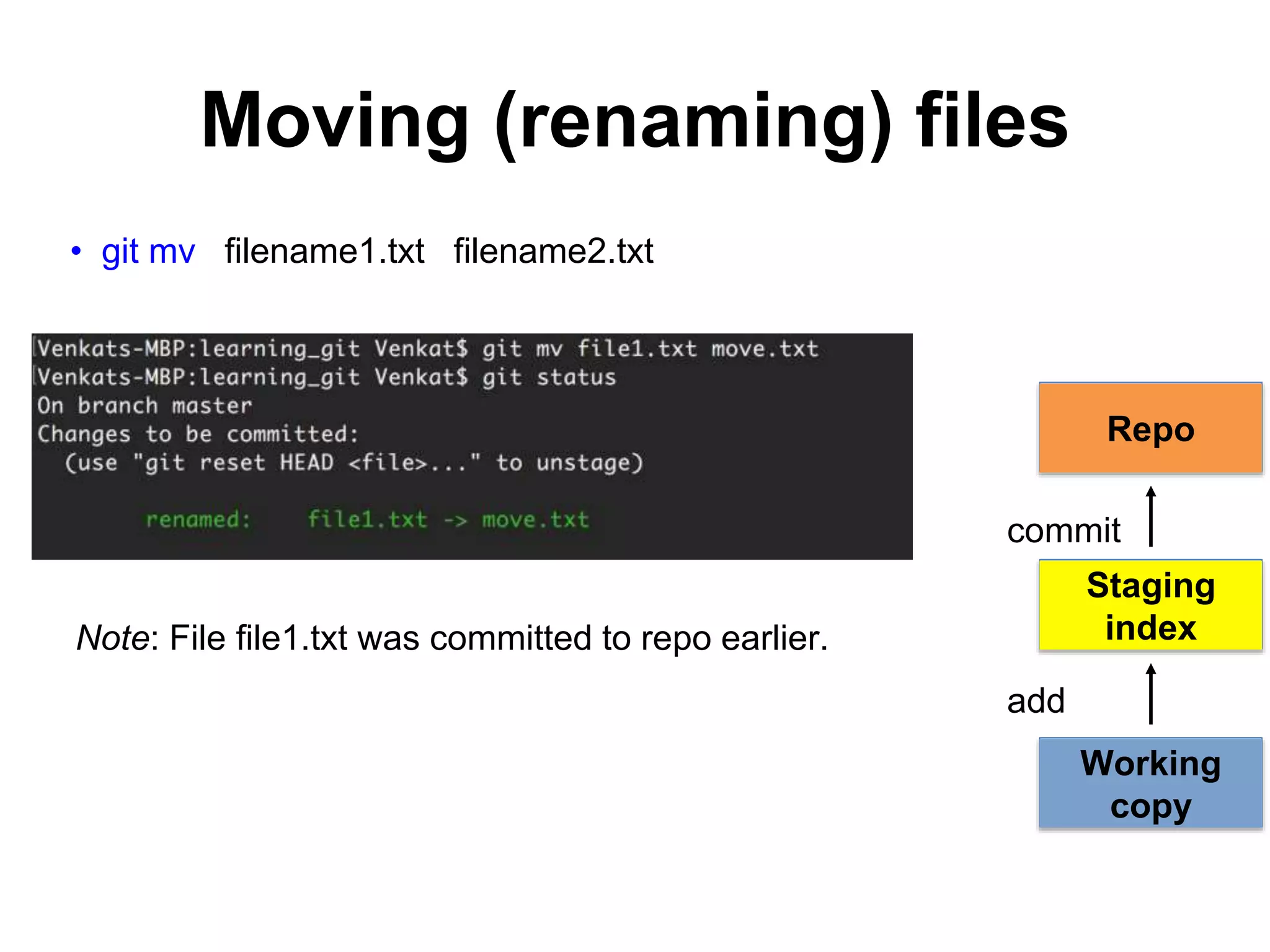
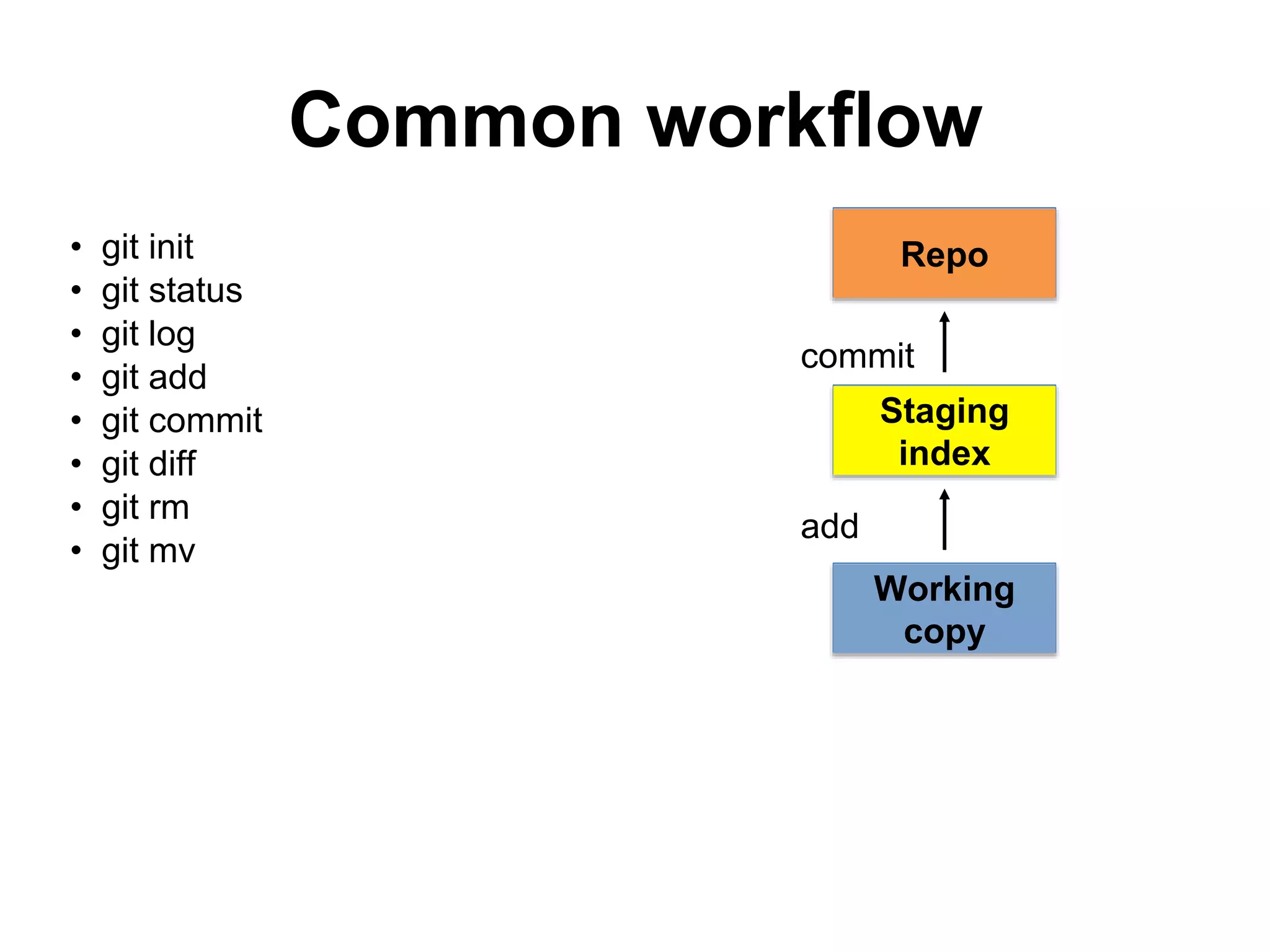
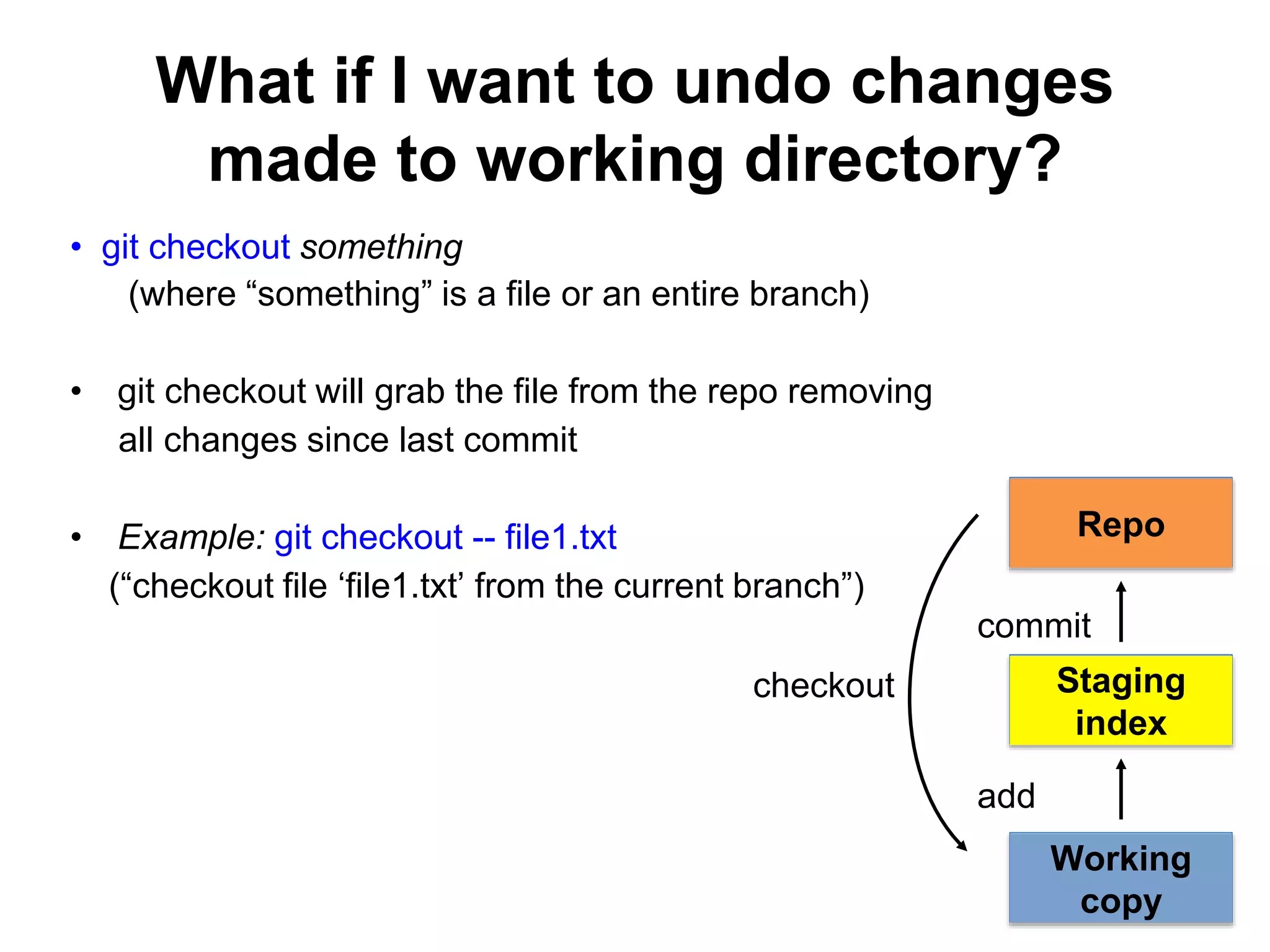
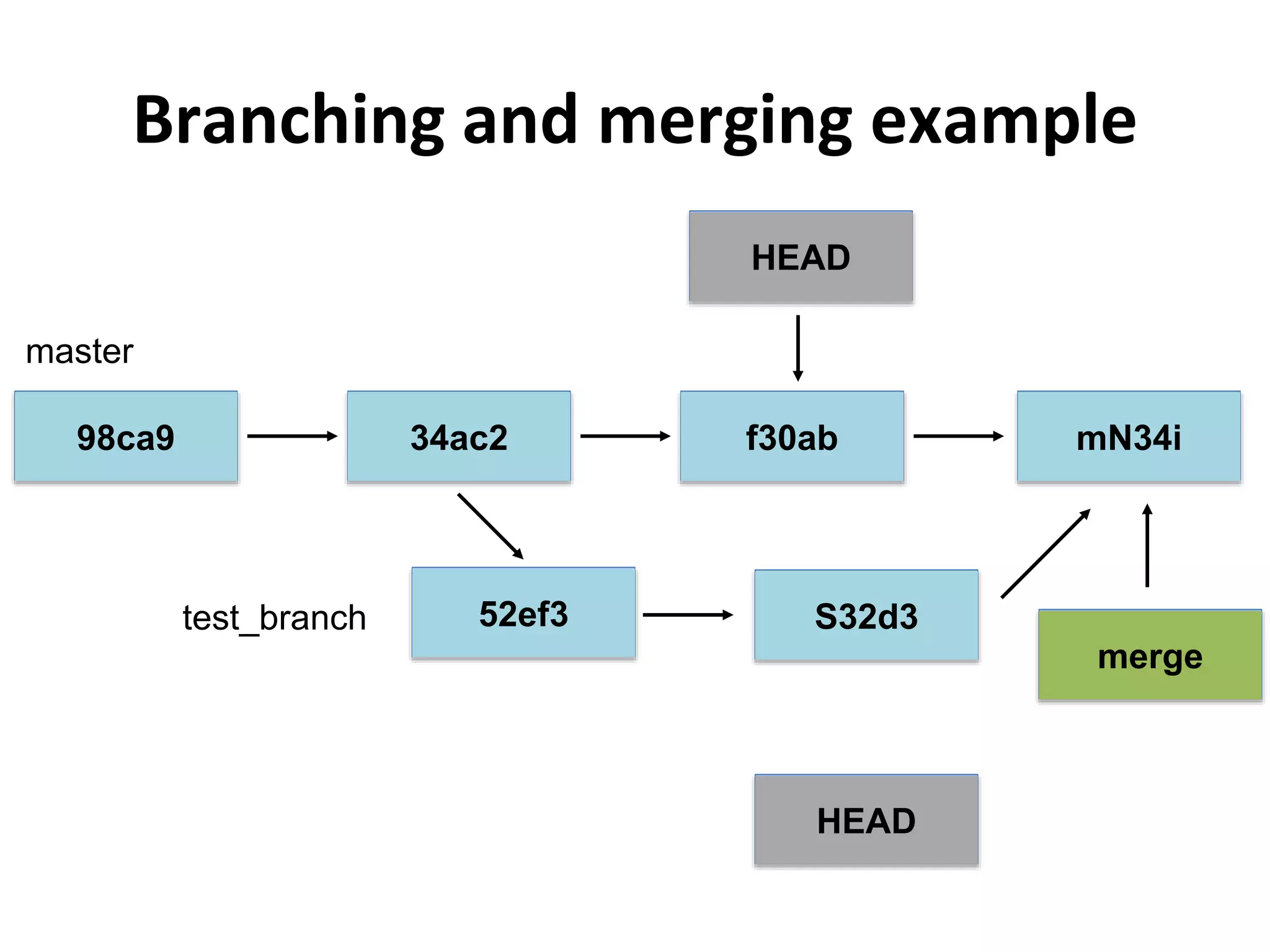
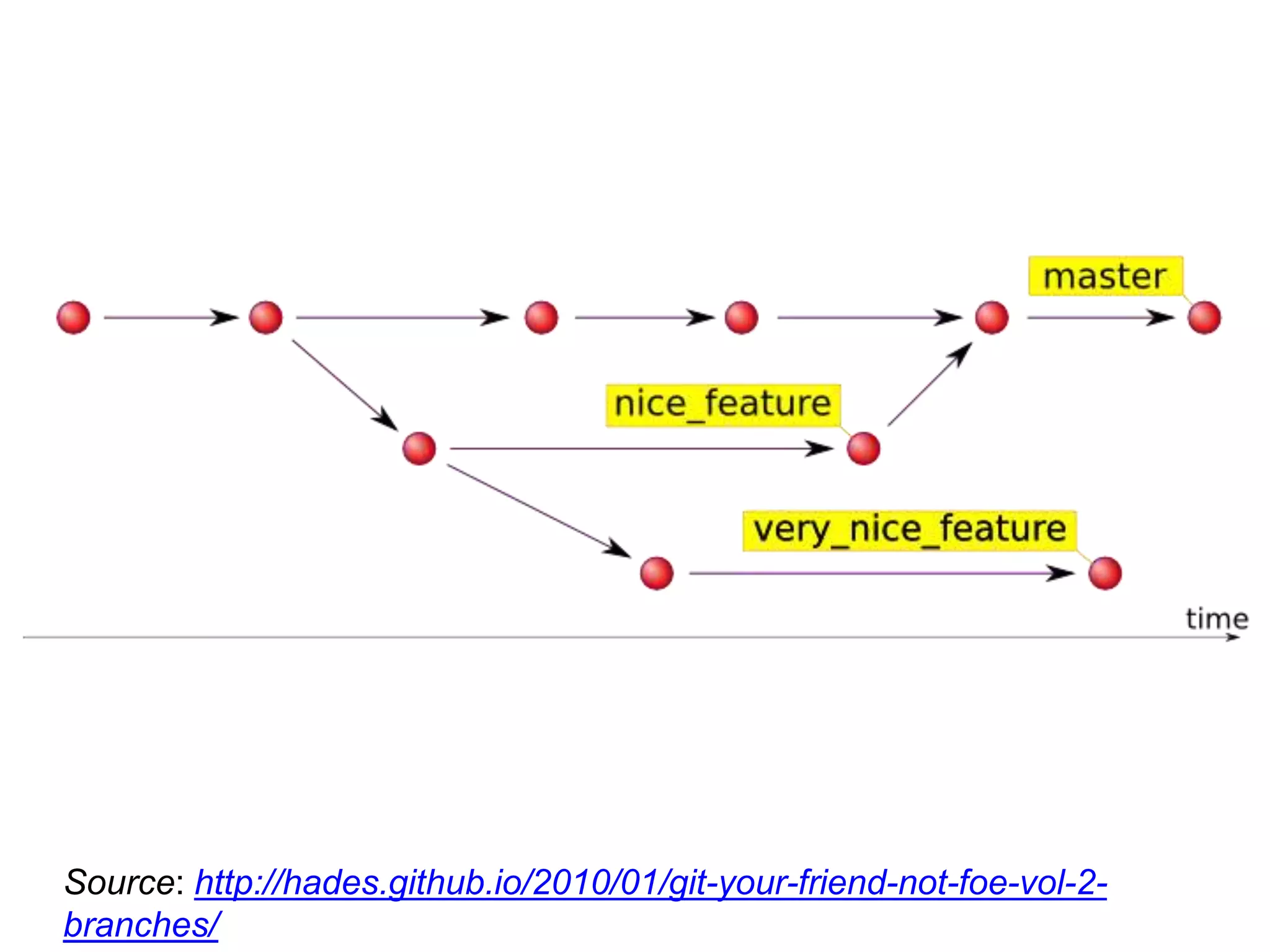
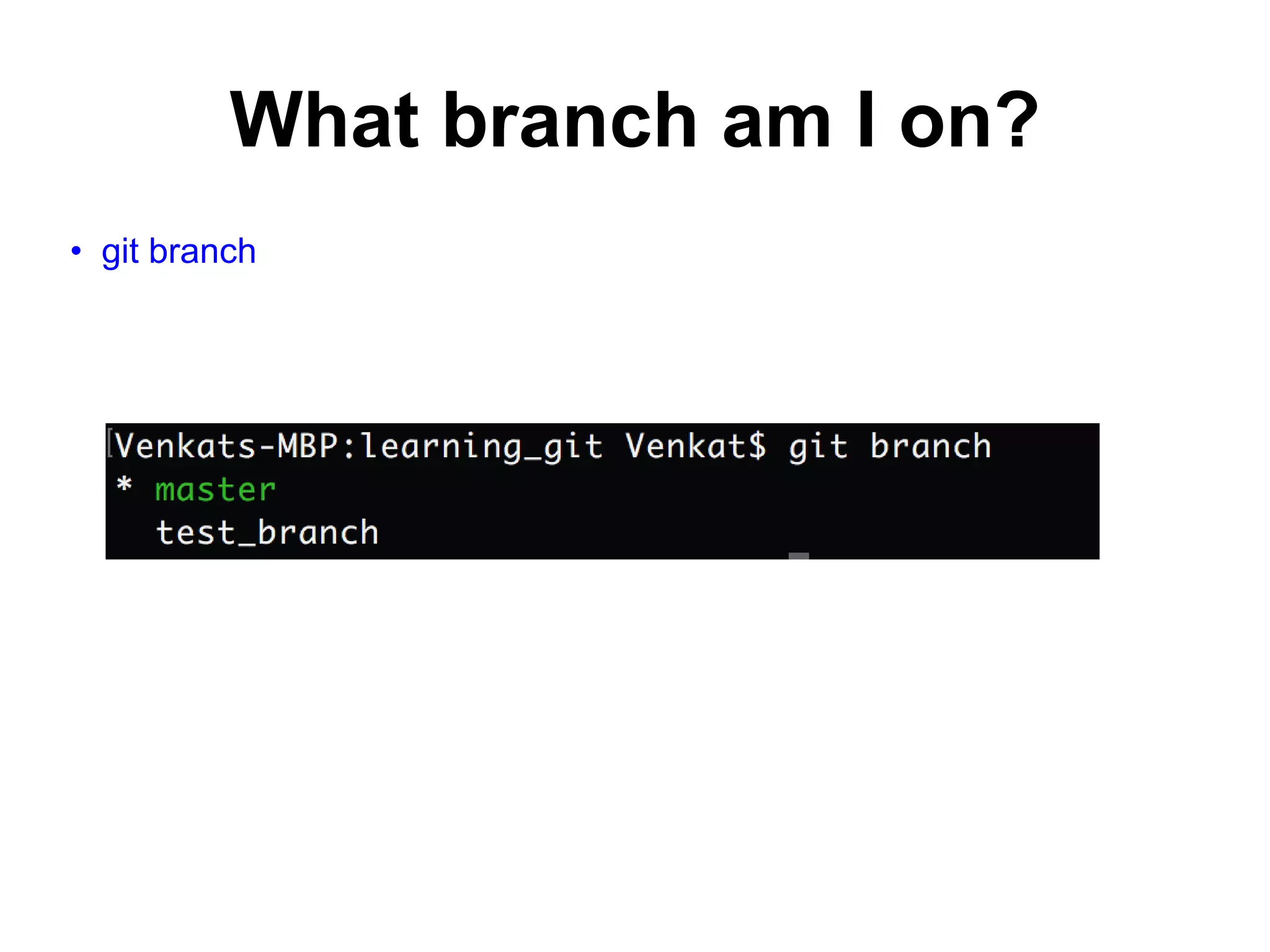
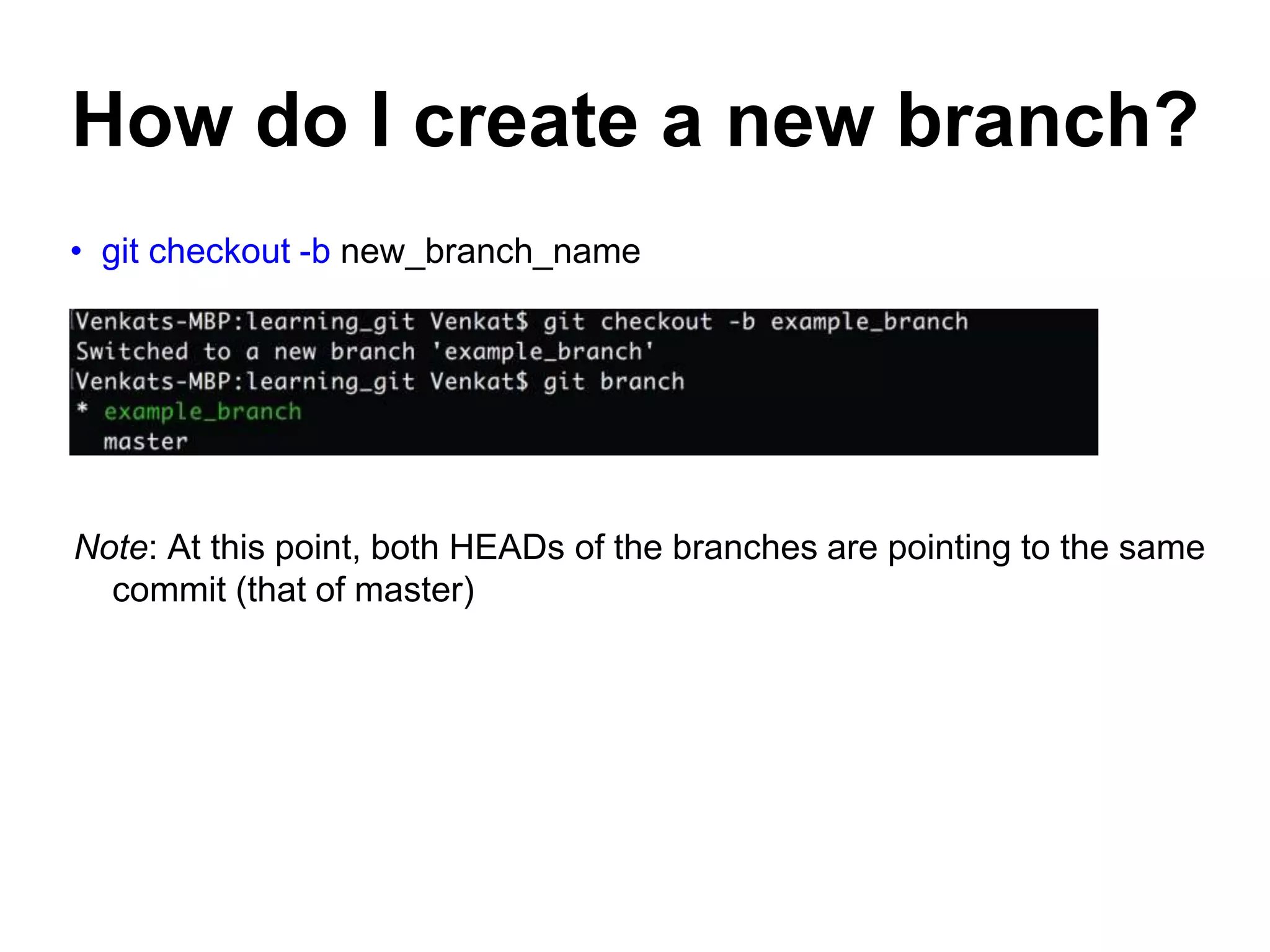
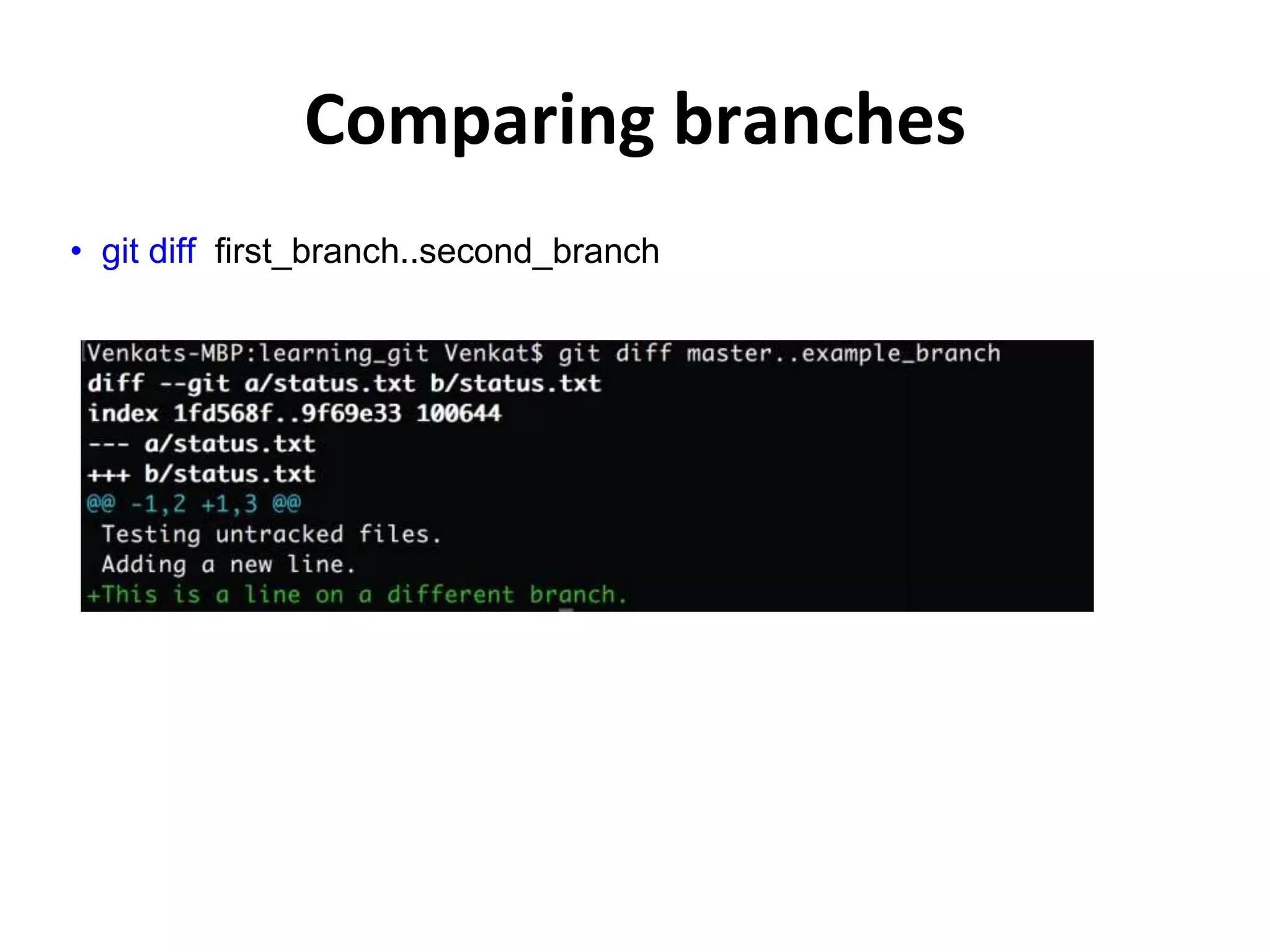
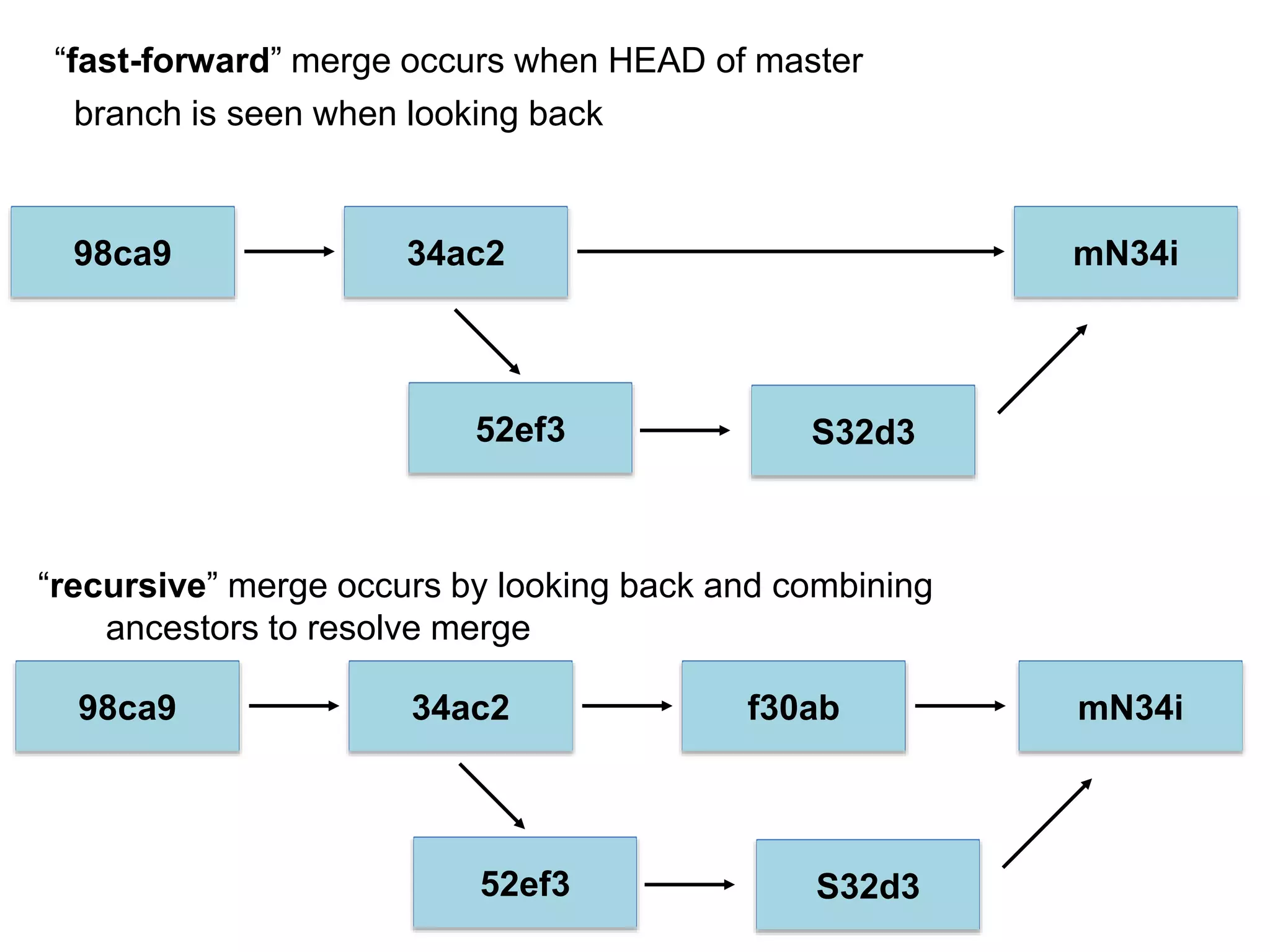
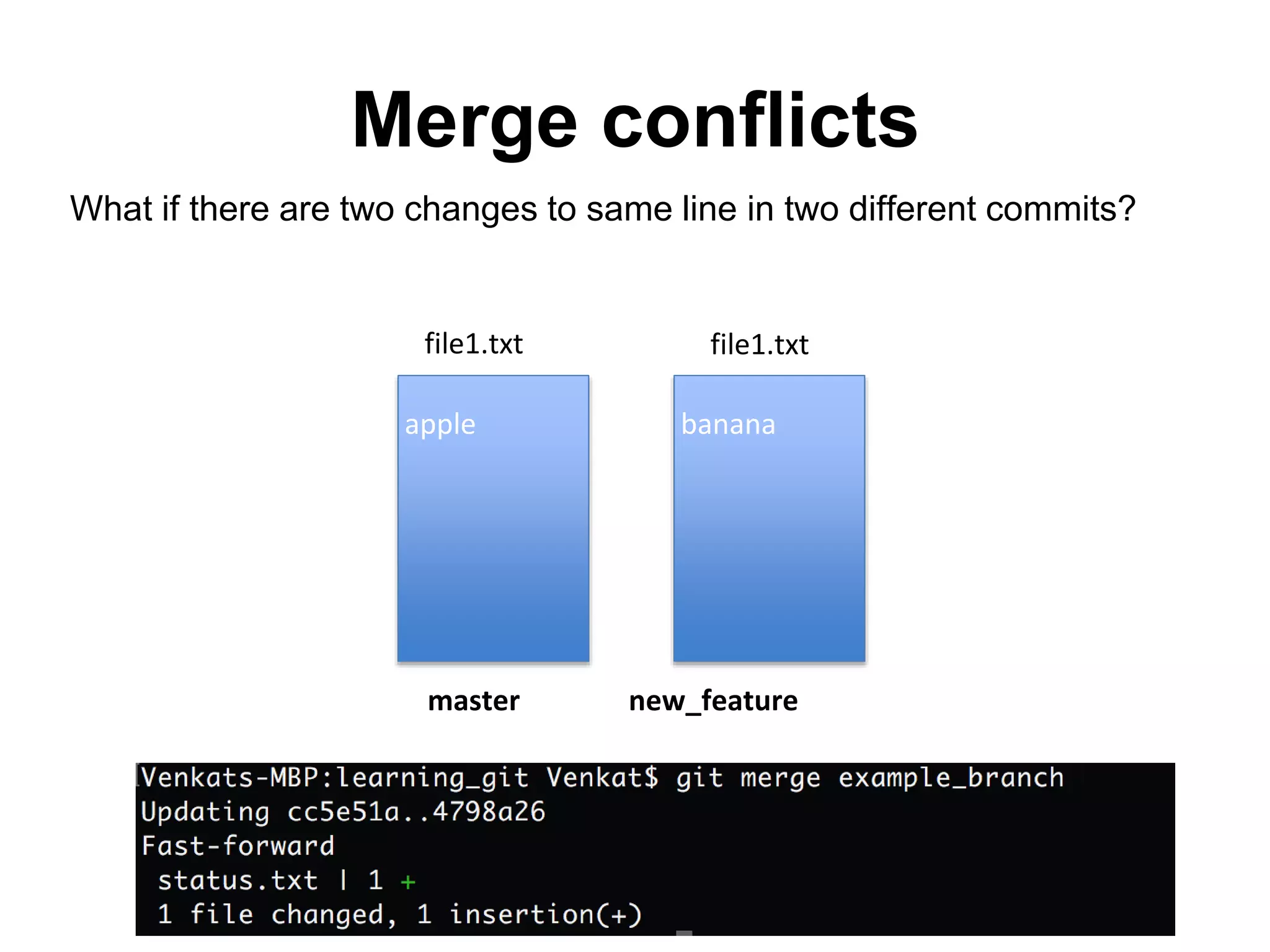
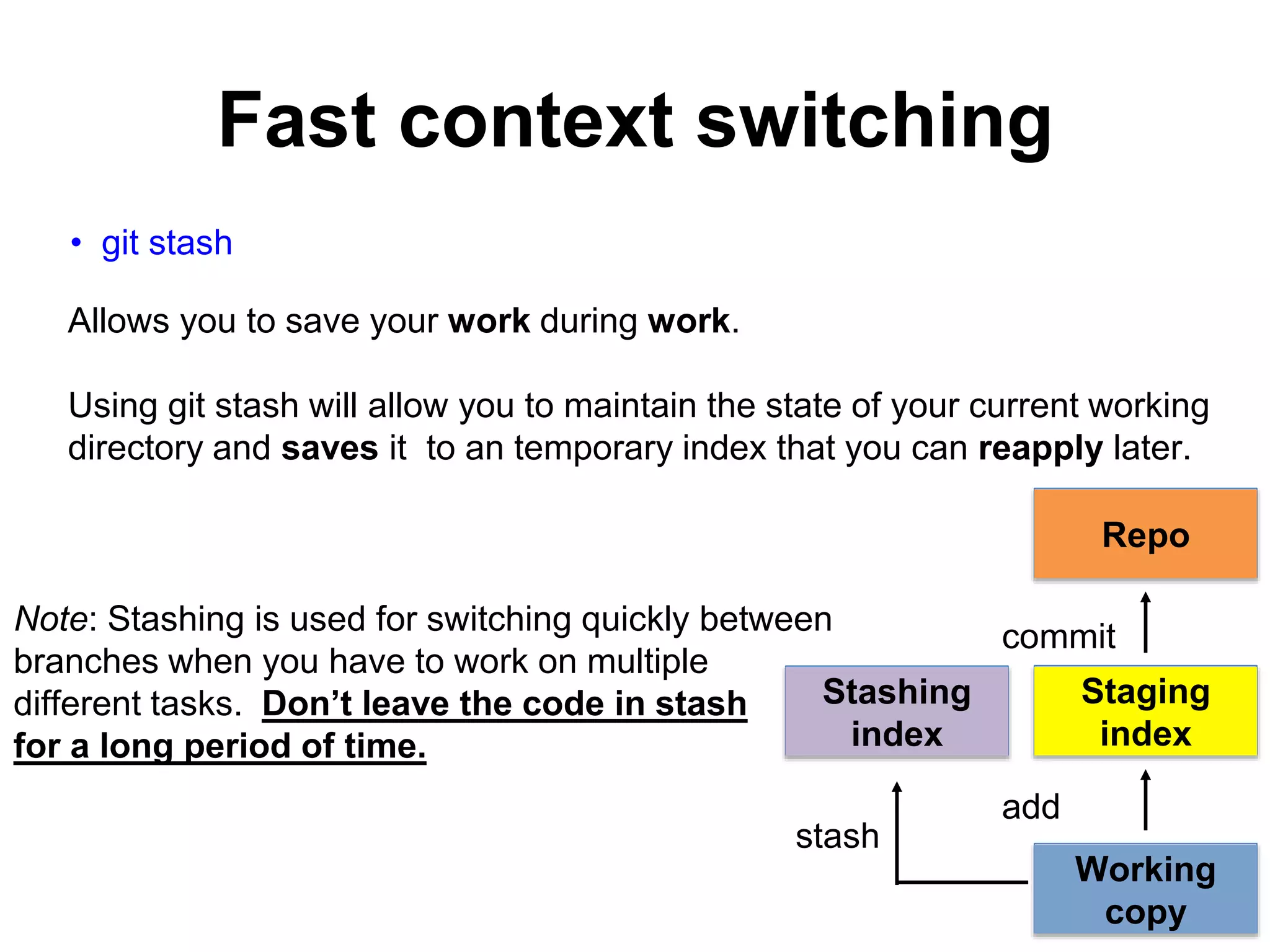
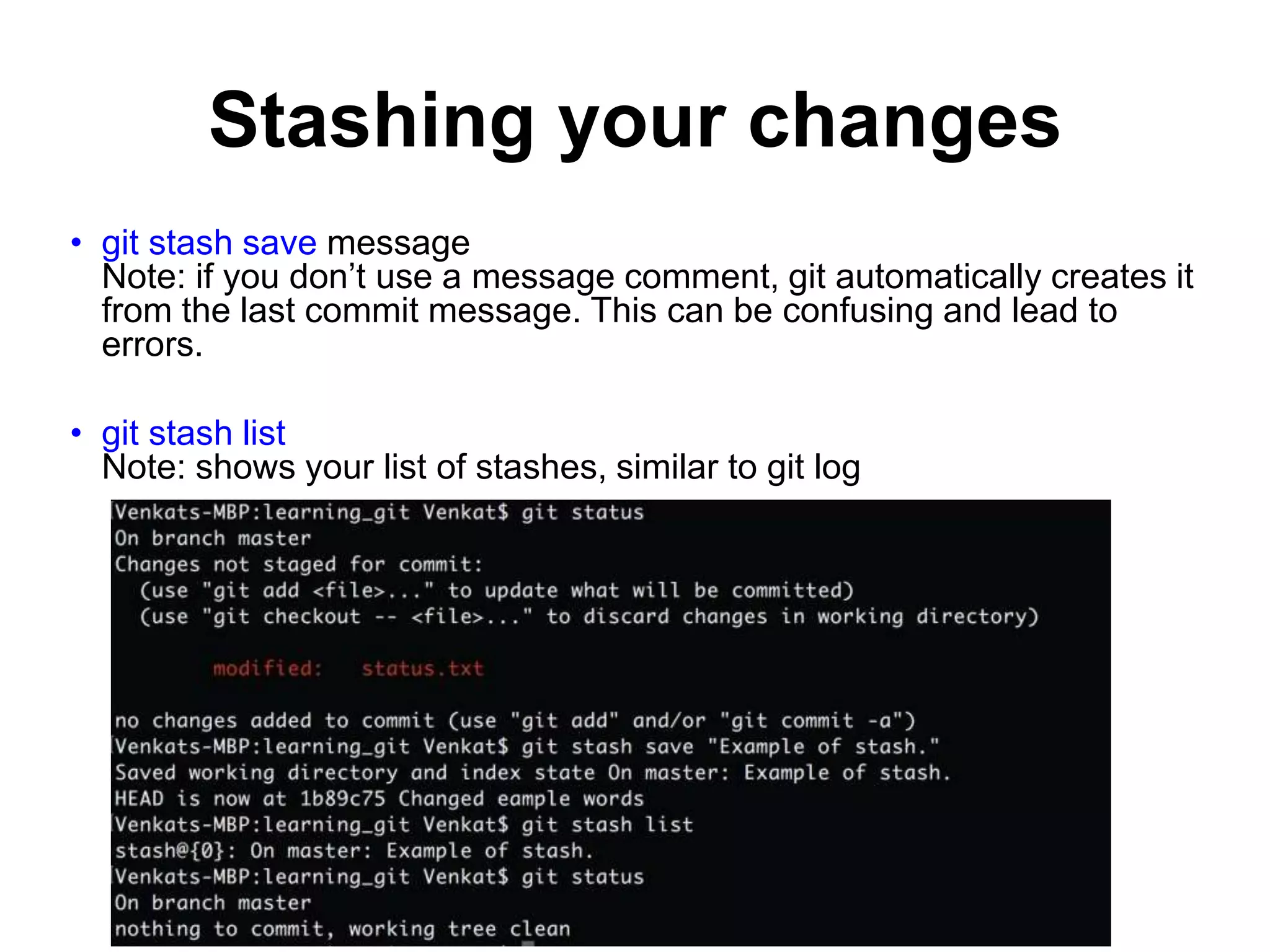
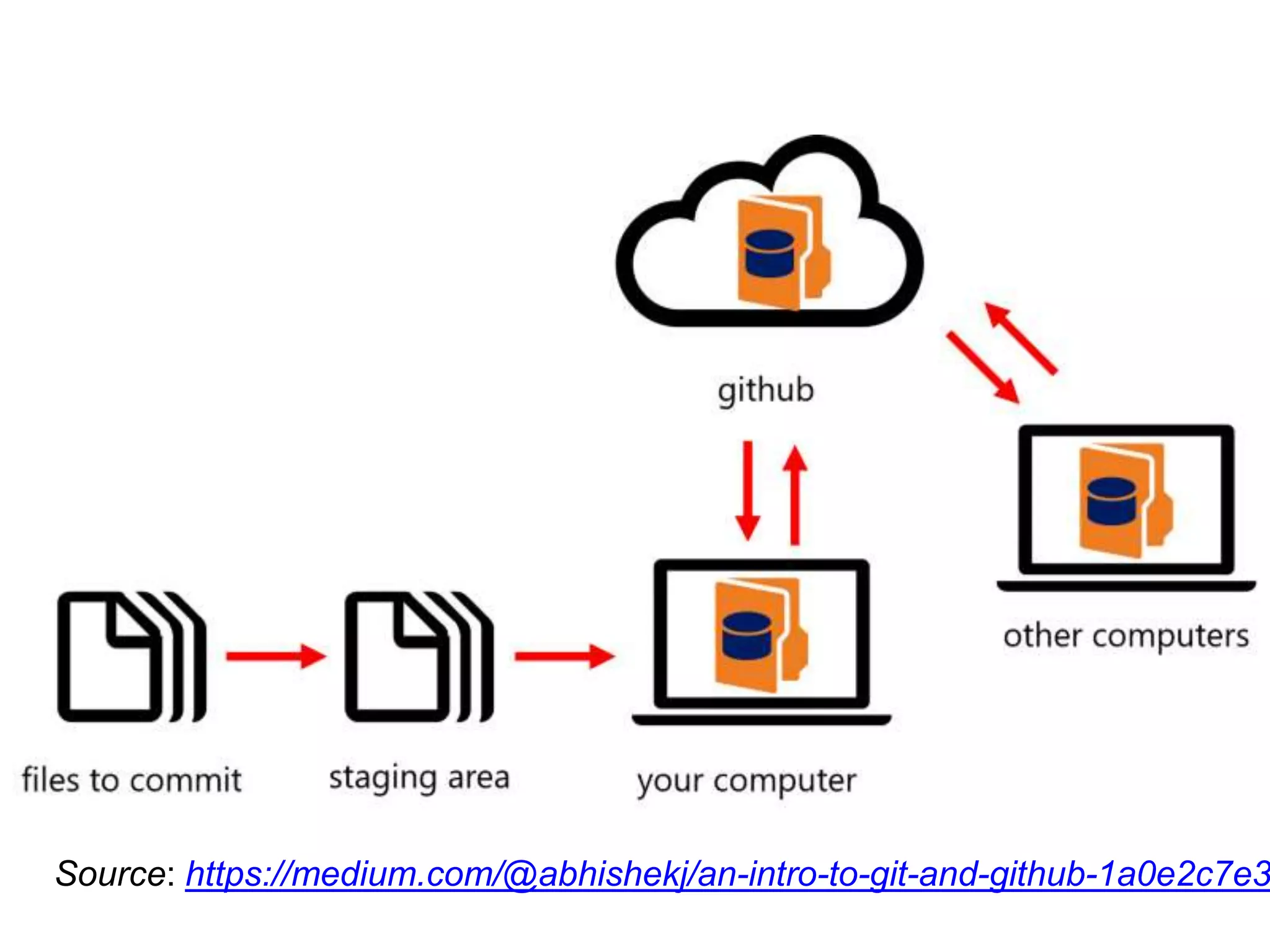
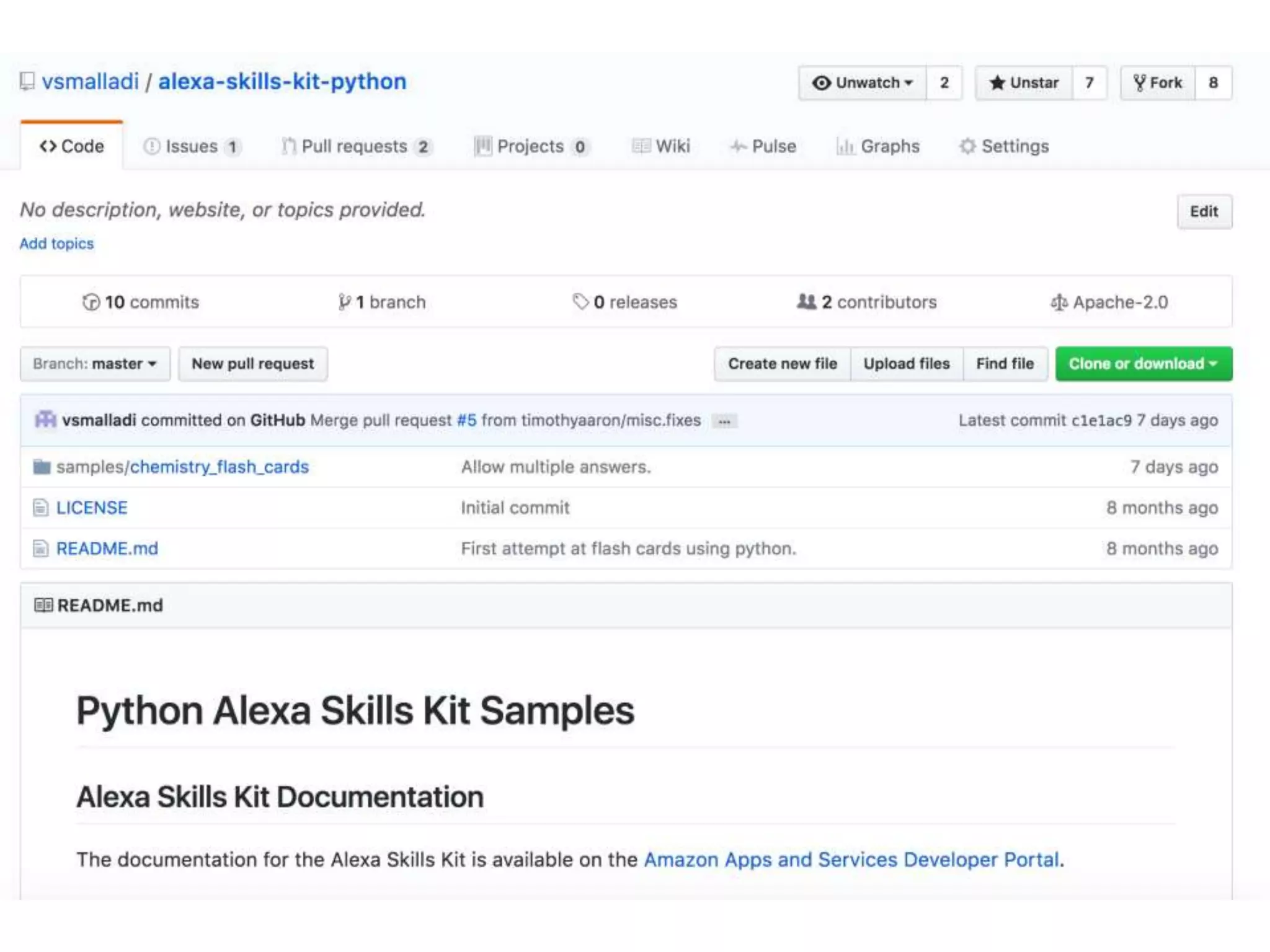
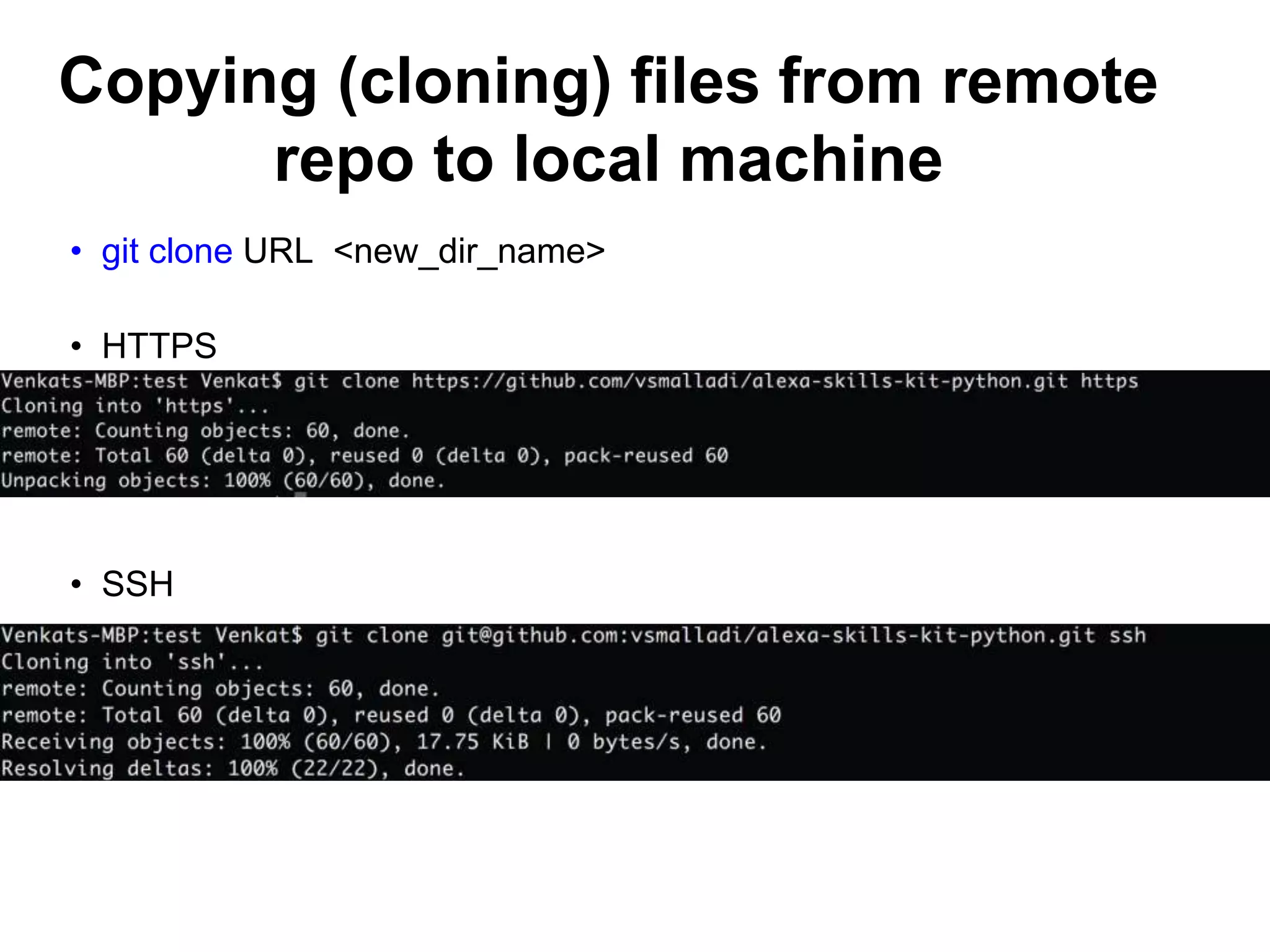
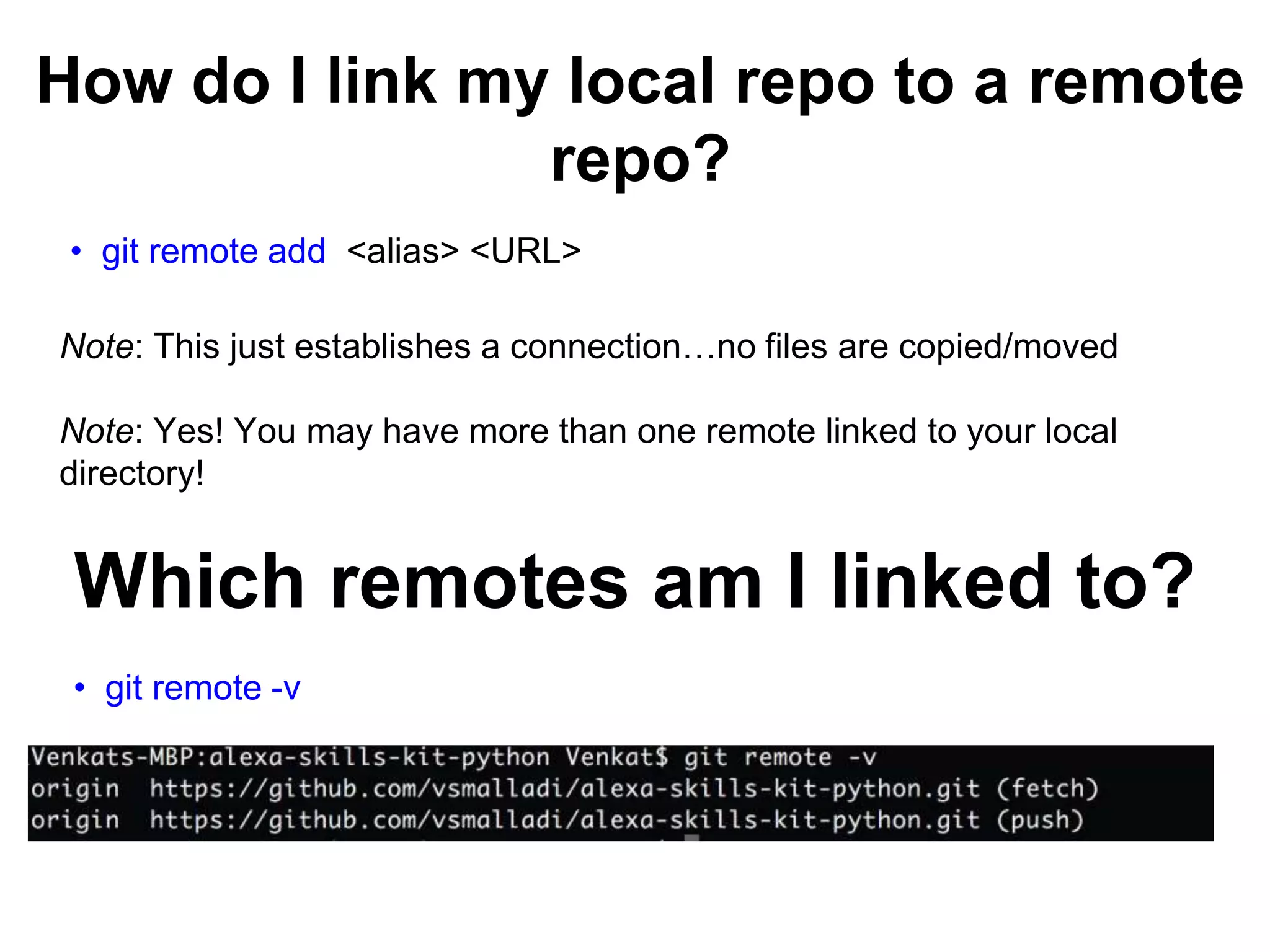
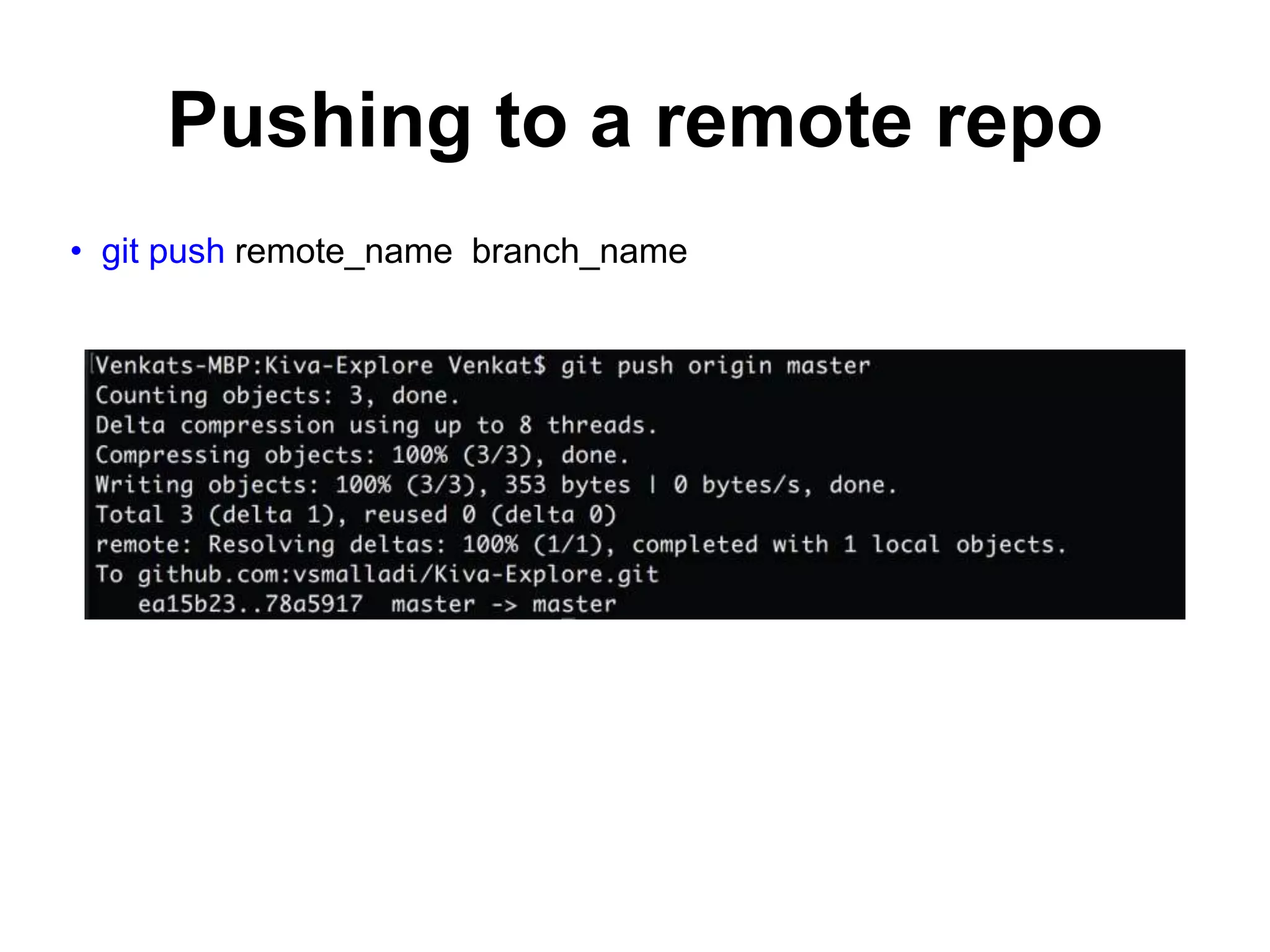
This document provides an introduction to Git and GitHub. It outlines the basics of Git including initializing repositories, tracking changes, branching, merging, and resolving conflicts. It also covers GitHub concepts such as cloning repositories from GitHub to a local machine and pushing/pulling changes between local and remote repositories. The document explains how to collaborate on projects hosted on GitHub using Git.